Surgery Lce 3 Dr.Usama
EMPYEMA & LUNG ABSCESS
Empyema
accumulation of pus in the pleural space whether it is localized (encapsulated) or
generalized involving the entire pleural space.
Pathogenesis:
Acute or Exudative phase
:
Thin pus,Mobile lung(expandable),Thin pleura
Trasitional or Fibrinopurulent phase: Turbid fluid viscus,thick pleura, Less
expandable lung
Chronic or Organization phase: fluid is viscus,thick pleura,restricted lung
Infection of the pleural space → inflammatory changes → serous exudation → fibrin
deposition on the pleural surfaces → invasion by blood vessels from adjacent lung and
chest wall → granulation tissue → fibrous tissue → progressive thickening of the wall of
the empyema
Secondary changes in surrounding structures as empyema continues:
Ribs drawn together & lose mobility
Diaphragm elevated and fixed
Mediastinum shifted
Lung encased in a rigid covering of fibrous tissue and is immobile and functionles
Causes:
1-Pulmonary infection : Lobar pneumonia,lung abscess
2-Trauma : Penetrating trauma,Postoperative (post-pneumonectomy ),Esophageal
perforation
3-Extrapulmonary spread : Osteomyelitis of dorsal spine, subphrinic abscess
4-Aspiration of pleural effusion (done under septic technique)
5-Ruptured emphysematous bullae and spontaneous pneumothorax → empyema
6-
Generalized sepsis
Microorganisms:
Surgery Lce 3 Dr.Usama
Most common organisms are streptococcus ,pneumococcus ,Staph aureus
Clinical features
constitutional symptoms of fever, malaise, tachycardia, anorexia, and weight loss in
late presentation
Pleuretic chest pain and sensation of heaviness
Shortness of breath and cough with purulent sputum
On Examination: signs of infection + signs of pleural effusion
Complications:
Invasion of the chest wall → osteomyelitis → empyema necessitatis
BPF( Bronchopleural fistula)
Mediastinal abscess
Septicemia
Metastatic abscess
Fibrothorax
Diagnosis:
1-CXR:
PA and lateral views show effusion, air fluid level
2-Thoracocentesis and fluid analysis :
Culture and sensitivity, gram stain, pH,, glucose, protein, LDH
3-Sputum culture:
Is often helpful because organisms responsible for pneumonia are a frequent cause of
empyema.
TB and fungal infection
4-Bronchoscopy: To exclude intrabronchial tumor or foreign body
5-Ultrasound
6-CT scan
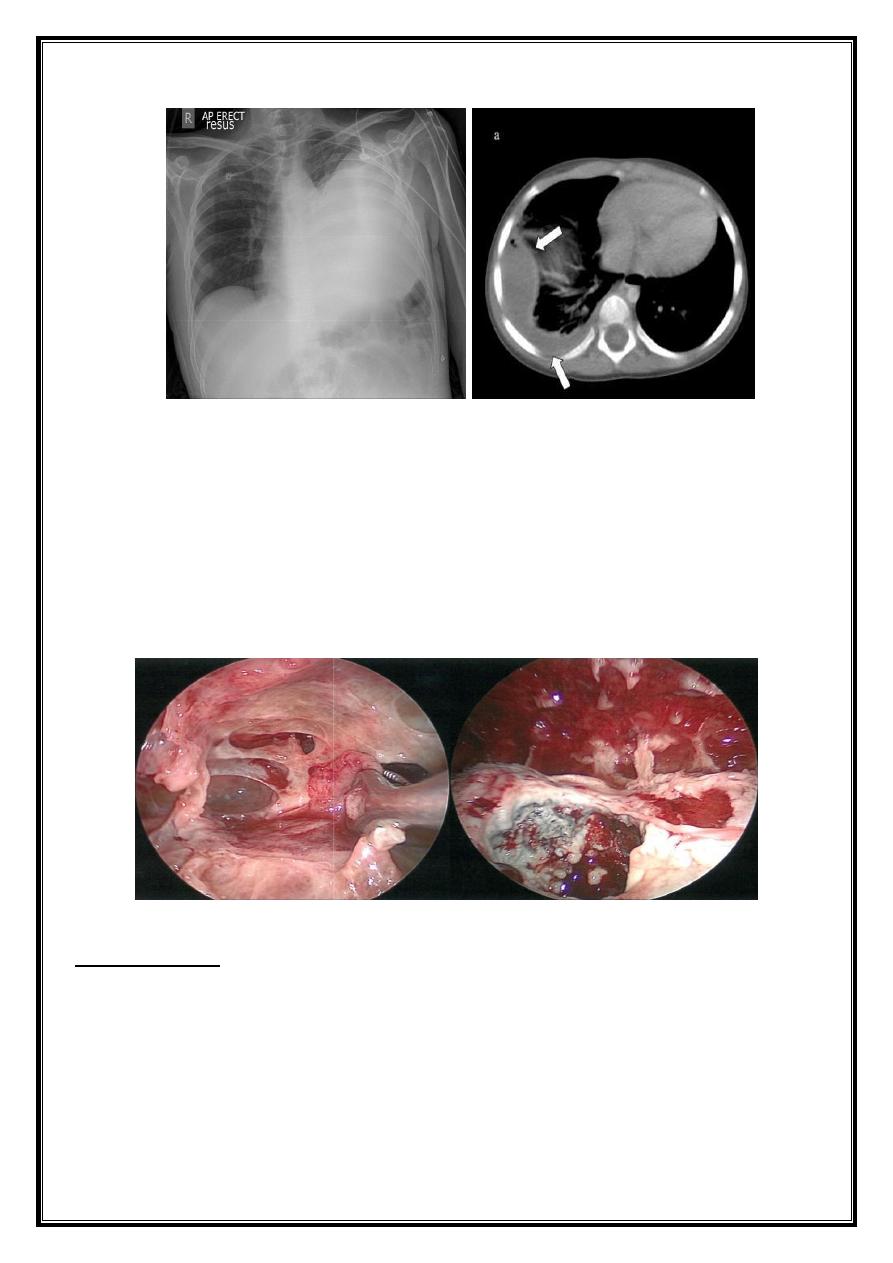
Surgery Lce 3 Dr.Usama
Treatment
1- Thoracocentesis : for diagnostic and therapeutic measures usualy for an early acute
phase
2- tube thoracostomy : done when there is large and thick fluid
3- Image guided catheter placement with fibrinolytic agents : for those where the 2
nd
option failed to evacuate the pleura
4- VATS or Thoracotomy : decortications with pleurectomy
L
UNG
A
BSCESS
localized area of suppuration and cavitation in the lung
Etiology:
1-Primary necrotizing pneumonia:Aerobic,Anaerobic
2- Aspiration pneumonia:Anesthesia,Stroke
3- Bronchial obstruction :Neoplasm,Foreign body
Surgery Lce 3 Dr.Usama
4-Complication of systemic sepsis
5-Complication of pulmonary trauma :Infected hematoma
6-Direct extension from extra-pulmonary infection: Pleural empyema, subphrinic
abscess
Predisposing factors :
1-Post-operatively
2-Systemic illness
3-Malignancy (especially of lung and oropharynx)
4-Prolong use of corticosteroids, immunosuppressive or radiotherapy
5-Long term use of antibiotics
Clinical picture
history of upper respiratory tract infection with high fever, malaise, fatigue, and often is
toxic with weight loss
Recent onset of cough with copious foul smelling sputum
Chest pain
Hemoptysis
Investigations;
CXR : Air fluid level is only seen in upright film
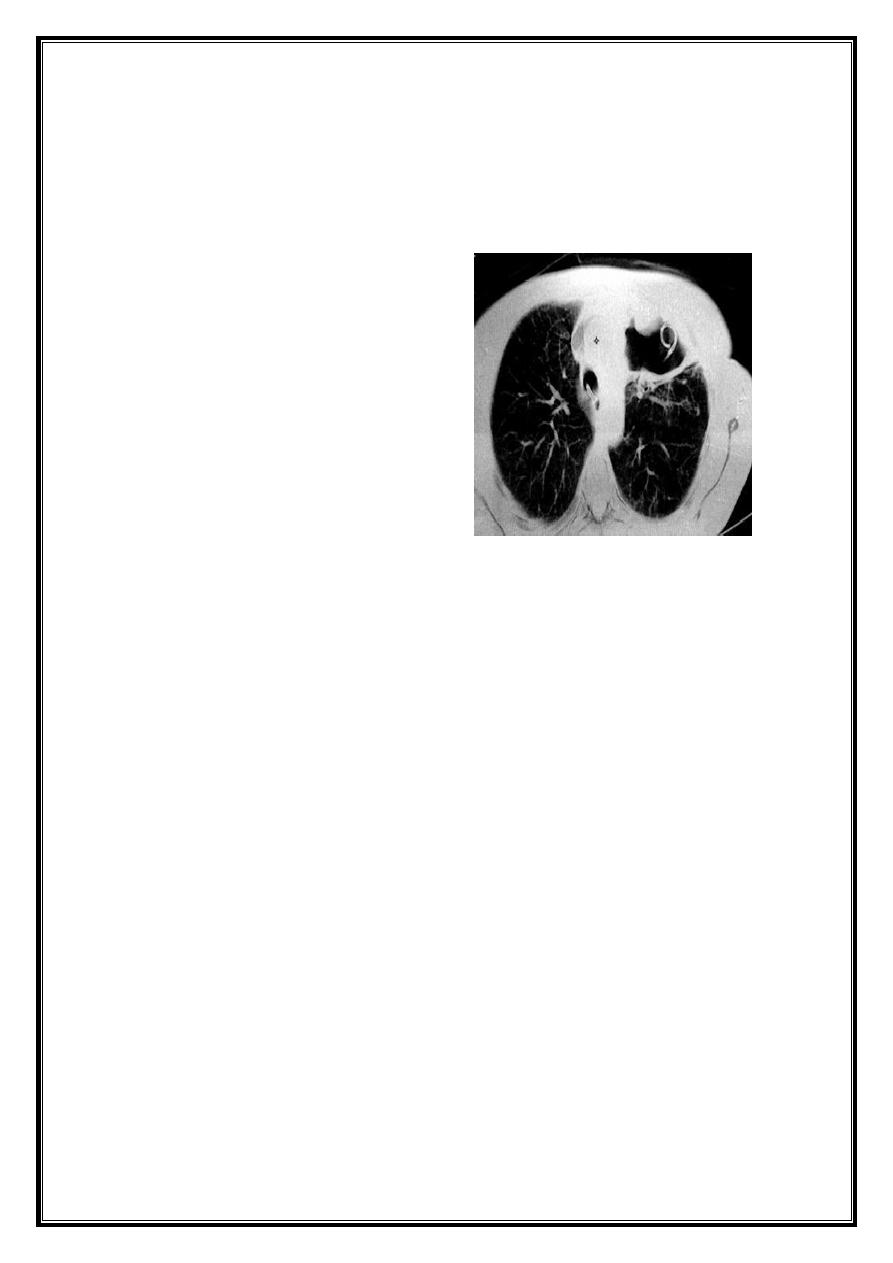
CT san : clarify the diagnosis when the CXR is equivocal
Bronchoscopy : To exclude or confirm Ca
To diagnose and remove foreign bodies
To drain an abscess
To obtain a bronchial wash for C/S
Differential diagnosis:
1-Cavitating lung carcinoma
2- Infected lung cyst or bullae
3-TB
4- Bronchiectasis
Differential diagnosis of a febrile patient with copious production of foul sputum:
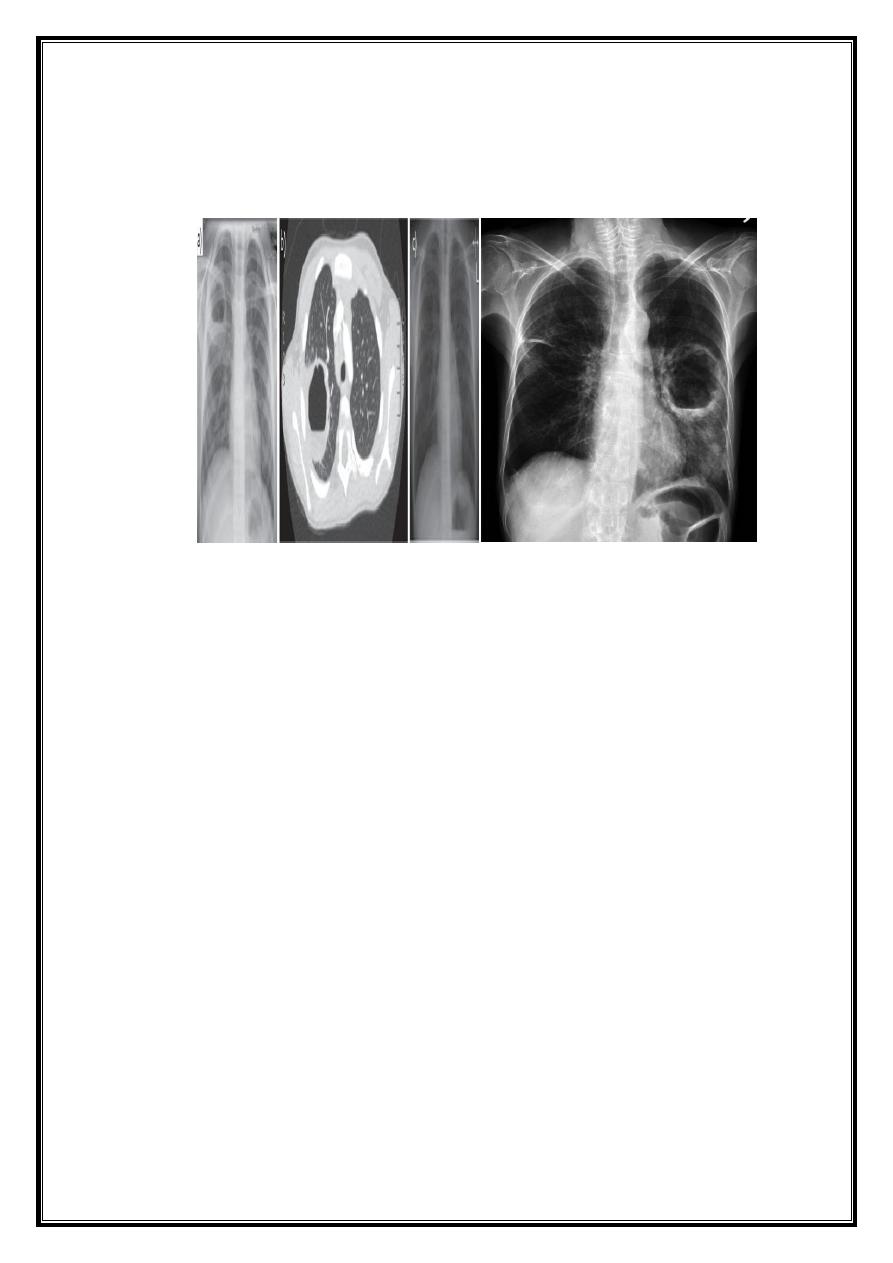
Surgery Lce 3 Dr.Usama
Lung abscess
Bronchiectasis
Cavitating carcinoma
Medical Treatment:
Identification of the caustic microorganism,Prolonged antimicrobial therapy
Surgical :
Indications of surgical treatment:
Lack of response to medical treatment
Suspeicion of malignancy
Significant and/or recurrent hemoptysis
Complications of lung abscess : Empyema,BPF
Options of surgical treatment:
External drainage ie. tube pneumonostomy
Pulmonary resection :lobectomy,segmentectomy,wedge resection and rarely
pneumonectony
Complications of lung abscess:
Massive hemoptysis
Endobronchial spread to other lung portions
Surgery Lce 3 Dr.Usama
Septicemia
Metastatic brain abscess
Rupture into pleural cavity → Empyema
BPF
