
RESEARCH
METHODOLOGY

The word research is composed of two syllables,
re and search. The dictionary defines the former
as a prefix meaning again, anew or over again
and the latter as a verb meaning to examine
closely and carefully, to test and try, or to
probe. Together they form a noun describing a
careful, systematic, patient study and
investigation in some field of knowledge,
undertaken to establish facts or principles.
DEFINITION

research is a structured inquiry that utilizes
acceptable scientific methodology to solve
problems and creates new knowledge that is
generally applicable.

‘scientific research is a systematic, controlled
empirical and critical investigation of propositions
about the presumed relationships about various
phenomena’
ANOTHER DEFINITION

From these definitions it is clear that research is a
process for collecting, analyzing and interpreting
information to answer questions. But to qualify as
research, the process must have certain
characteristics: it must, as far as possible, be
controlled, rigorous, systematic, valid and verifiable,
empirical and critical.
Let us briefly examine these characteristics to
understand what they mean:
THE RESEARCH PROCESS:
CHARACTERISTICS AND REQUIREMENTS

Controlled:
The concept of control implies
that, in exploring causality in relation to two
variables, you set up your study in a way that
minimizes the effects of other factors affecting
the relationship.

Rigorous
:You must be scrupulous in
ensuring that the procedures followed to
find answers to
questions are relevant, appropriate and
justified.

Systematic :This implies that the procedures
adopted to undertake an investigation follow a
certain logical sequence. The different steps
cannot be taken in a haphazard way. Some
procedures must follow others.
Valid and verifiable :This concept implies that
whatever you conclude on the basis of your
findings is correct and can be verified by you
and others.

Empirical :
This means that any conclusions
drawn are based upon hard evidence gathered
from
information collected from real-life experiences
or observations.
Critical :
Critical scrutiny of the procedures
used and the methods employed is crucial to a
research inquiry. The process of investigation
must be foolproof and free from any drawbacks.
The process adopted and the procedures used
must be able to withstand critical scrutiny.

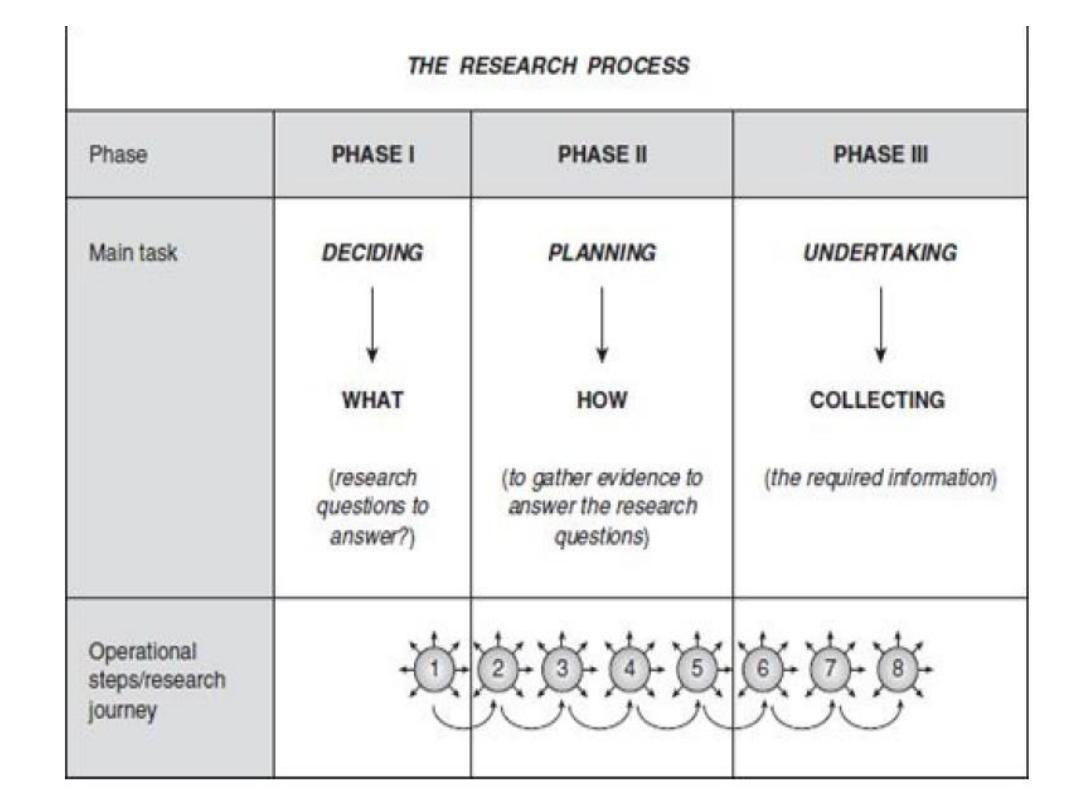
The eight-step model for carrying out
research
PHASE I DECIDING WHAT TO RESEARCH
Step I Formulating a research problem
PHASE II PLANNING A RESEARCH STUDY
Step II Conceptualizing a research design
Step III Constructing an instrument for data
collection
Step IV Selecting a sample
Step V Writing a research proposal
THE RESEARCH PROCESS:

PHASE III CONDUCTING A RESEARCH
STUDY
Step VI Collecting data
Step VII Processing and displaying data
Step VIII Writing a research report

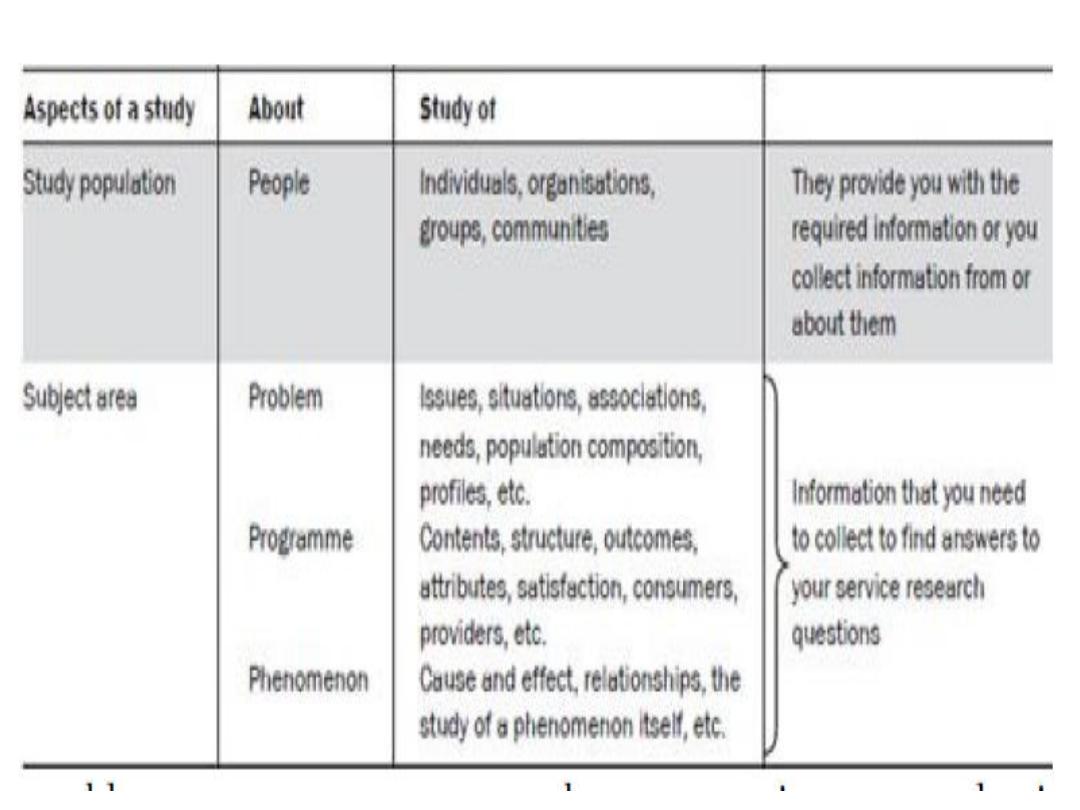
Most research in the humanities revolves
around four Ps:
-people;
-problems;
-programs;
-phenomena.
SOURCES OF RESEARCH PROBLEMS

When selecting a research problem/topic
there are a number of considerations to
keep in mind which will help to ensure
that your study will be manageable and
that you remain motivated.
These considerations are:
CONSIDERATIONS IN SELECTING A
RESEARCH PROBLEM

Interest
Magnitude
Measurement of concepts
Level of expertise
Relevance
Availability of data
Ethical issues

This may include the following:
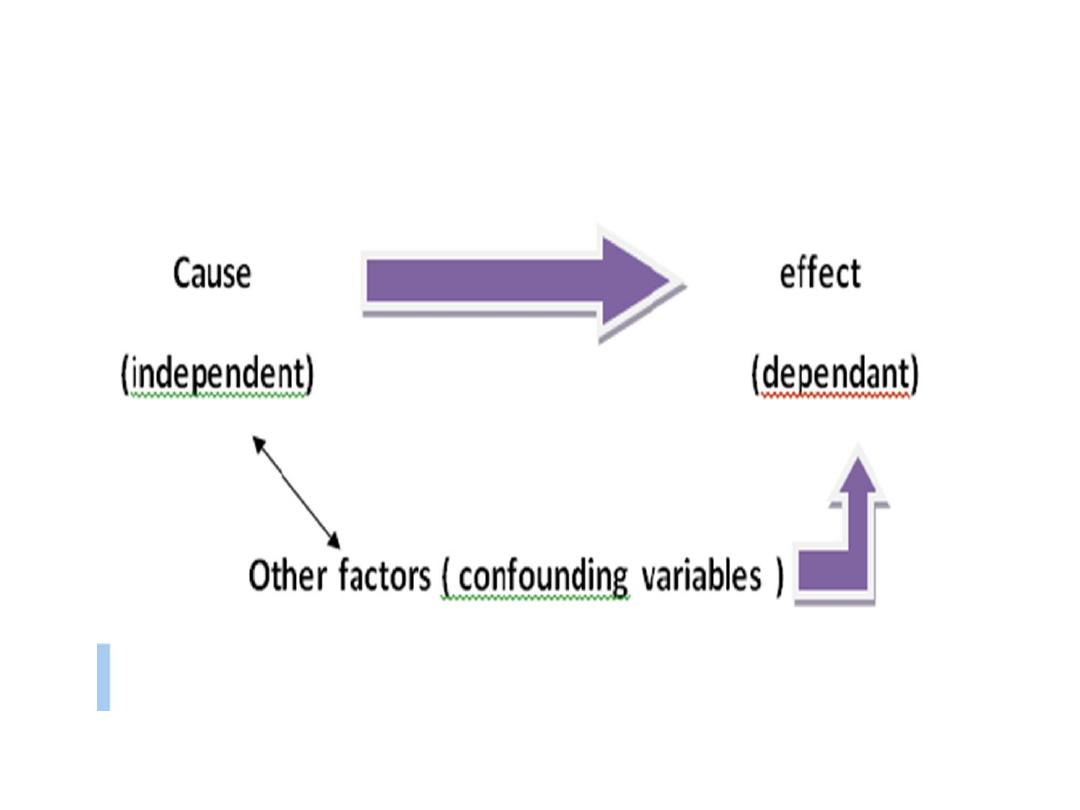
1.Variable to be measured:
a) numerical variable like age, wt. , income,
distance.
b) categorical variable like outcome of disease
for instance: recovery, chronic manifestations or
death.
c)dependable variable: used to describe or
measure problem under study.
OVERVIEW OF THE RESEARCH
METHODOLOGY’

d) independent variable: used to describe or
measure factors that are assumed to cause
or influence the problem.
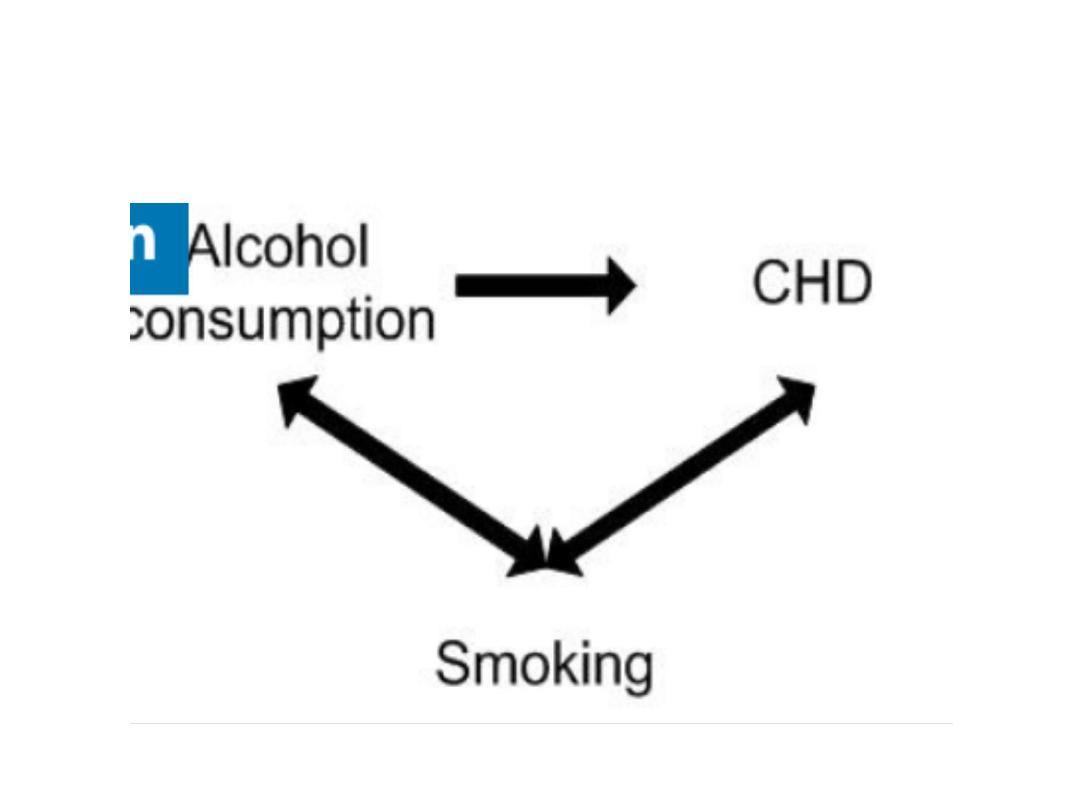
e) confounding variable: a variable that is
associated with problem, and with a
possible cause.

2. study type and technique to be
followed(design).
3.sampling method.
4.plan for data collection and for data
analysis.
5.pretest or pilot study.

is a small scale preliminary study conducted
in order to evaluate feasibility, time, cost,
adverse events, and effect size (statistical
variability) in an attempt to predict an
appropriate sample size and improve upon
the study design prior to performance of a
full-scale research project. General
guidelines, for example using 10% of the
sample required for a full study
WHAT IS PILOT STUDY

1- eliminate some variable to reduced
time of Interview
2- select appropriate sample
3-model of interview
4-estimate the time needed
5-Assessing whether the research protocol
is realistic and workable
6- to find potential difficulties
REASONS FOR CONDUCTING PILOT STUDIES

A research design is a plan, structure and
strategy of investigation so conceived as to
obtain answers to research questions or
problems. The plan is the complete scheme or
programme of the research. It includes an
outline of what the investigator will do from
writing the hypotheses and their operational
implications to the final analysis of data.
WHAT IS A RESEARCH DESIGN?

A traditional research design is a blueprint or
detailed plan for how a research study is to be
completed
—operationalizing variables so they
can be measured, selecting a sample of
interest to
study, collecting data to be used as a basis
for testing hypotheses, and analyzing the
results.

A research design has two main functions.
The first: relates to the identification and/or
development of procedures and logistical
arrangements required to undertake a study,
The Second: emphasizes the importance of
quality in these procedures to ensure their
validity, objectivity and accuracy.
THE FUNCTIONS OF A RESEARCH DESIGN

Hence, through a research design you:
1-conceptualize an operational plan to
undertake the various procedures and
tasks required to complete your study;
2-ensure that these procedures are
adequate to obtain valid, objective and
accurate answers to the research
questions.
