INTRODUCTION TO OPERATING SYSTEMS
1.1 General DefinitionOperating Systems OS is a program which acts as an interface between computer system users and the computer hardware.
OS, is low-level software that enables a user and higher-level application software to interact with a computer’s hardware and the data and other programs stored on the computer.
OS performs basic tasks, such as recognizing input from the keyboard, sending output to the display screen, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling peripheral devices such as printers.
It provides a user-friendly environment in which a user may easily develop and execute programs.
Otherwise, hardware knowledge would be mandatory for computer programming and users.
So, it can be said that an OS hides the complexity of hardware from uninterested users.
1.1 General Definition
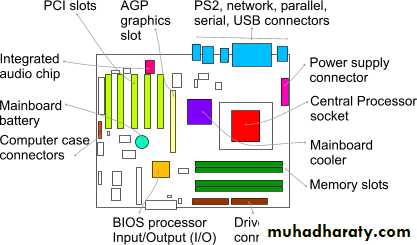
In general, a computer system has some resources which may be utilized to solve a problem. They areMotherboard (Mainboard)
Memory
Processor(s)
I/O
File System
etc.
1.1 General Definition
Mainboard
processor
RAM
1.1 General Definition
The OS manages these resources and allocates them to specific programs and users.With the management of the OS, a programmer is rid of difficult hardware considerations.
OS provides services for:
• Processor Management
• Memory Management
• File Management
• Device Management
• Concurrency Control
1.1 General Definition
Another aspect for the usage of OS is that: it is used as a predefined library for hardware-software interaction.
This is why, application programs apply to the installed OS since they cannot reach hardware directly.
Application Programs
Applecation ProgramsOperating System
Machine Language
HARDWARE
Types of OS
Microsoft WindowsMainframe
DOSOS/2
LinuxMac OS
Operating systems continued…
Introduction to MS-DOSMS-DOS basicsWhat is MS-DOS?
MS-DOS stands for Microsoft Disk Operating System. MS-DOS controls the computer’s hardware and provides an environment for programs to run. This system program must always be present when working with your computer.Why You Need MS-DOS
There are a variety of reasons why you need MS-DOS. A few of them are listed below:• 1. Windows is built upon MS-DOS and it is easy and fast to learn
• programming under MS-DOS as compared to Windows. So, it is good
• for beginners
2. MS-DOS controls the flow of information between you and the computer.
• 3. MS-DOS allows you to store information on your computer.
• 4. MS-DOS allows you to retrieve information stored on your computer.
• 5. MS-DOS interprets and translates the software you have on your computer.
• 6. MS-DOS gives you access to all its function (i.e. saving, copying, and printing files).
When you first turn on your computer, you will see some cryptic information flash by. MS-DOS displays this information to let you know how it is configuring your computer. You can ignore it for now. When the information stops scrolling past, you'll see the following:
C:\> _ (flashing underscore)
This is called the command prompt or DOS prompt. The flashing underscore next to the command prompt is called the cursor. The cursor shows where the command you type will appear.
If your command prompt looks like the sample command prompt above, skip to the following section, "Typing a Command."
If your command prompt does not look like the example, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
cd \
Note that the slash leans backward, not forward. You will learn more about the cd command later in the tutorial. If your command prompt still doesn't look like the example, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
prompt $p$g (Your command prompt should now look like the example)
MS-DOS commands
The Command PromptThis section explains how to type a command at the command prompt and demonstrates the "Bad command or file name" message.
To type a command at the command prompt try this training:
nul Type this letters at the command prompt (you can type the command in either uppercase or lowercase letters): If you make a typing mistake, press the BACKSPACE key to erase the mistake, and then try again.
Press ENTER. (You must press ENTER after every command you type)
The following message appears: Bad command or file name
The "Bad command or file name" message appears when you type something that MS-DOS does not recognize. Because nul is not a valid MS-DOS command, MS-DOS displays the "Bad command or file name" message.
• Now, type the following command at the command prompt:
ver (The following message appears on your screen):
MS-DOS version 6.22 (The ver command displays the version number of MS-DOS)
MS-DOS commands
Typing a Command
To view the contents of a directory
• Type the following at the command prompt:dir (A list similar to the following appears)
Volume in drive C is MS-DOS_6.22
Volume Serial Number is lE49-15E2Directory of C:\
WINDOWS <DIR> 09-08-92 10:27p
TEMP <DIR> 05-15-92 12:09pCONFIG SYS 278 09-23-92 10:50a
COMMAND COM 53014 09-18-92 6:00a
WINA20 386 9349 11-11-91 5:00a
DOS <DIR> 09-02-92 4:23p
AUTOEXEC BAT 290 09-23-92 10:54a
7 file(s) 62931 bytes
8732672 bytes freeMS-DOS commands
Viewing the Contents of a Directory
This is called a directory list. A directory list is: a list of all the files and subdirectories that a directory contains.
In this case, you see all the files and directories in the main or root directory of your drive.
All the files and directories on your drive are stored in the root directory.
MS-DOS Help program is a good companion when you are learning DOS commands. The following table shows five different ways to activate the DOS help program.
• Commands used*
• Description• HELP
• "MS-DOS Help: Command Reference"
• It provides complete, interactive Help information for MS-DOS commands. A full list of commands is shown for selection.
• HELP [command name]
• "MS-DOS Help: [command]"
• Provides complete, interactive Help information for the specified MS-DOS command.
• You can see the specific help information including syntax, notes and examples.
• Example: HELP XCOPY
• FASTHELP [command]
• Provides summary Help information for MS-DOS commands.
• It includes the description of the specific command, syntax of using it, and the explanation of the available switches.
• Example: FASTHELP XCOPY
• [command] /?
• Provides summary Help information for MS-DOS commands. It includes the description of the specific command, syntax of using it, and the explanation of the available switches.
• Example: XCOPY /?
MS-DOS Help
• CD Displays the name of or changes the current directory.
• CLS Clears the screen.
• DEL Deletes one or more files
• COPY Copies one or more files to another location.
• BREAK Sets or clears extended CTRL+C checking.
• CALL Calls one batch program from another.
• CHDIR Displays the name of or changes the current directory.
• DATE Displays or sets the date.
• DIR Displays a list of files and subdirectories in a directory.
• EXIT Quits the COMMAND.COM program (command interpreter).
• MD Creates a directory.
• RENAME Renames a file or files. REN Renames a file or files.
• RD Removes a directory.
• TYPE Displays the contents of a text file.
Brief Description of Internal MS-DOS commands
Brief Description of Internal MS-DOS commands continues….
• FOR Runs a specified command for each file in a set of files.• GOTO Directs MS-DOS to a labelled line in a batch program.
• IF Performs conditional processing in batch program.
• PATH Displays or sets a search path for executable files.
• PAUSE Suspends processing of a batch file and displays a message.
• PROMPT Changes the MS-DOS command prompt.
• REM Records comments (remarks) in a batch file or config.sys.
• SET Displays, sets, or removes MS-DOS environment variables.
• VERIFY Directs MS-DOS to verify that your files are written correctly to a disk.
EXTERNAL commands
External commands are MS-DOS utilities / programs. These are the .EXE or .COM programs located on your hard drive. They are normally placed under C:\DOS, the default directory. MS-DOS will load external commands if and only if you instruct to execute them at the DOS prompt and /or in a batch program.