
i
Introduction to cardiovascular system
Dr. Hassanain Mohammed Saeed
Interventional cardiologist
FICMS ( Med), FICMS (Cardiol)

Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of
adult death world wide.

anatomy

Anatomy
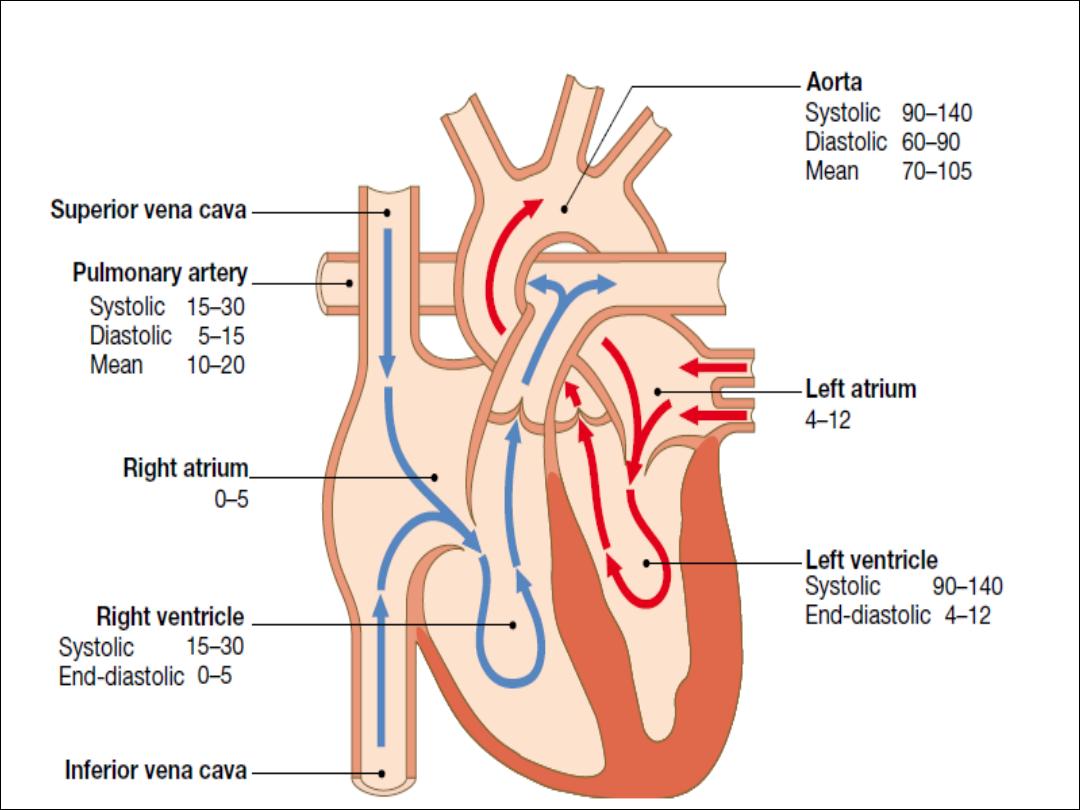
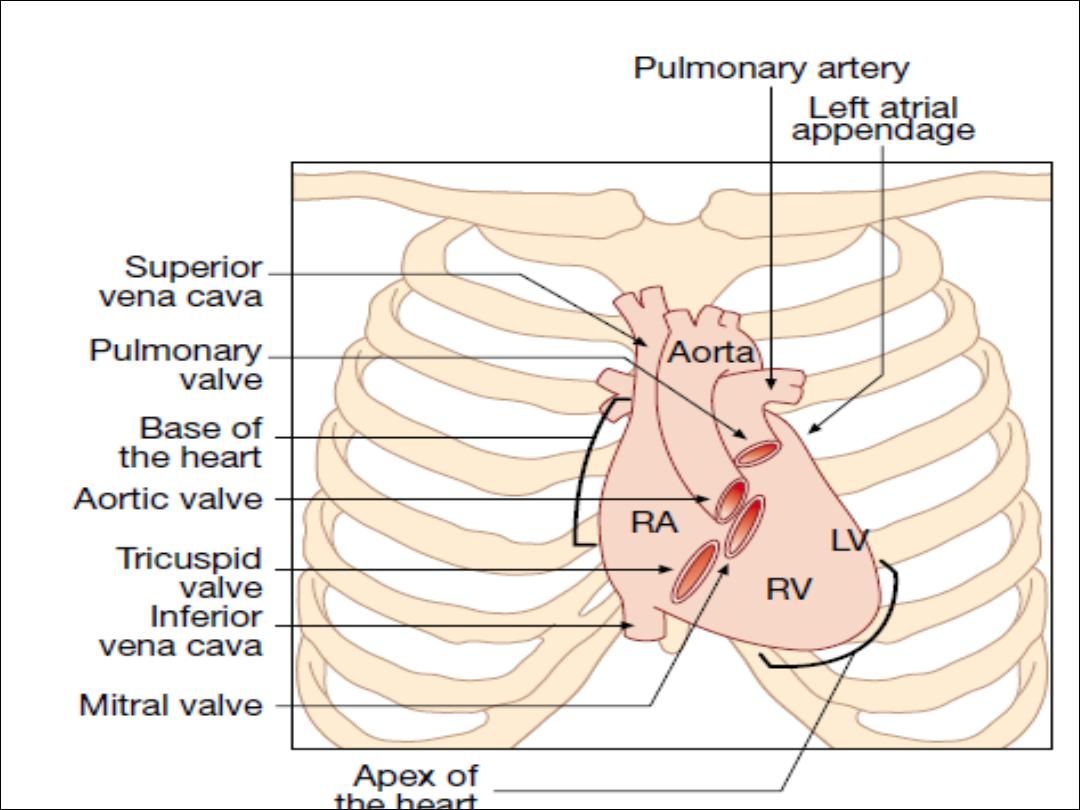
The atria are thin-walled structures
that act as priming pumps
for the ventricles, which provid most of the energy to the
circulation. Within the mediastinum, the atria are
situated
posteriorly
and the left atrium (LA) sits anterior to the
oesophagus and descending aorta.
The interatrial septum separates the two atria
In 20% of adults a patent foramen ovale is found
; this
communication in the fetal circulation between the right and
left atria normally closes at birth

The ventricles are thick-walled structure
adapted to
circulating blood through large vascular beds under
pressure.
The atria and ventricles are separated by the
annulus
fibrosus
, which forms the skeleton for the atrioventricular
(AV) valves and which electrically insulates the atria from
the ventricles

The right ventricle is roughly triangular in shape. The RV
sits anterior to and to the right of the left ventricle (LV).
The LV is more conical in shape and in cross-section is
nearly circular.
The LV myocardium is normally around 10 mm thick (c.f.
RV thickness of 2–3 mm)
because it pumps blood at a
higher pressure.

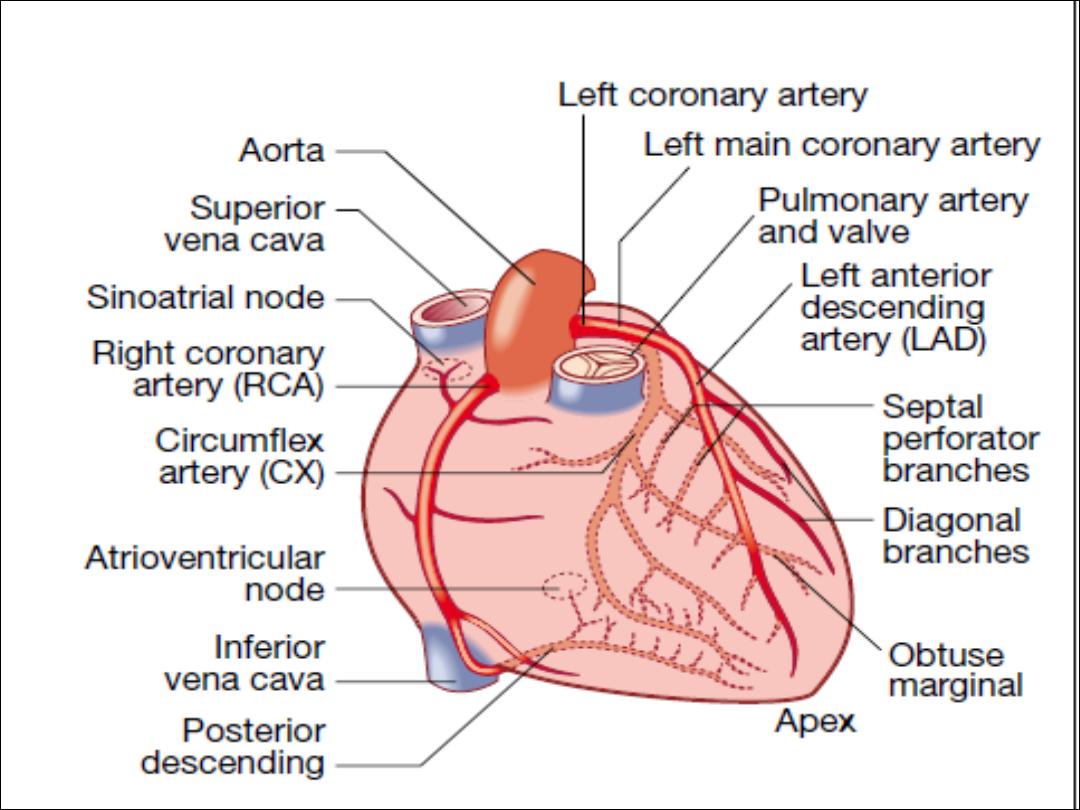
Coronary circulation

Ø
The left main and right coronary arteries arise from
the left and right sinuses of the aortic root, distal to
the aortic valve.
Ø
Within 2.5 cm of its origin, the left main coronary
artery divides into the left anterior descending artery
(LAD), which runs in the anterior interventricular
groove, and the left circumflex artery (CX), which runs
posteriorly in the atrioventricular groove.
Ø
The LAD gives branches to supply the anterior part
of the septum (septal perforators) and the anterior,
lateral and apical walls of the LV. The CX gives
marginal branches that supply the lateral, posterior
and inferior segments of LV.

Ø
The right coronary artery (RCA) runs in the right
atrioventricular groove, giving branches that supply
the RA, RV and inferoposterior aspects of the LV. The
posterior descending artery runs in the posterior
interventricular groove and supplies the inferior part
of the interventricular septum.
Ø
This vessel is a branch of the RCA in approximately
90% of people (dominant right system) and is supplied
by the CX in the remainder (dominant left system).
The coronary anatomy varies greatly from person to
person and there are many normal variants

Ø
The RCA supplies the sinoatrial (SA) node in about
60% of individuals and the AV node in about 90%.
Proximal occlusion of the RCA therefore often results
in sinus bradycardia and may also cause AV nodal
block.
Ø
Abrupt occlusion of the RCA, due to coronary
thrombosis, results in infarction of the inferior part of
the LV and often the RV. Abrupt occlusion of the LAD
or CX causes infarction in the corresponding territory
of the LV, and occlusion of the left main coronary
artery is usually fatal.

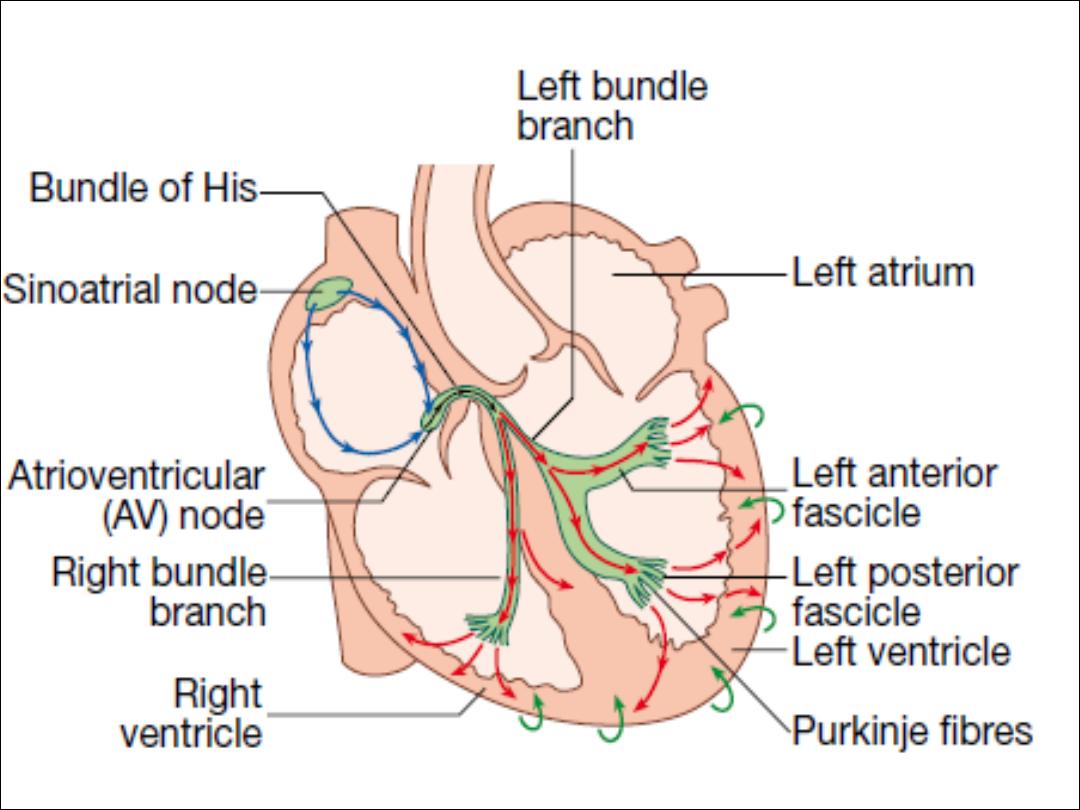
Conducting system of the heart

Ø
The SA node is situated at the junction of the superior vena cava
and RA .It comprises specialised atrial cells that depolarise at a
rate influenced by the autonomic nervous system and by
circulating catecholamines.
Ø
During normal (sinus) rhythm, this depolarisation wave propagates
through both atria via sheets of atrial myocytes. The annulus
fibrosus forms a conduction barrier between atria and ventricles,
and the only pathway through it is the AV node.
Ø
This is a midline structure, extending from the right side of the
interatrial septum, penetrating the annulus fibrosus anteriorly. The
AV node conducts relatively slowly, producing a necessary time
delay between atrial and ventricular contraction.
Ø
The His–Purkinje system is composed of the bundle of His
extending from the AV node into the interventricular septum, the
right and left bundle branches passing along the ventricular
septum and into the respective ventricles, the anterior and
posterior fascicles of the left bundle branch, and the smaller
Purkinje fibres that ramify through the ventricular myocardium. The
tissues of the His–Purkinje system conduct very rapidly and allow
near-simultaneous depolarisation of the entire ventricular myocardiu

CO = SV HR
SV= LVEDV - LVESV ( preload – after load)

The central arteries, such as the aorta, are predominantly
composed of
elastic tissue with little or no vascular smooth
muscle cells
. When blood is ejected from the heart, the
compliant aorta expands to accommodate the volume of
blood before the elastic recoil sustains blood pressure (BP)
and flow following cessation of cardiac contraction.
This ‘Windkessel effect
’ prevents excessive rises in systolic
BP whilst sustaining diastolic BP, thereby reducing cardiac
afterload and maintaining coronary perfusion.
These benefits are lost with progressive arterial stiffening: a
feature of ageing and advanced renal disease.

Passing down the arterial tree, vascular smooth
muscle cells progressively play a greater role until
the resistance arterioles are encountered. Although
all vessels contribute, the resistance vessels
(diameter 50–200 ìm) provide the greatest
contribution to systemic vascular
resistance
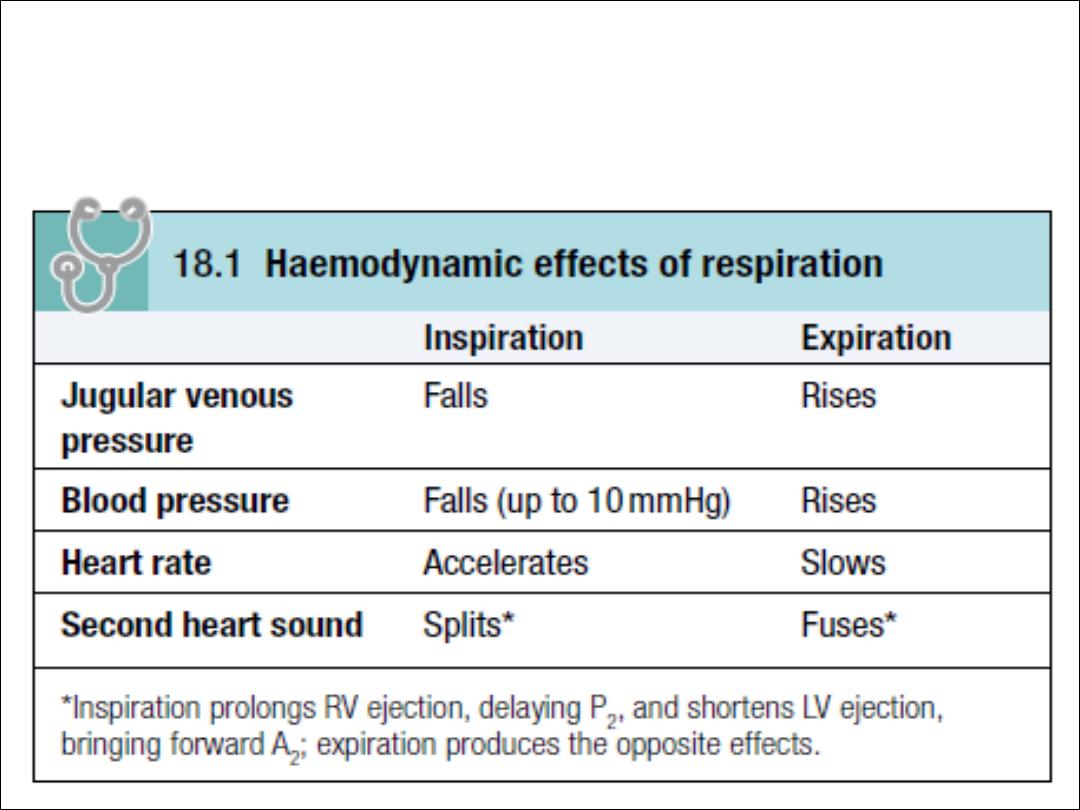
Effects of respiration

Investiagation of cardiovascular system
:
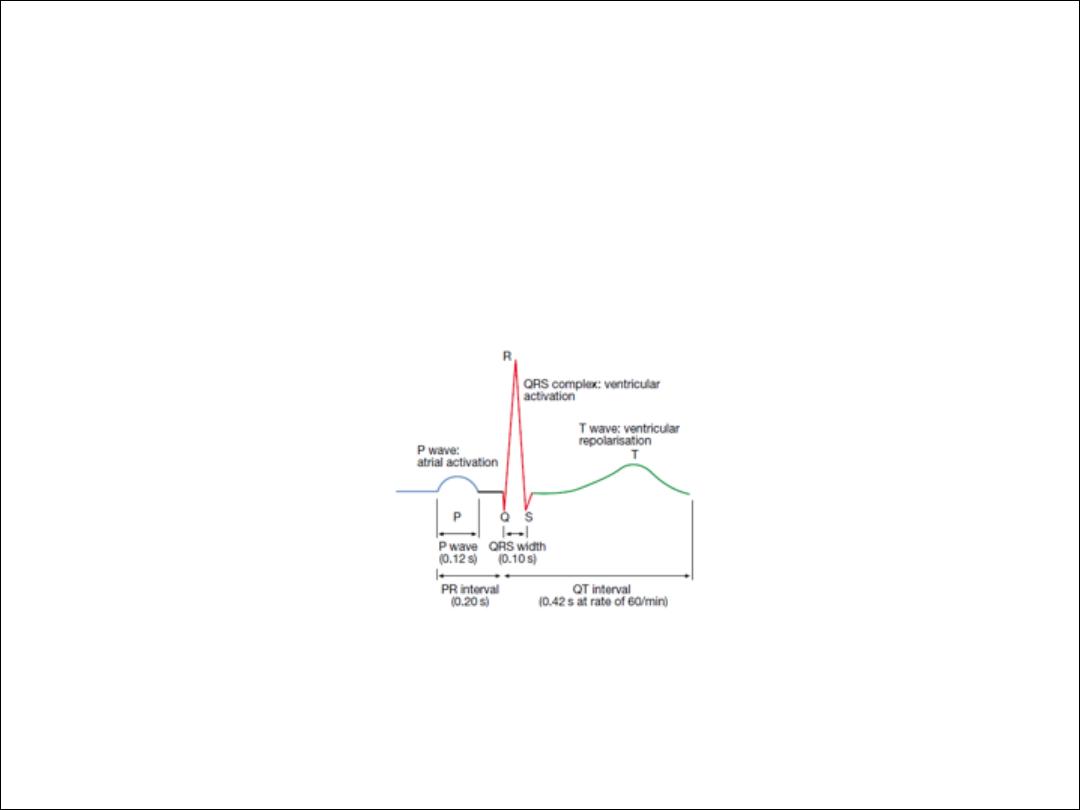
ECG
assess rhythm and conduction disorder and give
impression on chamber size, diagnosie myocarial
ischemia and infarction
12 leads resting ECG
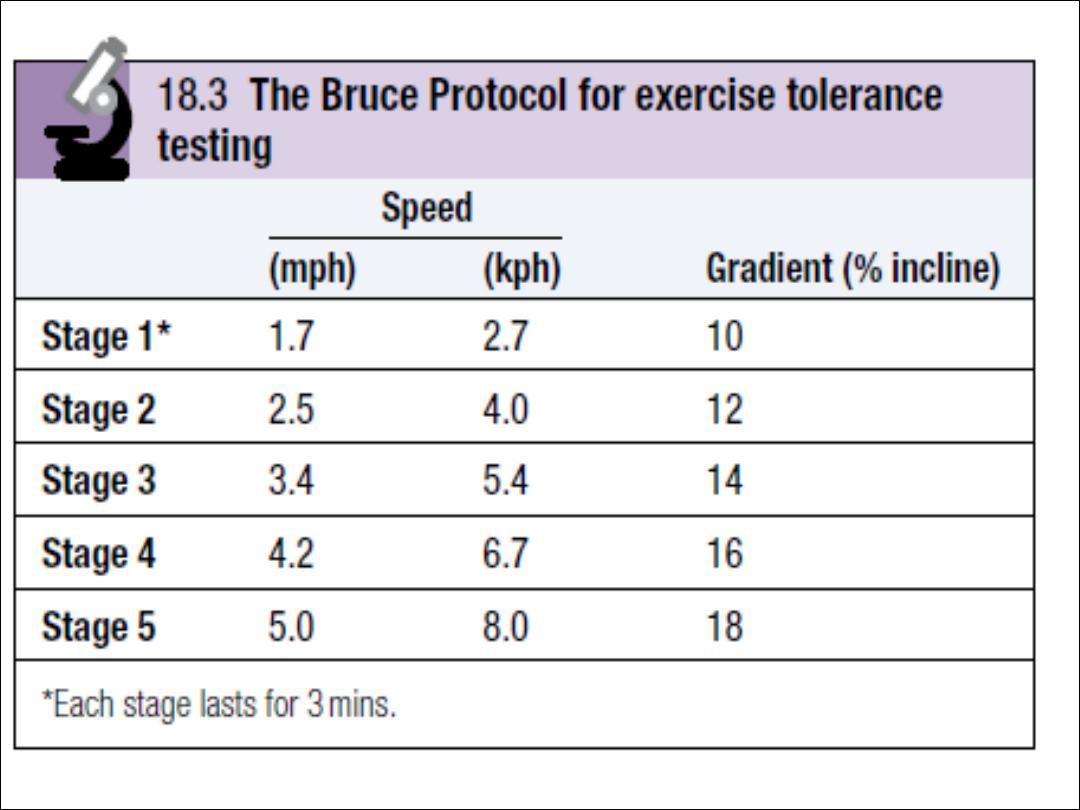
TMT or exercise ECG
Ambulatory ECG, 1 to 7 days or patient activated loop
recorder

Cardiac biomarkers
Brain natriuretic peptide
Cardiac troponin

CXR
This is useful for determining the size and shape of the heart, and the
state of the pulmonary blood vessels and lung fields. Most information
is given by a postero-anterior (PA) projection taken in full inspiration.
Anteroposterior (AP) projections can be performed when patient
movement is restricted but result in magnification of the cardiac
shadow.
An estimate of overall heart size can be made by comparing the
maximum width of the cardiac outline with the maximum internal
transverse diameter of the thoracic cavity.
The term cardiomegaly is used to describe an enlarged cardiac
silhouette when the ratio of cardiac width to the width of the lung
fields is greater than 0.5. Cardiomegaly can be caused by chamber
dilatation, especially left ventricular dilatation, or by a pericardial effusion,
but may also be due to a mediastinal mass or pectus excavatum.

•
Dilatation of individual cardiac chambers can be recognised
by the characteristic alterations to the cardiac silhouette:
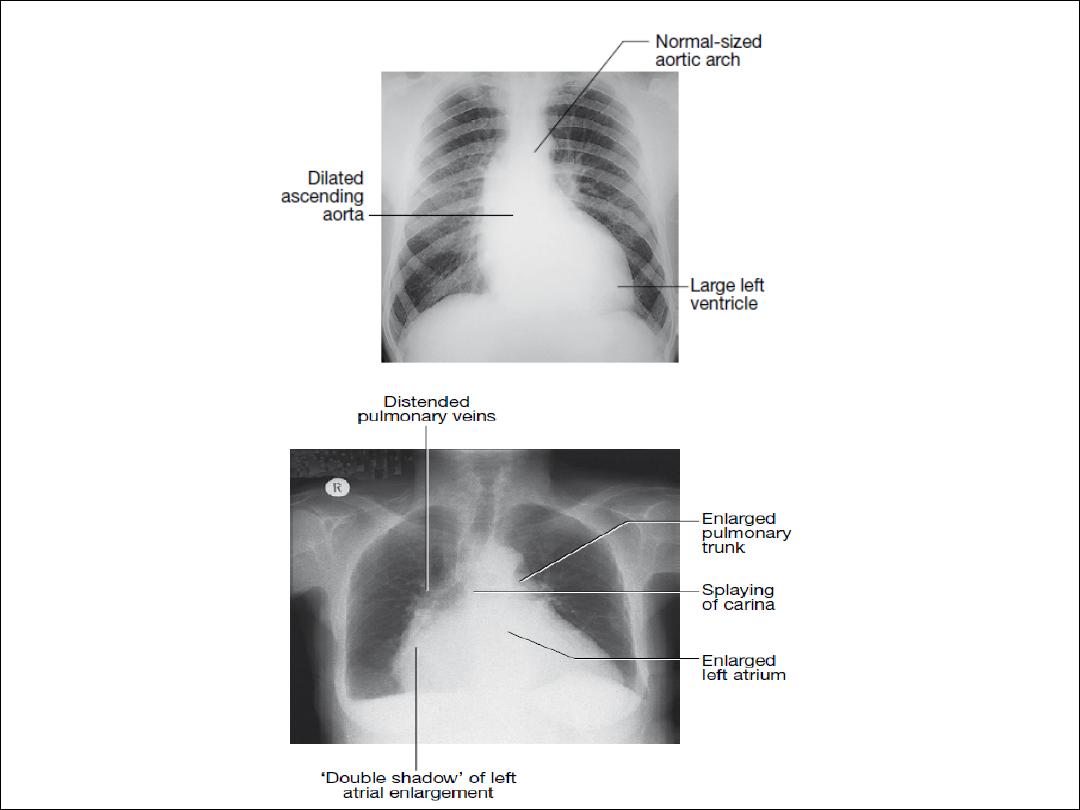
• Left atrial dilatation results in prominence of the left atrial
appendage, creating the appearance of a straight left heart
border, a double cardiac shadow to the right of the sternum,
and widening of the angle of the carina (bifurcation of the
trachea) as the left main bronchus is pushed upwards.
• Right atrial enlargement projects from the right heart border
towards the right lower lung field. • Left ventricular dilatation
causes prominence of the left heart border and enlargement
of the cardiac silhouette. Left ventricular hypertrophy produces
rounding of the left heart border.
• Right ventricular dilatation increases heart size, displaces the
apex upwards and straightens the left heart border.

Echocardiography
Trasthoracic
Tranesophageal echo
Stress echo
