Secret Lectures
(7)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
1
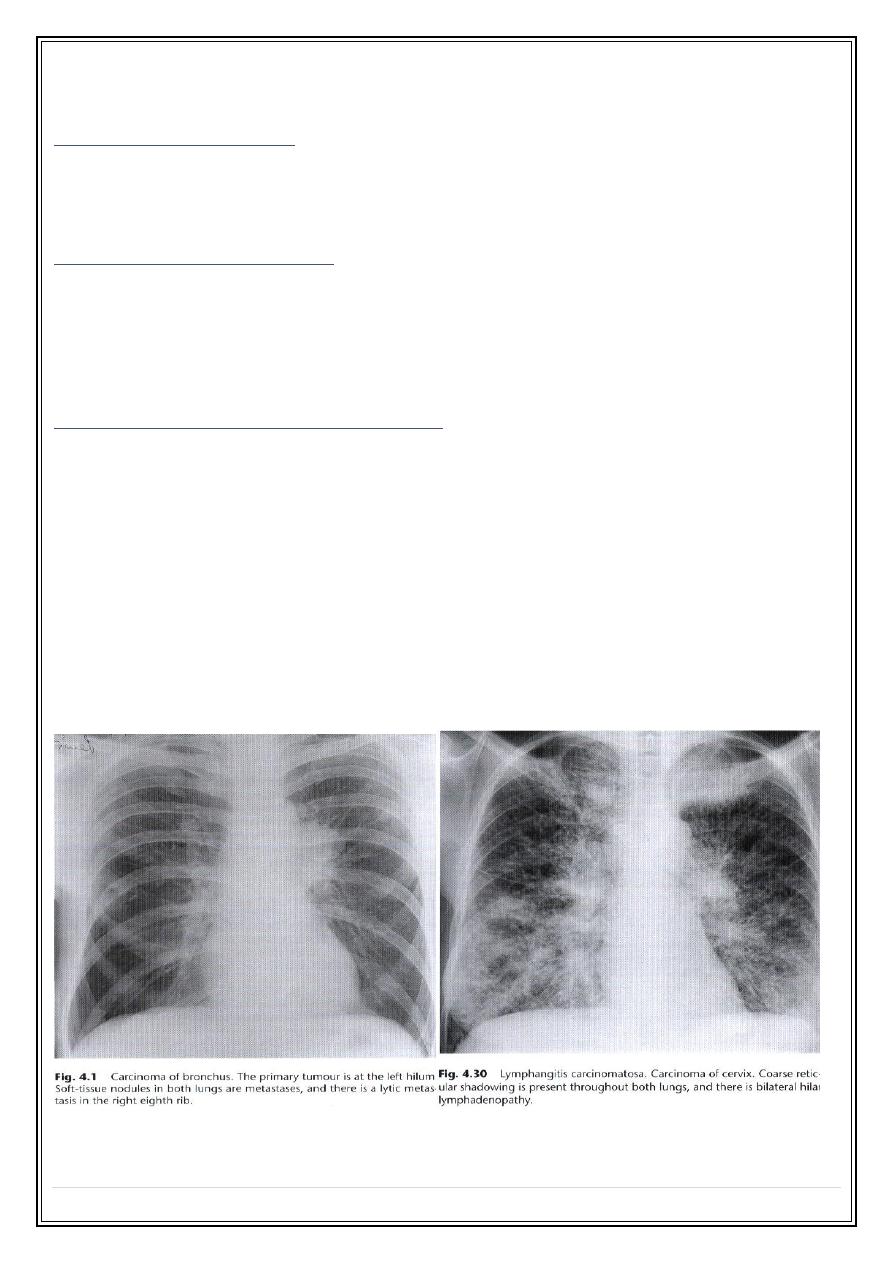
Carcinoma of bronchus
Signs of central tumour:
1.
Hilar mass
with or with out narrowing of the adjacent major bronchus.
2.
Collapse and/or consolidation
of lung beyond the tumour
Signs of peripheral tumour :
1. A round shadow (
solitary pulmonary nodule
) with an irregular borders (
lobulation, notching and infiltrating edge ).
2.
Cavitation
within the mass, the walls of the cavity is usually thick &
irregular, but thin-walled smooth cavities do occur.
Signs of Spread of bronchial carcinoma
1.
Lymphatic spread
—leading to hilar or mediastinal lymph node
enlargement.
2.
Pleural spread
--- pleural effusion.
3.
Mediastinal spread
---On plain films the signs are widening of the
mediastinal shadow and elevation of the hemidiaphragm suggesting
phrenic nerve involvement.
4.
Invasion of the chest wall
. --- destruction of a rib immediately adjacent to
a pulmonary shadow is virtually diagnostic of bronchial carcinoma with
chest wall invasion.
5.
Rib metastasis-
- usually lytic.
6.
Pulmonary metastasis
. Rounded shadows similar to secondary deposits
from other primary tumours.
7.
lymphangitis carcinomatosis-
course linear, reticular & nodular basal
shadowing often with pleural effusion, usually bilateral
Secret Lectures
(7)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
2
Metastatic neoplasms
1.
Pulmonary metastases :
typically spherical & well defined , occasionally irregular borders, usually multiple
and vary in size .
2.
Pleural metastases :
usually give rise to pleural effusion, individual pleural metastases are rarely seen.
3.
Ribs metastases :
All accept prostate and breast cancers produce mainly or exclusively lytic
metastases . Soft tissue swelling is frequently seen adjacent to the rib deposit.
4.
Lymphangitis carcinomatosis
Lymphoma
The common manifestations of intrathoracic malignant lymphoma are:
1.
Mediastinal &hilar lymphadenopathy.
2. Pleural effusion.
3
.
Pulmonary involvement
, is unusual, it may take the form of large areas of infiltration
of the lung parenchyma resembling consolidation or occasionally one or more
mass lesions which may cavitates.
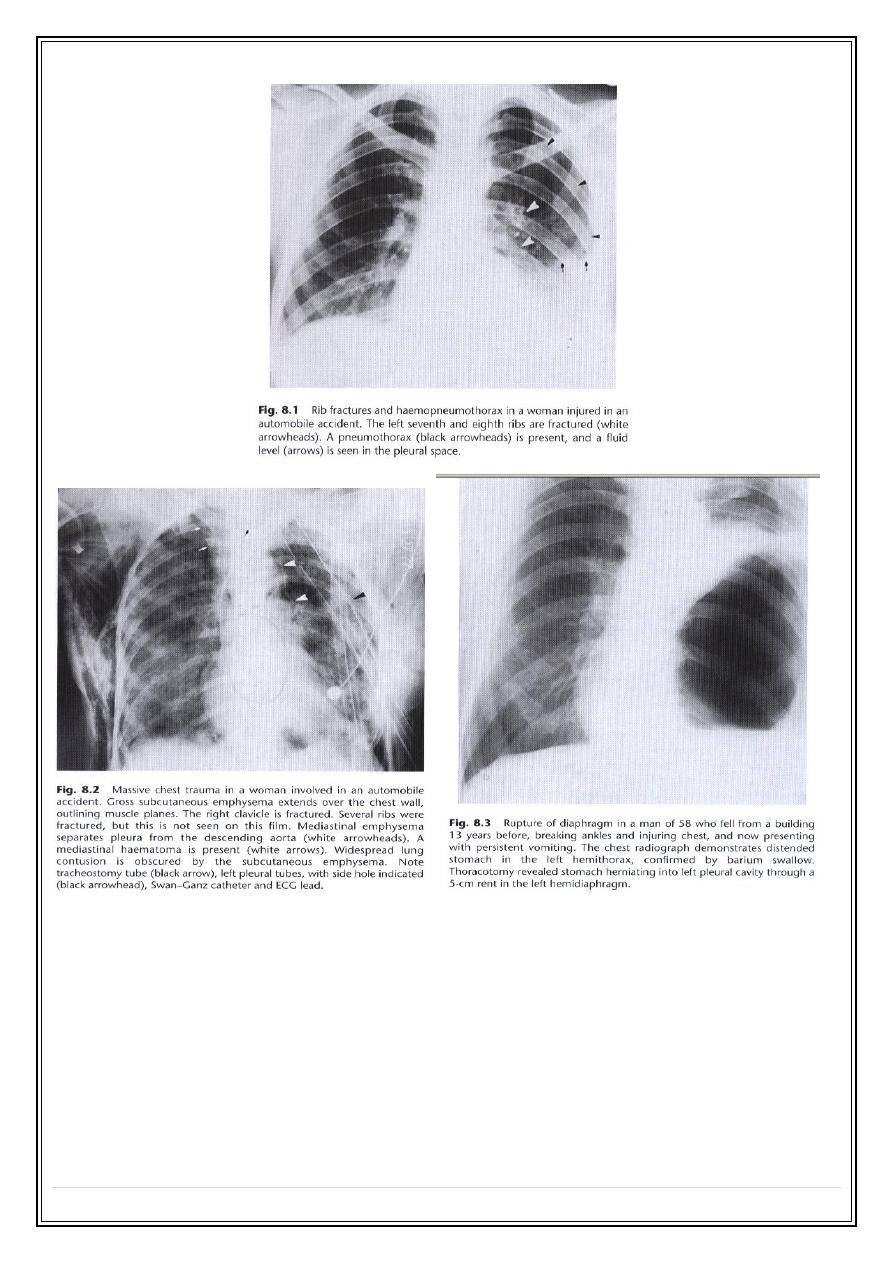
Chest trauma
1. Rib fracture
. frequently multiple & may results in a flail segment.
2
.
Pleural effusion.
is frequently accompanied rib fractures. the fluid frequently being
blood.
3
.
Pneumothorax
. Air fluid level due to associated haemorrhage (
haemopneumothorax
) is common in such situations.
4
.
Surgical emphysema
.
5.
Pulmonary contusion
. localized traumatic alveolar haemorrhage and edema
associated or not with rib fracture. Resulting shadow may be undistinguished
from other forms of pulmonary consolidation ( history is the rule )
5
.
Adults respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS ).
6. Ruptured diaphragm.
Commoner on the left than right. Gas shadows above
diaphragm & indistinct diaphragm are the features. Ba studies is supportive
test.
7. Rupture of aorta.
Mediastinal widening due to bleeding with or without pleural fluid is
the plain film signs of ruptured aorta.
Secret Lectures
(7)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
3
Thank You,,,
