
Dr. Sijal Fadhil Farhood AL-joborae
F.I.C.M.S community (Baghdad)
M.Sc. Community (Nahrain)
M.B.Ch.B (Babylon University)

Maternal and child health:
R
efers to the promotive,preventive,curative and rehablitative health
care for mothers and children.
I
s one of the important elements
of Primary Health Care.
It includes the subareas of:
maternal health.
child health.
Family planning.
school health.
handicapped children.
Adolescence.
health aspects of care of children in special settings such
as day care.

SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES OF MCH
A-Reduction of maternal , perinatal ,
infant and childhood mortality and
morbidity.
B-Promotion of reproductive health.
C-Promotion of physical and
psychological development of the child
and adolescent within the family.
The ultimate objective of MCH services is
life- long health.

PHASES OF MATERNITY CARE
1-PREMARITAL CARE PHASE.
2-PRENATAL(ANTENATAL) CARE
PHASE.
3-INTRANATAL CARE PHASE.
4-POST NATAL CARE PHSE.

1-Premarital care phase
Is the health care given to girls and boys before they
get married and is an essential part of adolescent
health care.
It include the following services:
Promotive health services such as education
regarding nutrition ,STD , contraception.
Preventive services such as
immunization(Tetanus toxoid for the female).

In the immediate premarital period, it
include the following services:
A-History regarding past medical history especially
hereditary diseases(thalassaemia , haemophelia, sickle
cell anemia).
B-Medical examination(eg. nutritional status of the
female , chest examination for those who have cough
more than 3 weeks).
C-Investigation(blood group and
Rh,VDRL,HIV,MCV,MCH).
D-counseling on family planning ,sex education
counseling.

2-Antenatal care(ANC)phase
Is the care of women during pregnancy ,
the primary aim of ANC is to achieve at the
end of the pregnancy a healthy mother and
healthy baby , ideally this care should
begin soon after conception and continue
throughout pregnancy.

Objectives of ANC


Antenatal visit schedule:
First 28 weeks of gestation: every 4
weeks.
28
th
-36
th
weeks of gestation: every 2
weeks .
36
th
weeks to term: every week.

PREVENTIVE SERVICES FOR MOTHERS(prenatal
services)
A-The first visit ,irrespective of when it occurs , should
include the following components:
-health history
-Physical examination
-Laboratory investigation:which include:
1-complete urine analysis
2-stool examination
3-complete blood count ,including Hb estimation
4-serological examination
5-blood grouping and Rh determination
6-chest x-ray , if needed
7-Pap test(if facilities exist)

B-On subsequent visits:
-physical examination(e.g. weight gain, blood pressure)
-Laboratory tests should include :urine examination and
Hb estimation.
C-Iron and folic acid supplementation and medication
as needed.
D-Immunization against tetanus.
E-Group or individual instruction on nutrition family
planning, self care ,delivery and parent hood.

F-Home visiting by a female health worker
G-referral services ,where necessary.

RISK APPROACH
The central purposes of antenatal care is to identify “high risk”
cases(as early as possible)from a large group of antenatal
mothers and arrange for them skilled care, while continuing to
provide appropriate care for all mothers, these cases comprise
the following:
1-Elderly primi (30 years and over)
2-short statured primi (140 cm and below)
3-malpresentation (breech , transverse lie)
4-Antepartam haemorrhage ,threatened abortion.
5-pre-eclampsia and eclampsia
6-anaemia
7-twins
8-previous stillbirth, intrauterine death, manual removal
of placenta

9-Elderly grand multiparas
10-prolonged pregnancy (14 days after expected date of
delivery
11-History of previous caesarean or instrumental delivery
12-Pregnancy associated with general diseases , diabetes,
tuberculosis, cardiovascular diseases.

The risk approach is a managerial tool for improved
MCH care, it’s purpose is to provide better services
for all ,but with special attention to those who need
them most.
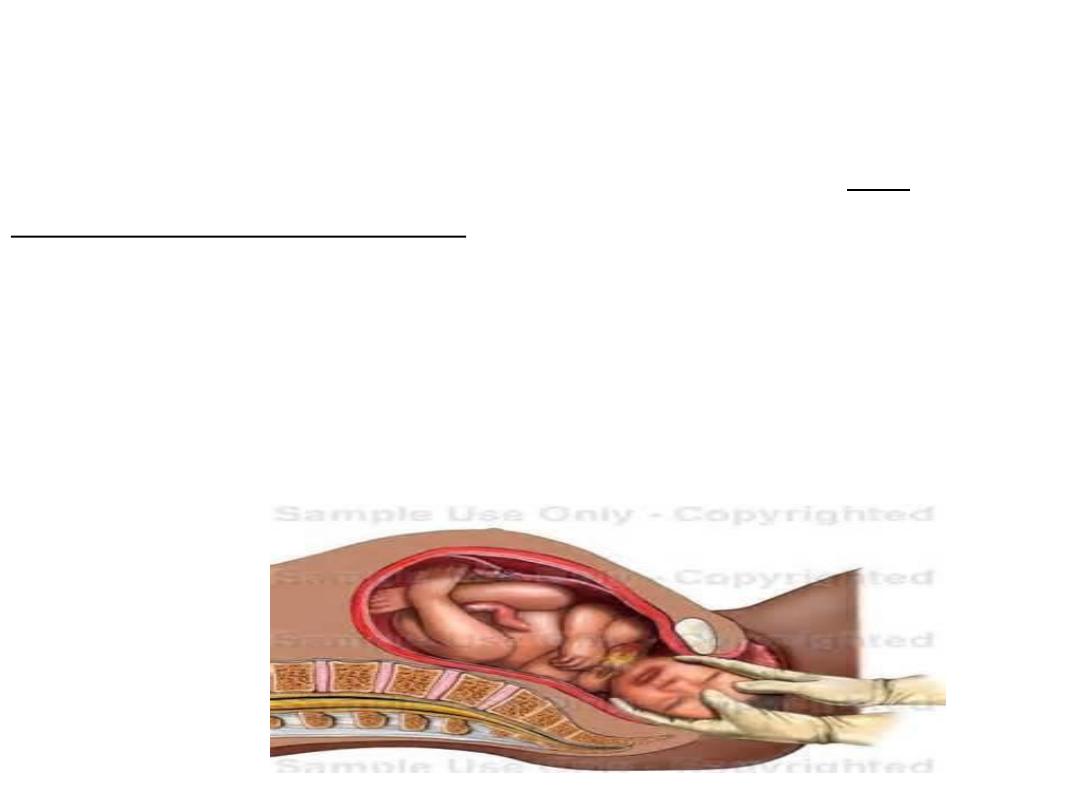
3- INTRANATAL CARE PHASE
Child birth is a normal physiological process, but
complications may arise.
Septicemia may result from unskilled and septic
manipulations and tetanus neonatorum from the use
of unsterilized instruments.
The need for intranatal care is therefore
indispensable, even if the delivery is going to be
normal one.
The aims of good intranatal
care are:
1-Thorough asepsis.
2-Delivery with minimum injury to the
infant and mother.
3-Readiness to deal with complications
such as prolonged labour, APH, convulsions
malpresentations , prolapse of the cord.
4-Take care of the baby at delivery-
resuscitation ,care of the cord, care of the
eyes.

4-POST NATAL CARE PHASE
Care of the mother (and the newborn) after delivery is known
as post natal or post partal care.
Broadly this care falls into two areas:
A-Care of the mother which is primarily the responsibility of
the obstetrician.
B-Care of the newborn, which is the combined responsibility
of obstetrician and paediatrician ,this combined responsibility
is also known as perinatology.

Care of the mother
The objectives of postpartal care are:
1-To prevent complications of the postpartal period.
2-To provide care for the rapid restoration of the
mother to optimum health.
3-To check adequacy of breast feeding.
4-To provide family planning services.
5-To provide basic health education to mother/family.

Complications of postpartal period
1-Puerperal sepsis.
2-Thrombophlebitis.
3-Secondary haemorrhage.
4-Others(UTI,mastitis).
It’s extremely important to look for these
complications in the post partal period and prevent
or treat them promptly.
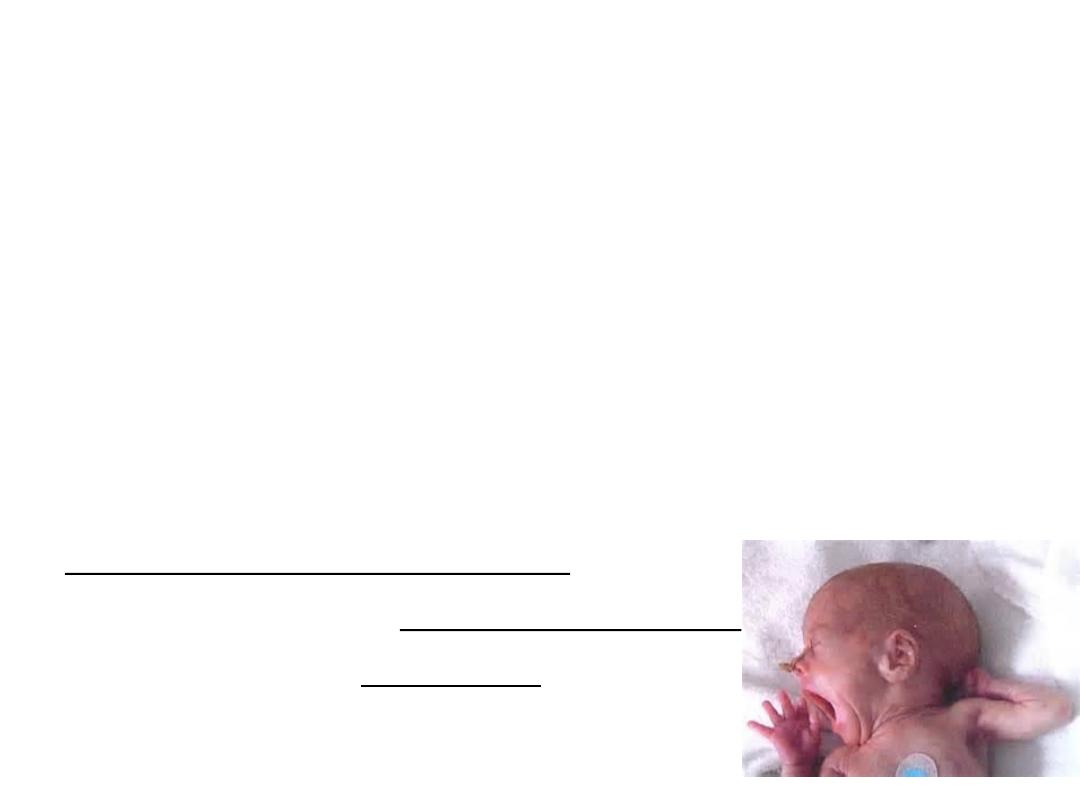
Neonatal care
1- EARLY NEOATAL CARE: the first week of life is the
most crucial period in the life of the infant.
The objective of early neonatal care is to assist the
newborn in the process of adoption to an alien
environment which involves:
i-Establishment and maintenance of the
cardiorespiratory functions.
ii-Maintenance of body temperature.
iii-Avoidance of infection.
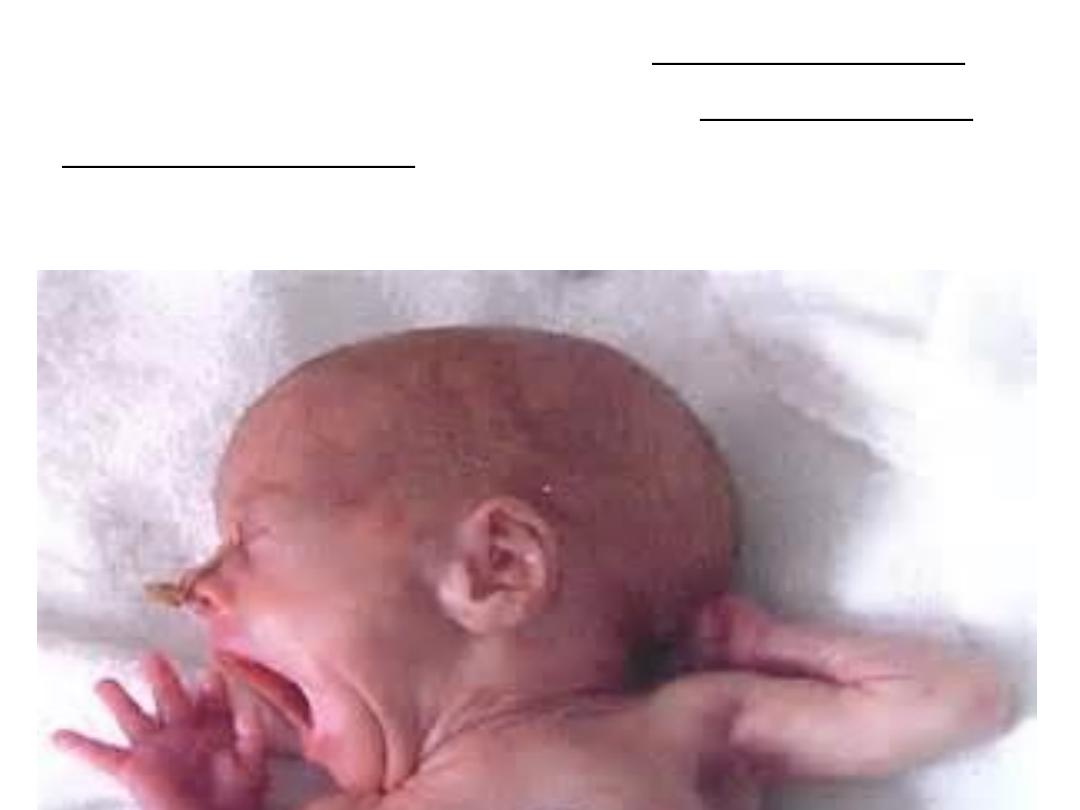
iv-Establishment of satisfactory feeding regimen.
v-Early detection and treatment of congenital and
acquired disorders ,especially infections.

GOBI-FFF
Selective PHC approach consists of techniques known
collectively under the acronym "GOBI-FFF". It focuses on
severe population health problems in certain developing
countries, where a few diseases are responsible for high
rates of
GROWTH MONITORING.
ORAL REHYDRATION THERAPY.
BREAST FEEDING.
IMMUNIZATION.
FAMILY PLANNING.
FEMALE EDUCATION.
FOOD SUPPLIMENTATION.

SAFE MOTHERHOOD:
For making motherhood safe, WHO has
recommended four strategic interventions
which should be delivered through PHC on
the foundation of equity for women
.
Family planning
Antenatal care
Clean/safe delivery
Essential obstetric care
26
SAFE MOTHERHOOD
EQUITY FOR WOMEN
PRIMARY HEALTH CARE
BASIC MATERNITY CARE
Es
sentia
l
Obst
etric
Car
e
F
amil
y
Plann
ing
Ant
enatal
car
e
Cle
an/Saf
e
Deli
ver
y
Health policy 1997

FP; to ensure that individuals & couples have the
information And services to plan timing, number &
spacing of pregnancies.
ANC: to prevent complications where possible and
ensure that complications of pregnancy are detected
early & treated appropriately.
C/S d: to ensure that all birth attendants have the
knowledge, skills & equipment to perform a clean &
safe delivery and provide postpartum care to mother &
baby.
E o c: to ensure that essential care for high risk
pregnancies & complications is made available to all
women who need it.

Family Planning
To ensure that individuals & couples have the
information and services to plan timing, number
& spacing of pregnancies.
Antenatal Care
To prevent complications where possible and
ensure that they are detected early & treated
appropriately.
Clean/Safe Delivery
To ensure that all birth attendants have the
knowledge, skills & equipment to perform a clean &
safe delivery and provide postpartum care to mother
& baby.
Essential Obstetric Care
To ensure that essential care for high risk
pregnancies is made available to all women who
need it and complications are dealt appropriately
and referred timely.
