1
Gynecology L1
Miscarriage and early pregnancy loss
Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy is always a cause for concern . It may
occur in cases of miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy , or with a cervical lesion
such as a polyp or carcinoma . On many occasions no certain cause of early
bleeding may be found .
Miscarriage :
- Is a pregnancy that ends spontaneously before the 24
th
week of
pregnancy(before the fetus has reached a viable gestational age) .
- Observation suggests that 10 – 20 % of clinically recognized pregnancies end
in early miscarriage , but the loss of very early embryos is greater than this .
The most common time for clinically evident abortion to occur is between 7 and
13 wks .
Aetiological factors :
Despite along list of aetiological factors , the cause of a particular miscarriage is
often uncertain .
1. Malformation of the zygote :
A common cause of miscarriage is an abnormality of the fetus severe enough
to cause fetal death . About 70% of these are caused by chromosomal
abnormalities , for which either parent may be responsible , although they often
arise from spontaneous , unexplained mutation in the zygote itself .
Types of chromosomal abnormalities :
a. Autosomal trisomies ( the most common ) with incidence 30 – 35 % ex:
trisomy 21 , 18 , 13 .
b. Triploides and tetraploidies .
c. Monosomy X ( Turner syndrome ) .
d. Translocation in 1.5 % .
- The incidence increase with increase maternal age .
2
2. Immunological rejection of fetus :
a. Investigations of maternal immune response to her pregnancy have now
focused on the complex interaction of immune and endocrine factors acting at
endometrial level .
- Hypotheses on immunodystrophism in which cytokines are being evaluated in
the context of implantation & embryonic growth will examine the relationships
between migrating trophoblast and the large granular lymphocytes ( which have
natural killer cell activity and under endocrine control) .
b- Immunological disorders :
1. Congenital ( thrombophillia ) .
2. acquired ( antiphospholipid syndrome ) .
3. Chronic medical diseases :
chronic renal failure , congenital heart disease , Tuberculosis ( TB ) , sickle ,
cell disease .
4. Endocrine disorders :
- Diabetes if the disease is not adequately controlled .
- Hypothyroidism , luteal insufficiency ( insufficient production of progesterone
by the corpus luteum before the placenta is fully formed will lead to inadequate
development of the deciduas and miscarriage ) , and polycystic ovarian
syndrome .
5. Infections :
a. Causing congenital abnormality like : Cytomegalovirus infection , rubella ,
toxoplasmosis , vaccinia and listeriosis .
b. Acute febrile illness like : malaria , Salmonella typhi , measles , brucella , and
mycoplasma hominis .
6. Uterine abnormalities : Mainly 2
nd
trimester loss )
: which include :
a. Uterine septa .
b. bicornuate uterus .
3
c. Endometrial adhesions ( post curettage or asherman"s syndrome ) .
d. Big fibroid which is closely related to the cavity .
e. Cervical incompetence : Previous lacerations of the cervix involving the
internal Os may be due to over vigorous surgical dilatation of the cervix or
cone biopsy or very rarely the cervical weakness is of congenital origin .
So the unsupported membranes bulge through the cervix and rupture ,
miscarriage follows .
7. Trauma :
a. Direct trauma to uterus as gun shot .
b. Indirect like surgical removal of ovary containing corpus luteum of
pregnancy .
8. Chemical agents :
Like tobacco , anesthetic gases , Arsenic compound , benzene , pesticides ,
lead , formaldehyde , and mercury .
9. Drugs :
Prostaglandins ( PGs ),PG analogue ex misoprostol , ergot derivatives
( methergene ) , and cytotoxic agent .
10. Psychological upset :
11. Sever malnutrition , especially vitamin E deficiency .
Pathological – Anatomy :
In the first trimester of pregnancy the attachment of the chorion to the
decidua is so delicate that separation may follow strong uterine contractions
produced by any cause . The resulting haemorrhage into the choriodecidual
space leads to further separation .
In other cases fetal death precedes uterine contractions , which may occur some
days later , or due to inadequate placentation , there's defect in transformation of
the spiral arteries and a reduced trophoblastic penetration into the decidua .
- The decidua basalis remain in the uterus , and in the majority of cases the
embryo , with its membranes & most of the decidua capsularis , expelled .
4
- In some cases the gestation sac is retained in the uterus for days or weeks as a
missed miscarriage . The embryo is reabsorbed and layers of blood clot collect
around it to form a " carneous mole " .
By 12
th
week , the placenta is a definite structure , and if it happens after this
time the process of miscarriage is similar to that of labour .
Bleeding and painful contractions are followed by dilatation of the cervix ,
rupture of the membranes and expulsion of the fetus and placenta .
If all the conceptus is expelled normal uterine involution follows , but frequently
part of the placenta is retained with some blood clot .
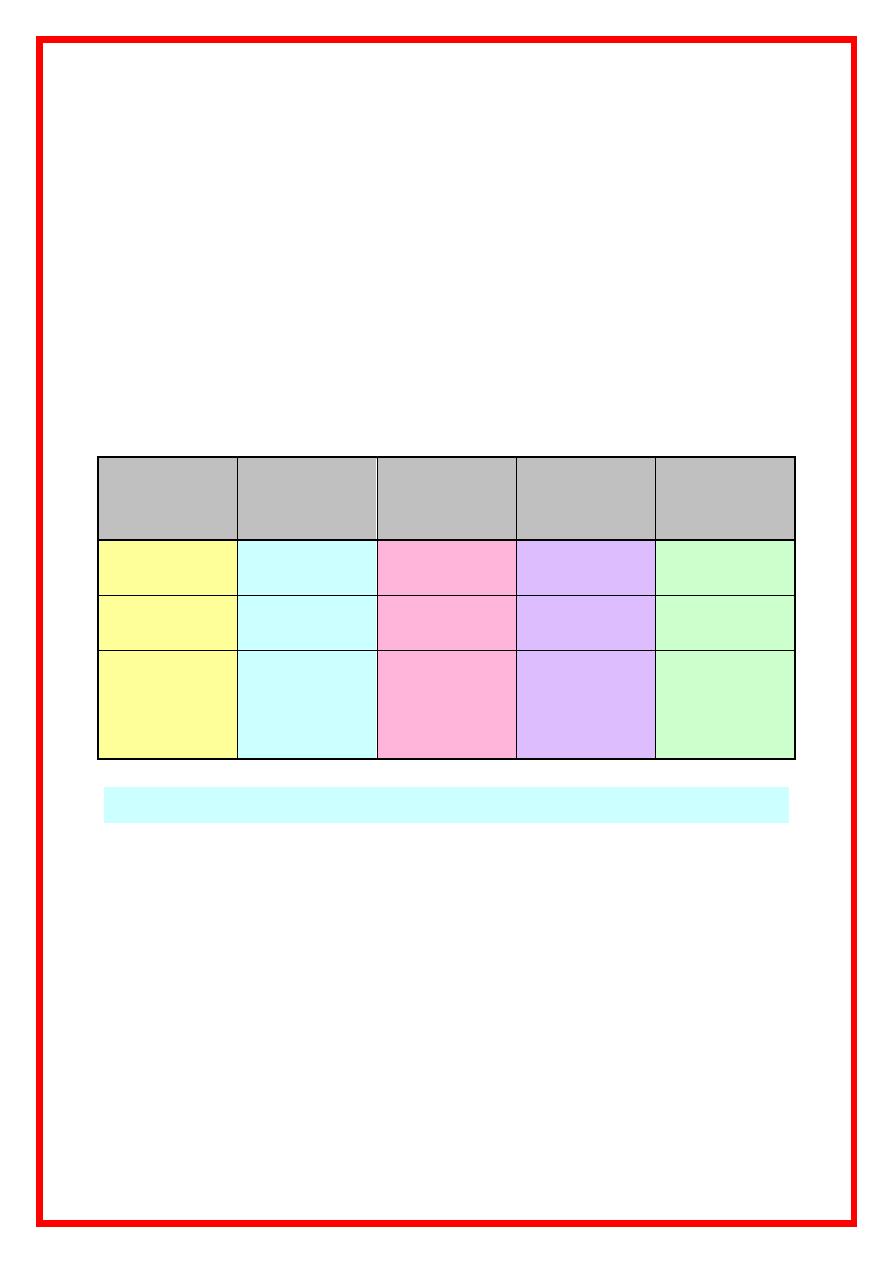
Modern Pregnancy loss classification :
Type loss
Typical
gestation
( weeks )
Fetal heart
activity
Principal
ultrasound
finding
Beta HCG level
Biochemical
loss
< 6
Never
Unknown
location
Low then fall
Early pregnancy
loss
6 – 8
Never
Empty sac
Initial rise then
fall
Late pregnancy
loss
> 10
Lost
Crown-rump
length and fetal
heart activity
identified .
Rise then static
or fall
Clinical varieties of miscarriage :
- The following terms are used to describe varieties of miscarriage :
1. Threatened 5. Septic
2. Inevitable 6. Missed
3. Complete 7. recurrent .
4. Incomplete .
1. Threatened miscarriage :
Vaginal bleeding occurs without dilatation of the cervix and with very little or
no pain .
- Incidence : 25% of all pregnancy complicated by threatened abortion .
5
- Prognosis : If the bleeding heavy , or increases , the prognosis is bad , but the
miscarriage should not be regarded as inevitable until cervical dilatation begins .
- There may be repeated short episodes of bleeding without the miscarriage
becoming inevitable .
Management :
The diagnosis usually based on clinical history& examination , and by
ultrasound ( usually transvaginal one ) , which is used to differentiate
miscarriage from other type of early pregnancy complication as ectopic
pregnancy or molar pregnancy , also to know the type of miscarriage .
Also the ultrasound examination can determine the size of the fetus and show it
the fetal heart is beating ; it can also give some clue to dilatation of the cervix ,
and to see subchorionic haematoma if present .
There's no specific treatment and the essential task is to establish that the
miscarriage is threatened and is not becoming inevitable .
- The patient may need to restrict some forms of activity , bed rest , avoidance of
sexual intercourse until warning signs are disappeared .
- Clinical surveillance including weekly ultrasound examination , and an
evaluation of serum measurements of the beta subunit of hCG , progesterone
and pregnancy associated placental protein A( PAPP-A) .
- Progesterone therapy : Its role is contraversial , It's relax smooth muscle
( myomterial muscles ) , but it may increase the risk of incomplete miscarriage .
- HCG injection may have a role in treatment of threatened miscarriage ( by
support the corpus luteum of pregnancy and stimulate it to produce more
progesterone ) .
2. Inevitable miscarriage :
The process is now irreversible . The cervix is open , there's more bleeding
and rhythmical and painful uterine contractions continue .
- The uterus usually expels its contents unaided .
All examinations are carried out with careful aseptic technique . Analgesics such
as pethidine may be required . If haemorrhage become sever or the miscarriage
is not quickly completed ergometrine or syntometrine , phostaglandins is
6
required and inevitable miscarriage can be complete or incomplete and the
surgical evacuation either by suction curettage or by sharp curettage .
In all cases inevitable miscarriage
anti-D gammaglobulin 500 Mg
is injected
intramuscularly unless the woman is known to be rhesus positive .
3. Complete miscarriage :
When all the uterine contents have been expelled spontaneously there is
cessation of pain, scanty blood loss and a firmly contracted uterus. ,
On examination : closed cervical OS . If there is no more active bleeding , or
if an ultrasound scan shows an empty uterine cavity , no further treatment is
required . ( expectant management ) , the patient should be observed for any
further bleeding and examine the product of conception .
Objectiv
The students should be know about:
This life threatening condition ,which is commonly seen in our
gynecology emergency department .
How can differentiate the miscarriage from other early pregnancy
complications .
Aetiological factors.
Pathological-Anatomy.
Clinical varieties of miscarriage &their management.
Modern classification of miscarriage.
