Lec(4) Pediatrics Dr.Ahmed Khalil 15/10/2018 Immunization&Prophylaxis
Immunization is one of the most beneficial and cost-effective disease-prevention measures available. It is the process of inducing immunity against a specific disease. Immunity can be induced either passively through administration of antibody-containing preparations or actively by administering a vaccine or toxoid to stimulate the immune system to produce a prolonged humoral and/or cellular immune response.
Passive immunization also occurs through transplacental transmission of antibodies to a fetus,and breast feeding which provides protection against many infectious diseases for the first several months of the infant's life.
The major indications for passive immunity:
1- Provide protection to immunodeficient children with B-lymphocyte defects who have difficulties making antibodies.
2- people exposed to infectious diseases or at imminent risk of exposure where there is not adequate time to develop an active immune response to a vaccine.
3- An infectious disease as part of specific therapy for that disease.
Types of Vaccines
1-Live attenuated viruses or bacteria( Oral polio, measles, mumps, rubella, varicella and BCG).
2- Inactivated or killed viruses or bacteria (Injectable polio, hepatitis A [HAV], influenza and Pertussis).
3-Recombinant products (hepatitis B [HBV]) .
4- Immunogenic components of bacteria (Acellular pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae type b [Hib] and Streptococcus pneumoniae).
5-Toxoids (diphtheria and tetanus).
Schedule of Immunization
Birth: HB OPV-0 BCG2 months: Rota1 OPV 1 Hexa+ Pneumo
4 months: Rota 2 OPV2 Hexa+ Pneumo
6 months: --------- OPV 3 Hexa+ Pneumo
9 months: Measles Vit.A
15 months: MMR
18 months: +OPV(Booster1) Vit.A Penta-2
4-6 years: +OPV(Booster2) MMR2 DTaP
Hexa vaccine : Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis , tetanus , Viral hepatitis type (b), Haemophilus influenza type B & inactivated polio vaccine.
Penta-1 vaccine: Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis , tetanus , Viral hepatitis type (b), Haemophilus influenza type B
Penta-2 vaccine: ; Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis, Tetanus, Haemophilus influenzae type B & inactivated polio vaccine.
Hepatitis B vaccination should be deferred in infants weighing <2 kg at birth until 30 days of age, if born to an HBsAg-negative mother.
BCG
BCG : Is a live attenuated vaccine given as 0.1ml intradermally at the insertion of deltoid muscle of the left arm ,it is an attenuated strain of Mycobacterium Bovis ,it is indicated to be given in developing countries where T.B. Is highly prevalent.
Contraindications :-
1.Burns.
2.Skin infections.
3.Celleular or combined immune deficiency.
4.Patients on immuno -suppressive agents.
5.Patients with AIDS.
Dose :- 0.05 ml for neonates.0.1 ml for infants & young children.
Following successful vaccination a small papule forms at the inoculation side gradually enlarges to form pustule then crust , then disappear at (8-12) weeks , & whenever possible tuberculin skin test should be done (2-3)month later after BCG vaccine, if negative ,BCG should be repeated.
Side Effects of BCG Vaccine :-
Are uncommon and include :
1.Cutaneous ulceration.
2.Localized lymphadenopathy.
3.Subcutaneous abscess formation.
4.Osteomyelitis.
Severe local reactions can be controlled by Anti tuberculous drugs.
DTP
Diphtheria , Tetanus toxoid & Pertussis vaccine (DTaP the same but it is with acellular Pertussis ).
Dosage :-
DTP and DTaP are administered in a dose of 0.5 ml intramuscularly. Following DTP there may be a minor reactions including local swelling and tenderness at the site of injection with slight fever and irritability.
Contraindications
1-Severe allergic reaction after a previous dose or to a vaccine component.
2-Encephalopathy (e.g., coma, decreased level of consciousness; prolonged seizures) within 7 days of administration of previous dose of DTP or DTaP.
Precautions (Reactions but not true contraindications)
1-Progressive neurologic disorder, including infantile spasms, uncontrolled epilepsy, progressive encephalopathy; defer DTaP until neurologic status clarified and stabilized.
2- GBS <6 weeks after previous dose of tetanus-toxoid–containing vaccine.
3-Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Polio Virus Vaccine
There are two types :
1. OPV : a live attenuated trivalent Polio Virus Vaccine (SABIN).
2.IP:Inactivated (killed) trivalent Polio Virus Vaccine (SALK).
The OPV was recommended by the WHO for routine immunization of children in addition to yearly seasonal (spring & autumn) journeys for vaccination .Now IPV introduced into schedule.
Contraindications of OPV :-
1-Severe allergic reaction to previous dose or vaccine component.
2.Congenital or acquired immunodeficiency .
3.House hold contacts of immunodeficient patients.
4. Siblings of congenital immunodeficient patients.
In those situations(2,3,4) IPV should be given .
Precautions:-
1.Pregnancy.
2.Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
MMR [ Measles , Mumps , Rubella]
Dosage :- It Is a live attenuated vaccine given by deep S.C injection at the extensor surface of the arm in a dose of 0.5 ml, whether alone or in combination.
Measles & Mumps vaccines are grown in chick embryo cell culture , so it’s contraindicated in children with egg allergy.
Side effects :-
They are attributed to the measles component and include transient rash , fever up to 39.4 C occurs in some children 6_11 days after the vaccine .
SSPE :- [subacute sclerosing panencephalitis] occurs after measles vaccine and is doubtful .
Rubella component may cause transient arthralgia ,arthritis & may occur in 1_2% of children but in higher % in adult females.
Contraindications
1-Severe allergic reaction after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
2-Pregnancy
3-Known severe immunodeficiency (e.g., hematologic and solid tumors; congenital immunodeficiency; long-term immuno suppressive therapy, or severely symptomatic human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] infection)
Precautions:-
1-Recent (witin11 months) receipt of antibody-containing blood product (specific interval depends on product).
2-History of thrombocytopenia or thrombocytopenic purpura.
3-Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
4-Need for tuberculin skin testing or interferon-gamma release assay
(IGRA) testing
HBV Vaccine
Hepatitis B Vaccine is prepared from [cloned DNA fragment coding for HBs Ag] and produced by yeast cells.
Dosage :- HBV should be given to adolescents and children only in the deltoid muscle, and to infants and neonates in the anterolateral thigh muscle as IM injection of 0.1 ml. Administration intradermally or in the buttocks has resulted in poor immune responses in some individuals, and these sites are not recommended.
For infants of HBsAg-positive mothers, both HBV and HBIG (0.5 ml intramuscularly) should be administered simultaneously at different sites as soon as possible, preferably within 12 hours after birth but with allowance up to 1 week.
Contraindication:-
1-Severe allergic reaction after a previous dose or to a vaccine component.
2- Hypersensitivity to yeast.
Precautions:-
Infant weighing <2,000 grams.
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Rotavirus (RV) vaccines.
Minimum age: 6 weeks for both RV1 [Rotarix] and RV5 [RotaTeq]
1- If Rotarix is used, administer a 2-dose series at ages 2,4 months.
2- If RotaTeq is used, administer a 3-dose series at ages 2,4,6.
3- If any dose in the series was RotaTeq or vaccine product is unknown , a total of 3 doses of RV vaccine should be administered. 4-The maximum age for the first dose in the series is 14 weeks, 6 days; vaccination should not be initiated for infants aged 15 weeks, 0 days, or older.
5- The maximum age for the final dose in the series is 8 months, 0 days.
Contraindication:-
1- Severe allergic reaction e.g., anaphylaxis after a previous dose or to a vaccine component.
2-SCID.
3-History of intussusception.
Precautions:-
1-Altered immunocompetence other than SCID.
2-Chronic gastrointestinal disease.
3-Spina bifida or bladder exstrophy.
4-Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Conditions incorrectly perceived as contraindications or
precautions to vaccination (i.e., vaccines may be given under theseconditions)
1-Mild acute illness with or without fever.
2-Mild to moderate local reaction (i.e., swelling, redness).
3- low-grade or moderate fever after previous dose.
4-Current antimicrobial therapy .
5-Convalescent phase of illness.
6-Preterm birth (hepatitis B vaccine is an exception in certain circumstances)
7-Recent exposure to an infectious disease
8-History of penicillin allergy, other nonvaccine allergies,
9-relatives with allergies, or receiving allergen extract
10-History of GBS
Rabies postexposure management
1- immediate thorough cleansing of the bite using soap and water.
2- RIG at a dose of 20 IU/kg should be administered, with the full dose of RIG infiltrated subcutaneously into the area around the wound, if possible. Any remaining RIG should be administered as an intramuscular injection.
3-Inactivated rabies vaccine should be administered simultaneously as soon as possible, at a site away from where RIG was administered, with additional vaccine doses at 3, 7, and 14 days.
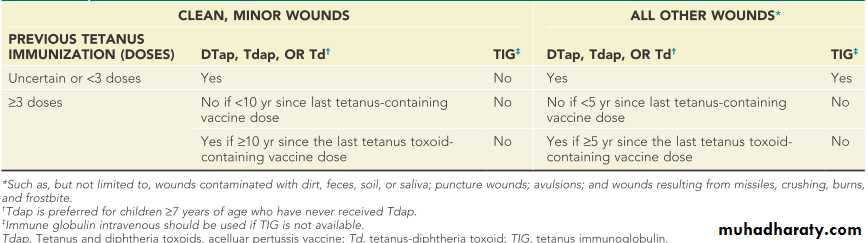
Guide to Tetanus Prophylaxis in Routine Wound Management