TEMPROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISORDERSLecture 8
Dr. Lana Shabur Talabani• Temporomandibular joint and muscle disorders, commonly called “TMJ,”disorder are a group of conditions that cause pain and dysfunction in the jaw joint and the muscles that control jaw movement.
• Myofascial pain involves discomfort or pain in the
• muscles that control jaw function.• Internal derangement of the joint involves a displaced disc, dislocated jaw, or injury to the condyle.
• Arthritis refers to a group of degenerative/ inflammatory joint disorders that can affect the temporomandibular joint.
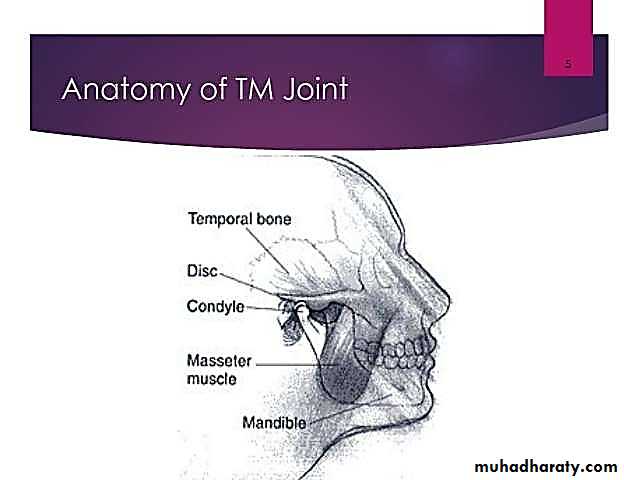
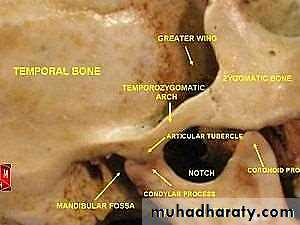
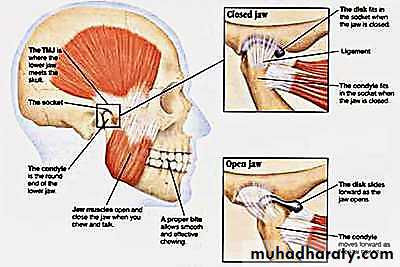
TMJ Disorder
• ETIOLOGY
• TRAUMA• BAD BITE- CLENCHING, GRINDING
• HORMONAL
• GENETIC
• Muscle disorders may include spasm of the masticatory muscles, most frequently involving the lateral pterygoid
• Fibromyalgia or myofascial pain syndrome
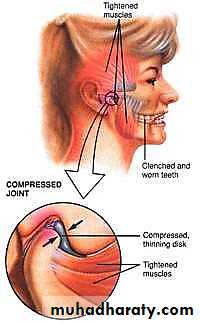
• Emotional stress/tension which may lead to bruxism
• Postural dysfunction, namely forward head posture, may also lead to muscle pain in the jaw from repetitive stress
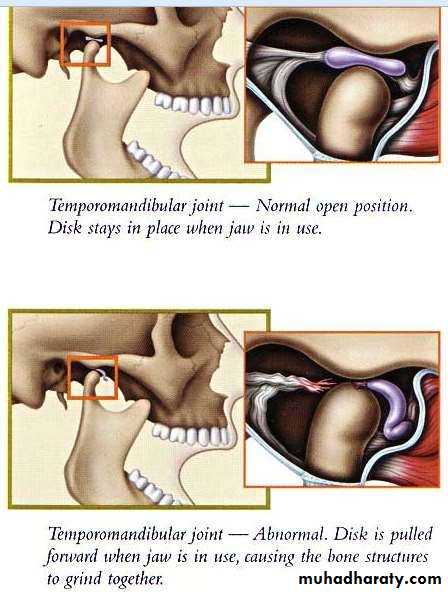
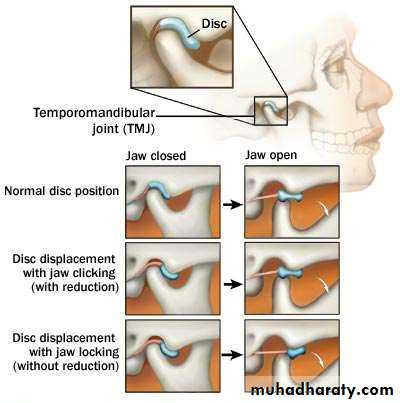
• Disc displacement is the most common TMJ arthropathy and is defined as an abnormal relationship between the articular disc and condyle.
• Clinically, this popping sound or clicking is regarded as an initial symptom of the temporomandibular joint internal derangement (TMJ-ID).
• If the displaced disc returns to its normal position when the mouth is opened, accompanied by a popping sound, it is referred to as disc displacement with reduction
• If the displaced disc does not return to the normal position and acts as an obstacle during attempted mouth opening, the joint appears as locked. This is referred to as disc displacement without reduction
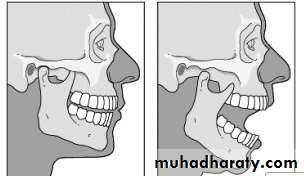
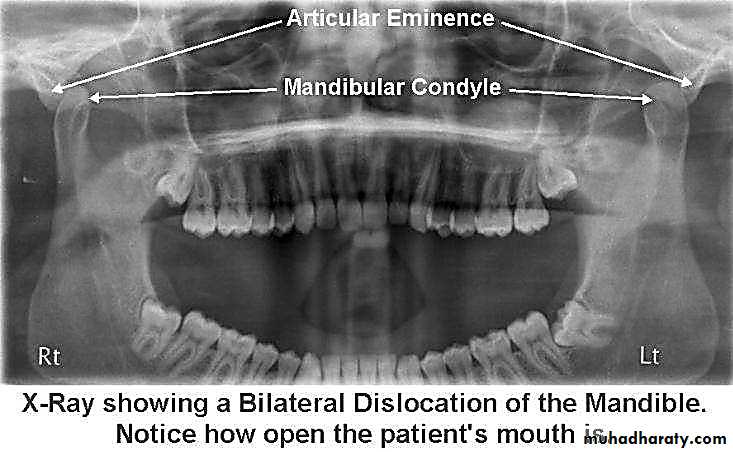
• Subluxation or hypermobility in the temporomandibular joint is defined as the clinical condition with repeated episodes of partial dislocation of the jaw.
• It is a self-reducing incomplete dislocation of the jaw which generally follows stretching of the ligaments and the capsule surrounding the tempero-mandibular joint.
• Common Symptoms
• TMJ DisorderManagement of TMJ Disorder
• Moist heat
• Ice application• Soft diet
• Jaw exercise
• Relaxation techniques
• Sleep on one side
• 1. Pharmacologic Agents
• The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are the mainstays in the pharmacologicaltreatment of musculoskeletal disorders where pain and inflammation are prominent features• Low dose tricyclics are effective in controlling pain from nightime bruxism, when doses are adjusted to provide improved sleep.
• After psychiatric consultation, if it is determined that clinical depression is an aggravating factor, antidepressant medication can be helpful as part of the treatment.
• Injections
• Injections of tender muscles, trigger areas, and/or joint spaces with local anesthetic solution is used for diagnosis and relief of symptoms.• Corticosteroid injection can be effective in reducing capsulitis
• The use of Botox to eliminate muscle spasm and reduce strength of contraction, while retaining voluntary control
• Self-Care Physical therapy is often used by TMD patients to keep the synovial joint lubricated, and to maintain full range of the jaw motion.
• One such exercise for the jaw is to open the mouth to a comfortable fully-open position and then to apply slight additional pressure to open the mouth fully.
• Another exercise includes stretching the jaw muscles by making various facial expressions
• Behavior Modification
• Behavior modification is intended to help patients understand and avoid stress-related lifestyle habits, such as clenching, bruxism, and excessive gum chewing
• Psychological consultation may be indicated for stress management.
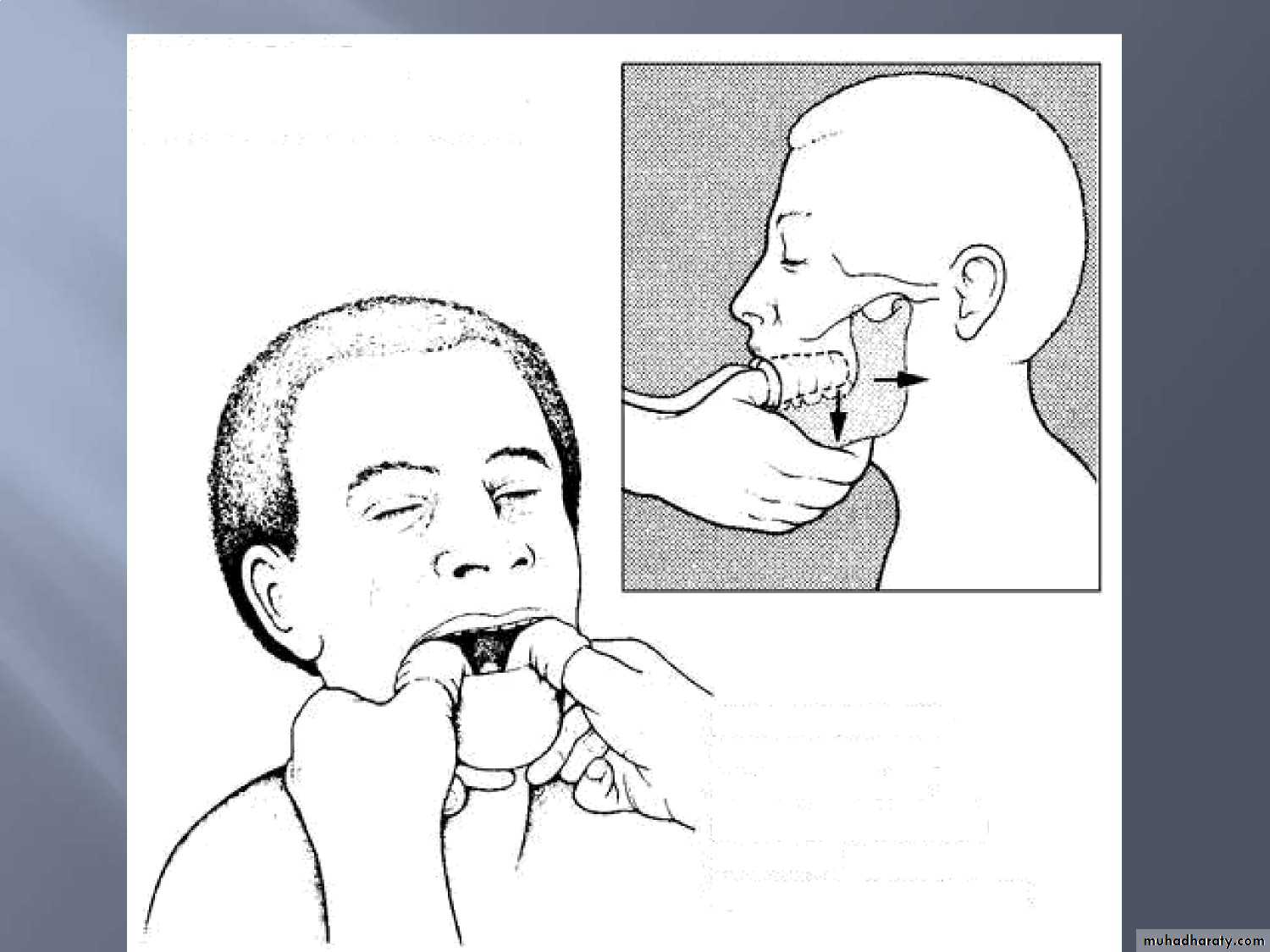
• REDUCING A
• DISLOCATED JAW• pasa his pramolar
• oek downwards.
• at thR 6BITtB ÈÏfTiB
• press the underneaEh of his chin
• upwards and backwards
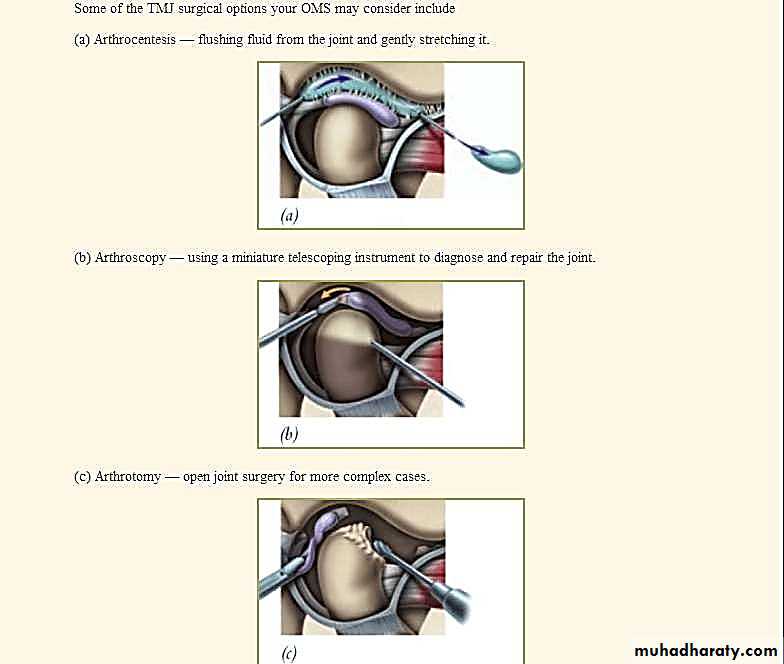
• ARTHROCENTESIS
• ARTHROSCOPY• ARTHROTOMY
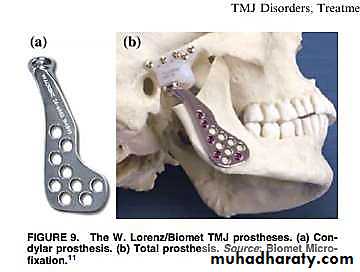
• TMJ IMPLANTS
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
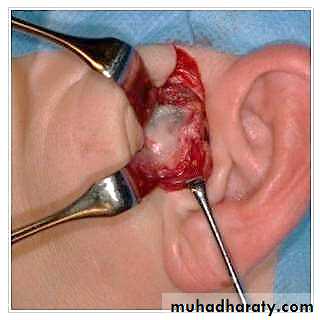
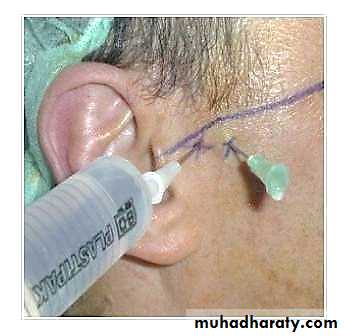
• Discectomy
• Discectomy is a surgical treatment, which is often performed on individuals with severe TMD, to remove the damaged and very often dislocating articular disc without going to a more extreme treatment such as a joint prosthetic.• However, removal of the painful pathologic disc causes the TMJ reduced absorbency and increased loading during articulation