Introduction to general orthopedicsد. مثنى حموشي
OrthopedicsDeals with the skeletal system and all structures that makes it move; bone, joint, muscle, tendons and nerves.
symptoms
Pain: most common complain.Throbbing; abscess.
Stabbing; cut tendon.
Aching ; arthritis.
Referred pain; e.g. knee pain with hip jt problems, gluteal pain from lumbr spine,…
Symptoms
Stiffness;Generalized early morning in rheumatoid arthritis,
Localized after immobilization in osteoarthritis.
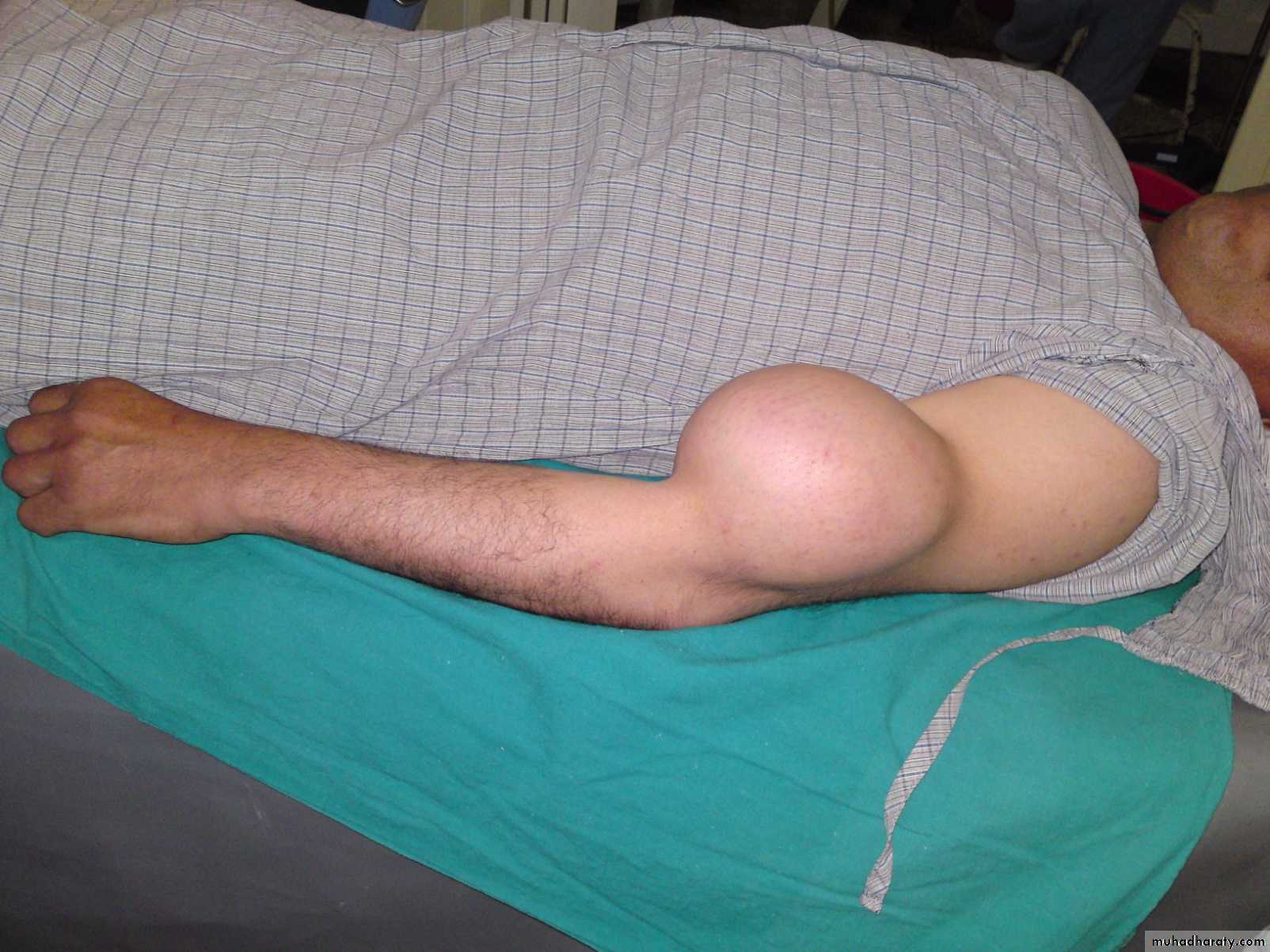
Swelling;
Sudden; eg hemarthrosis,
Gradual ; tumor. Infection.
Deformity;
Sudden; eg elbow dislocation,
Gradual; eg knock knees of rickets
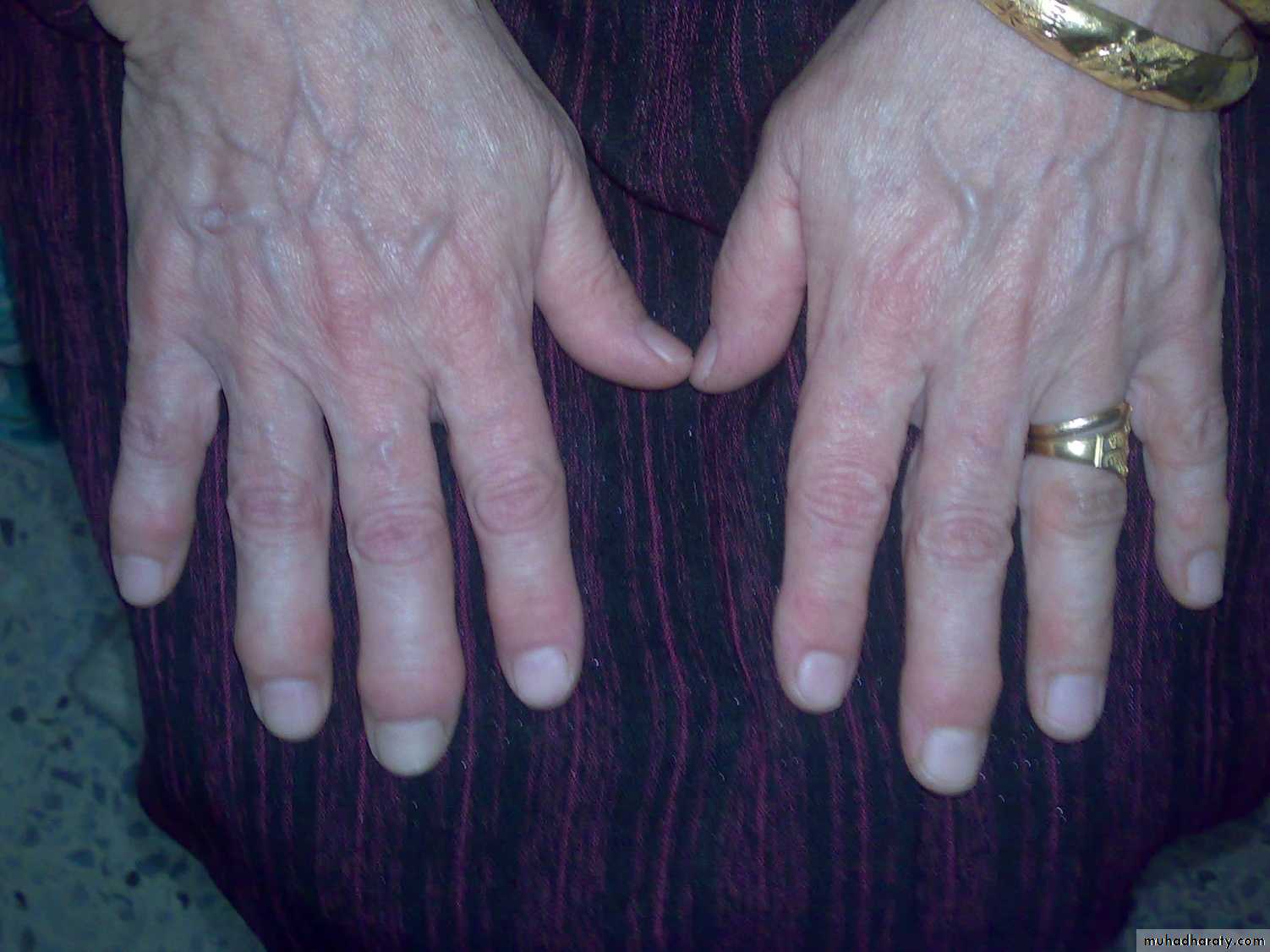
Heberden nodes
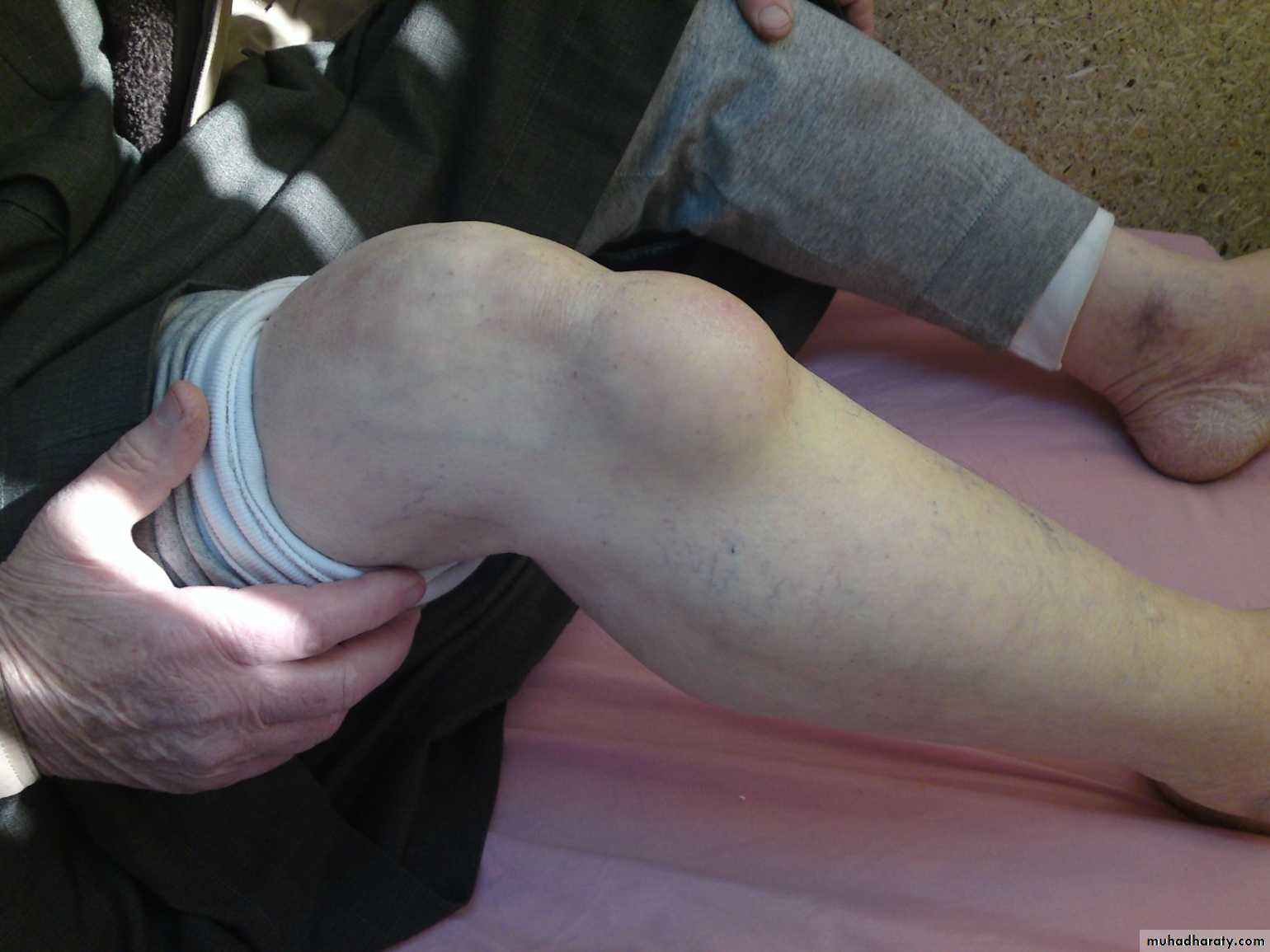
Knee Joint effusion
Lipoma
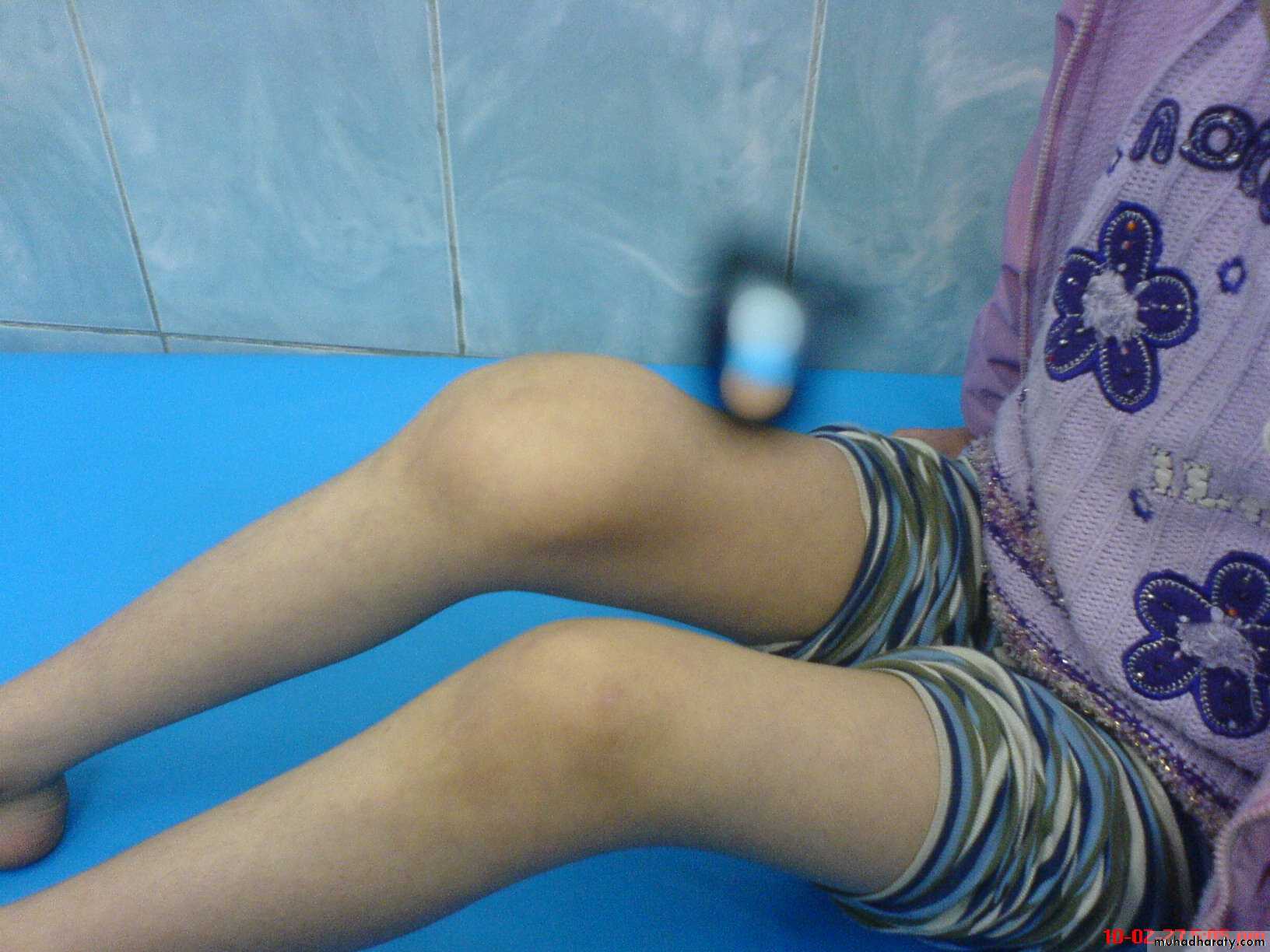
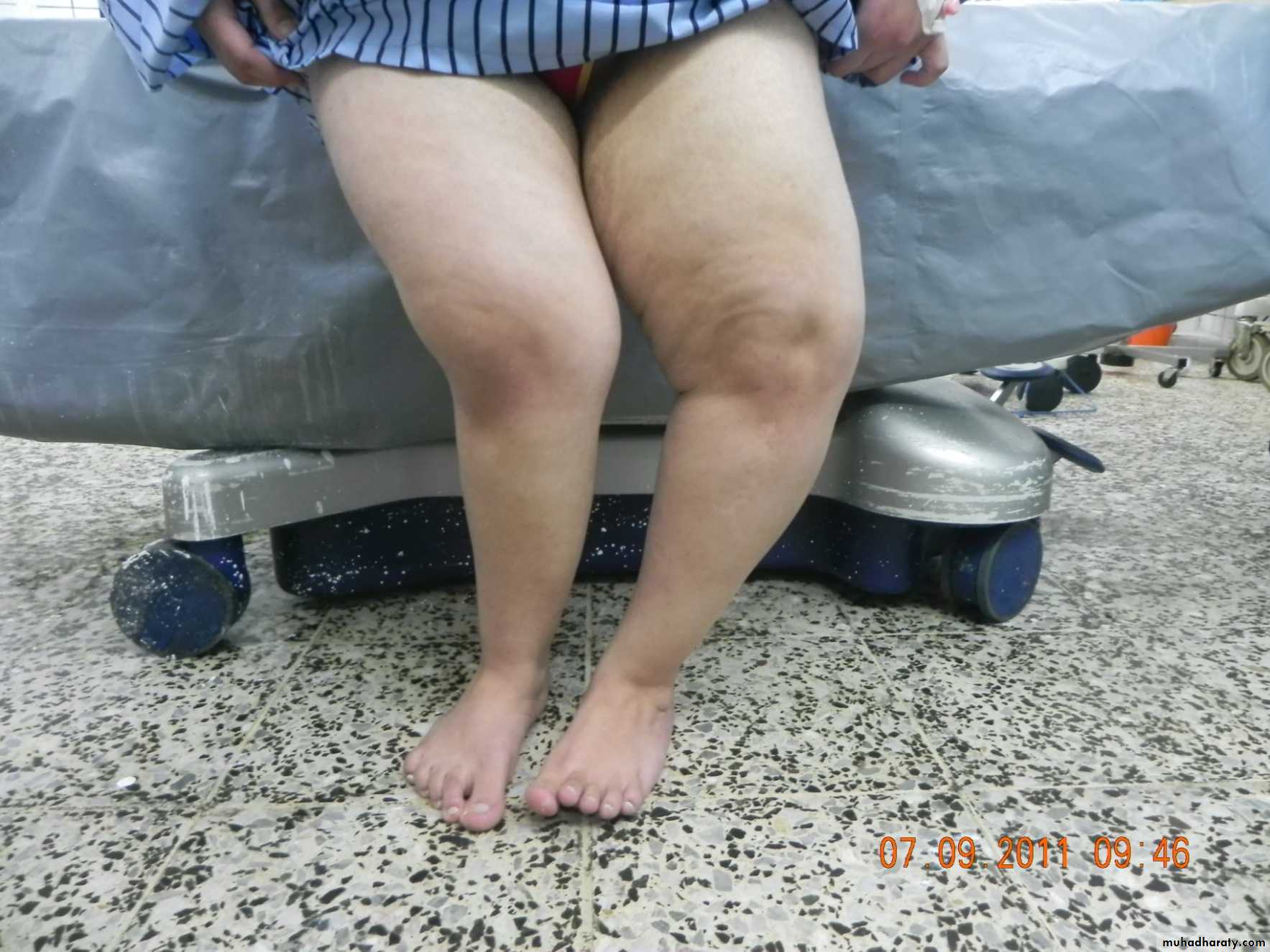
Genu varum and valgum
Symptoms
Weakness; suggest neurological or muscle disorder.Instability (giving way); ligament laxity or rupture.
Change in sensibility; tingling or numpness eg nerve root compression from prolapsed intrvertebal disc, median nerve entrapment in carpal tunnel syndrome, peripheral neuropathy in DM,…
Symptoms
Loss of function; eg inability to climb stairs in knee OA, inability to comb hair in frozen shoulder,….
Past history;
Ankle trauma; secondary OA.
Corticosteroid therapy; osteoporosis,
Chronic diarrhea; ankylosing sponylitis,…
Examination
Generalized appearance, posture, and gait.Undress the patient properly.
LOOK, FEEL, MOVE.
LOOK
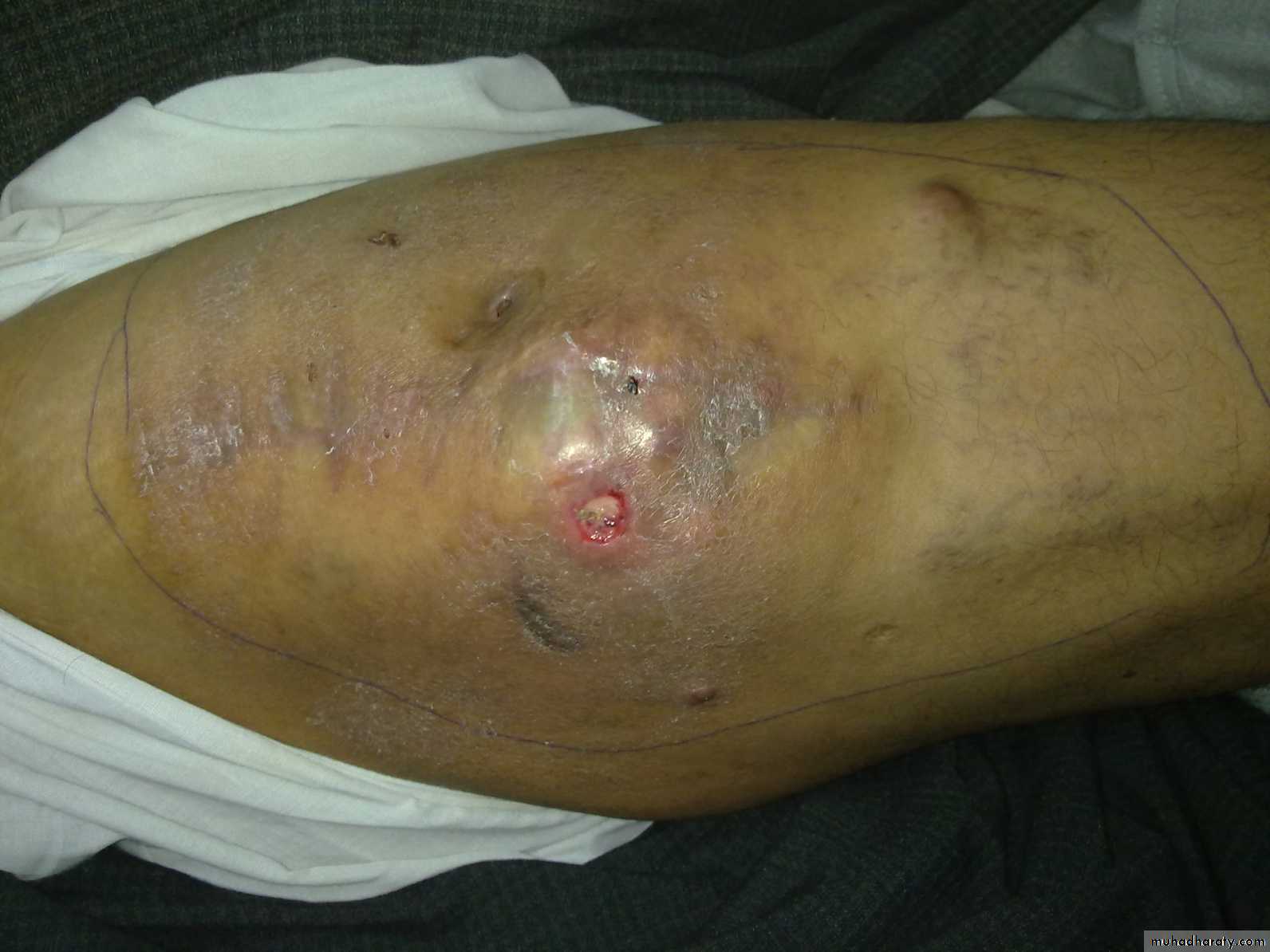
Skin; scars, color (eg red inflamed),Shape; swelling, wasting, lump, deformity.
Position; eg fixed flexion of the knee,…
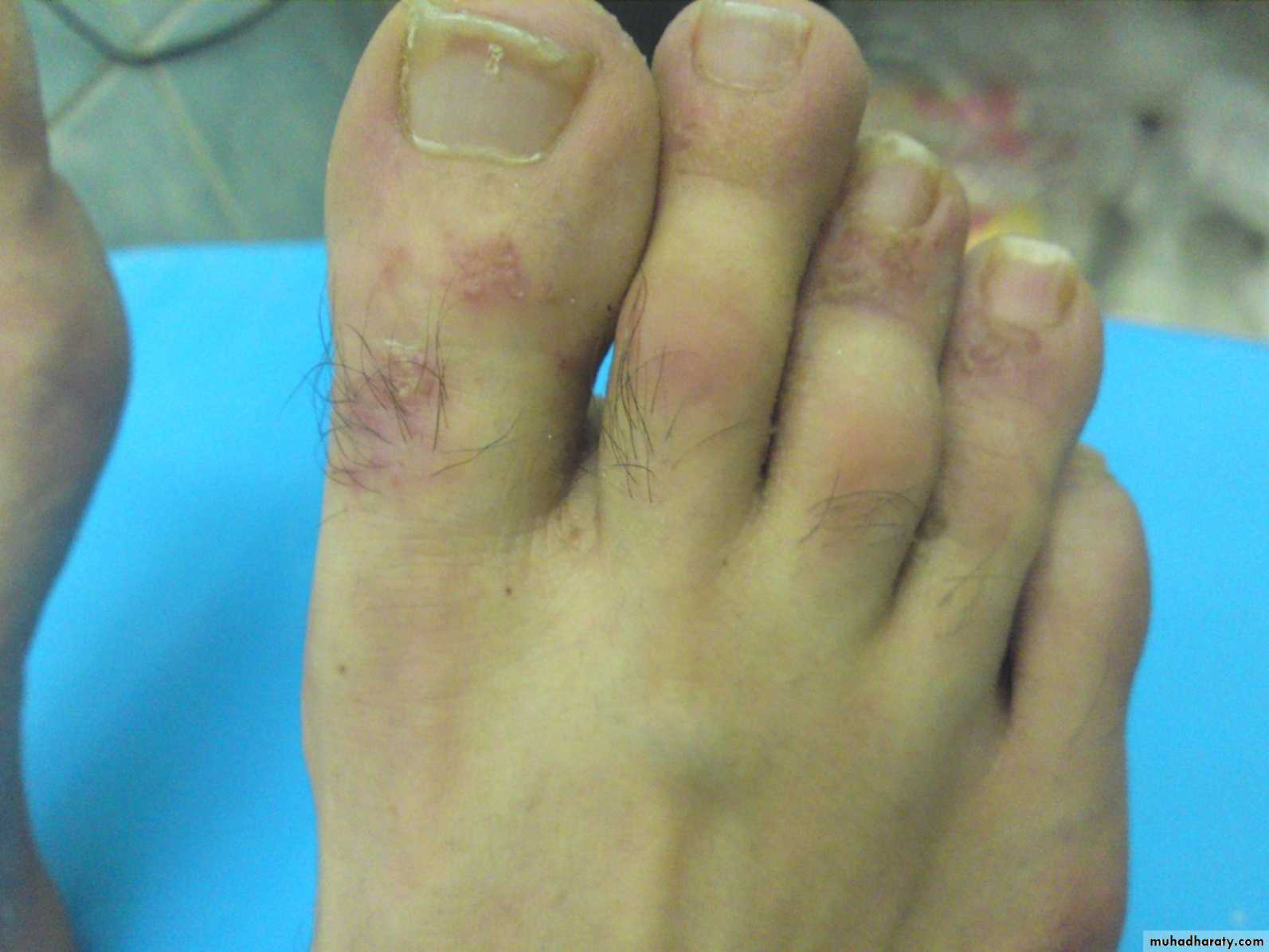
Skin; psoriatic arthritis
Bow leg deformity
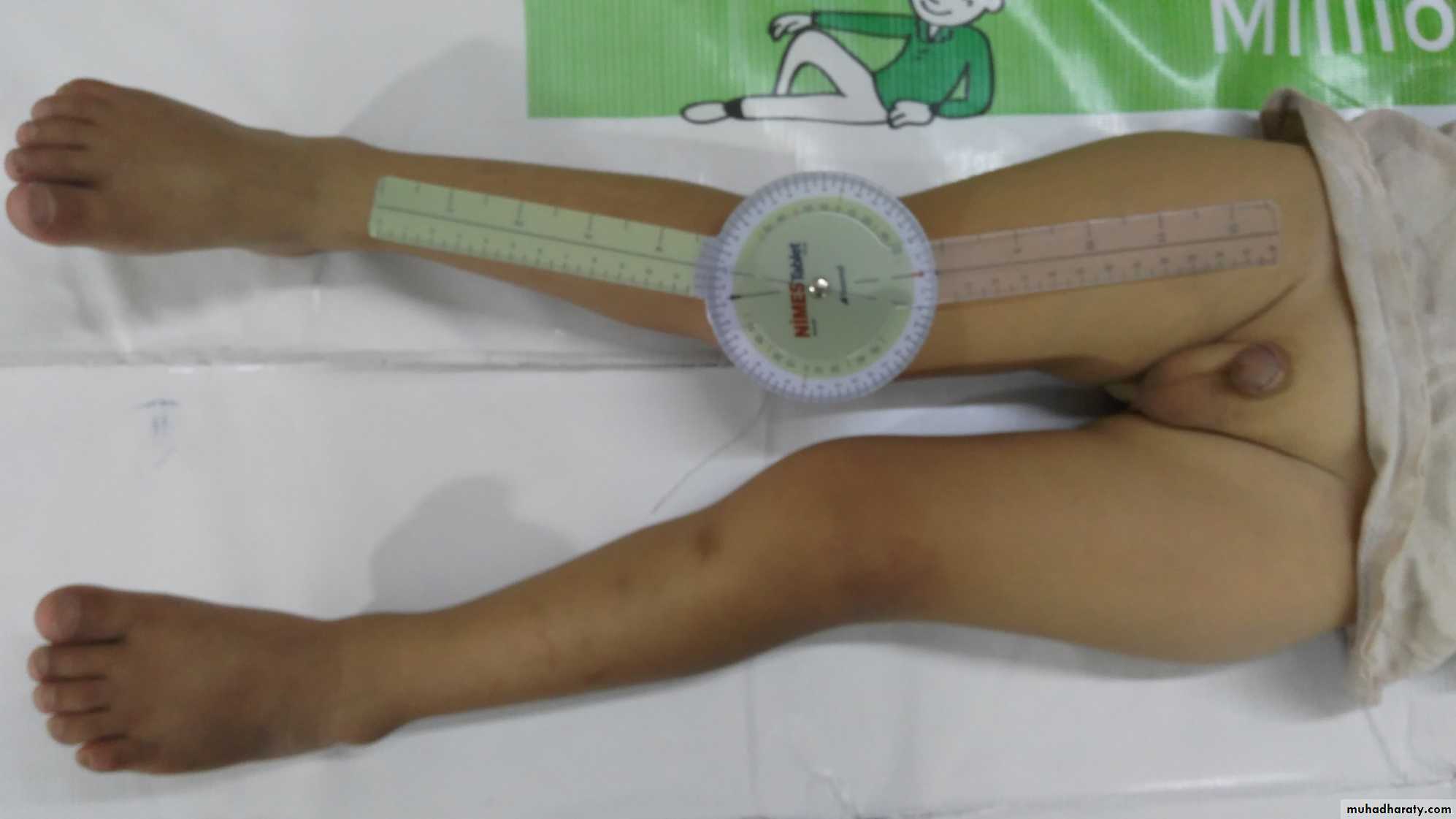
Measurement of Genu Valgum
Localized swelling of infrapatellar bursa
Skin ulcer of sarcoma
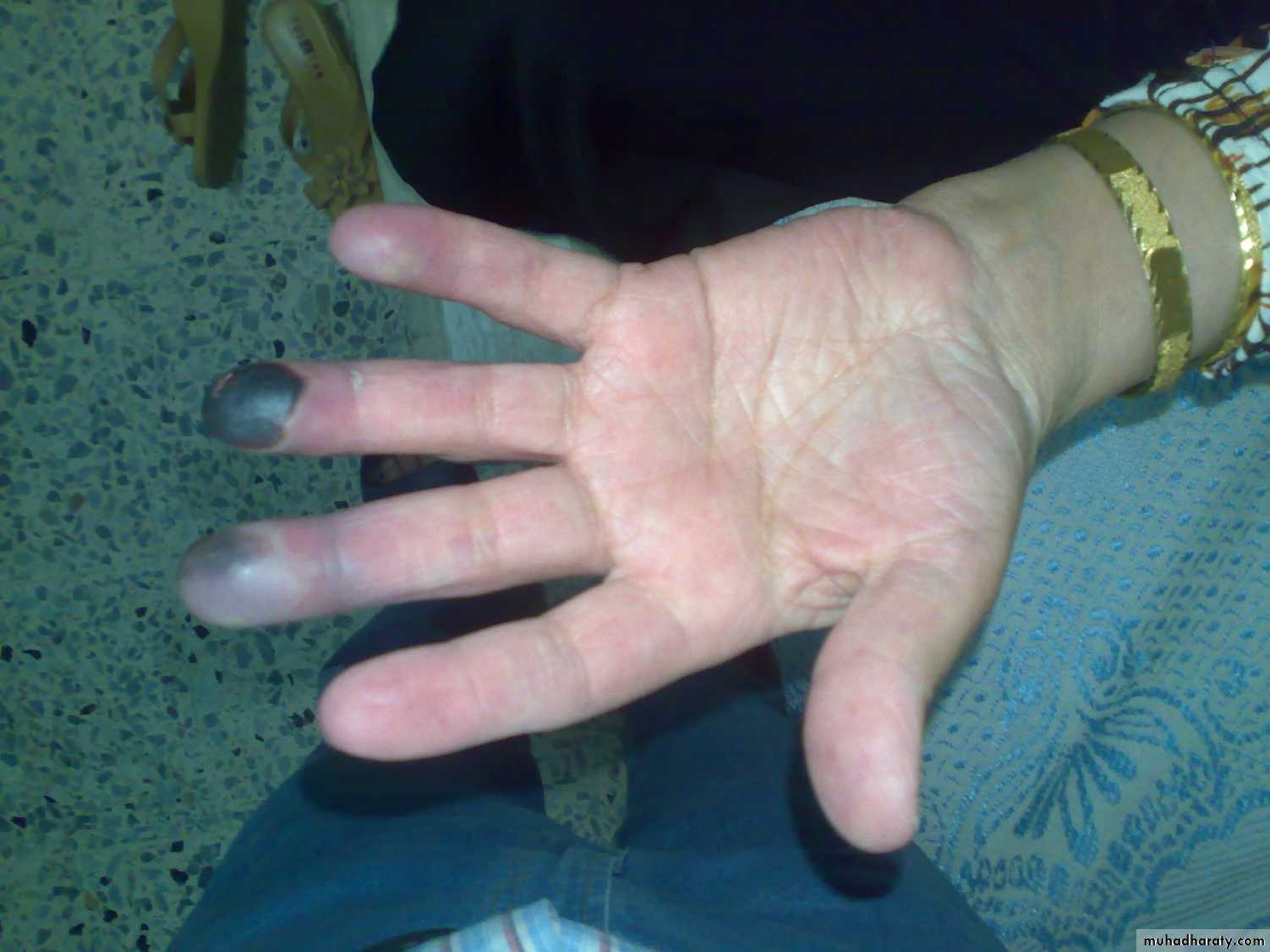
Finger gangrene; Raynaud’s disease
Feel
Skin temperature,Lump,
Effusion,
Tender points.
Move
Active movement; range of motion (ROM), and power.
Passive; ROM, crepitus.
Provocative tests; eg induce dislocation in unstable joints.
Move
Joint stiffness
All movements absent;Ankylosis (pathological) eg fibrous ankylosis of TB.
Surgical (arthrodesis).
All movements limited; eg post traumatic adhesions.
Some movements limited; eg torn meniscus block full knee extension.
Joint laxity
Normal in children.5% of people have persistent hypermobility and are more susceptible to dislocation (eg shoulder and patella) and arthralgia.
Deformity
Varus; part distal to the joint displaced toward the midline.Valgus; part distal to the joint displaced away from the midline.
Kyphosis; increased posterior convexity of the spine.
Scoliosis; lateral curvature of the spine.
Cubitus Varus
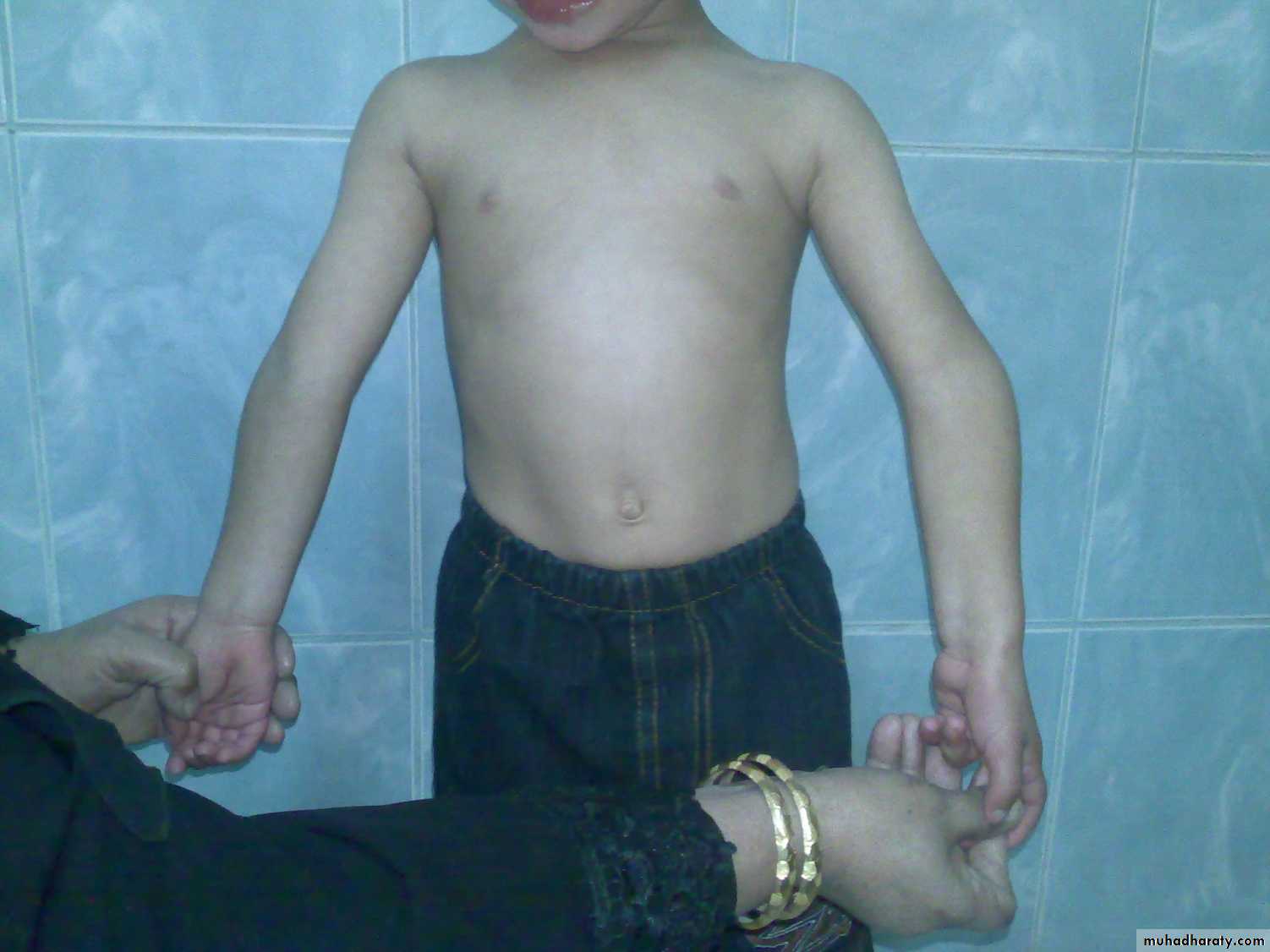
Arthrogriposis
Neurological examination
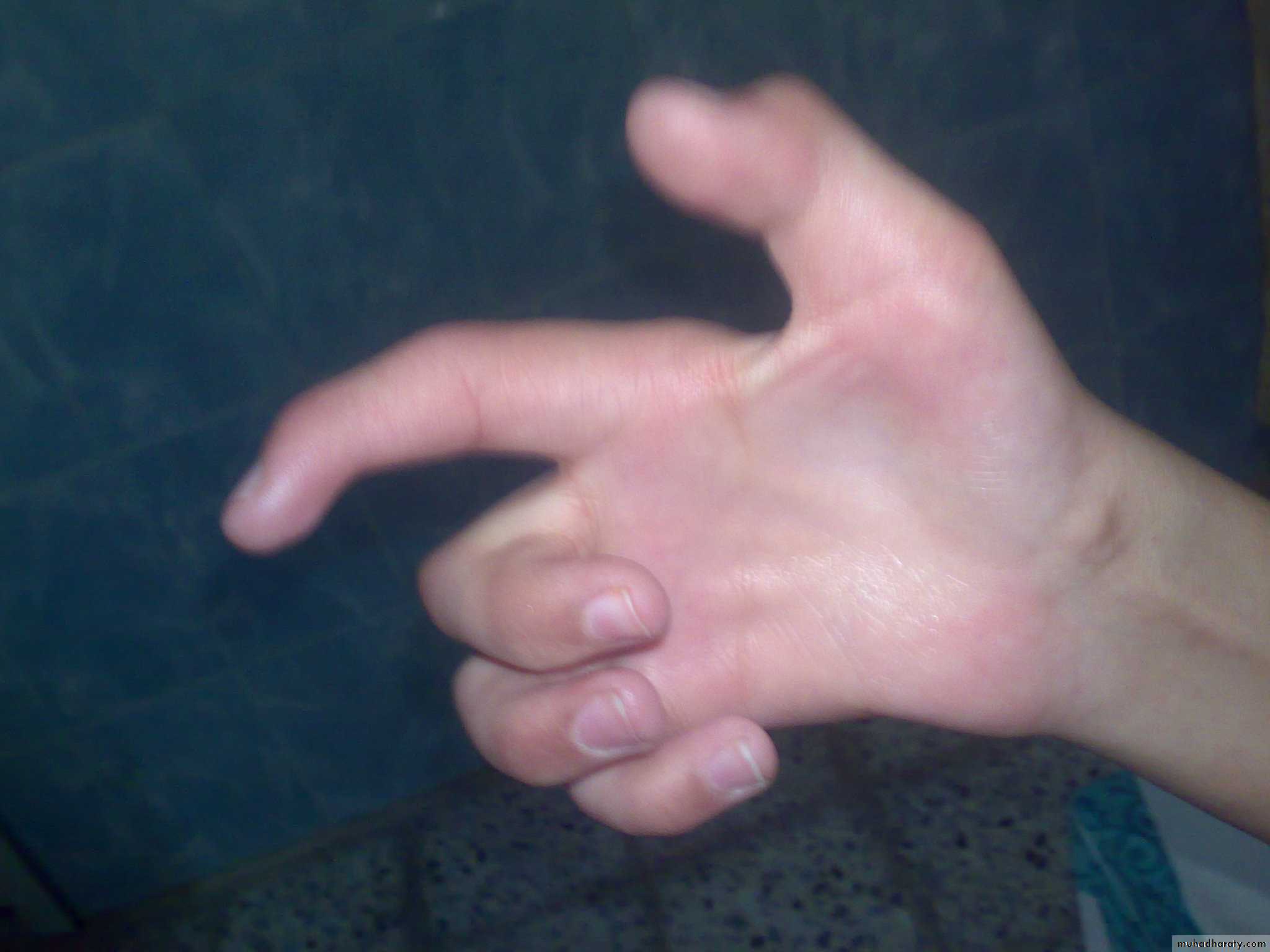
Appearance:Abnormal posture; eg claw hand of ulnar nerve injury.
Abnormal gait; foot drop of sciatic nerve injury.
Muscle wasting, trophic ulcers, shiny skin and hair loss.
Tone and power.
Tendon reflexes.
Sensibility.
Claw hand of ulnar nerve injury
Diagnostic imaging
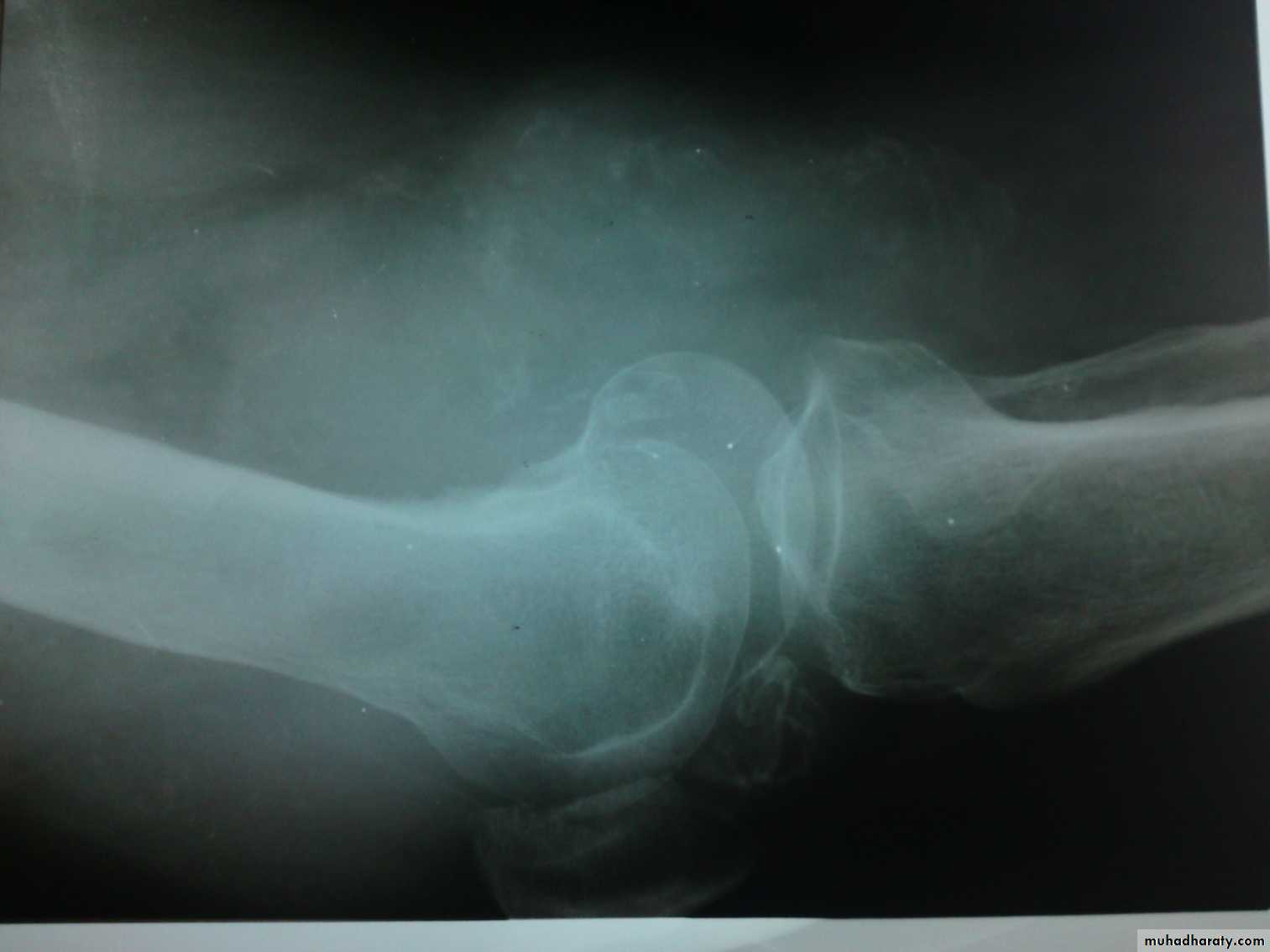
Plain film radiography; most useful diagnostic imaging.
How to read an X-Ray:
The patient name, age, date, clinical summery.
Projection; eg AP and lateral.
Side; left or right.
Soft tissue:
Shape: swelling, wasting, effusion.
Density: calcification, FB,…
Bones
Shape:Deformity; eg bow legs.
Periosteal reaction; eg fracture, infection, tumor.
Cortex distruction; eg fracture, tumor.
density:
Increased density; sclerosis.
Decreased density; oseoporosis.
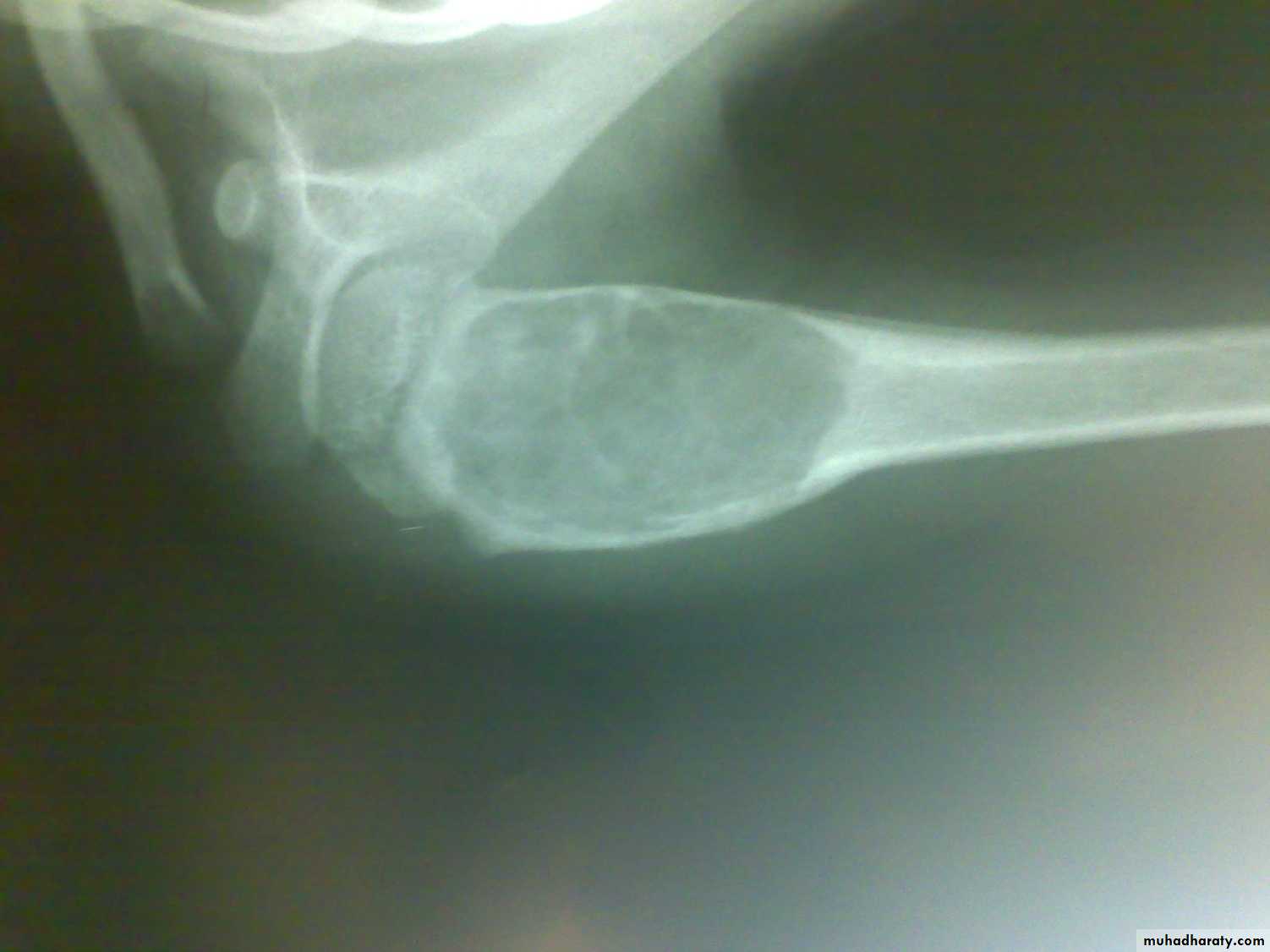
Bone defects or cysts.
Bone cyst
Myositis ossificansJoints
Shape:Decreased joint space and oseophytes in osteoarthritis.
Dislocation or subluxation.
Density: increased in chondrocalcinosis, loose bodies…
Calcification in knee jointsynovial carcinoma
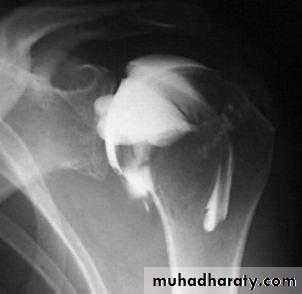
X-ray with contrast media
Water soluble based iodine liquids.Sinography in chronic discharging sinus.
Arthrography in joints.
Myelography in spinal disorders.
Arthrography of shoulder joint
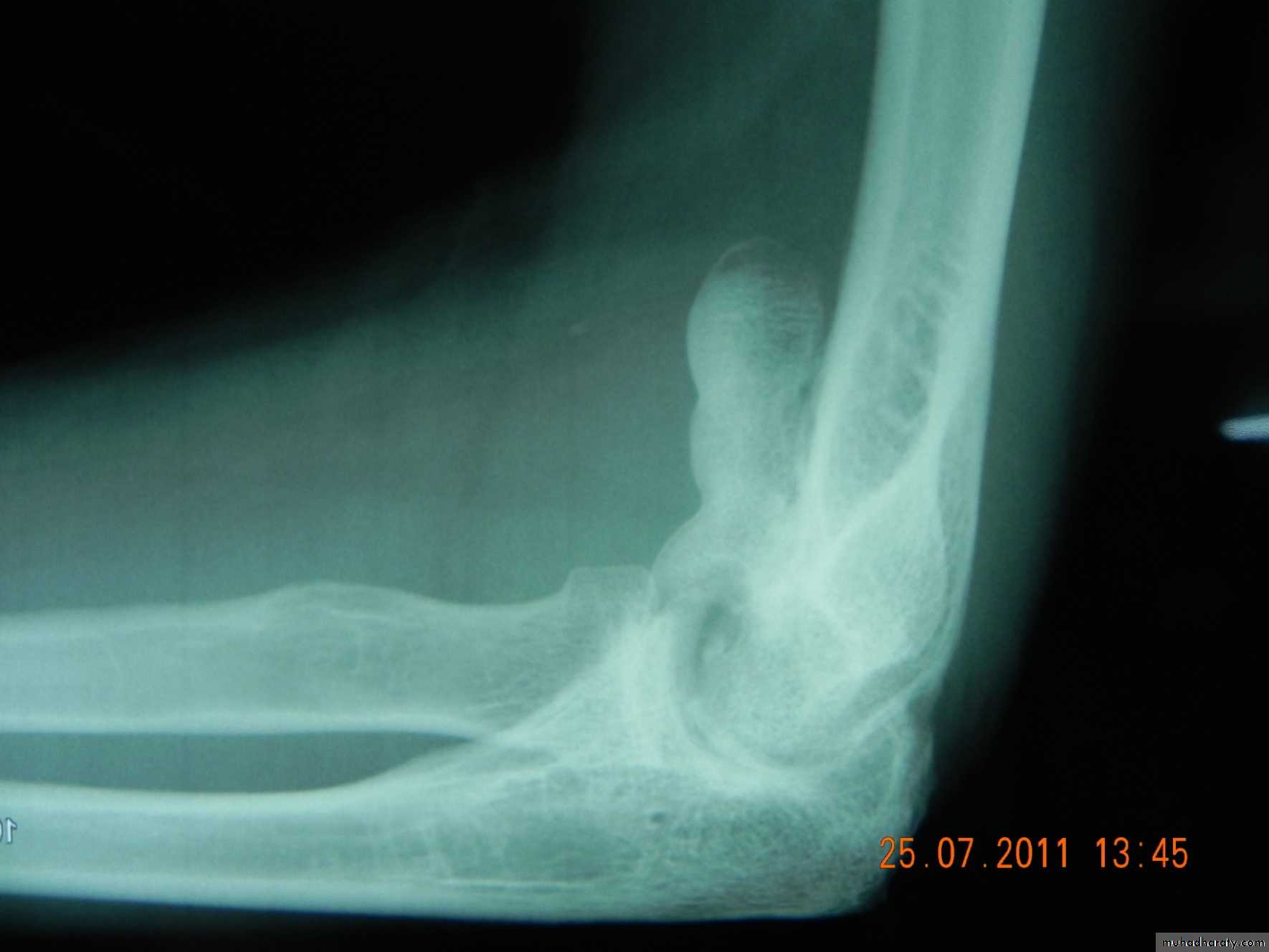
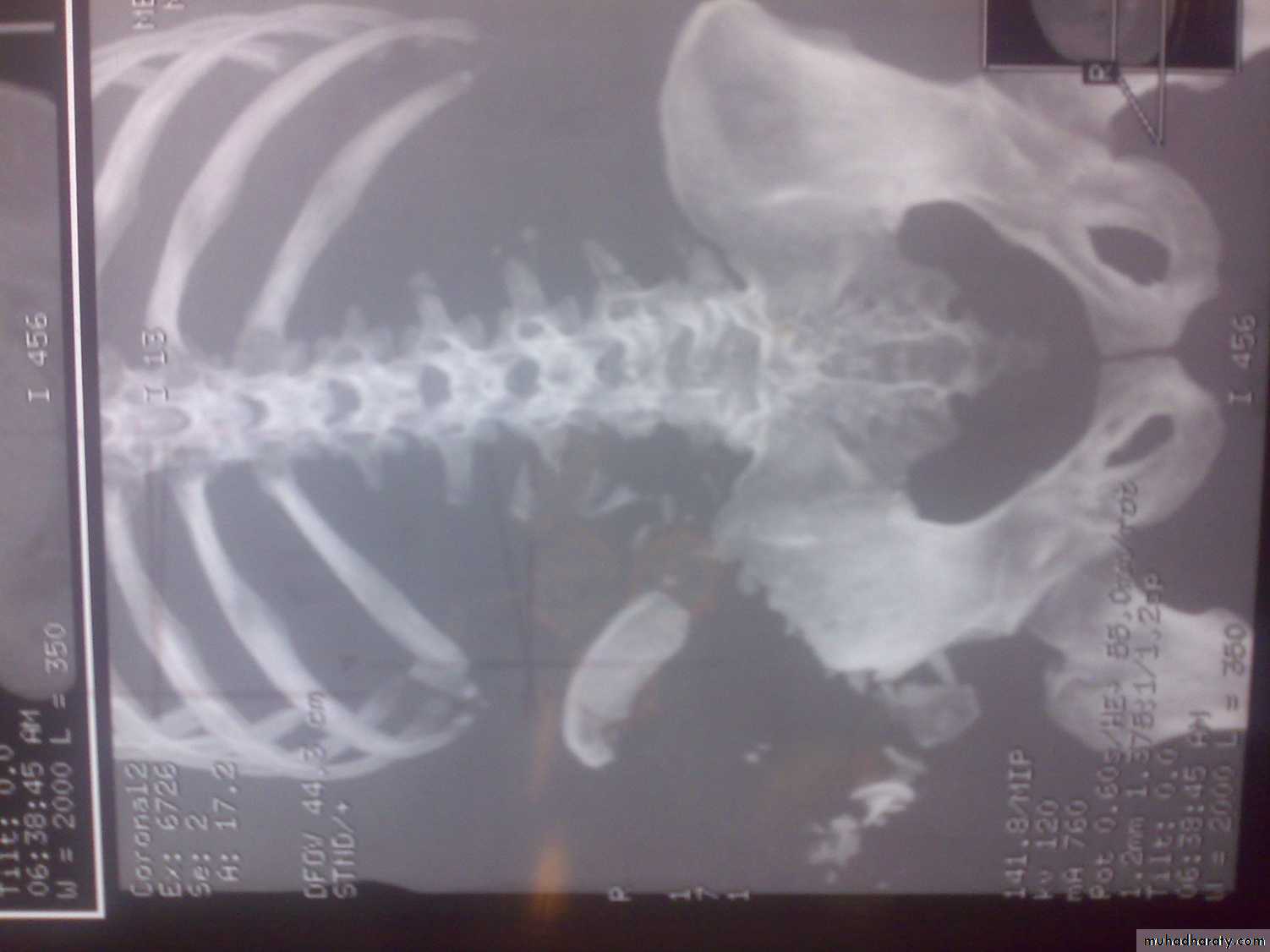
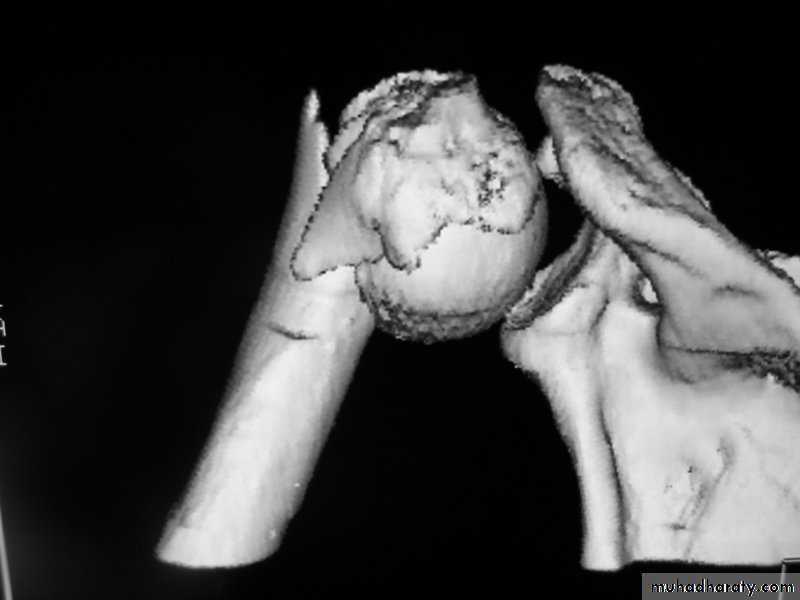
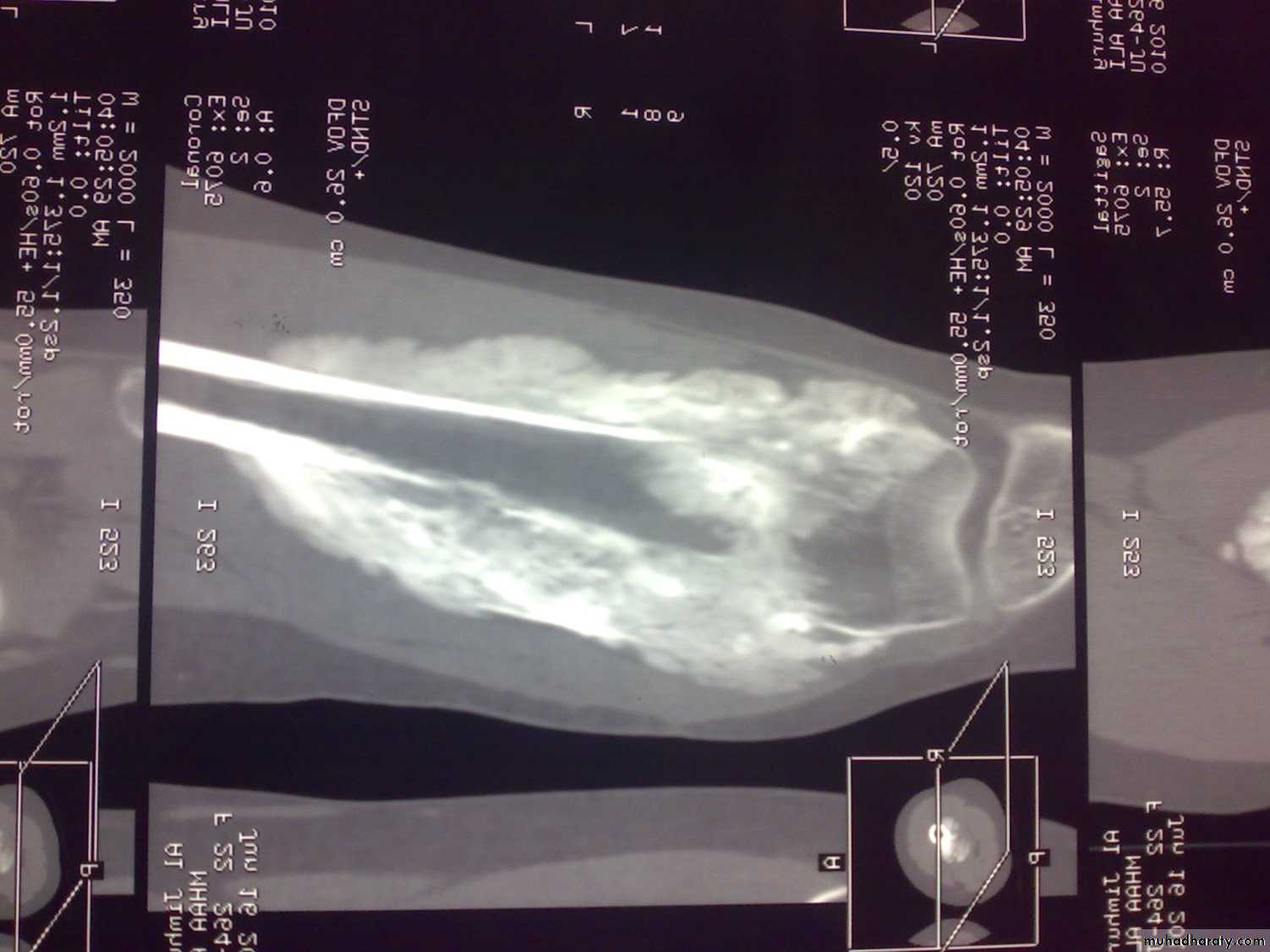
C-T scan
Indications:Segmental bone necrosis.
Depressed fracture in cancellous bone.
Small radiolucent lesion; eg oseoid osteoma.
Bone and soft tissue tumors.
Complex fractures of spine, pelvis, tarsal and carpal bones.
3-D reconstructed images.
Disadvantage: high radiation exposure.
3-D C-T in fracture pelvic ilium
C-T of shoulderMRI
Reading of radiofrequency emissions from atoms and molecules of tissues exposed to static magnetic field.
Indications:
Bone tumors; size and spread.
Spinal disorders; eg disc prolapse.
Cartilage and ligament. Eg meniscus and anterior cruciate ligament injuries.
MRI of osteosarcoma of femur
MRIFree of ionizing radiation.
Limitations:
Metallic foreign bodies and implants.
Overweight.
Fear of closed spaces.
Irritable patients and children.
Diagnostic ultrasound
Advantages: simple, portable, applied anywhere, no side effects.
Indications:
Cystic lesion, eg abscess, hematoma, aneurism.
DDH.
Rotator cuff tear.
Knee problems; eg ACL injury, meniscal tear, synovial cysts….
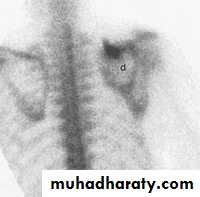
Radionucleide imaging
Technitium-99m (Tc 99m) for bone scanning.Selectively concentrated in skeletal tissues.
Increased activity (hot spots) in inflammation, infection, metastatic tumors, healing (stress) fractures.
Decreased activity (cold spots) in ischemic necrosis (eg Perthe’s disease).
Radioisotope scan
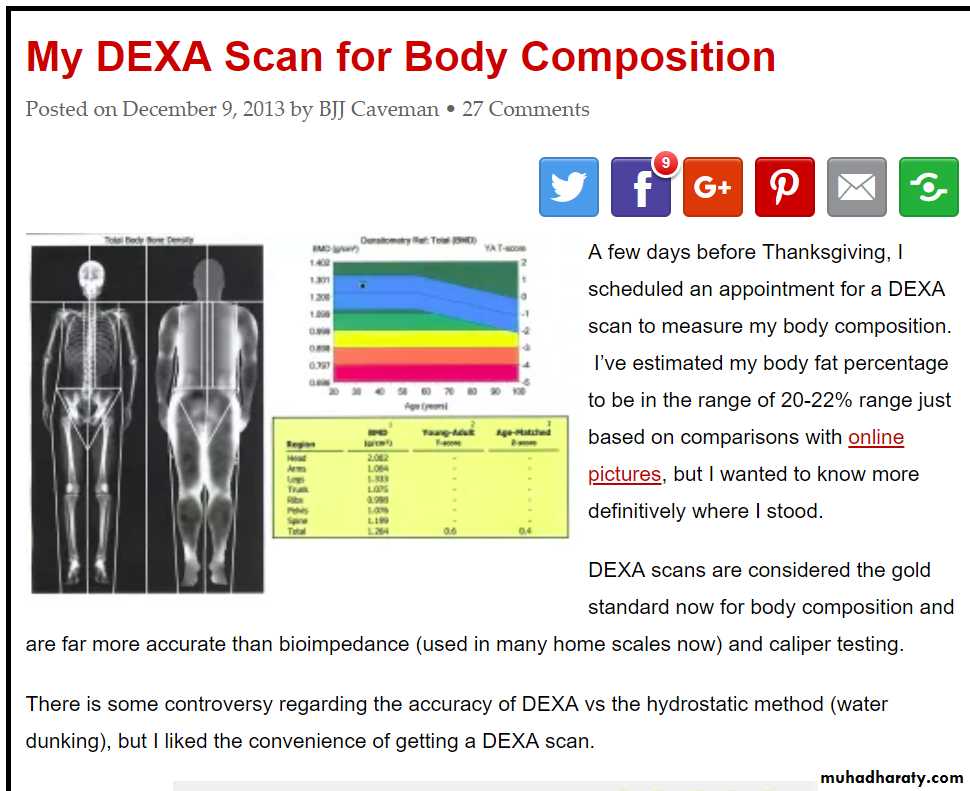
Bone Meniral densitometry (BMD)
Double Enrgy X-ray Absortiometry (DEXA) is the most reliable in measurement of osteoporosisBlood tests
Leukocytosis: in infection, rheumatoid arthritis, gout…High ESR- acute and chronic inflammatory disorders and injury, multiple myeloma.
C-reactive protein (an acute phase protein); in chronic inflammatory arthritis.
Rheumatoid factor; negative in seronegatve arthritis eg ankylosing spondylitis, reiter’s disease, psoriatic arthritis,…
Tissue typing; eg HLA B27 on chromosome 6 In seronegative arthritis.
Synovial fluid analysis
Indications:Swelling after injury- hemarthrosis.
Suspected infection.
Gout and pseudogout.
Chronic synovitis- eg TB.
Bone biopsy
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) or open biopsy.For suspected tumors.
Primary or secondary.
Benign or malignant.
Arthroscopy
Diagnostic- eg meniscal injury, cruciate ligament injury, biopsy.
Therapeutic: eg menisectomy, repair of cruciate ligament, loose body removal.
Electrodiagnosis
Nerve conduction study (NCS):Measurement of velocity of nerve conduction; normally 50-60 m/second.
Slowed in peripheral nerve damage or compression.
Elecromyography (EMG):
For diagnosis myopathy or muscle denervation.