1
Forth stage
Surgery(Urology)
Lec-4
د.محمد
الشهواني
21/10/2015
URINARY SYSTEM INJURIES
About 10% of all injuries in the emergency room include the genito - urinary system.
Renal injuries are the most common type of urinary system injury.
Causes
:
1-Blunt trauma: RTA, sport, FFH, blunt abdominal trauma and fights.
2-Penetrating trauma: stab, messiles, shells and bullets, (high or low velosity).
3-Surgical and endoscopic causes.
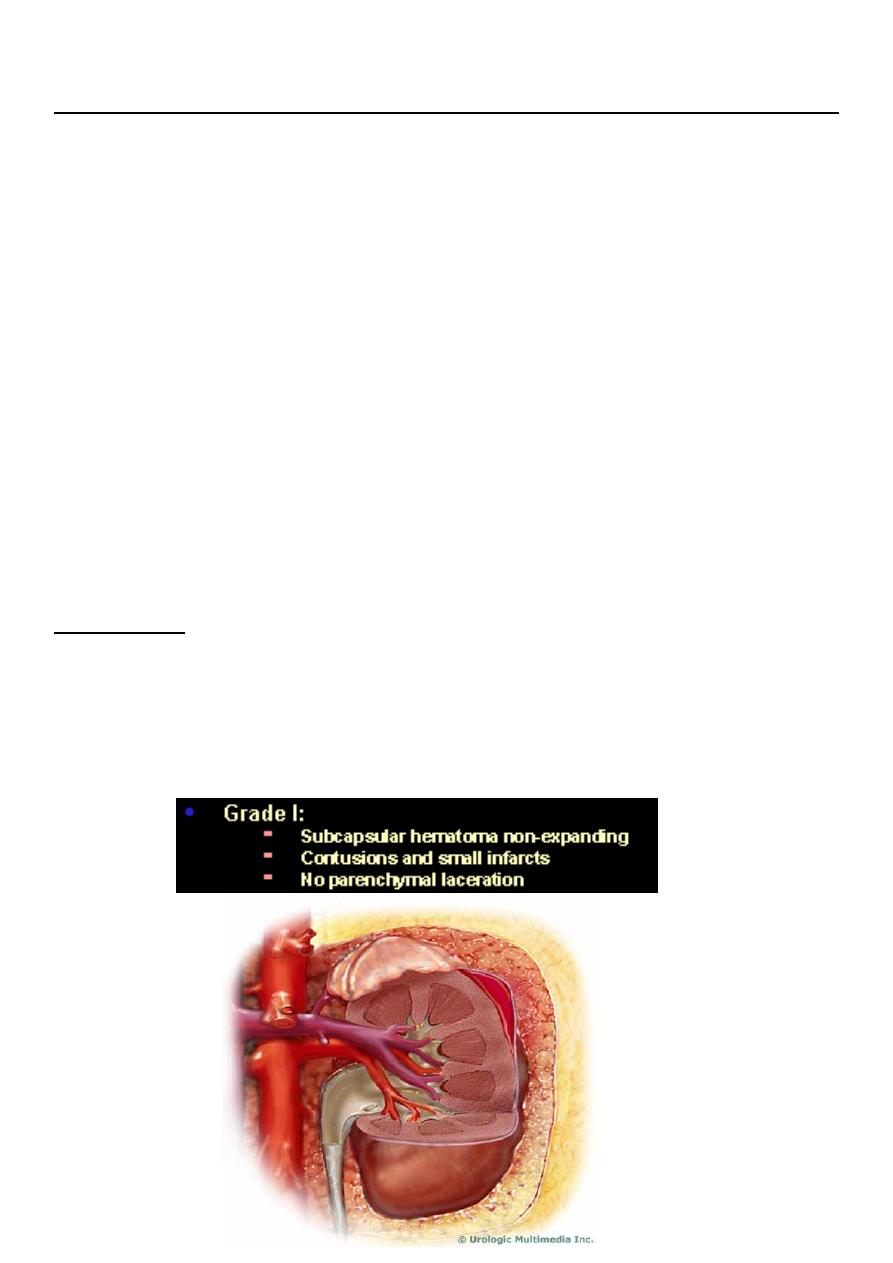
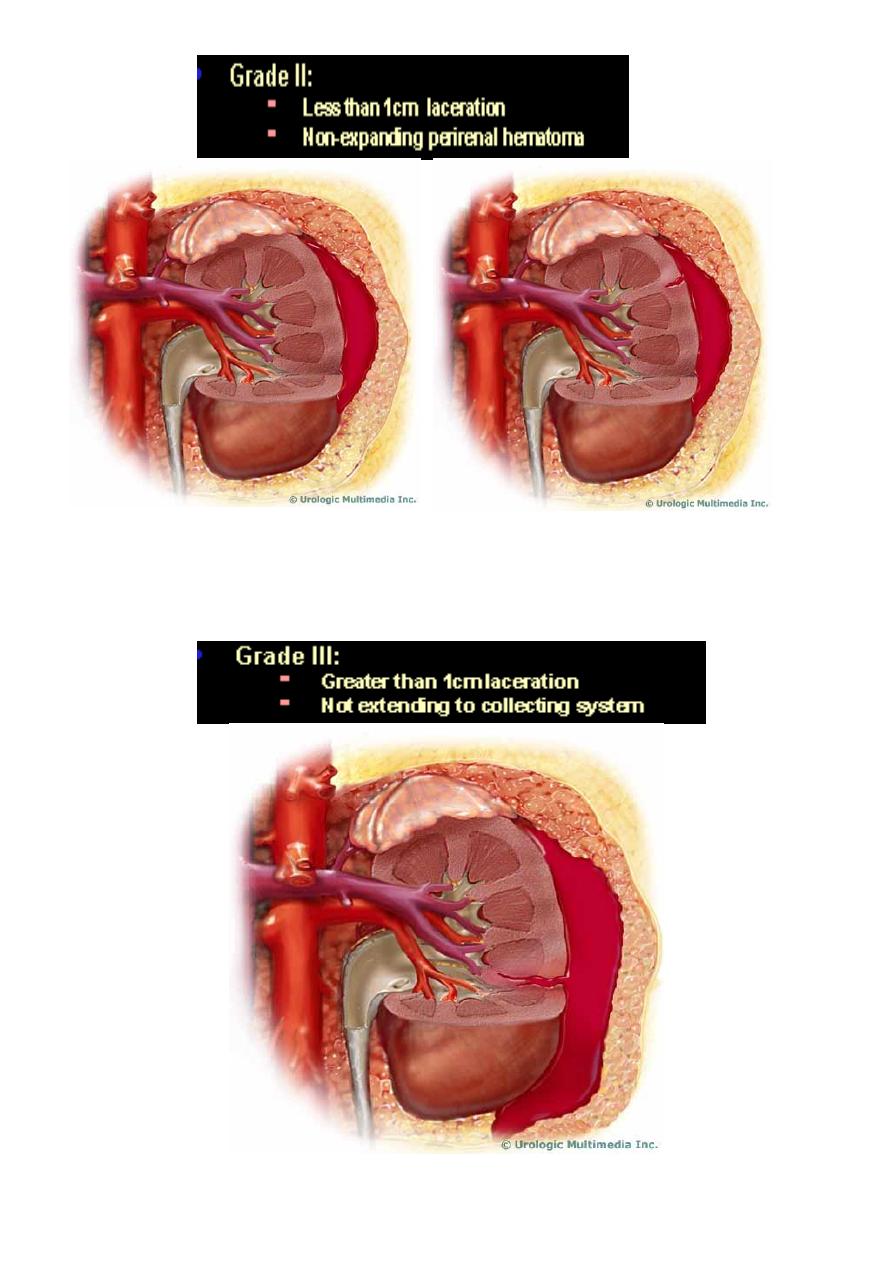
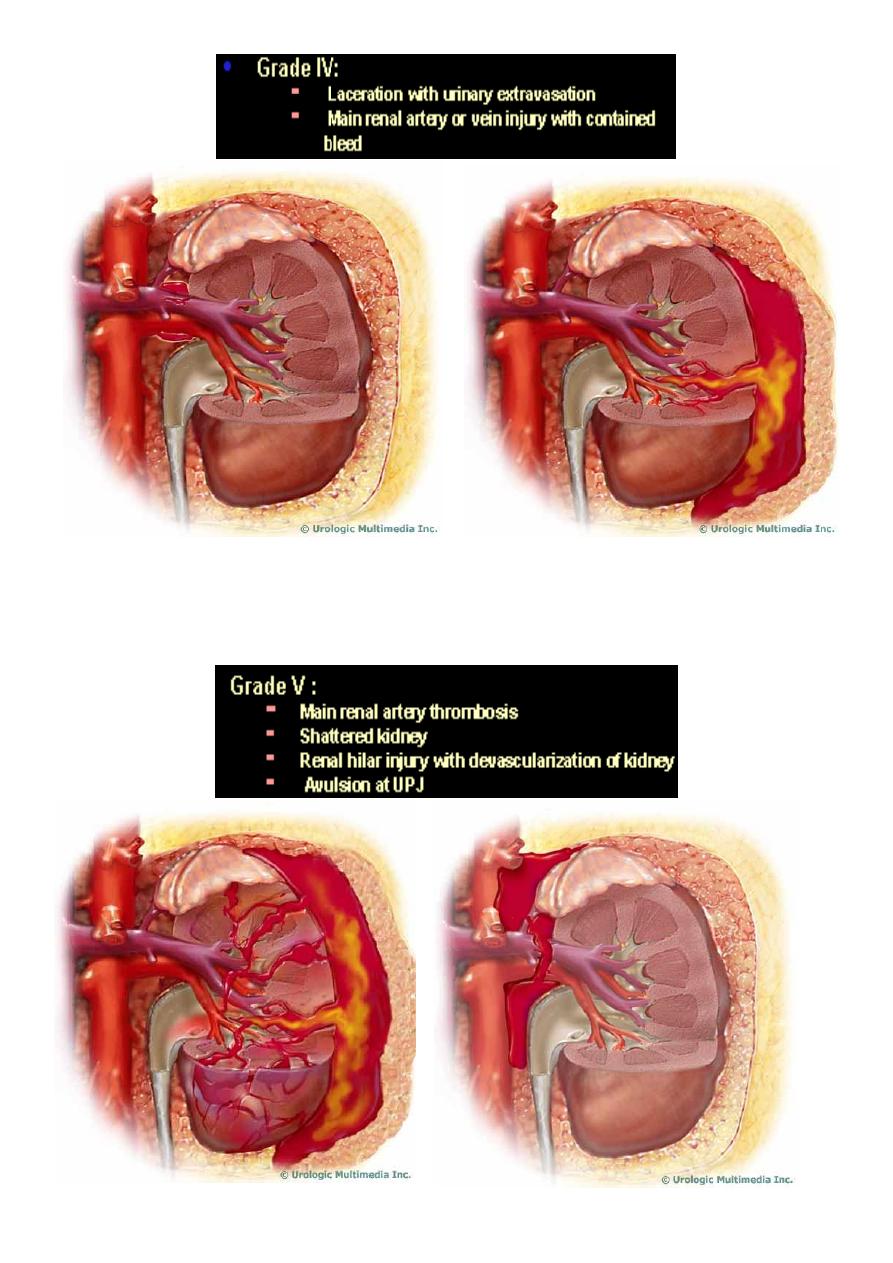
Renal injuries
PRENCEPLES:
1- In 85% it’s of minor degrees.and can be treated conservatively
2- In 80% of high grade, there is associated abdominal visceral injury.
3- Diseased kidneys ( hydronephrosis, tumor or cyst) are more readily injured with minimal
trauma.
2
3
4
Clinical picture
Haematuria: is the most important symptom or sign of renal injury, microscopic or gross,
early or late.
Degree of haematuria does not reflects the severity of renal injury.
In severe hematuria clot retention may occure.
Abdominal pain:
or acute abdomen.
Signs of renal injury:
Ecchymosis, bruises in the flank, shell inlet and outlet, acute abdomen, palpable loin
masses of hematoma or urinoma.
Intra-peritoneal leak may cause ileus.
Fracture lower ribs and transverse processes are indirect signs of renal injury.
Investigations:
GUE: hematuria.
Renal function test: usually normal.
Hematocrit: usually normal.
5
Imaging study
U/S: retroperitoneal collection indicats hematoma or urinoma.
KUB: # ribs or transverse process and soft tissue shadow of blood or urine collection.
IVU: normal,or contrast leak or non-functioning kidney (avulsion).
Renal angiography: the best diagnostic tool for vascular injury especially avulsion, but
it’s invasive and needs special center.
CT scan: shows the extent of renal parenchymal laceration, urinary extravasation and
extent of retroperitoneal hematoma.
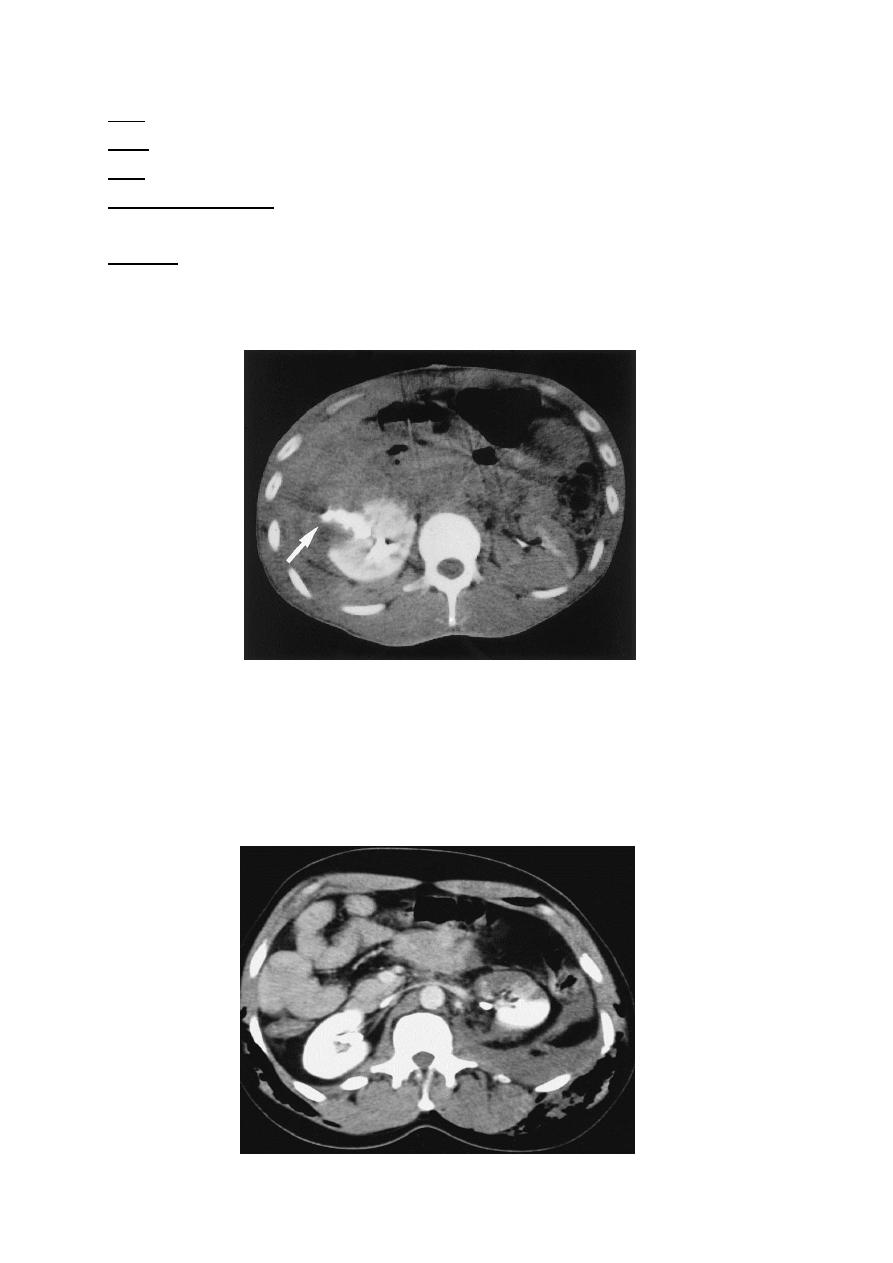
Computed tomographic scan of a right renal stab wound (grade IV), demonstrating
extensive urinary extravasation and large retroperitoneal hematoma.
Segmental renal infarction; blunt trauma.
6
Management
ABCDE
A: Airway & cervical spine protection.
B: Breathing.
C: Circulation & control of ext. bleeding.
D: Disability or neurological status.
E: Exposure (undress) & environment (temperature control)
Renal injury management:
In most cases renal injury is mild form and treated conservatively, includes:
Bed rest, hydration, pulse and blood pressure monitoring, analgesia and prophylactic
antibiotics .monitoring the the urine color for the resolution of hematuria.
SURGERY CONSIDRED IF:
1-Hemodynamically is not recoverable.
2-The renal vessels are injured.
3-Other organs involvement cannot be excluded.
4-Expanding perinephric hematoma.
5-Pulsatile perinephric hematoma.
6-high grade renal injury
7 .Urin extravasation.
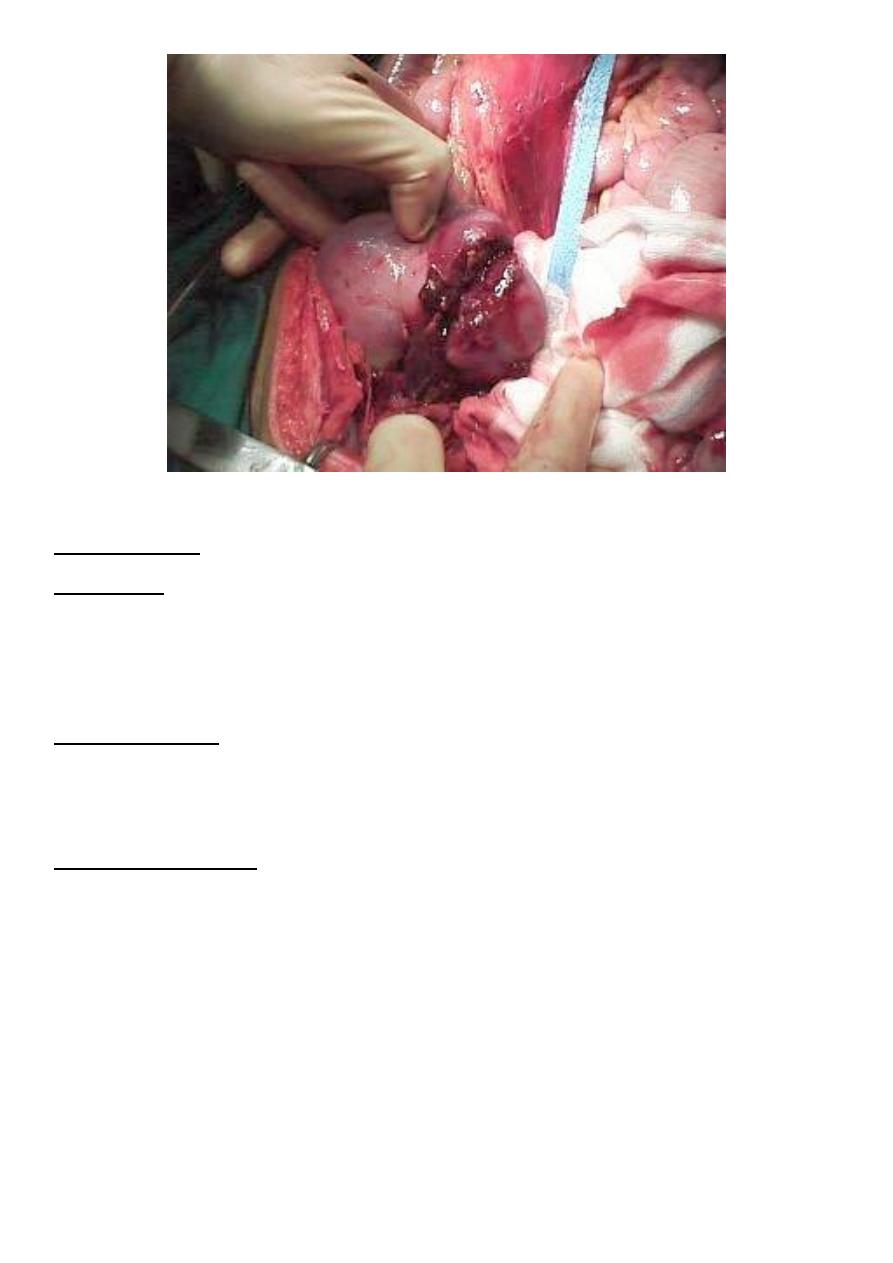
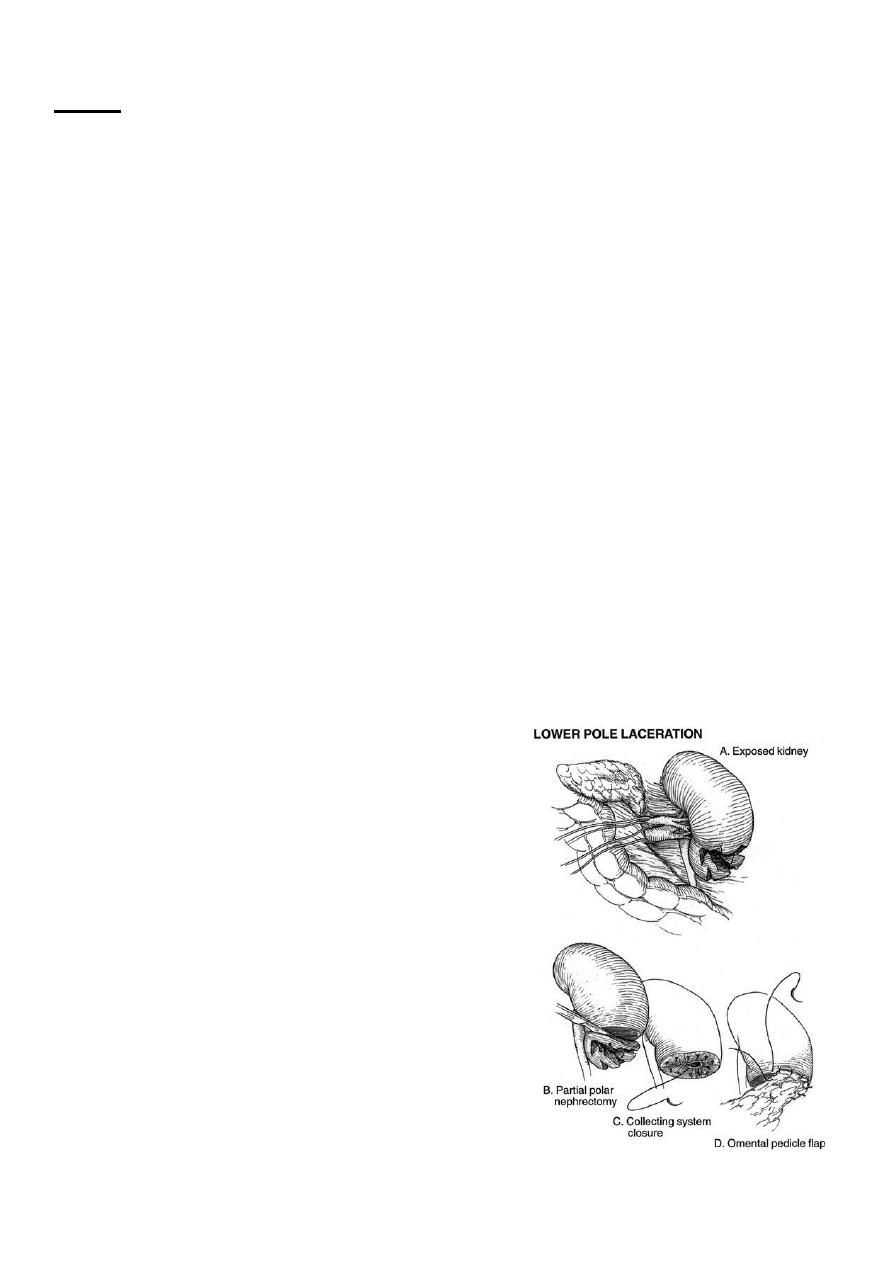
Technique for partial nephrectomy
7
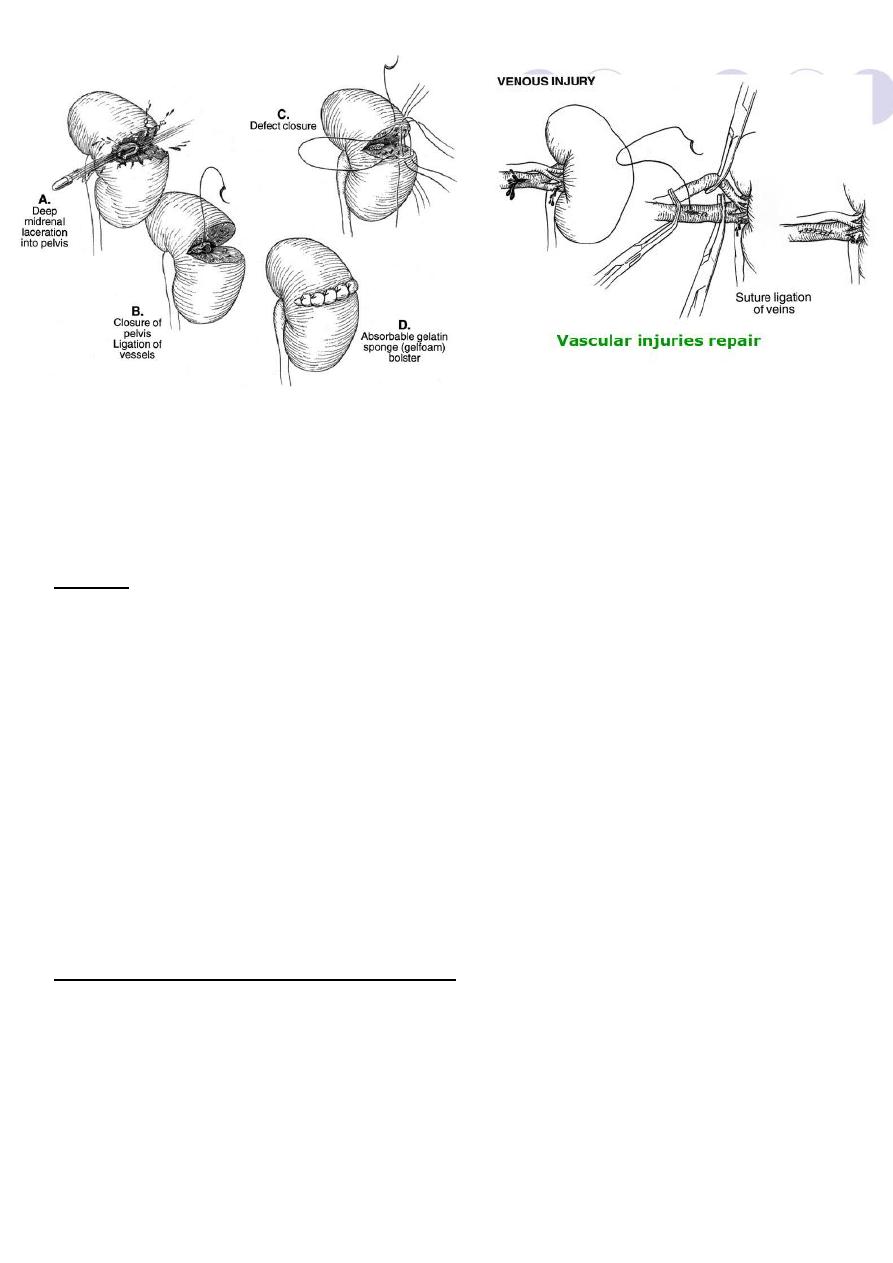
Technique for renorrhaphy
Ureteric injury
Ureteric injury (rare)
Causes:
1- Gun shot, bullet and shells.
2- Hyperextension injury of the spine.
3- Difficult pelvic surgery
specially gynaecological (hysterectomy &CS).
4- Endoscopic: ureteroscope, TUR & dormia basket stone extraction.
Types:
perforation, division or ligation
Ligation: mainly in difficult histerectomy
1- Asymptomatic resulting in renal atrophy.
2- Ureteric colic or pain post operatively with or without fever of UTI, and tender renal
angle.
3- In single kidney, unuria
4-if both ureters ligated it result in unuria with uremia (obstructive uremia).
8
Division:
Result in urine collection (urinoma) then super added by infection resulting in abscess
formation, fever, rigor and abdominal pain.
More commonly urine leak from the wound or vagina (ureterocutaneous or ureterovaginal
fistula) at 10
th
post operative day.
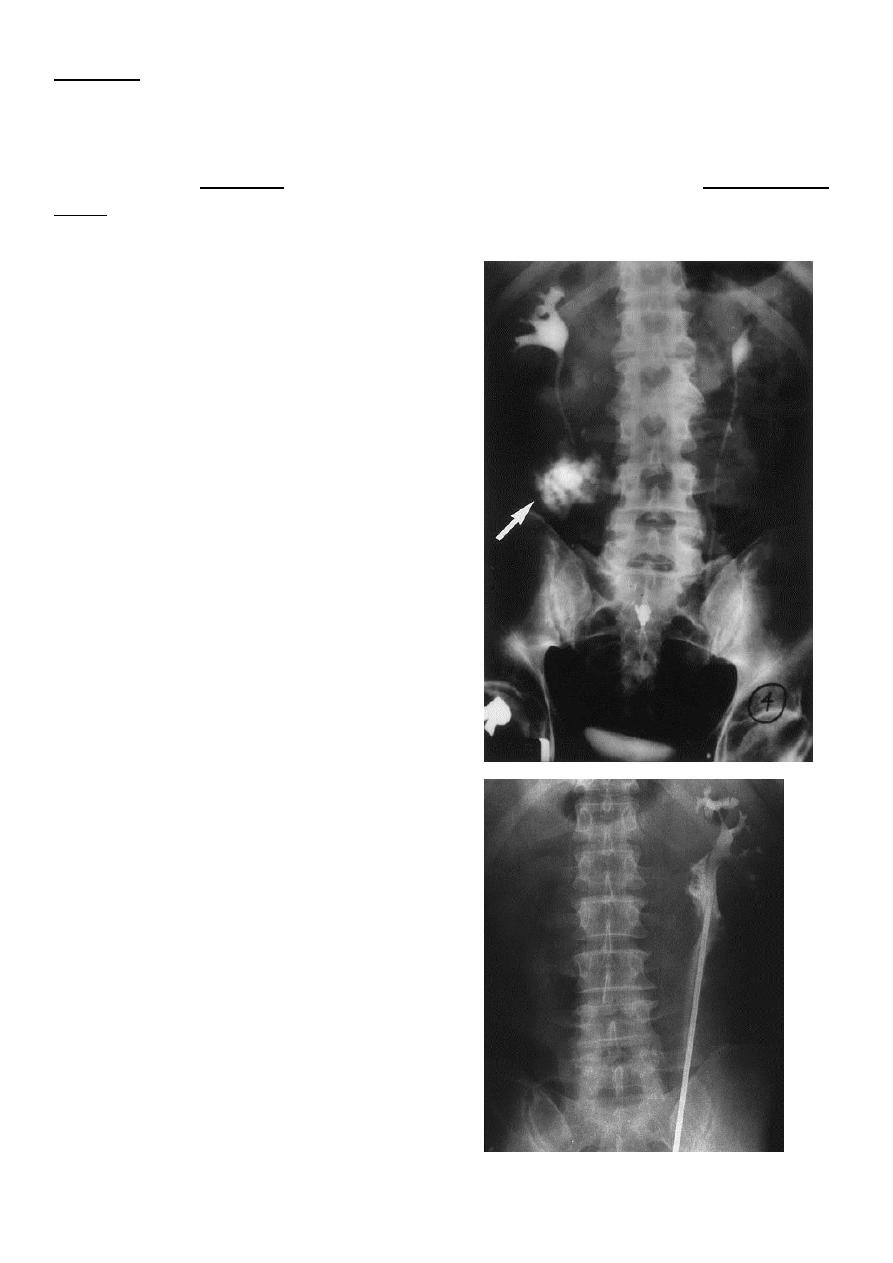
Excretory urography demonstrating
extravasation in the upper right ureter
consequent to stab wound. Note lack of
contrast below the the site of injury
indicating complete ureteral transection.
Ureteroscopy with a rigid ureteroscope
to attempt retrieval of a calculus from the
midureter resulted in perforation

9
Management of ureteric injury
Prevention is better than treatment.
pre-operative stenting of ureter will fasillitate easy identification of the ureter during
difficult pelvic surgery
So proper identification of the ureter before uterine artery ligation in hysterectomy will
prevent ureteric injury
Aim of management is to regain the continuity of the ureter, preserving renal function and
decreasing the morbidity.
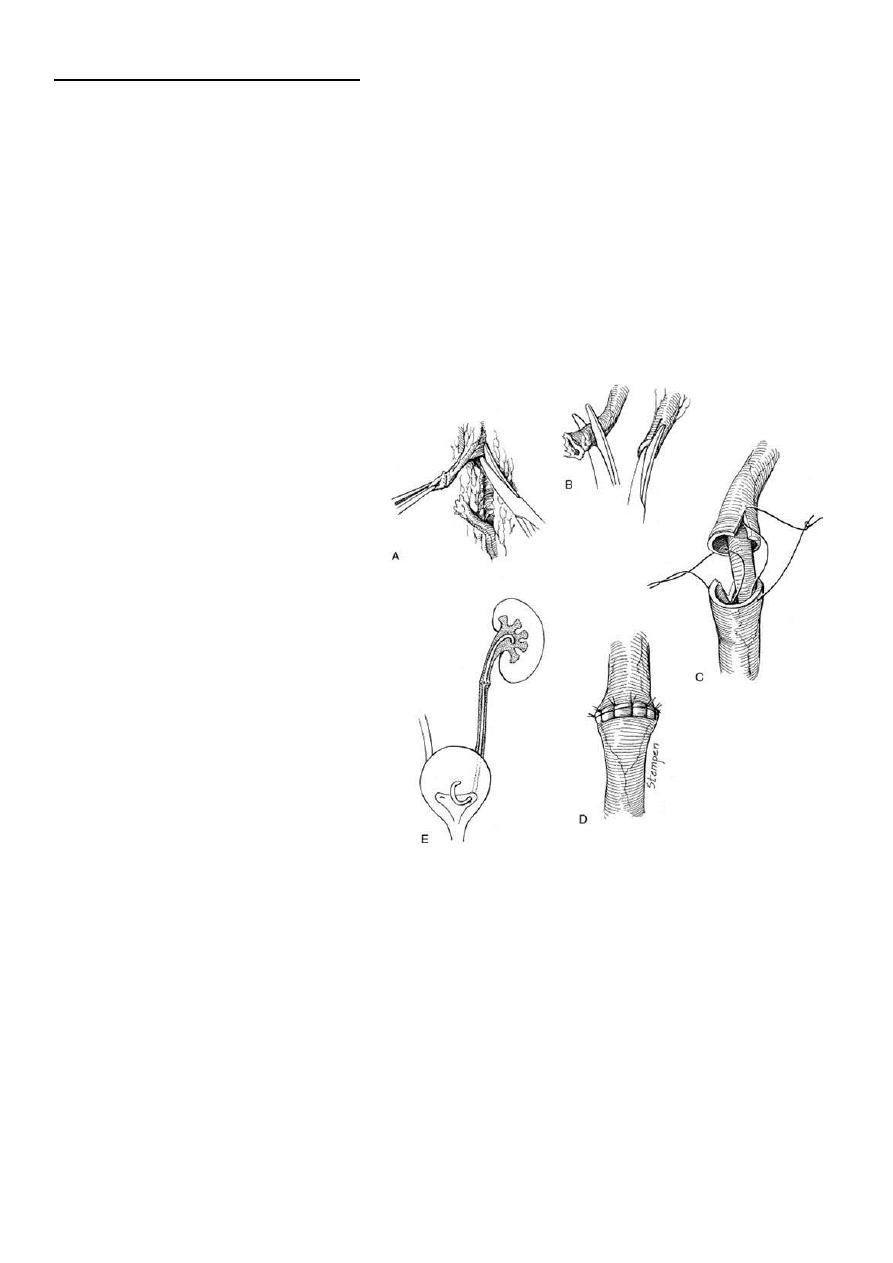
Technique of
ureteroureterostomy
after traumatic
disruption
End to end anastamosis should be
Debridment of ureteric ends
With out tention
Water tight
Spatulated
Stenting
Drainage
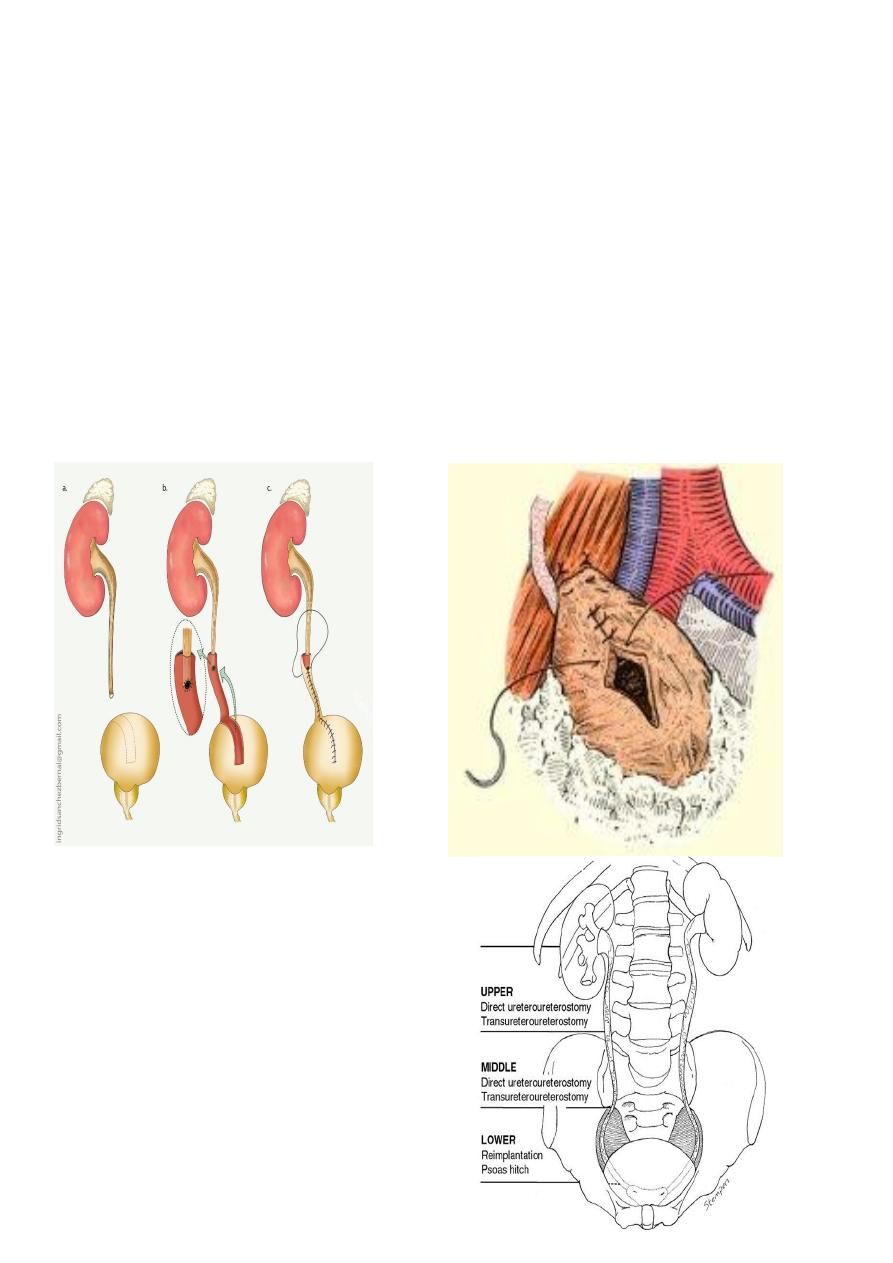
11
Surgical options in ureteric injury:
Reimplantation to the bladder.
Psoas hitch.
Boari’s flap.
Ileal transposition.
Using the appendix to bridge the defect in the right side.
Auto-transplantation.
Transureteroureterostomy
Boari flaf psoas hitch
Suggested management options for ureteral
injuries at different levels.
