Yeast Infection
ByDr.Alaa Al-sahlany
Nov. 11, 2018
Pityriasis versicolor
Caused by malassaezia furfur and M. globosa,are part of the normal follicular flora
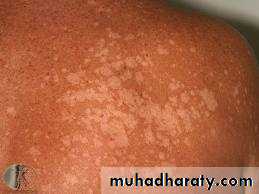
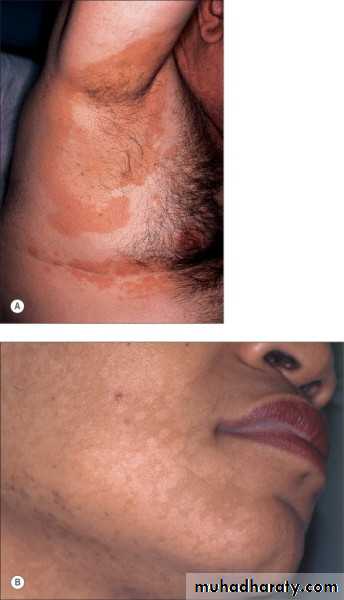
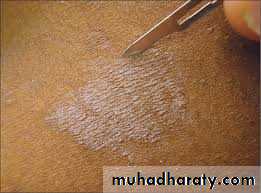
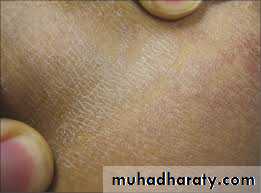
Present with multiple hyperpigmentd or hypopigmented patches with fine(fluffy or furfuraceous) scale. Demonstration of this associated scale may require scratching or stretching the skin surface
Fluffy
Furfuraceous (bran-like)
Decreased pigmentation may be secondary to the inhibitory effects of dicarboxylic acids on melanocytes (these acids result from metabolism of surface lipids by the yeast) or decreased tanning, due to the ability of the fungus to filter sunlight(work as a sunscreen).
More common during the summer months owing to high temperature and humidity
Usually asymptomaticMalassezia is lipophilic: therefore,(1) seborrheic regions, in particular the upper trunk and shoulders, are the favored sites of involvement and (2) adolescents are frequently affected.
Malassezia is dimorphic i.e. grow both as a yeast and hyphae
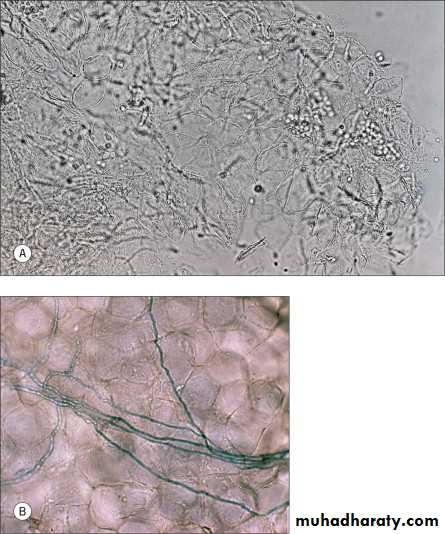
Dx: KOH examination of scale scraping which shows “Spaghetti and meatballs” which are hyphae and spores, respectively
Spaghetti and meatballs
Dermatophyte hyphaeTreatment
Topical treatment : selenium sulfide or ketaocoazole shampoo applied daily for a week. Others: Other imidazoles, zinc pyrithion, sulfur, and benzyl peroxideSystemic : itraconazole (200 mg/day) for a week, fluconazole (300 mg) weekly for two weeks
Candidiasis(Candidosis or Moniliasis)C. albicans is a common inhabitant of the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts, and skin
C. albicans is an opportunistic organism. Under the right conditions e.g. decreased immunity, moisture and decreased competing flora, It can cause lesions of the skin, nails, and mucous membranes
Predisposing factors:
Diabetes mellitusXerostomia(saliva inhibit growth of candida)
Occlusion e.g. under adhesive plaster
Hyperhidrosis
Use of corticosteroids and broad- spectrum antibiotics
Immunosuppression, including HIV infection
Diagnosis
Microscopical KOH examination show budding yeast and pseudohyphae in stratum corneum and superficial mucosaHistological exam with PAS stain
Sabouraud culture . It takes about 4 days to grow colonies
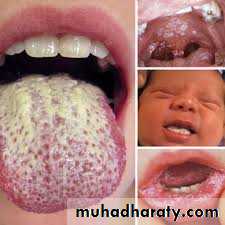
Oral candidiasis (Thrush)The mucous membrane of the mouth may be involved in healthy infant
In the newborn the infection may be acquired from contact with the vaginal tract of the mother
(1)Pseudomembranous Candidiasis (Thrush):
White-to-creamy plaques on any mucosal surface. Removal with a dry gauze pad leaves an ery- thematous mucosal surface. Can involve dorsum of tongue, buccal mucosa, hard/soft palate, pharynx, esophagus.(2) Erythematous (Atrophic) Candidiasis: Smooth, red, atrophic patches(atrophic papillae)
(3) Hyperplastic candidiasis: white plaques that cannot be wiped off.
It is often the first manifestation of AIDS.Rx:
Topical:oral nystatin suspension or clotrimazole troches that dissolve in the mouthSystemic: fluconazole and itraconazole.
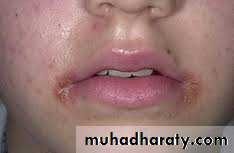
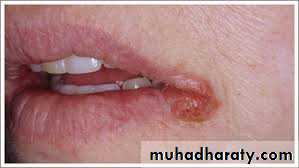
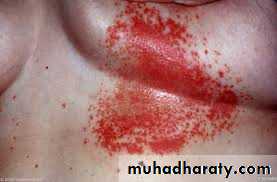
Angular Cheilitis(Perleche)
White plaques with slight erythema of the mucous membrane at the angles of mouth. Maceration and fissures may ensueIs commonly related to C. albicans, but may be caused by coagulasepositive S. aureus and Gramnegative bacteria. Similar changes may nutritional deficiency e.g. riboflavin and iron.
Drooling in persons with malocclusion caused by ill fitting denture or overlap of angles of mouth in edentulous elderly are predisposing factors.
RX: Topical anticandidal
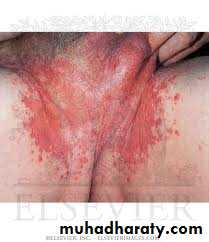
Candidal vulvovaginitis
Overgrowth of candida can cause the labia to be erythematous, moist.There might be a pruritus, burning and curd-like discharge
Pregnancy, high-dose estrogen and longterm tamoxifen treatment are a predisposing factorsAbout 20% of asymptomatic women are vaginal %carriers. During pregnancy, this rises to 40
Candidiasis can be sexually transmitted and this is probably most important in recurrent infections(more than 3 episodes per year)Rx:vaginal suppositories containing nystatin or imidazole. Single-dose oral fluconazole is an alternative
Balanitis and Balanoposthitis
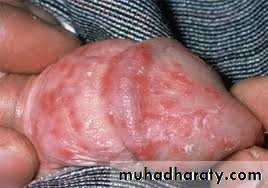
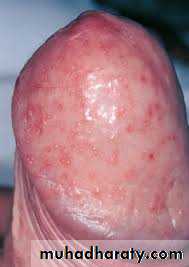
Balanitis is more common in the uncircumcised manThe skin is erythematous and glazed with pustules and erosions
Rx: topical anticandidal agents or single dose oral fluconazole. Treatment of sexual partner is essential
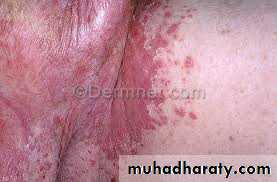
Candidal intertrigo
Can involve groins or armpits; intergluteal cleft; under large breasts; under overhanging abdominal folds; or in the umbilicus.Red moist patches surrounded by a fringe of macerated epidermis (“collarette” scale).
Tiny pustules and papules are observed closely adjacent to the patches, termed “satellite or daughter” lesionsRx: Topical anticandidal preparations are usually effective. Oral anti-candidal agents are alternative
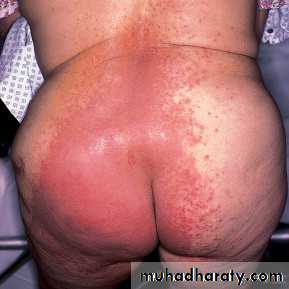
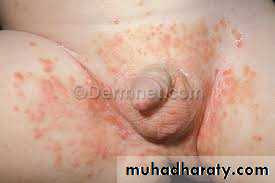
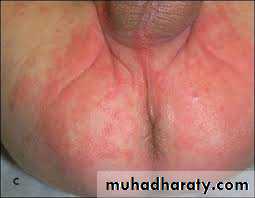
Diaper candidiasis
Differentiated from contact dermatitis by:(1) Involvement of the folds
(2) Occurrence of many small erythematous “satellite” or “daughter” lesions scattered along the edges of the larger patch(es)
Rx: Topical anticandidal agents are effective. Recurrent cases may be associated with gut colonization and need Rx with oral nystatin
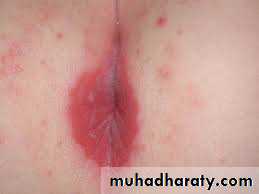
Perianal candidiasis
May present as a pruritus aniPruritus and burning can be very severe
Characterized by erythema, maceration and less commonly fissureRx: topical anticandidal agents are effective. Oral antifungals are alternative
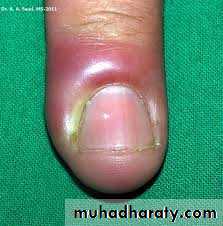
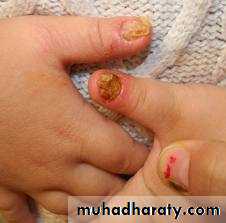
Candidal paronychia
Redness, edema, and tenderness of the proximal and lateral nail foldsUsually the fingernails are affected more than toenails
Patients commonly have an atopic backgroundFrequently seen in diabetics and those who work
Two types:
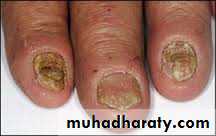
Acute: usually caused by staph. aureusChronic: multifactorial i.e. Irritant dermatitis and candidiasis
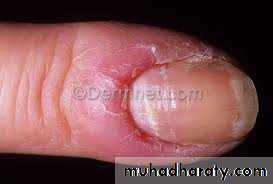
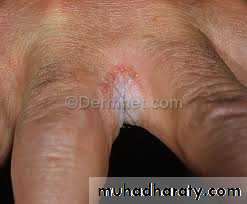
Rx: Avoidance of chronic exposure to water and irritants and bringing the diabetes under control in addition to topical steroids in combination with topical anti-candidal agentsAcute paronychia
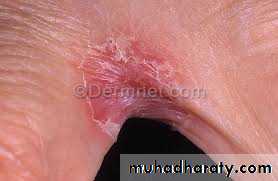
Chronic paronychiaErosio interdigitalis blastomycetica
Oval shaped area of macerated white skin associated with fissures and raw red skin at the center on the web between fingersNearly always between the middle and ring fingers
Moisture beneath the ring predispose to infectionOn the feet it is the fourth web space that is most often involved
Clinically, this may be indistinguishable from tinea pedisRx: drying and topical anticandidal agents
Antifungals
Comment
Spectrum of actionAntifungal agent
In general, the longest course of treatment is for tinea unguium followed by tinea capitis followed by other types of dermatophytosis
Griseofulvin is the first choice for treatment of tinea capitis (4-12 weeks course)
Imidazoles and allylamines are the first choice for treatment of tinea unguium but griseofulvin is not used for tinea unguium because it require a long course (4-6 months to one year)
Dermatophytes, Candida and Pityrosporum
• Imidazoles e.g. ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, clotrimazole:
Dermatophytes
• Allylamines e.g. terbinafinCandida only
• Polyenes e.g. amphotericin B and nystatinDermatophytes only
GriseofulvinCandidid(id reaction)
They are much less common than the reactions seen with dermatophytosis.