
Public Health
Dr.Sijal Fadhil Farhood AL-Joborae
F.I.C.M.S (Baghdad)
M.Sc. Community Medicine(Al-Nahrain)
M.B.Ch.B (Babylon University)

Is the science and art of preventing disease ,prolonging
life , and promoting health and efficiency through
organized community efforts for the sanitation of the
environment, the control of communicable infections, the
education of the individual in personal hygiene, the
organization of medical and nursing services for early
diagnosis and preventive treatment of disease , and the
development of social machinery to ensure for every
individual a standard of living adequate for the
maintenance of health ,so organizing these benefits as to
enable every citizen to realize his birthright of health and
longevity.

It would be useful to explore the concepts
contained in the four terms that are commonly
used to describe different aspects of public health.
The modern concept of public health includes all
these elements – preventive medicine, social
medi- cine, community medicine, community
health. Important features of modern public
health include the following characteristic
features. It is:

Public health services perform a wide range of
functions, which can be classified as four key elements
• assessing and monitoring of the health of the
population.
• planning, implementing and evaluating public
health programmes.
• identifying and dealing with environmental hazards.
• communicating with people and organizations to
promote public health.

it is a branch of medicine that concentrates on
keeping people well; this is by disease
prevention & health promotion.


Target population
: entire population with
special attention to
healthy individuals .
Objective:
prevent onset of illness
Methods:
education, immunization,
nutrition, sanitation, etc.
Target population :
sick individuals
Objective:
early diagnosis and treatment
to prevent
further damage to the individual and in cases of
infectious diseases, prevent spread to the
community.
Methods: screening of high risk groups e.g. Pap
smears ,sputum examination for TB, monitoring
of vulnerable groups – children, pregnant women.
Target population:
sick patients
Objective: reduce damage from disease and
restore function
Method: clinical care and rehabilitation

1-General health promotion
2 -Specific prophylaxis
3- Early diagnosis and treatment
4- Limiting damage
5- Rehabilitation

DEFINITION OF HEALTH
It is a state of complete physical , mental
and social wellbeing and not merely the
absence of disease or infirmity ( WHO
1948) .
was added to this
spiritual wellbeing’
Then , ‘
definition and in recent years the statement
ability to lead a
was amplified to include the
socially and economically productive life .

DEFINITION OF HEALTH
It is a state of complete physical , mental
,social and spiritual wellbeing , the ability to
lead a socially and economically productive
life and not merely the absence of disease or
infirmity.

DETERMINANTS OF HEALTH
WHO,
According to the
the main determinants of health include:
-Social and economic environment,
-Physical environment,
-Person's individual characteristics and
behavior.


Is essential health care made universally
accessible to individuals and acceptable to them
, through their full participation and at a cost
the community and country can afford.
**There are three levels of PHC:
1-HOME LEVEL.
2-COMMUNAL LEVEL.
3-HEALTH SERVICES LEVEL.
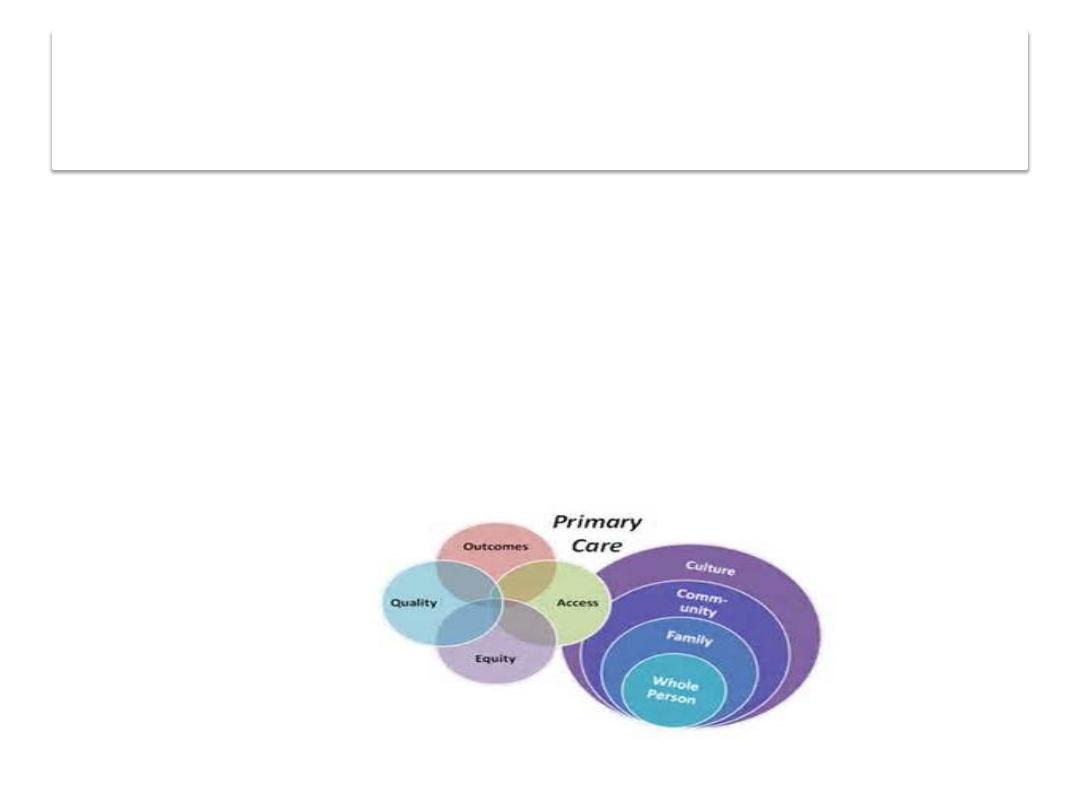
ELEMENTS OF PHC
Although specific services provided will vary in
different countries and communities , the Alma-
Ata Declaration by the year 2000 has outlined 8
essential components of PHC:

8 Essential Health Services in Primary Health Care
(ELEMENTS)
1.
E – Education for Health
2.
L – Locally endemic disease control
3.
E – Expanded program for immunization
4.
M – Maternal and Child Health including
responsible parenthood
5.
E – Essential drugs
6.
N – Nutrition
7.
T – Treatment of communicable and non-
communicable diseases
8.
S - Safe water and sanitation

The Basic Requirements for Sound PHC (the 8 A’s and
the 3 C’s)
• Appropriateness
• Availability
• Adequacy
• Accessibility
• Acceptability
• Affordability
• Assessability
• Accountability
• Completeness
• Comprehensiveness
• Continuity

STRATEGIES OF PHC
1-Intersectoral co-operation: primary health care
programs should be set in the context of integrated
development, housing, transport, agriculture,
communications, etc.
2-Basic infrastructure :some basic health facilities should
be established within reach of every family, this distance
will depend on road, available transport ,but an
acceptable average walking distance is usually taken to
be five kilometers.

3-Referral system: the health facilities need to be
connected through a referral mechanism to the hospital
service.
4-Auxillary health workers: need to be trained to work in
the health facilities.
5-Village health workers: need to be trained to work in
the community.
6-Traditional medical system: research is needed into the
effectiveness of some traditional remedies training of TBA
is providing a successful co-operation with and training of
other traditional medical workers should be encouraged.

7-Health education: is fundamental only through
understanding the basis of healthy life.
8-Commnity participation: each community should be
involved in the PHC services through the functioning of
active responsible health committee.
9-health care should be relevant to the main health
problems of each community.
10-Essential drugs for treating common conditions should
be provided.
11-Cost effective and self reliant: as the country and
community develops, the provision of health care should
grow.

Comparison
MEDICAL MODEL
• Treatment
• Illness
• Cure
• Episodic care
• Individual practitioners
• Health sector alone
• Professional dominance
• Passive reception
PHC
• Health promotion
• Health
• Prevention ,Care ,Cure
• Continuous care
• Team of practitioners
• Intersectoral cooperation
• Community participation
• Joint responsibility

HEALTH SYSTEM IN IRAQ
*Ministry of Health (MoH)
*General Health Directorate.
*Health Care Institutions: Could be:
(health centers, hospitals and
specialized centers)

•
Referral system is a process, which
ensures the accessibility to higher levels
of medical care to the patients from the
community or primary level health care
facility.
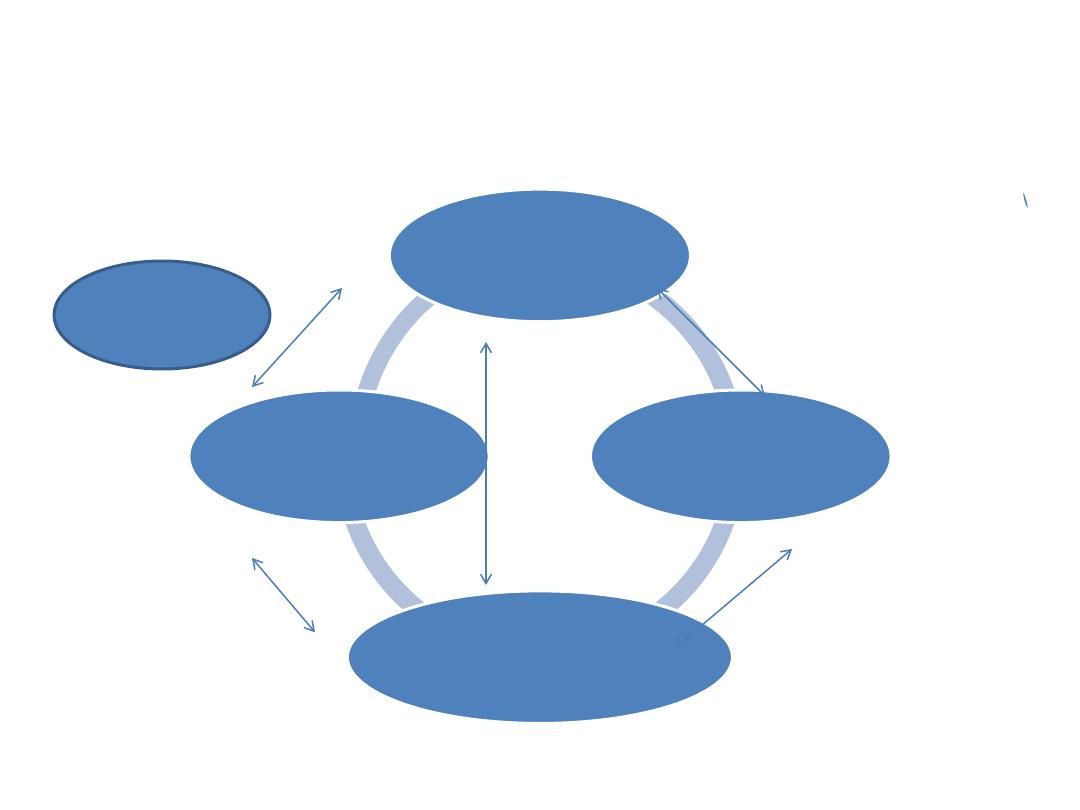
REFFERAL SYSTEM IN PHC
PHC centers in the
catchment's area
District general
hospital(first
referral level
Special teaching hospital
Health information
system
feedback
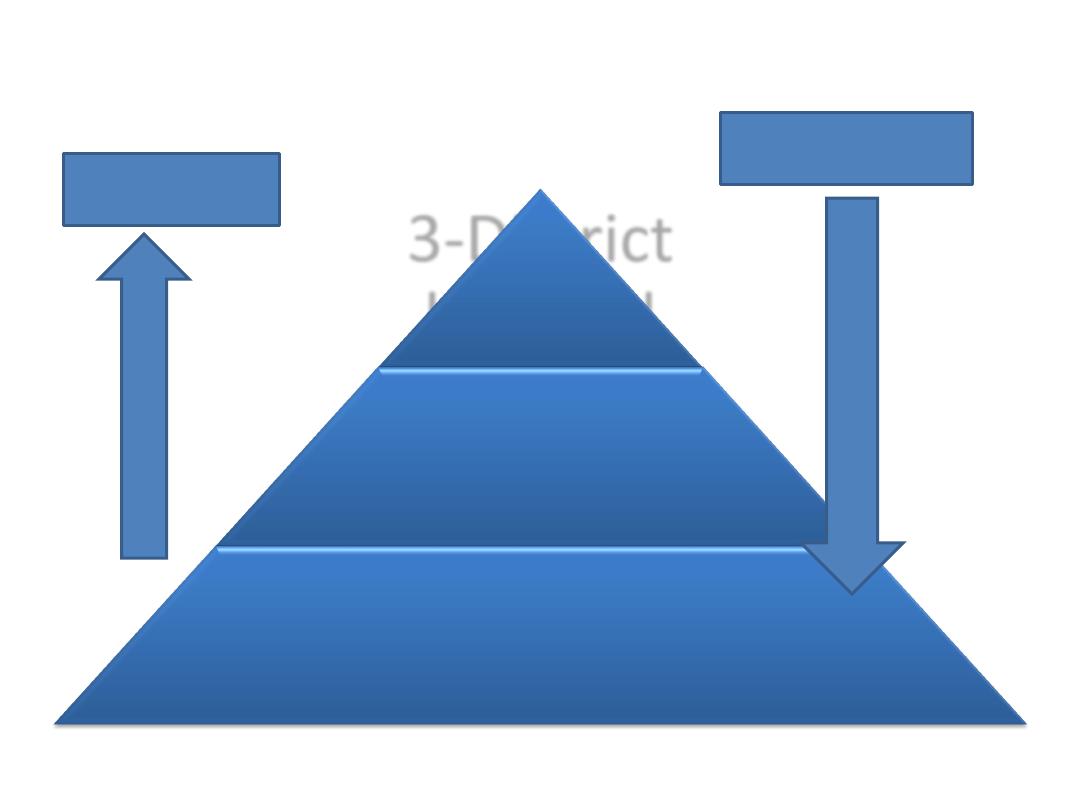
Health care pyramid at district level
3-District
hospital
2-Health
center
1-Family/community
level of care
REFFERAL
SUPERVISION

Millennium DEVELOPMENT GOAL(MDG)

Millennium DEVELOPMENT GOALs (MDG)
1-Eradicating extreme poverty and hunger.
2-Achieving universal primary education.
3-Promoting gender equality and empowering
women.
4-Reducing child mortality rates.
5-Improving maternal health.
6-Combating HIV/AIDS,malaria and other diseases.
7-Ensuring environmental sustainability.
8-Developing a global partnership for development.

“1000 days” concept
• Health authorities all over the world have
highlighted the importance of good nutrition
in the first 1000 days of the child’s life.
• Definition:
The first 1000-day period of the
child’s life begins right from the moment of
conception(day 0)and lasts through the entire
pregnancy(day 0-270) right up to his/her
second birthday (day 1000).

Explanation of the concept:
• The importance of the proper nutrition during
this 1000-day period cannot be stressed enough.
• During this critical period of the child’s life, there
is a tremendous amount of growth and
development that occurs in several key areas
such as cognitive(brain)development and physical
growth and development.
• By ensuring that, we can provide the right
nutrition during this 1000-day period and also
ensuring child’s future health ,wellbeing and
success.

conclusion
PRIMARY HEALTH CARE :
WORKING TOGETHER FOR BETTER HEALTH

