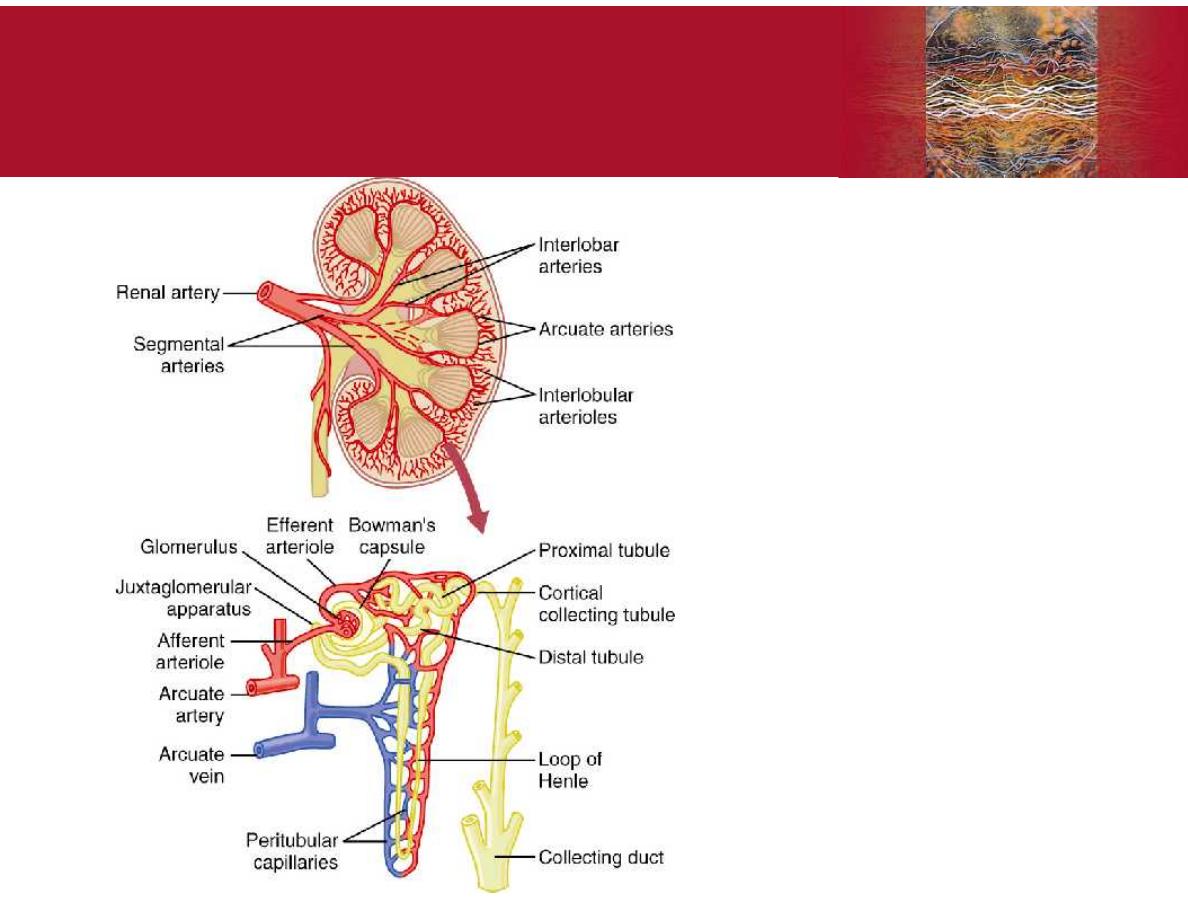
Figure 26-3;
Guyton and Hall
Nephron:
functional unit of
the kidney
Nephron:
functional unit of
the kidney
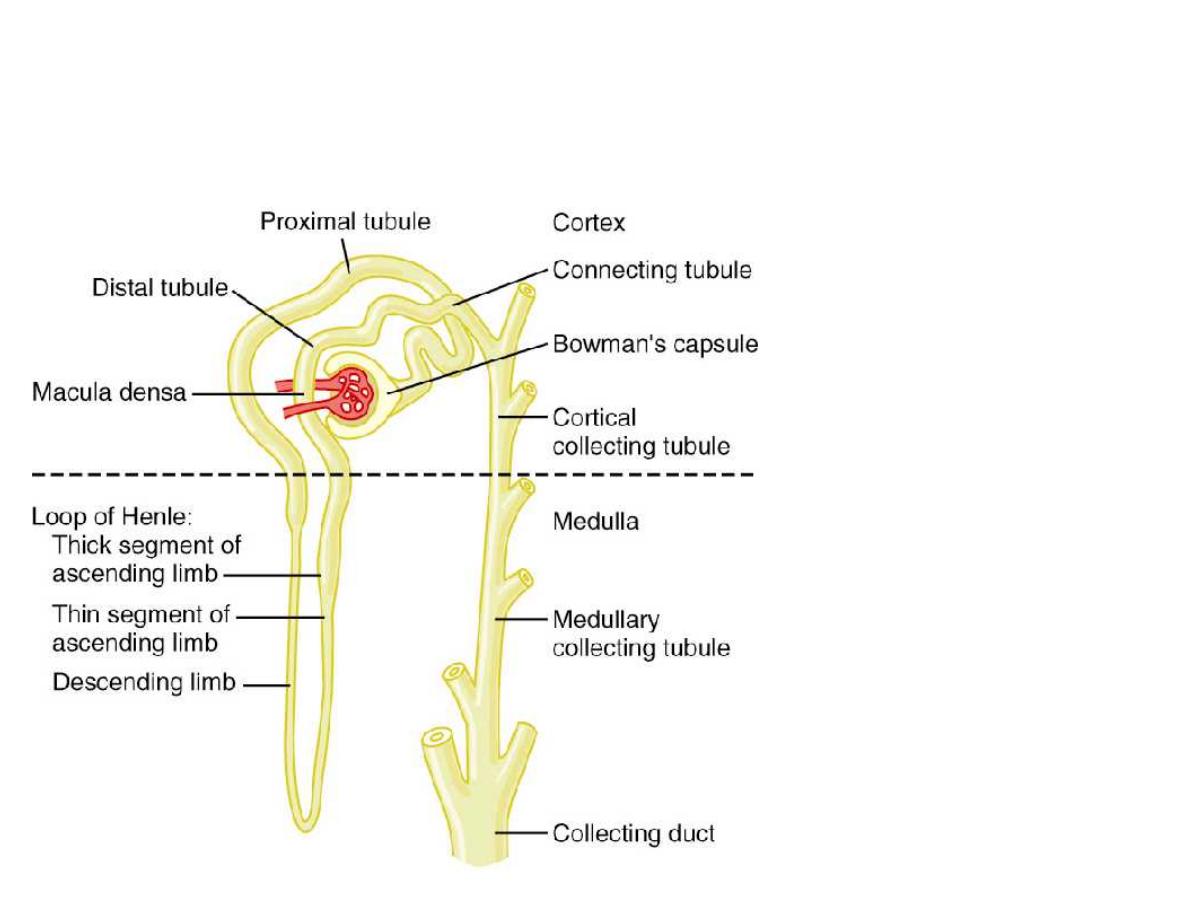
Figure 26-4;
Guyton and Hall
Nephron Tubular Segments
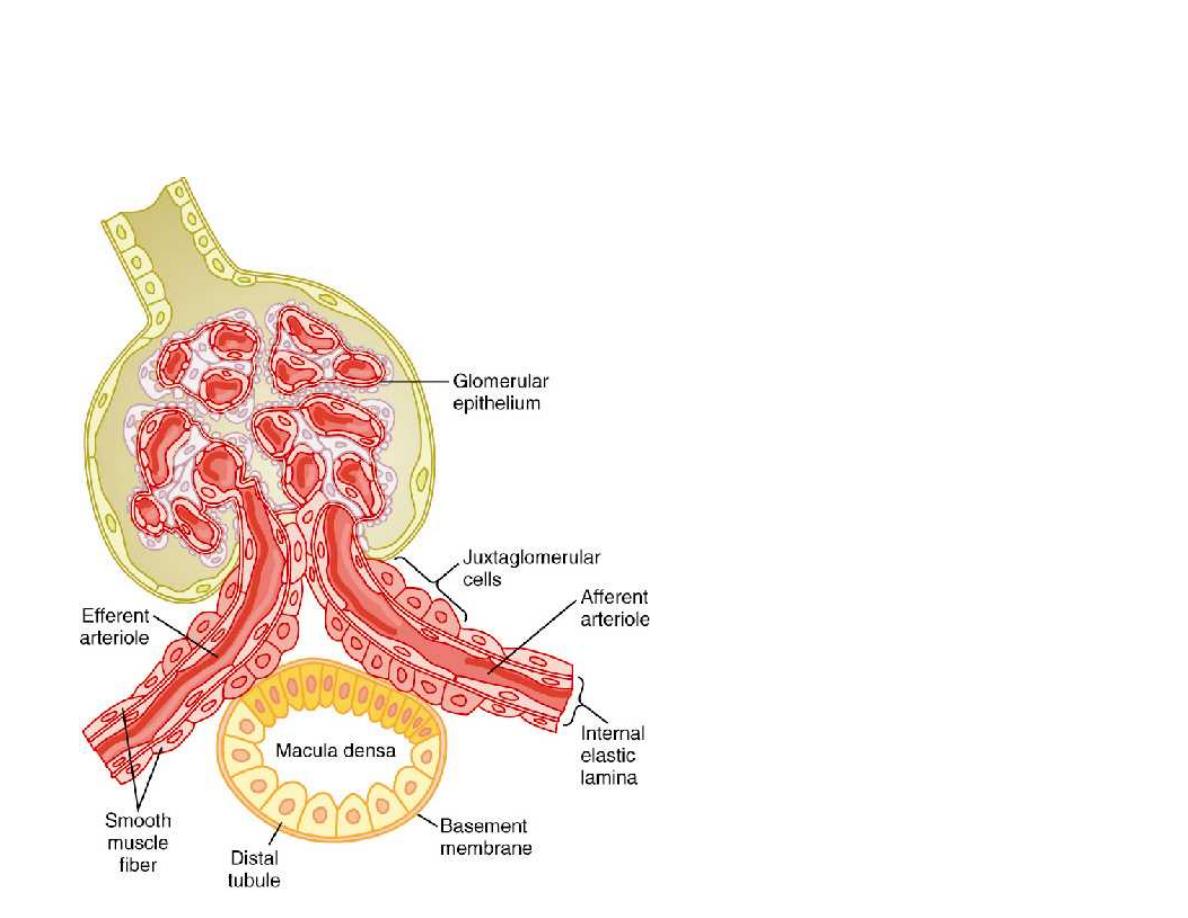
Structure of
the juxtaglomerular
apparatus: macula
densa
Structure of
the juxtaglomerular
apparatus: macula
densa
Figure 26-17;
Guyton and Hall
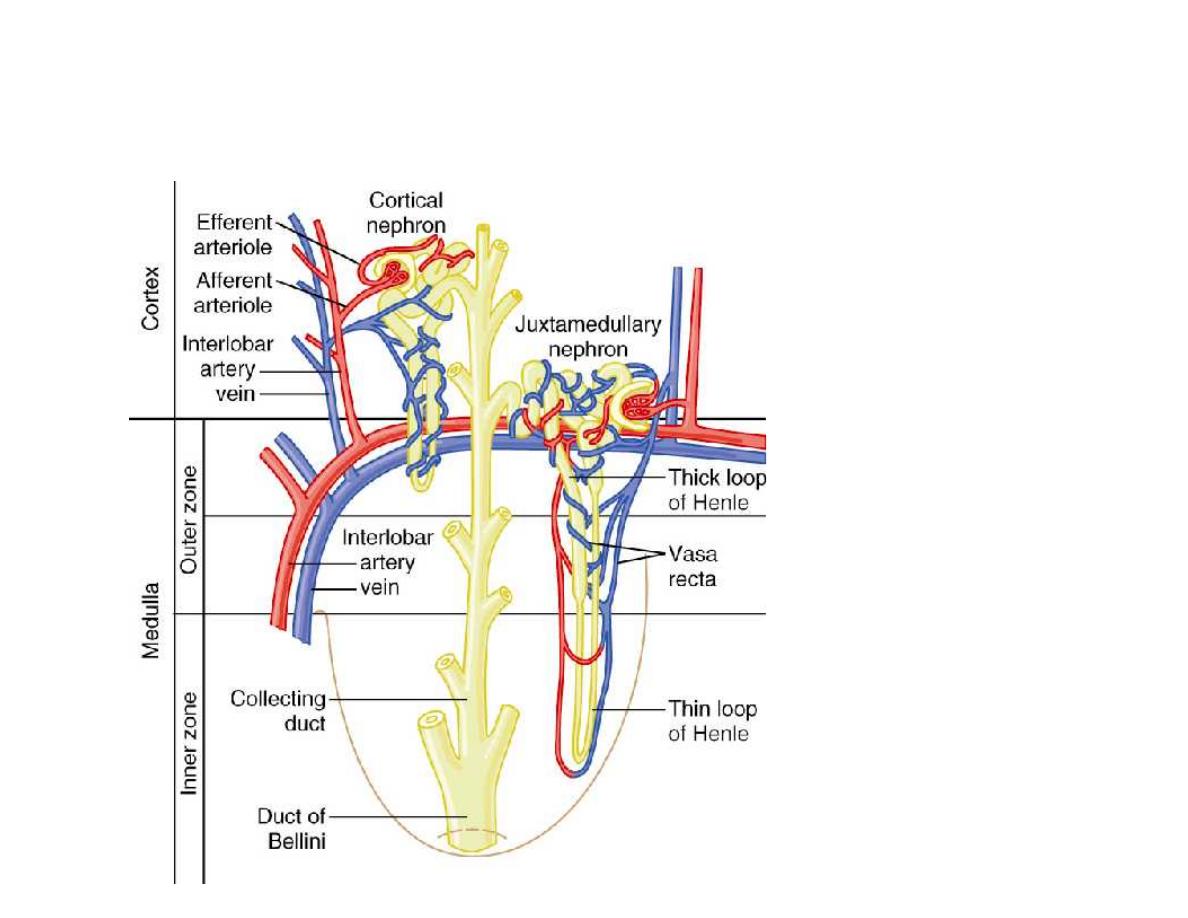
Figure 26-5;
Guyton and Hall
Cortical and Juxtamedullary
Nephron Segments

•
Excretion of metabolic waste products: urea,
creatinine, bilirubin, hydrogen
•
Excretion of foreign chemicals: drugs, toxins,
pesticides, food additives
•
Secretion, metabolism, and excretion of hormones
-
renal erythropoetic factor
-
1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol (Vitamin D)
-
Renin
•
Regulation of acid-base balance
•
Gluconeogenesis: glucose synthesis from amino
acids
•
Control of arterial pressure
•
Regulation of water & electrolyte excretion
Summary of Kidney Functions
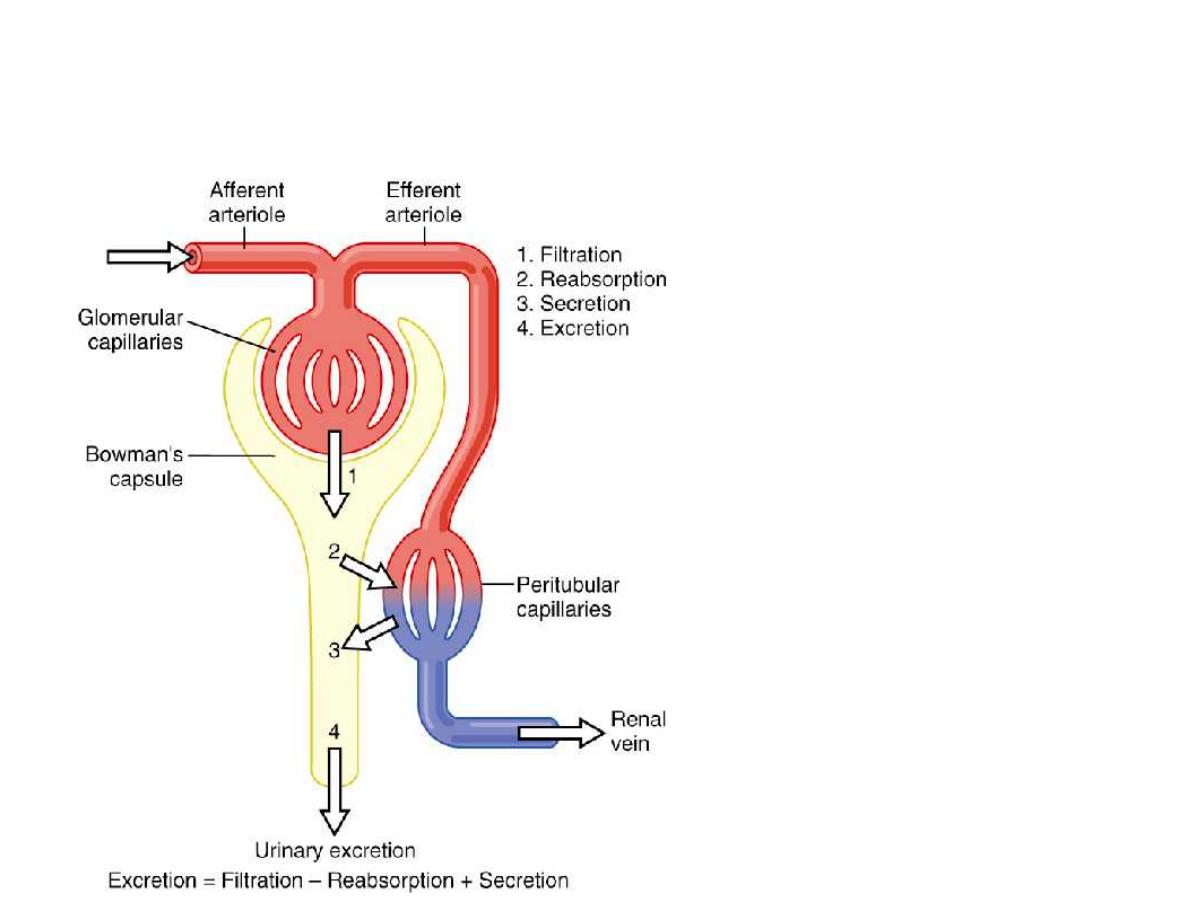
Basic Mechanisms
of Urine Formation
Figure 26-8;
Guyton and Hall
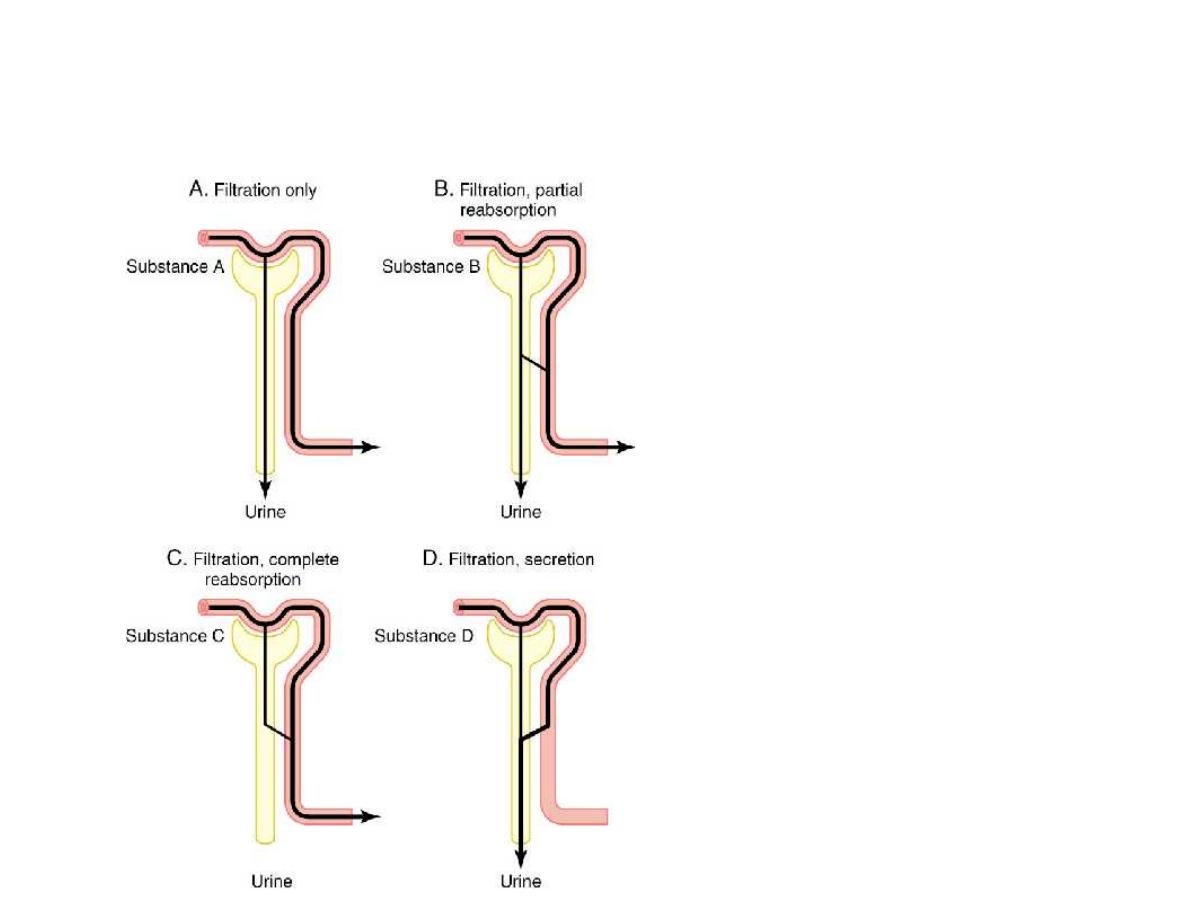
Renal Handling of
Different Substances
Figure 26-9;
Guyton and Hall
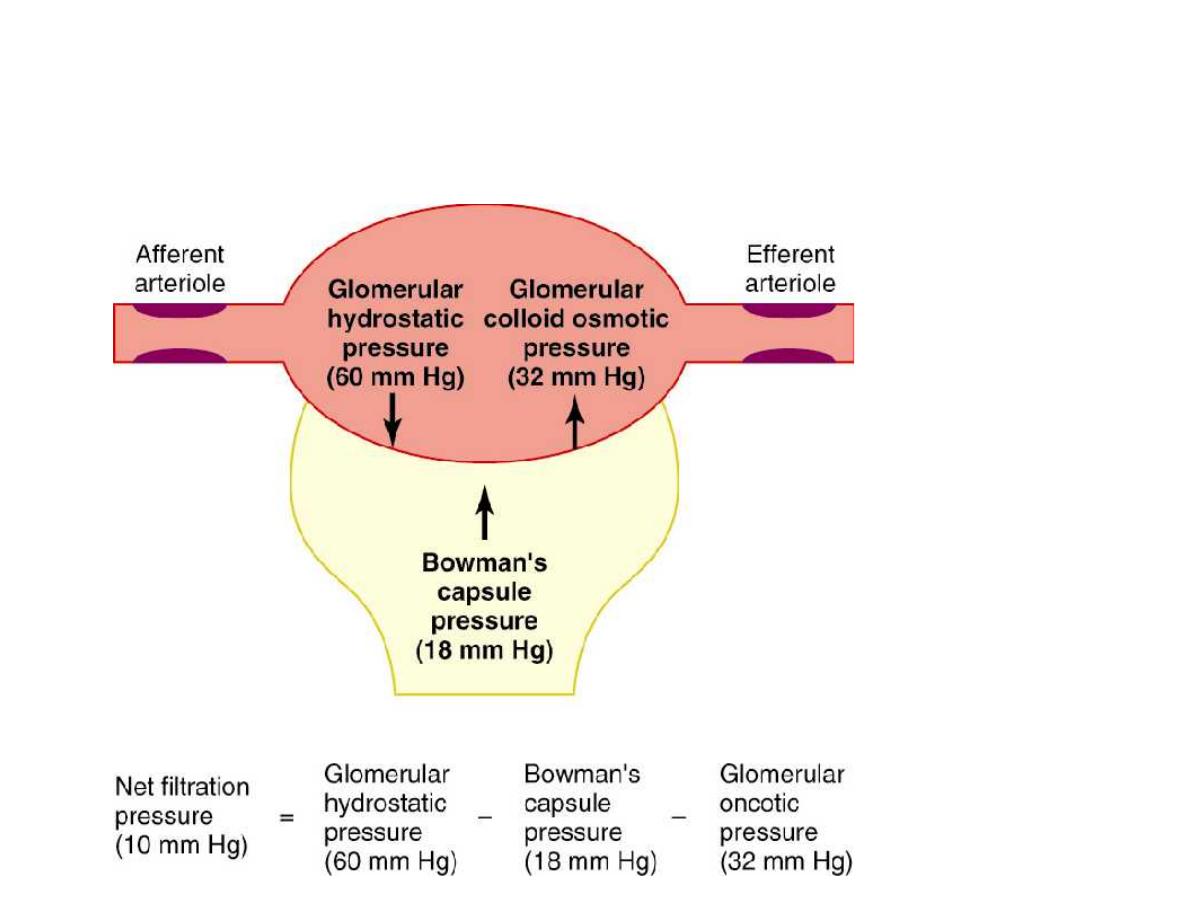
Figure 26-12;
Guyton and Hall

ASSESSING KIDNEY FUNCTION
•
Albumin excretion (microalbuminuria)
•
Plasma concentration of waste products
(e.g. BUN, creatinine)
•
Urine specific gravity, urine concentrating ability
•
Imaging methods (e.g. MRI, PET, arteriograms,
iv pyelography, ultrasound etc)
•
Isotope renal scans
•
Biopsy
•
Clearance methods
(e.g. 24-hr creatinine clearance)
•
etc

• Clearance
is a general concept that describes the
rate at which substances are removed (cleared)
from the plasma.
Clearance

Renal clearance of a substance is the
volume
of
plasma completely cleared of a substance per min.
Cs
= Us x V
Ps
Cs
x Ps = Us x V
Where:
Cs
= clearance of substance S
Ps = plasma conc. of substance S
Us = urine conc. of substance S
V = urine flow rate
Clearance Technique
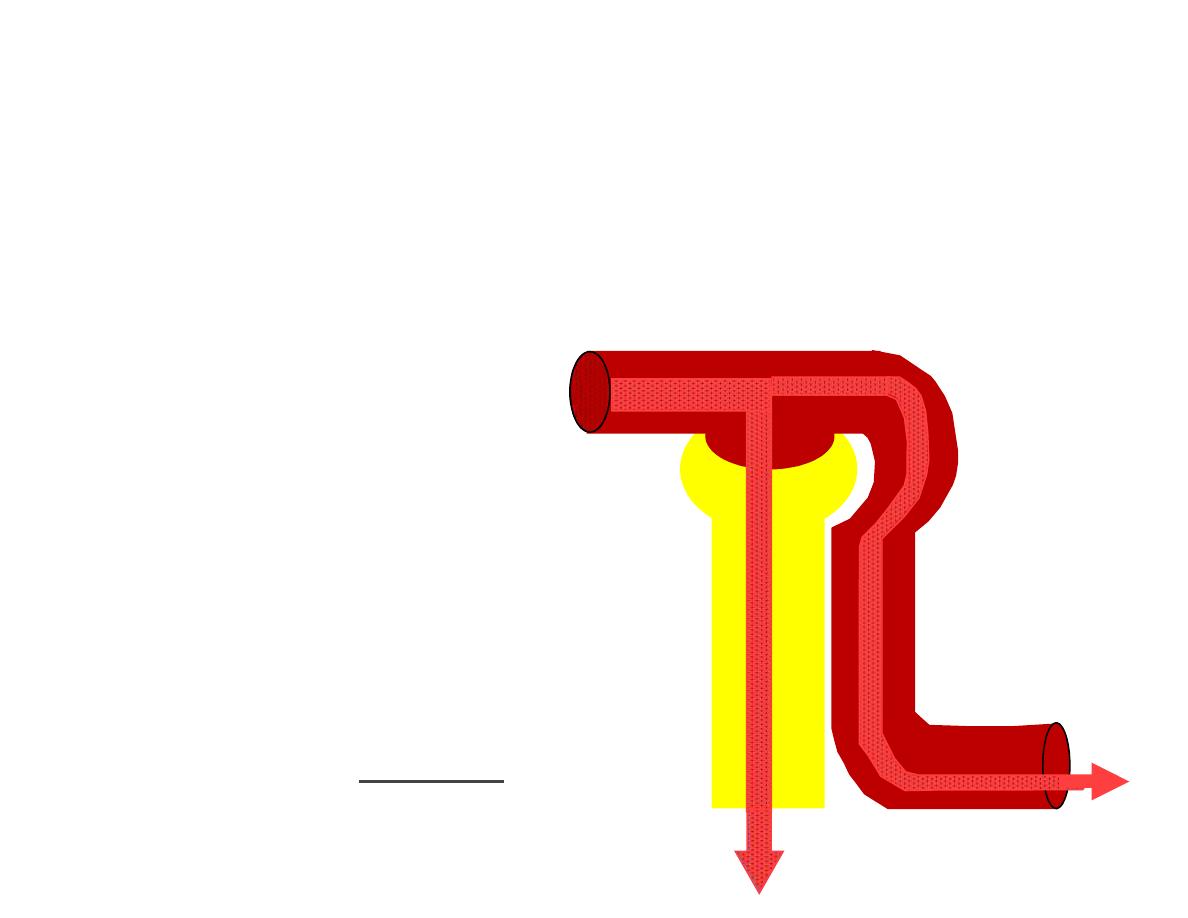
renal clearance = GFR
amount filtered = amount excreted
GFR x P
in
= U
in
x V
GFR =
P
in
U
in
x V
Use of Clearance to Measure GFR
For a substance that is freely filtered, but not reabsorbed or
secreted
(inulin,
125
I-iothalamate, ~creatinine),

PROPERTIES OF MATERIAL
1- easy to be taken by individual.
2- not digest or metabolize by the body
glomerulus
it is completely filtered at the
-
3
4--neither secreted nor reabsorbed by the tubules
5 - not naturally present in the body (because the
amount infused will be known)

Calculate the GFR from the following data:
P
inulin
= 1.0 mg / 100ml
U
inulin
= 125 mg/100 ml
Urine flow rate = 1.0 ml/min
GFR =
125 x 1.0
1.0
= 125 ml/min
GFR = C
inulin
=
P
in
U
in
x V

CLEARANCES OF DIFFERENT SUBSTANCES
Clearance of inulin (C
in
) = GFR
if Cx < Cin: indicates reabsorption of x
Substance
Clearance (ml/min)
inulin
125
glucose
0
sodium
0.9
urea
70
if Cx > Cin: indicates secretion of x
