5/4/2015
The adrenal medulla
By pharmacist
Maha A. Hamdi
Adrenal Medulla
•
Norepinephrine,
•
epinephrine,
•
and dopamine
•
are secreted by the adrenal medulla
5/4/2015
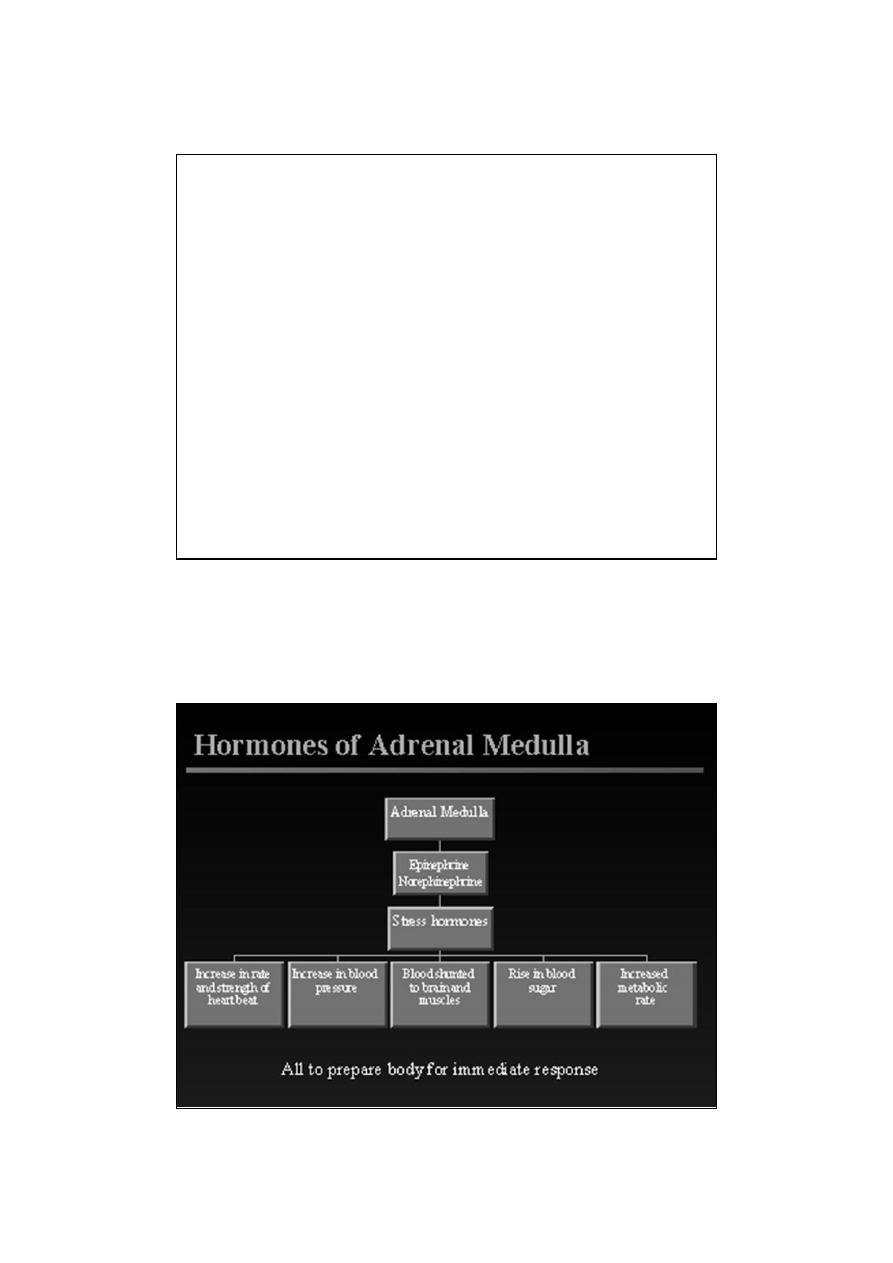
Effects of Epinephrine & Norepinephrine
•
1-mimicking the effects of noradrenergic nervous discharge
•
2-glycogenolysis in liver and skeletal muscle
•
3- mobilization of free fatty acids (FFA
•
4-increased plasma lactate, and stimulation of the metabolic rate
•
5- E &nE both increase the force and rate of contraction of heart (
inotropic effect).
Effects of Epinephrine & Norepinephrine
•
6-catecholamines also increase myocardial excitability,
•
7-nE produces vasoconstriction in most if not all organs viaᾳ
1
•
8- E dilates the blood vessels in skeletal muscle and the liver via ß
2
receptors.
•
9-Catecholamines increase alertness , epinephrine usually evokes
more anxiety and fear.
5/4/2015
Effects of Epinephrine & Norepinephrine
•
10- catecholamines increase the secretion of insulin and glucagon .
•
11- produce a prompt rise in the metabolic rate that is independent
of the liver .
5/4/2015
Effects of Epinephrine & Norepinephrine
•
The effects of nE & E are brought about by actions on two classes of
receptors: Alpha receptors are subdivided into two groups, ᾳ
1
and ᾳ
2
receptors,
•
There are three subtypes ofᾳ
1
receptors and three subtypes ofᾳ
2
receptors
•
andß receptors into ß
1
, ß
2
, andß
3
receptors,.
Effects of Dopamine
•
Dopamine is made in the renal cortex.
•
The physiologic function of the dopamine in the circulation is unknown.
However, injected dopamine produces
•
1-renal vasodilation,
•
2-It also produces vasodilation in the mesentery.
•
3-Elsewhere, it produces vasoconstriction, probably by releasing
norepinephrine,
•
4-it has a positively inotropic effect on the heart by an action on ᾳ
1
-
adrenergic receptors.
•
The net effect of moderate doses of dopamine is an increase in systolic
pressure and no change in diastolic pressure.
•
Because of these actions, dopamine is useful in the treatment of traumatic
and cardiogenic shock
5/4/2015
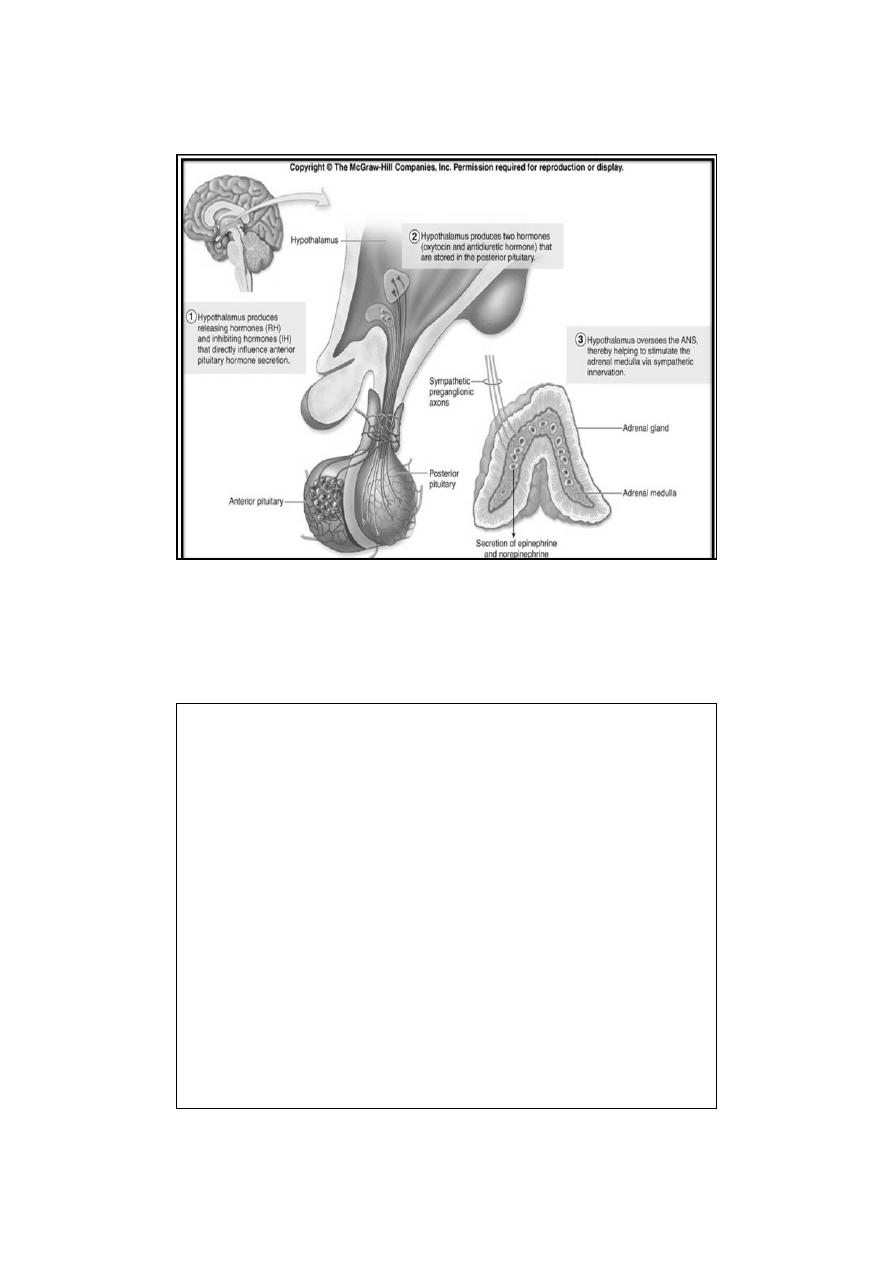
Regulation of Adrenal Medullary Secretion
•
1-Neural Control
•
physiologic stimuli affect medullary secretion through the nervous
system.
•
Catecholamine secretion is low in basal states, the secretion of
epinephrine and, norepinephrine is reduced during sleep.
5/4/2015
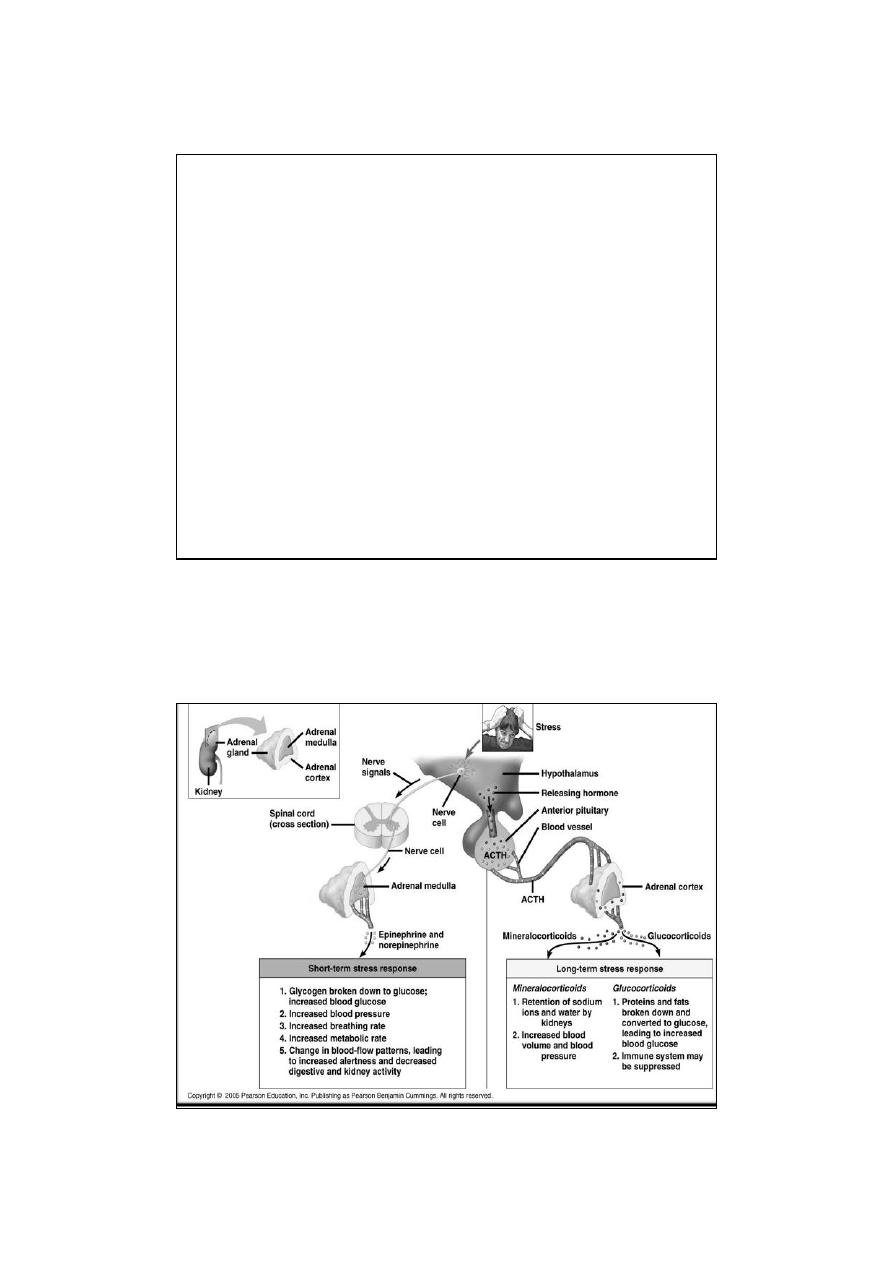
•
Increased adrenal medullary secretion is part of the diffuse
sympathetic discharge provoked in emergency situations,
•
called the "emergency function of the sympathoadrenal system.“
•
or
•
“flight or fight”
5/4/2015
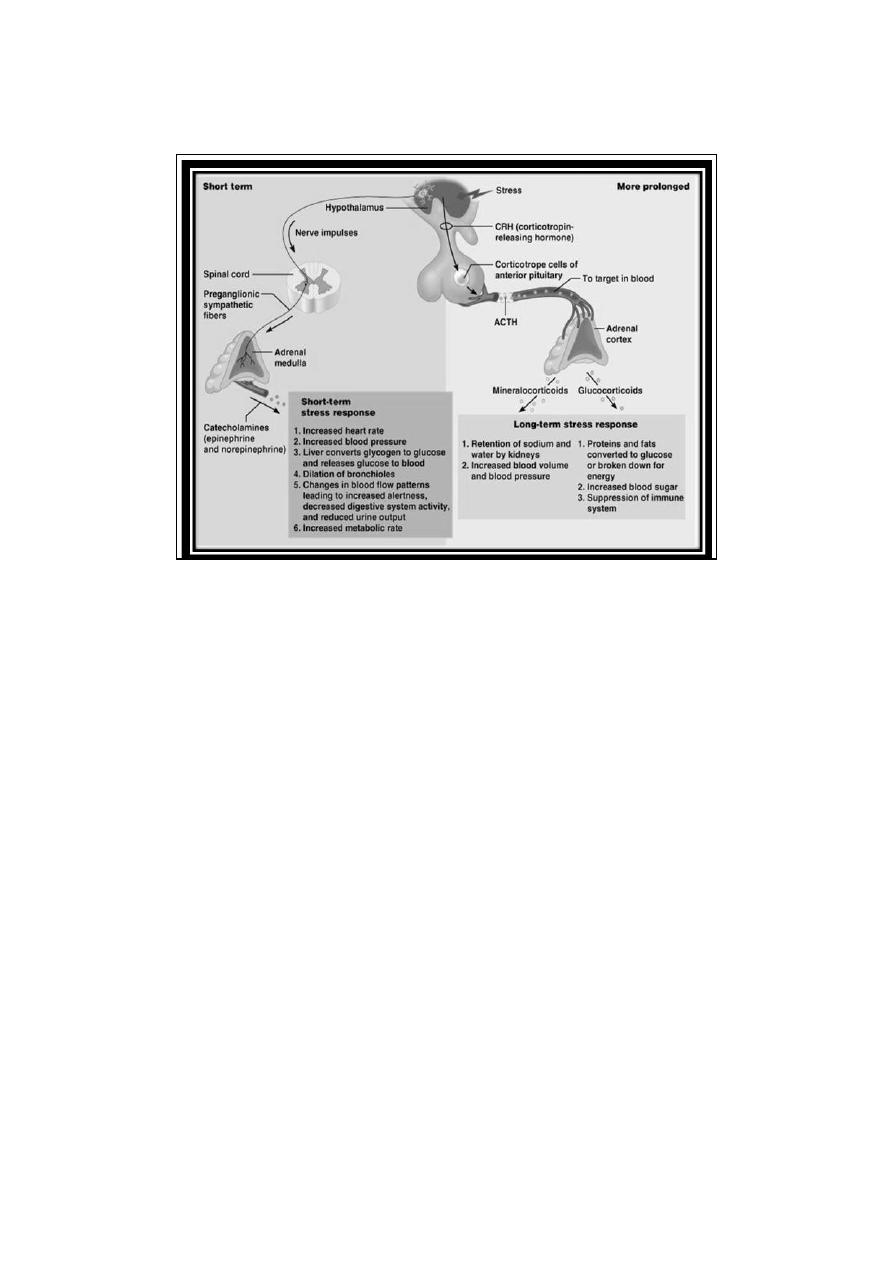
Regulation of Adrenal Medullary Secretion
•
2-Selective Secretion
•
norepinephrine secretion tends to be selectively increased by emotional
stresses with which the individual is familiar.
•
epinephrine secretion rises selectively in situations in which the
•
(individual does not know what to expect)
5/4/2015
