
Breast Feeding
Dr. Sijal Fadhil Farhood
F.I.C.M.S.(Baghdad)-M.Sc.(Nahrain)-M.B.Ch.B.(Babylon)

The International Breast
feeding Symbol
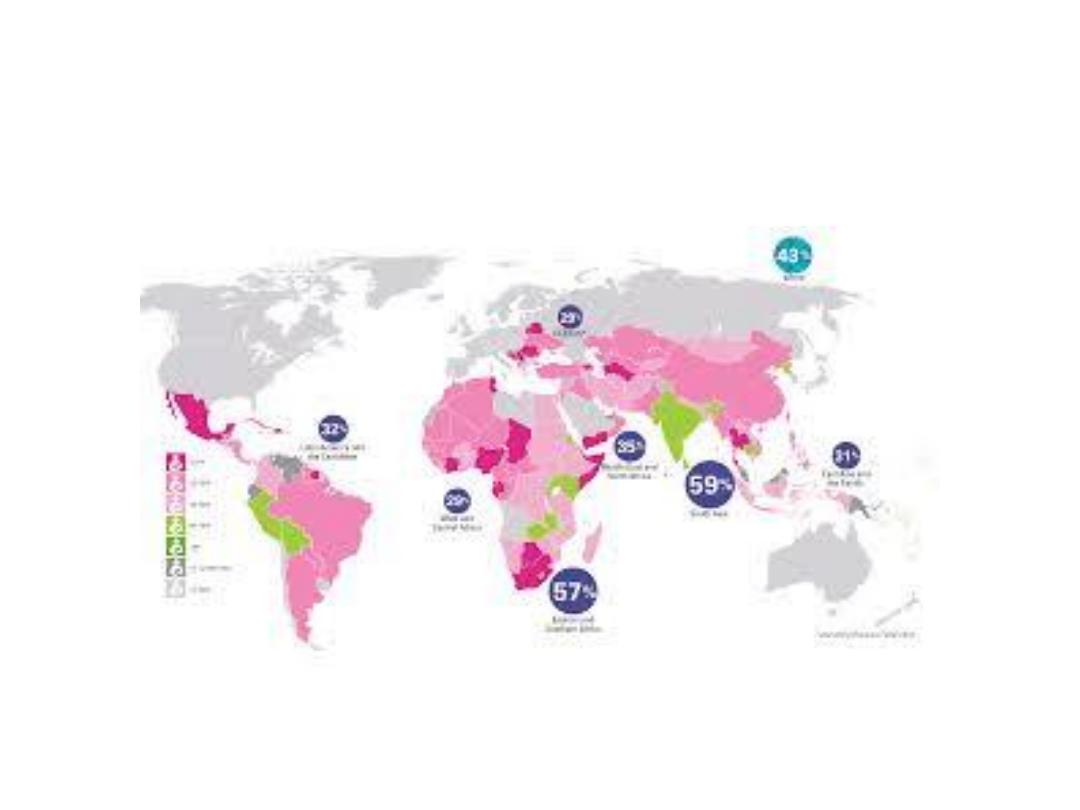
Current global breastfeeding rates
(40%)


Introduction:
•
Breast feeding is one of the most important
contributors to neonatal, infant and child health,
growth and development.
•
The benefits are greatly enhanced if it is started
within one hour after birth ,with demand feeding .
Breast Feeding
Facts WHO

Breast feeding should be
initiated within one hour
after birth. It should be
exclusive for 6 months. It
should continue for 2
years

Breast feeding is one of
the most important
contributors to neonatal,
infant and child health,
growth and
development.

Many neonatal health
problems are greatly
ameliorated , such as
hypothermia,
hypoglycemia, infections
and neonatal jaundice.

Apart from the clear
nutritional superiority of
breast milk ,breast
feeding protects against
infant deaths and
morbidity .

Exclusively breast fed
infants are likely to
suffer only a quarter as
many episodes of
diarrhea and respiratory
infections as babies who
are not.

Mothers benefit from
breast feeding as it
reduces the risk of PPH
and lowers the risk of
breast and ovarian
cancers.
It contributes to child
spacing.

It offers
98
%
protection against
pregnancy in first 6
months of exclusive
breastfeeding

HIV infected
mothers
should
breastfeed

Breast feeding needs:
• Positioning
• Patience
• Practice
• persistence

Breast feeding needs:
•
Positioning
•
Patience
•
Practice
•
persistence

Infant Weight Gain

Breastfed infants
generally gain weight
according to the
following guidelines:
0–4 months : 170 gr per week
4–6 months : 113–142 gr/ week
6–12 months : 57–113 gr / week

At 5-6 Months
• The average breastfed baby doubles
its birth weight .

At the 1
st
Birthday & Onwards
•
A typical breastfed baby will weigh about 2½ times
its birth weight.
• At one year, breastfed babies tend to be leaner but
healthier than bottle fed babies.
• By two years, differences in weight gain and growth
between breastfed and formula-fed babies are no
longer evident

ROOMING
IN
BASSINET
S

Exclusive breast feeding
An infant receives no other food or drink besides breast
milk. Guidelines recommend that all infants be breastfed
exclusively for the first six months of life. Breastfeeding
may continue with the addition of appropriate foods, for
two years or more. Exclusive breastfeeding has
dramatically reduced infant deaths in developing
countries by reducing
and
.

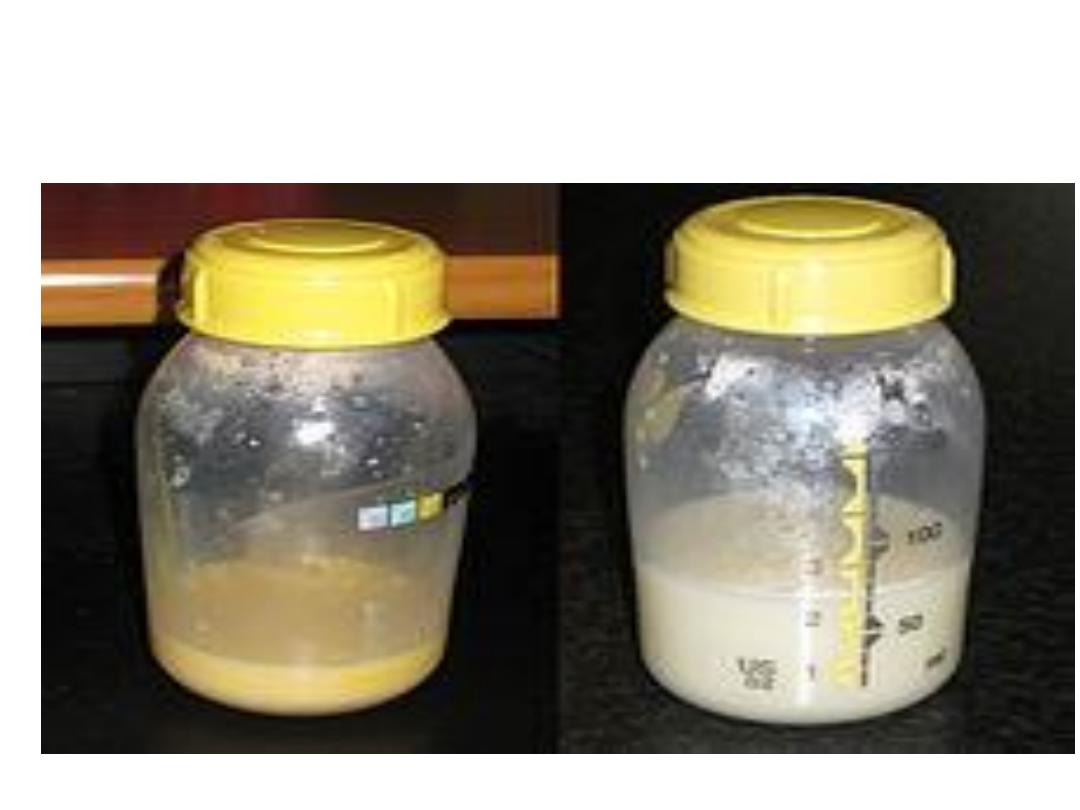
Two 25ml samples of human
breast milk. The left hand sample
is foremilk, the watery milk
coming from a full breast. The
right hand sample is hindmilk, the
creamy milk coming from a nearly
empty breast.

Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative
(BFHI)

• A global
program
sponsored by
WHO and
UNICEF

• It encourages and
recognizes
hospitals and
birthing centers
that offer an
optimal level of
care for lactation

Ten steps of successful breast feeding
• 1-Have a written breast feeding policy that is
routinely communicated to all health care staff.
• 2-Train all health care staff in skills necessary to
implement this policy.
• 3-Inform all pregnant women about the benefits
and management of breast feeding.
• 4-Help mothers initiate breast feeding within an
hour of birth.
• 5-Show mothers how to breast feed,and how to
maintain lactation even if they are seperated
from their infants.

• 6-Give newborn infants no food or drink other than
breast milk, unless medically indicated.
• 7-Practice rooming-in-allow mothers and infants to
remain together 24 hour a day.
• 8-Encourage breast feeding on demand.
• 9-Give no artificial teats or pacifiers to breast feeding
infants.
• 10-Foster the establishment of breast feeding
support groups and refer mothers to them on
discharge from hospital or clinic.

Composition of breast milk
• The composition of breast milk varies according to
the variation of several factors;these are:
• 1-Stage of lactation: colostrum is produced during
the first week after birth, followed by transitional
milk during the second week, and mature milk
thereafter.
• 2-Time of the day: fat content is highest at mid day.
• 3-sampling time within the same feed(at the
beginning of the feed, foremilk there is more water
and at the end there is hindmilk ,there is more fat.

• 4-Maternal nutrition.
• 5-Climate:in hot climates there will be more water,so
the mother does not have to give water to the infant in
addition to their breast milk.
• In cold climates the fat content is higher leading to
increased energy intake.
• 6-Individual variation from one mother to another.

Advantages of
breast feeding
• 1- It is safe, clean ,
hygienic ,cheap &
available to the infant at
a correct temperature.
• 2-It fully meets the
nutritional requirements
of the infants in the first
few months of life.
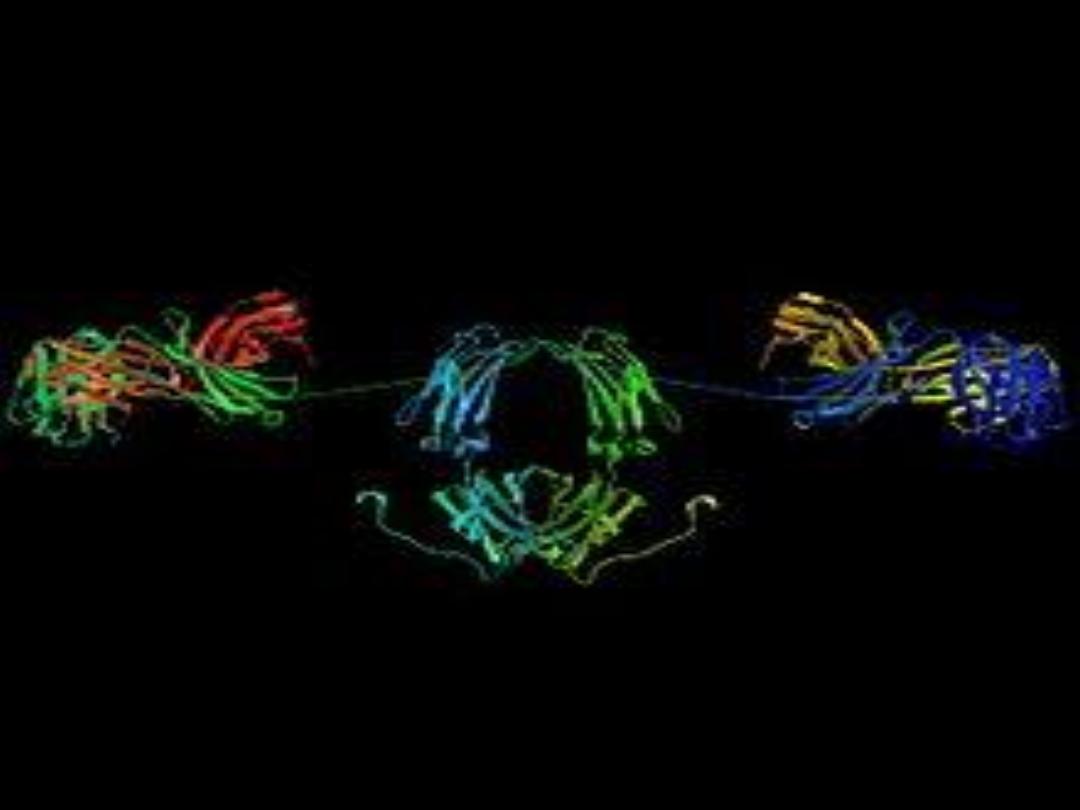

3-Contains antimicrobials such as macrophages, lymphocytes
,secratory Ig A,anti streptococcal factors, lysozyme and lactoferrin
which provide protection not only against diarrheal disease and
necrotizing enterocolitis, but also against respiratory infections in
the first few months of life.

• 4-It is easily digested and utilized by normal and
premature babies.
• 5-It promotes bonding between mother and infant.
• 6-Sucking is good for baby, it helps the development of
jaws and teeth.
• 7-It protects babies from the tendency to obesity.
• 8-It prevents malnutrition and reduces infant mortality.

• 9-It provides several biochemical advantages such as
prevention of neonatal hypocalcaemia.
• 10-It helps parents to space their children by
prolonging the space of fertility.
• 11-Special fatty acid in breast milk leads to increase
intelligence quotients(IQ or
DQ
of around 8 points
higher) and better visual acuity.

Phases of lactation
•
A-Colostrum:
• 1-first week
• 2-yellowish thick fluid
• 3-small quantity
• 4-mean energy value=67 Kcal/100ml
• 5-higher electrolyte content than the others
• 6-higher protein minerals
and fat soluble vitamins

• 7-facilities establishment of bifidus flora in the GIT
which protect against gastro enteritis
• 8-facilitates passage of meconium from the GIT
• 9-rich in antibodies, mainly Ig A against bacteria and
viruses inhabiting the birth canal, also rich in
leukocytes

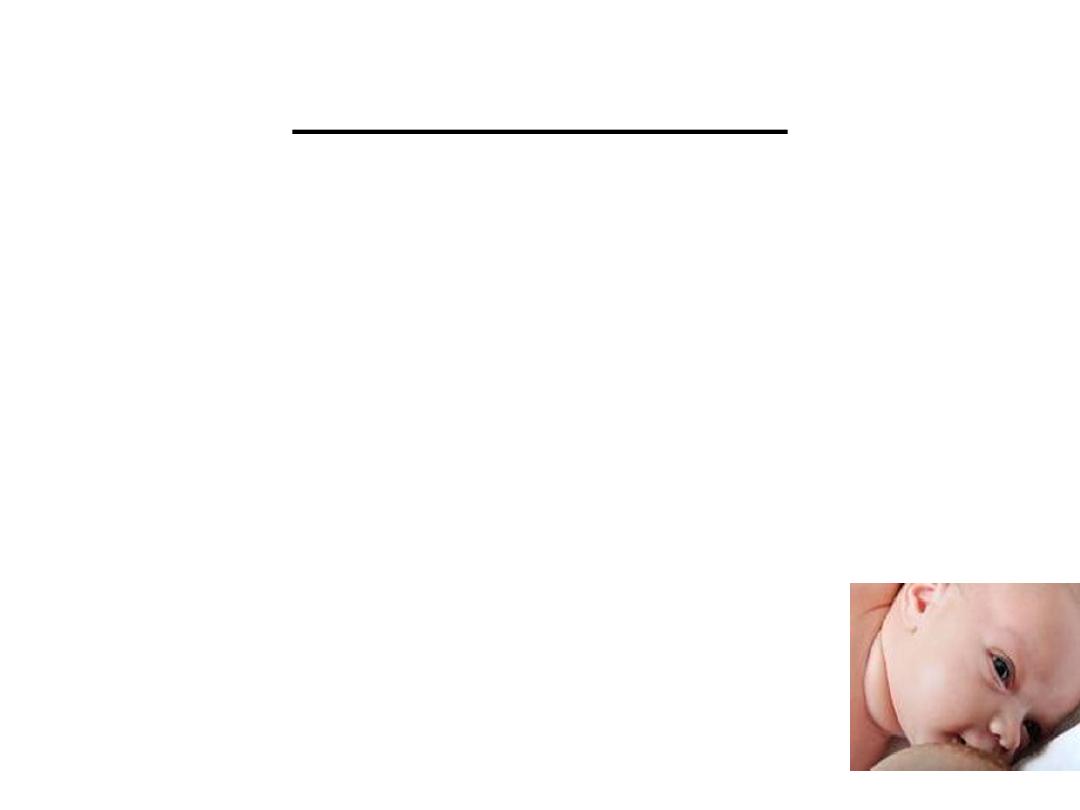
Colostrum
•
.

• Is produced in small but adequate amounts to cover the
nutritional and immunological needs of the neonate.
• A feeling of emptiness gives the mothers the
false belief that she is not producing enough milk
.
• Following this and during the second week after
delivery ,the mother will feel fullness in the
breasts ,which means that mean that milk
production has started.
• This process can be accelerated by putting the
infant on the breast more soon after birth(within
30 minutes)and to continue breast feeding on
demand ,this will enhance the production of
prolactin and hence milk production.

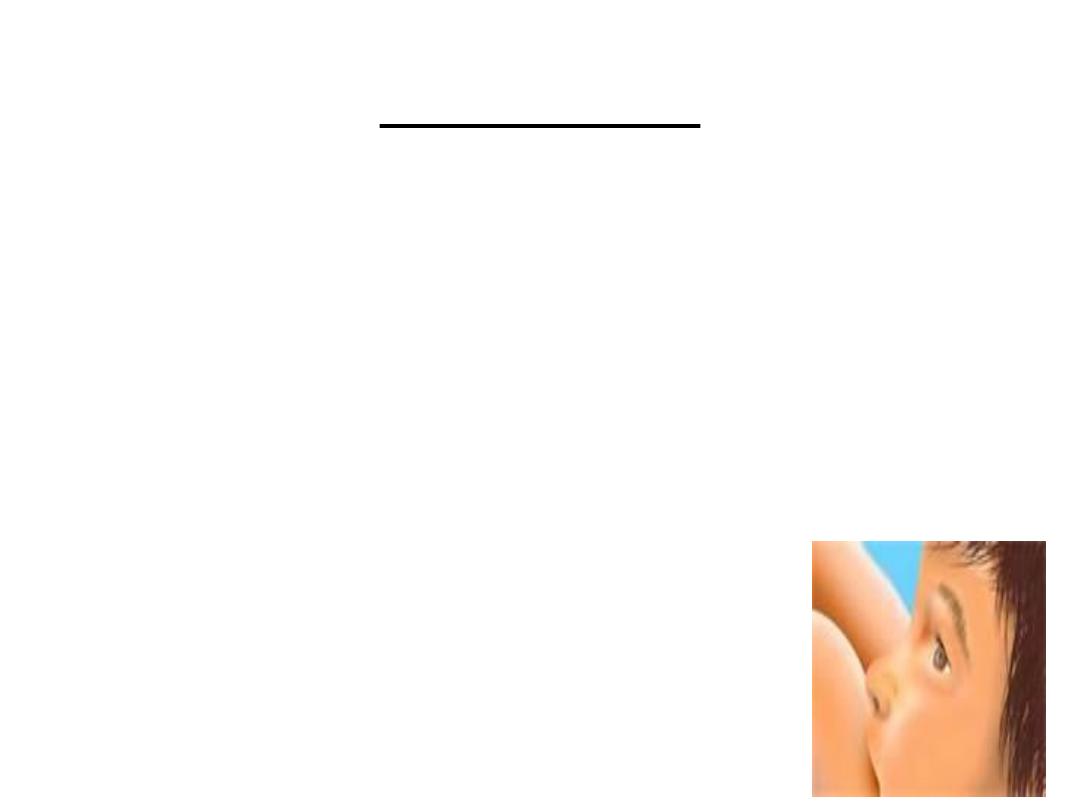
Transitional milk
-
B
• 1-Second week
• 2-Bluish thin fluid
• 3-Large quantity
• 4-Higher energy value
• 5-Low electrolyte content
• 6-Less protien,more water soluble vitamins

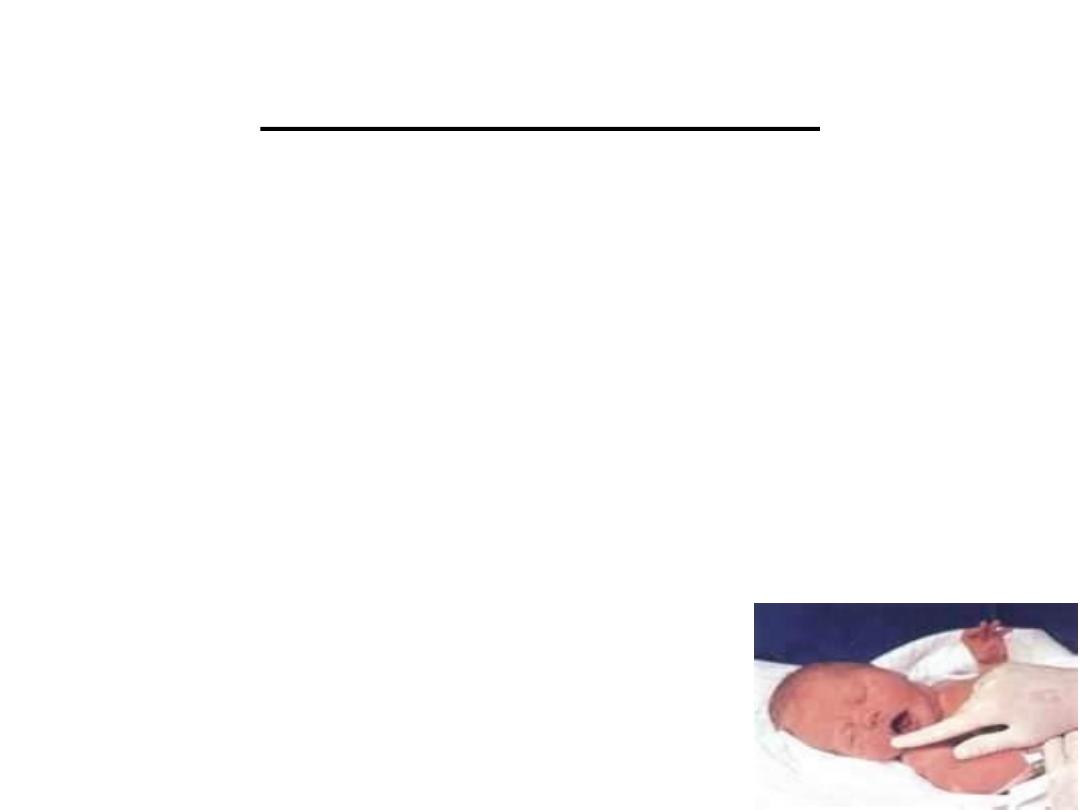
Mature milk
-
C
• 1-After the second week
• 2-Bluish thin fluid
• 3-Larger quantities
• 4-Mean energy value=75Kcal/100ml

Breast feeding process
• Reflexes:
• 1-Rooting reflex
• 2-Suckling reflex
• 3-Swallowing reflex

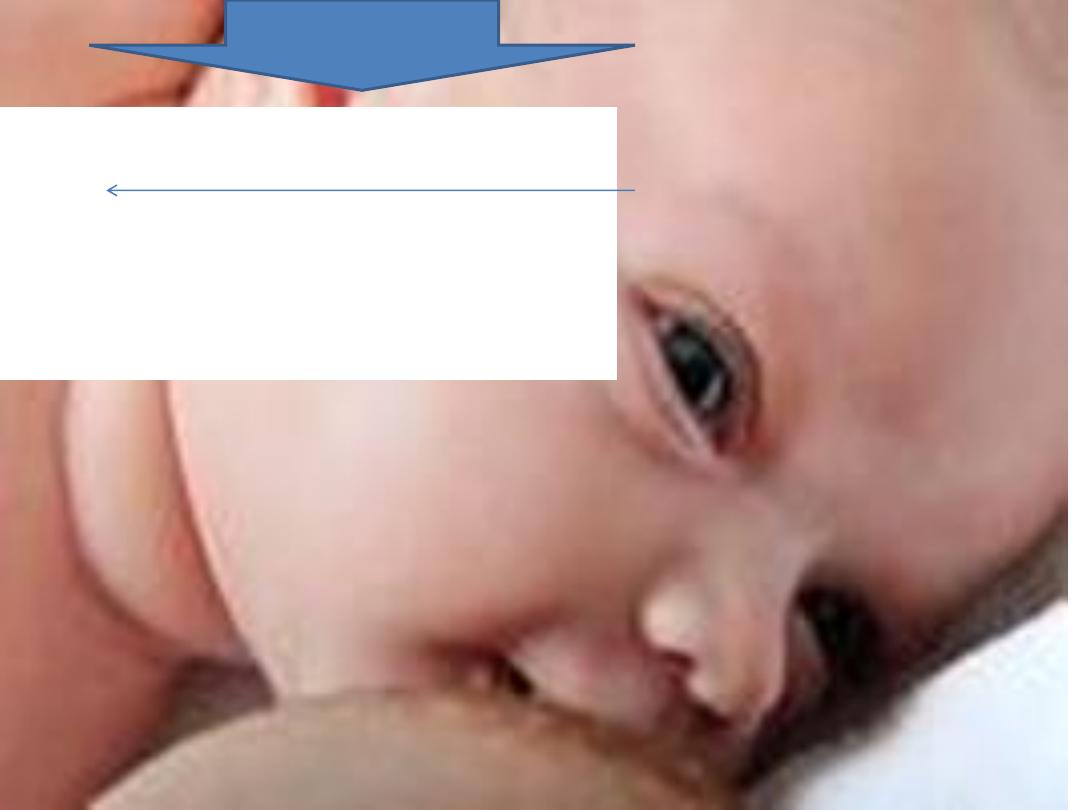
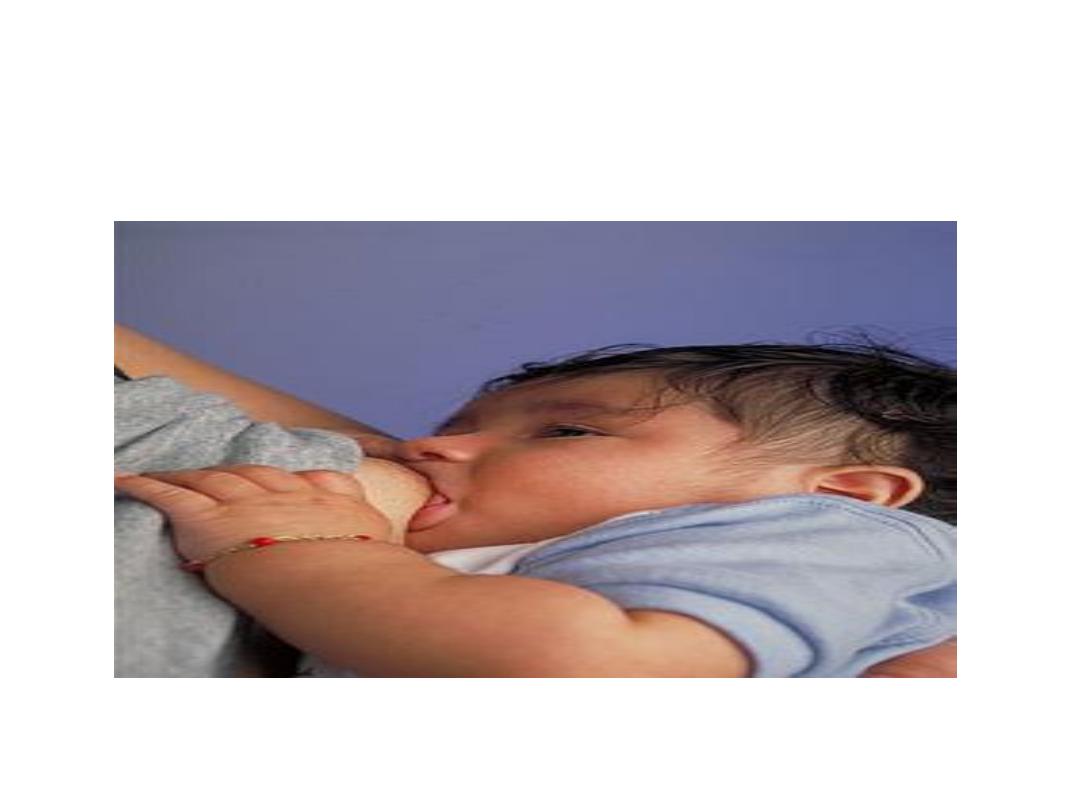
Positioning of breast feeding
• 1-Positioning of the mother:She must breast feed in
a comfortable and relaxed position,because if not
she will feel tired and end the feed quickly.
• 2-position of the infant:
• Head and body in one line with a straight neck
• Infant facing the mother
• Infant well supported
• Infant close to the mother

Attachment to the breast
• Mouth should be wide open
• Chin touching the breast
• Lower lip turned outward
• The lower part of the areola should not be
seen and the upper part should be partly
visible
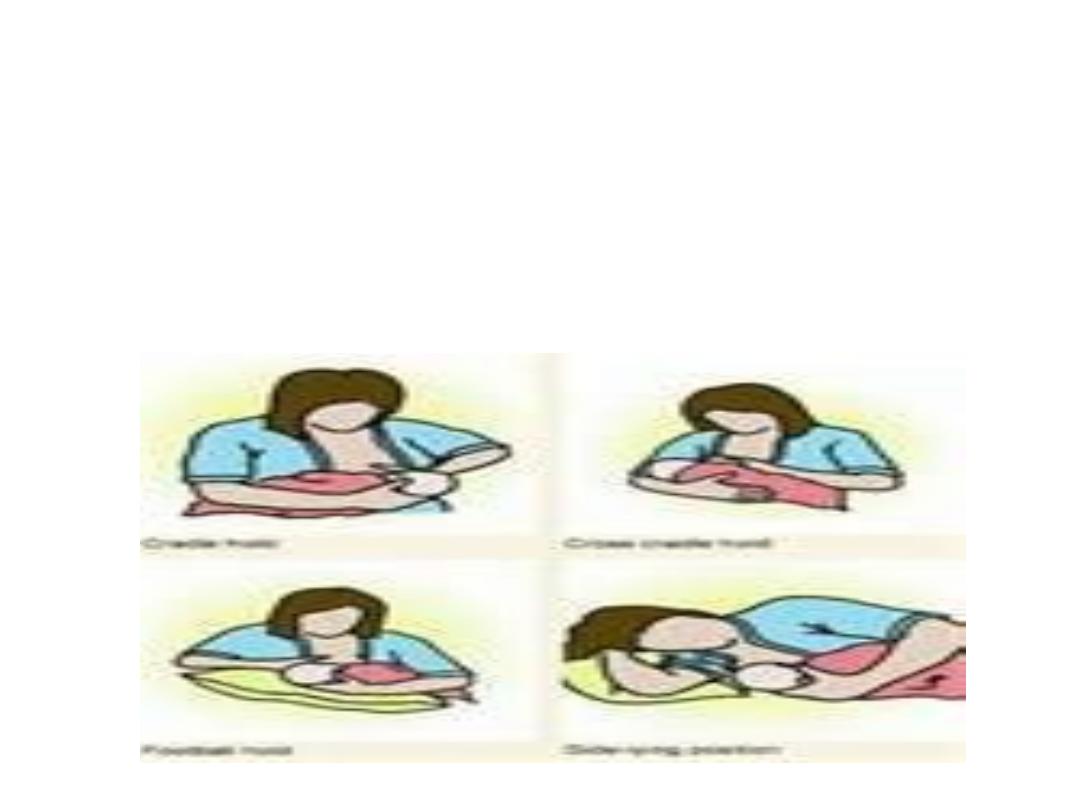
Effective suckling
• Slow deep sucks ,pauses from time to time,
swallowing can seen, the mother feels no
pain

Positioning of breast feeding
• 1-cradle hold position
• 2-cross over hold position
• 3-clucth or football hold position
• 4-reclining position

Disadvantages of bottle feeding
• Baby misses out on the immunity present in breast milk
• Everything that is used for preparing the milk and feeding
baby must be thoroughly sterilized
• The artificial milk affects the gut lining making babies more
susceptible to stomach bugs
• If you are going out you must keep the milk cool (below
8ºc) until you are ready to use it and then have a facility to
heat milk up to body temperature.
• There is increased risk of breast cancer in mothers who do
not breast feed
• There is increased risk of infection in babies who are bottle
fed, particularly vomiting and diarrhoea
• The baby is more prone to allergic conditions, such as
asthma and eczema

Disadvantages of bottle feeding

Examples of Contraindications of
breast feeding
• 1-Galactosaemia.
• 2-Breast cancer(the mother is receiving anti
metabolite or other chemo therapeutic
agents)
• 3-Drug abuse
• 4-Radioactive therapy to the mother

contraindicated
not
Breast feeding is
in:
• 1-Viral infection of the mother such as
HBV,HCV,CMV
• 2-Neonatal jaundice
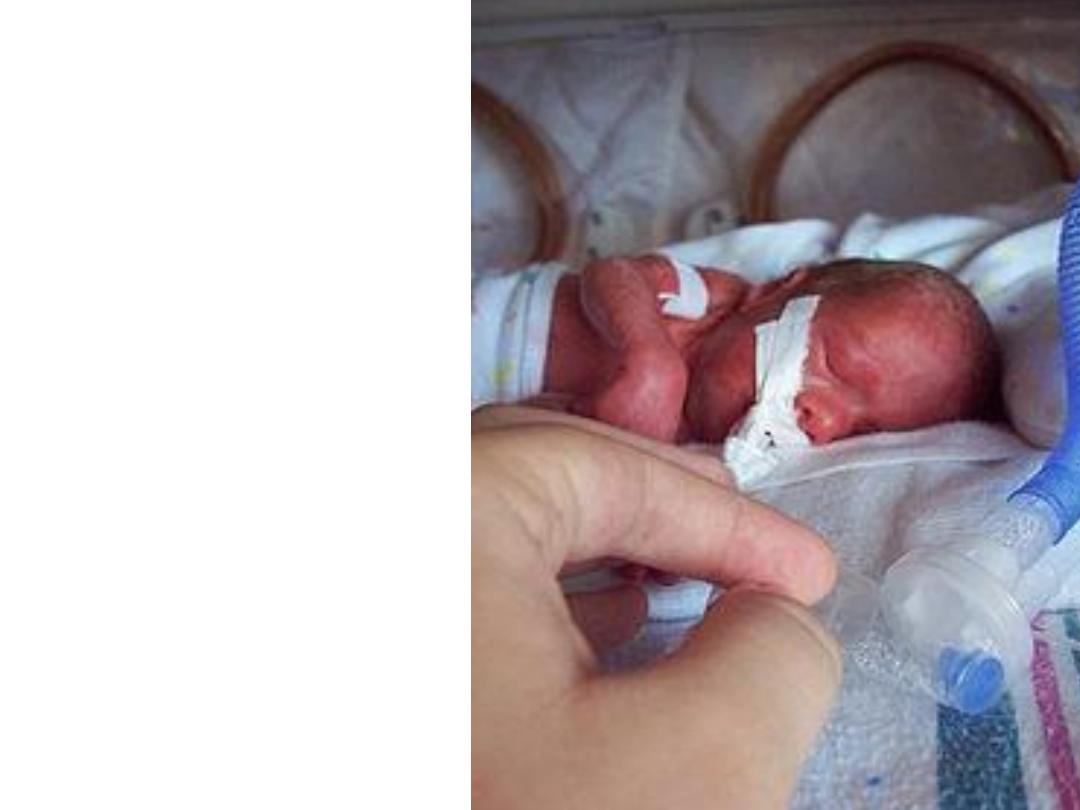
• 3-Prematurity
and low birth
weight
• 4-A New
Pregnancy
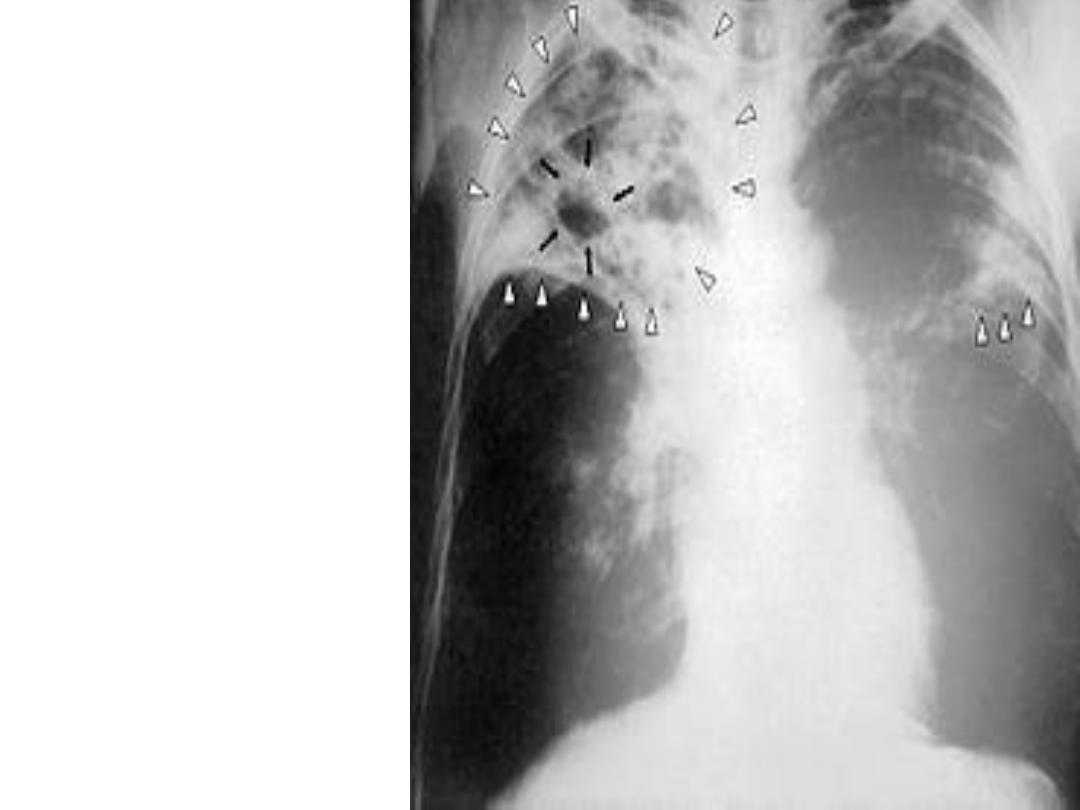
• 5-Maternal TB: As
an infant usually
receives BCG &
chemoprophylaxis
and the mother
should receive anti
TB drugs

• 6-congenital malformation of the mouth(cleft
palate)where breast milk can be expressed and
given by cup and spoon.
• 7-Fetal distress and hypoxia.

• 8-multiple
births

Problems of breast feeding
• 1-Engouraged and congested breast
• 2-milk fever
• 3-nipple pain and crack
• 4-refusal to suckle
• 5-mastitis and breast abscess
Remember !!!!
Cow’s Milk is for cows Human Milk
is for humans

Thank you
