Investigation of respiratory
system
Assistant prof Dr.Ahmed Hussein Jasim
F.I.B.M.S (resp)
F.I.B.M.S ( med)
Investigation of respiratory system
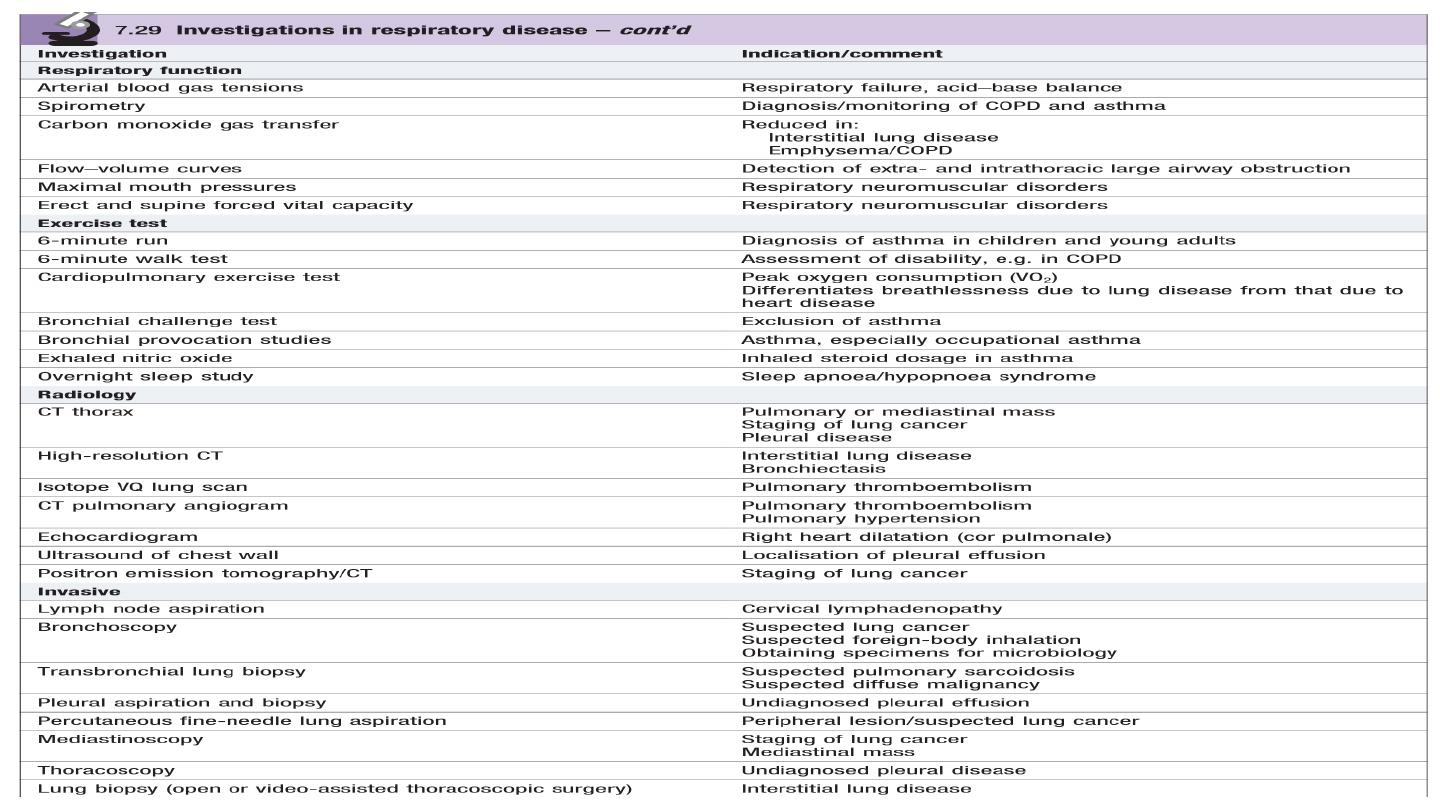
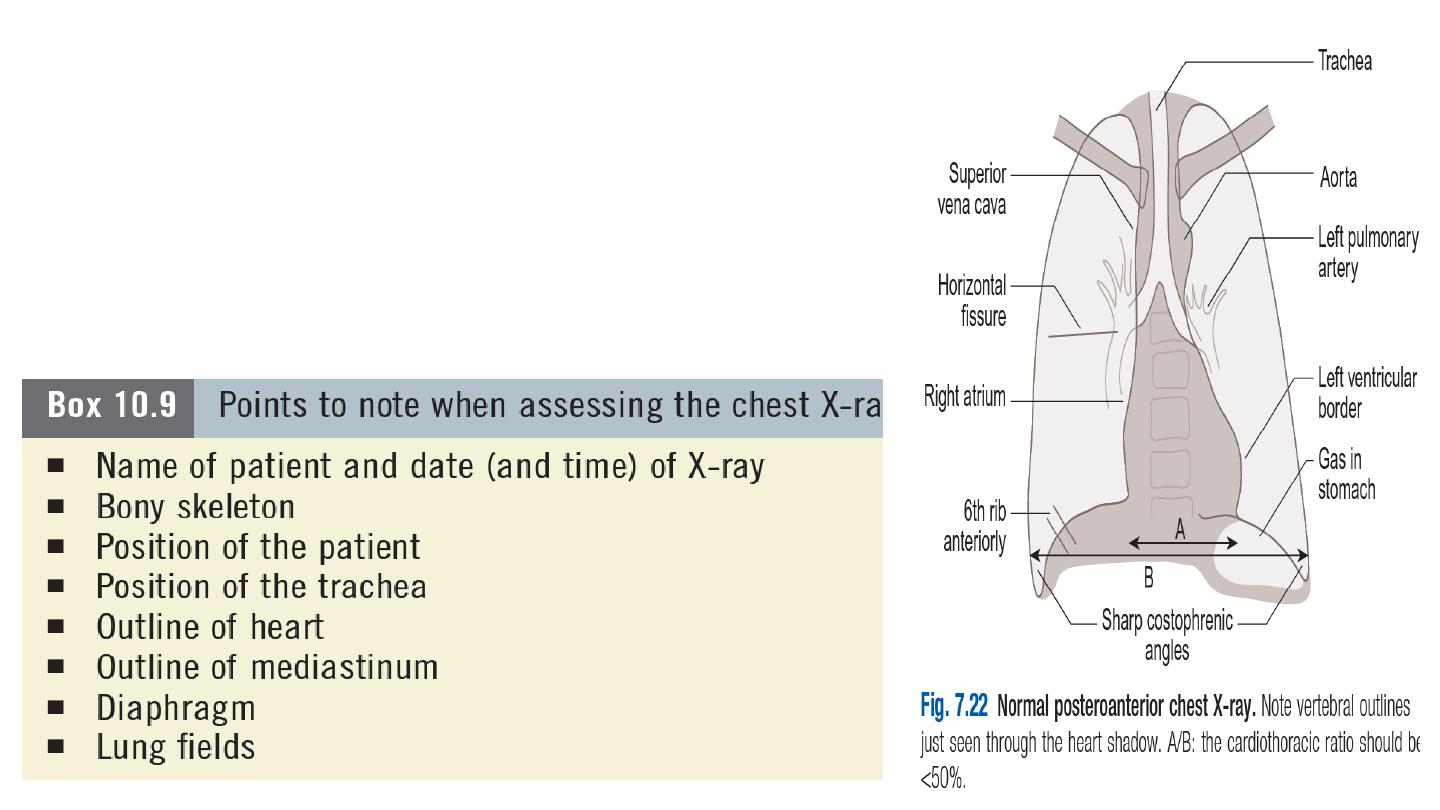
1- Chest X-ray
The standard chest X-ray is a posteroanterior (PA) view
taken with the film in front of the anterior chest and the X-
ray source 2 metres behind the patient.
Always compare an abnormal chest X-ray with previous
films to see if abnormalities are resolving or longstanding.
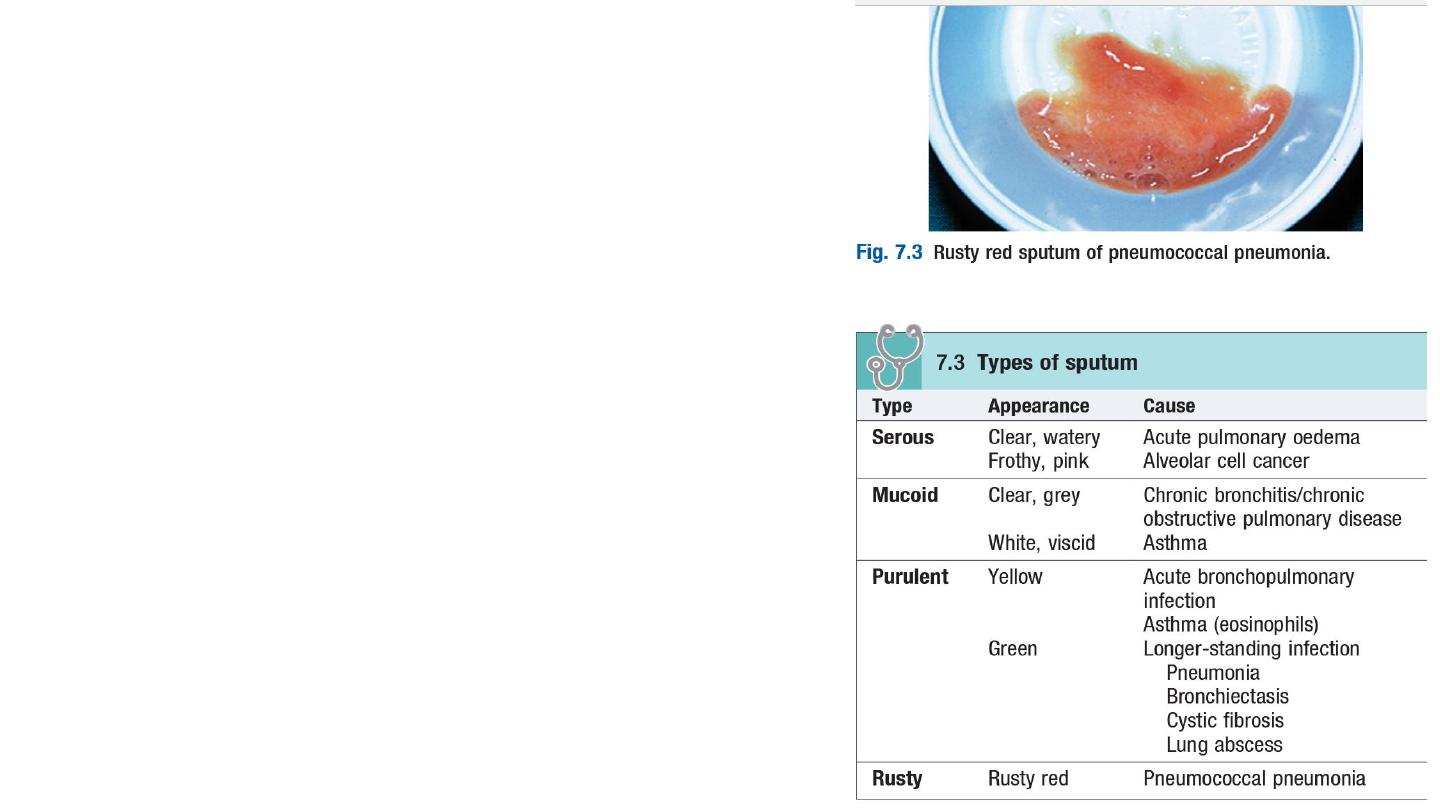
2- Sputum examination
Inpatients with respiratory symptoms should have a
sputum pot for inspection.
Gram stain helps rapid identification of the causative
organism: for example,
Gram-positive – pneumococcus or staphylococcus;
Gram-negative – Haemophilus influenzae.
If the patient’s symptoms and chest X-ray suggest
tuberculosis send several sputum samples urgently
for auramine staining (screening); if these are
positive, obtain a Ziehl–Neelsen stain.
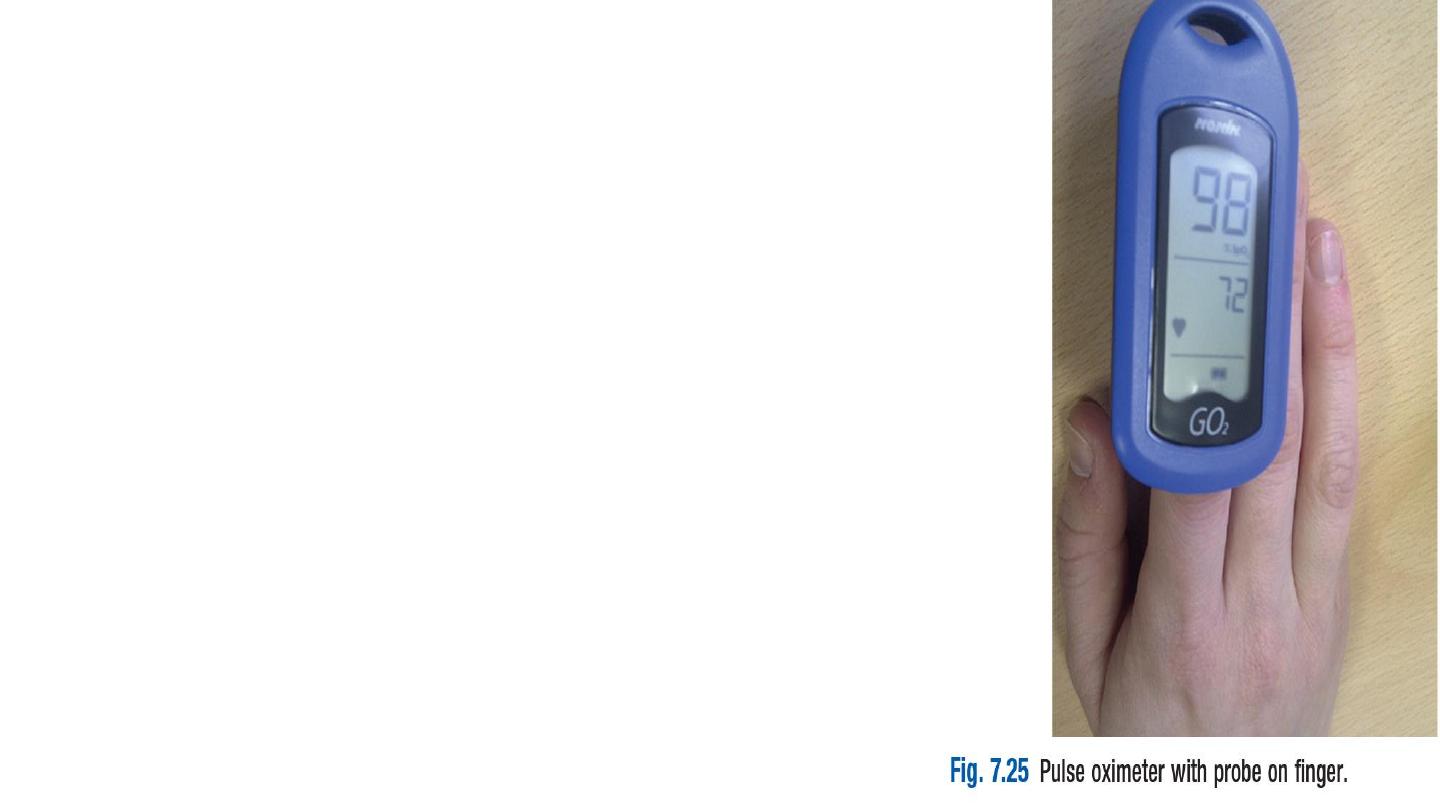

3- Pulse oximetry
An oximeter is a spectrophotometric device that measures
arterial oxygen saturation (SpO2) by determining the
differential absorption of light by oxyhaemoglobin and
deoxyhaemoglobin.
Modern oximeters use a probe incorporating a light source
and sensor attached to a patient’s ear or finger.
Oximeters are easy to use, portable, non-invasive and
inexpensive. They are widely used for the continuous
measurement of SpO2 and to adjust oxygen therapy.
In acutely ill patients with no risk of CO2 retention, SpO2
should be maintained at 94–98%. Movement artifact, poor
tissue perfusion, hypothermia and nail varnish can lead to
spuriously low SpO2 values.
Dark skin pigmentation and raised levels of bilirubin or
carboxyhaemoglobin can result in false increases in SpO2.
Oximetry is less accurate with saturations <75%.

4-Arterial blood gas analysis
In a sample of arterial blood, the partial pressures of oxygen (PaO2) and of carbon
dioxide (PaCO2), and the pH, can be measured. The arterial PaCO2 will reflect the
effective ventilation of alveoli that are adequately perfused with blood so that efficient
gas exchange can take place. The normal range Paco2
4.7-6.0 kPa (36-45 mmHg). When alveolar ventilation is reduced, the PaCO2 will rise.
The PaO2 is normally in the range 11.3-14.0 kPa (80-100 mmHg).
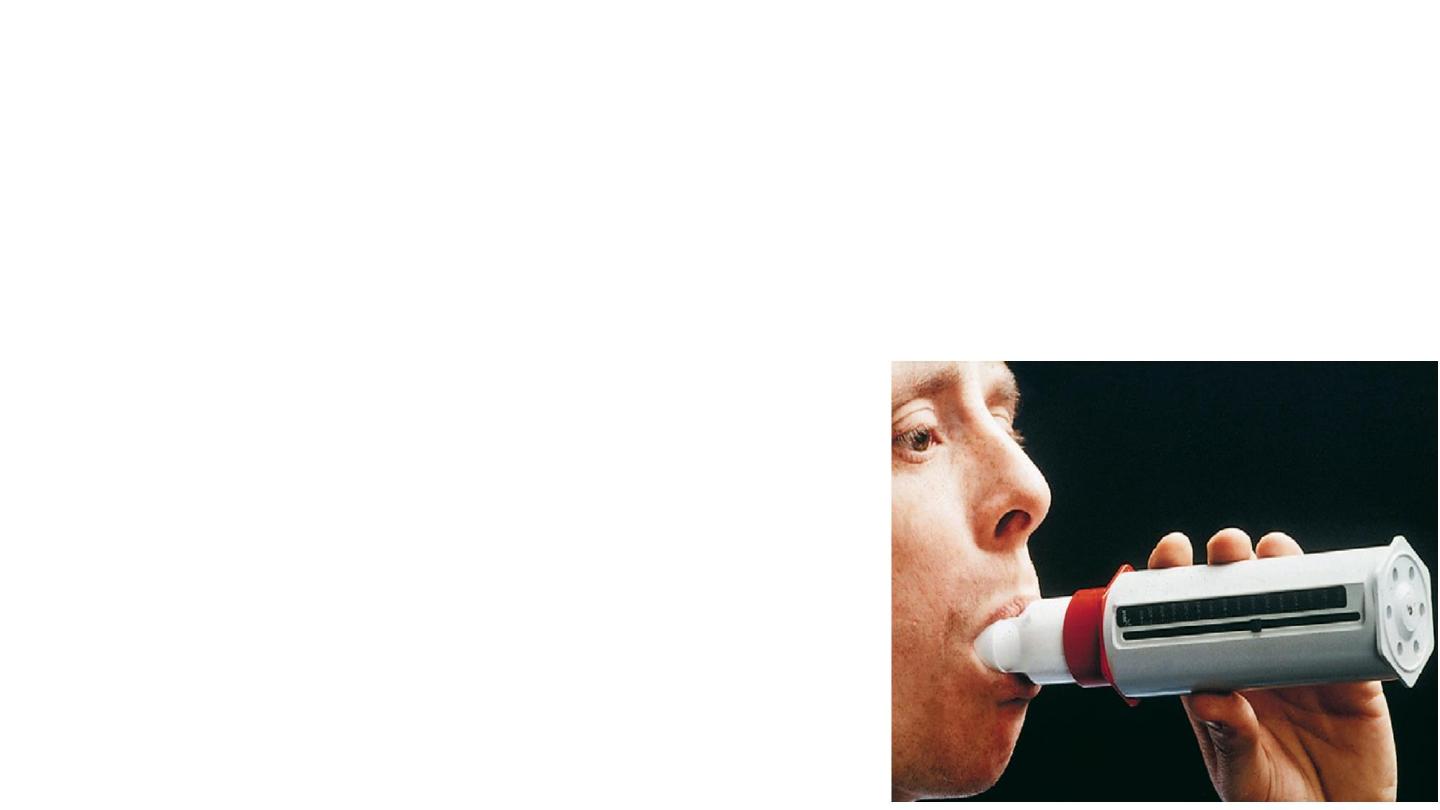
5- Spirometry
Dynamic lung volumes are measured by inhaling to total
lung capacity and then exhaling into a spirometer with
maximal effort to residual volume.
The volume exhaled in the first second is the FEV1 and
the total volume exhaled is the FVC.
Normal predictive values for FEV1 and FVC are
influenced by age, gender, height and race. In healthy
young and middle-aged adults the FEV1/FVC ratio is
usually >75%
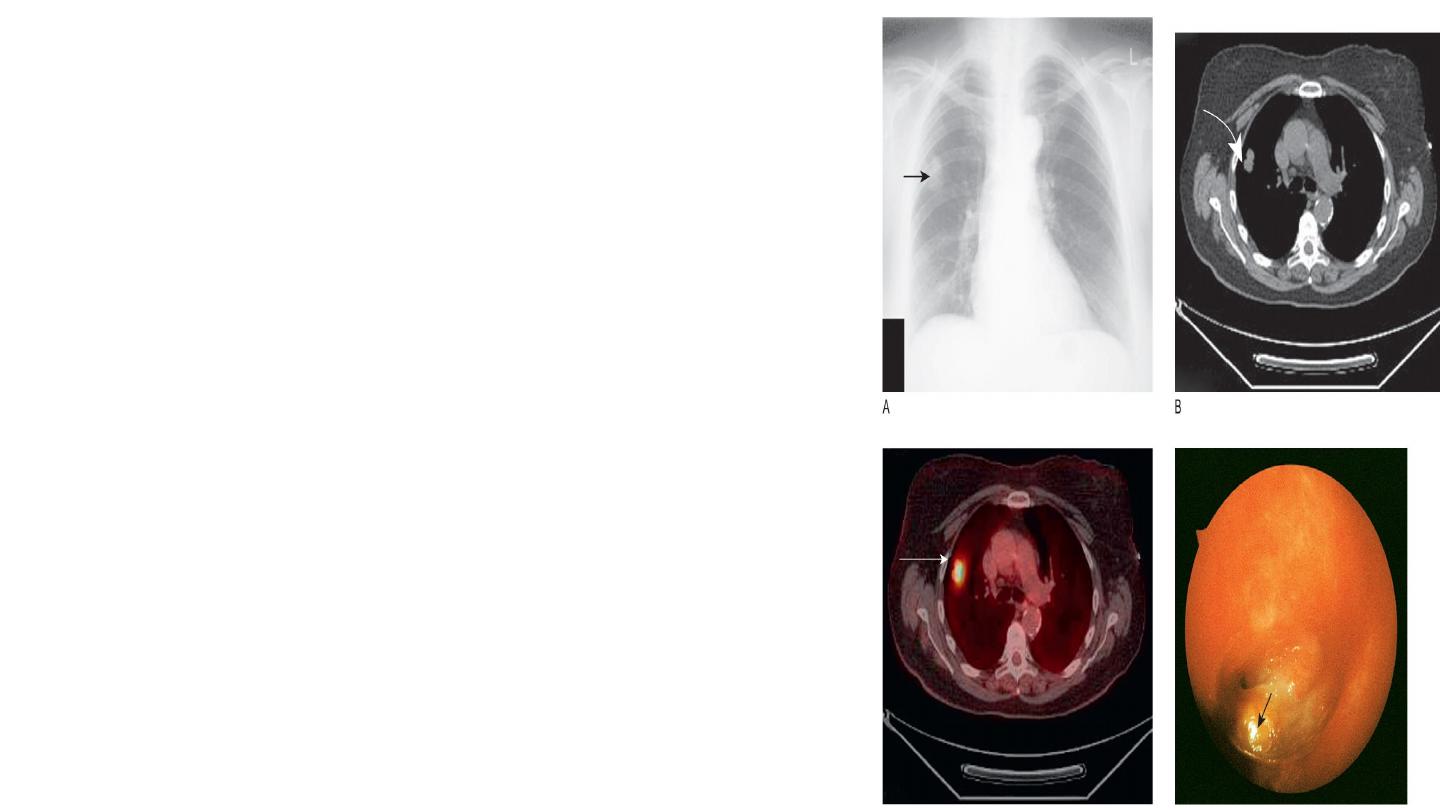
6- The computed tomography scan
In computed tomography (CT) scanning, X-rays are
passed through the body at different angles and the
resulting information is processed by computer to
generate a series of cross-sectional images.
A thoracic CT scan thus comprises a series of cross-
sectional ‘slices’ through the thorax at various levels.
The CT scan is a vital part of the staging of lung
cancer, and inoperability may be demonstrated by
evidence on CT of mediastinal involvement.
CT scanning will demonstrate the presence of dilated
and distorted bronchi, as in bronchiectasis.
Diffuse pulmonary fibrosis will be shown by a
modified high-resolution/thin-section scan technique.
Emboli in the pulmonary arteries can be
demonstrated by a rapid data acquisition spiral CT
technique, and has advantages over isotope lung
scanning

7- Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is useful in demonstrating mediastinal
abnormalities and can help evaluate invasion of the mediastinum and chest wall by
tumour. Apart from the fact that it does not use ionizing radiation, currently it has
few other advantages over CT in imaging the thorax.
8-Ultrasound
Ultrasound reveals much less detail than CT scanning but has the advantages that it
does not involve radiation and, as it gives ‘real-time’ images.
Ultrasound is used for examining diaphragmatic movement.
Ultrasound is also valuable in distinguishing pleural thickening from pleural fluid. With
real-time imaging, the latter can be seen to move with changes in posture.
ultrasound may be used to aid placement of a catheter to drain the collection, and
also to steer a draining catheter accurately into an intrapulmonary abscess.
9- Positron emission tomography (PET) scanning
In this technique, a radiolabelled 18-
flurodeoxyglucose (FDG) molecule is administered,
which is taken up by metabolically active tissues,
such as cancers, showing as ‘hot spots’ on the
image.
It is useful in detecting regional and mediastinal
lymphadenopathy and is now widely used to
assess suitability for surgery in patients with lung
cancer.
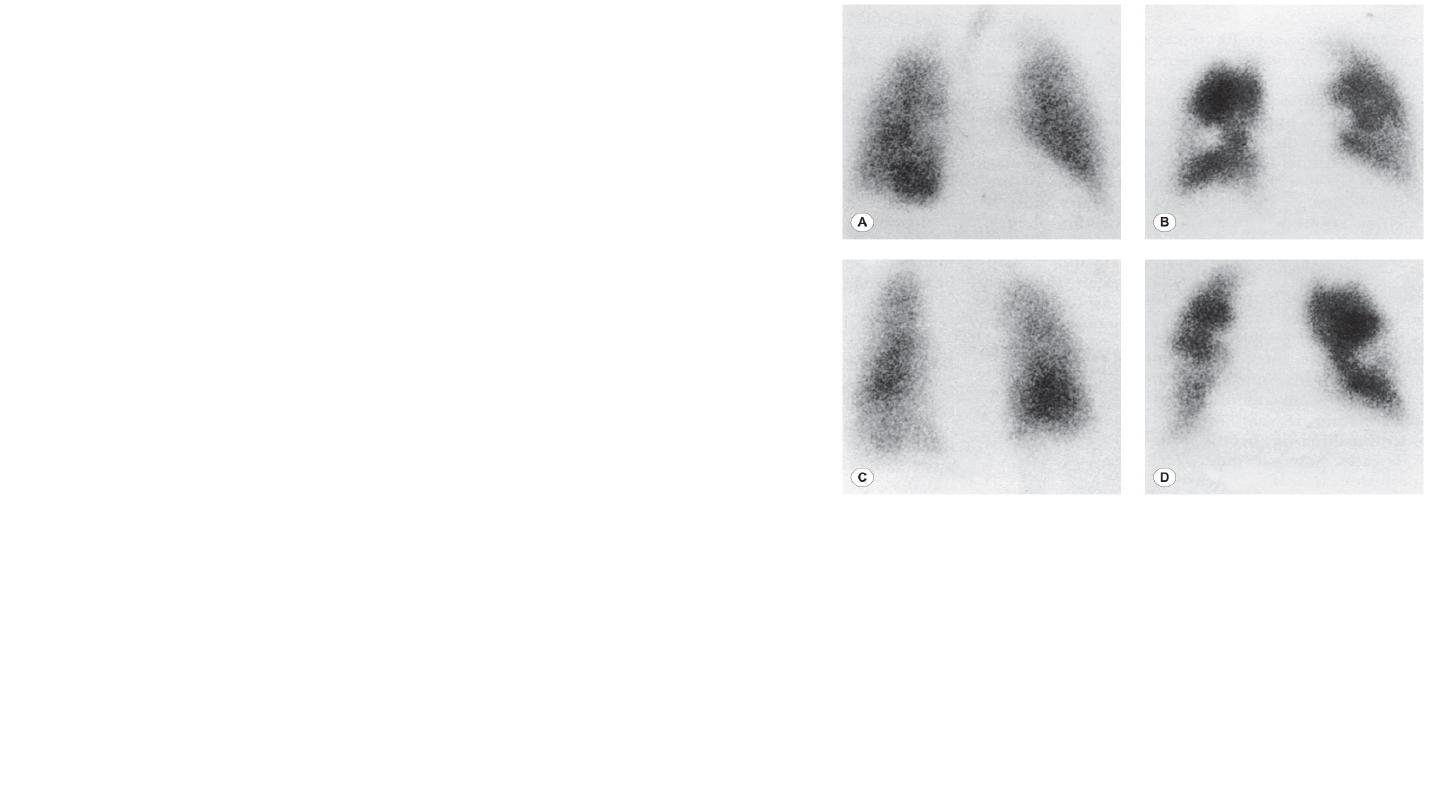
10-Radioisotope imaging
In the lungs, the most widely used radioisotope technique is combined ventilation and perfusion scanning,
used to aid the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. The perfusion scan is performed by injecting
intravenously a small dose of macroaggregated human albumin particles labelled with technetium-99m
(99mTc). A gamma-camera image is then built up of the radioactive particles impacted in the pulmonary
vasculature; the distribution of perfusion in the lung can then be seen.
The ventilation scan is obtained by inhalation of a radioactive gas such as krypton81m (81mKr), again using
scanning to identify the distribution of the radioactivity.
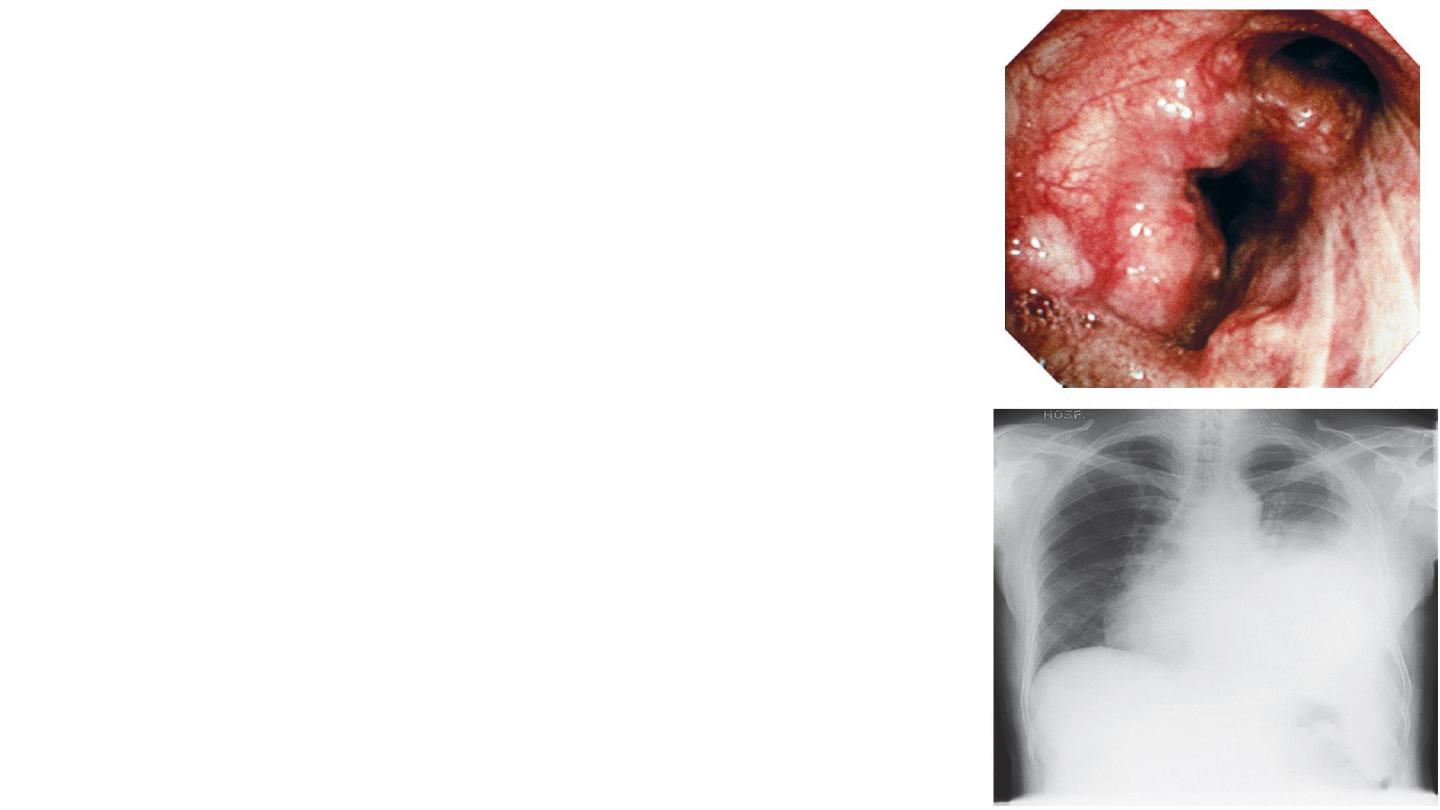
11- Flexible bronchoscopy Bronchoscopy
is an essential tool in the investigation of many forms of
respiratory disease.
For discrete abnormalities, such as a mass seen on chest
X-ray and suspected to be a lung cancer, bronchoscopy is
usually indicated to investigate its nature.
Under local anaesthesia, the flexible bronchoscope is
passed through the nose, pharynx and larynx, down the
trachea, and the bronchial tree is then inspected.
12- Pleural aspiration and biopsy A pleural effusion can
give rise to diagnostic problems and, sometimes,
management problems when the amount of fluid causes
respiratory embarrassment.
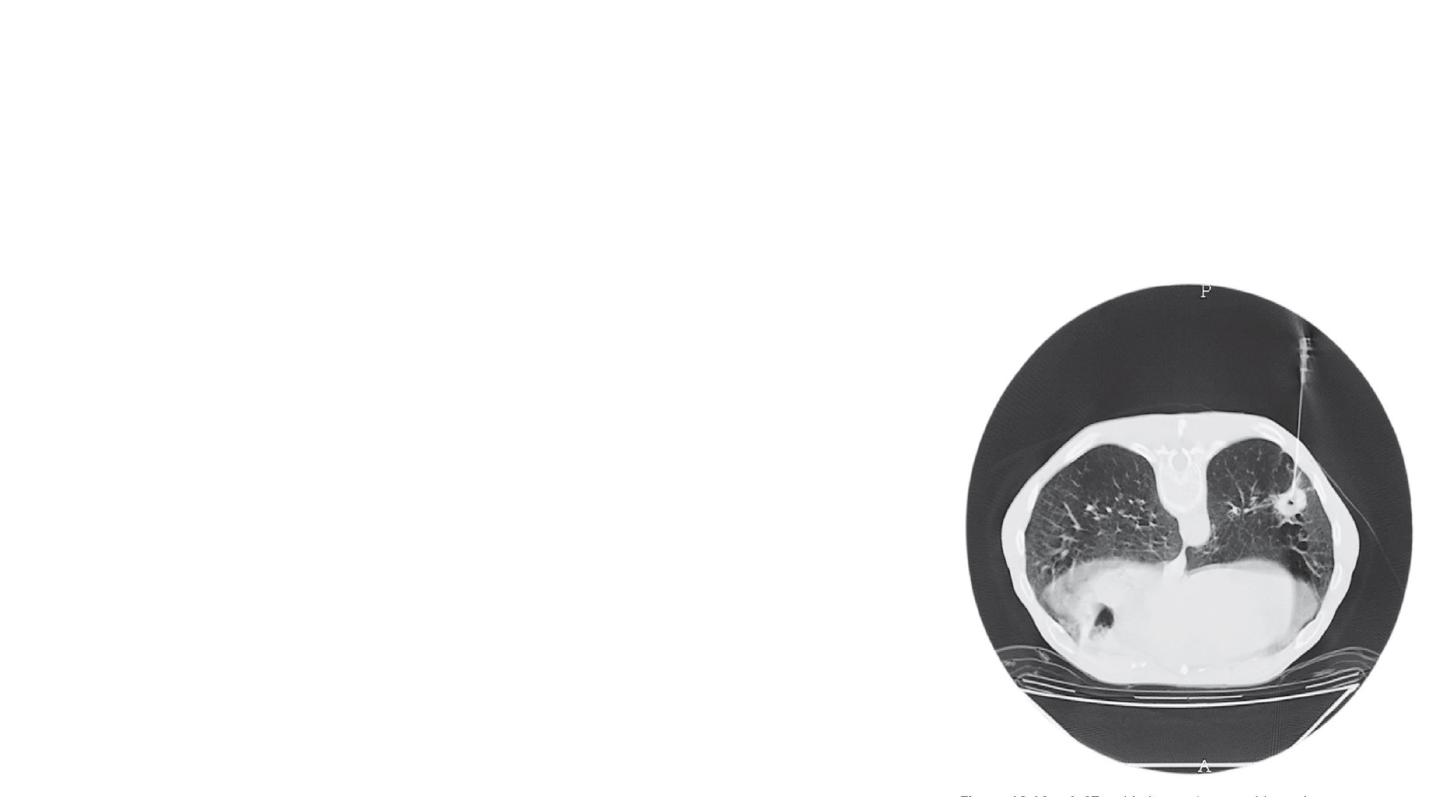

13- Thoracoscopy
This technique enables the pleural cavity to be examined directly and biopsies taken under
direct vision.
The procedure is commonly performed under a general anaesthetic by a surgeon who uses a
rigid thoracoscope after the lung has been deflated. Increasingly, however, more minimally
invasive procedures using flexible thoracoscopes attached to cameras are being used (video-
assisted thoracoscopic surgery or VATS).
14- Lung biopsy
When there is a discrete, localized lesion, it may be possible
to obtain a biopsy percutaneously with the aid of CT
scanning to direct the insertion of the biopsy needle