
Urticaria
Wheal (lesion): pruritic evanescent pink to red swelling of superficial dermis
Angioedema (lesion): swelling of deep dermis and subcutaneous or submucosal
tissue
Urticaria (disease): recurrent wheal and /or angioedema of skin
Urticaria affects 1-5% of population
Overall, urticaria is more common in women than men
Wheals and Angioedema
Angioedema
Wheals
Swelling of deep dermis,
subcutaneous tissue
Swelling of upper dermis
Skin-colored, painful and ill-
defined
Red and itchy and well-defined
Last more than 24 hours
Last less than 24 hours
Involves skin and mucosae
Involves skin only
Pathogenesis
Urticaria is type I hypersensitivity reaction which involve:
Mast cells are distributed throughout the body and they are the most important
cells implicated in pathogenesis of urticaria.
Mast cells express IgE receptors
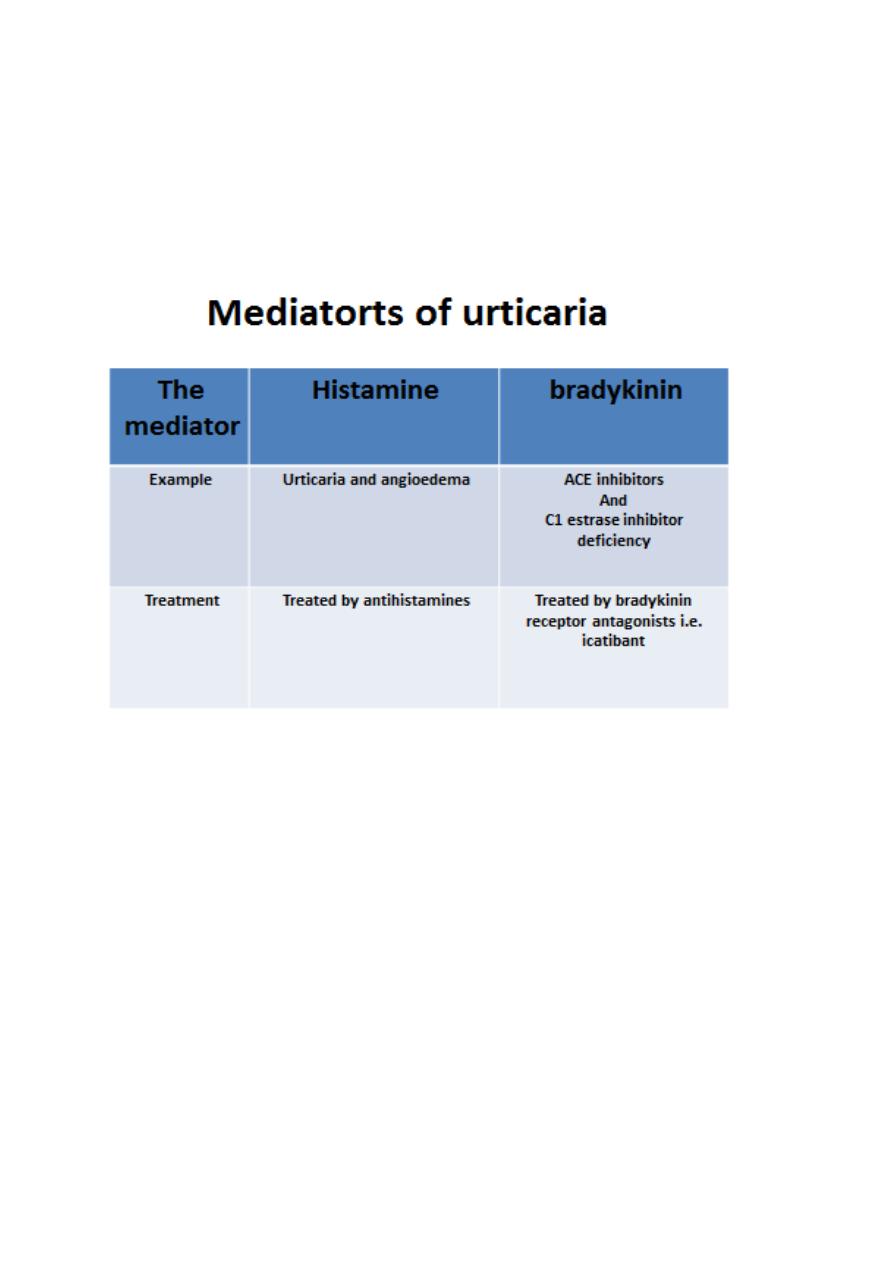
Auto-immune urticaria: anti-IgE receptor antibodies and to lesser extent anti-IgE
antibodies are detected in sera of 25-50% of patients with a chronic ordinary
urticaria and this can be detected by a test called autologous serum skin test(ASST)
which involve intradermal injection of the patient's own serum and appearance of
a wheal within 30 minutes
Etiology
Acute ordinary urtcaria:
Idiopathic(50%) > upper respiratory tract infection (40% ) > drugs and food
Chronic ordinary urticaria:
Idiopathic > autoimmune > food, drugs and infection
Classification
(I) Acute type and chronic type (the cutoff is 6 wks)
(II) Clinical classification:

1. Ordinary urticaria
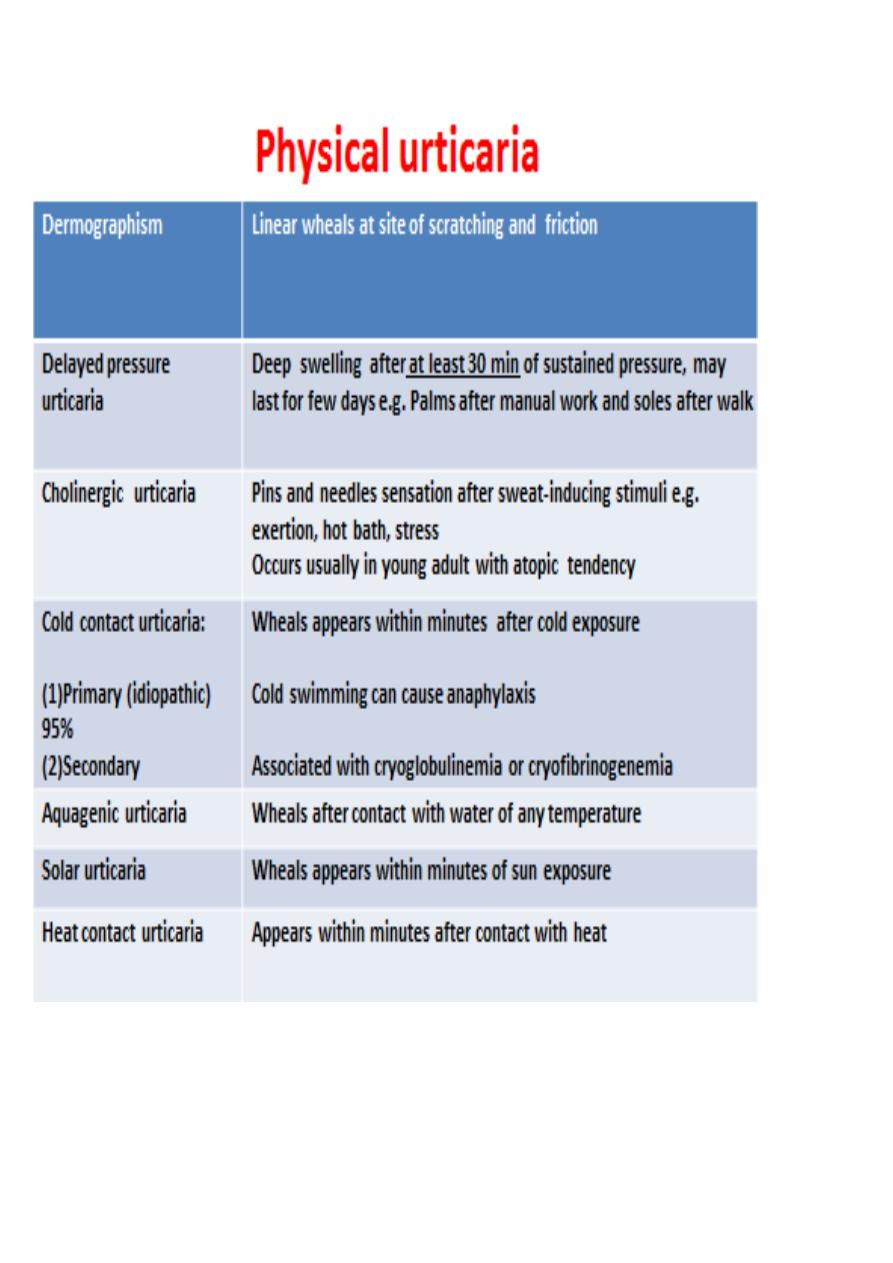
2. Physical urticaria
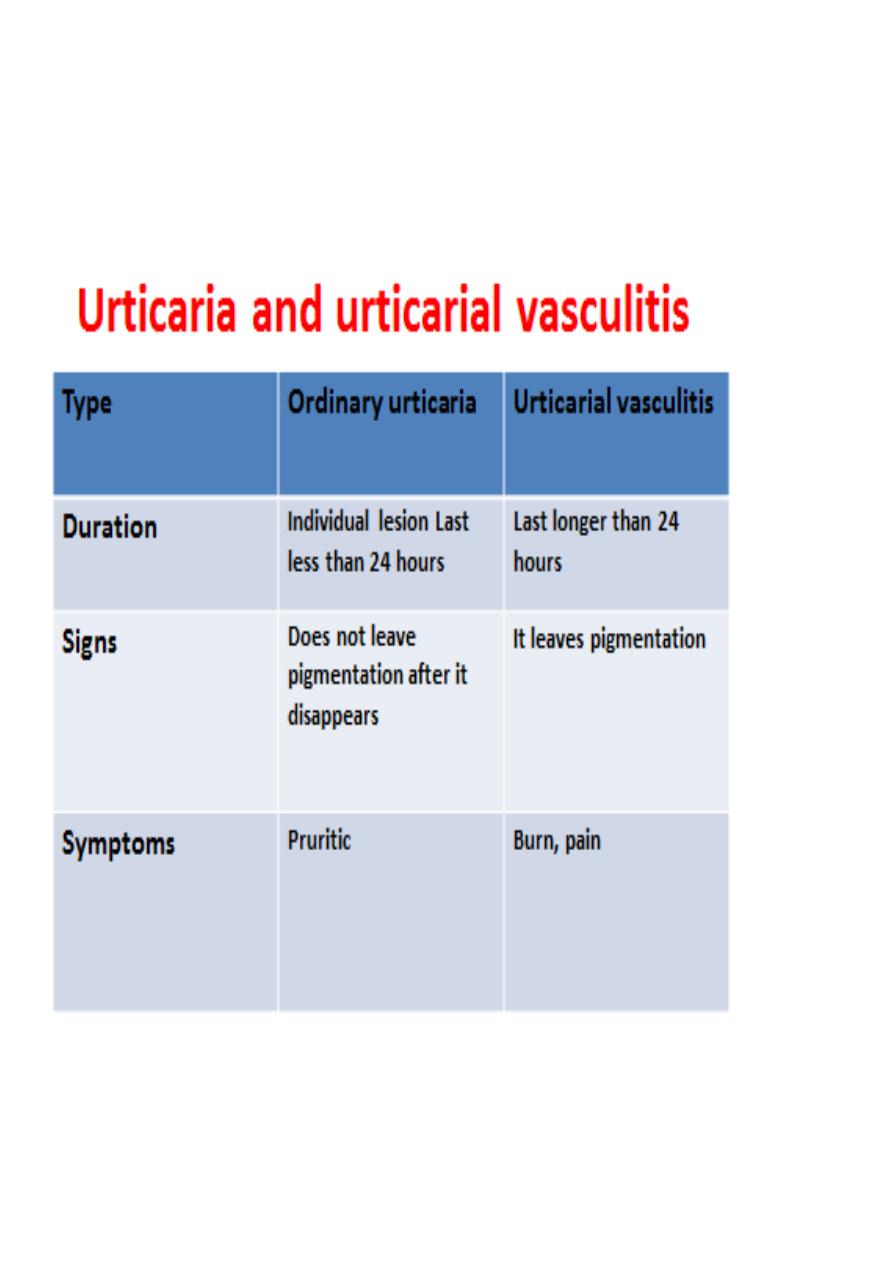
3. Urticarial vasculitis
4. Angioedema without wheals i.e. C1 estrase inhibitor deificiency in which C4 is
low

Diagnosis
(1)
Detailed history
: e.g. a Hx of recent infection and drug Hx (in acute urticaria
), a Hx of duration(less or more than six weeks), a Hx of difficulty of breathing (to
assess the severity), a Hx of exacerbating factors e.g. embarrassment trigger
cholinergic urticaria
(2)
Physical exam
: e.g. circling the wheal to see if the individual lesion last more
than 24 hours or to look for a pigment left after disappearance of wheal as in
urticarial vasculitis, look for the shape of wheal i.e. linear in dermographism
(3) Investigations
:
.
Acute urticaria
: no need except if (1) not responsive to Rx , (2) the individual
wheal last longer than 24 hrs
.
Chronic urticaria
: CBC, ESR, WBC diiferential, C4 and if this is normal
ASST
.
Urticarial vasculitis
: biopsy
.
Physical urticaria
: challenge test, for example;
(1) applying an ice cube on skin for cold urticaria,
(2)stroking the skin for dermographism,
(3) making the patient run for cholinergic urticaria

