• The practical of InflammationThird year
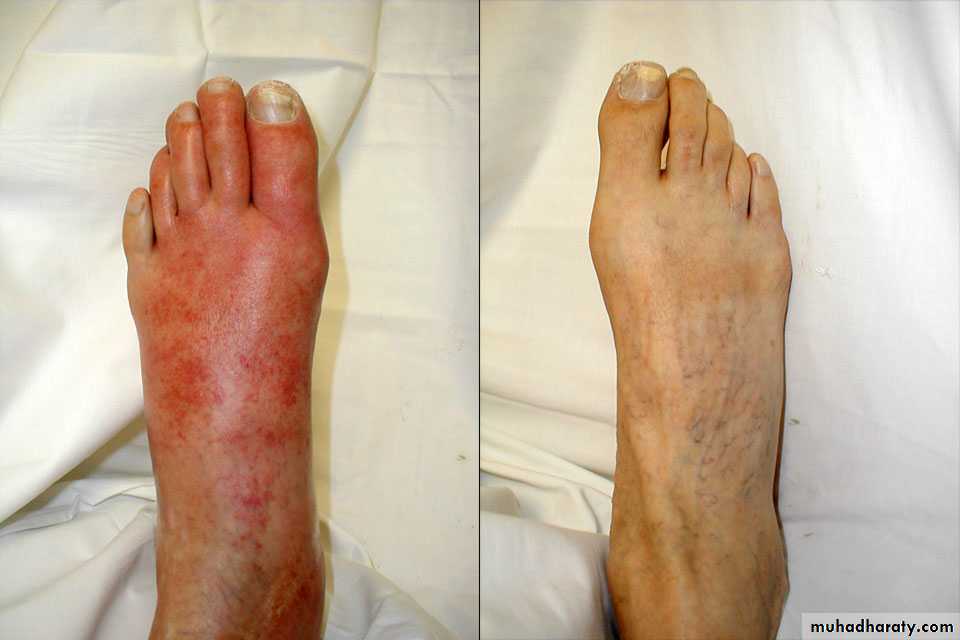
Acute inflammation, swelling and redness of the skin of left foot compared to the normal skin of the right foot.
Edema, or fluid collection within tissues. depression
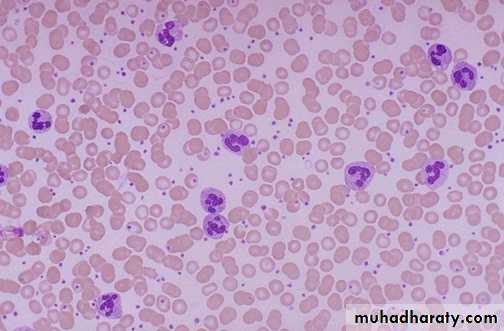
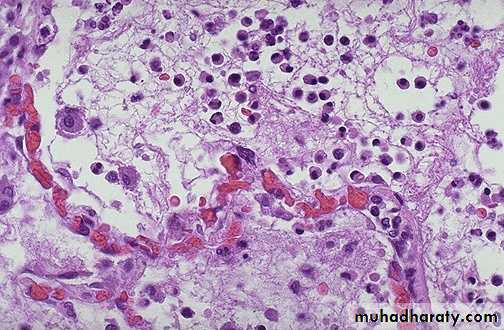
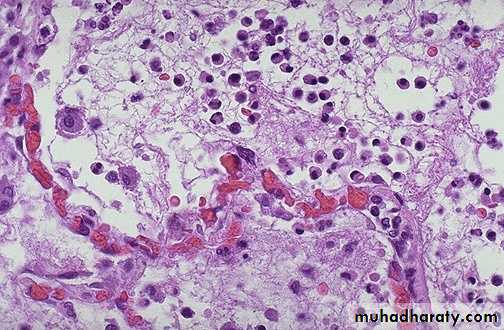
Acute inflammation is marked by an increase in inflammatory cells. predominantly neutrophils (polymorph-nuclear leukocytes (PMN's)).
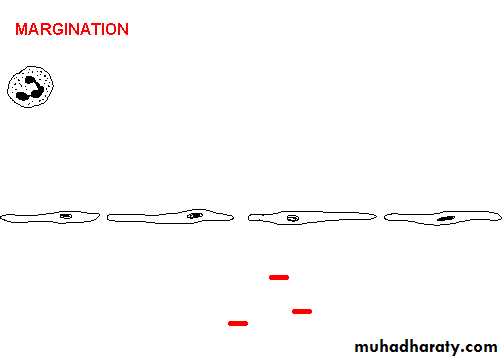
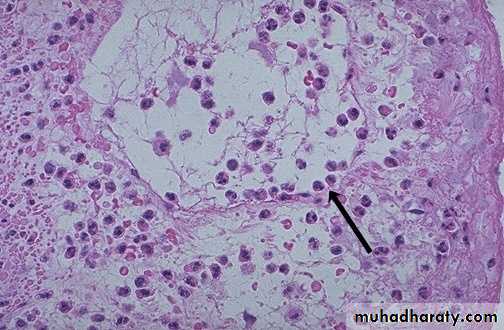
• Here PMN's that are marginated along the dilated venule wall (arrow) are squeezing through the basement membrane (the process of diapedesis) and spilling out into extravascular space.
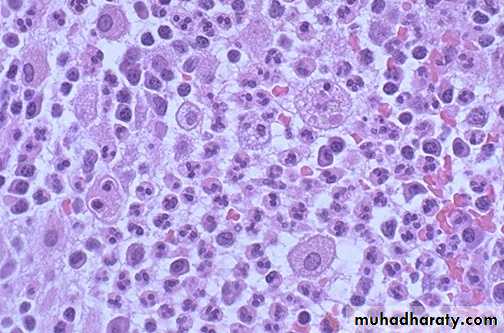
• Acute inflammation Seen here are mainly neutrophils,
• but there are also lymphocytes, and macrophages. Macrophages• can phagocytoze other cells as well as cellular debris
Acute inflammation (pneumonia) , dilated capillaries in the alveolar walls from vasodilation with numerous neutrophils fill the alveolar spaces.
• Acute inflammation (pneumonia) , dilated capillaries in the alveolar walls from vasodilation with numerous neutrophils fill the alveolar spaces
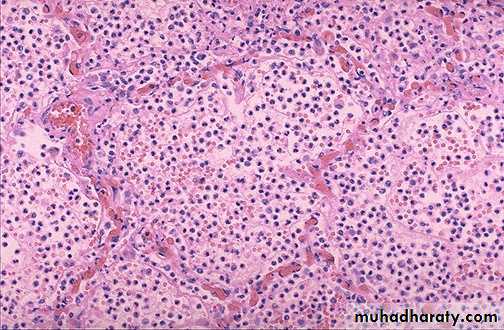
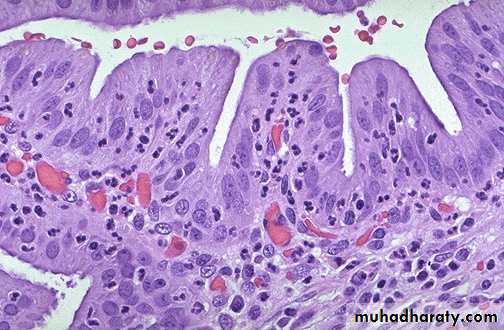
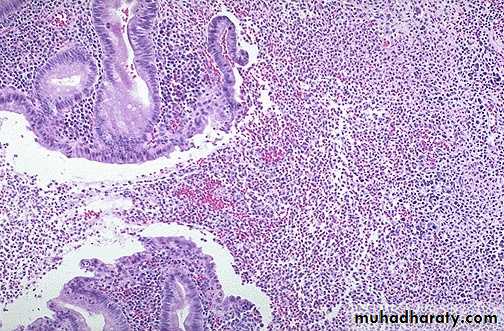
• Acute inflammation of a gall bladder, the neutrophils are seen infiltrating the mucosa and submucosa of the gallbladder with congestion of small blood vessels
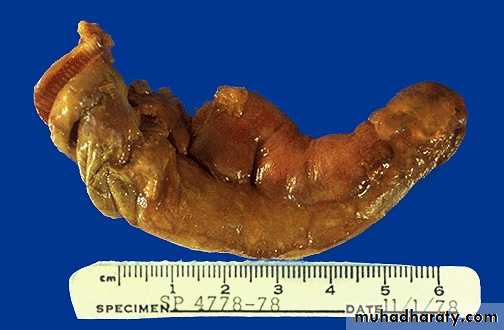
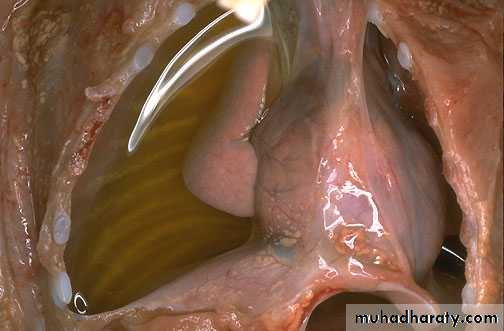
Acute appendicitis with yellow to tan exudate and hyperemia,
including the periappendiceal fat superiorly.Acute appendicitis: The mucosa shows ulceration and the acute inflammatory cells (Neutrophils) infiltrating the whole layers (transmural).
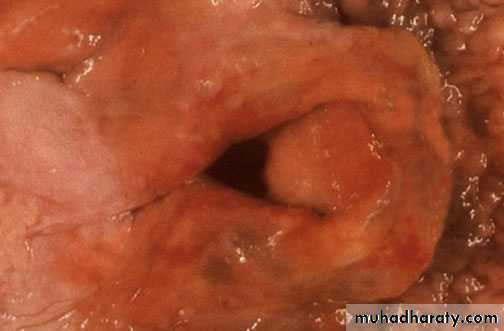
Acute laryngitis , swelling and redness of the larynx may cause difficulty in breathing due to narrowing in the lumen
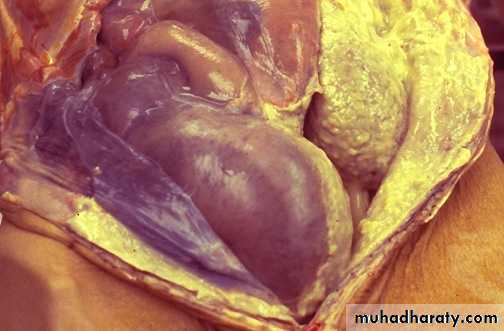
A right side serous effusion, a fluid collection into a body cavity (right side), the fluid is clear, pale yellow in appearance.
Acute inflammation (Suppurative (Purulent))
The abdominal cavity is opened at autopsy and revealan extensive purulent peritonitis(A thick yellow exudate
coats the peritoneal surfaces)
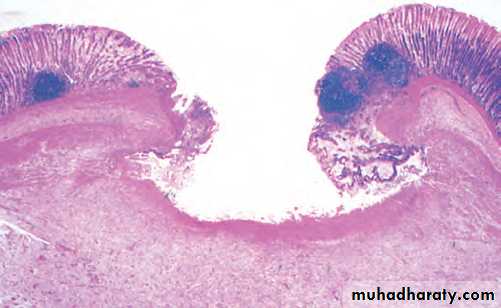
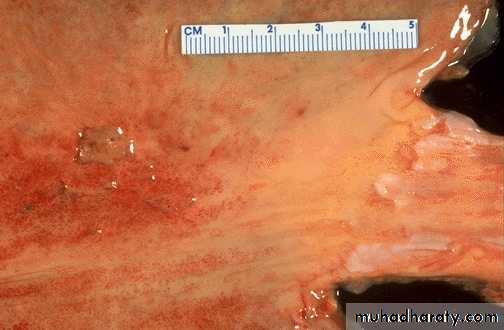
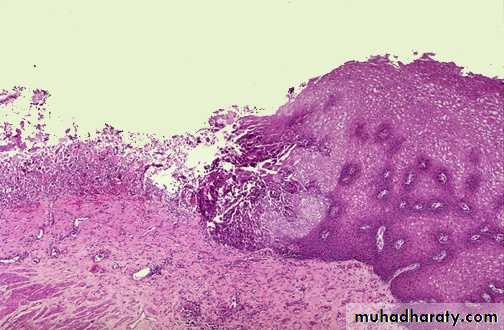
Acute inflammation (ulcer), the gastric mucosa has
been lost, or ulcerated.An esophageal acute ulcer ,in which the squamous mucosa has been lost and in the ulcer base there are inflammatory cells and fibrin
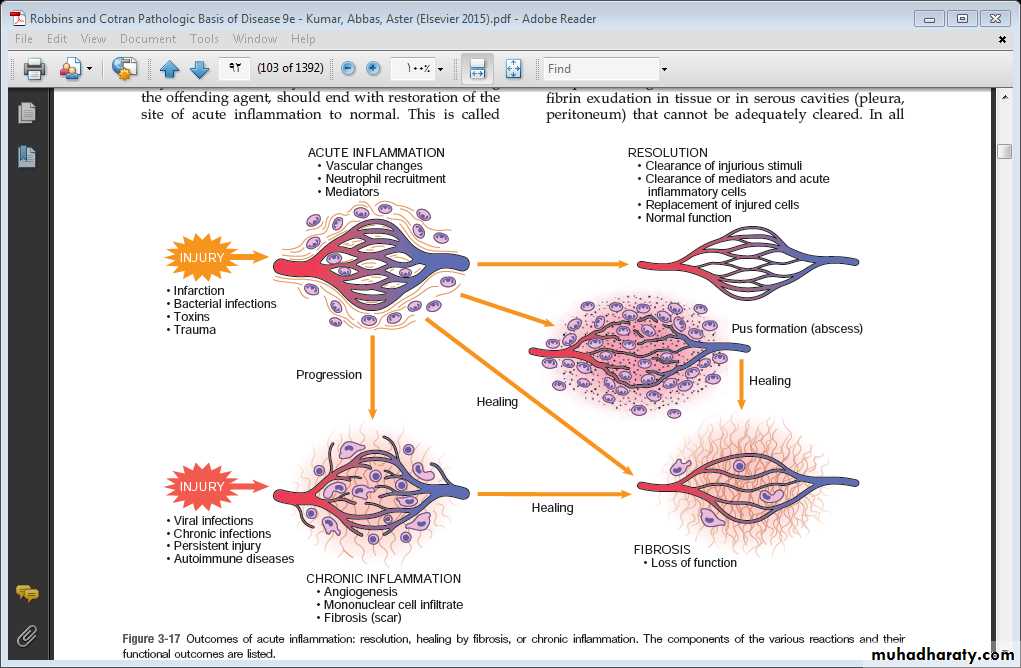
Causes and outcomes of acute inflammation
Complete resolutionExtensive acute inflammation may lead to abscess formation (The liquefactive necrosis), as seen here with rounded abscesses (the purulent material has drained out after sectioning to leave a cavity)
Acute inflammation (Suppuration (early abscess)) extensive neutrophilic exudate and the normal tissues are destroyed in the region of the abscess.
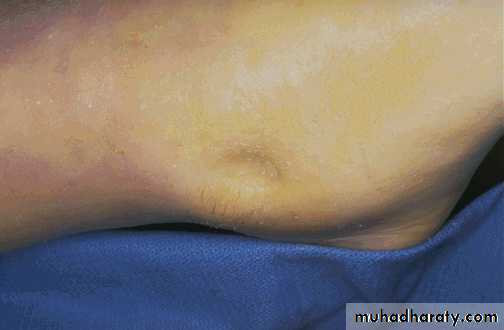
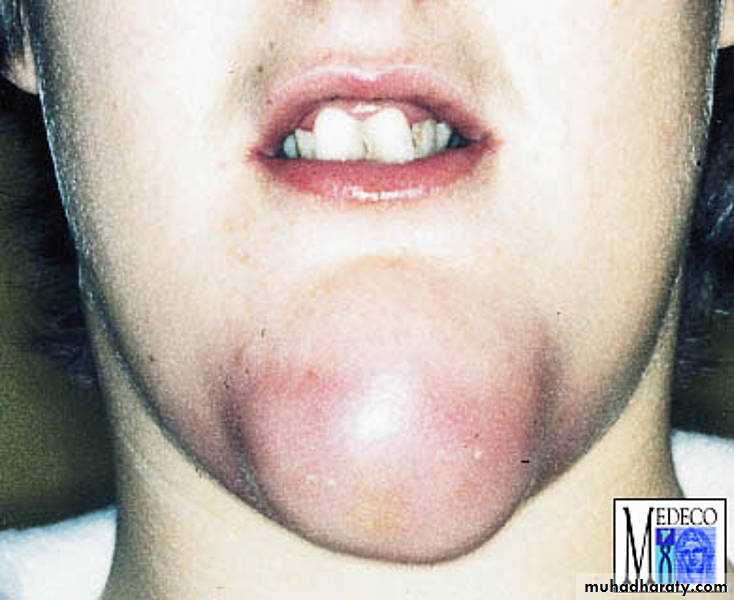
Perimandibular abscess in the chin region (redness, swelling)
chronic inflammation of the bronchi had led to dilation of bronchi&deposition of tan to white collagenous tissue (scarring)
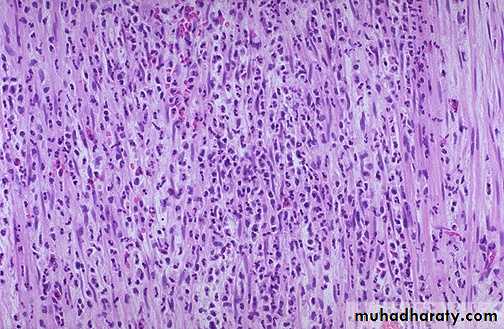
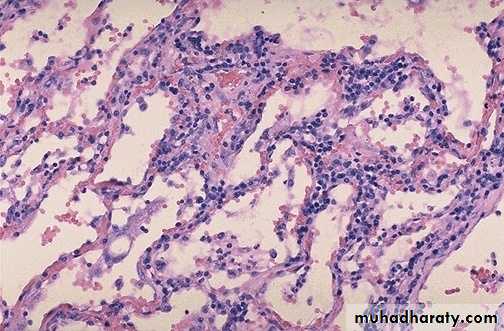
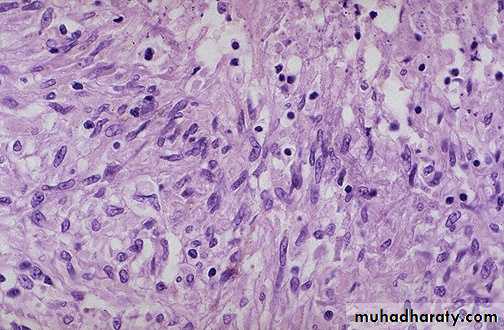
Chronic inflammation of the lung, the inflammatory cells
(mononuclear cells) are more likely to be interstitial (withintissues) rather than exudative
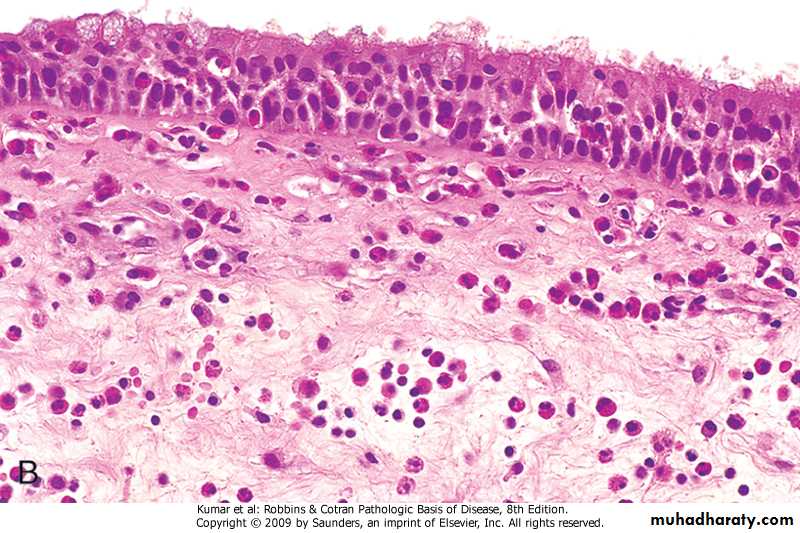
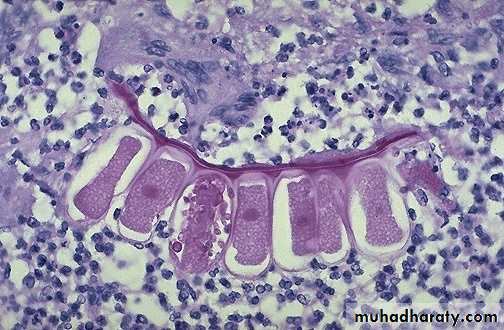
Chronic inflammation due to hypersensitivity reaction: chronic inflammatory cells infiltrate mainly eosinophils
(allergic nasal polyp)
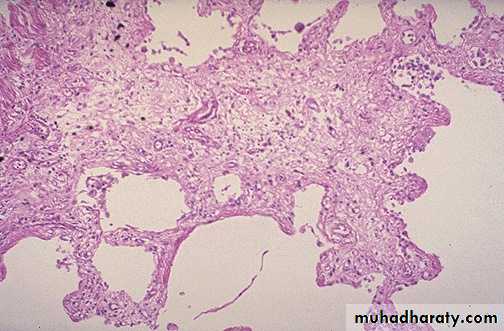
Chronic inflammation (lung) The end result of inflammation
can be scarring. Here, the alveolar walls are thickened andfilled with pink collagen.
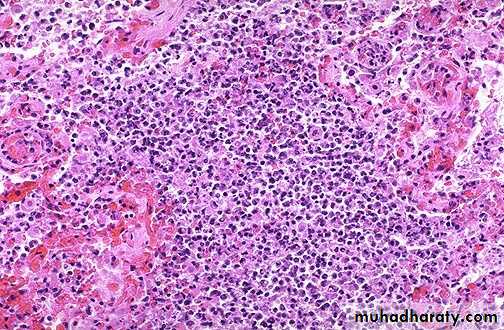
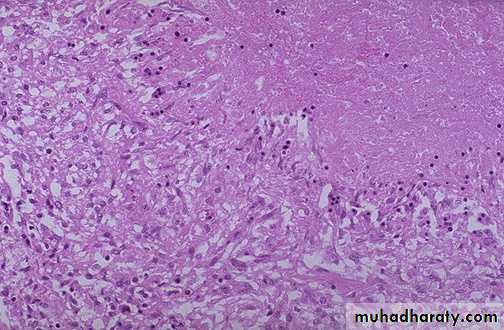
Granuloma, aggregate of epithelioid macrophages
Granuloma with Foreign body GC
Granuloma with Langhan’s GC pulmonary granulomas,
consist of epithelioid macrophages, with Langhan’sgiant cell surrounded by lymphocytes & fibroblasts..
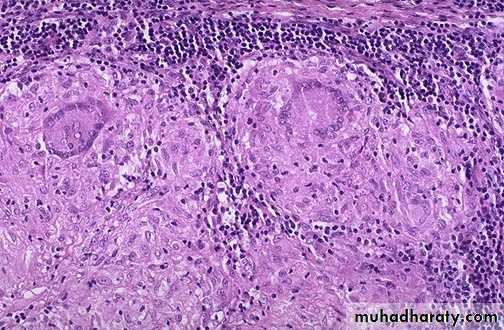
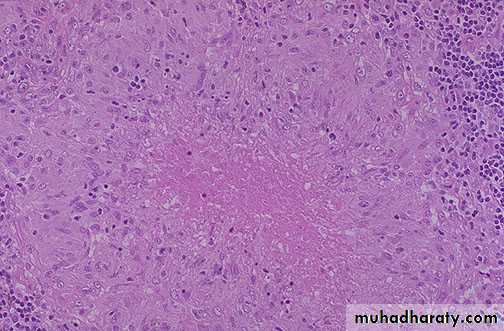
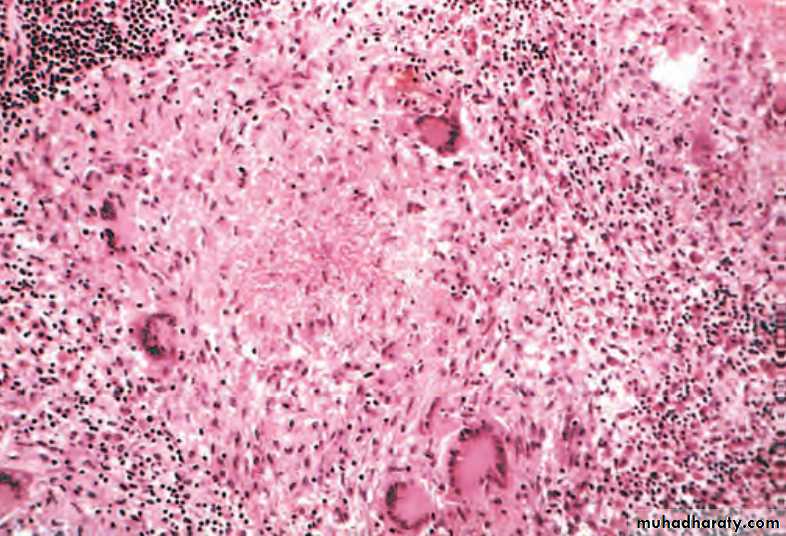
This is a caseating granuloma. Epithelioid cells surround a central area of necrosis(caseous) that appears irregular, amorphous, and pink.
Granuloma with central necrosis Epithelioid cells surround a central area of necrosis(caseous) that appears irregular, amorphous, and pink.