History & Examination
1- Demographic DataAge,name,gender,occupation&race
Inherited disorder present at younger age while retinal vascular occlusion at old age
X-linked colour blindness are more common in male,special inflammatory condition more in female
Behcet disease is common in middle –east & Japan
Primary angle glaucoma is common in blacks
Patient occupation may affect ophthalmic treatment plan.
2- Chief complaint
History of present illness,onset,duration,frequency,intermittency, location,severity,associated symptoms & circumstances.3- Past ocular history
Chronic ocular disease (glaucoma , refractive error , amblyopia)
Surgical & laser procedures(phacoemulsificatiom , trabeculectomy , PRP & refractive procedures)
Ocular eye drops used as antiglaucoma
4- Past medical history
As D.M.,HT,IHD,CVA,RA,SLE. Describing duration & severity.Chronic infection TB,lyme,HIV & syphilis
Systemic diseases either affect directly as manifestation as retinopathy or complication as retinal vascular disease or indirectly through their medication.
5- Medication
As those used for chronic illness.
Steroid-cataract,chlorquine-maculopathy,ethambutol-optic neuropathy
Amiodarone-vertex keratopathy(deposition)
Aniconvulsant-nystagmus
6-Ocular family history
Refractive errors,squint,glaucoma,retinal dystrophy, retinal detachment& retinal tumours.
Basic ocular examination
1.Visual acuityDetermine the resolving power of the eye to see two different points as separate & usually tested by Snellen chart with decreasing size at fixed distance 6 m & represented by ratio comparing patient to normal values
Where numerator indicate the test distance & the denominator indicates lowest line seen written by metric 6/6, 6/9 ,…6/60, feet 20/20….20/200 or centile 1.0---0.1
Who failed decreasing distance to 3meters
Very poor vision CF then HM then LP
Non responding NPLPinhole is useful to detect poor vision due to refractive error by increasing the field of focus & decreasing most of defocused rays, while macular lesion may become worse.
2- Visual field
Confrontation test….Automated perimeter appropriate testing of field defect either static or kinetic.
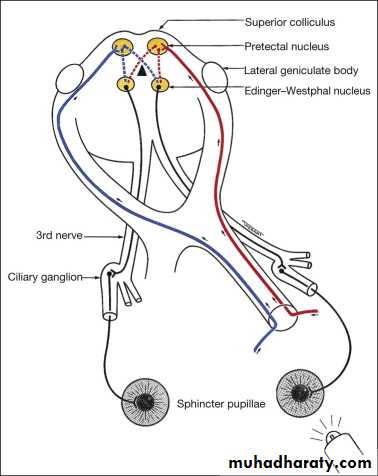
3-Pupillary examination
Size miosis = constricted mydriasis =dilated
Unequal size = anisocoria
Shape
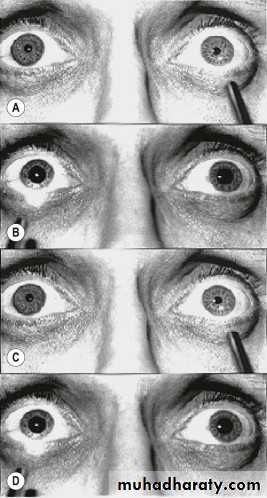
Light reflex direct , indirect(consensual)
Swinging light reflex in RAPD ”Marcus Gunn pupil” (paradoxical dilatation)
Light near dissociation : near response is much greater than light reflex
RAPD
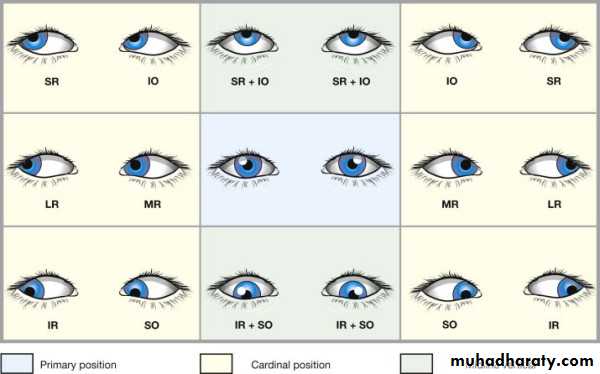
4-Ocular motility
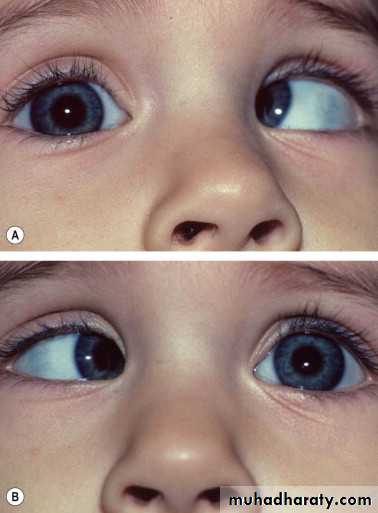
Corneal light reflection testEsotropia Exotropia
Version= conjugate (same direction)
Vergence = disconjugate (opposite direction)
Convergence & divergence
Cover test for manifest squint (tropia)
Alternate cover test for latent squint(phoria)
Commitant squint equal angle of deviation in all gazes
Incommitant squint different angle of deviation in different gazes
5- IOP
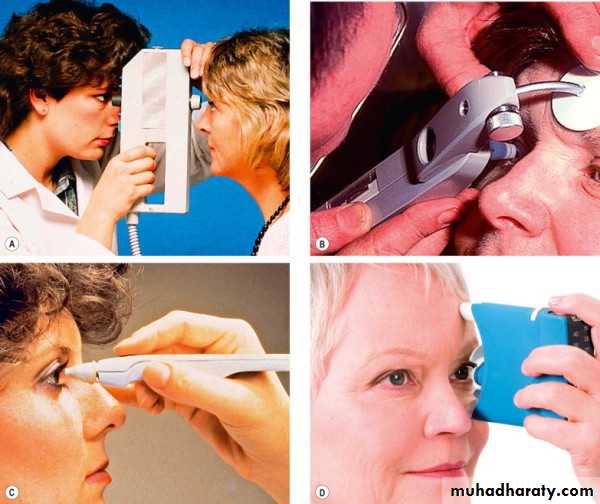
Normal rangeTonometer device measuring IOP
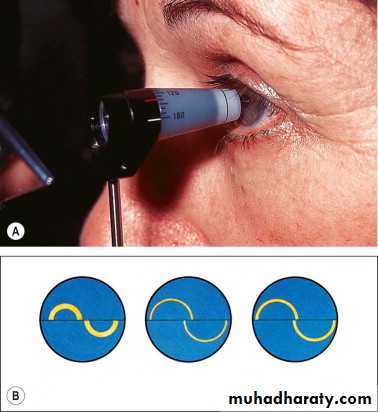
Applanation tonometer Goldmann fixed to slit lamp (gold standard) Perkines (portable)
Indentation tonometer Shiotz
Air puff (non contact)
Tonopen
6- External examination
• Face any skin lesion (zoster,hemangioma) or devietion(Bell`s palsy) or periorbital swelling as ecchymosis or depositionB. Globe
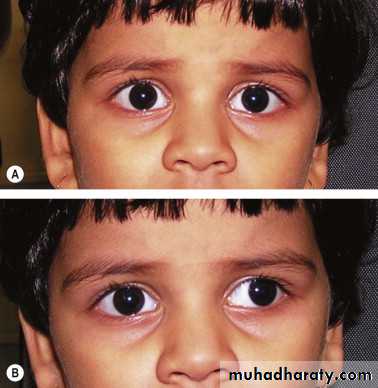
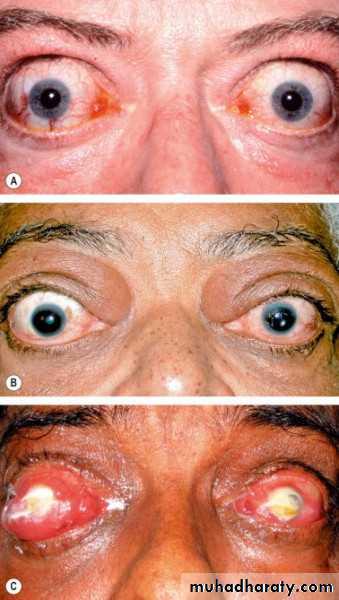
Position proptosis enophthalmos
size small(microphthalmos or nanophthalmos)
large (myopic or buphthalmos)
C. Eye lid
position ptosis or lid retractiondefect coloboma
Inflammation blepharitis
Swelling cyst or chalazion
Ulceration as in malignant tumour
Eye lash madarosis or poliosis or trichiasis
Lid margin entropion or ectropion
Other finding by inspection
Any facial spasm or twitchingAbnormal head posture or nodding
Globe pulsation
Nystagmus
Jaw winking (ptotic lid retract with jaw movements)
7- Slit lamp examination
Minimum light with systemic stepsLid…skin…lid margin…eye lashes
Conjunctiva 3parts+lid evertion
Cornea diffuse light … slit (cross section) to see the layers
Ant. Chamber depth , cells, blood(hyphyma),
Iris atrophy , nodule , rubeosis
Lens status (phakic, aphakic, pseudophakic)
opacity (cataract)
position(sublaxated,dislocated)
Ant. Vitreous cells & opacities
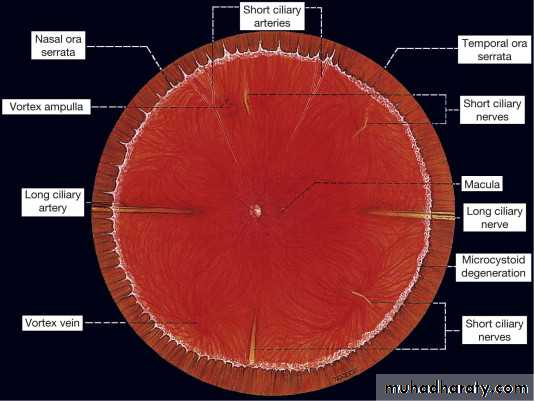
8- Fundoscopy
Retinal & optic disc exam. need pupilary diltationDirect ophthalmoscope
Uniocular..large image..small field..close to patient
Indirect opththalmoscope
Binocular..small image..large field.. auxiliary lens
Slit lamp biomicroscopy
large image with fine retinal details
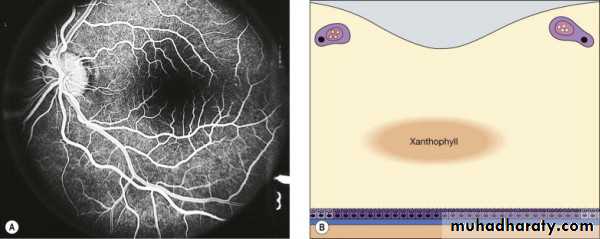
Fluorescein dye:
orang-yellow in colour but fluorescence green with blue light
Uses:
epithelial defect detection in cornea or conjunctiva
ocular wound leakage( siedle test)
Goldmann tonometer
Patency of lacrimal passages detection
IV fluorescine for retinal & choroidal vessel study
Pupilary diltation:
(mydriasis) uses• examination of mid & peripheral retina
• before cataract surgery to facilitate lens extraction & avoid iris damage
• prevention or break up of synechia
Common mydriatics
parasympatholytic:
Tropicamide(mydriacel),Cyclopentolate(cyclogel)
& Atropine
sympathomemitic : Phenylphrine
Adjunctive examination
Lid evertionfluorescine stain
gonioscopy
prism
ruler
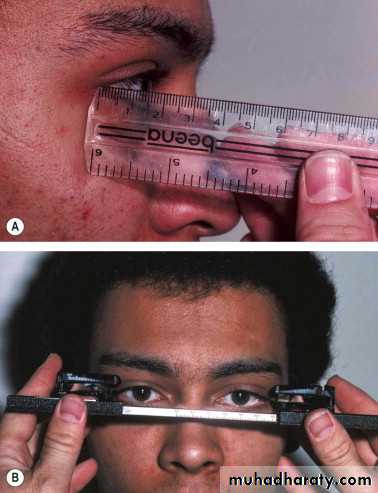
Hertel exophthalmometer
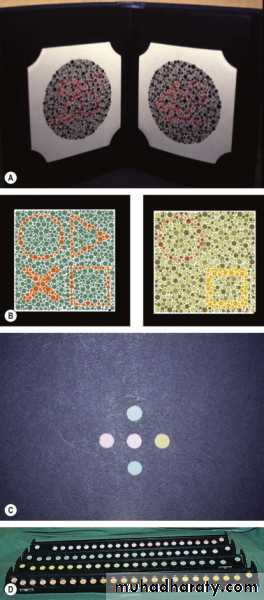
colour vision as Ishihara plates
perimetry
keratemeter
topography
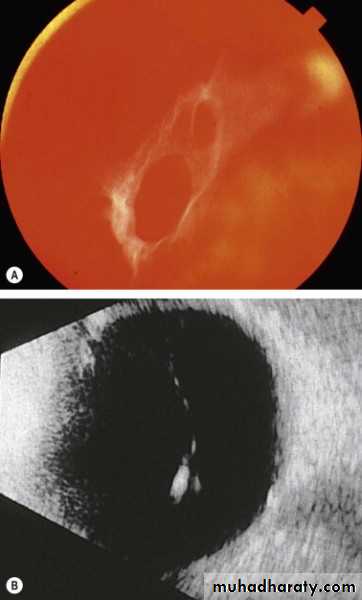
U/S of eye
A-scan one dimension axial lengthB-scan two dimensions RD,VH in opaque media
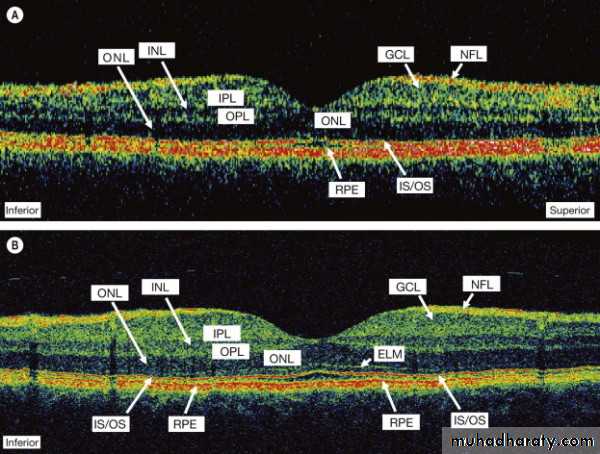
OCT
Schirmer test qualitative test for dry eye
Biometry
Optic nerve analyzer