Fifth Stage
E.N.T
Dr. Mushtaq – Lecture 2
1
DISEASES OF THE EXTERNAL EAR
AURICALE
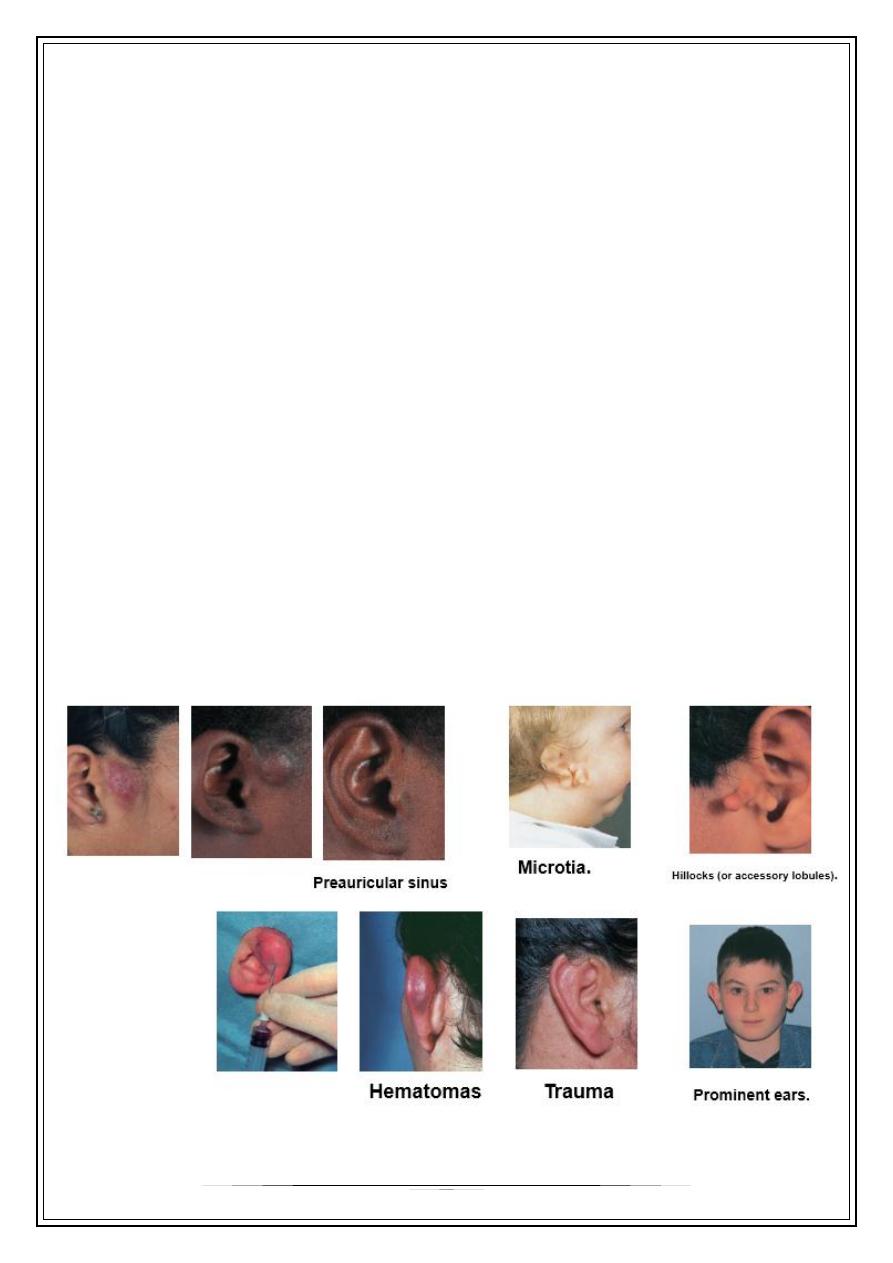
1. Congenital: Artesia ,microtia ,
secondary auricle,
& preauricular sinus / fistula
2. Trauma: * haematoma
*laceration
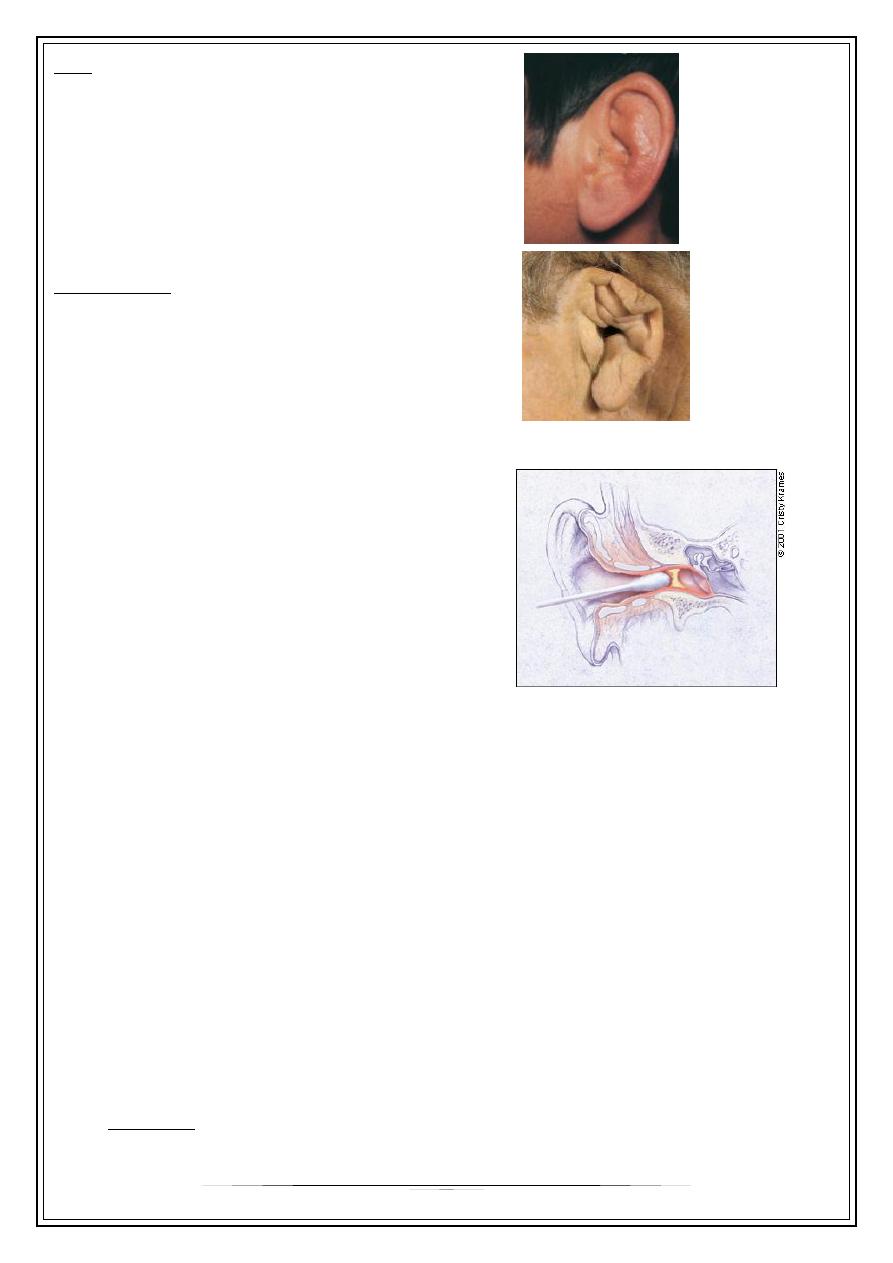
3. Perichondritis: infection of the skin and tissue surrounding the cartilage of the outer
ear.
- causes: - haematoma
- extension of infection from EAM
- iatrogenic/ self-induced
-> Pseudomonas pyocyanea
2
C/F:
- severe pain
- swollen , hot & dusky color
- necrosis &deformity
Treatment :
1- ticarcillin
2- 3
rd
generation cephalosporin
3- incision
WAX
•
pilosebacious & ceruminous glands
•
A.A, F.A., Lysozymes & I.g.
•
migration X impaction
•
Deafness , otalgia & vertigo
•
Softening (bicarbonate)/ Syringing
•
Removed by cerumen hook
OTITIS EXTERNA
o
Is an inflammation of the skin of the external ear arising from local or general
causes or from both.
o
Predisposing factors:
a- heat, humidity, bathing
&swimming
b- trauma via cotton buds, dirty
finger& hair grips
c- hereditary / narrow canal.
Classification
A. Infective :
1-bacterial :
Cauliflower

3
- diffuse otitis ext.
- localized (furunculosis)
- malignant otitis ext.
- erysipelas
- perichondritis
- impetigo
2- fungal :
- Aspergillosis
- candidiasis
3- viral :
- herpes simplex
- herpes zoster
B- Reactive
1) Eczematus
2) Seborrhoeic
3) Neurodermatitis
4) Keratitis obturans
5) psoriasis
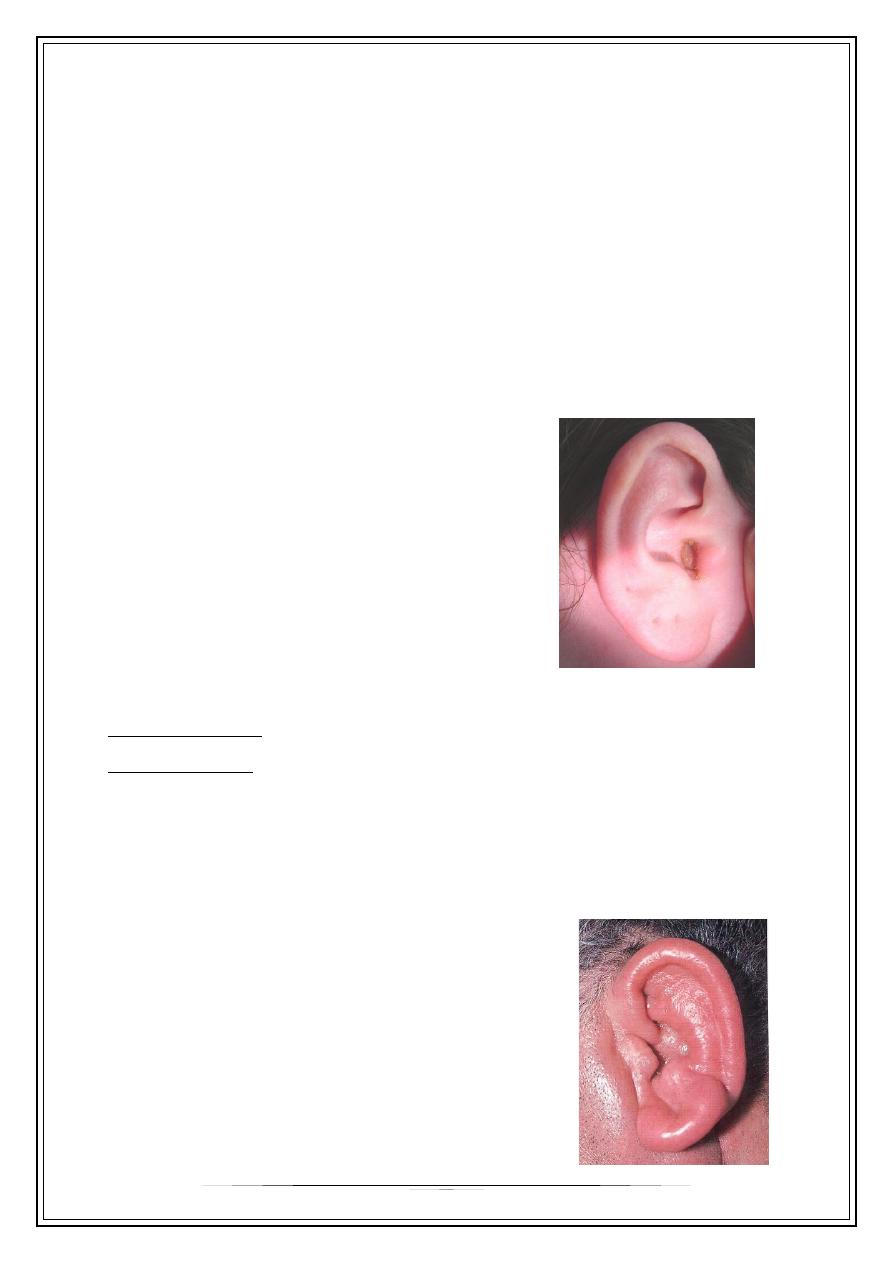
Furunculosis
•
Staphylococcal infection of the hair follicle affects
the cartilaginous part of the EAM.
C/F ; * itching
* pain
* hearing difficulty /large
* regional lymphadenitis
Diffrential Diagnosis
1) ACUTE MASTOIDITIS / OM.
2) HERPETIC LESIONS/ vesicles
3) EXOSTOSIS / hard swelling//bony
4
Treatment
•
Antistaph/antibiotics
•
Local soothing agent (oint.)
•
Analgesia +/- sedation
•
Incision
Diffuse otitis externa
•
Infective dermatitis
•
Mixed inf. / strept. , staph , & G-ve
•
C/F: - itching
- pain
- redness
- swelling
- serous oozing
- crust
- LN.
- scaling, fissuring& stenosis /chronic
Treatment
•
Systemic AB. Broad spectrum
•
Local treatment
* aural toilet
* wick soacked with 8% alminium acetate
* AB / steroid wick
Erysipelas
•
Acute superficial cellulitis
•
Group A, beta hemolytic streptococci
•
Skin: bright red; well demarcated,
•
Advancing margin
• Rapid treatment with oral or IV antibiotics
5
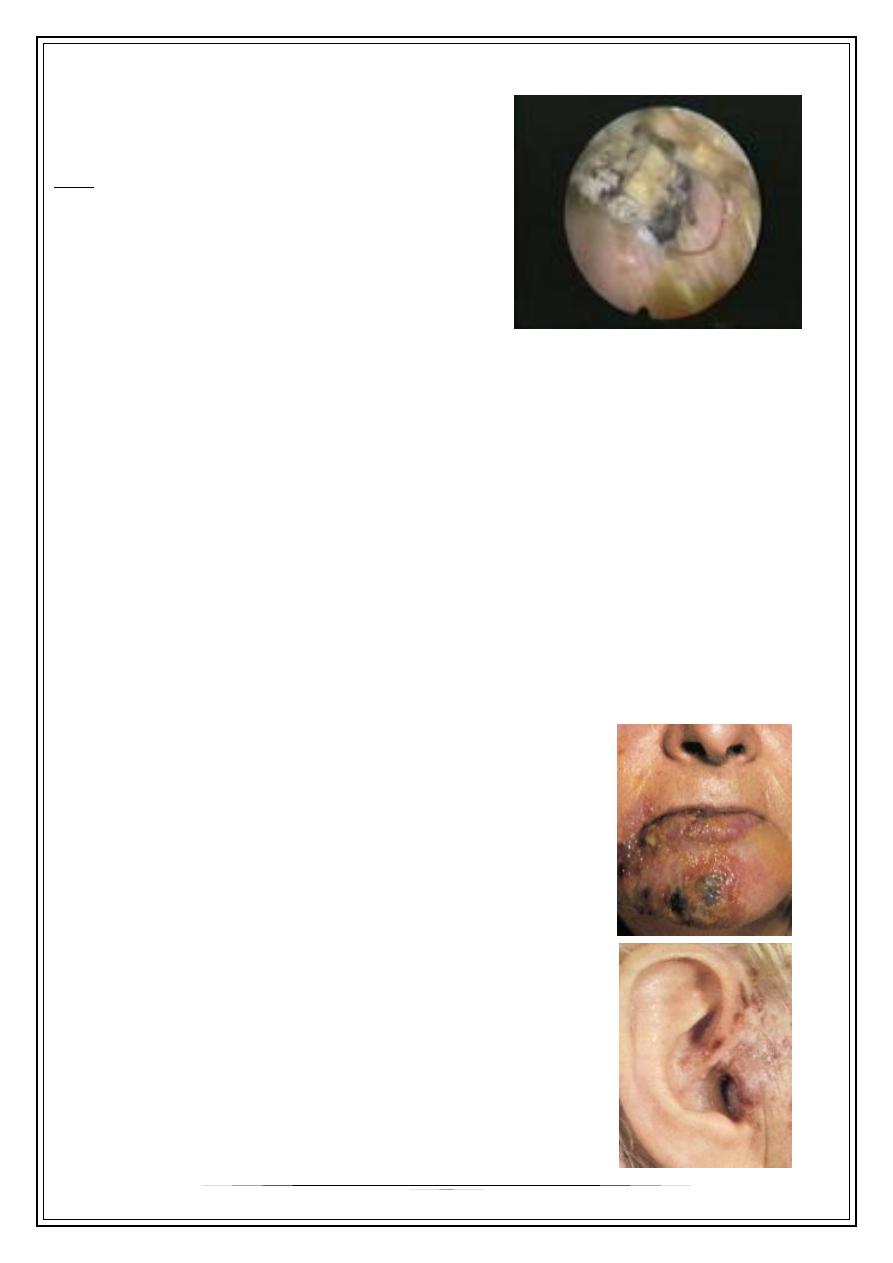
Otomycosis
•
Aspergilla spp. ,candida
•
Hot& moist climates
C/f :
* thick discharge
* mass like wet newspaper
* granules containing hyphae, & spores
* pain is unusual X pyogenic infection
Dx: - direct ex.
- culture
R/:
•
Removal of mass
•
Keratolytic agent
•
Fungicides / nystatin , clotrimazole, amphotericin B
Herpetic lesion
1) H. simplex
2) H. zoster oticus
3) Otitis externa haemorrhagica
Herpes zoster oticus
•
C/f : D.M //immunosuppressive
pain may present several days before
rash
Vesicular rash /concha /disappear early
cranial n. palsies ( VII.)
vertigo
SNHL
•
R/ :
antiviral ( acyclovair)
analgesia
6
Malignant otitis externa
•
Pseudomonal inf.
•
Not infrequently fatal/ involvement of the sigmoid sinus or meninges
•
Elderly diabetic & immunocompromised pt.
•
Osteitis +/_ osteomyelitis
•
Cr. N n (V, VI, VII, --- IX,X, XI, XII)
Clinical features
Pain
Discharge , may be seropurulent
Granulation tissue / floor
Cr. N. palsies
Treatment
1. Medical:
•
Control of DM
•
3
rd
generation cephalosporin
•
Gentamycin
•
Topical application of the gentamycin.
2-Surgical R/ :
Removal of the gr. T. /mastoidectomy
•
Prognosis: -worse with cr , n . Involvement
- may be fatal
Bullous Myringitis
•
• Viral infection
•
• Confined to tympanic membrane
•
• Primarily involves younger children
Symptoms:
•
Sudden onset of severe pain
•
No fever
•
No hearing impairment
•
Bloody otorrhea (significant) if rupture

7
Signs:
•
Inflammation limited to TM & nearby canal
•
Multiple reddened, inflamed blebs
•
Hemorrhagic vesicles
Treatment
•
Self-limiting
•
Analgesics
•
Topical antibiotics to prevent secondary infection
•
Incision of blebs is unnecessary
Reactive otitis externa
Eczematous ot, ext.
•
Aetiology:
*- extrensic factors :
- general/ food, inhalation allergy
- local / contact dermatitis//nickle
( spectacle frame).
* - intrensic factors : psychosomatic (neurodermatitis)
•
C/f:
* Iritation ,redness , +/_ oedema
* Weeping & crust formation
* Scaling & fissuring in chronic state
•
R/ :
* local & systemic steroid
* antihistamine
Thank you,,,
