Practical of Cell Injury
Third Year
2018-2019
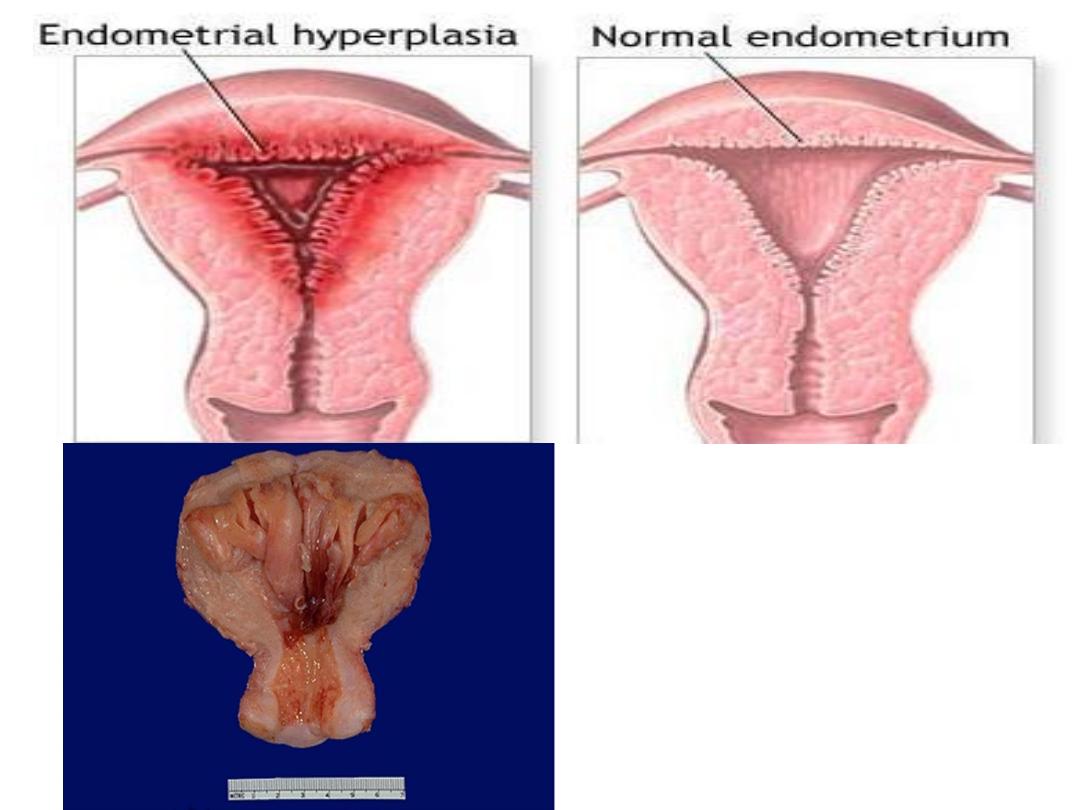
Endometrial
hyperplasia is an
example of
hormone-induced
hyperplasia due to
hyperestrogenism
.

Left ventricular hypertrophy.
pathological hypertrophy due to increase demand, this
results in increase in the size of the organ
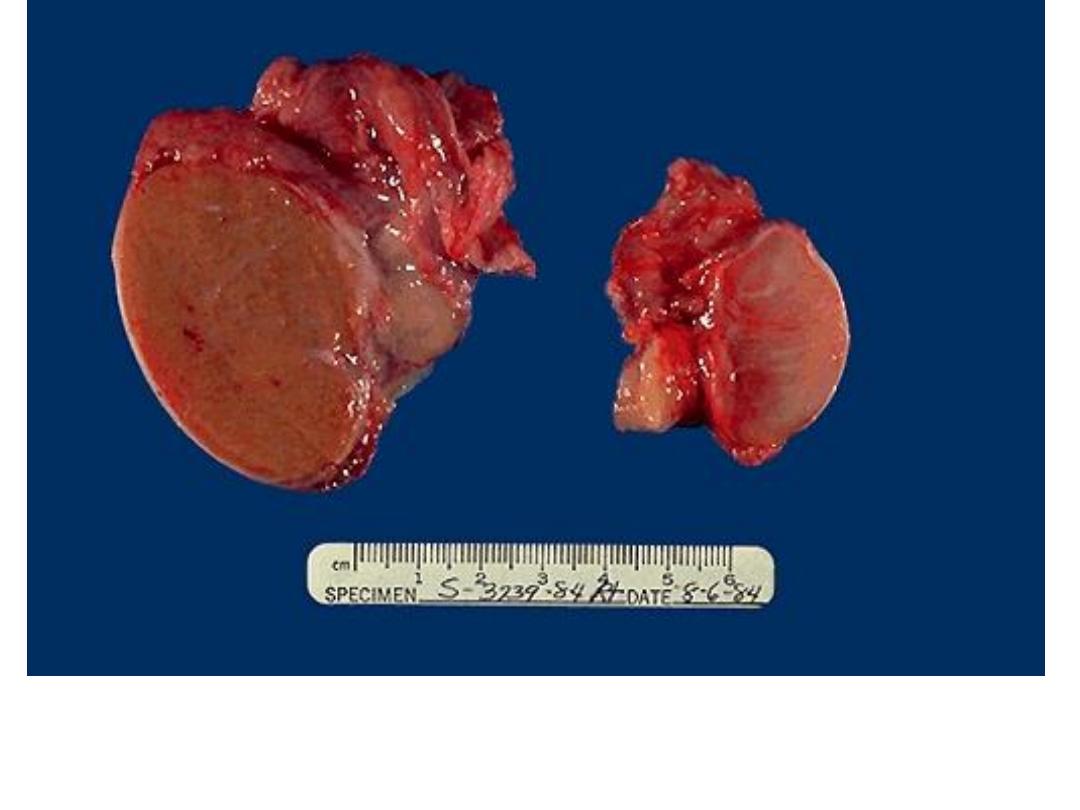
On the left is a normal testis. On the right is a testis
that has undergone atrophy
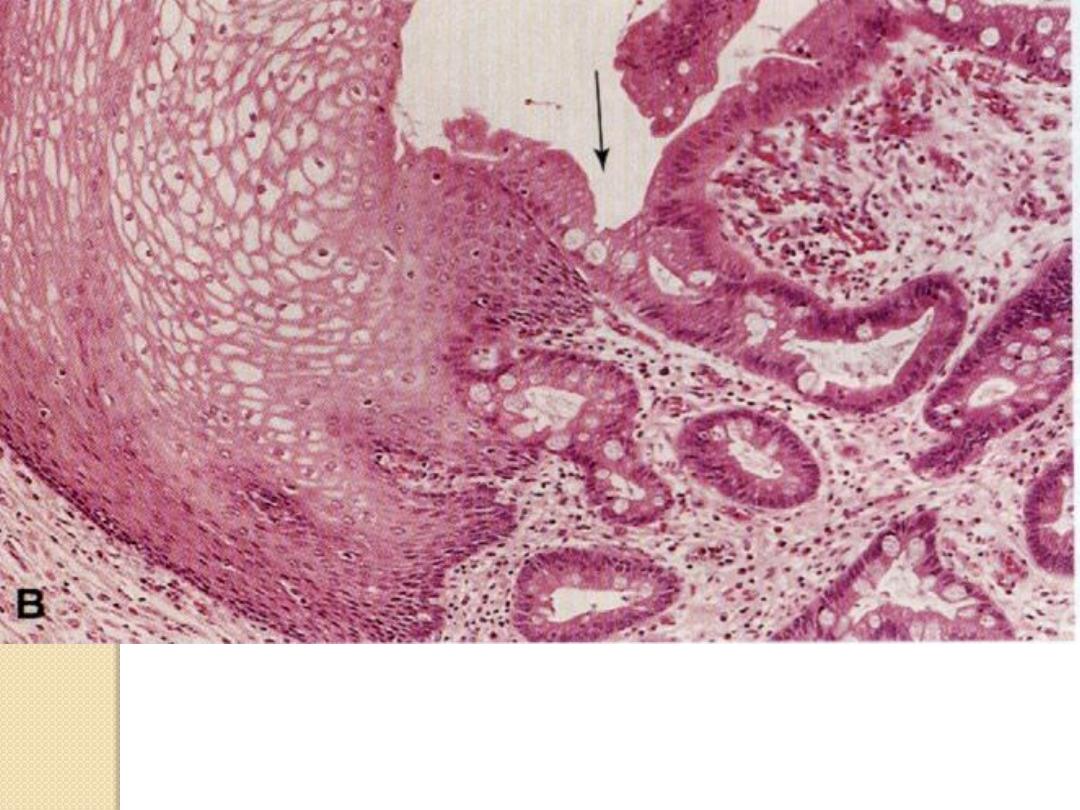
Metaplastic transformation (arrow) of the normal
esophageal stratified squamous epithelium (Lt) to mature
columnar epithelium
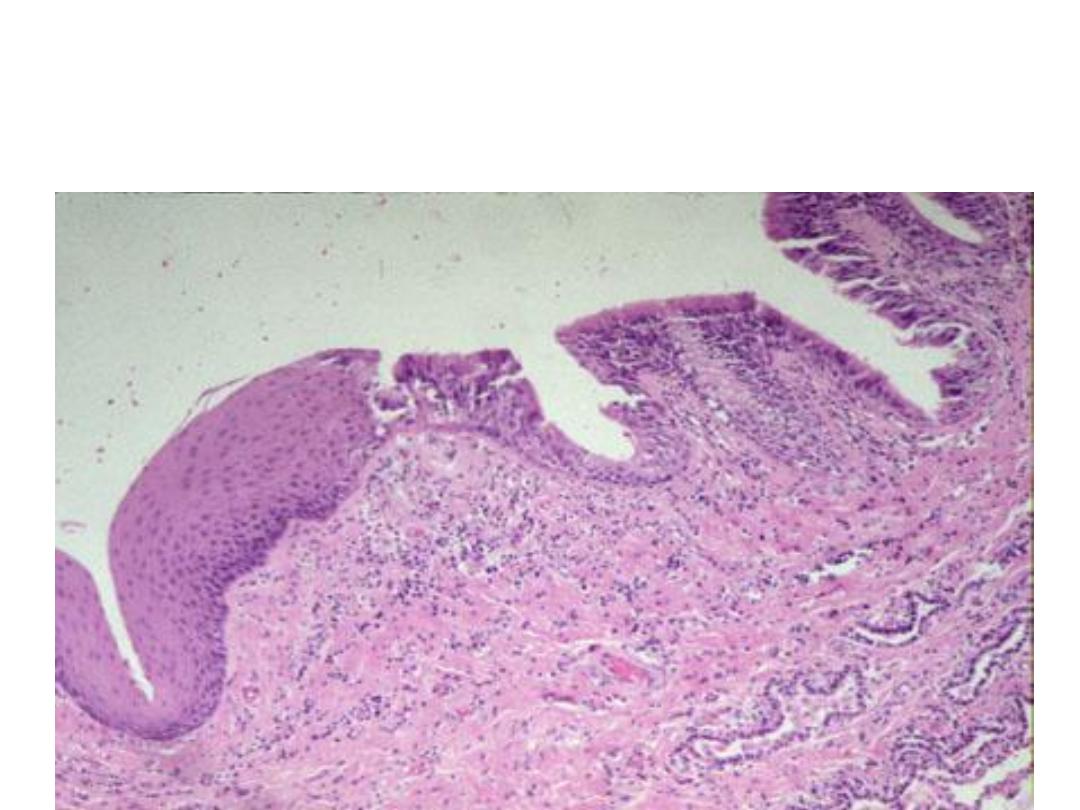
Squamous metaplasia of bronchial
epithelium
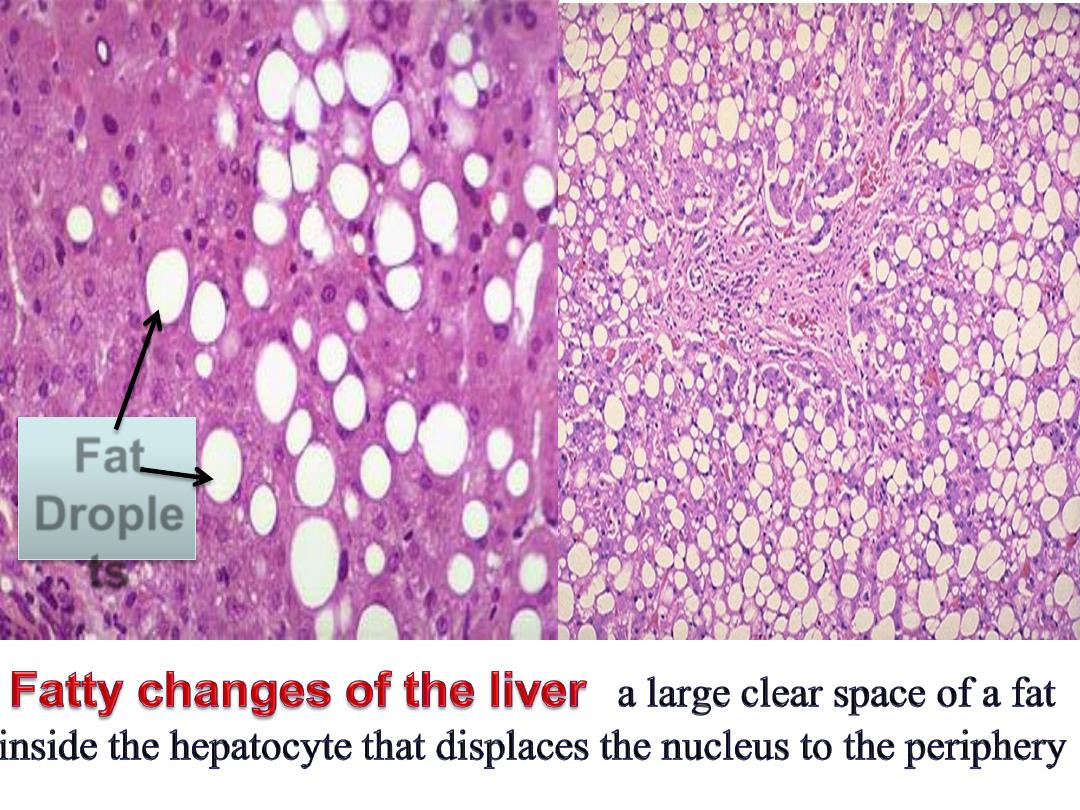
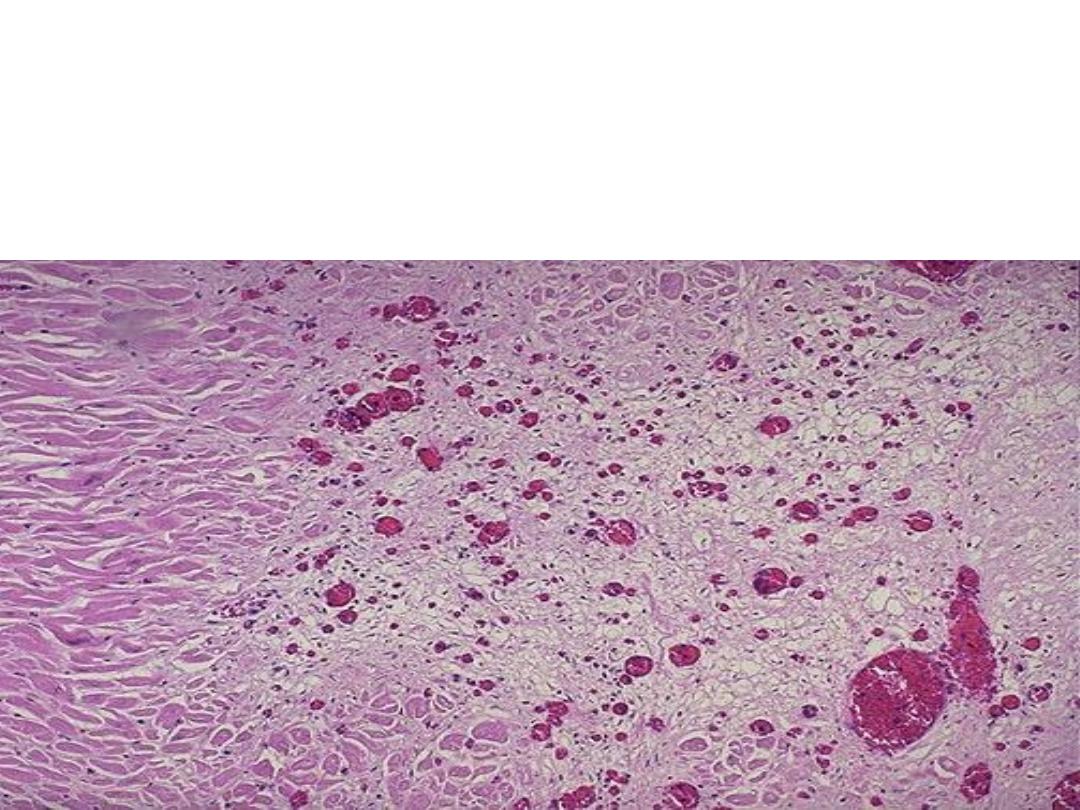
Fat
Drople
ts
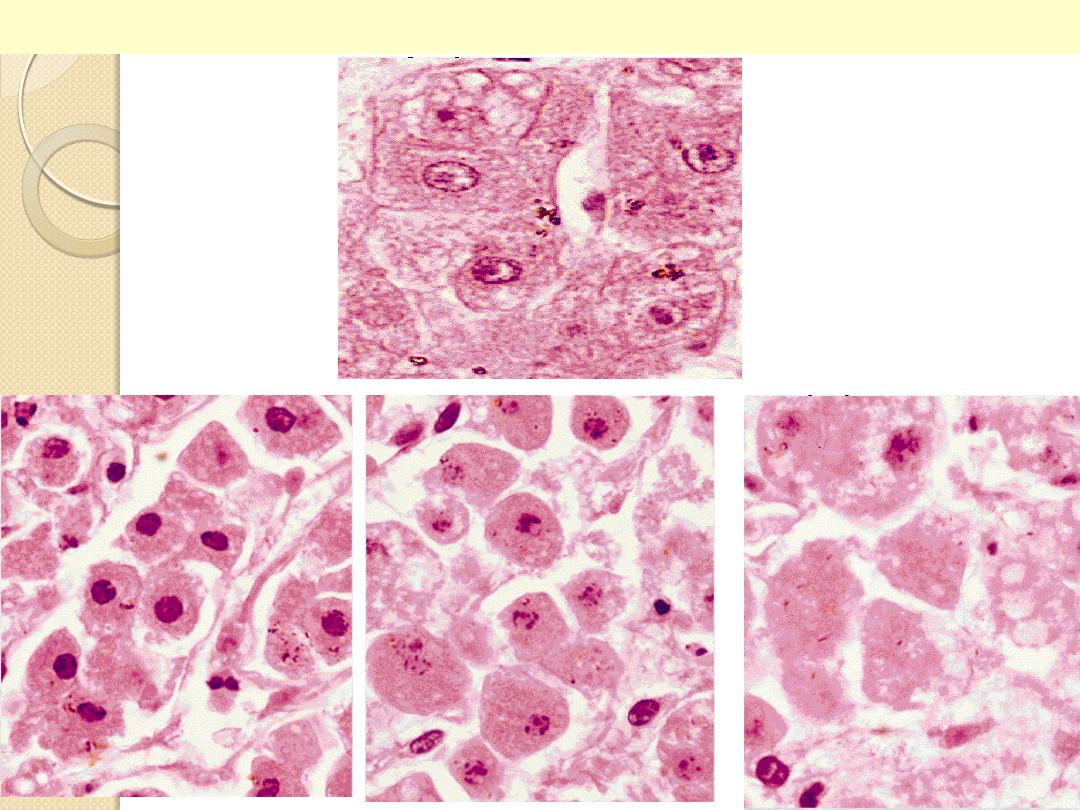
Liver cell necrosis: Nuclear changes
normal
pyknosis
k
aryorrhexis
karyolysis
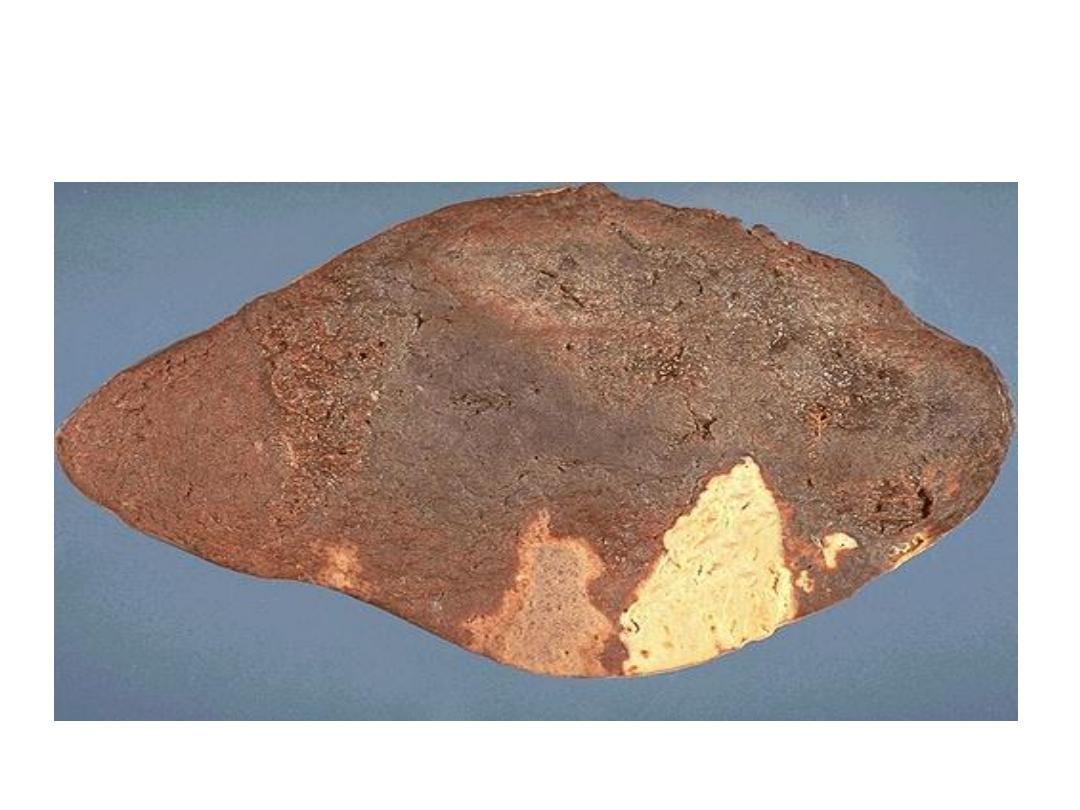

Coagulative necrosis(infarction)-
Spleen
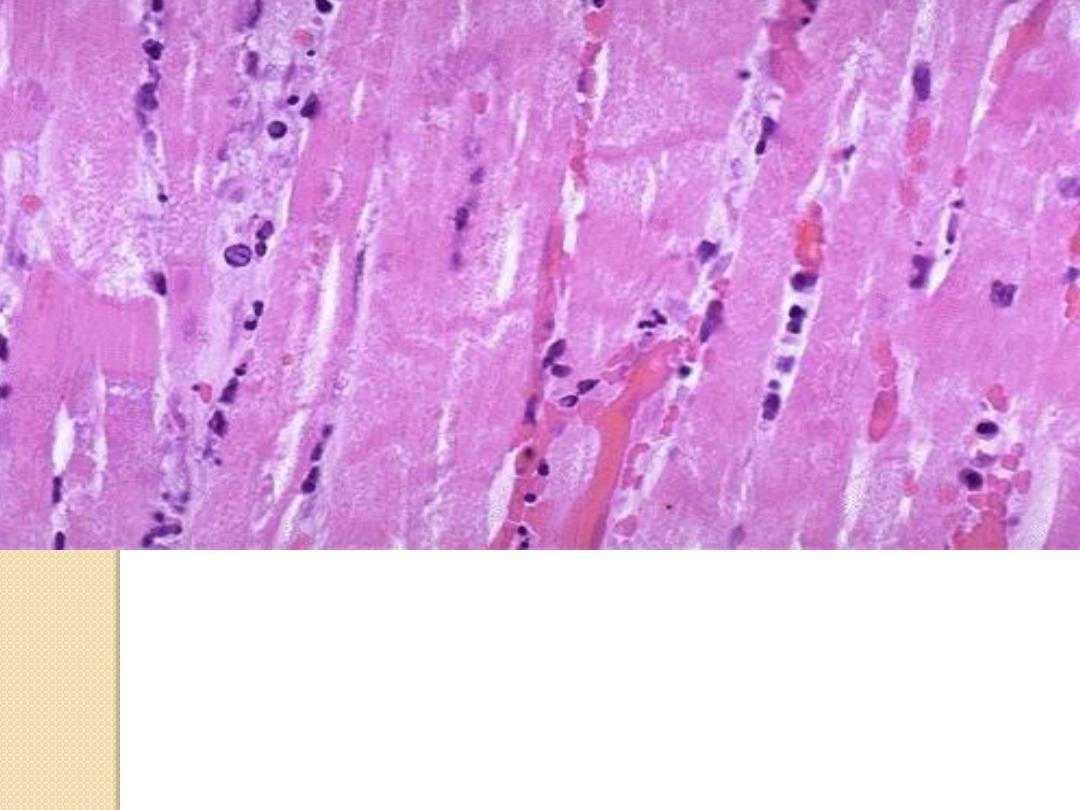
Myocardial infraction, the cells become more
eosinophilic , loss of striation, absence of nucleus &
their outline are preserved
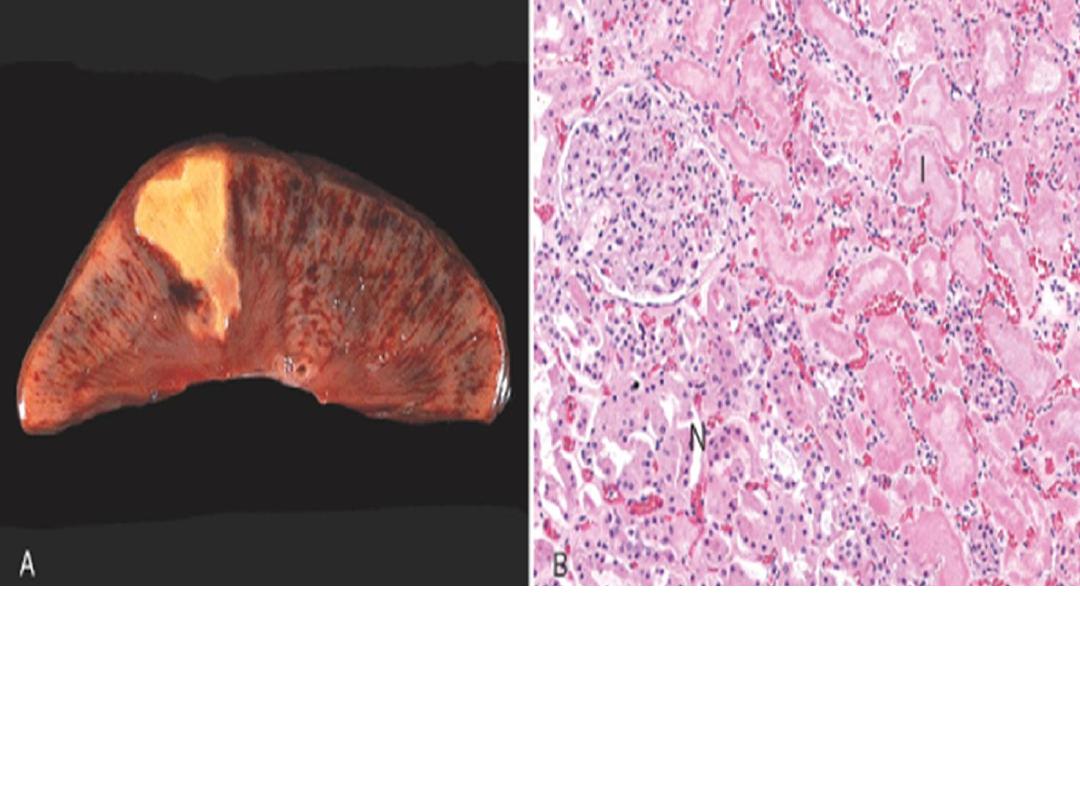
Coagulative necrosis(infarction)-kidney
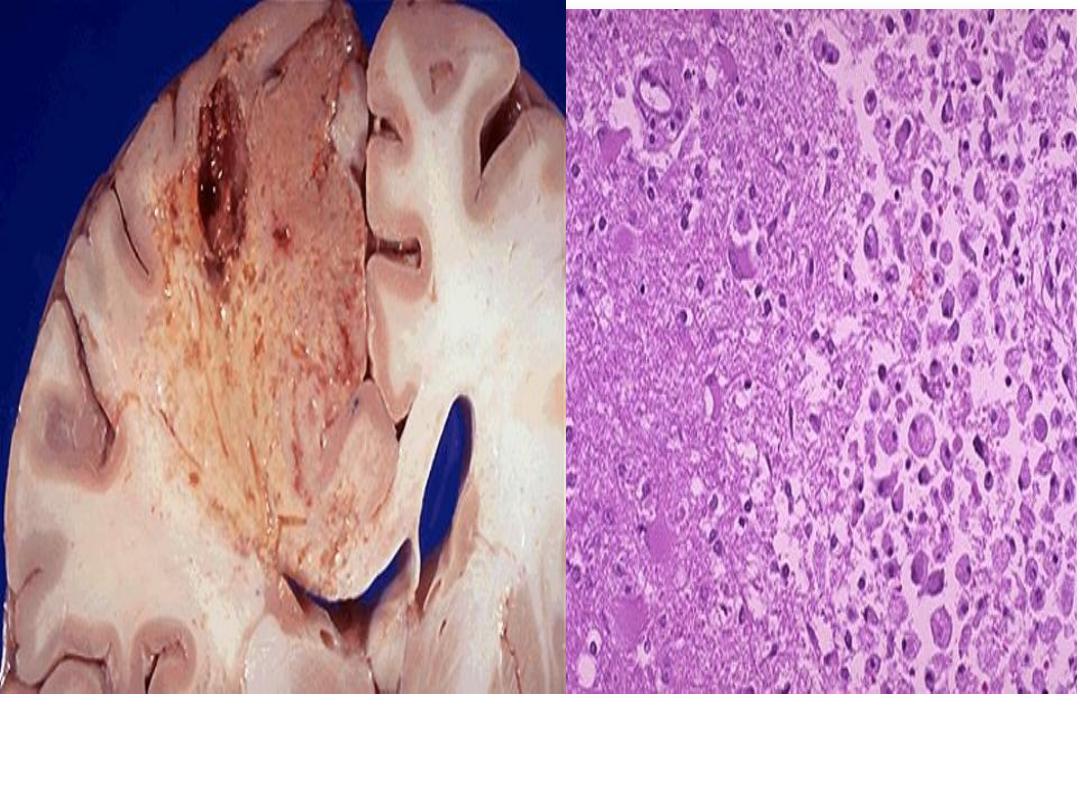
Liquefactive necrosis- Brain infarction
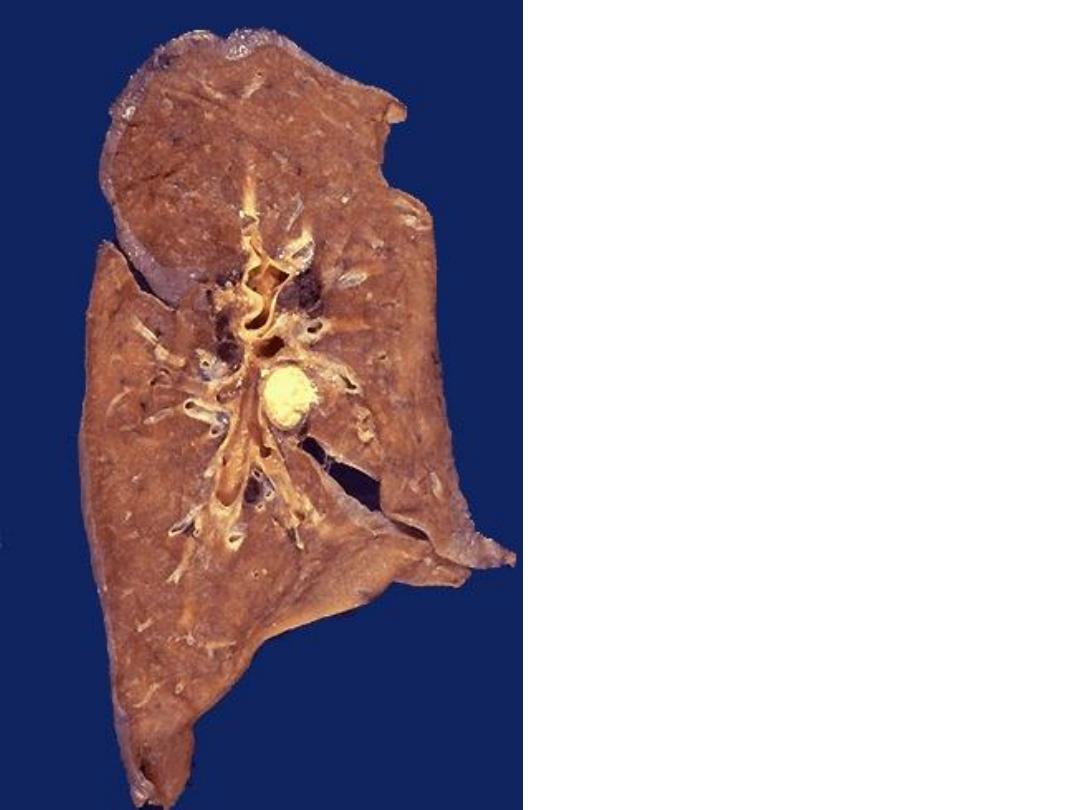
Caseous necrosis (TB)
involving
hilar
LN,
yellow white appears as
cheese-like
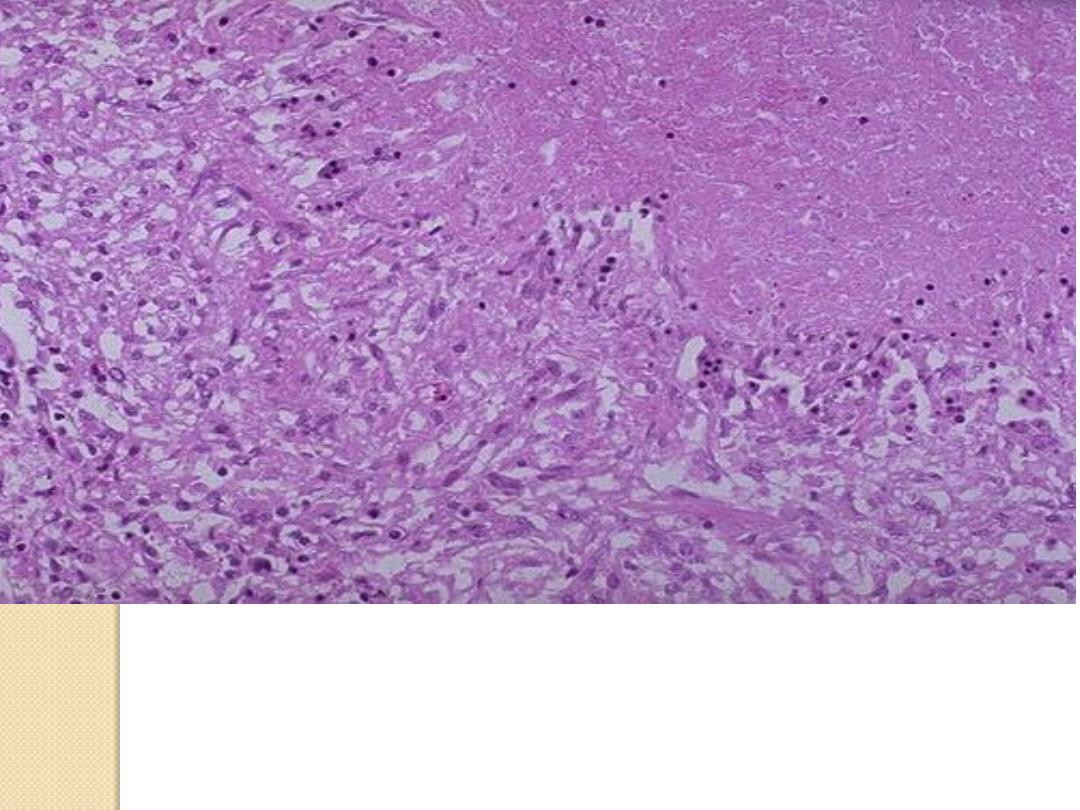
Caseous necrosis (Lung TB),
amorphous structureless granular eosinophilic material
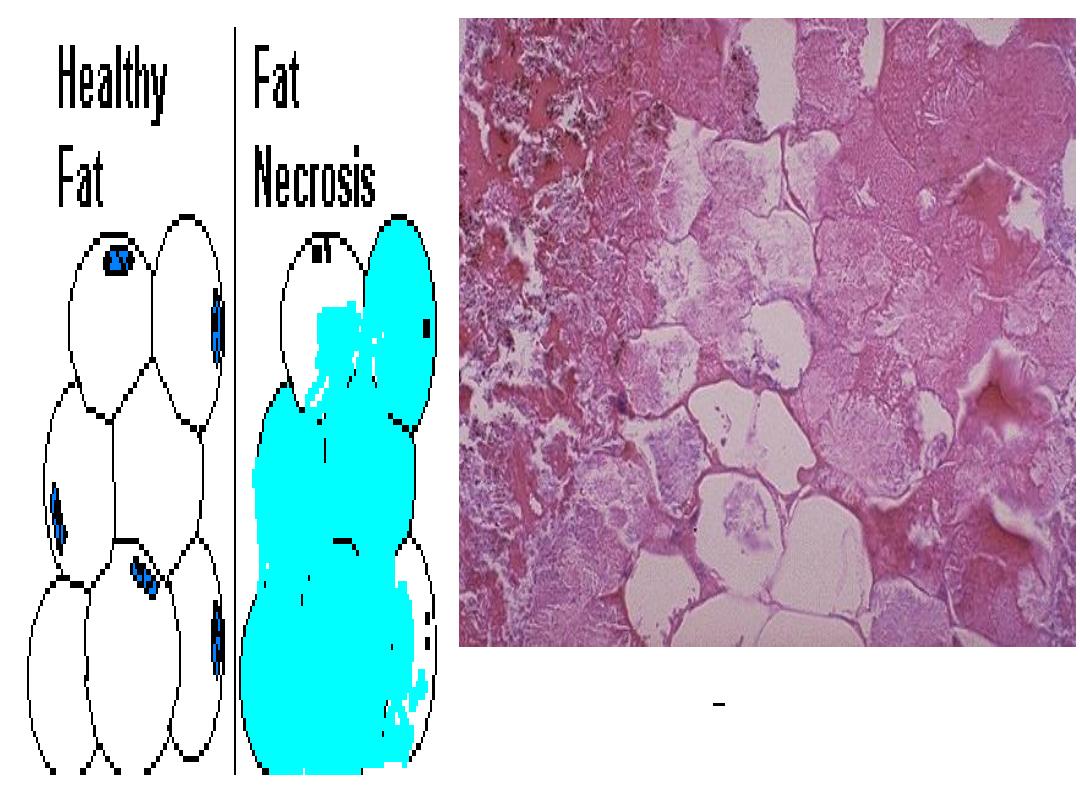
Fat necrosis
shadowy outlines of necrotic fat cells, with
basophilic calcium deposits, surrounded by an
inflammatory reaction
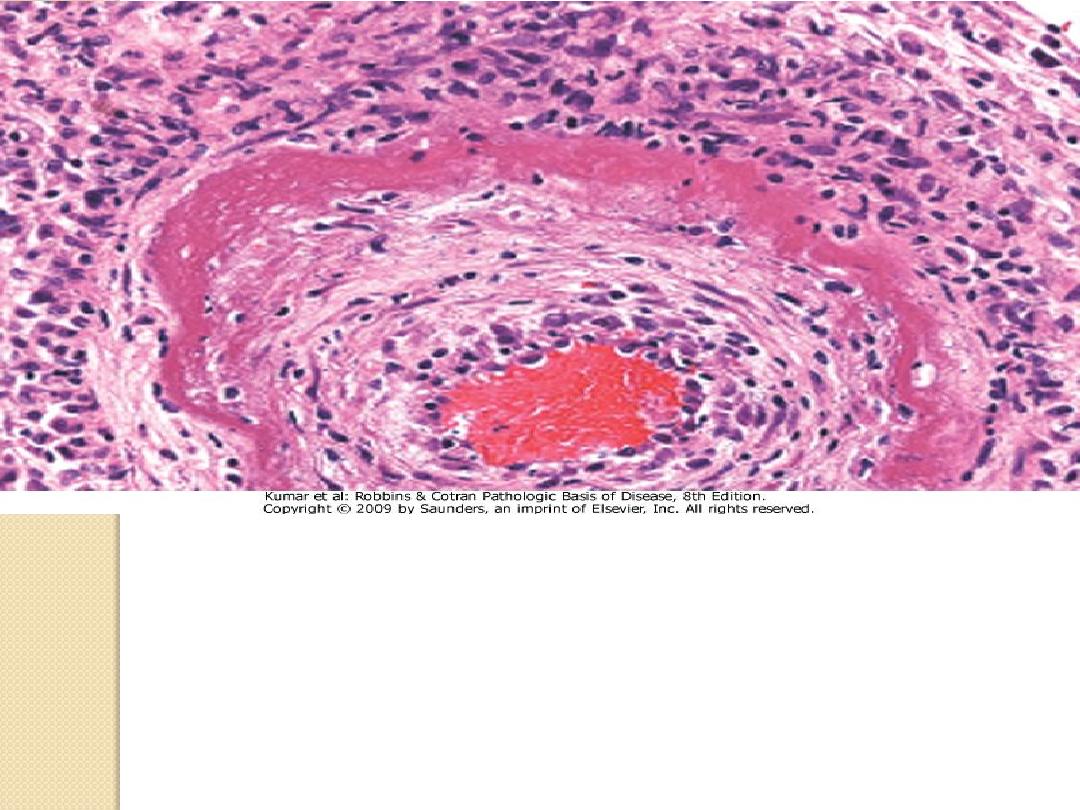
Fibrinoid necrosis.
It is marked by deposition of fibrin-
like proteinaceous material in arterial walls, which appears
eosinophilic on light microscopy.
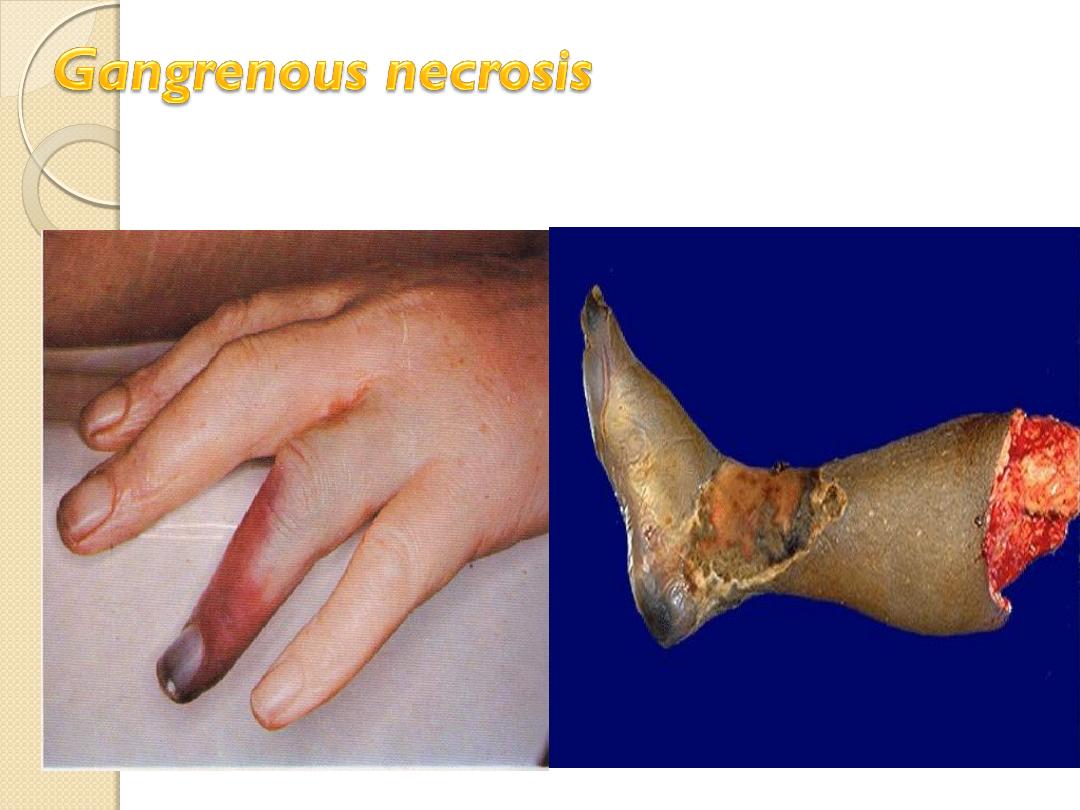
It is a form of a necrosis of the tissue with superadded
putrefaction.
Dry gangrene -Ischemia
Wet gangrene –D.M
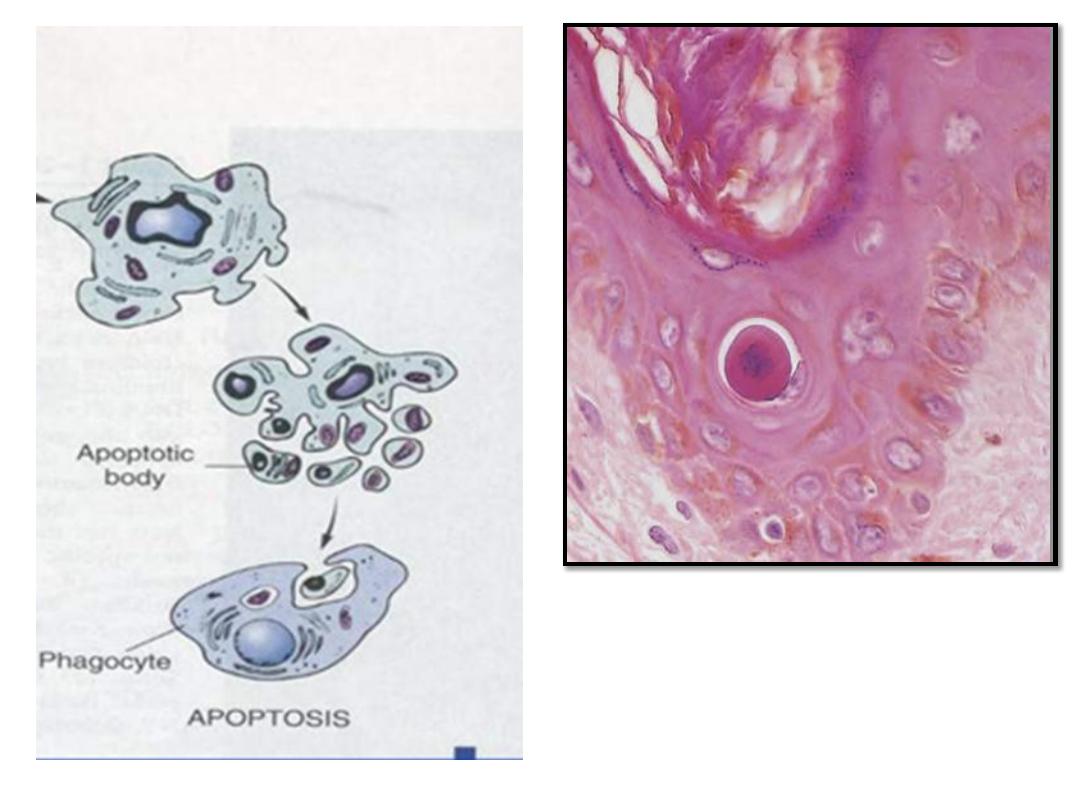
Apoptosis of an epidermal cell.
The cell is reduced in size and
contains brightly eosinophilic
cytoplasm and a condensed
nucleus
.
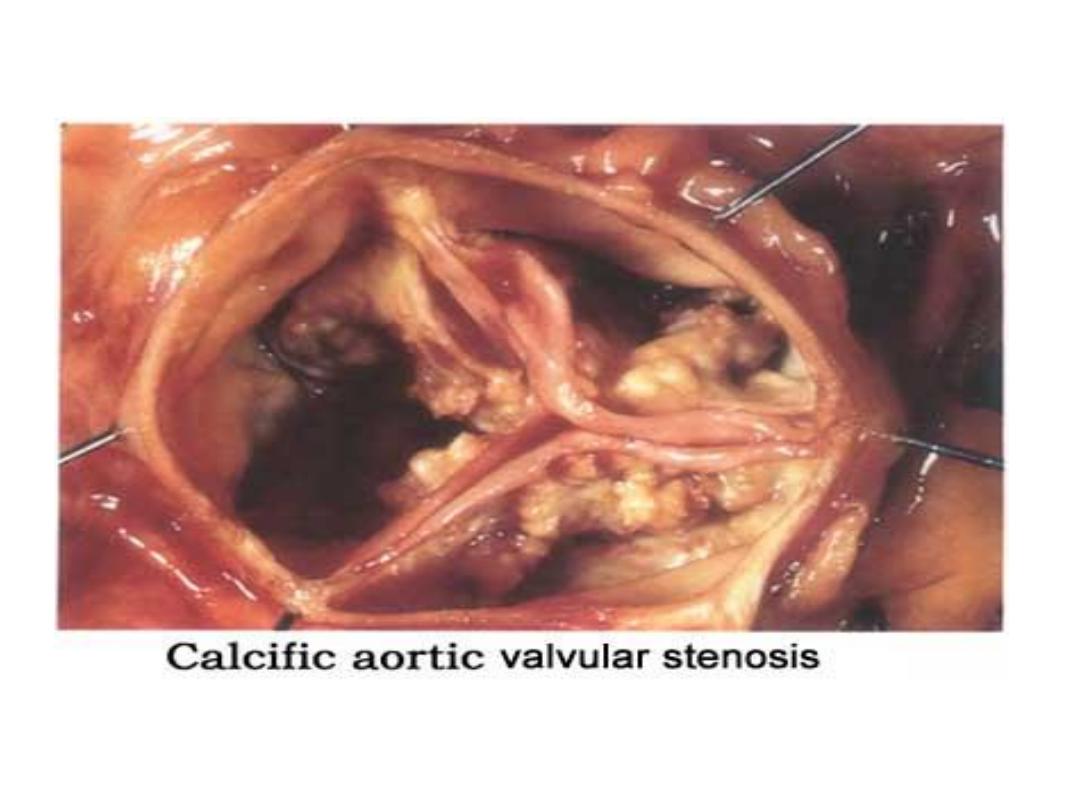
dystrophic calcification
Fine, white granules or clumps, often felt as gritty deposits.
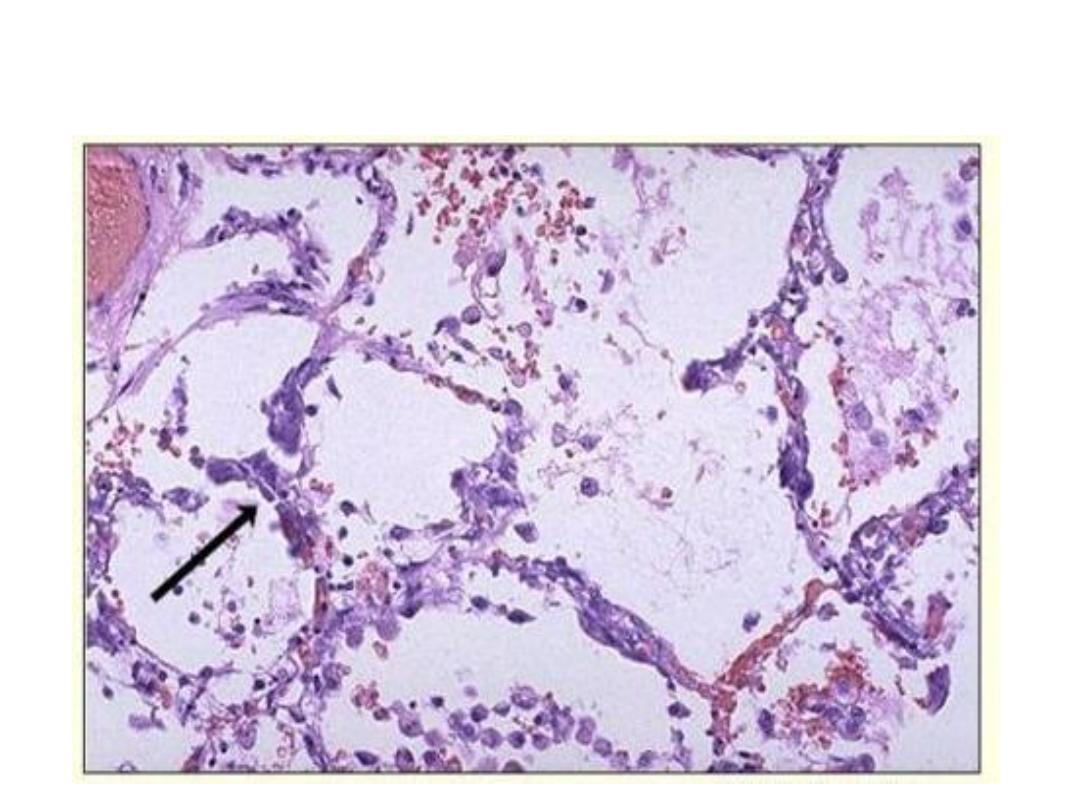
metastatic calcification lung

The practical of
Inflammation
Third year
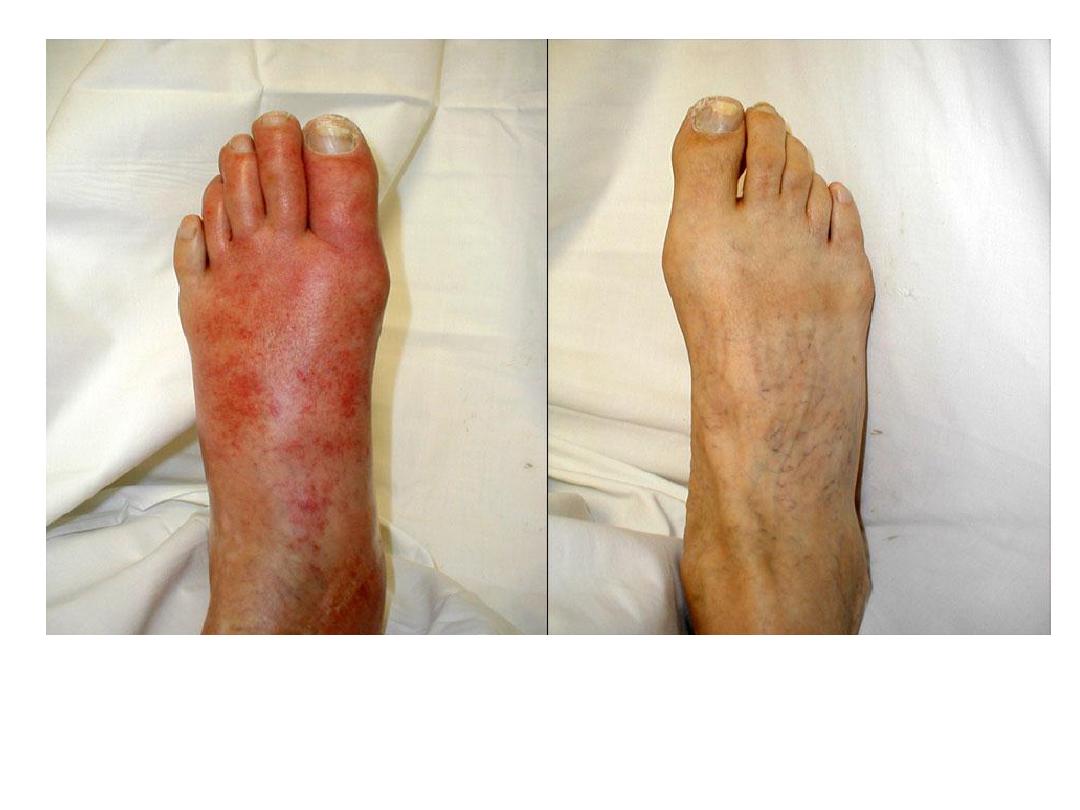
Acute inflammation, swelling and redness of the skin of left
foot compared to the normal skin of the right foot.
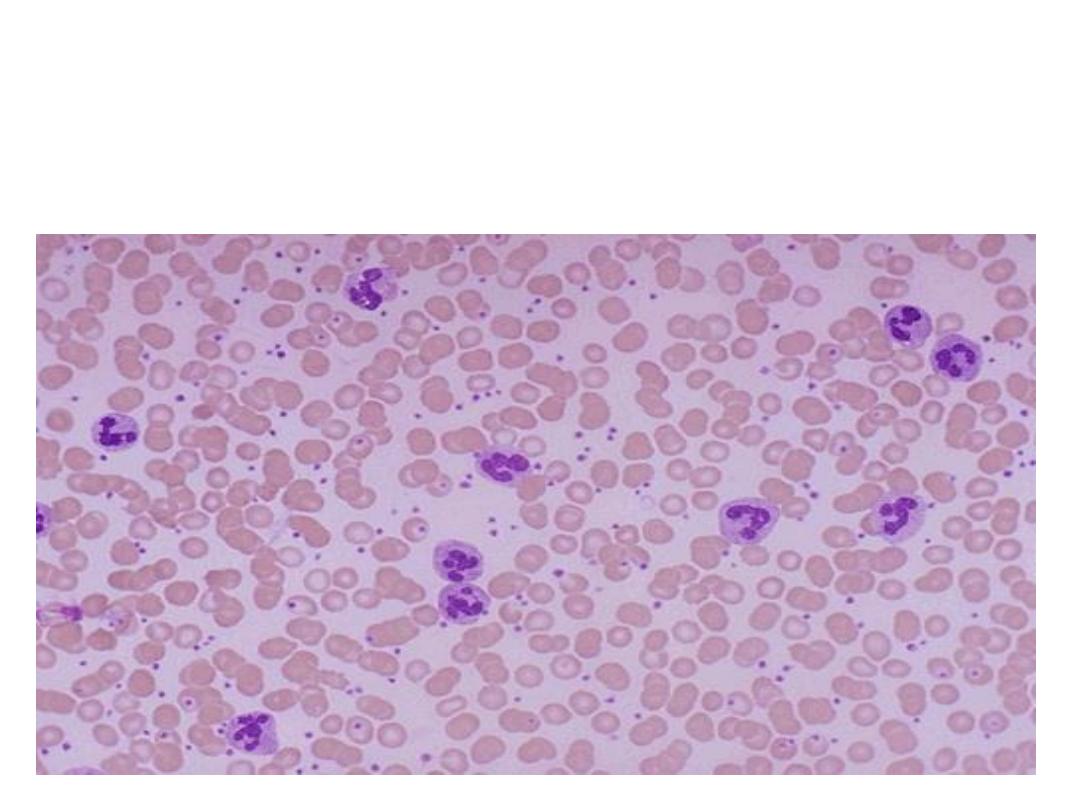
Acute inflammation is marked by an increase in
inflammatory cells. predominantly
neutrophils
(polymorph-
nuclear leukocytes (PMN's)).
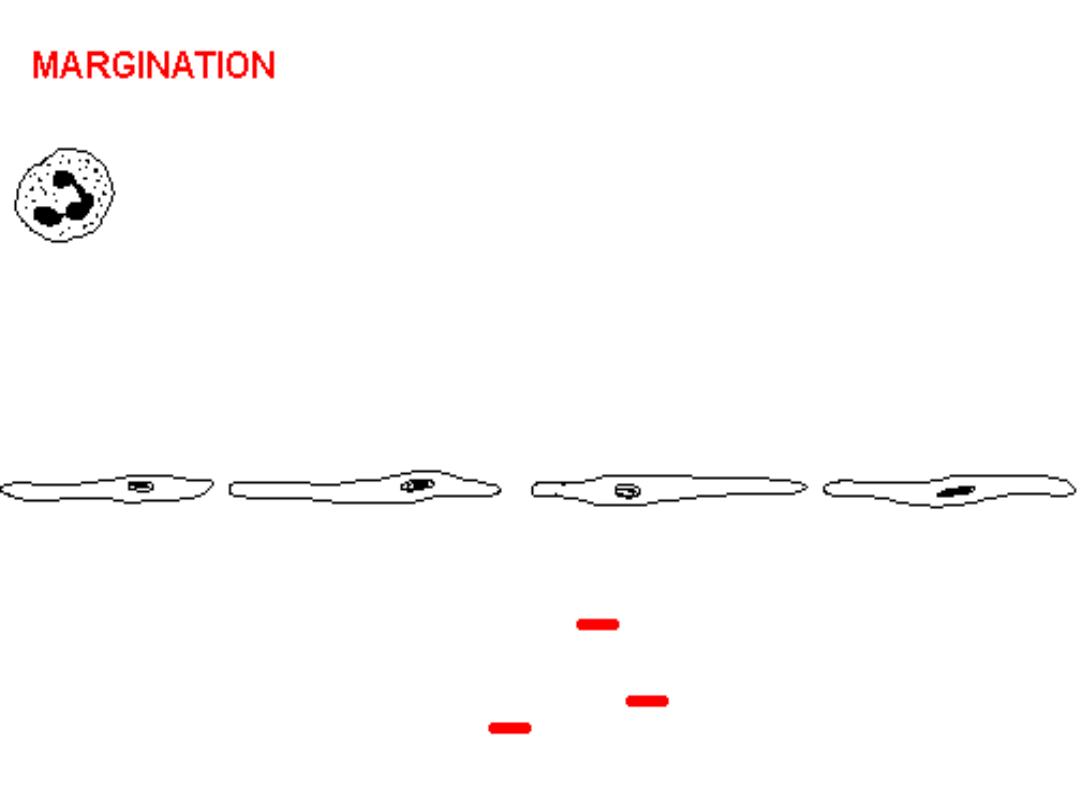
Here PMN's that are marginated along the dilated venule wall
(arrow) are squeezing through the basement membrane (the
process of diapedesis) and spilling out into extravascular space.
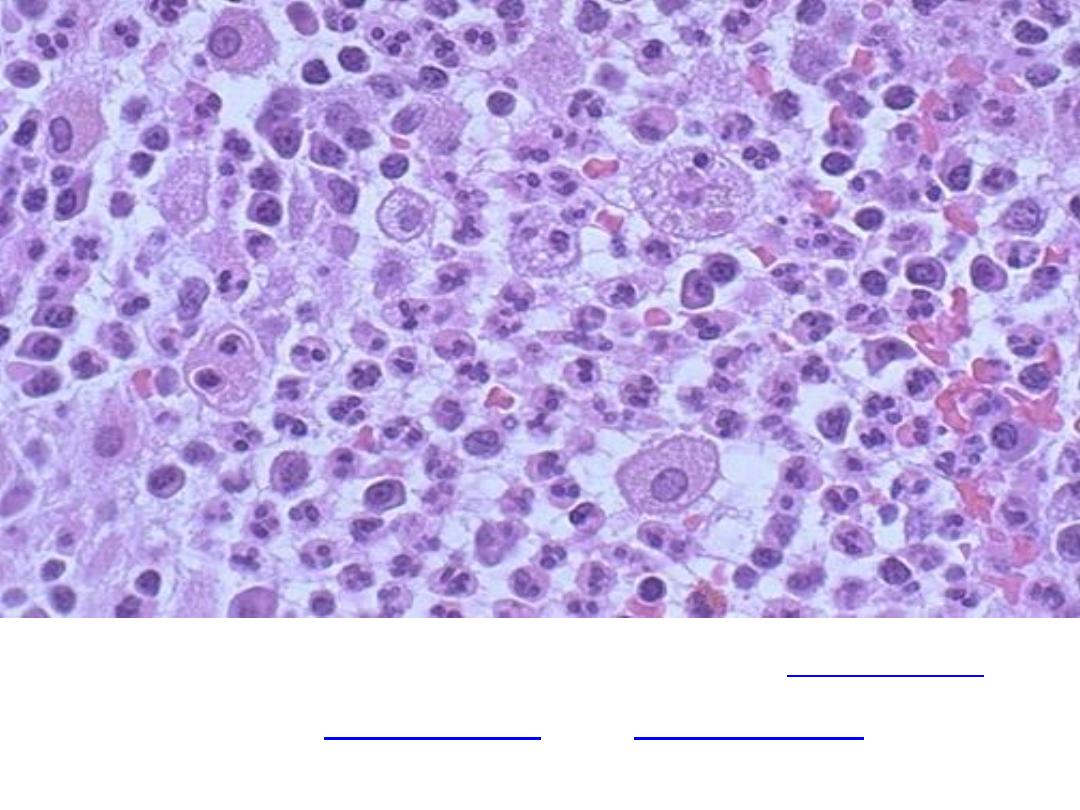
Acute inflammation
but there are also
, and
. Macrophages
can phagocytoze other cells as well as cellular debris
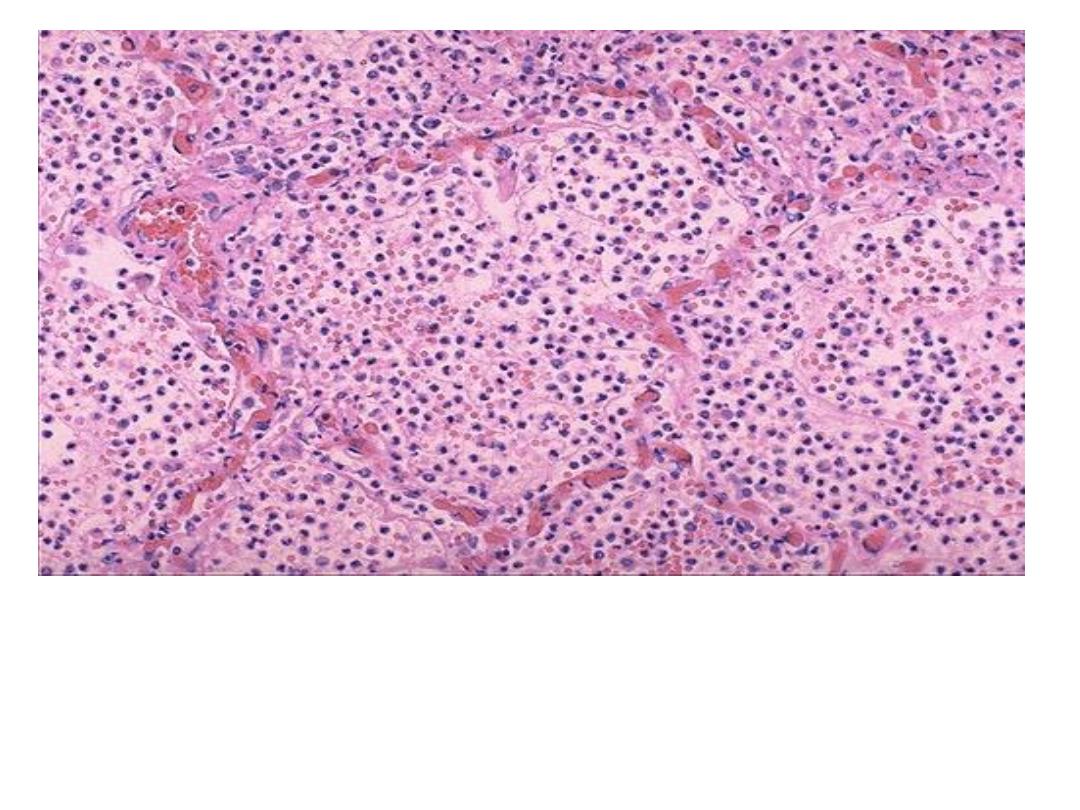
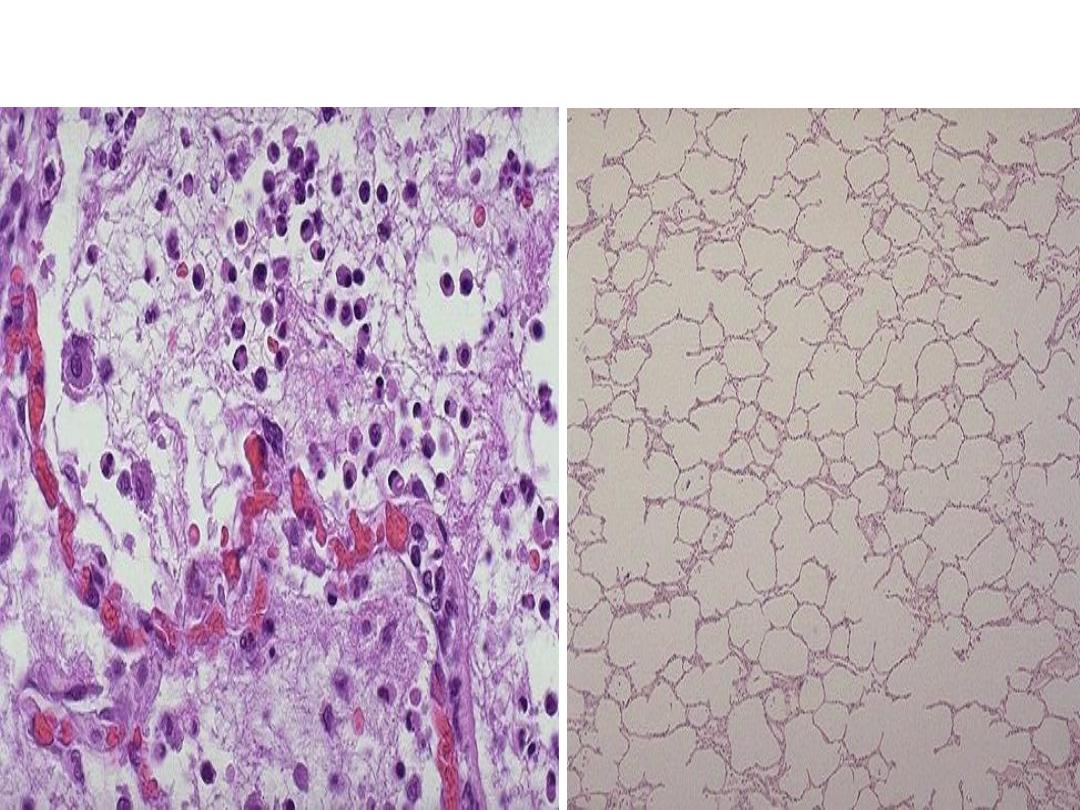
Acute inflammation (pneumonia) , dilated capillaries in the
alveolar walls from vasodilation with
numerous neutrophils
fill the alveolar spaces
.
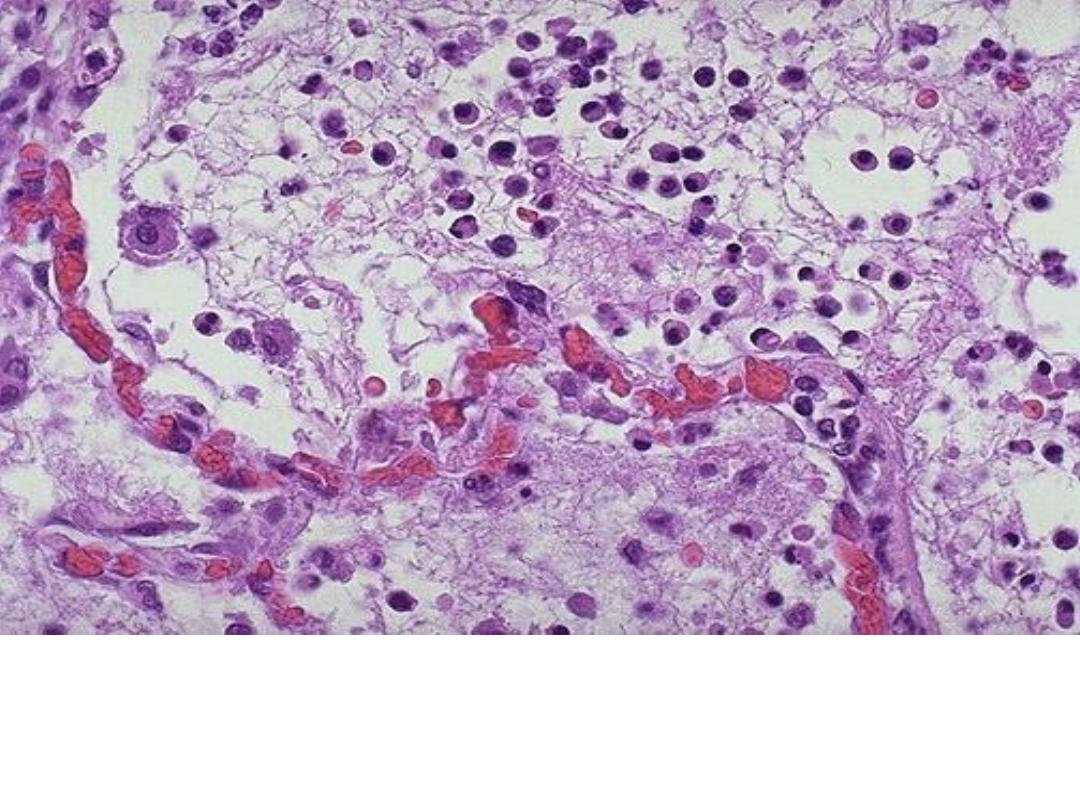
Acute inflammation (pneumonia) , dilated capillaries in the
alveolar walls from vasodilation with
numerous neutrophils
fill the alveolar spaces
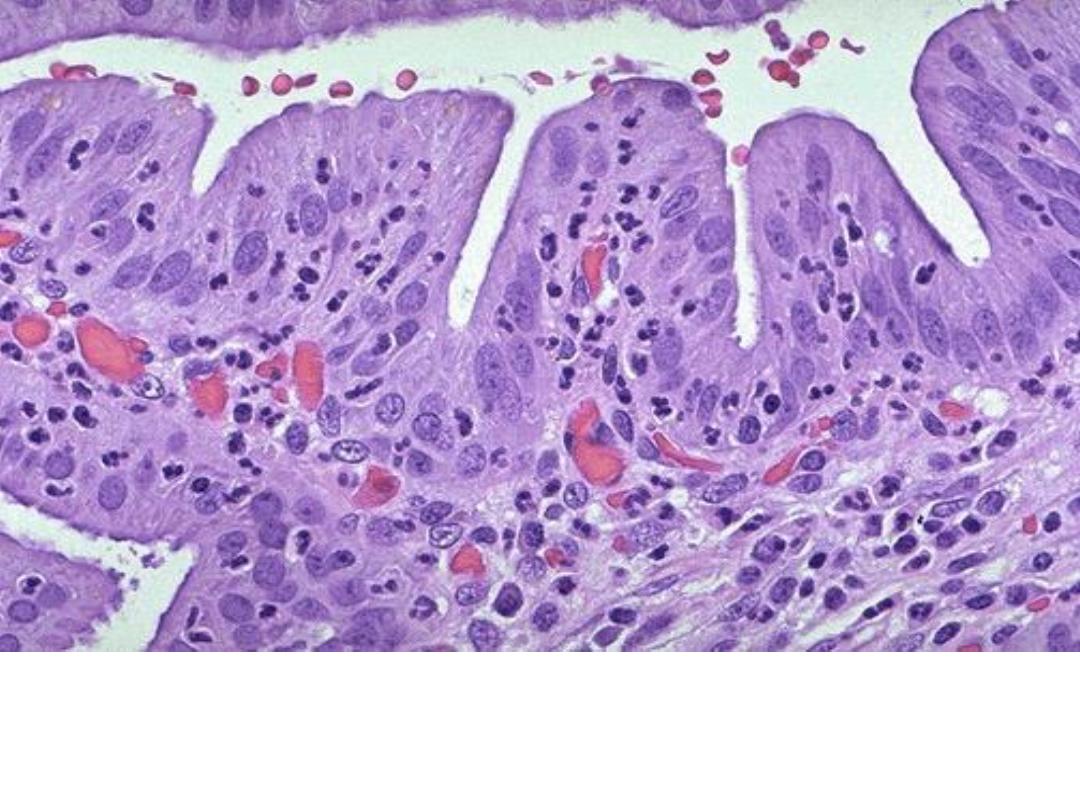
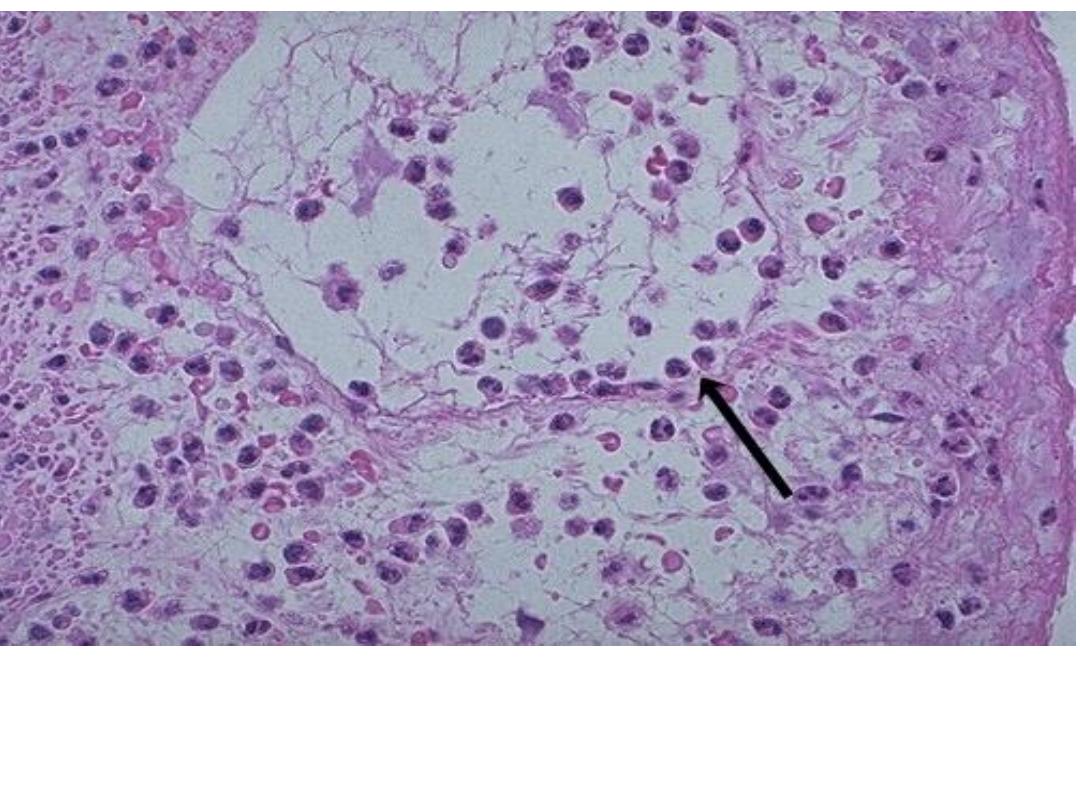
Acute inflammation of a gall bladder,
the neutrophils are
seen infiltrating the mucosa and submucosa of the
gallbladder with congestion of small blood vessels
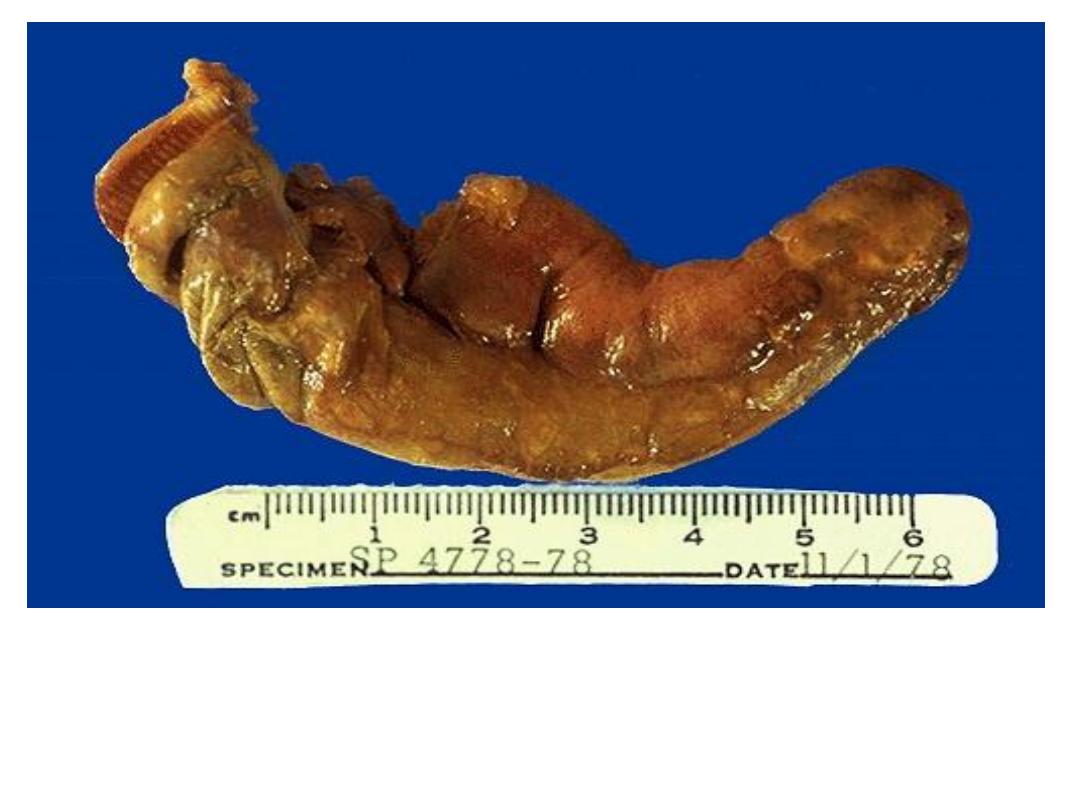
Acute appendicitis with yellow to tan exudate and hyperemia,
including the periappendiceal fat superiorly.
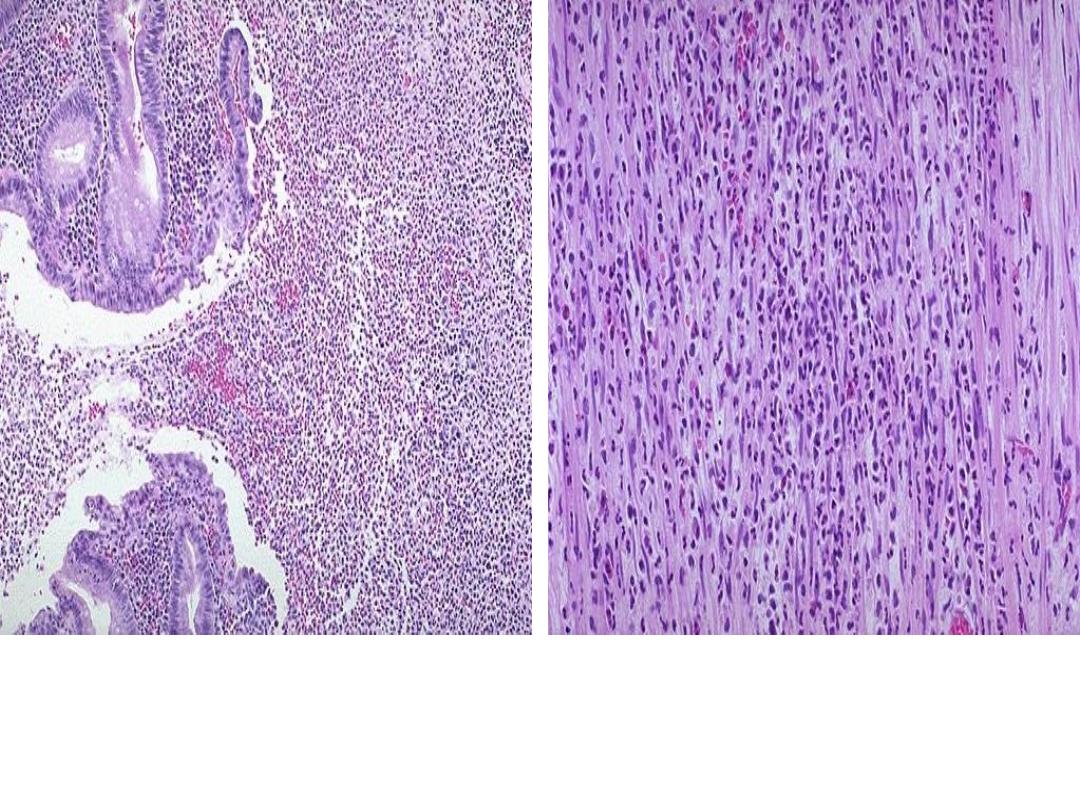
Acute appendicitis:
The mucosa shows ulceration and the acute inflammatory
cells (Neutrophils) infiltrating the whole layers (transmural).
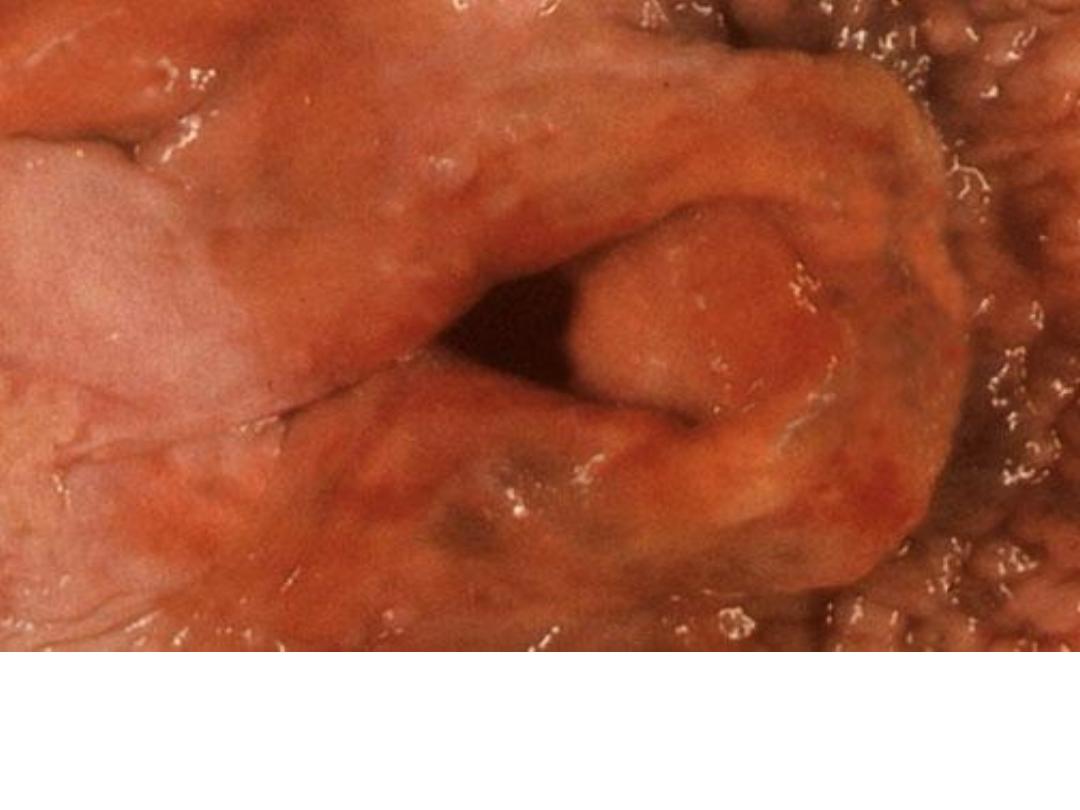
Acute laryngitis , swelling and redness of the larynx may
cause difficulty in breathing due to narrowing in the lumen
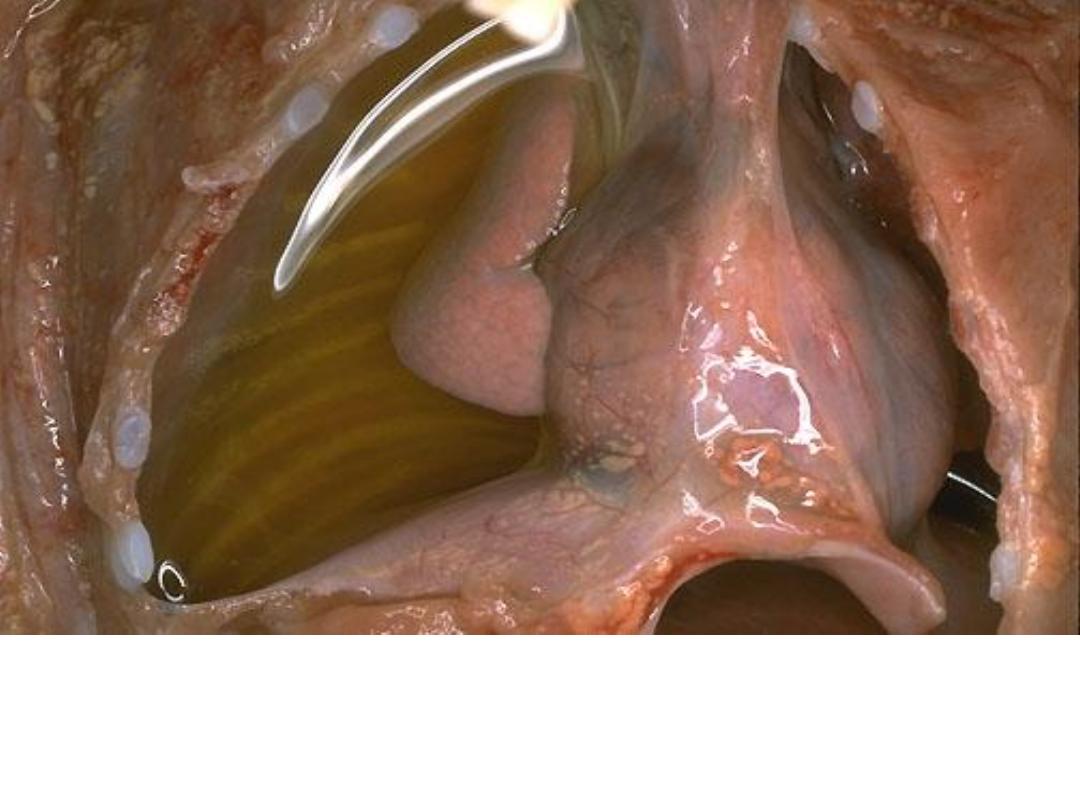
A right side serous effusion, a fluid collection into a body
cavity (right side), the fluid is clear, pale yellow in
appearance.
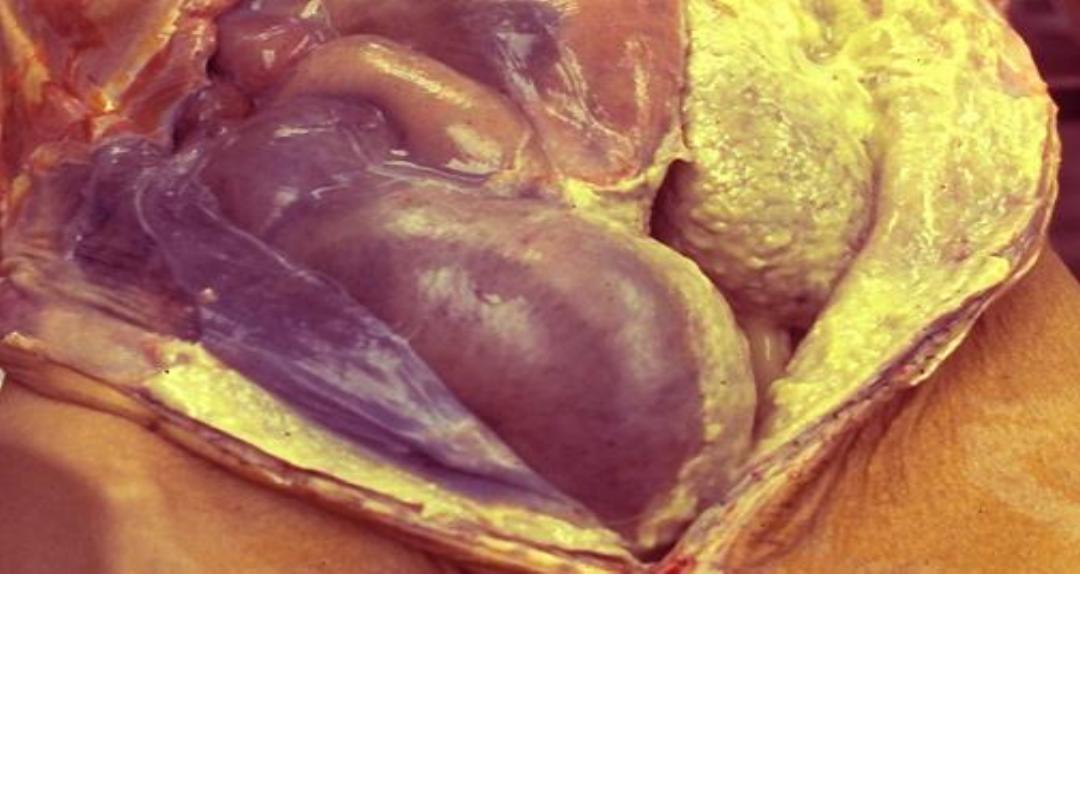
Acute inflammation (Suppurative (Purulent))
The abdominal cavity is opened at autopsy and reveal
an extensive purulent peritonitis(A thick yellow exudate
coats the peritoneal surfaces)
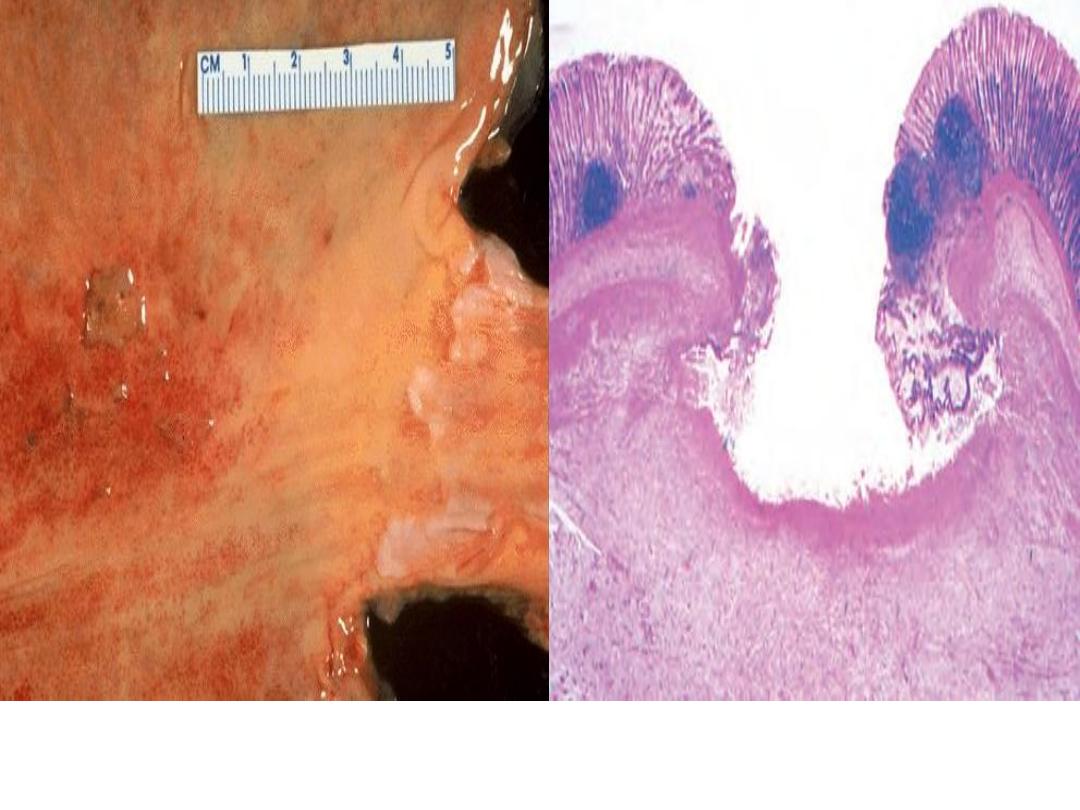
Acute inflammation (
ulcer),
the gastric mucosa has
been lost, or ulcerated.
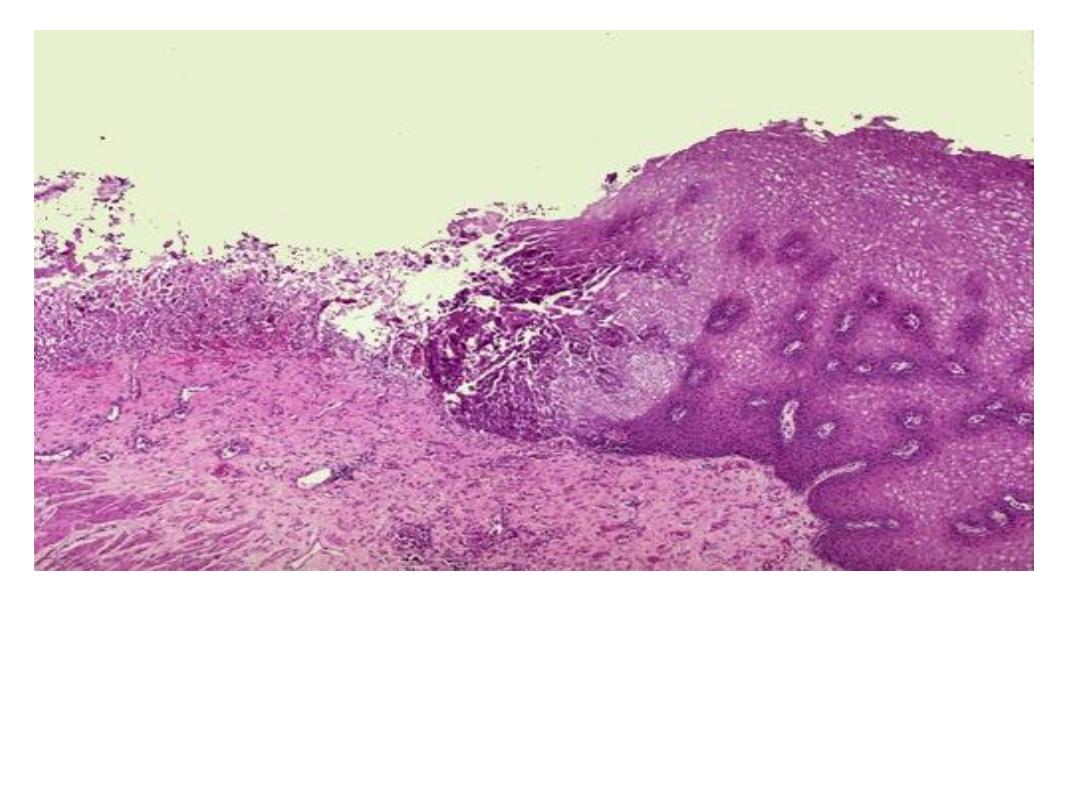
An esophageal acute ulcer ,in which the squamous
mucosa has been lost and in the ulcer base there are
inflammatory cells and fibrin
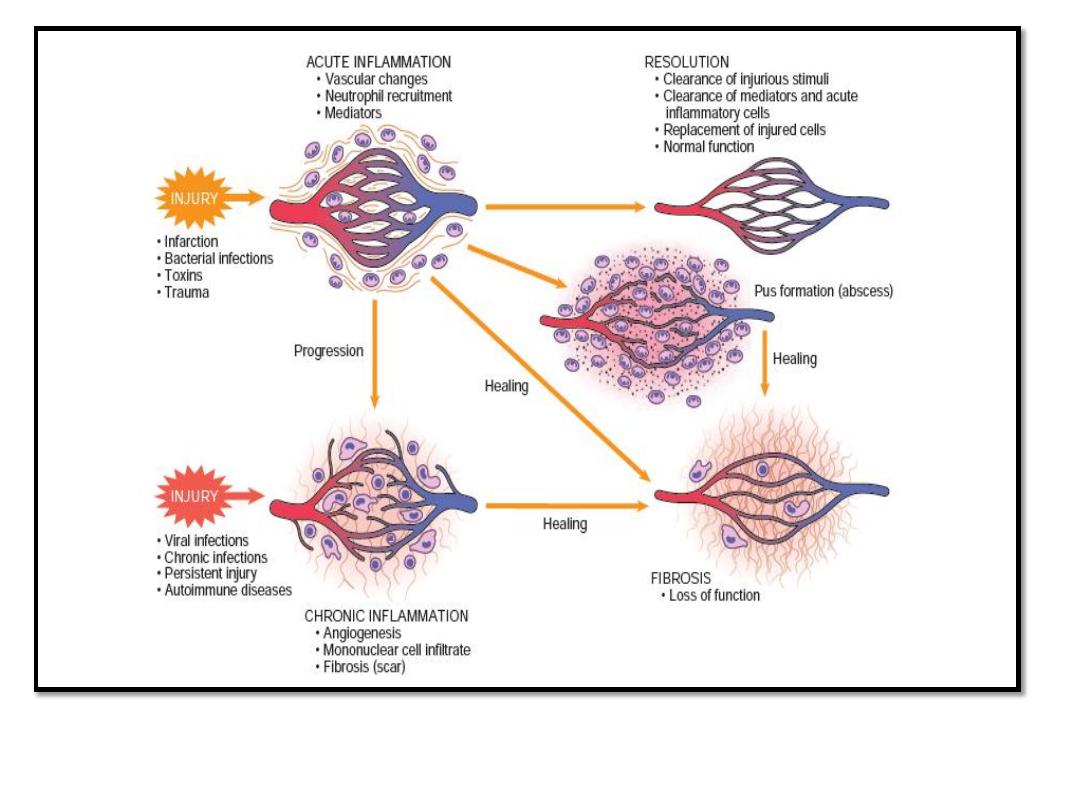
Causes and outcomes of acute inflammation
Complete resolution
Extensive acute
inflammation
may
lead to
abscess
formation
(The
liquefactive
necrosis), as seen
here with rounded
abscesses (the
purulent material
has drained out
after sectioning to
leave a cavity)
Acute inflammation
(Suppuration (early abscess))
extensive neutrophilic exudate and the normal tissues are
destroyed in the region of the abscess.
Perimandibular abscess in the chin
region (redness, swelling)
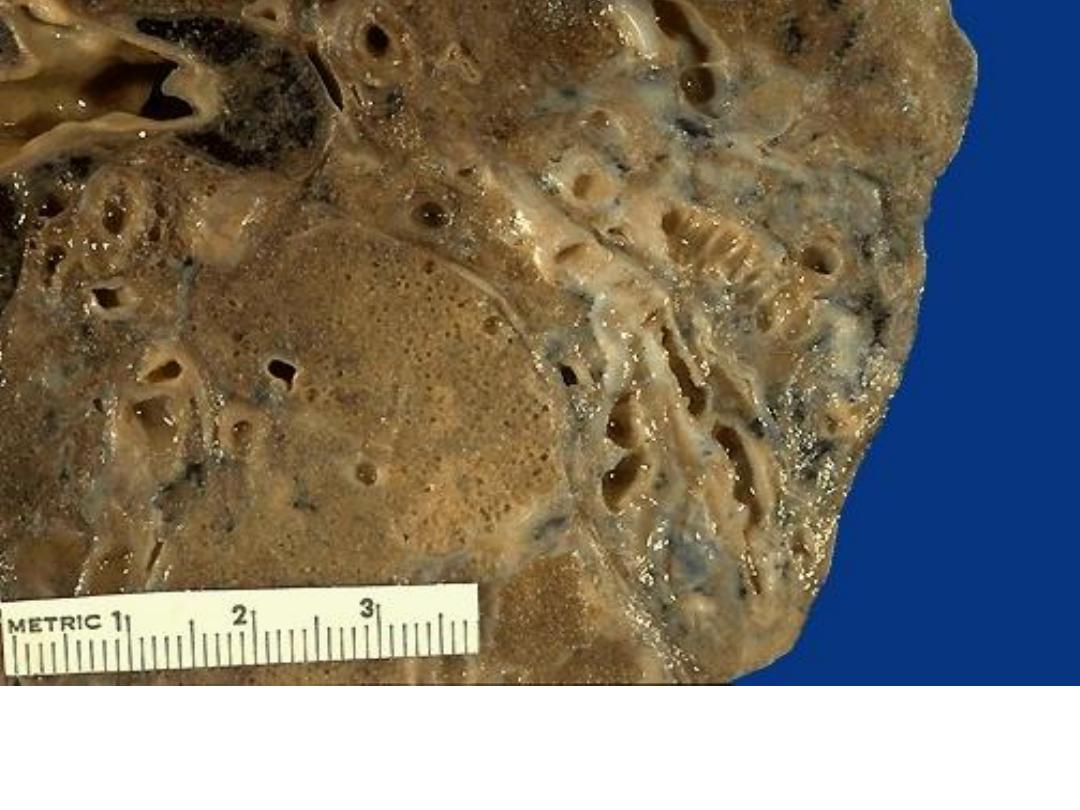

chronic inflammation of the bronchi had led to dilation of
bronchi&deposition of tan to white collagenous tissue (scarring)
Chronic inflammation of the lung,
the inflammatory cells
(mononuclear cells) are more likely to be interstitial (within
tissues) rather than exudative
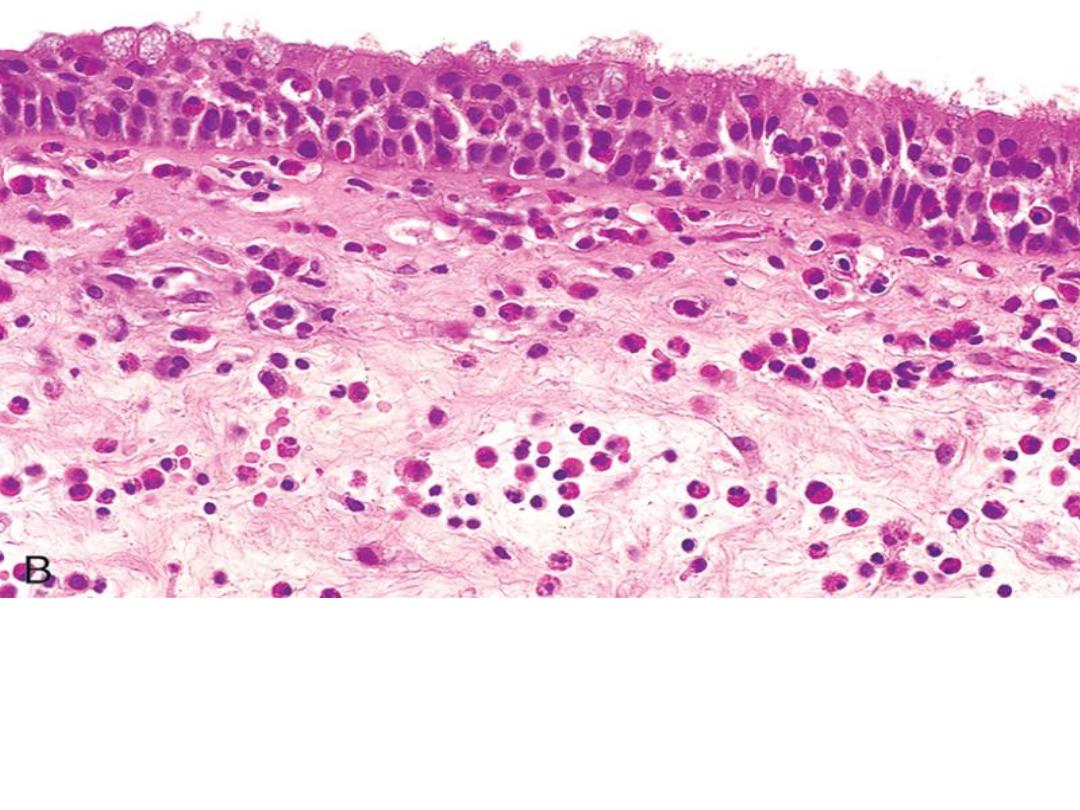
Chronic inflammation due to hypersensitivity reaction:
chronic inflammatory cells infiltrate mainly eosinophils
(allergic nasal polyp)
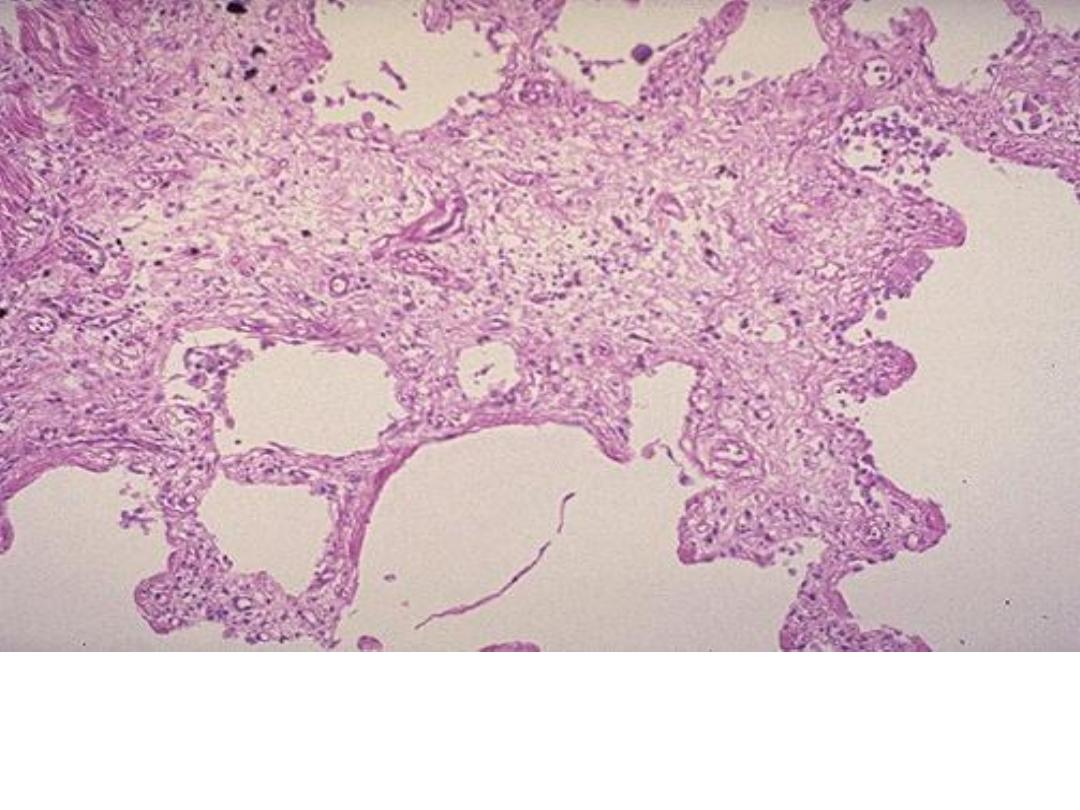
Chronic inflammation (lung)
The end result of inflammation
can be scarring. Here, the alveolar walls are thickened and
filled with pink collagen.
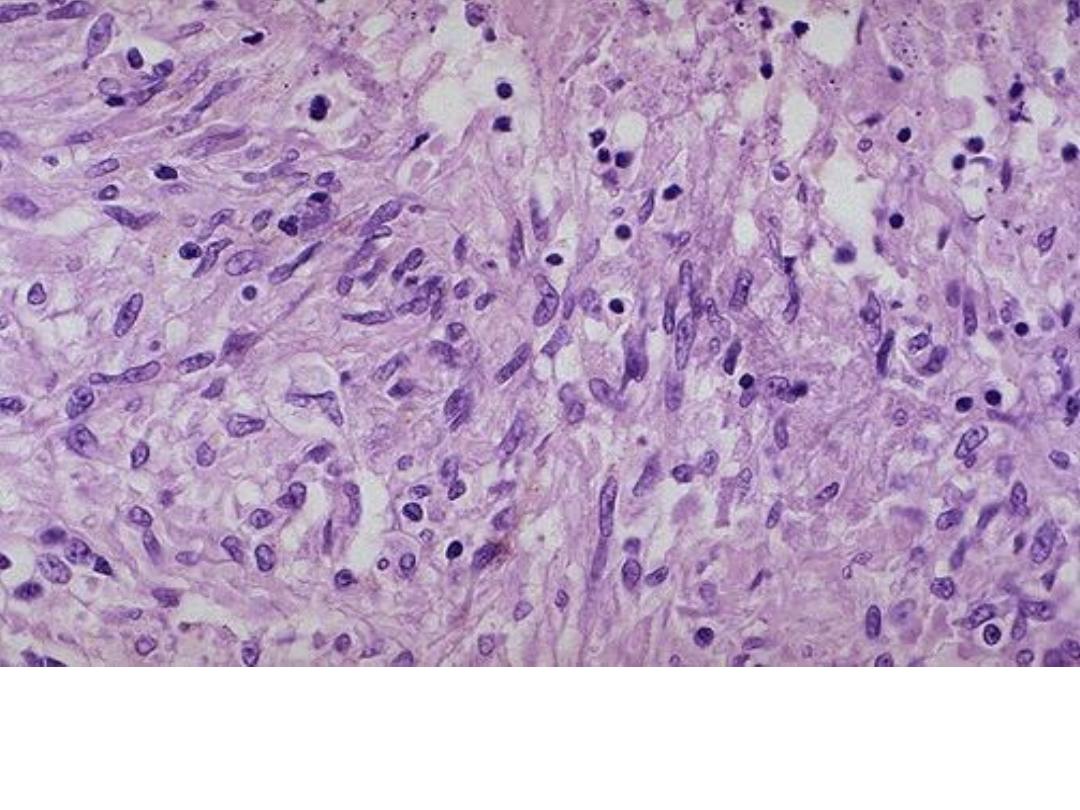
Granuloma, aggregate of epithelioid
macrophages
Granuloma with Foreign body GC
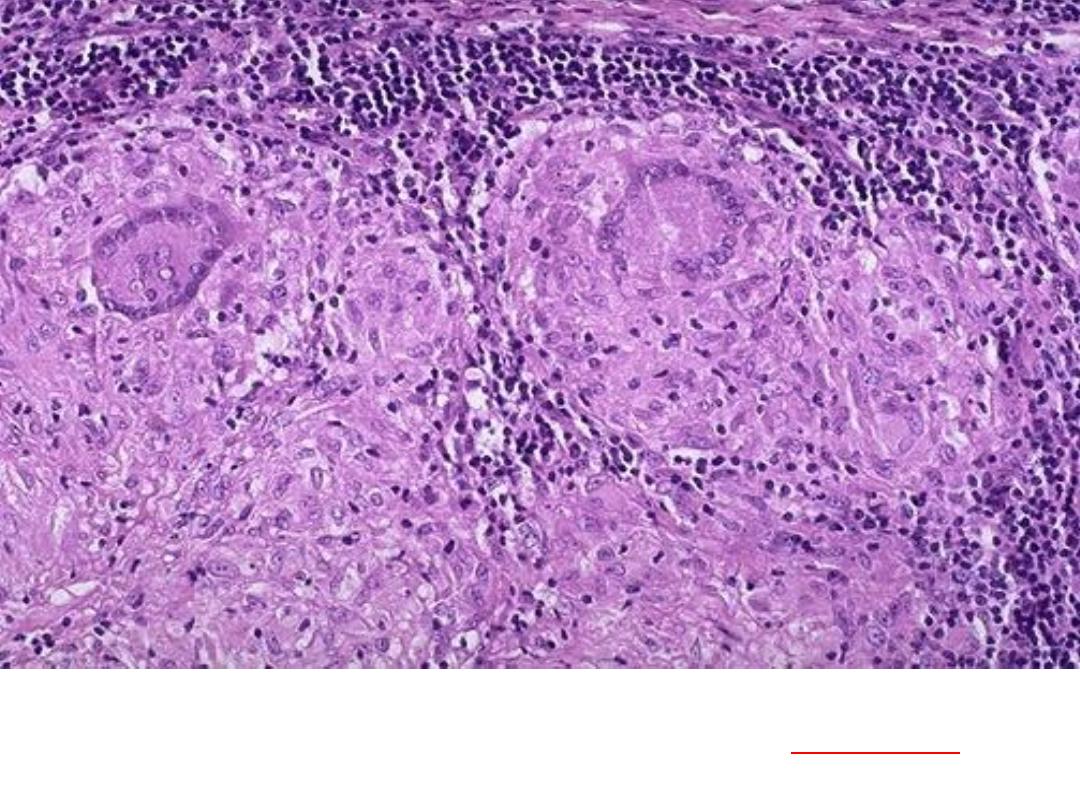
Granuloma with Langhan’s GC
pulmonary granulomas,
consist of epithelioid macrophages, with
Langhan’s
giant cell surrounded by lymphocytes & fibroblasts
..
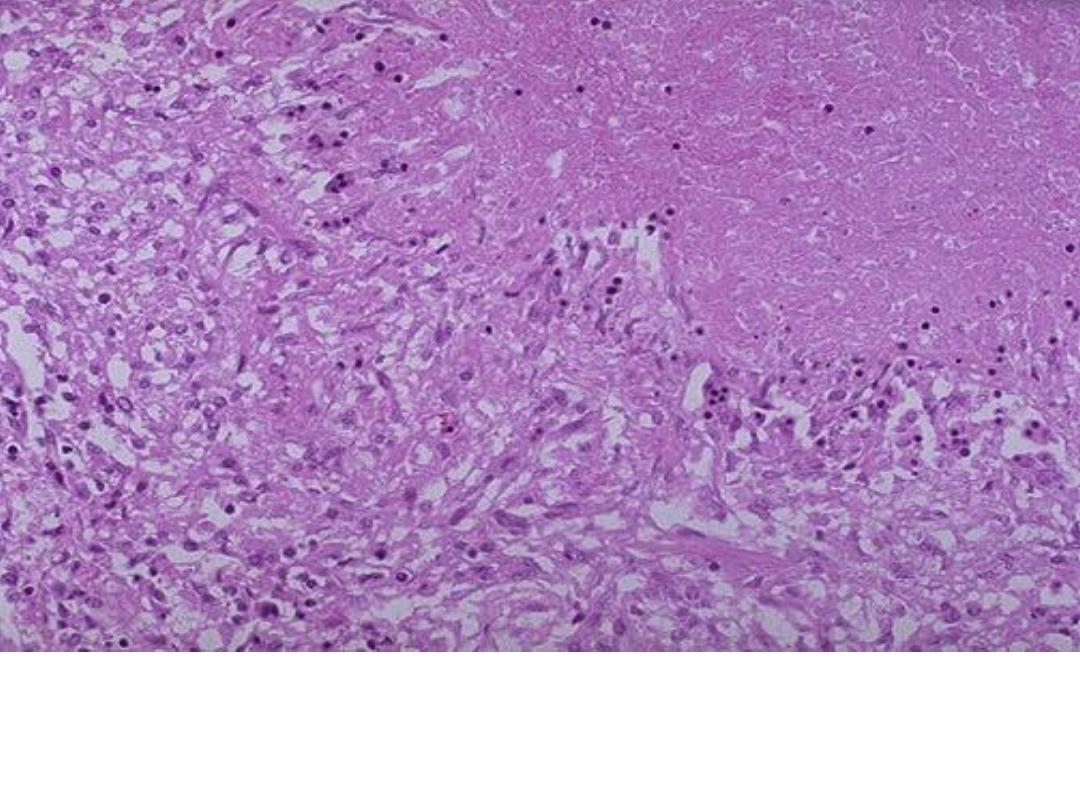
This is a caseating granuloma. Epithelioid cells surround a
central area of necrosis(caseous) that appears irregular,
amorphous, and pink.
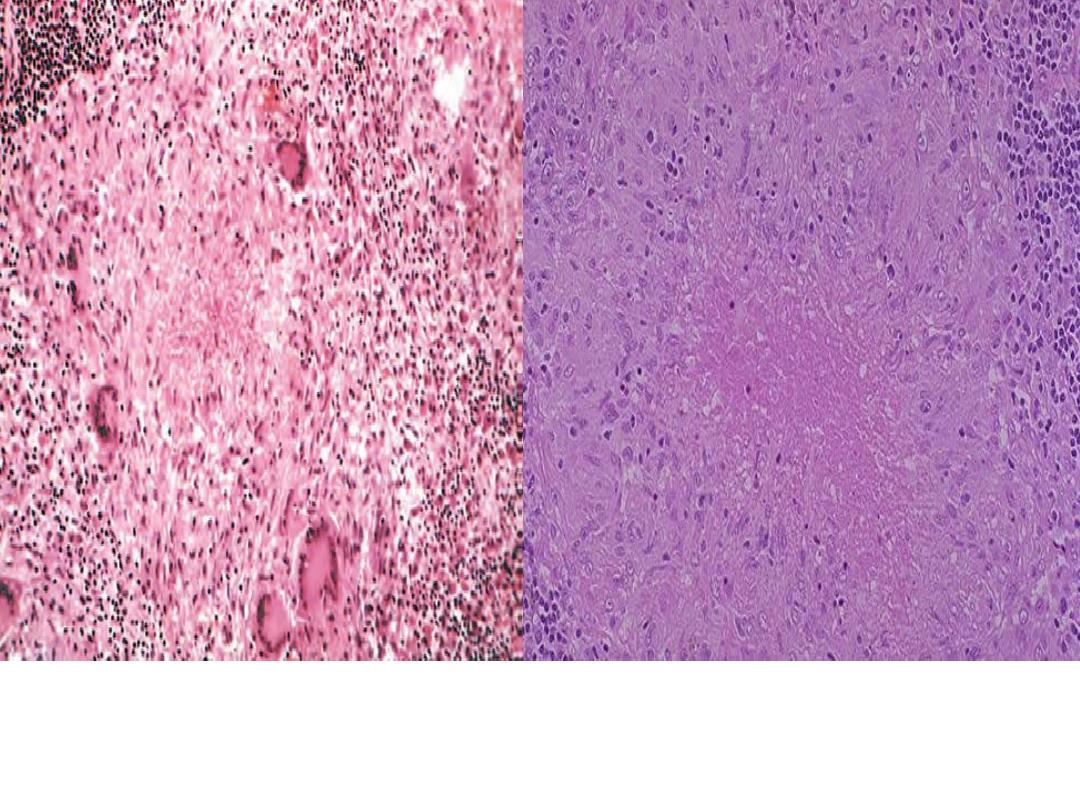
Granuloma with central necrosis
Epithelioid cells surround a
central area of necrosis(caseous) that appears irregular,
amorphous, and pink.

The Practical of Healing & Repair
Third Year
Healing of inflammation often involves in growth of capillaries
and fibroblasts. This forms granulation tissue. Here, an acute
myocardial infarction is seen healing. There are numerous
capillaries, and collagen is being laid down to form a scar.
Non-infracted myocardium is present at the far left.
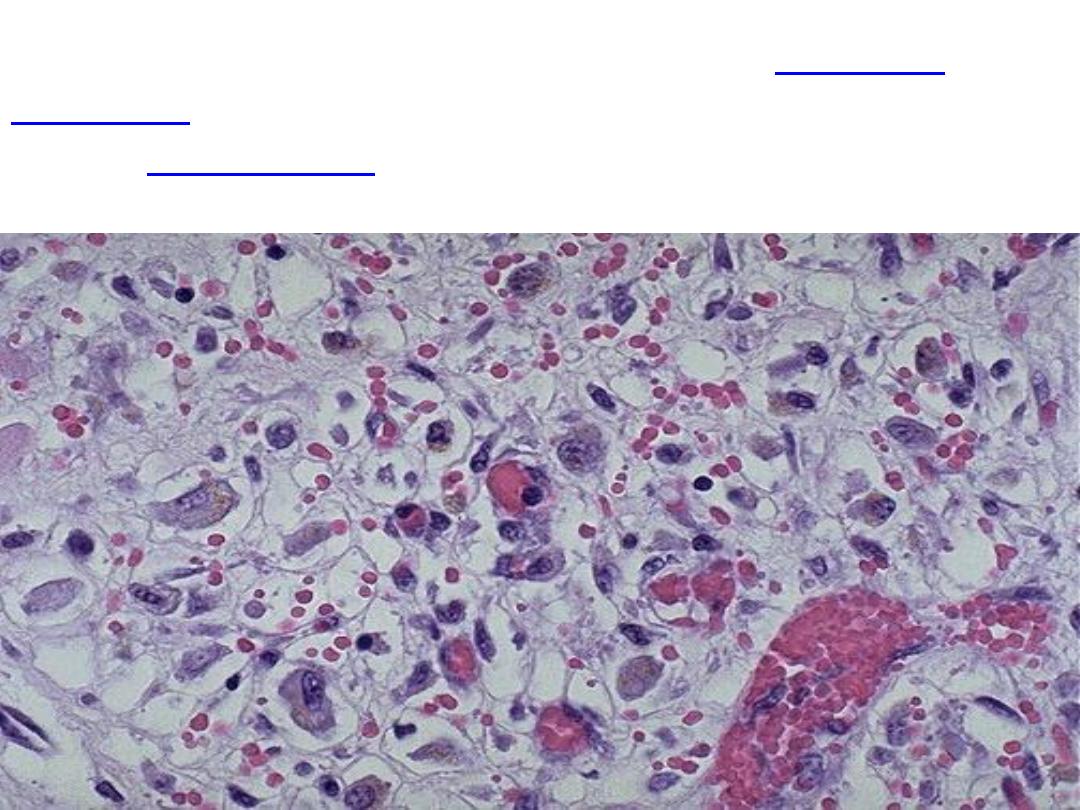
At high magnification, granulation tissue has
, and a variable amount of inflammatory cells
)
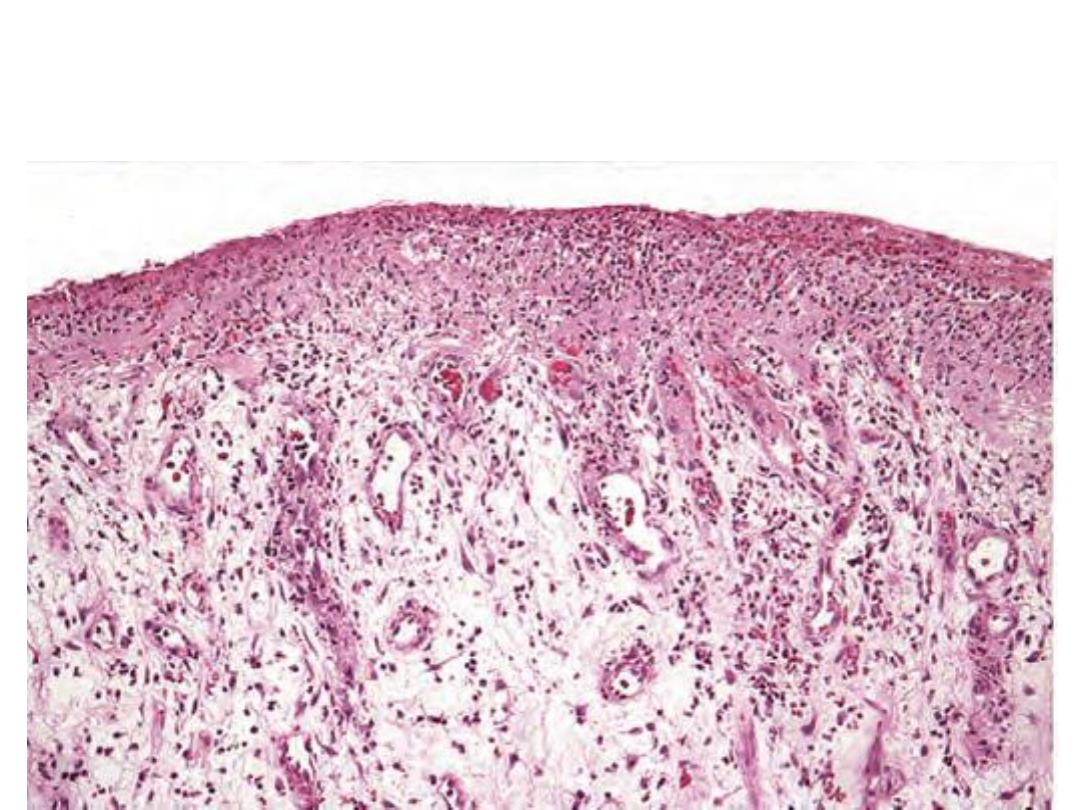
A thin layer of epidermal reepithelialization and
extensive granulation tissue formation in the dermis
.
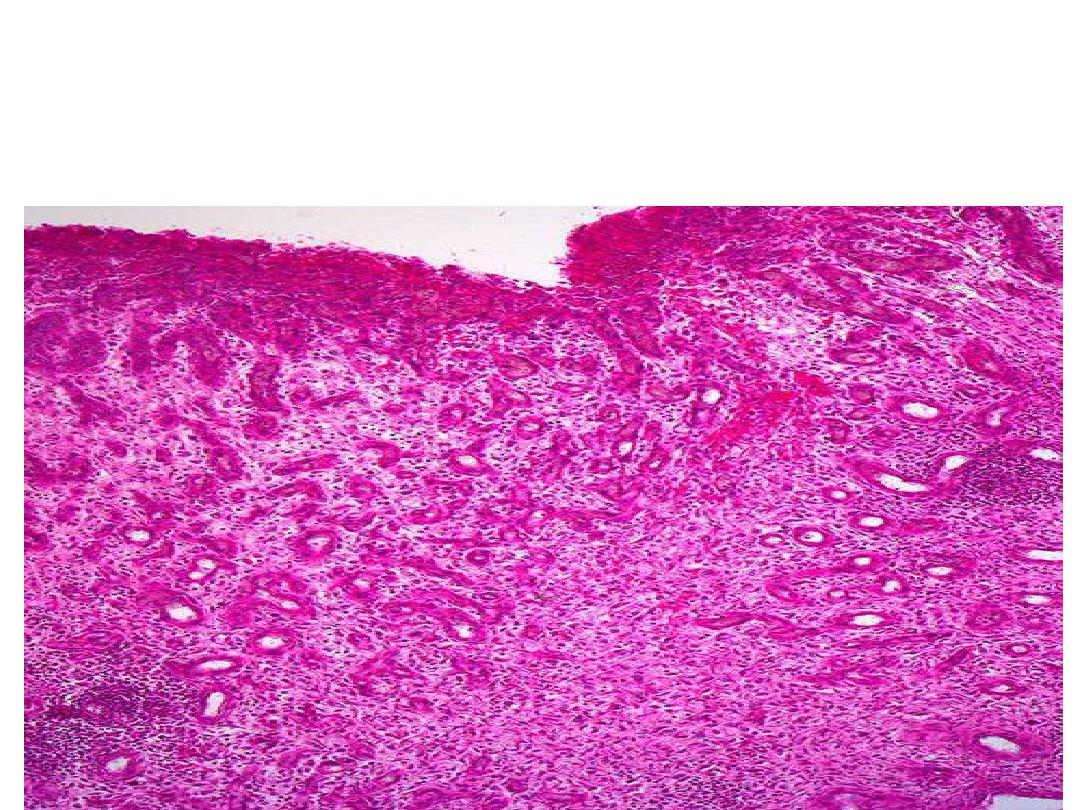
Granulation tissue ( capillaries, fibroblasts & collagen
fibers) formed at site of incised wound, the overlying
epidermis heals by regeneration.
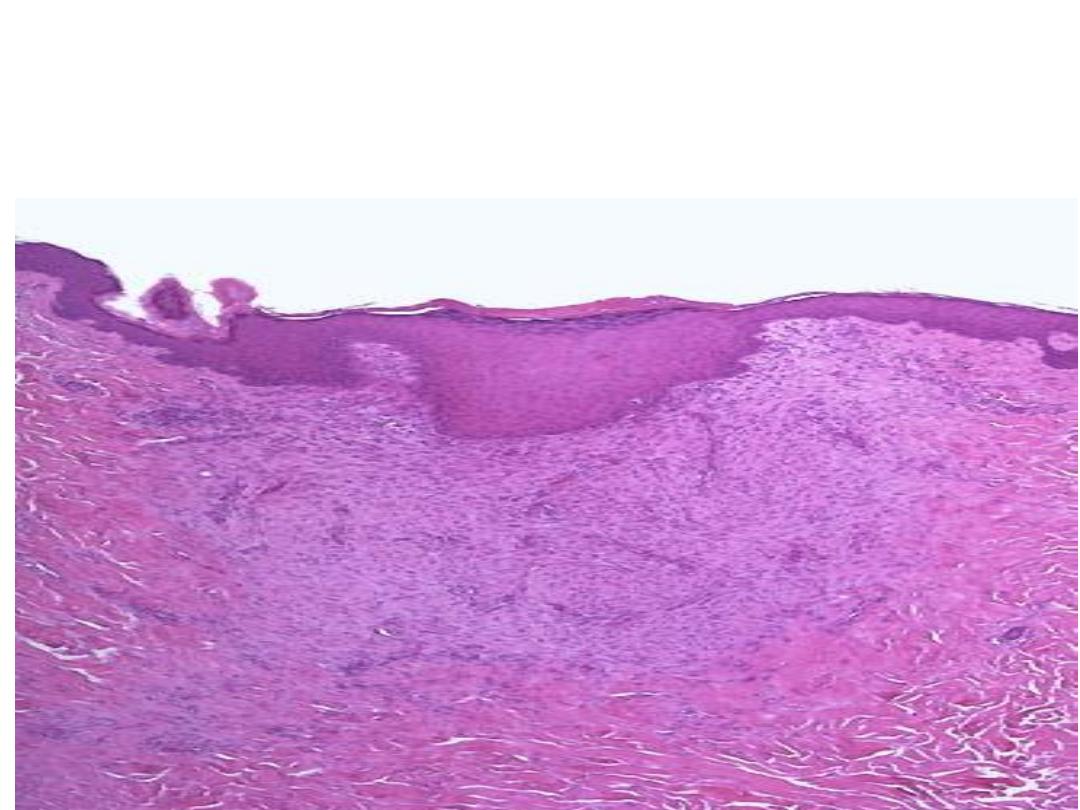
This is a healing biopsy site on the skin seen a week following
the excision, The skin surface has re-epithelialized, and below
this is granulation tissue with small capillaries and fibroblasts
forming collagen
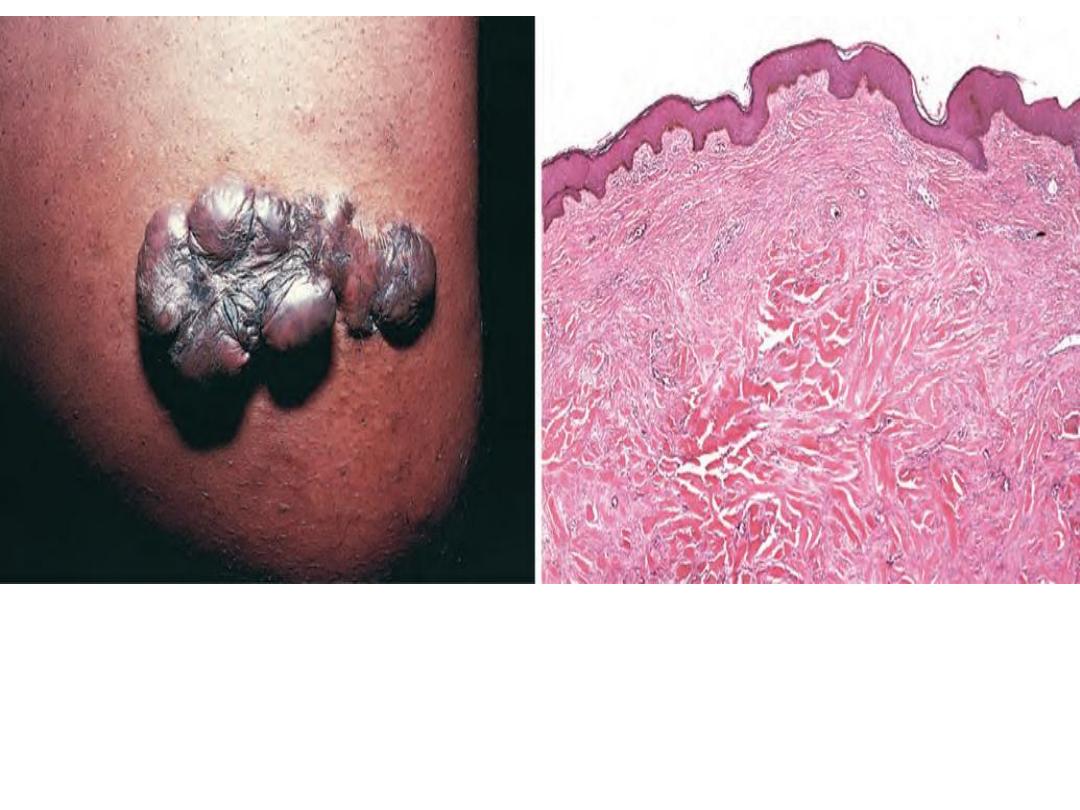
Excess collagen deposition in the
skin forming a raised scar known
as keloid (
Hypertrophic scar)
The accumulation of excessive amounts of
collagen in the
dermis
(keloid)
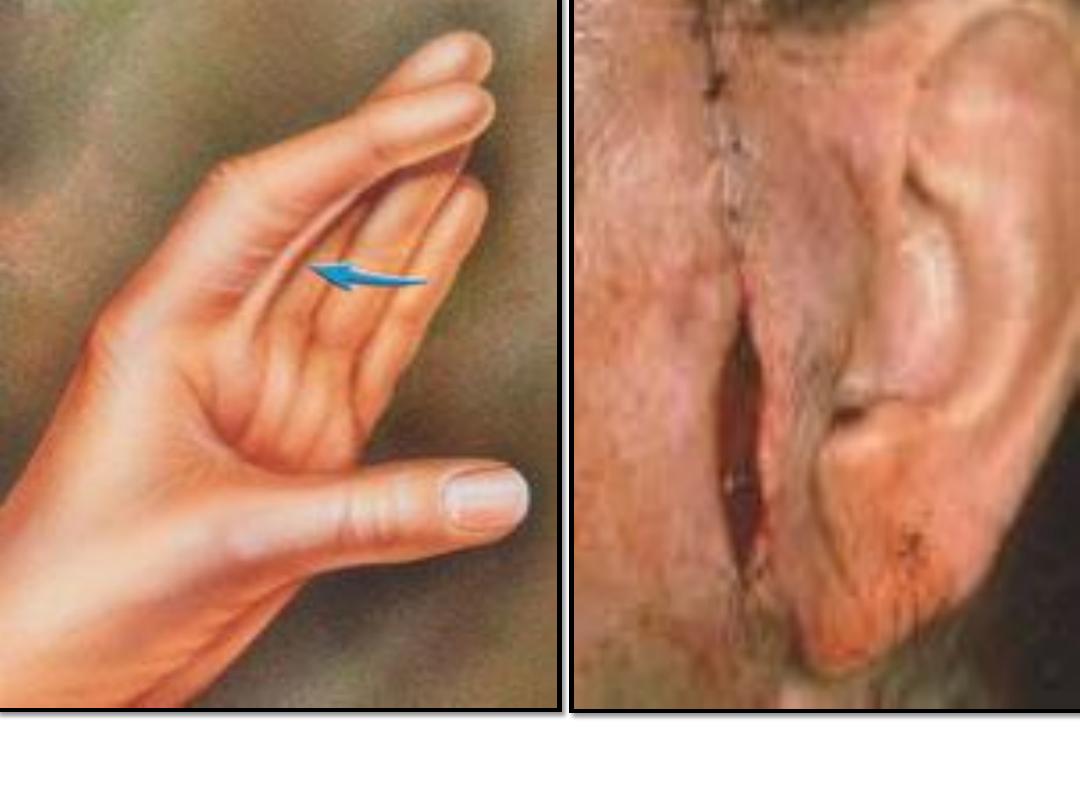
2.Wound dehiscence
Wound dehiscence
Cicatrisation

Practical infectious diseases
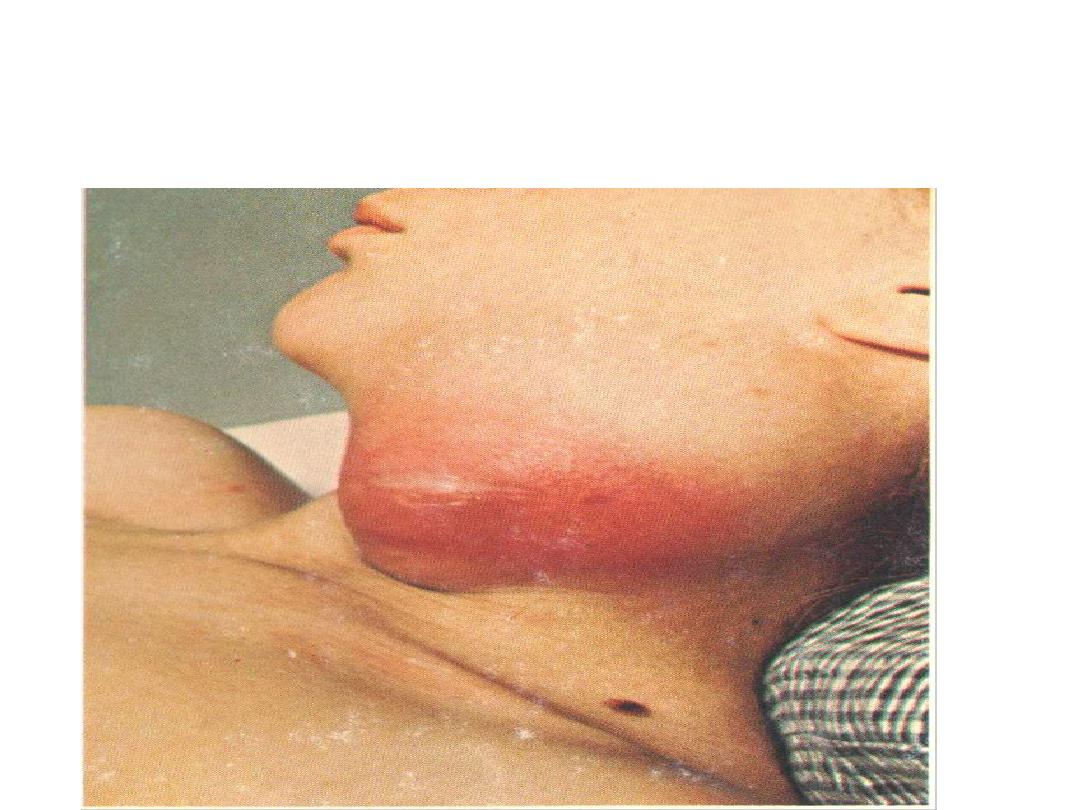
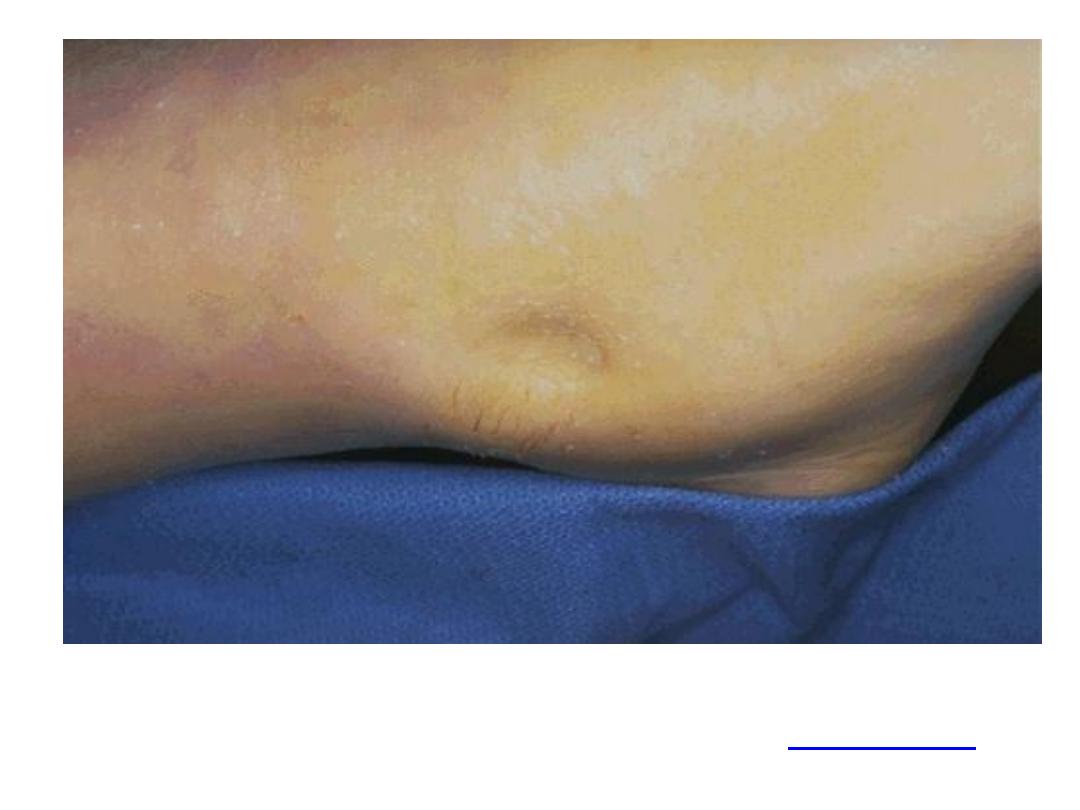
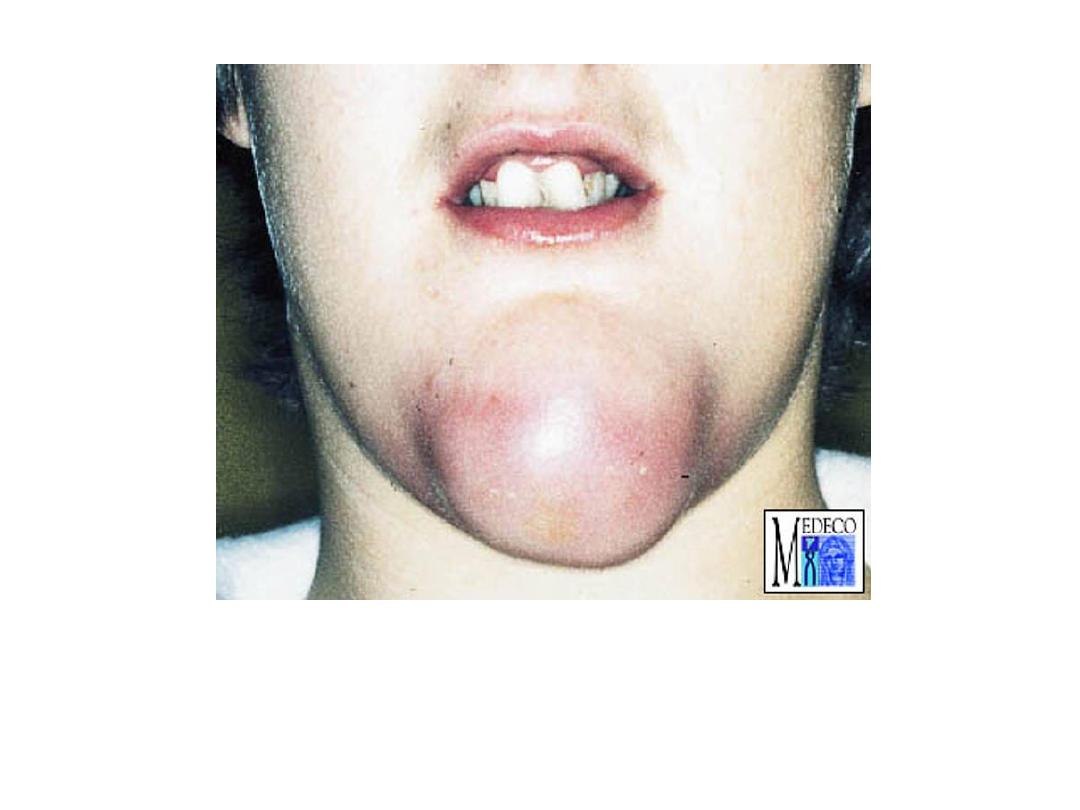
Localization of pus leads to abscess formation which
appear here as red congested swelling at the side of the
neck. Diagnosis: abscess
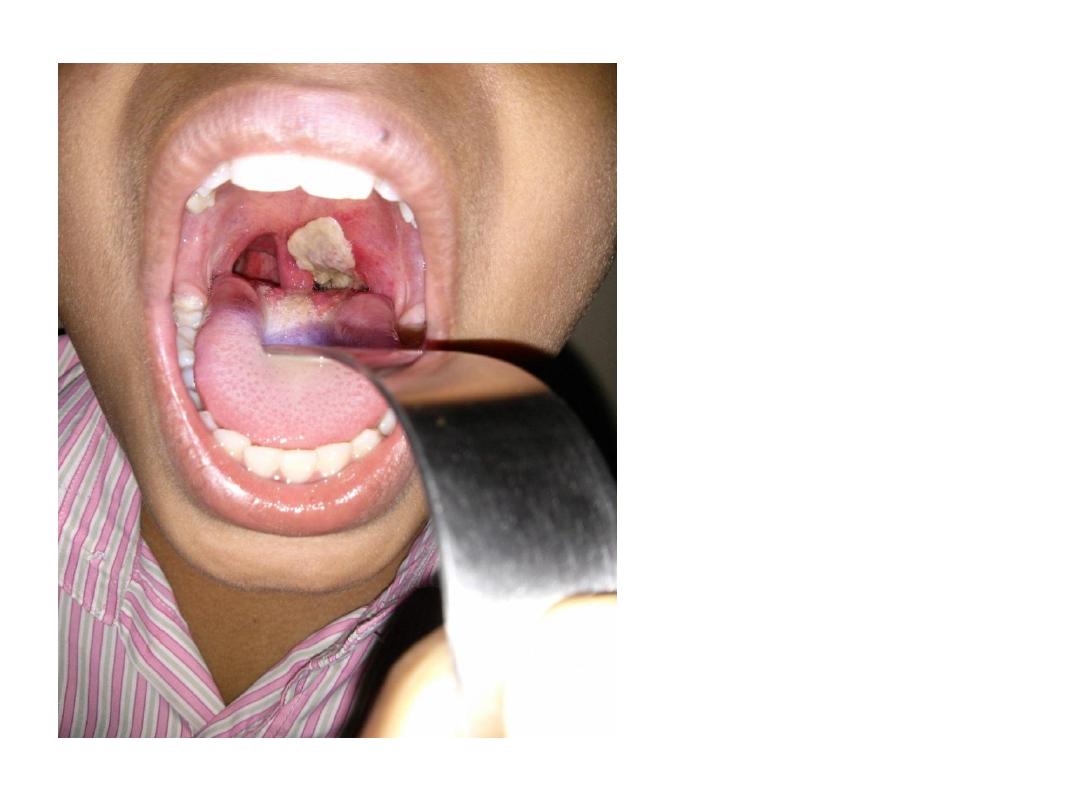
Formation of a
superficial, dirty-
gray
pseudomembrane
of diphtheria on
the soft palate.
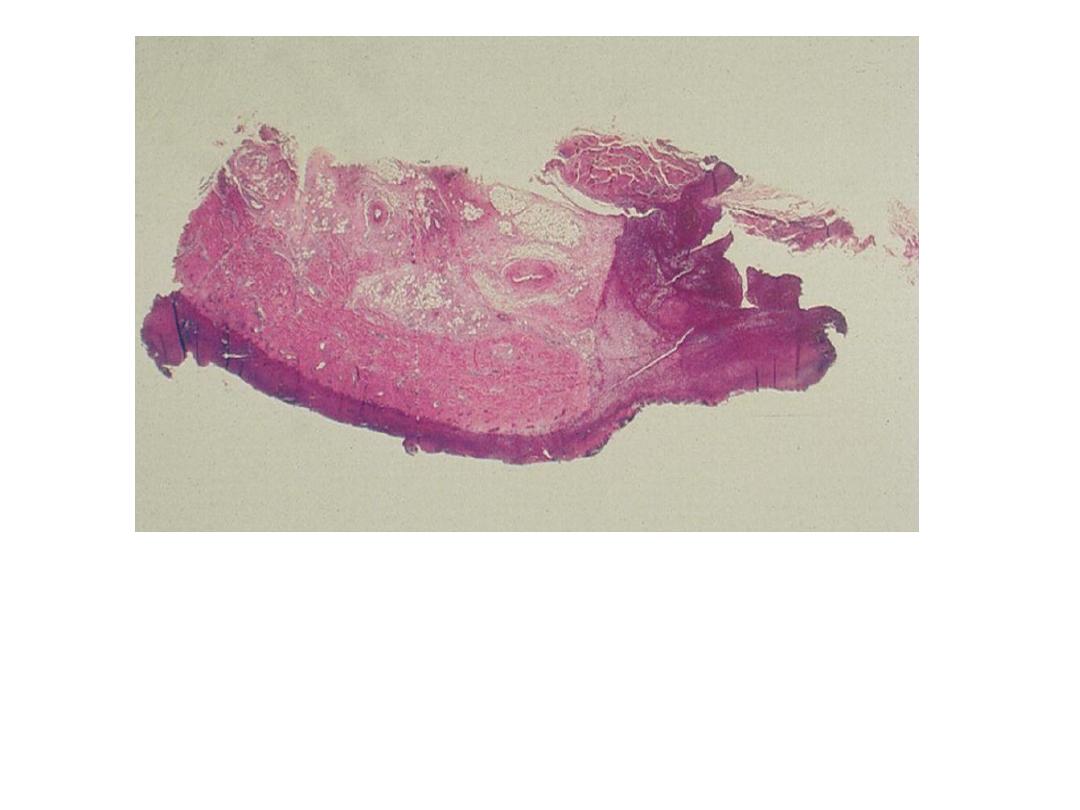
Pharyngeal pseudomembrane. Epithelium is absent; at
one side, inflammatory exudate extends to underlying
muscle
Diagnosis : Diphtheria
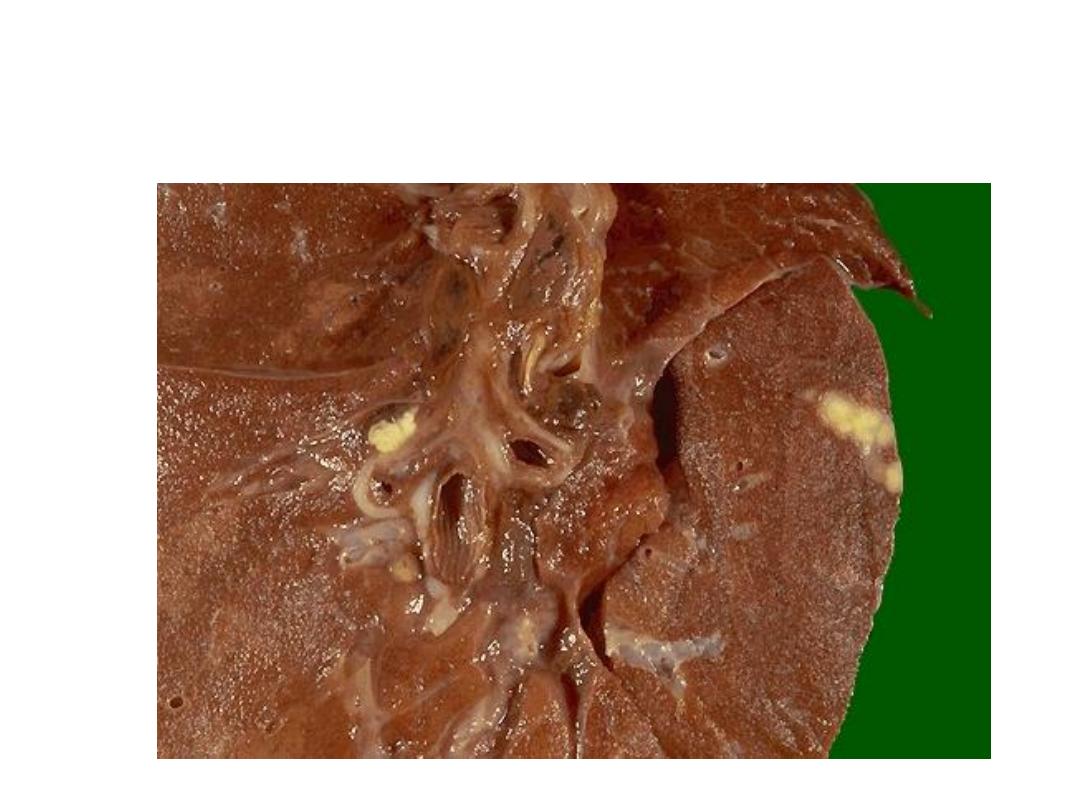
Peripheral sub pleural small whitish yellow lesion (Ghon focus)
& hilar lymph node enlargement in primary T.B (cheesy like
material)
Diagnosis: Ghon’s complex of primary TB.
.
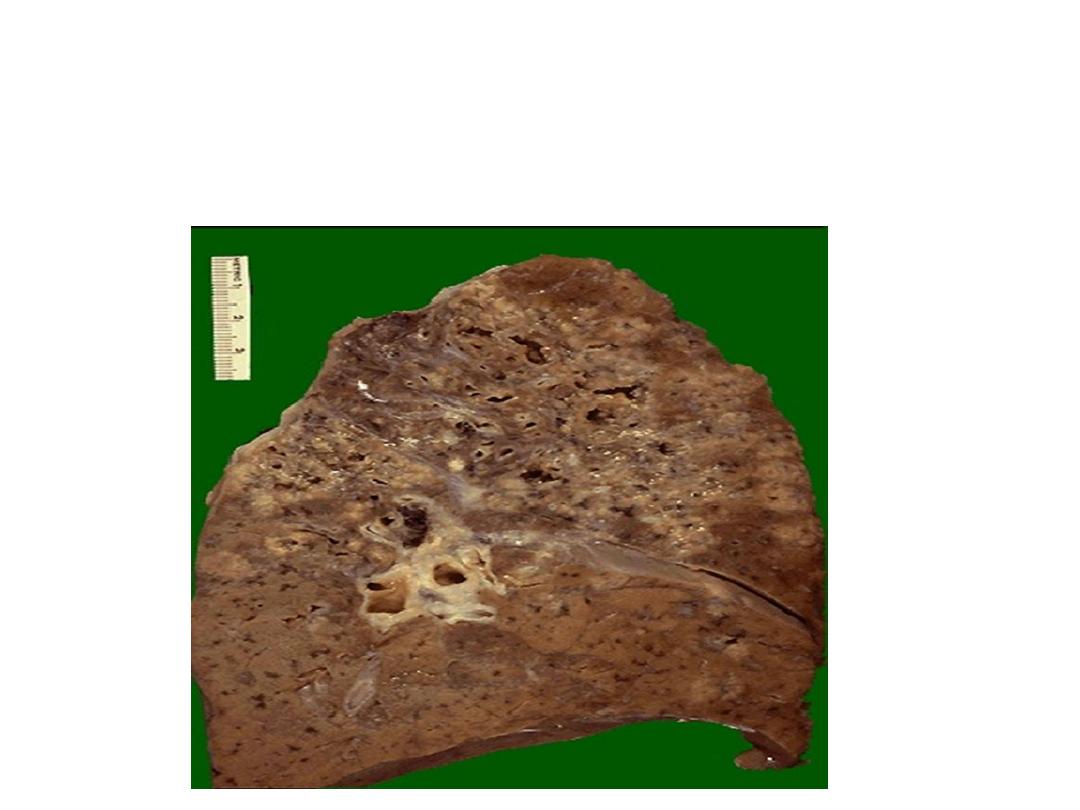
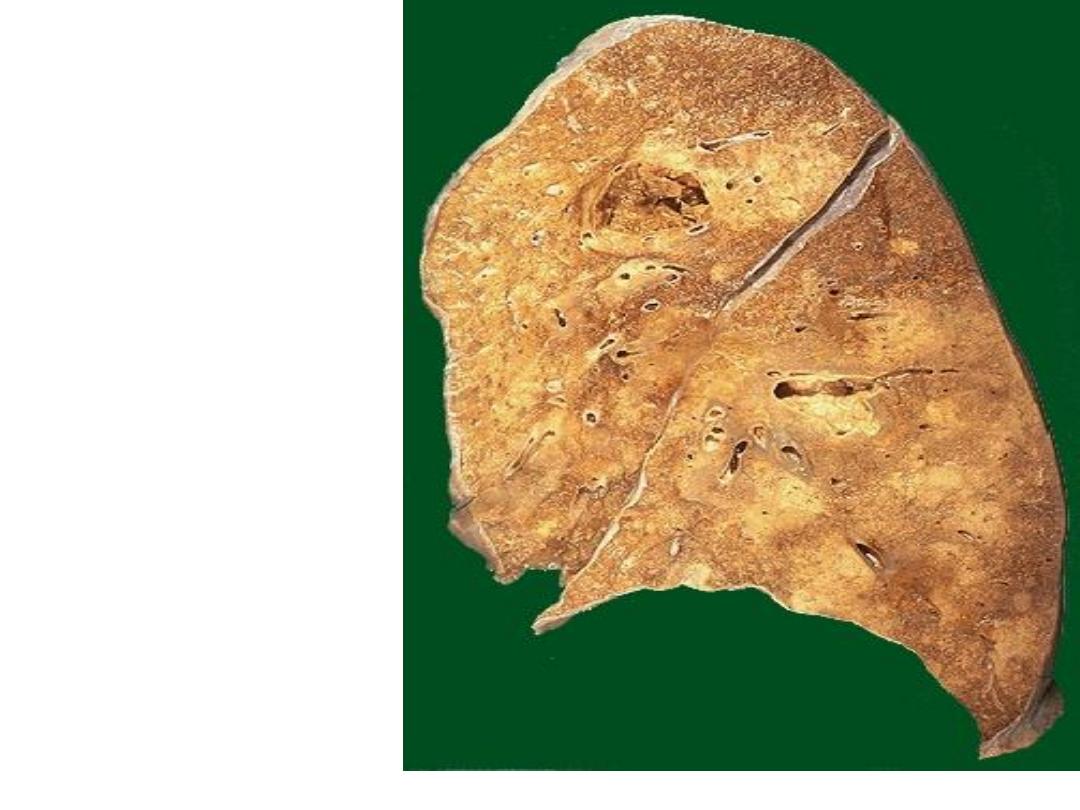
Multiple irregular cavitations & extensive area of
necrosis involving the upper lobe of the lung
Diagnosis: secondary T.B
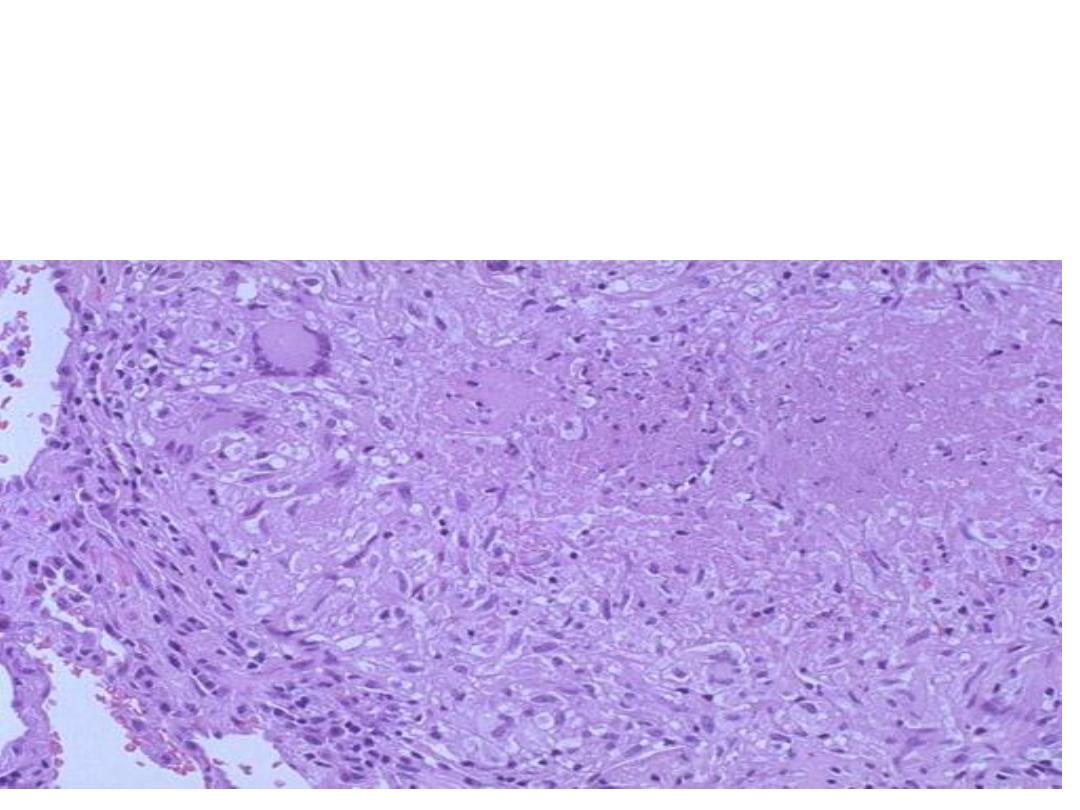
Granuloma with central caseous necrosis surrounded by
epithelioid cells & Langhans giant cell (multinucleated giant cells)
surrounded by a rim of lymphocytes
Diagnosis: T.B lung (caseating granuloma)
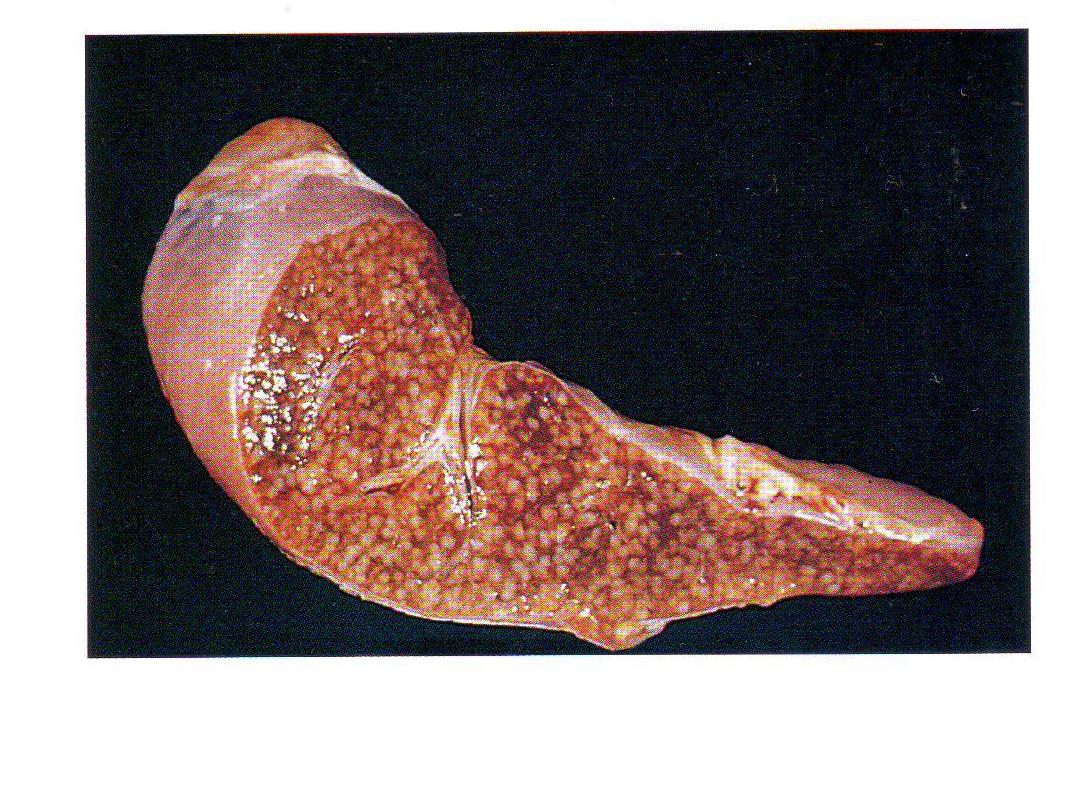
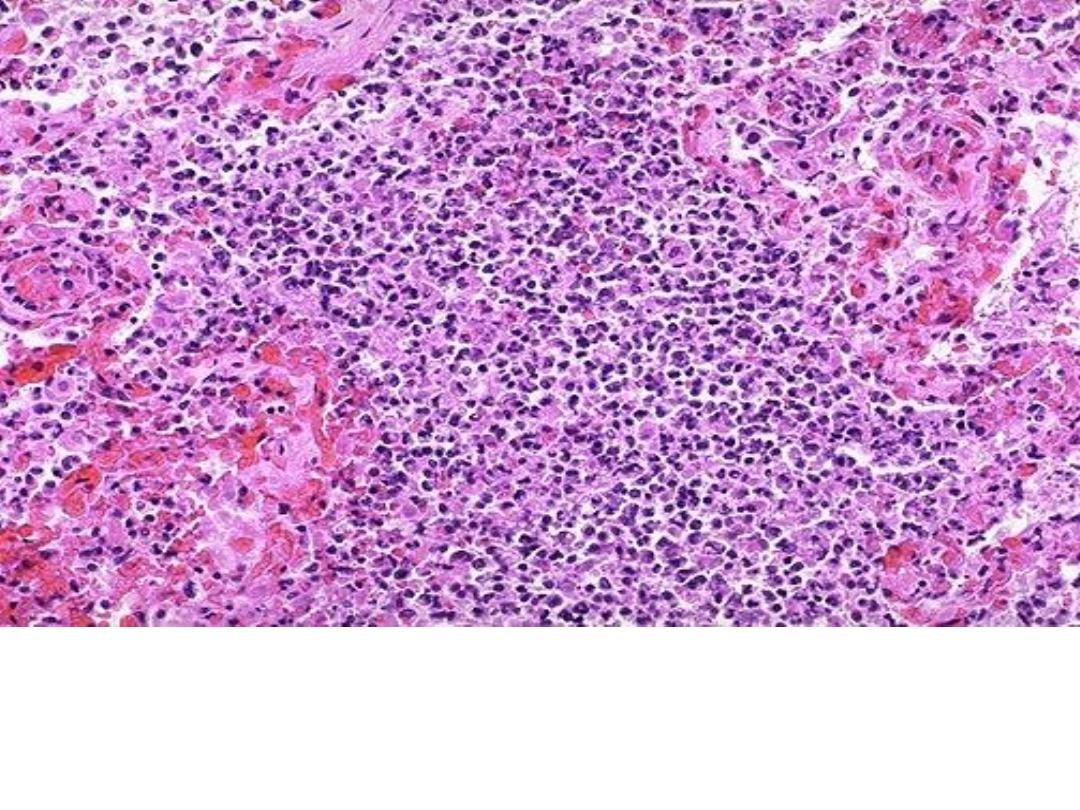
Miliary tuberculosis of the spleen,cut surface show
numerous gray-white granulomas
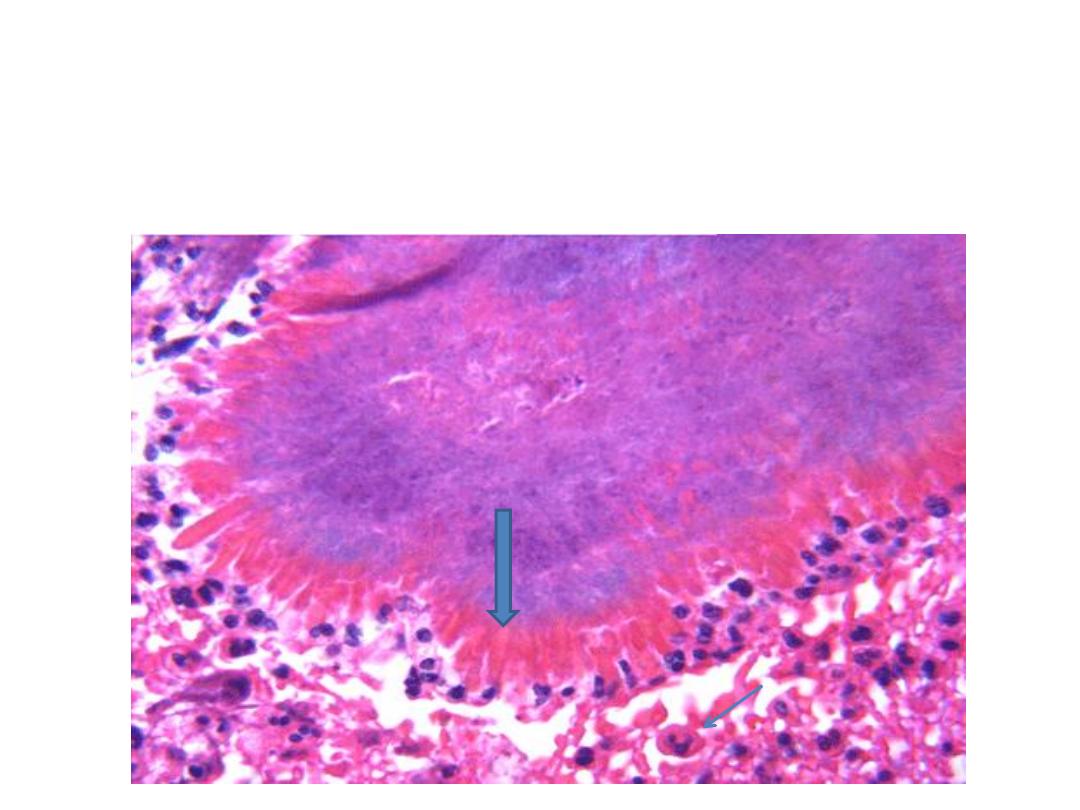
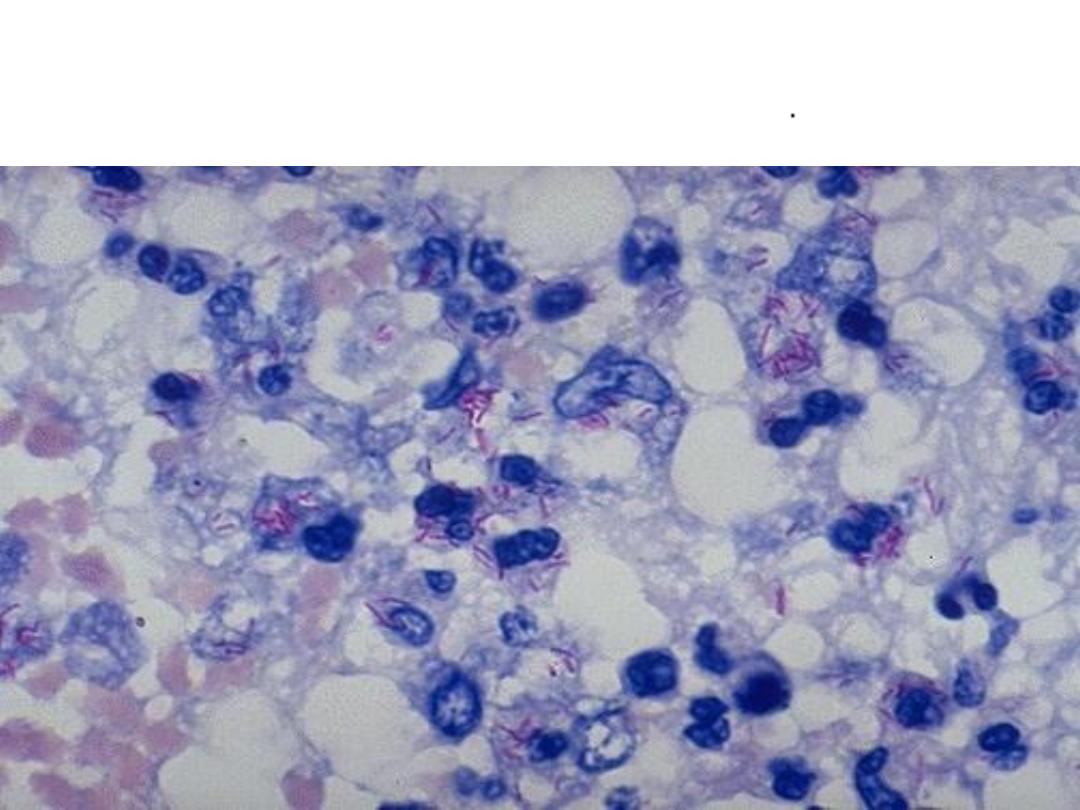
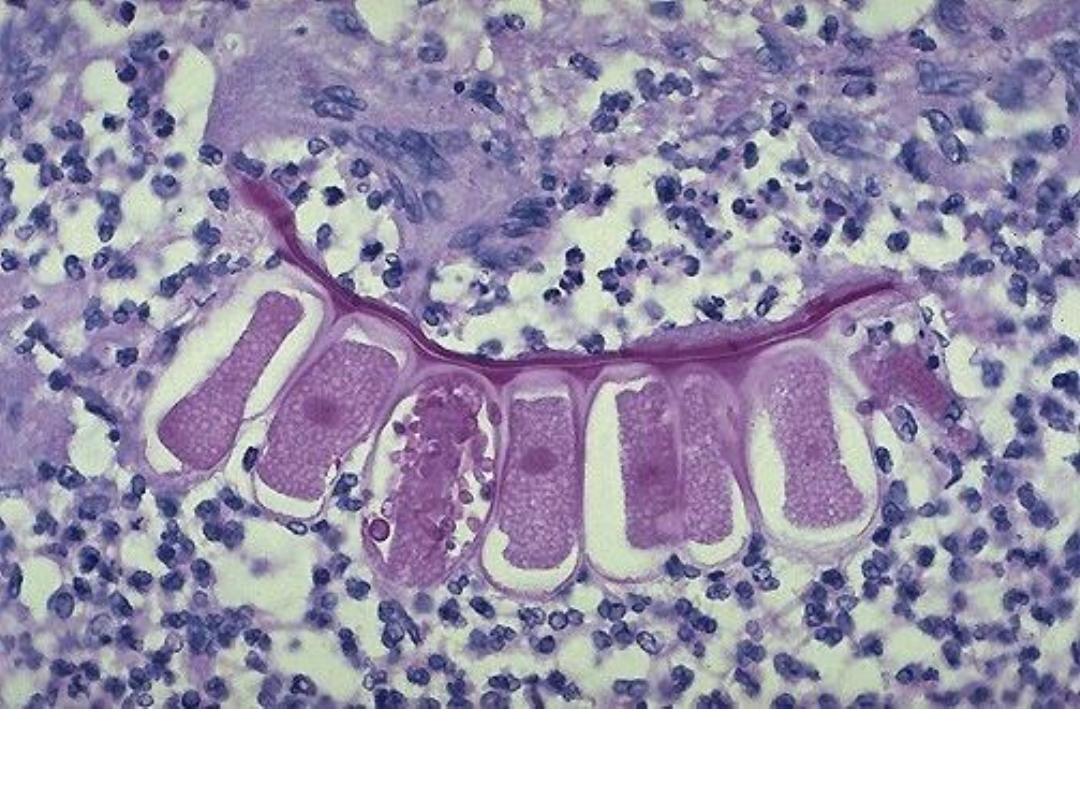
The colony of actinomycosis at high magnification. The micro
organism is filamentous & the filaments project as red specular
at the periphery of the colony (large arrow) which is
surrounded by neutrophils (mycetoma) small arrow.
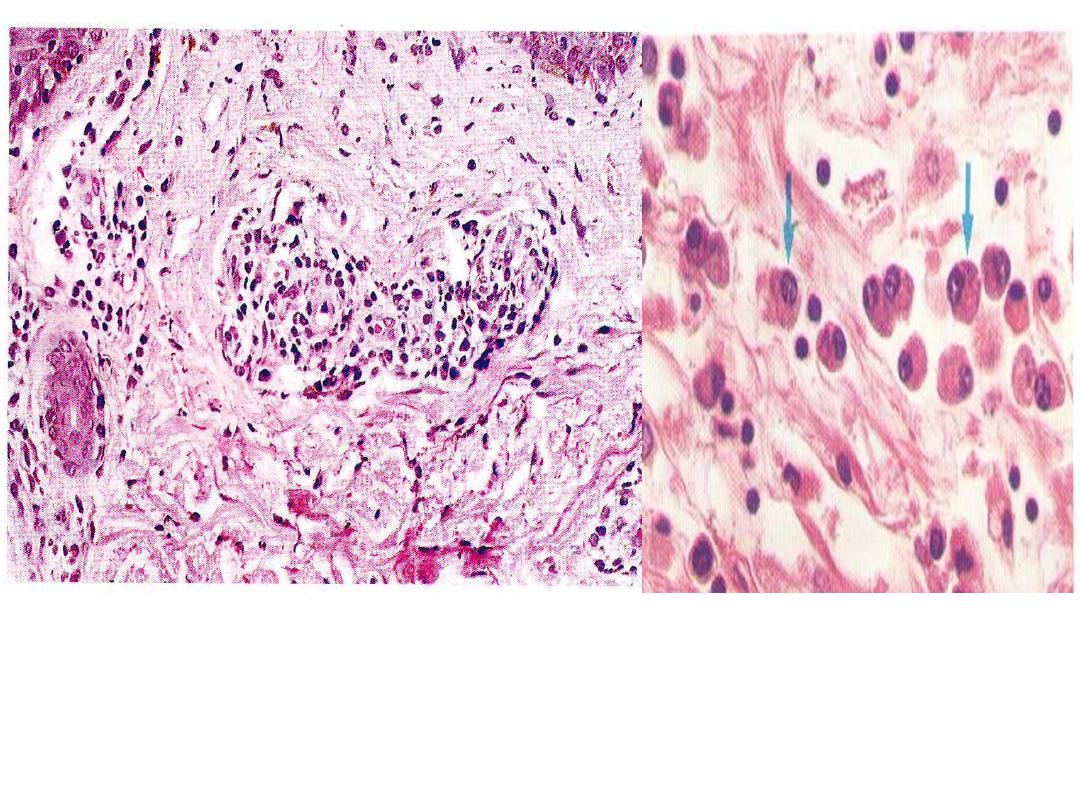
Secondary syphilis, in the dermis
with perivascular lymphoplasmacytic
infiltrate & endarteritis obliterance
.
Plasma cells infiltration in
syphilis
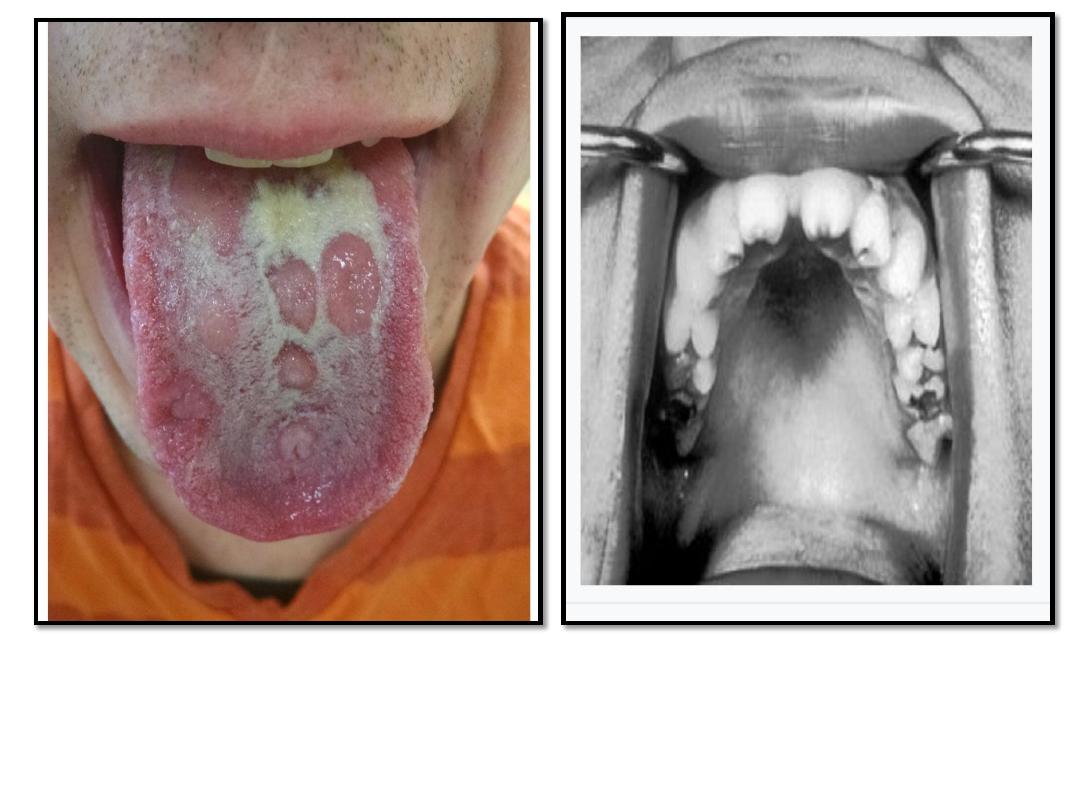
‘notched incisor Known as
Hutchinson's teeth which are
characteristic of congenital
syphilis
Multiple shallow, lingual
ulcerations in patient with
secondary syphilis
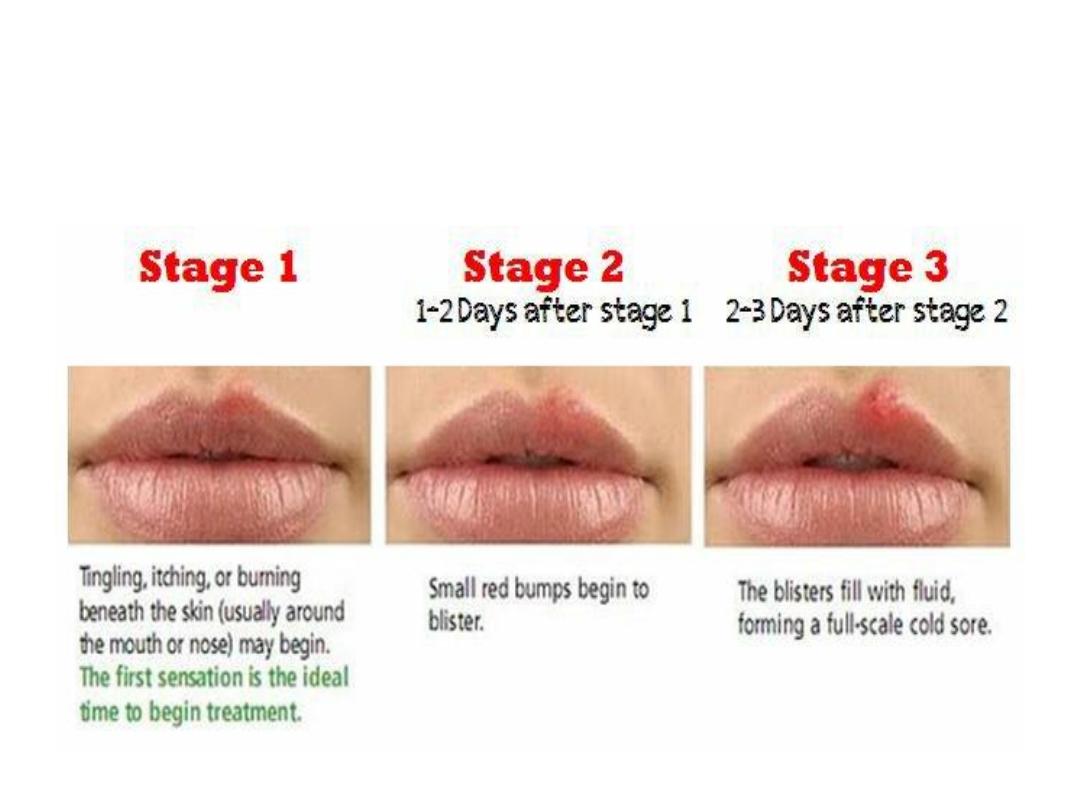
Stages of Herpes Simplex infection
(oral sore)
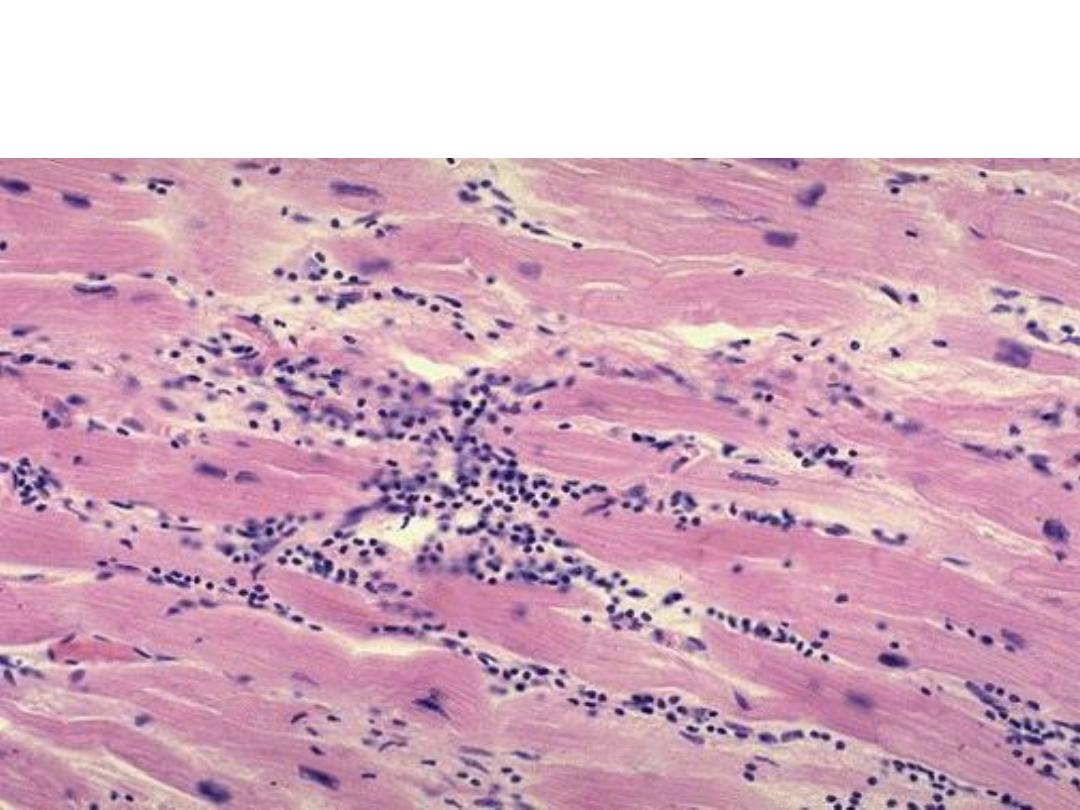
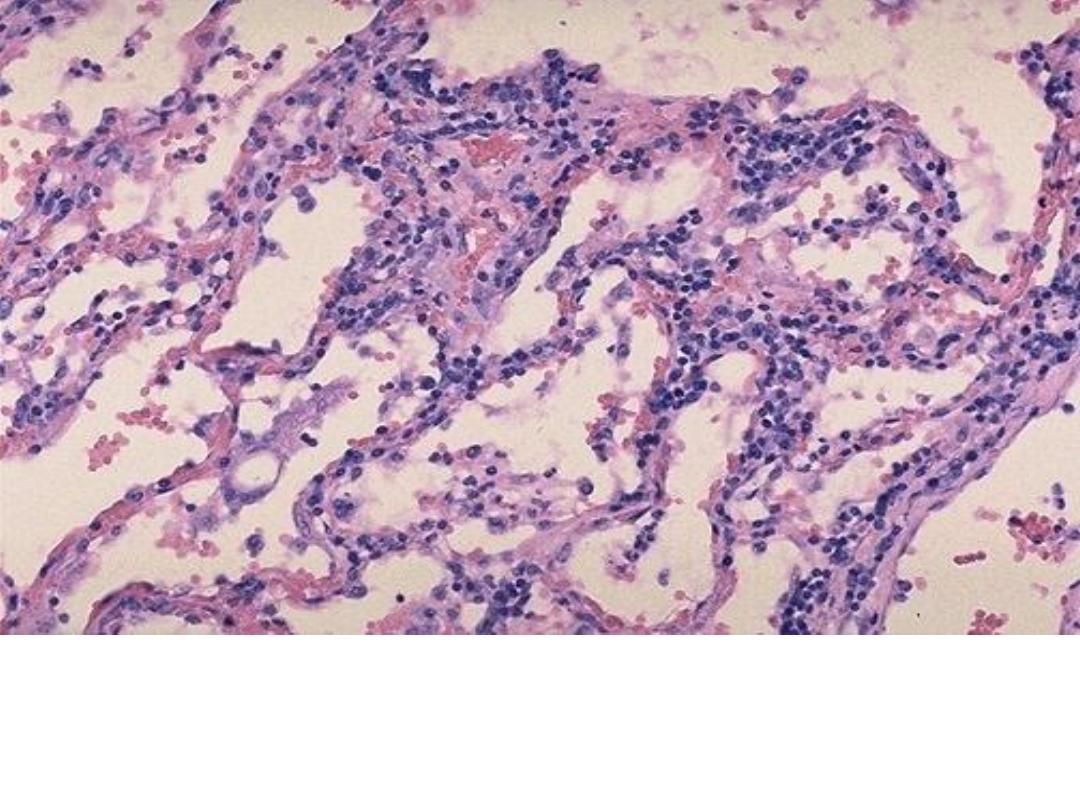
Cardiac muscle fibers show a lymphocytic infiltrate
Diagnosis: Viral myocarditis
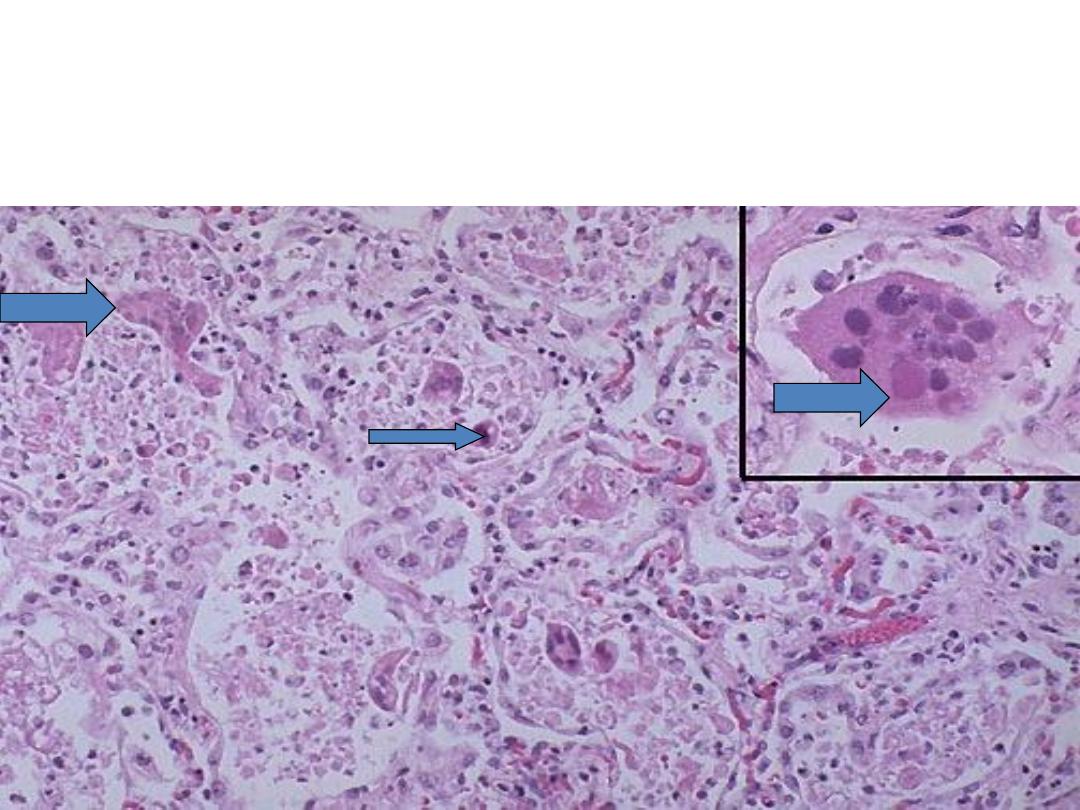
viral infection in the alveolar wall. Showing giant cell originate from
epithelial cells with inclusion body of virus within the giant cells
Diagnosis: Viral pneumonia (interstitial pneumonia)
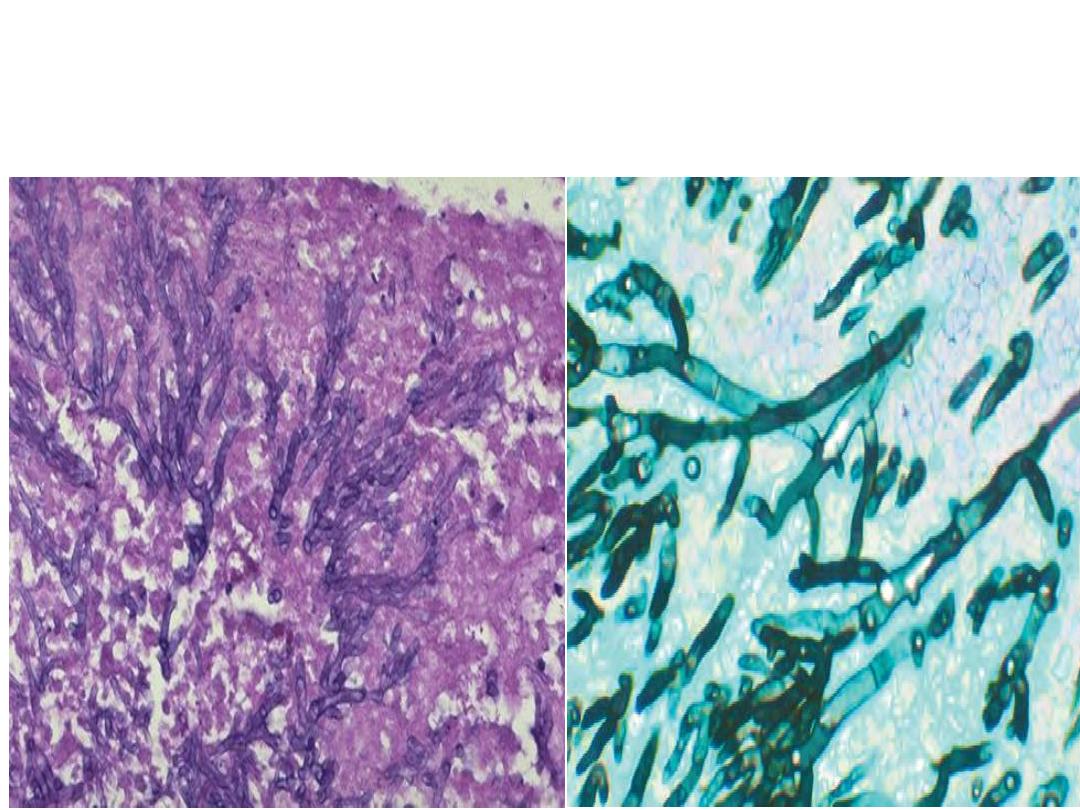
Mold ,Septate hyphae are close-packed
with acute-angle
branching.
Diagnosis Aspergillus infection, :
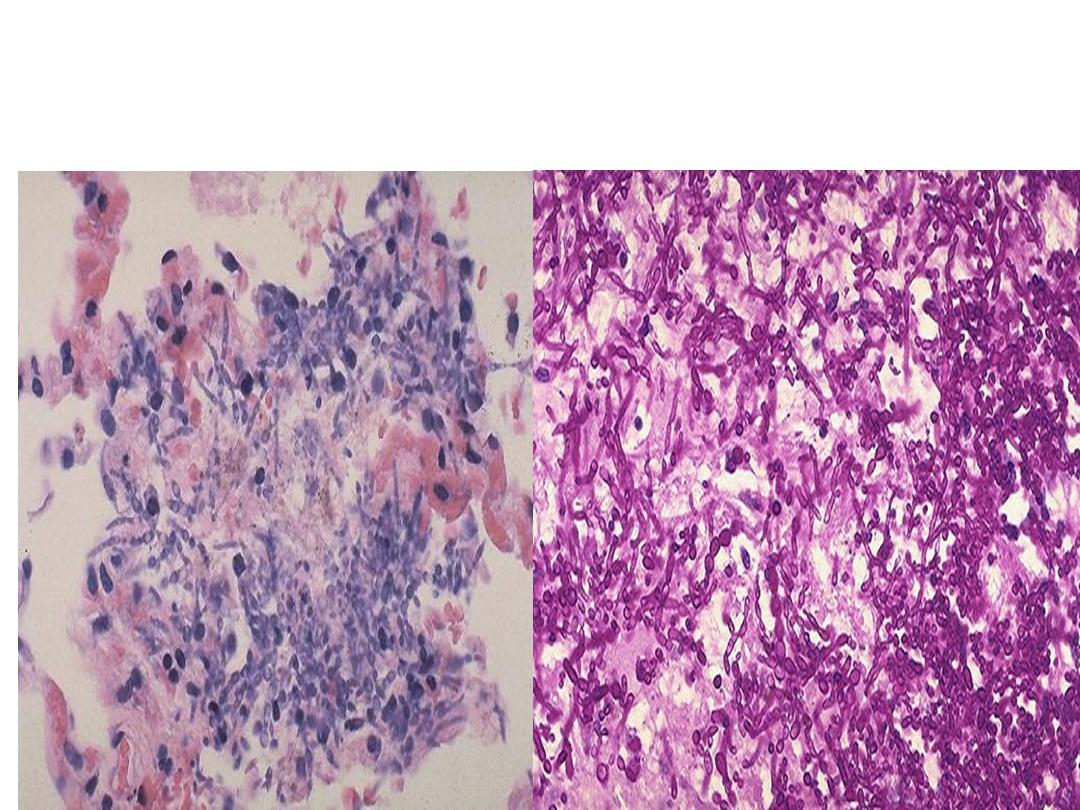
Yeast
A numerous budding cells and pseudohyphae
characteristic for Candida.
Diagnosis: Candidial infection (fungal infection)
lung
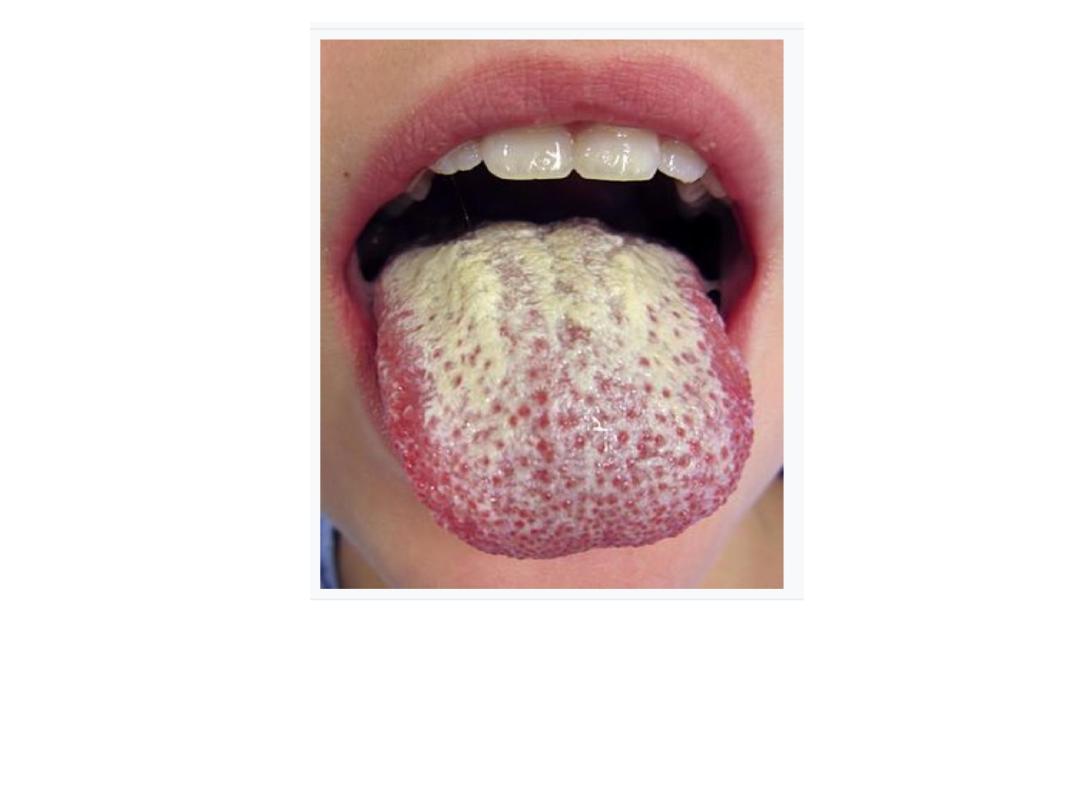
Oral candidiasis (candidal stomatitis), the fungi
creates gray-white, dirty-looking pseudomembranous
on the tongue

Practical
Neoplasia
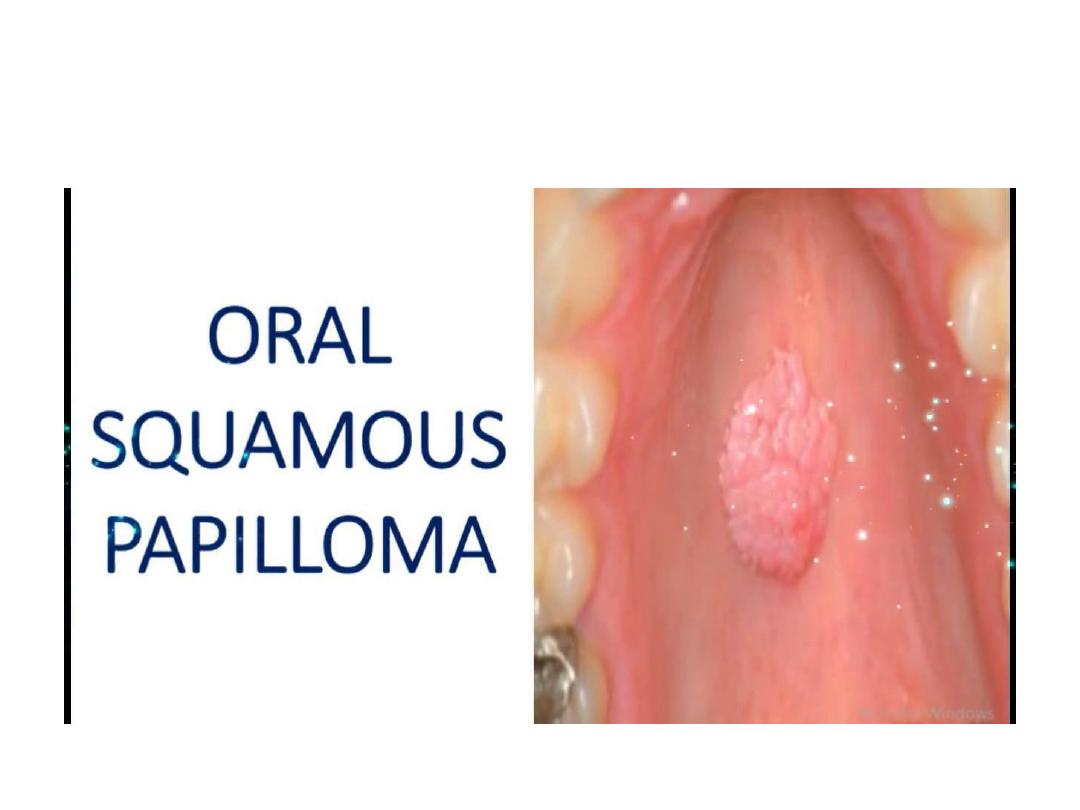
Small well circumscribed cauliflower like growth, whitish in color, occasionally
sessile.
Diagnosis: squamous papilloma
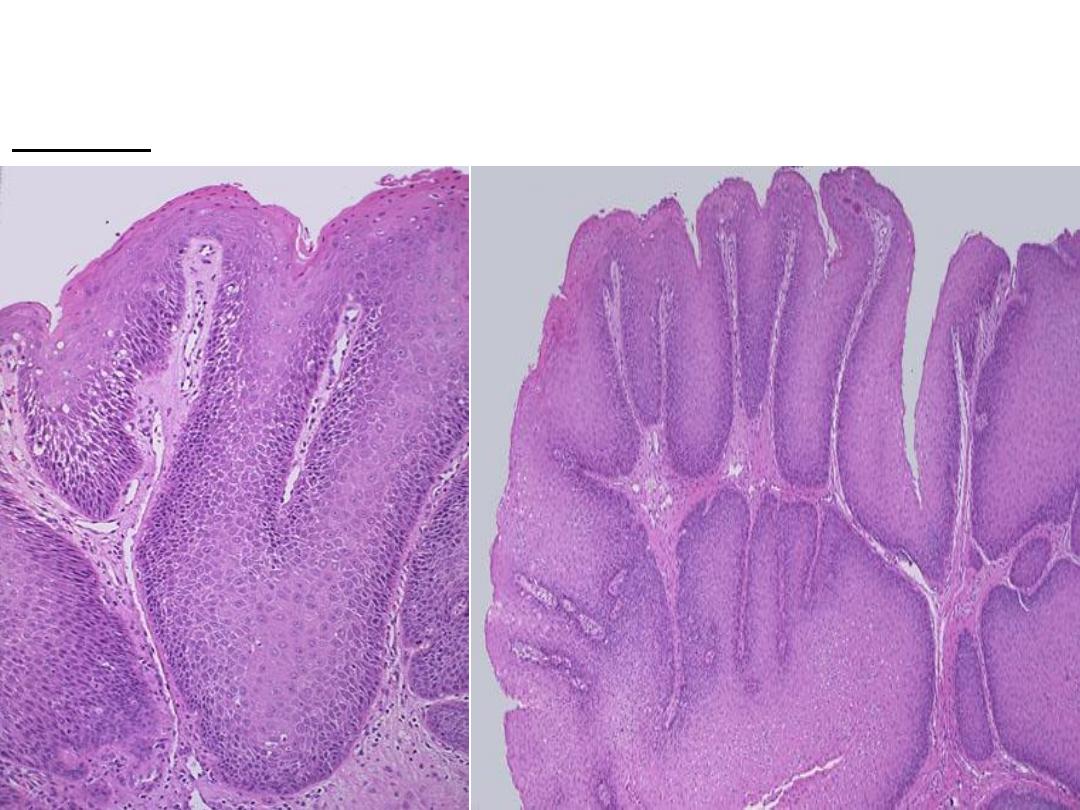
Microscopically: finger like projections, lined by several layers of benign
looking squamous cells , with central fibrovascular core
Diagnosis: squamous cell papilloma
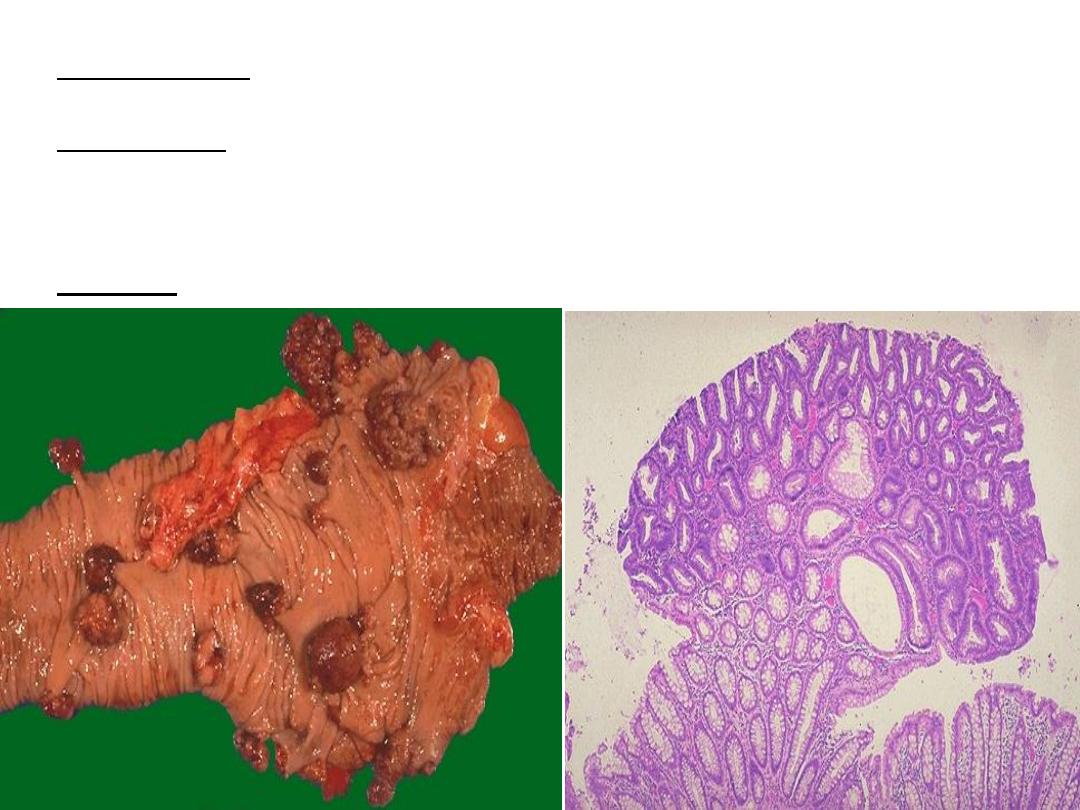
: grossly, multiple nodules of different sizes attached to colonic
Slide on the left
mucosa by stalk
microscopically, nodule composed of proliferating glandular
Slide on right:
structure some with cystic spaces (crowded, disorganized glands,
hyperchromatic and some with cystic spaces) , the polyp is connected to the
mucosa by stalk.
: adenomatous polyp
Diagnosis
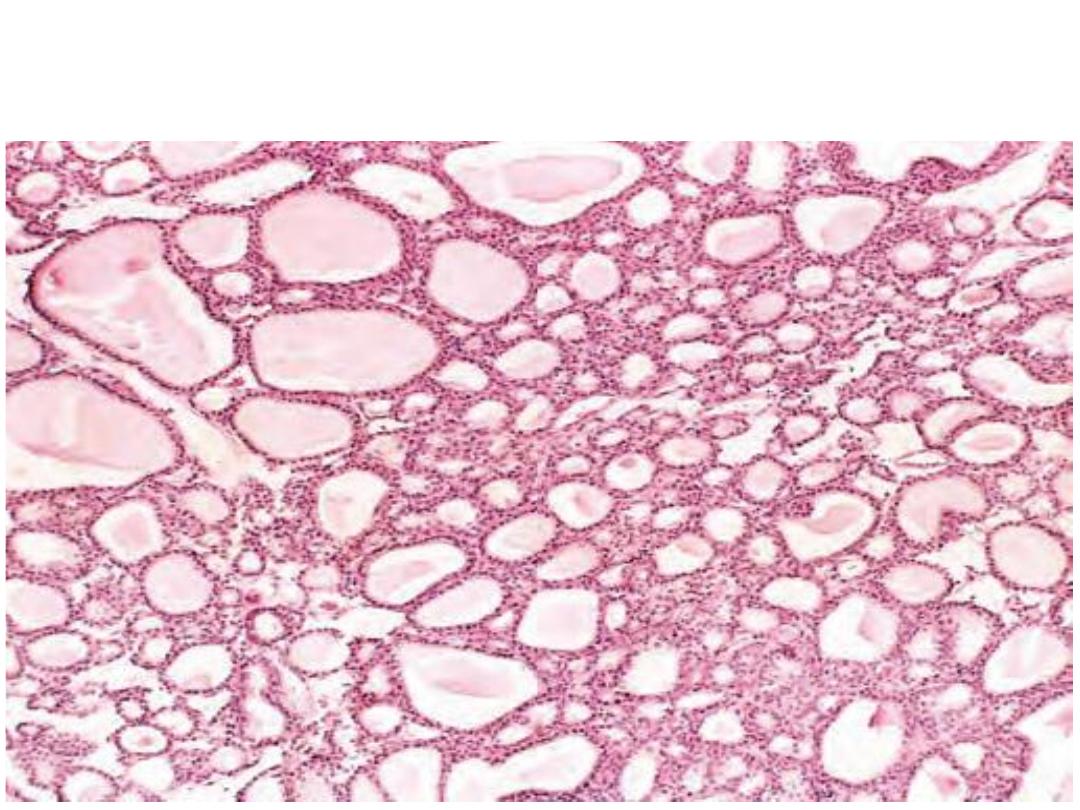
Microscopically: there is proliferation of normal-looking, colloid-filled
thyroid follicles.
Diagnosis: Thyroid adenoma.
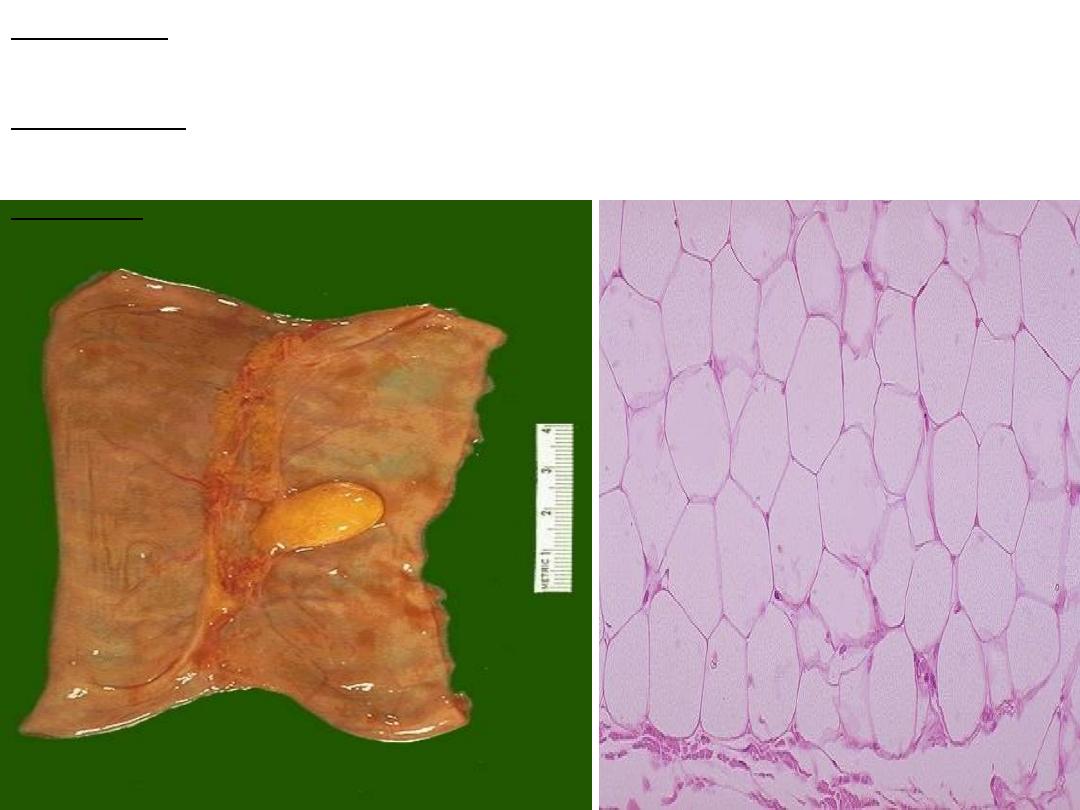
Slide on left: grossly, well circumscribed mass of homogenous yellowish color
with lobulated smooth surface on serosal surface of small intestine
Slide on right : Microscopically: proliferation of mature, benign looking fat cells
(lipocytes) and there is a capsule in the lower part of the slide.
Diagnosis: lipoma
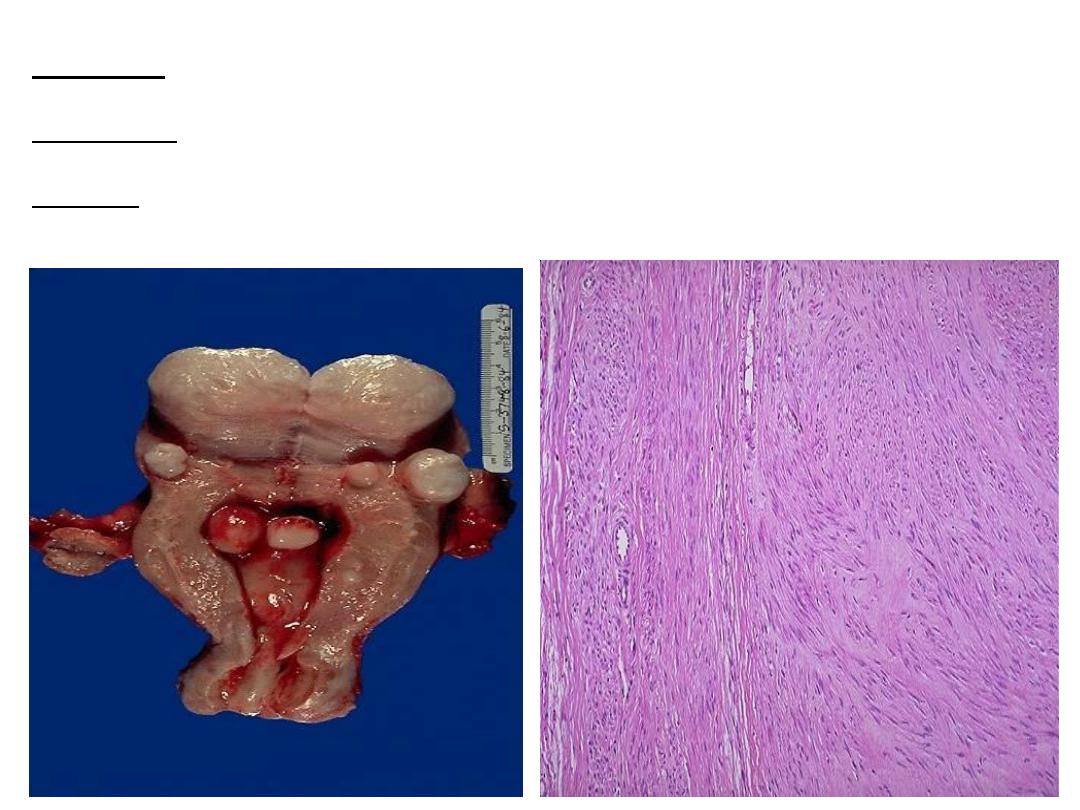
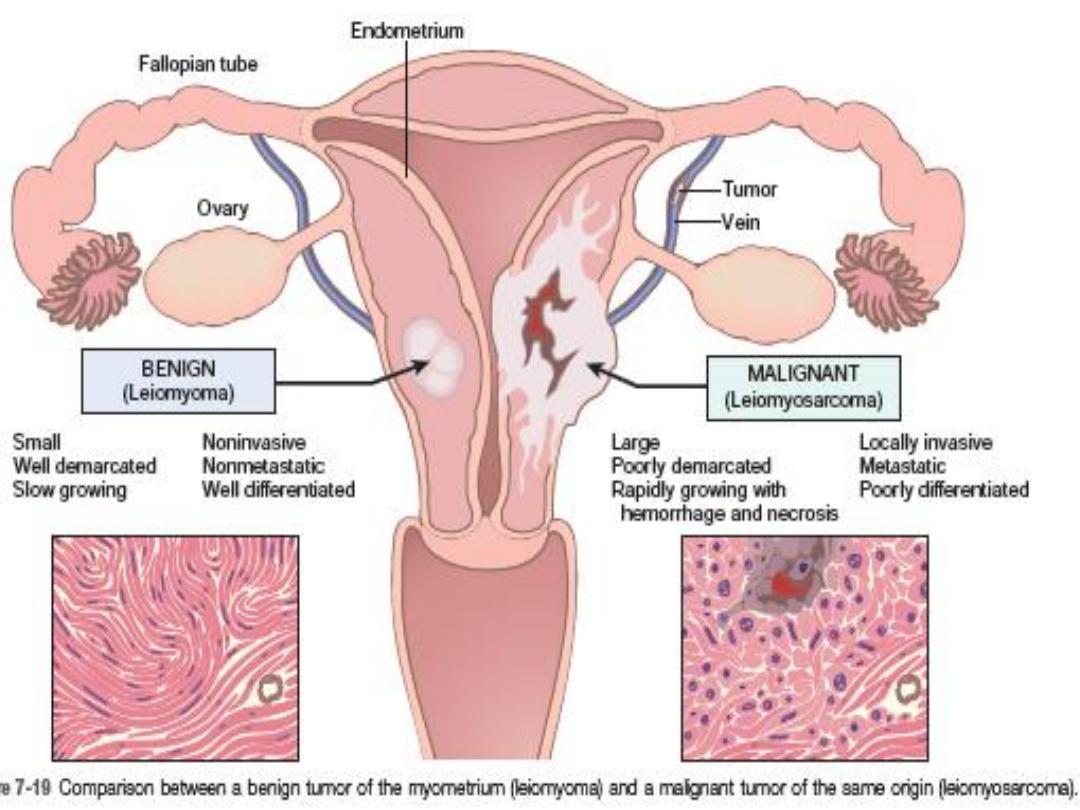
Slide on left: incised uterus showing multiple masses of different sizes rounded regular
smooth surface on the mural submucosal & subserosal surfaces of the uterus.
slide on right: microscopically, Interlacing bundles of proliferating benign looking spindle
cells (smooth muscle cells) with formation of pseudocapsule
Diagnosis : lieomyoma
of uterus
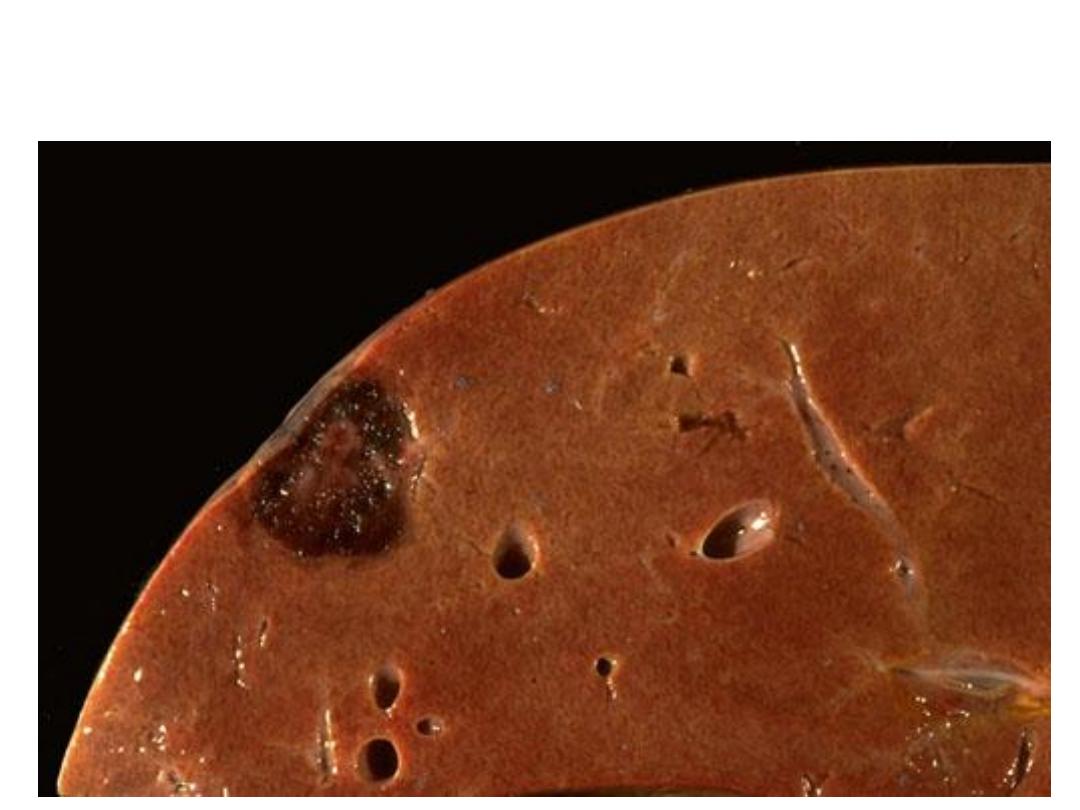
Grossly: section in the liver showing just beneath the capsule there is
a well circumscribed mass, dark red in color.
Diagnosis:Hemangioma in the liver.
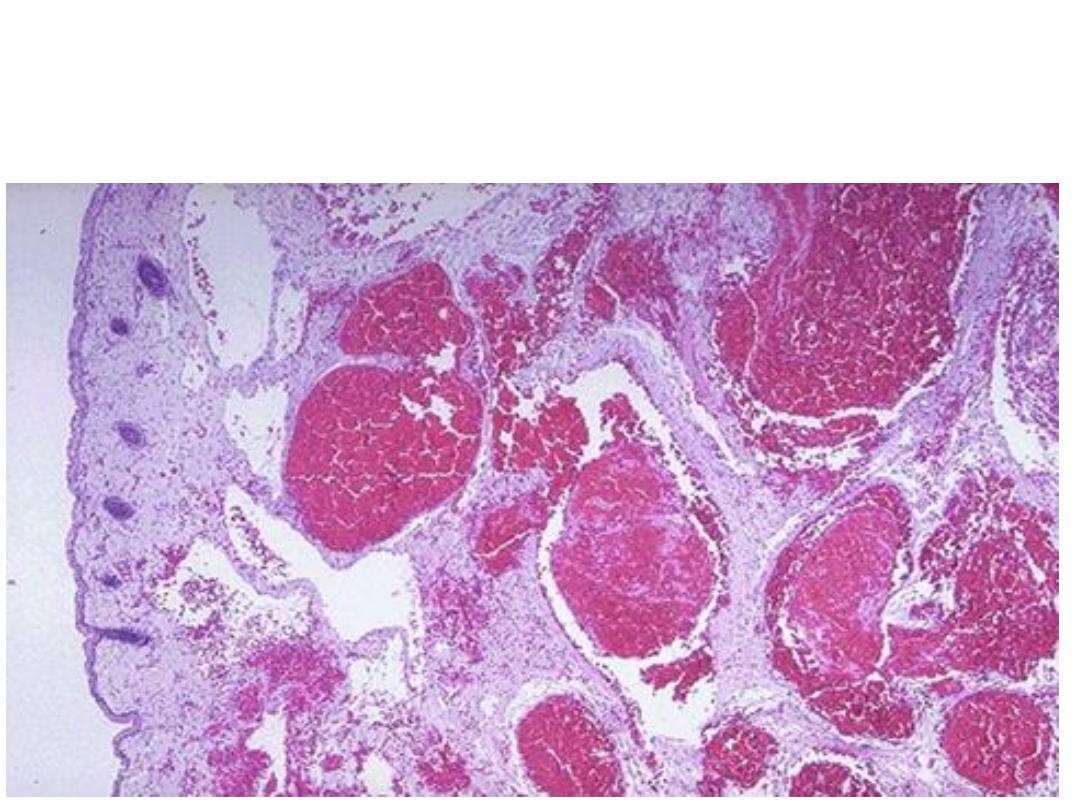
Microscopically: Multiple dilated thin walled blood vessels
filled with blood.
Diagnosis: Cavernous haemangioma
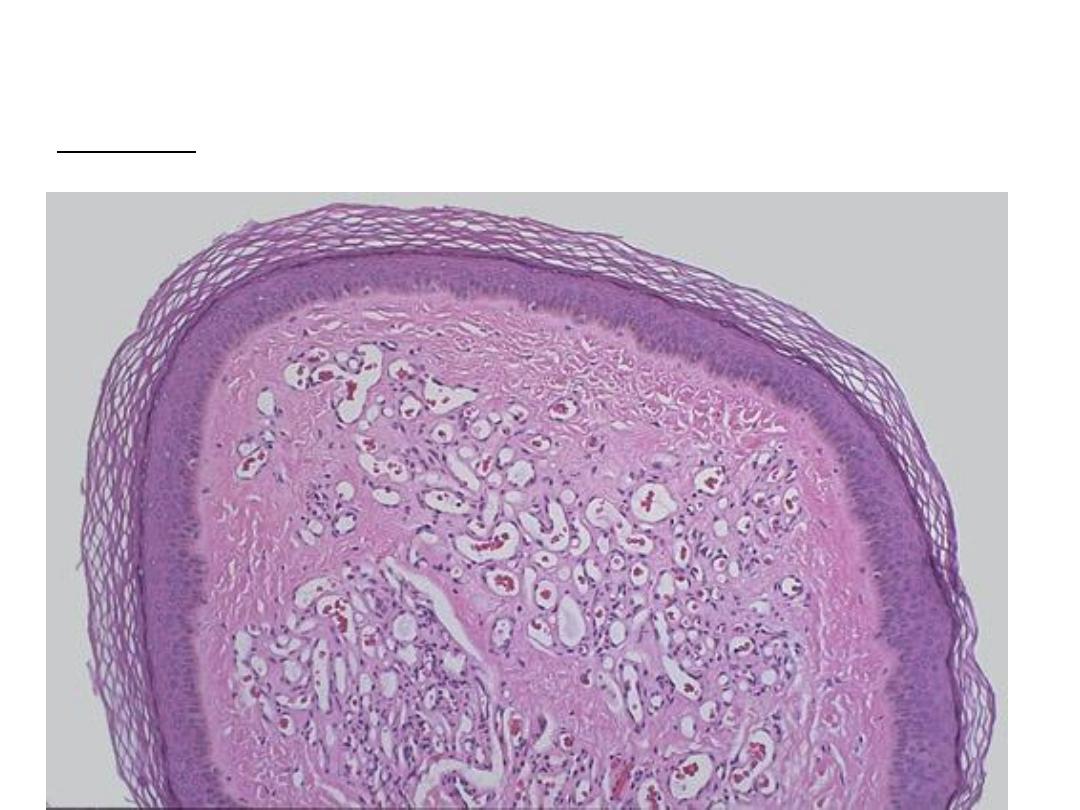
Microscopically , dermal proliferation of small blood vessels
(capillary size) lined by endothelial cells and containing RBCs.
Diagnosis : capillary hemangioma
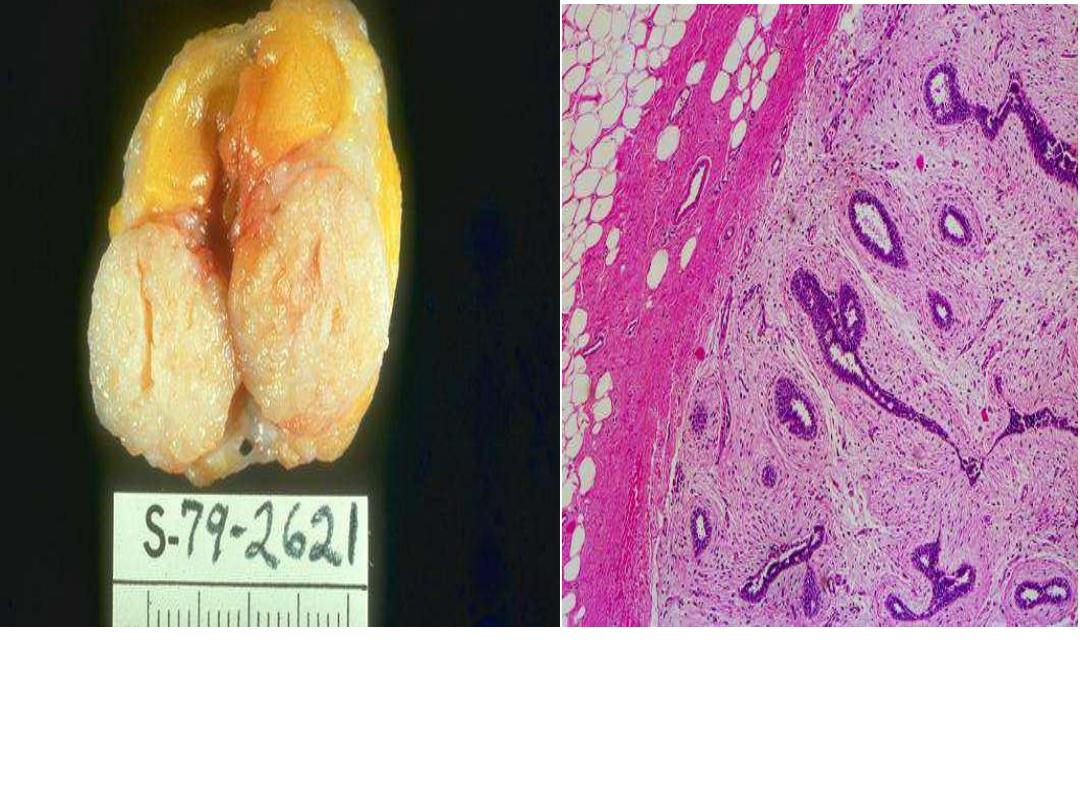
Grossly:Well-defined rounded mass surrounded by fibrotic capsule.
Microscopically consists of proliferation of
ducts
and
fibroblastic
stroma
and the mass surrounded by capsule.
Diagnosis: Fibroadenoma of breast (
mixed tumor
)
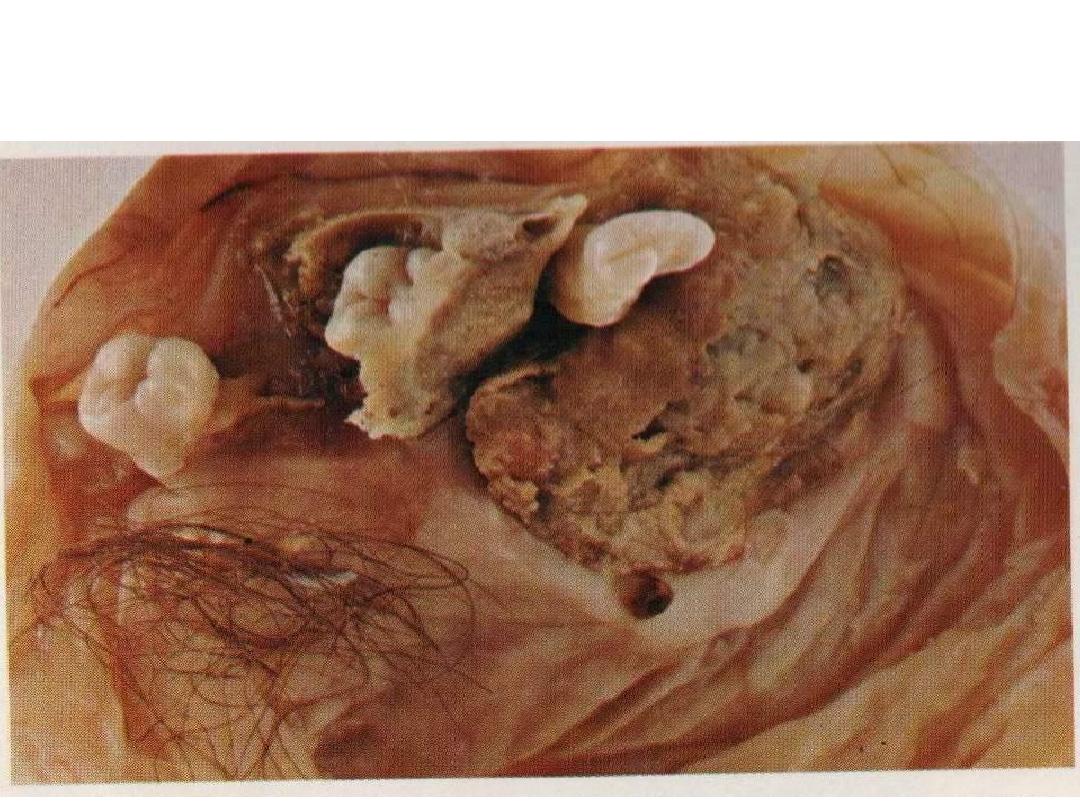
Grossly: cystic mass contains skin, hairs, teeth and
cartilage.
Diagnosis: Mature teratoma.
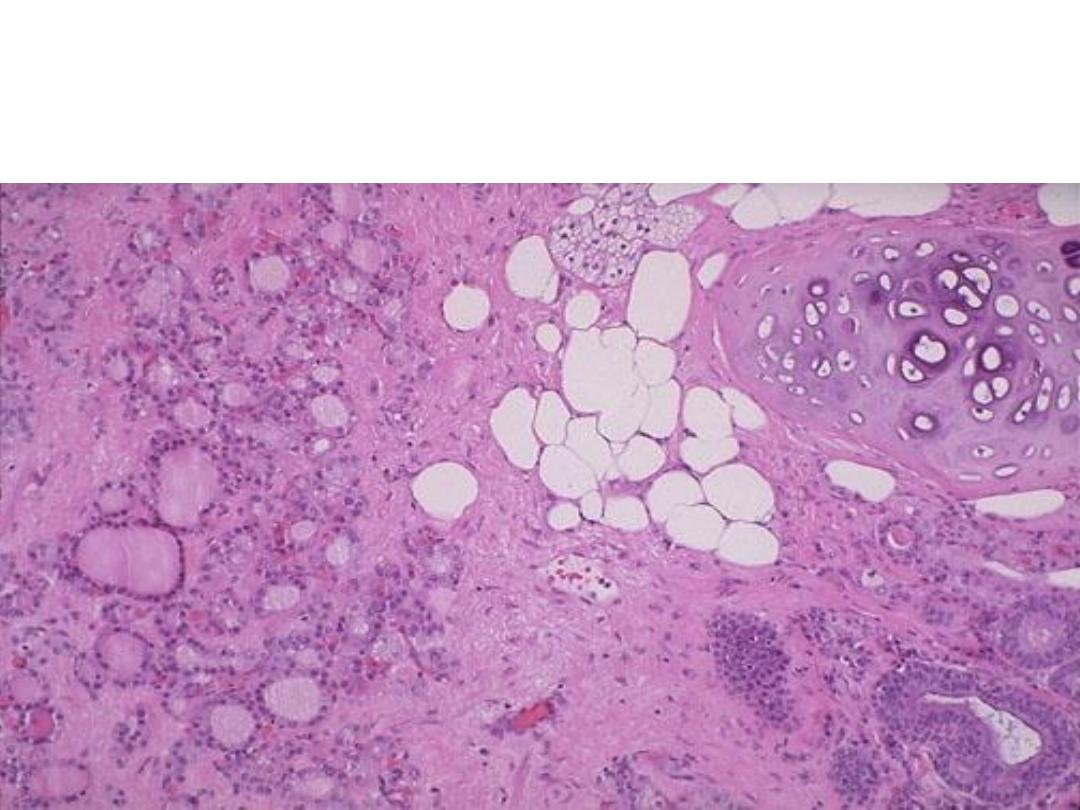
Microscopically: A mass consist of mature normal looking cartilage,
adipose tissue, intestinal glands, sebaceous glands and thyroid
tissue.
Diagnosis : mature teratoma
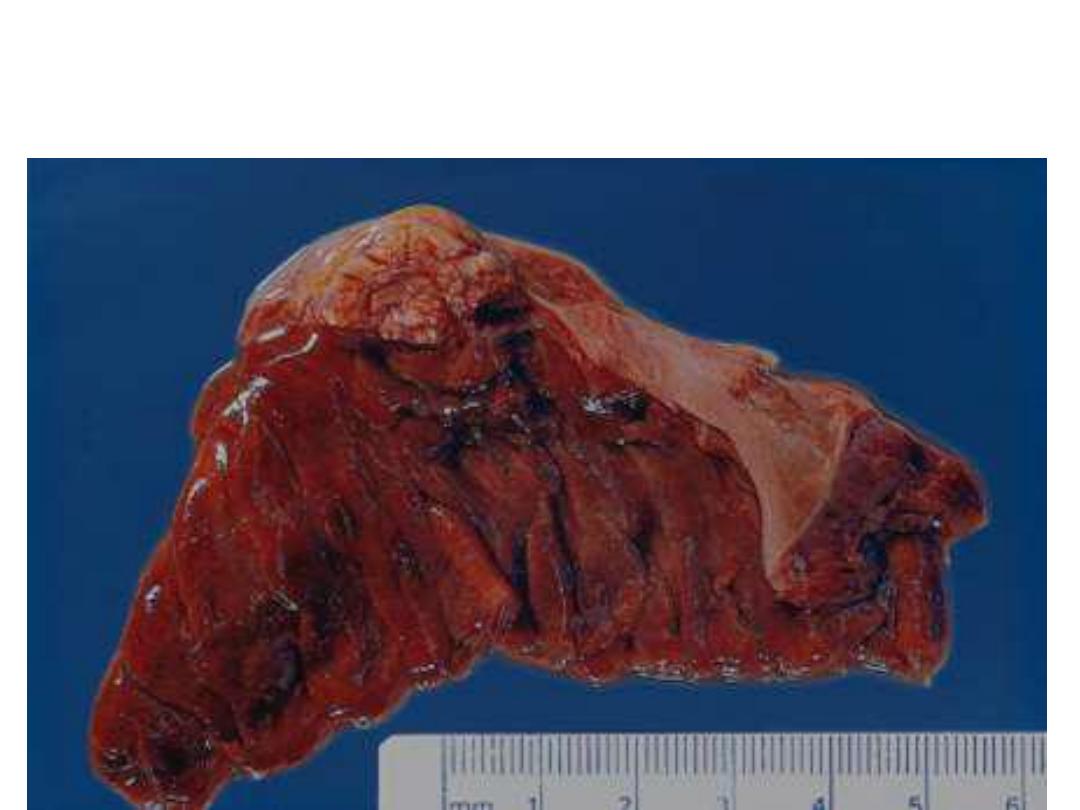
Ectopic pancreas on the wall of jejunum
Diagnosis: choristoma (presence of a normal tissue in an
unexpected location)
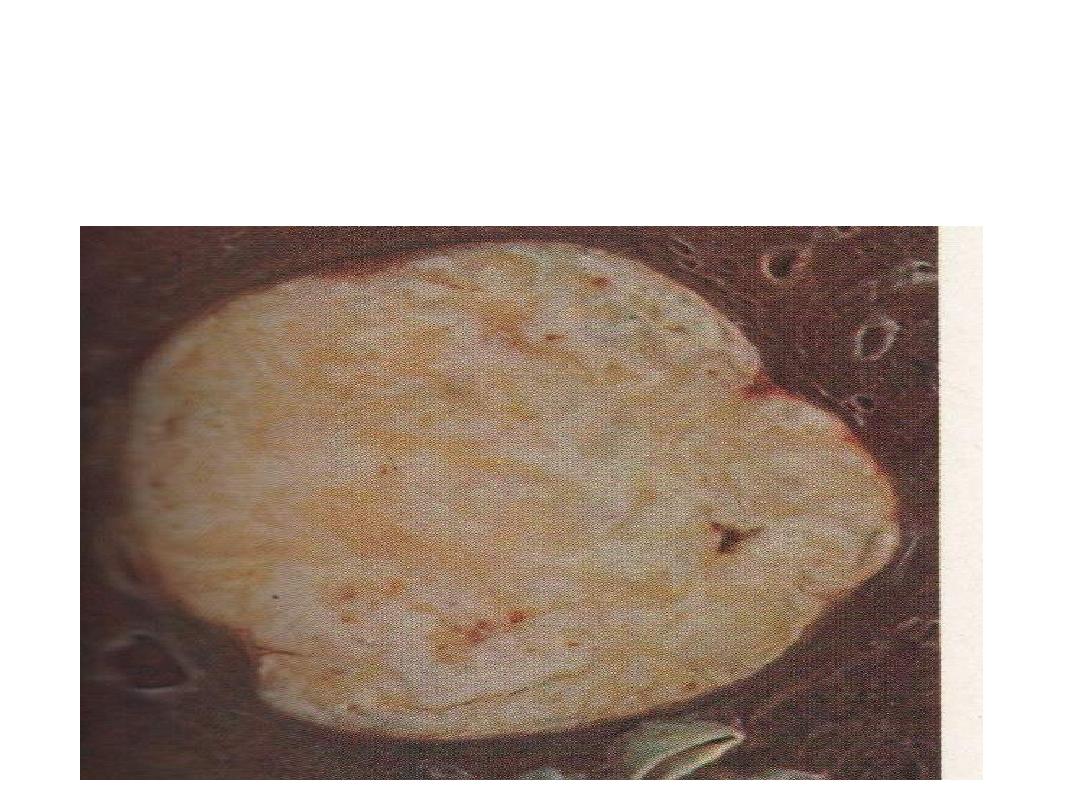

Grossly: solitary mass, whitish to yellowish in cut section and
well circumscribed. (relatively common lesion that is usually
discovered as an incidental, (rounded radio-opacity (coin lesion)
on a routine chest x-ray).
Diagnosis:
Hamartoma (lung)
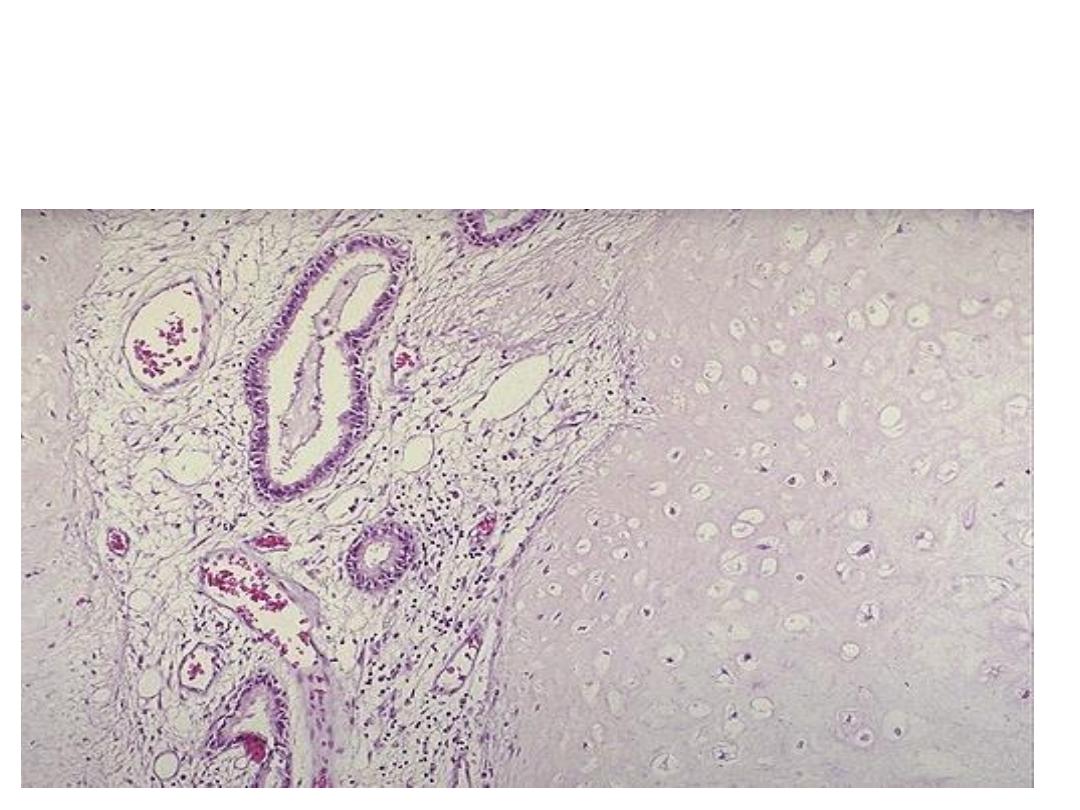
Microscopically :mass consists of benign cartilage, fibrovascular
stroma and scattered bronchial gland lined by ciliated
columnar epithelium,
all tissues are mature and normal
Diagnosis
:
Hamartoma (lung)

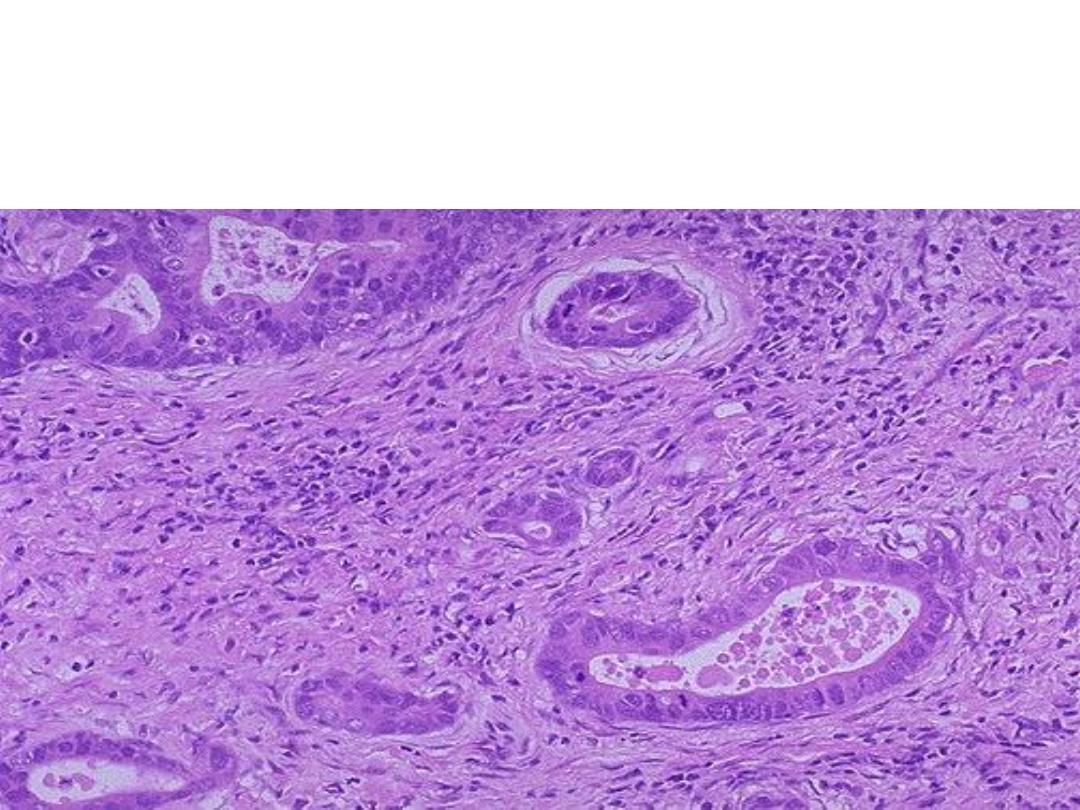
Grossly: a large exophytic growth (mass) with irregular margins
arising from the luminal surface of the colon causing partial
obstruction.
Diagnosis: adenocarcinoma of the colon,
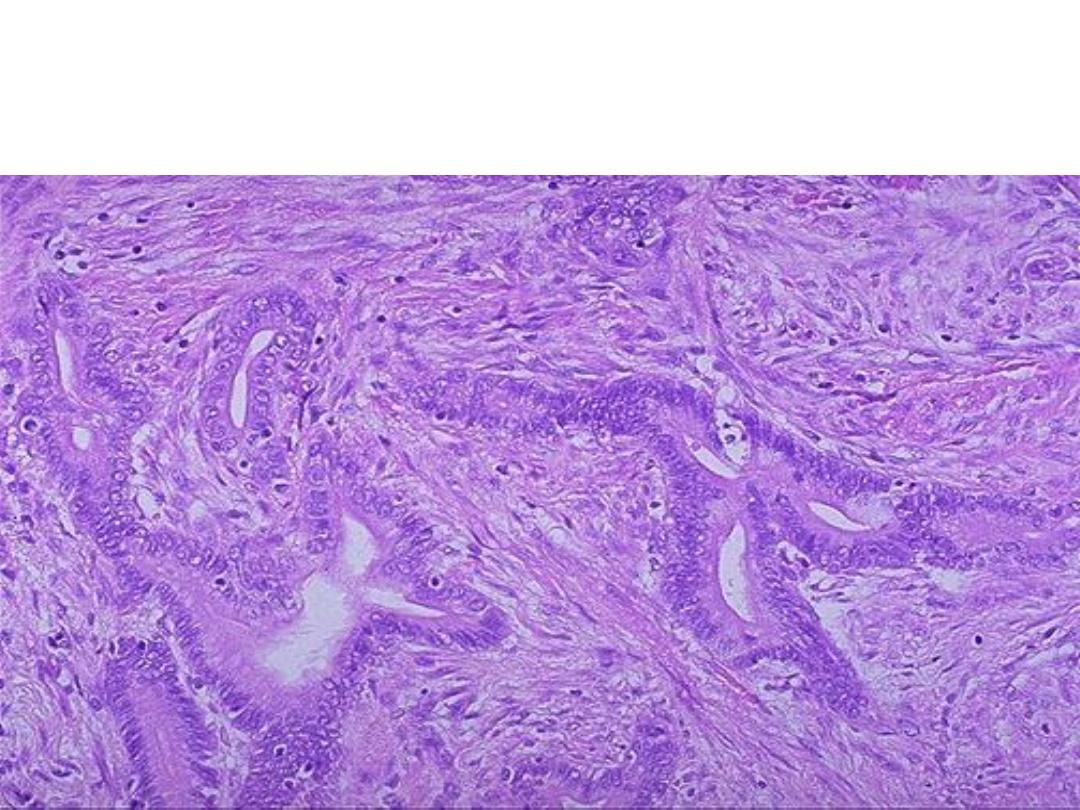
Microscopical slide shows multiple glands lined by malignant cells
(increased nuclear/cytoplasmic ratios, mitosis and hyperchromatism). There is
a desmoplastic stromal reaction to the infiltrating glands.
Diagnosis: Well differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the stomach
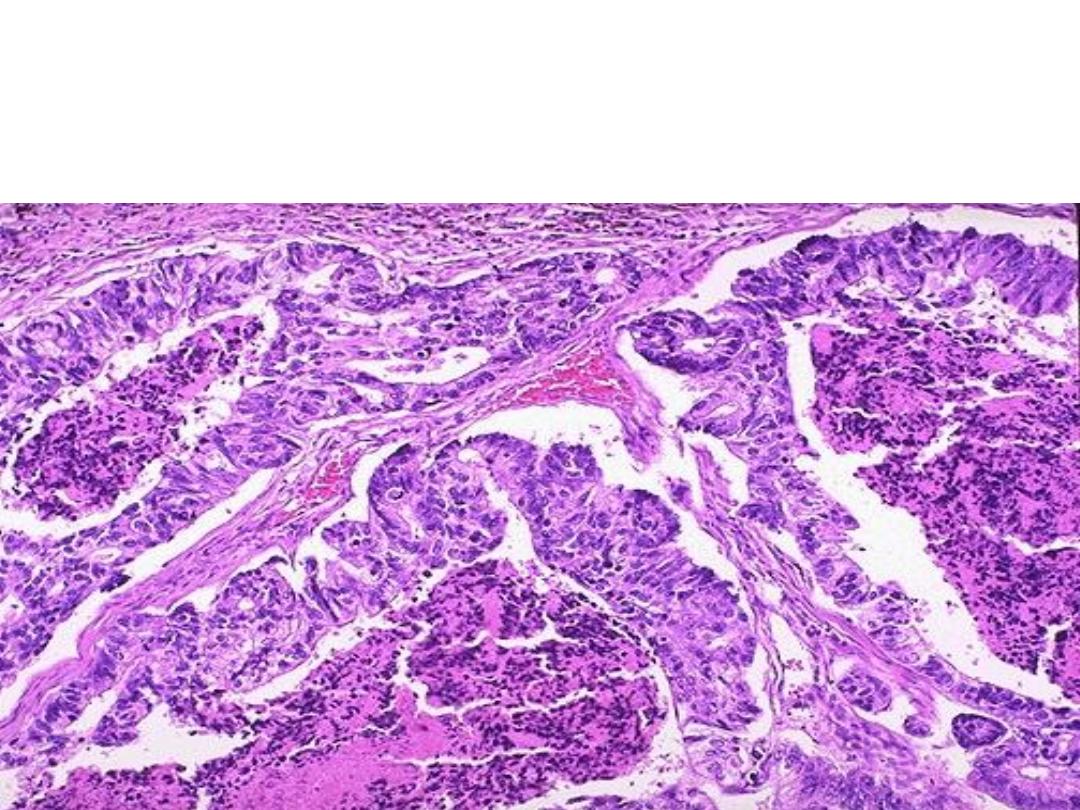
Microscopically: malignant epithelial cells (demonstrate mitosis, high
nuclear/cytoplasmic ratios & hyperchromatism) forming a gland like structure, but
the glands are irregular and branching).
Diagnosis: A moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of colon.
Multiple neoplastic like glands have crowded nuclei with
hyperchromatism and pleomorphism & filled with necrotic debris.
Diagnosis:Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the colon
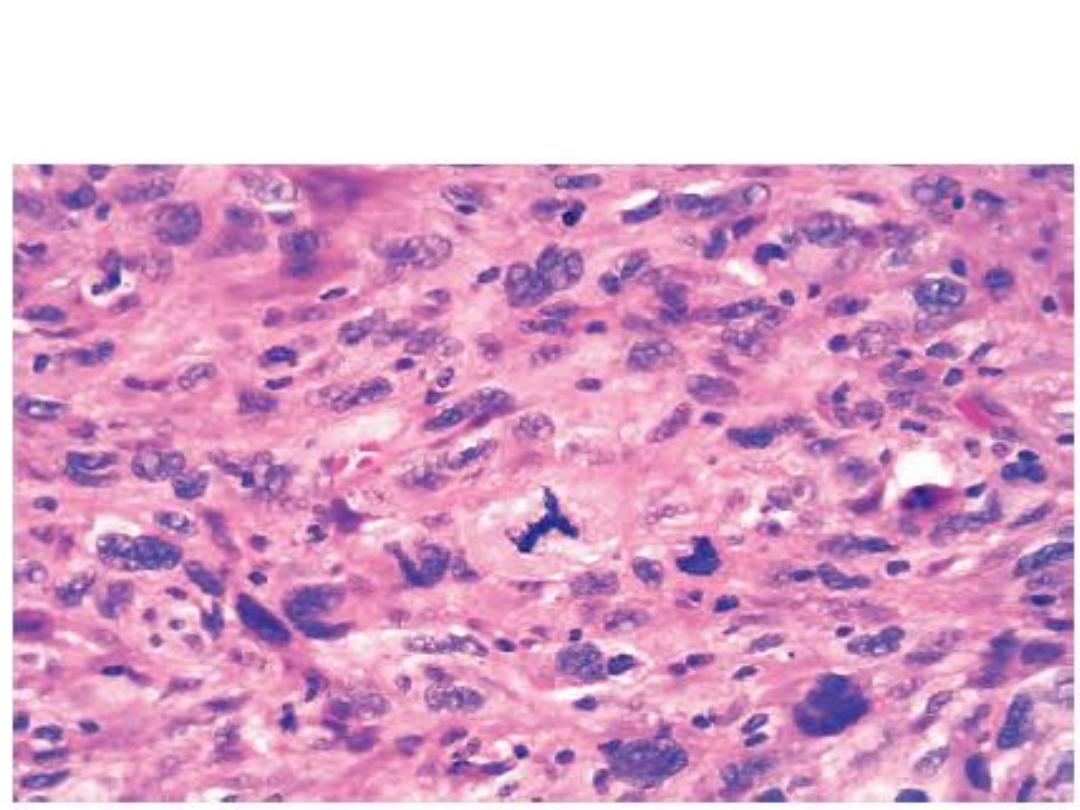
Highly cellular tumor showing hyperchromatism, cellular and nuclear
pleomorphism & the prominent cell in the center field has an abnormal
(tripolar) mitosis.
Diagnosis: Anaplastic tumor
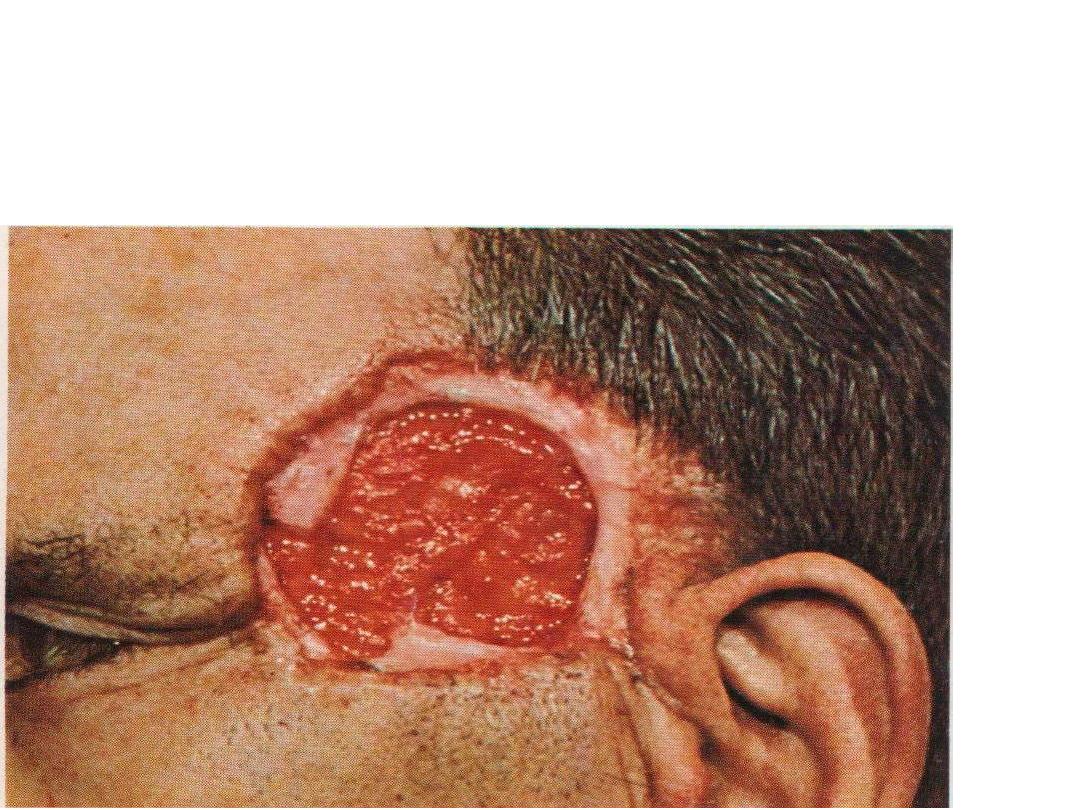
large rounded, rodent ulcer with necrotic base at the
lateral angle of left eye .
diagnosis:Basal cell carcinoma
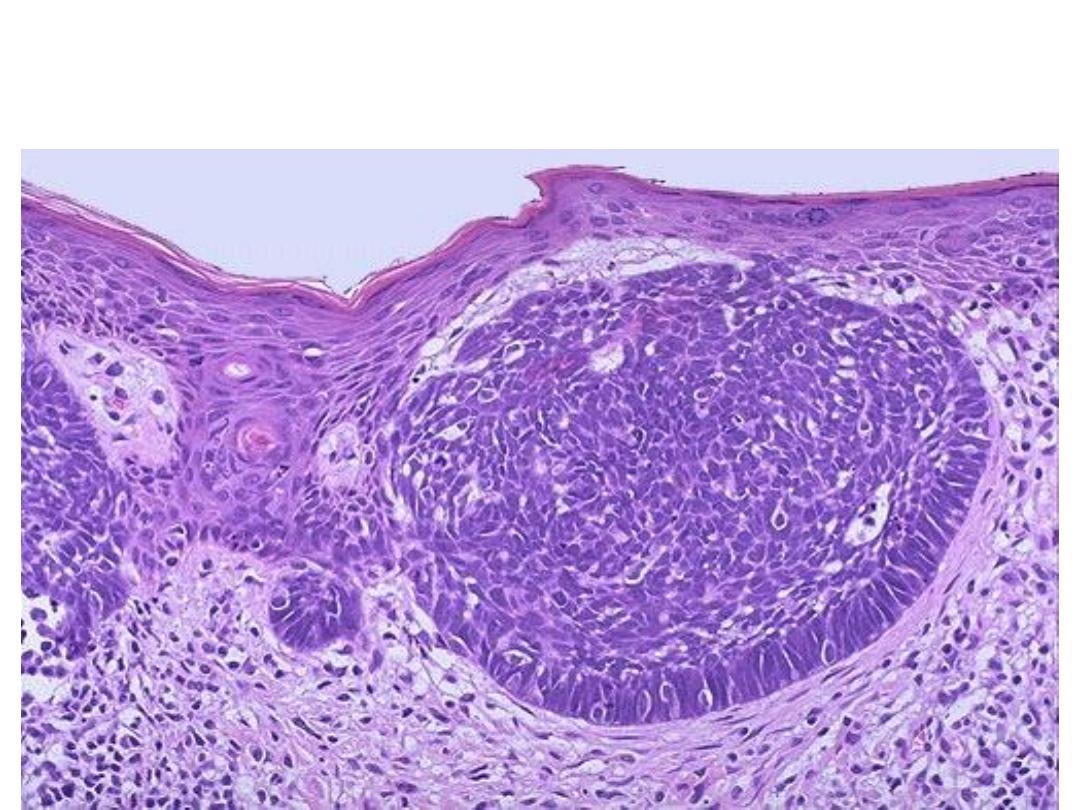
Microscopically, dermal islands of small ,rounded to oval dark basophilic
(hyperchromatic) cells with scant cytoplasm resemble basal keratinocytes ,the cells
at the periphery are elongated and arranged in palisading pattern.
.Diagnosis : basal cell carcinoma
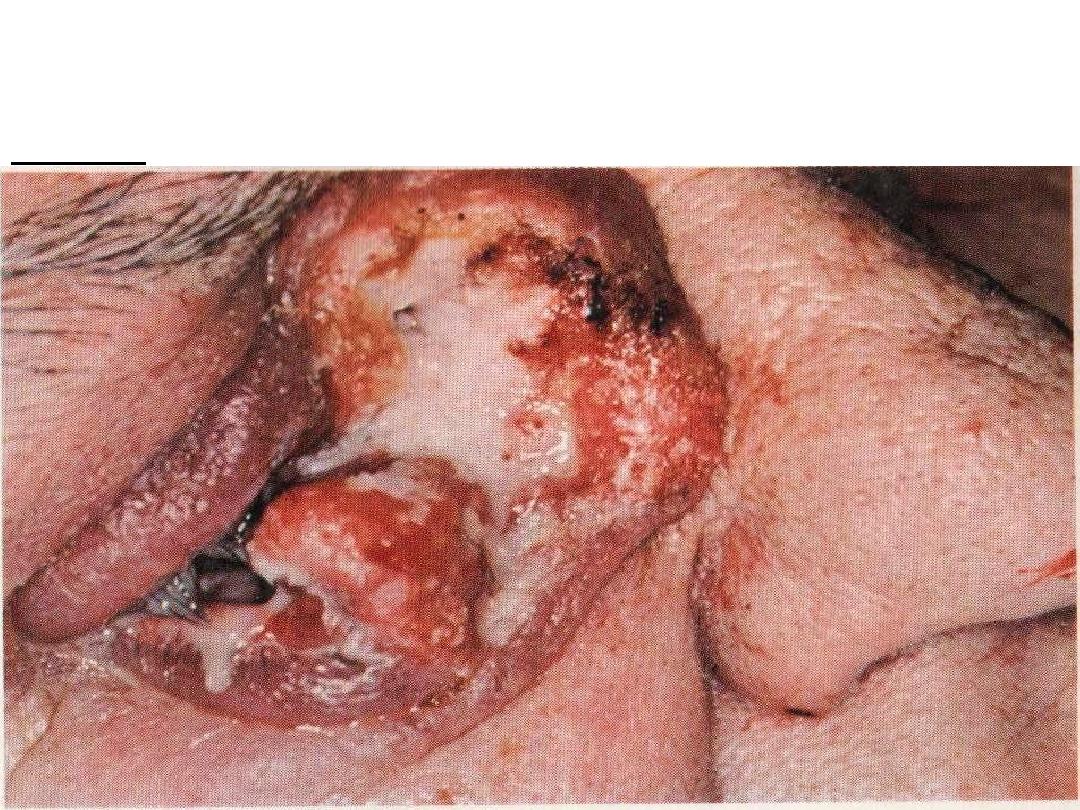
There is ulcer in the inner angle of right eye near the nose destructed
the eye , this ulcer is large irregular margins with area of hemorrhage &
necrosis
diagnosis: squamous cell carcinoma
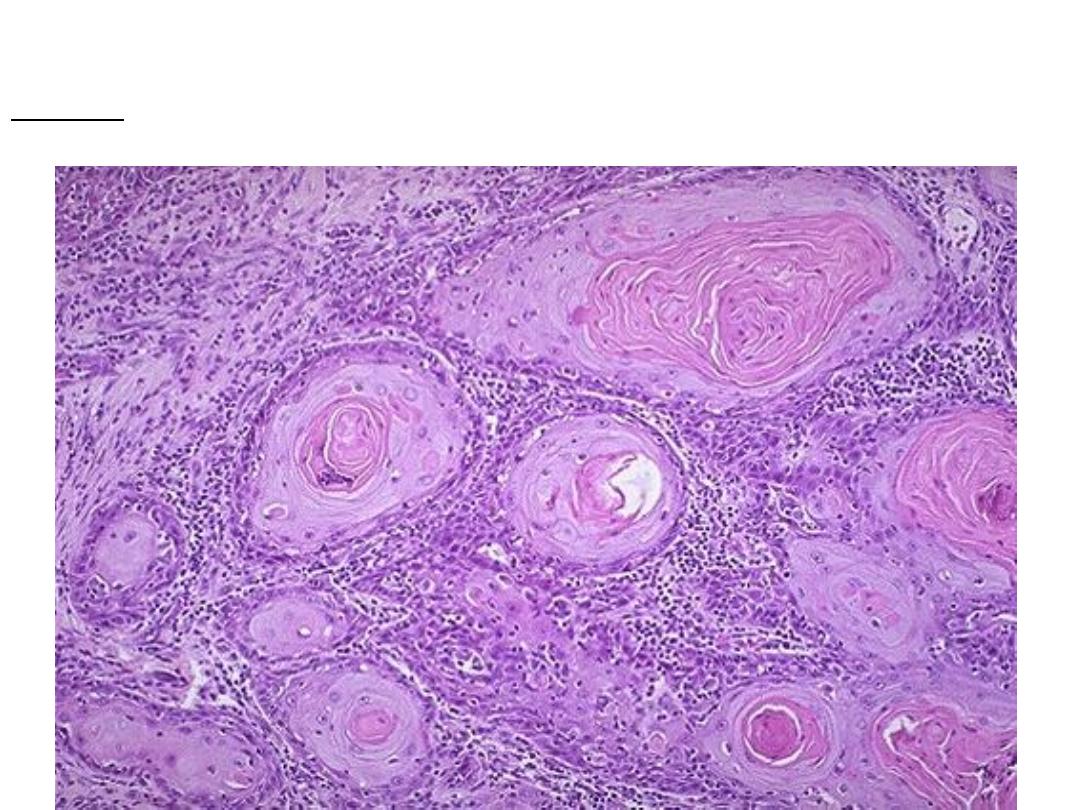
Microscopically: multiple cell nests with keratin pearls , the cell nest composed of
malignant squamous cells ( pleomorphic, hyperchromatic nuclei & high N/C ratio)
diagnosis: well differentiated squamous cell carcinoma
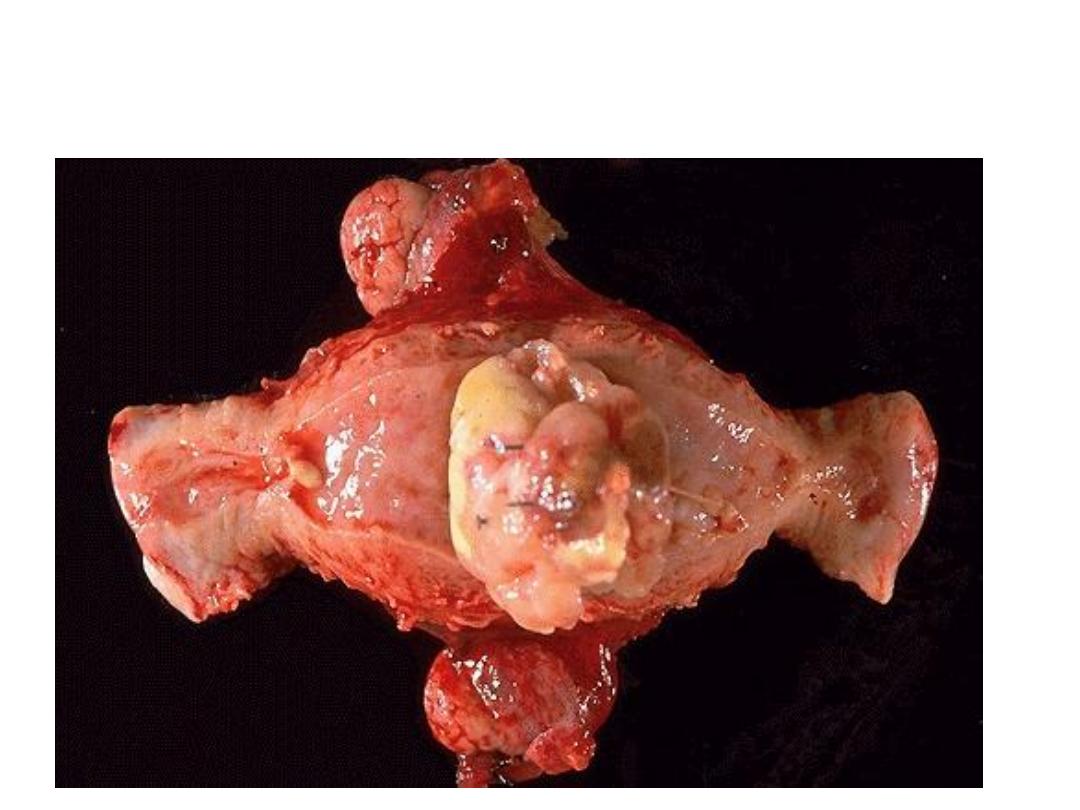
Grossly: There is large irregular mass arise from the fundus of the
uterus with area of hemorrhage & necrosis.
diagnosis:Leiomyosarcoma
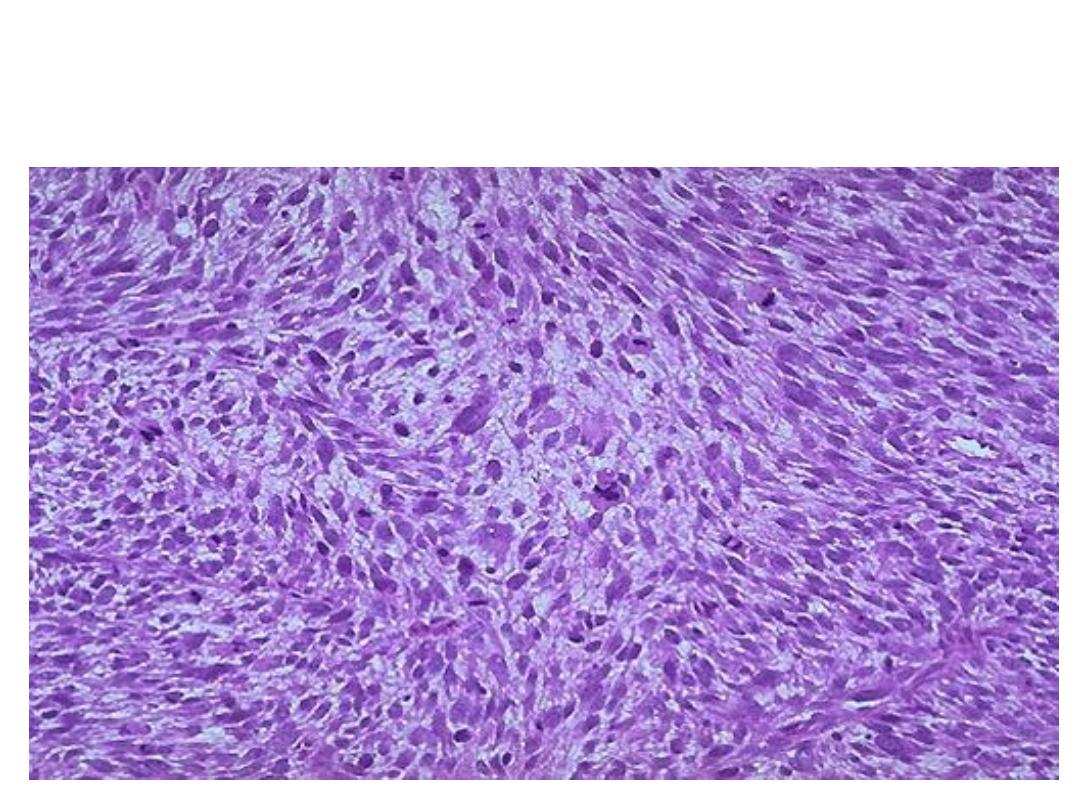
Highly cellular tumor showing proliferation spindle cells(smooth muscle
cells), the cells are showing pleomorphism,hyperchromatic nuclei, high
mitotic figure with abnormal mitosis).
diagnosis:Leiomyosarcoma
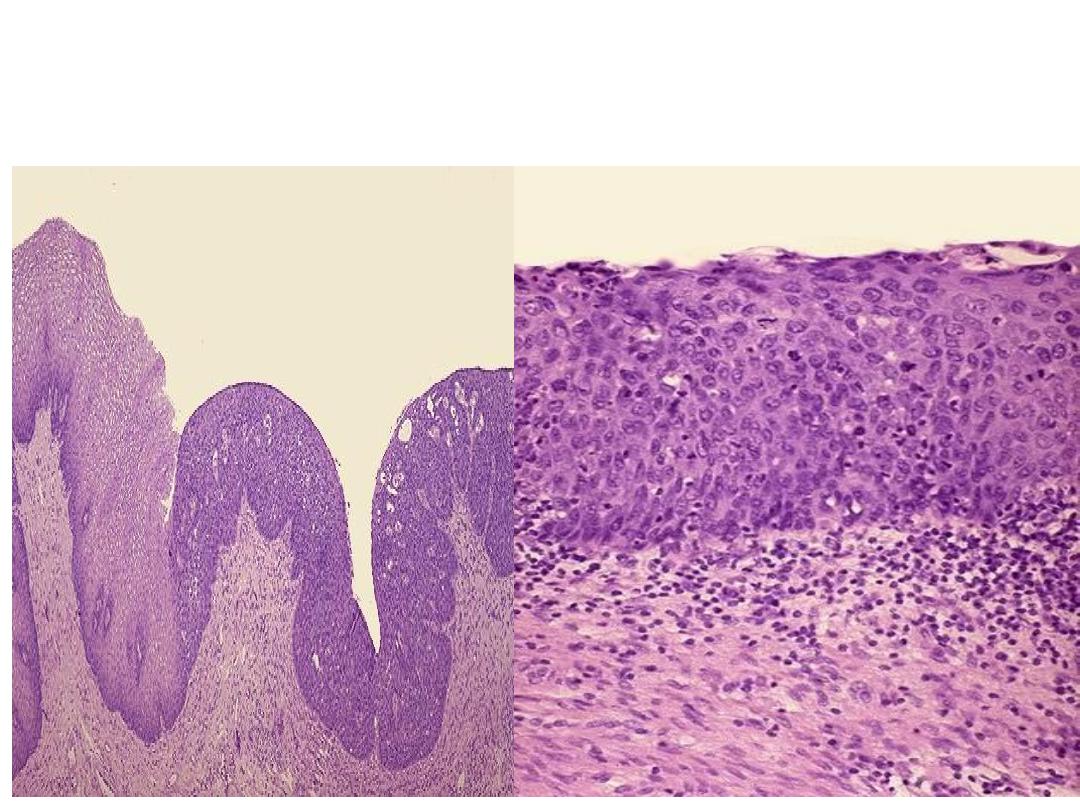
Microscopically: slide of cervix shows part of stratified squamous epithelium
with disorderly arranged cells, hyperchromatic nuclei and mitosis but still
within the basement membrane
Diagnosis: Carcinoma In situ of cervix.
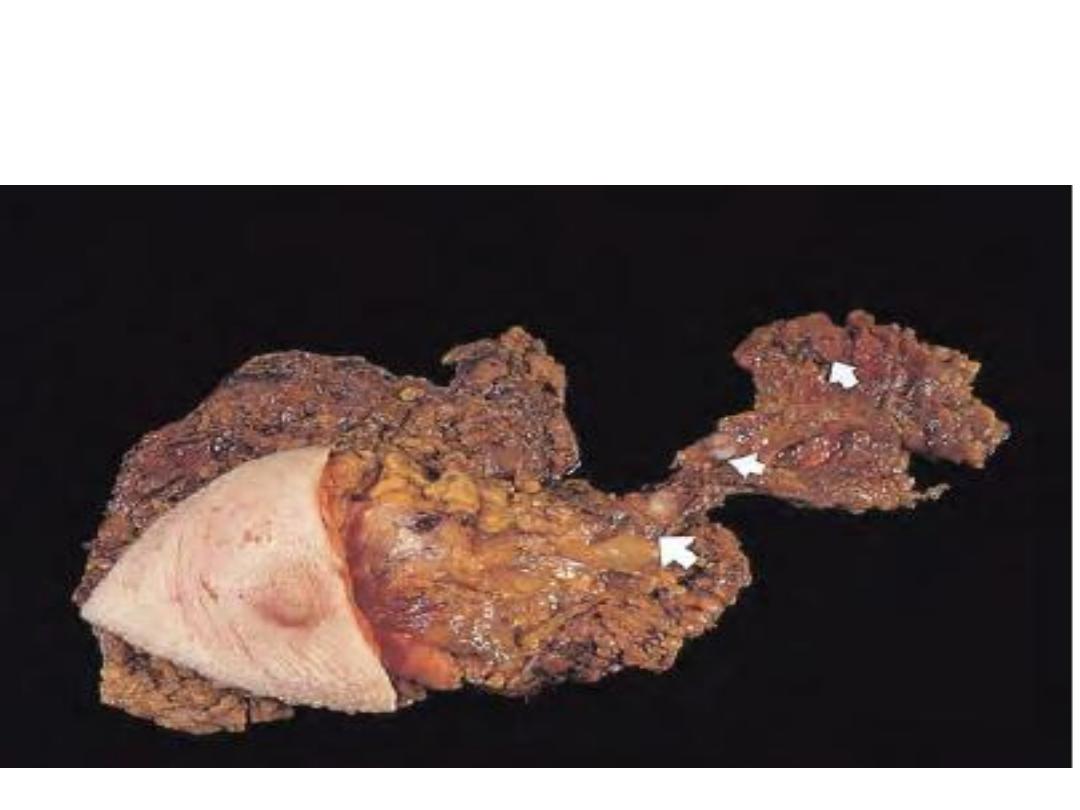
Large ill-defined mass lies just lateral to the nipple with the
regional lymph nodes enlargement. The largest arrow indicates the
first node in the chain (sentinel node).
Diagnosis: Breast carcinoma with lymph node involvement
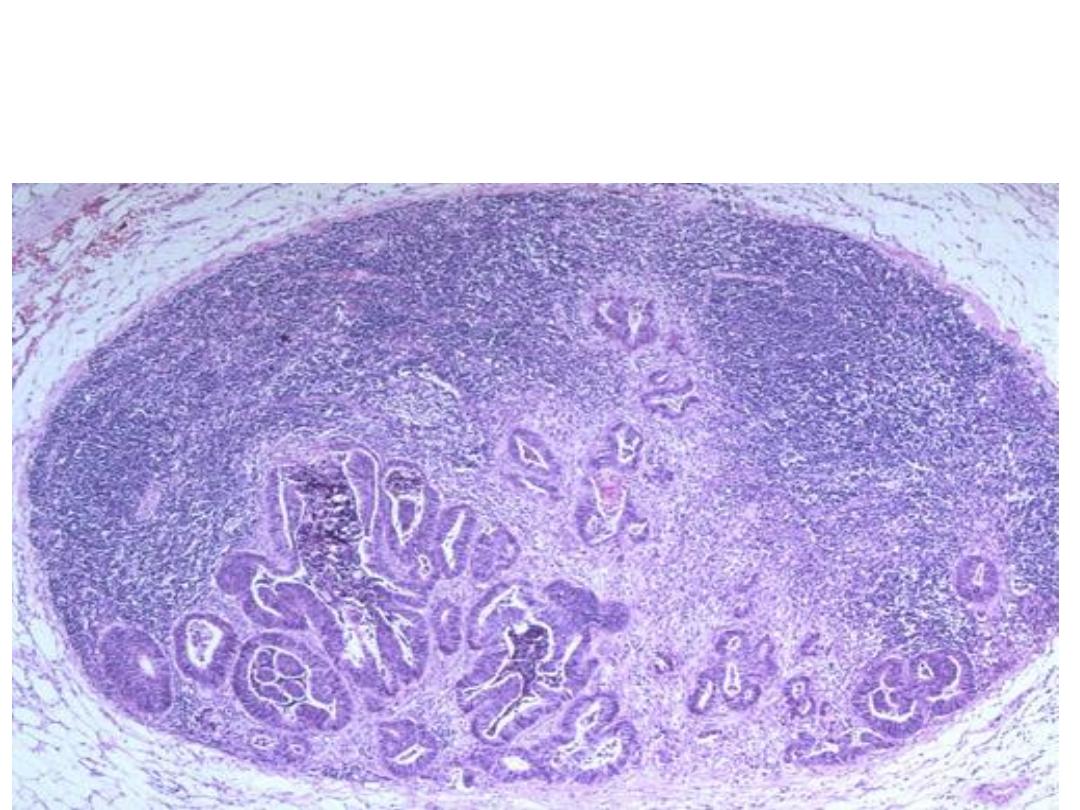
Multiple irregular gland like structure lined by malignant cells
infiltrating the lymph node.
Diagnosis: Metastatic adenocarcinoma in a lymph node. (lymphatic
spread)
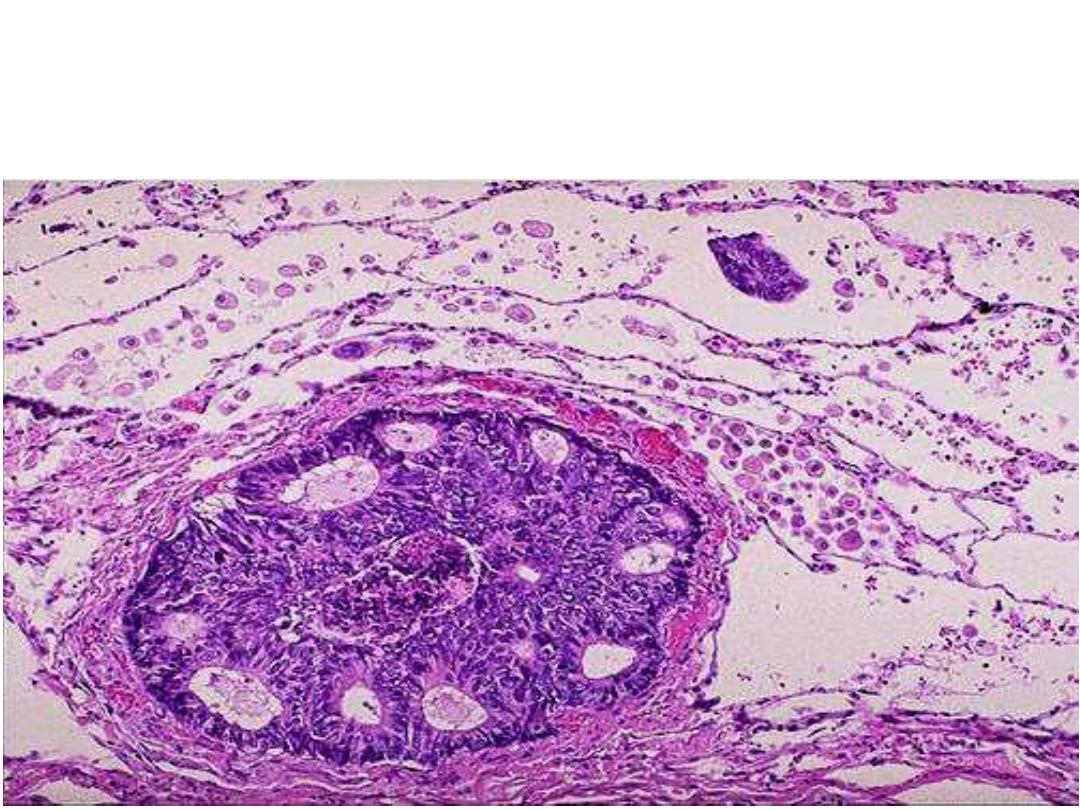
Lung tissue showing a large vessel containing malignant cells which forming a
glands like structure.
Diagnosis: Metastatic adenocarcinoma to the lung (Heamatogenous spread to the
lung )
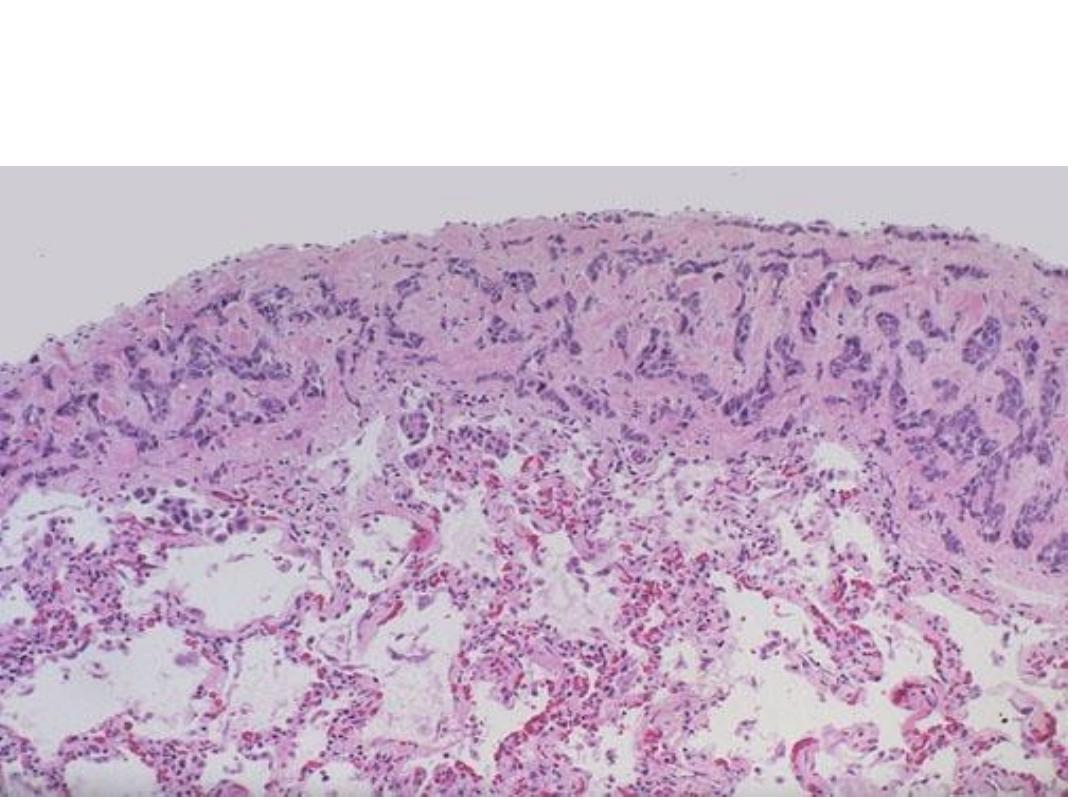
Microscopically: Sheets & cords of malignant cells over the pleural
surface of the lung
Diagnosis: pleural spread of breast carcinoma(transcoelomic spread)
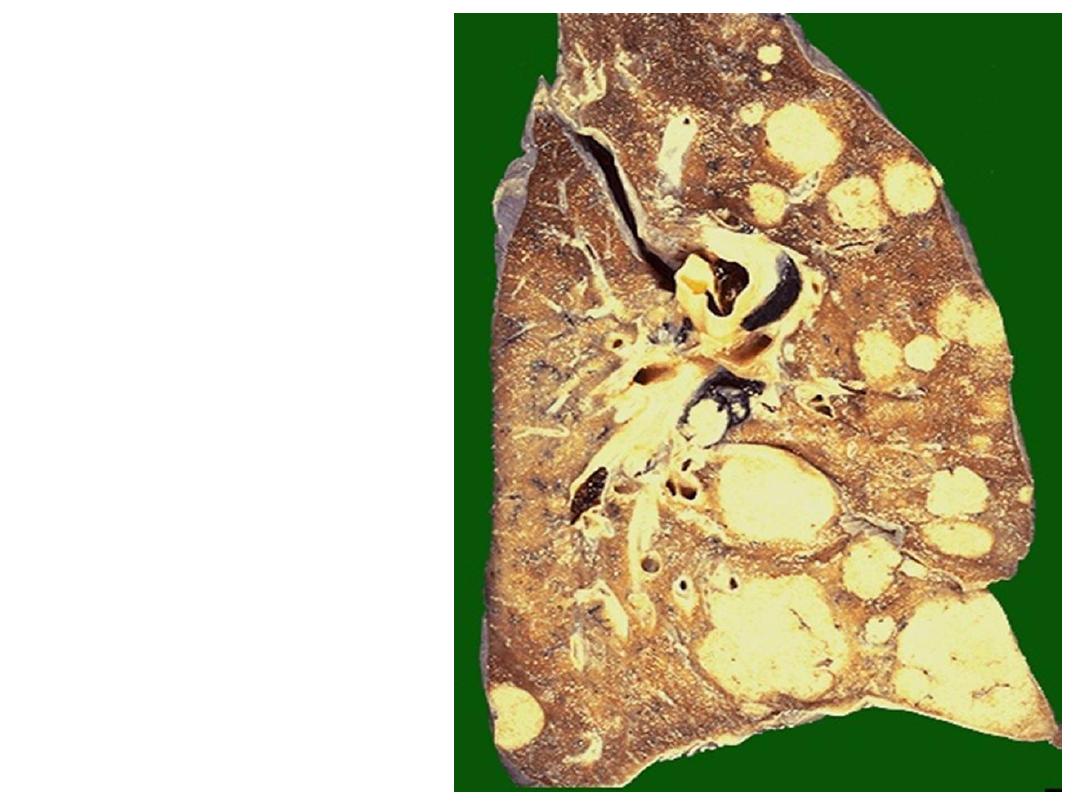
Grossly: section of the
lung showing multiple
different sizes whitish
to yellowish nodules
distributed within the
lung (Cannonball
appearance)
Diagnosis: secondary
in the lung