White and Red Lesionspractice
Dr. Lana Shabur TalabaniLekodema
Lekodema
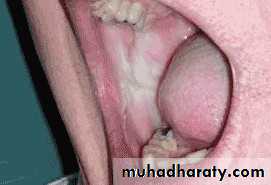
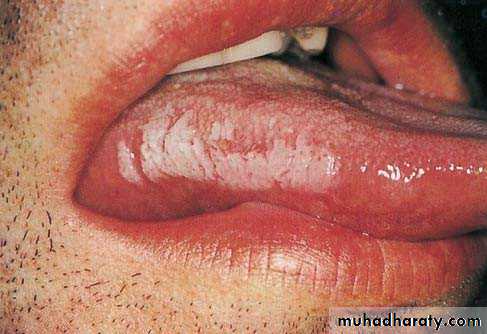
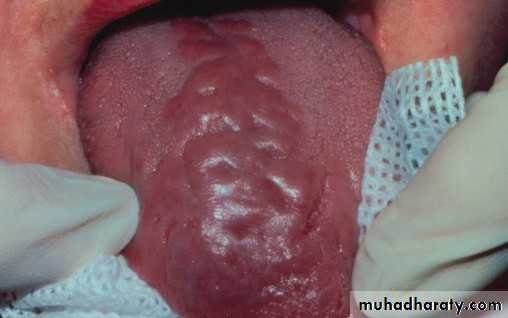
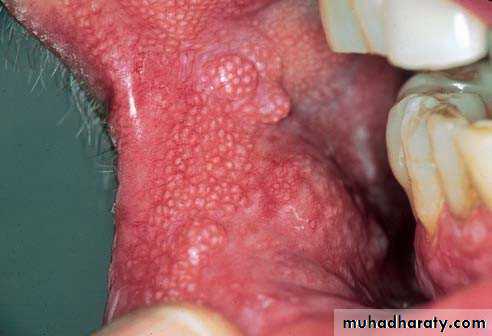
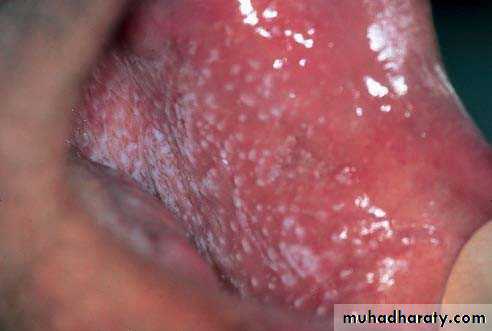
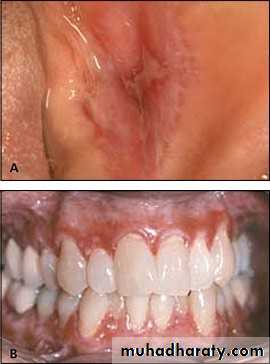
• :Hereditary white lesions• White spongy nevus:
• White spongy nevus:
• White spongy nevus:
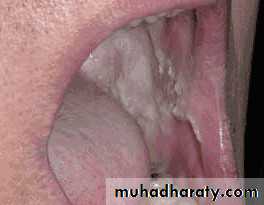
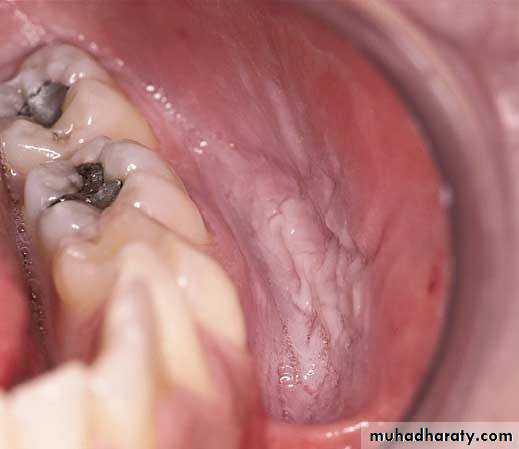
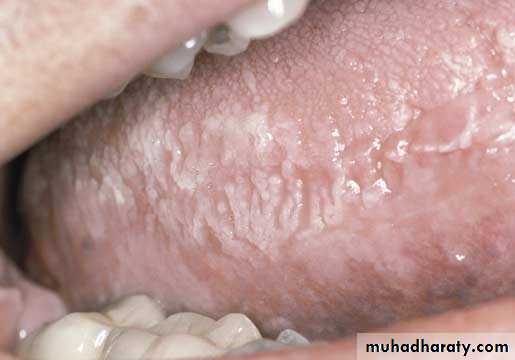
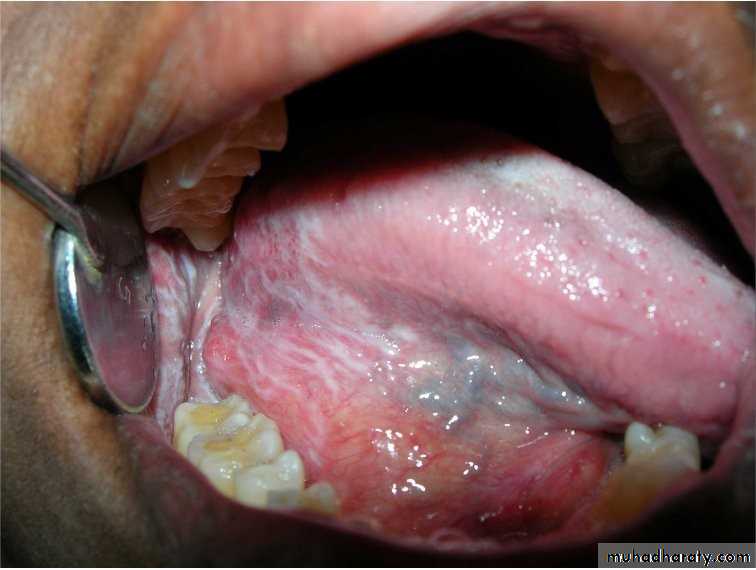
• Frictional keratosis• Frictional keratosis
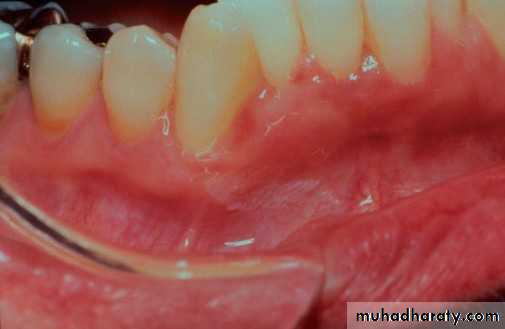
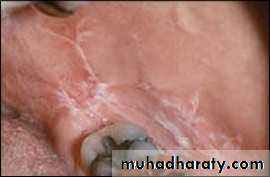
• Linea alba
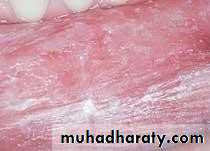
• Cheek chewing• Cheek chewing
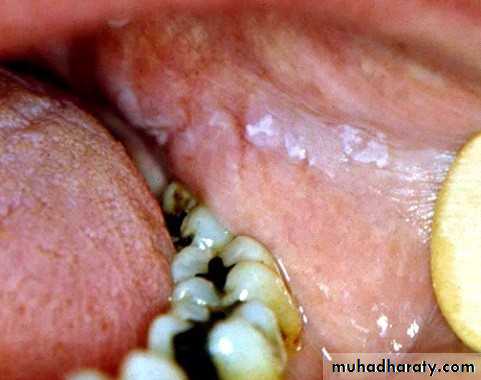
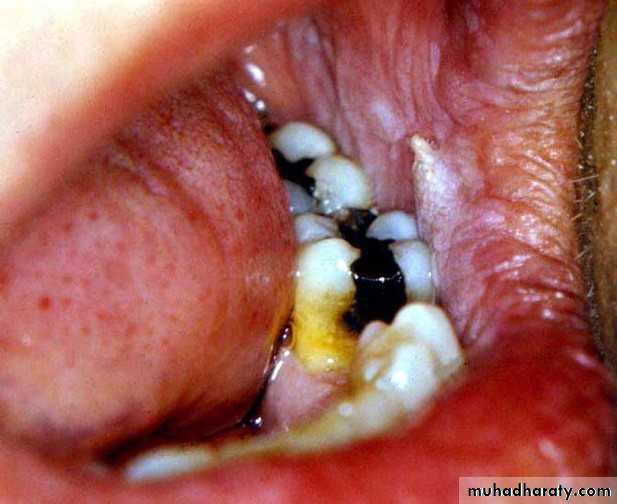
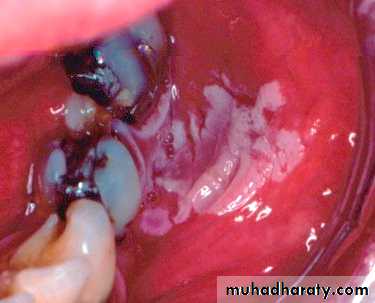
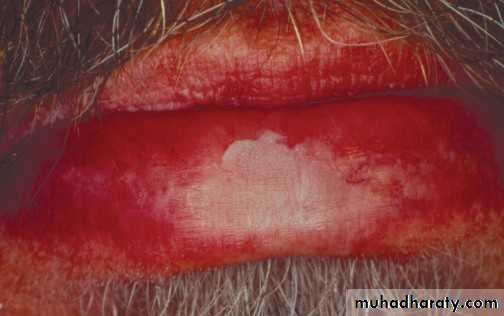
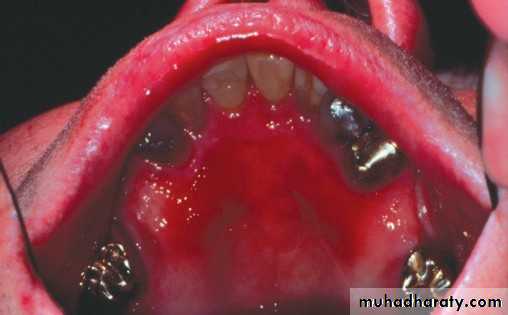
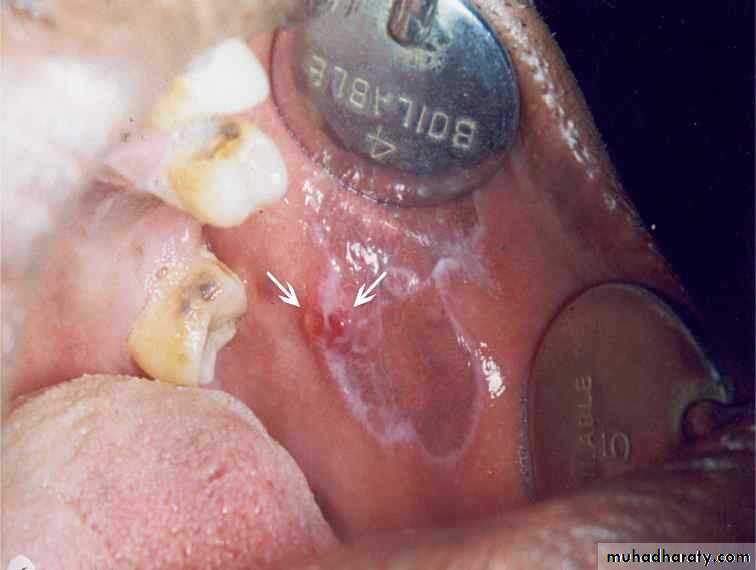
Chemical burn
• Chemical burn (phenol)•
•
•
• Transient nonkeratotic lesion
• due to caustic as formcresol, etchant
Chemical burn
Asprin burn
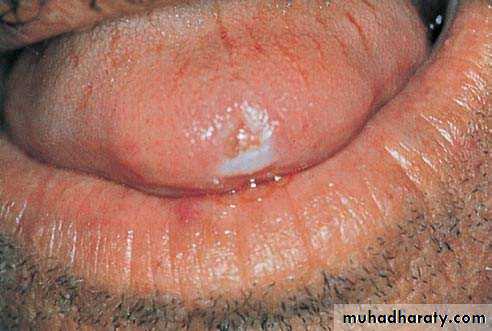
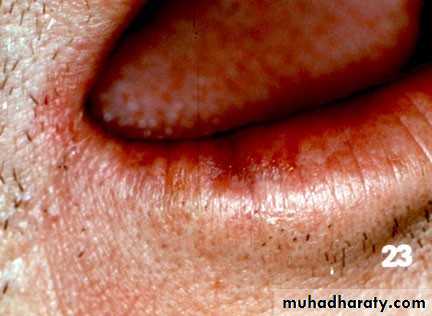
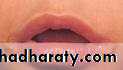
• Actinic keratosis• Premalignant
• Due to long term sun exposure
• Vermillion border of lower lip
• Treatment : surgery
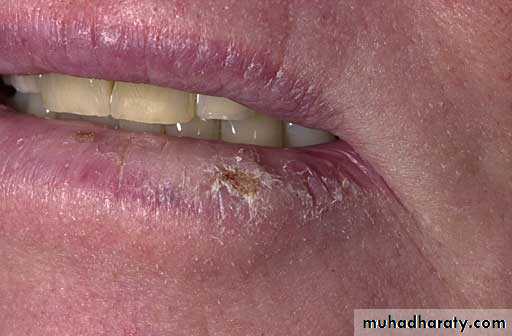
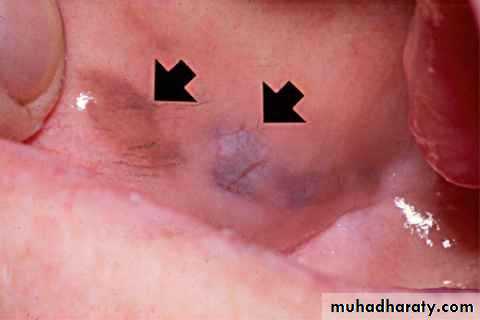
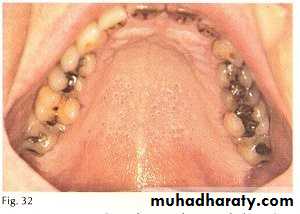
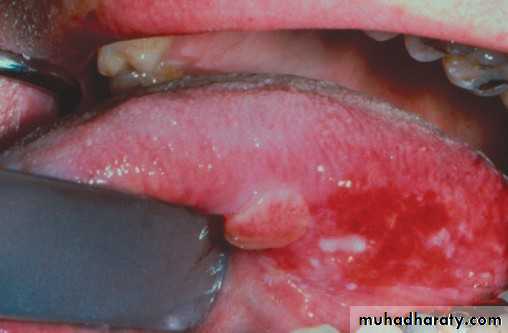
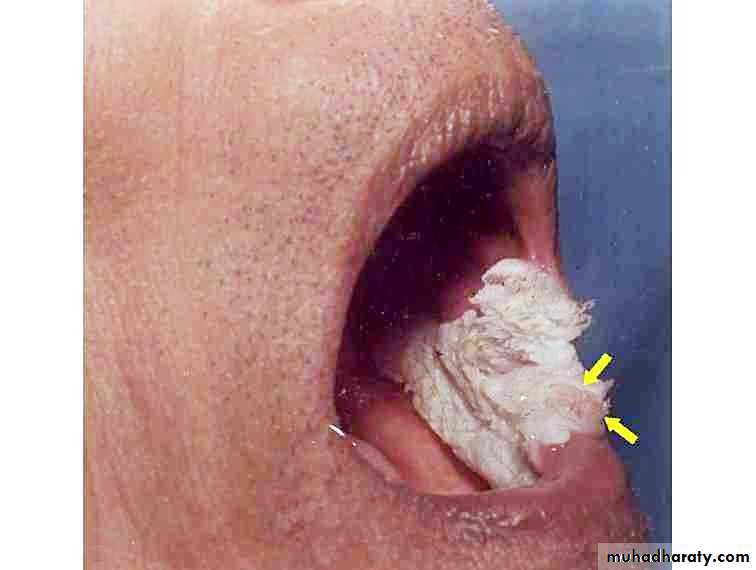
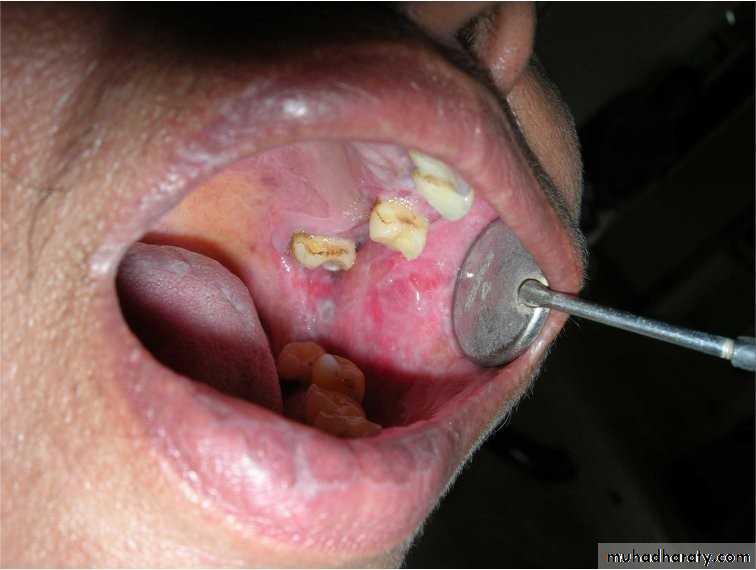
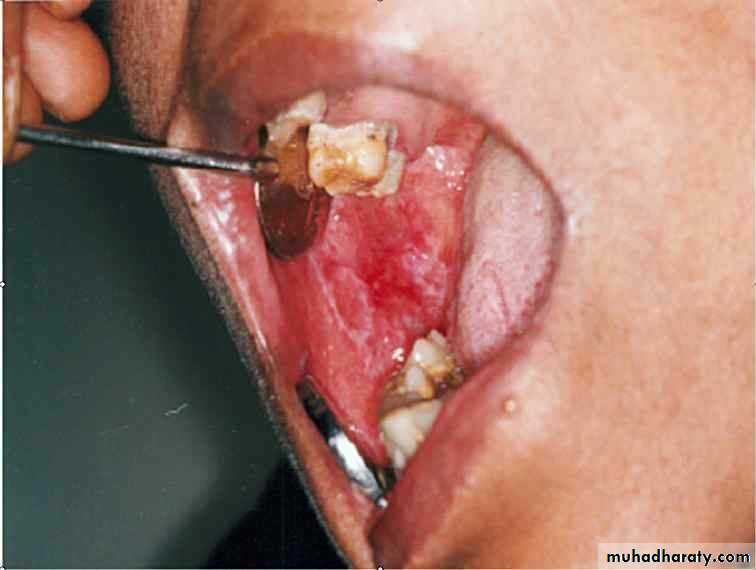
• Smokeless tobacco induced keratosis
• In the area of tobacco contact• Precancerous
• Smokeless tobacco
• Smokeless tobacco
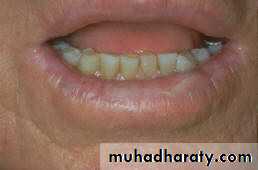
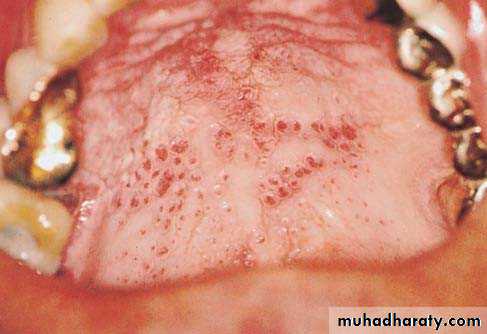
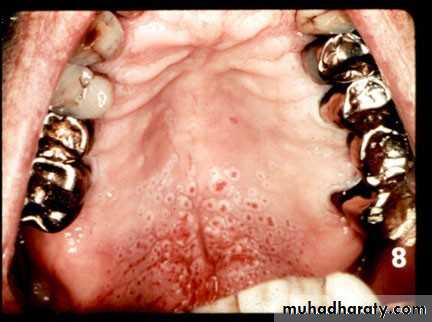
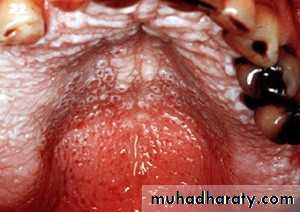
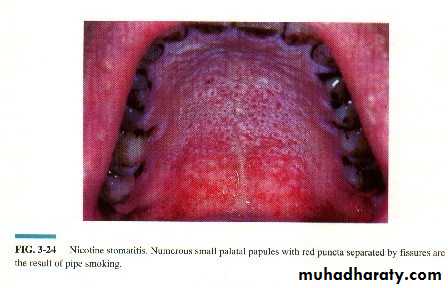
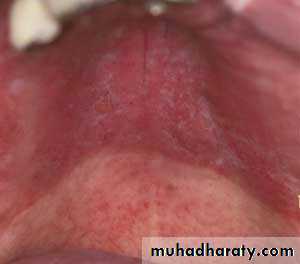
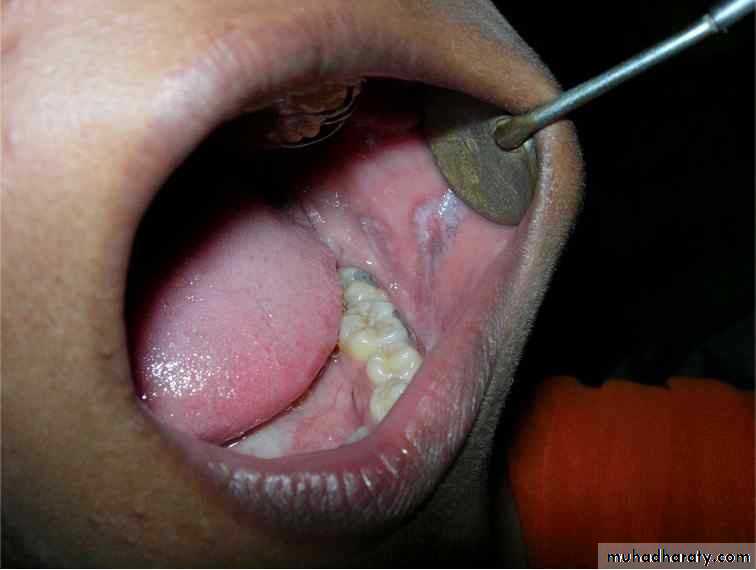
Nicotine stomatitis
Nicotine stomatitis
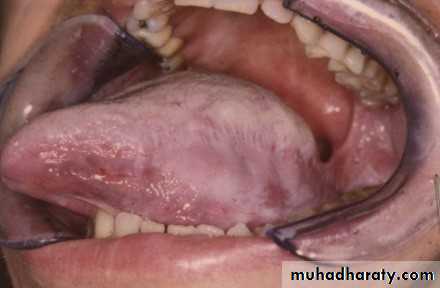
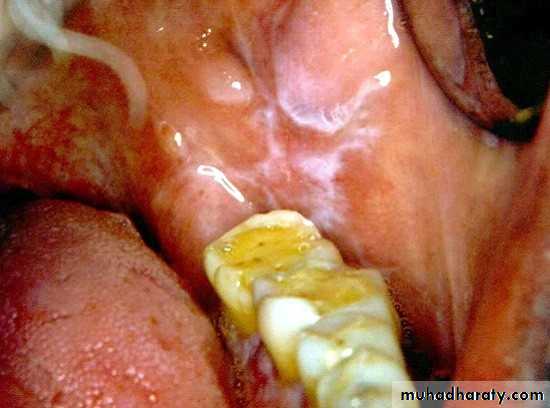
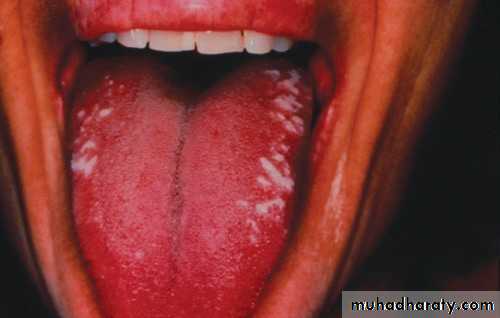
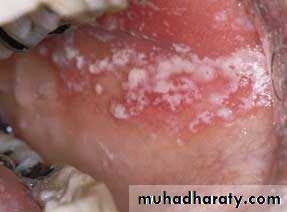
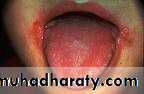
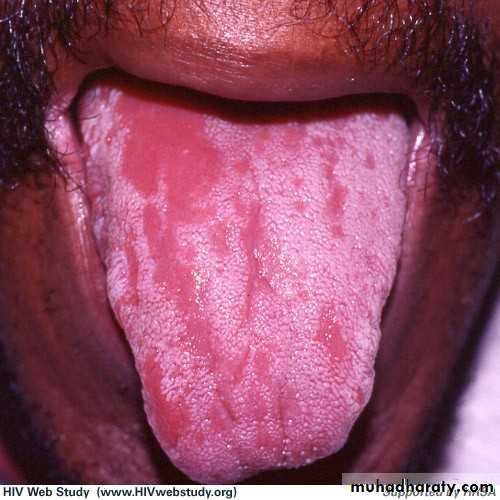
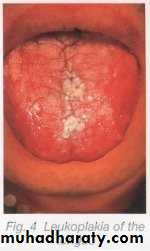
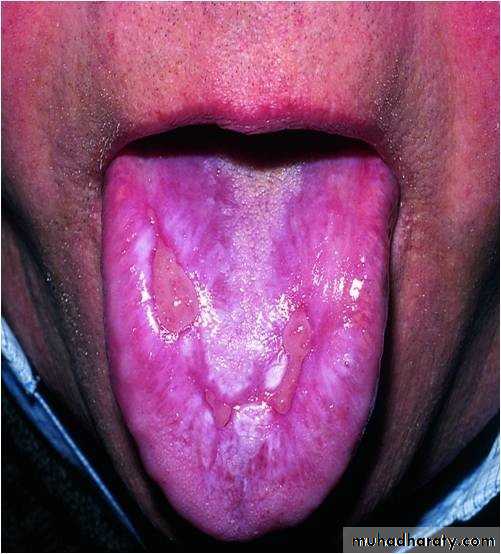
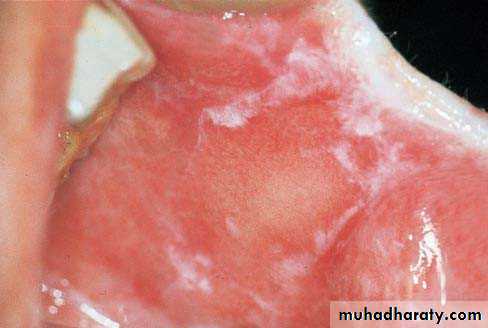
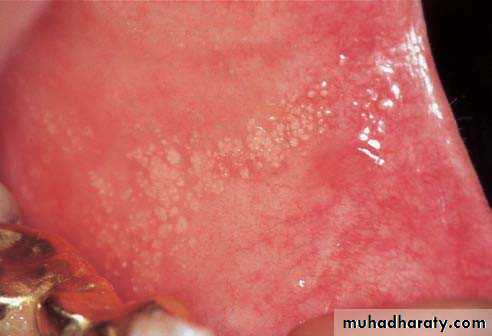
• Hairy Leukoplakia
• By epstain barr virus.• In HIV patient.
• Mainly on lateral border or ventral surface of the tongue
• Treatment: antiviral drugs.
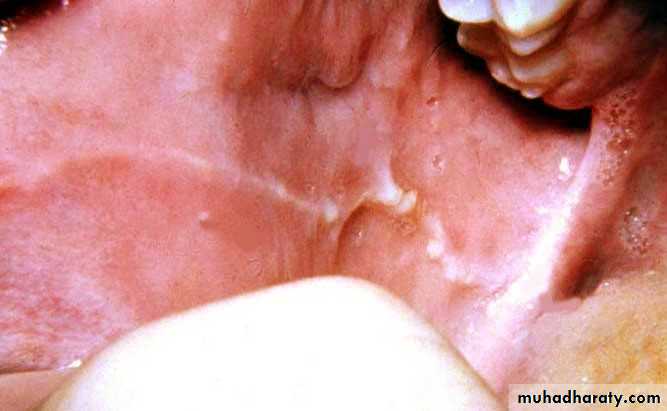
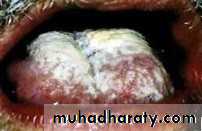
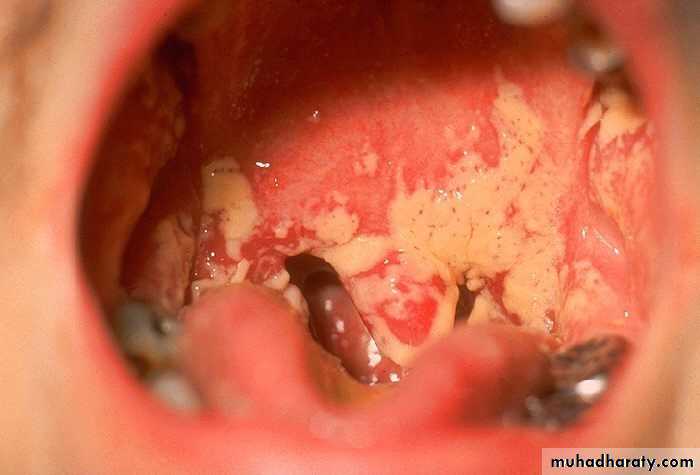
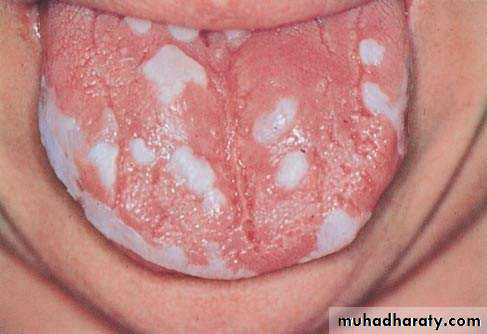
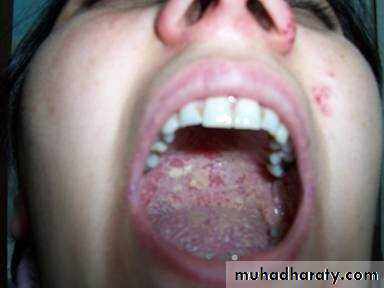
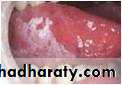
• Acute pseudomembranous cand. (thrush)
• Painless• Soft friable creamy plaque
• Easily wiped off
• Prodrome : bad taste or loss of sensation
• Acute pseudomembranous cand. (thrush)
Acute antibiotic stomatitis (atrophic or erythamatous(
• Follow overuse of antibiotics• The whole mucosa: red & glazed
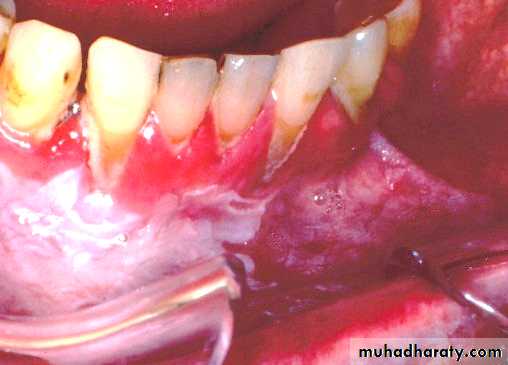
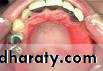
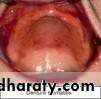
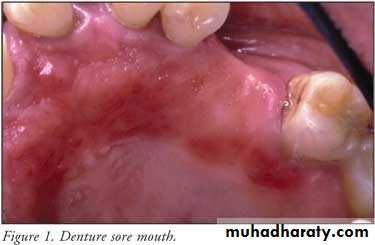
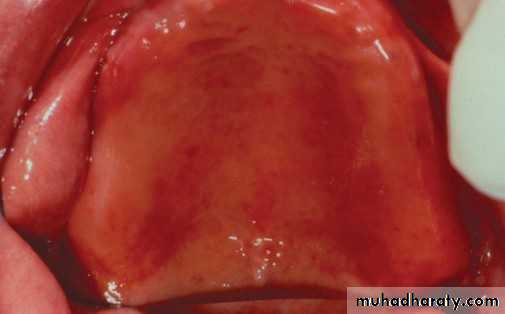
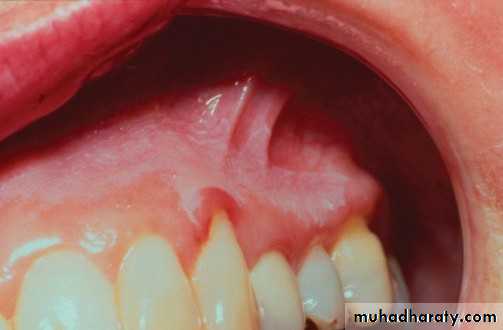
• Denture induced stomatitis
• Upper denture• Due to well fitting denture cutting the washing effect of saliva
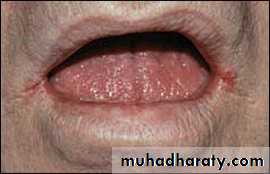
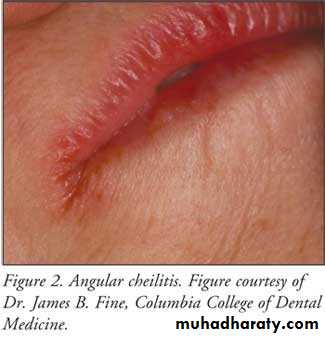
• Painless red area• Angular stomatitis
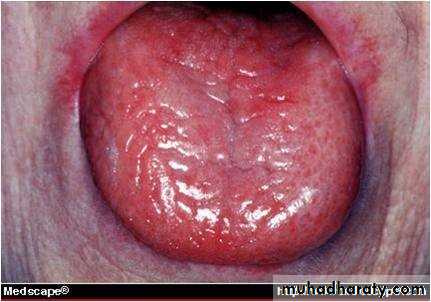
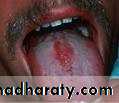
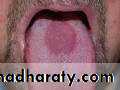
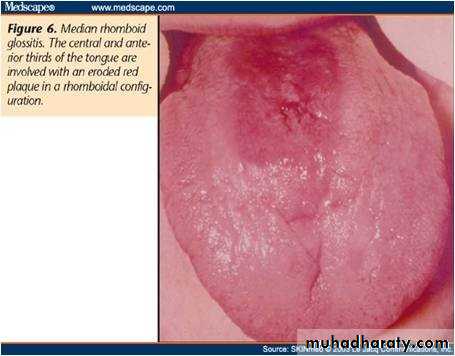
• Median rhomboid glossitis
• Red patch of atrophic papillae• Central area of dorsum of tongue
Chronic mucocutaneous candidosis
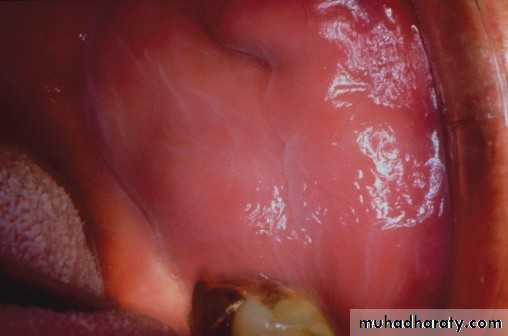
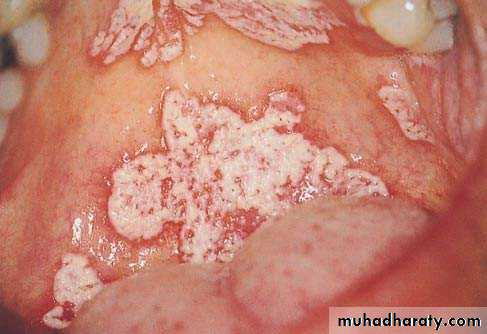
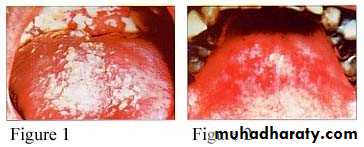
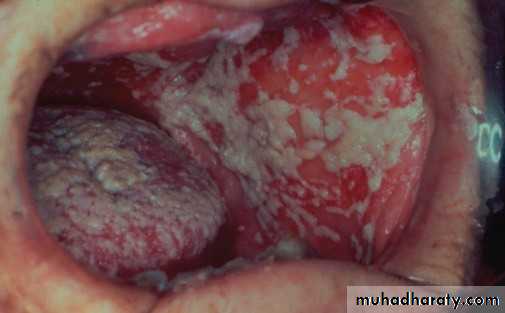
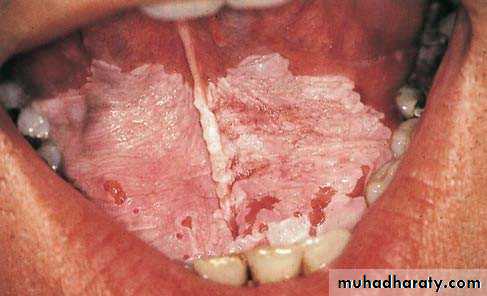
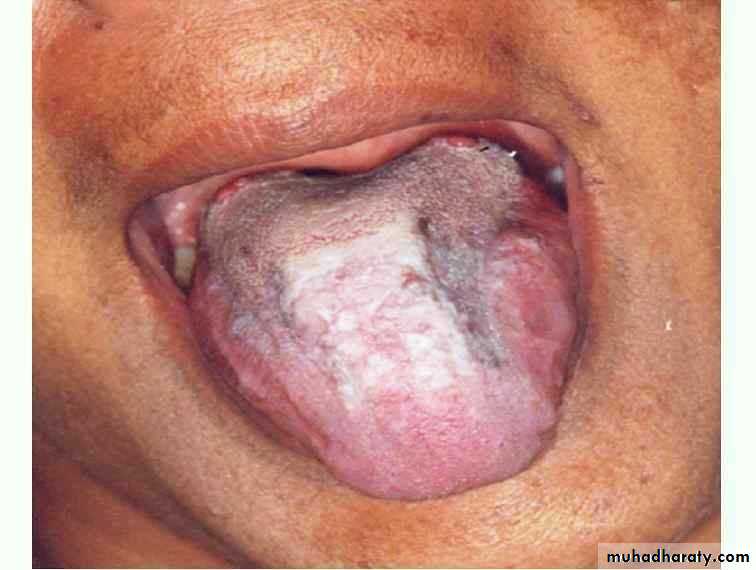
Candidal leukoplakia (chronic. Hyperplastic(
• Firm white leathery plaques• Cheek ,lip ,tongue
• ,palate
• Erythematous candidiasis
• Red macules• Mainly on hard palate , dorsum of tongue ,soft palate
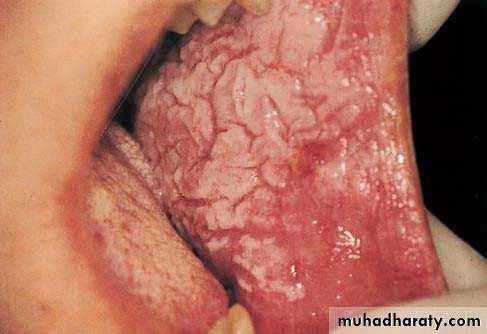
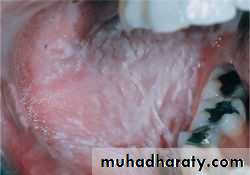
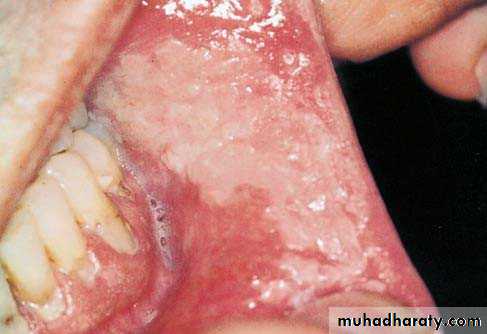
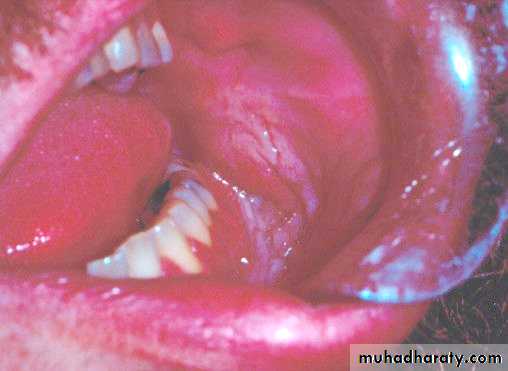
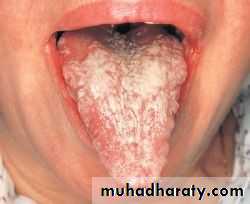
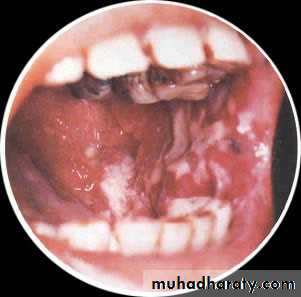
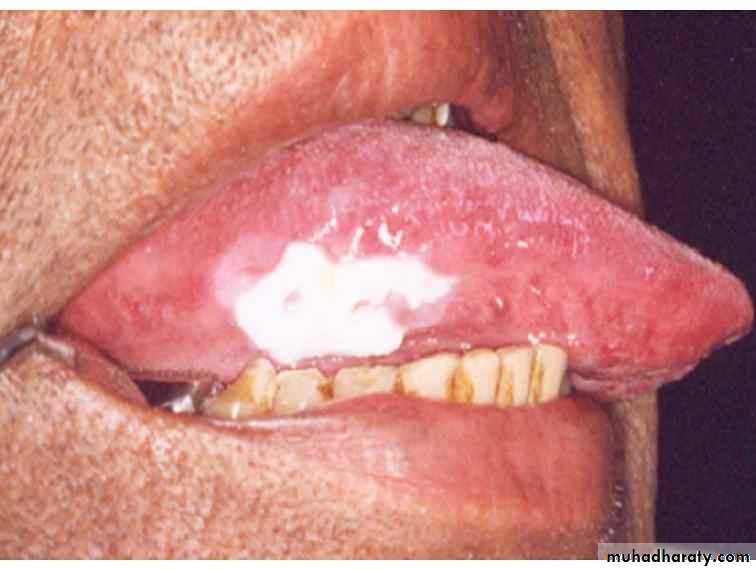
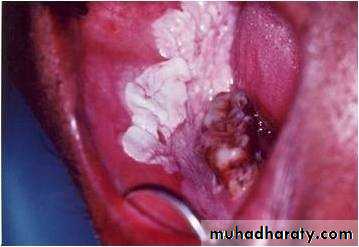
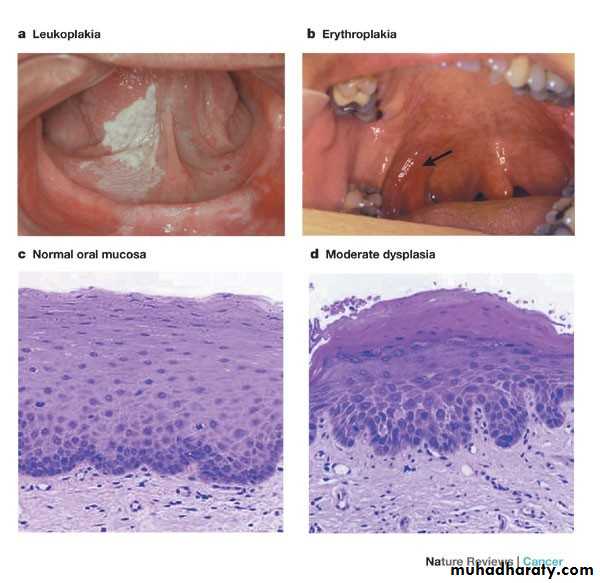
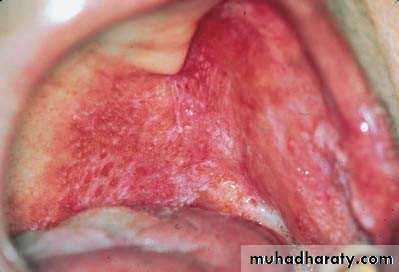
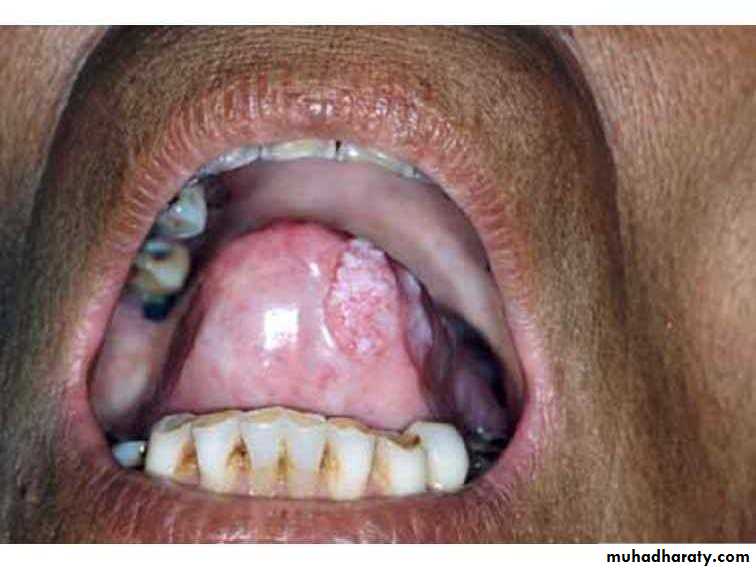
• Idiopathic (true) leukoplakia
• 1. Homogenous Leukoplakia:
• •
•
• Well defined patch Elevated ,fissured
• ,wrinkled
• Palpation: leathery or dry cracked mud like
• Idiopathic (true) leukoplakia
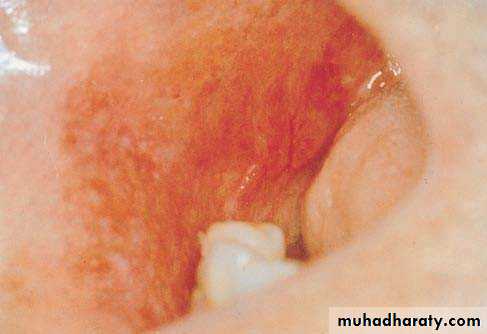
• 2. Speckled• Leukoplakia:
•
• •
• Mixed red & white
• Keratotic nodules on atrophic red base
• High malignant transformation
• Idiopathic (true) leukoplakia
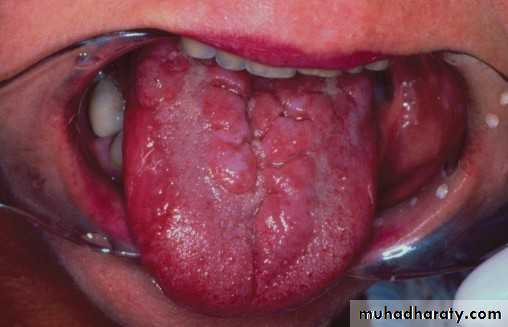
• 3. Verrocous• leukoplakia:
•
• Thick with papillary surface•
• Heavily keratinized
•
• In older pt
• Idiopathic (true) leukoplakia
• 4. Proliferative Verrocous• leukoplakia:
•
• •
• Extensive papilary plaque
• Involve multiple mucosal sites
• Transform to sq. cell carcinoma
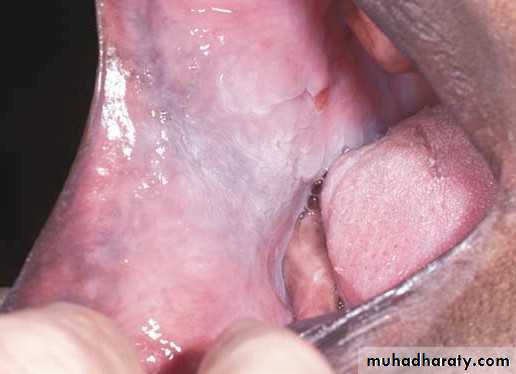
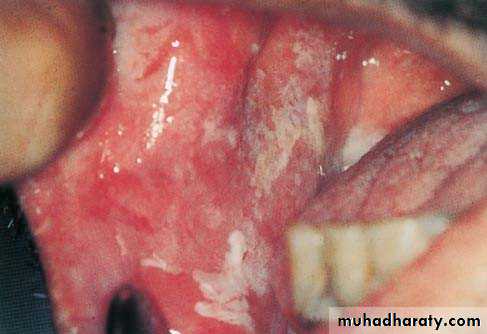
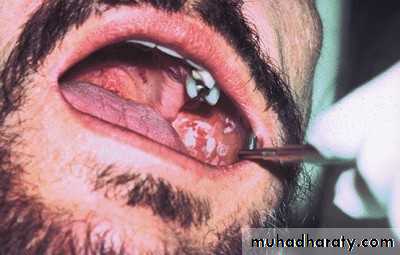
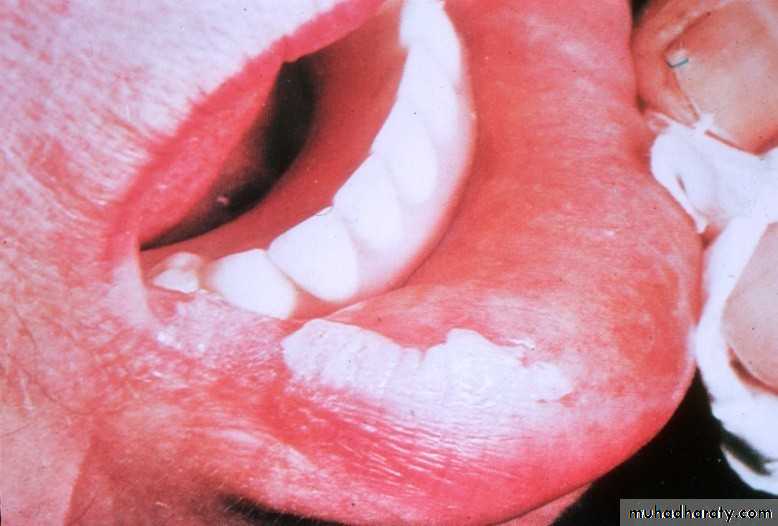
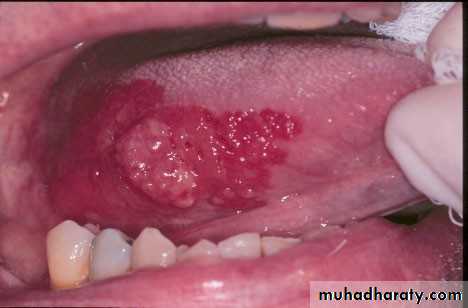
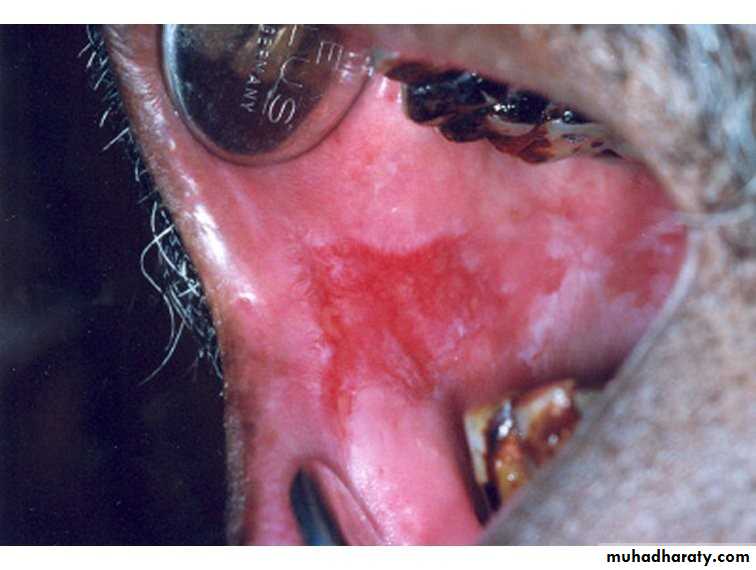
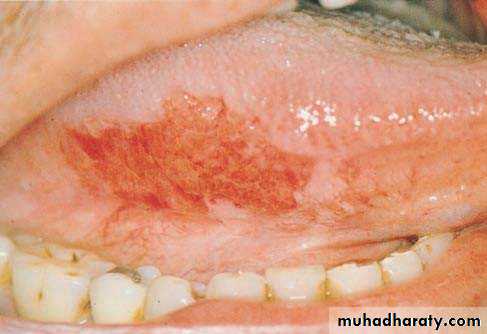
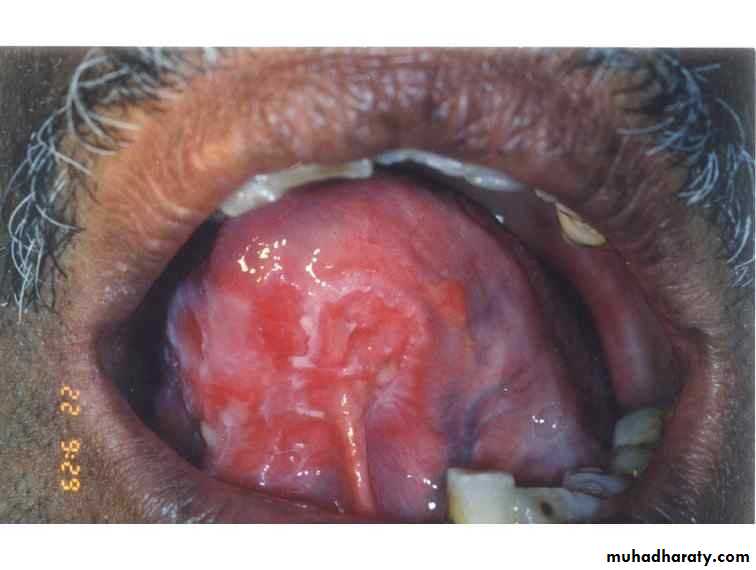
• Erythroplakia
• Red bright velvety area• Tongue ,floor of mouth , soft palate
• ,ant.tonsillar pillars
• Asymptomatic
• High malignant transformation
• Erythroplakia
• Erythroplakia
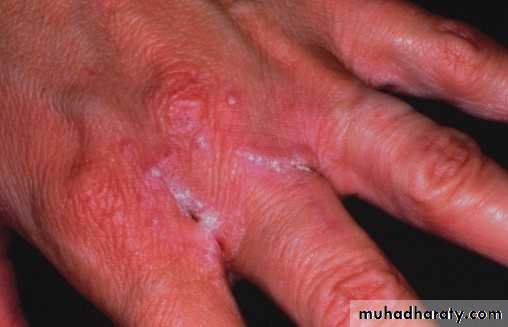
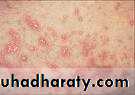
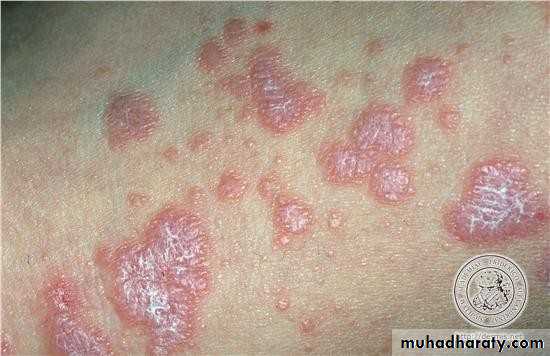
• Lichen Planus
• 1. Skin lesion :• Koebners phenomenon
• Lichen Planus
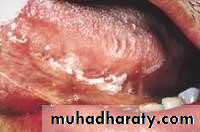
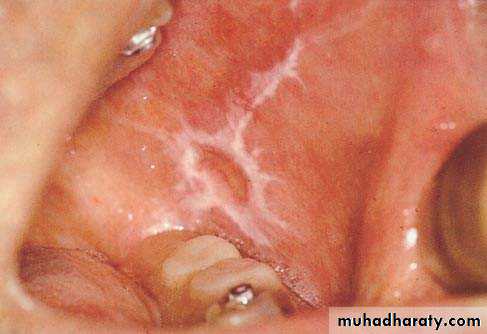
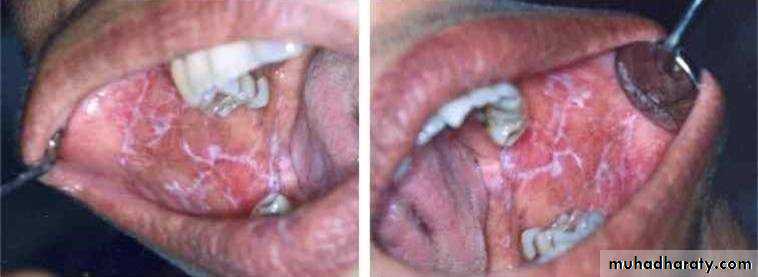
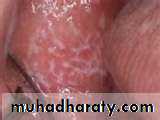
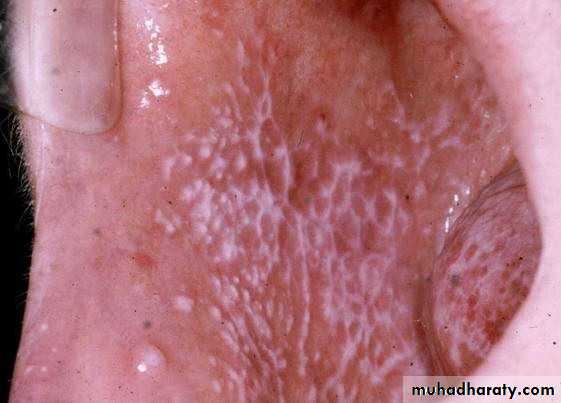
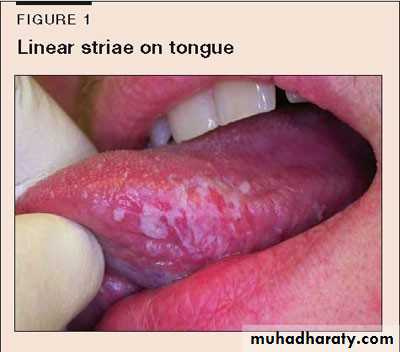
• • Lichen Planus (reticular)
• • Slightly elevated lines “wickham’s striae”
• Buccal mucosa
• Lichen planus (papular & reticular)
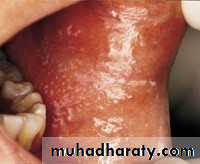
• Lichen Planus (atrophic)
• Inflammed areas of oral mucosa• Covered by thinned red epithelium
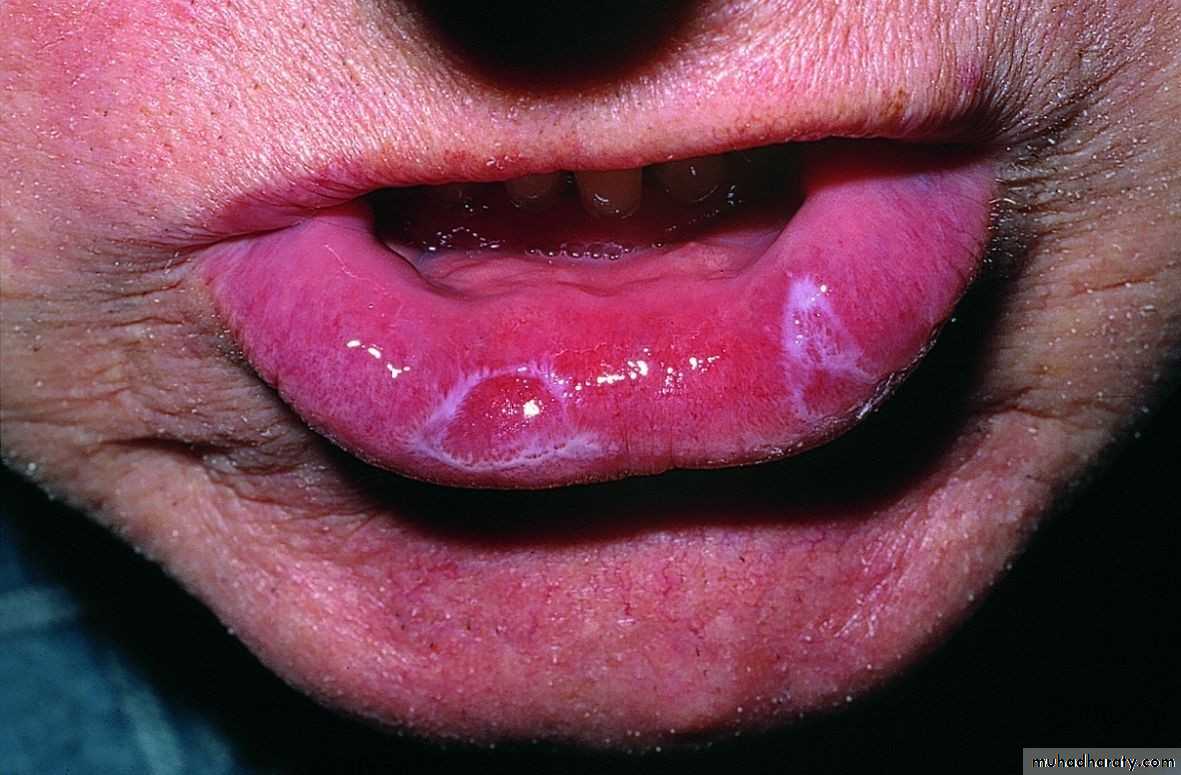
• symptomatic• Lichen Planus (erosive)
• Complication of atrophic type• Thin epithelium become abraded or ulcerated
• Lichen Planus (bullous(
• Lichenoid reaction
• L.P like lesions• Due to systemic drug treatment
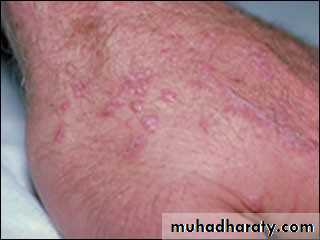
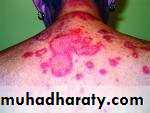
• Lupus erythematosus:
• Autoimmune C.T disease•
•
• Forms:
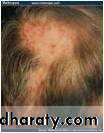
• Discoid (DLE)
• Systemic (SLE) D. L. E :•
•
• cheeks, nose bridge, ears, side of neck & scalp
• Bilaterally not necessarily symmetrical
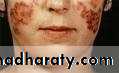
• Lupus erythematosus
• Butterfly rash• Tin-tack sign
• Lupus erythematosus
• S.L.E:•
• Cutaneous erythema especially on light exposed areas• Butterfly rash
• Lupus erythematosus
• Oral lesion:• White striated, atrophic or erosive areas
• Variable patterns of white & red areas