TMJ
“There is no area of oral and maxillofacial surgery that engenders more discussion
and legitimate difference of opinion than that of temporomandibular joint
surgery.”
PETER D. QUINN
Disease of ----
DevelopmentalInflammatory / infectious condition
Degenerative / autoimmune
Cystic lesion
Traumatic injury
Neoplasm
Miscellaneous
Disease of the TemporoMandibular Joint (TMJ)
Developmental DisturbancesHypoplasia
Unilateral, Bilateral
Example “first arch syndrome” , Hemifacial microsomia ( 1st & 2nd arch syndrome or otomandibular dysostosis), Treacher Collins Syndrome (mandibulofacial dysostosis)
Hyperplasia
Hemifacial hyper atrophy
Condylar hypoplasia
Is facial deformity caused by a short mandibular ramus.
This condition usually results from trauma, infection, or irradiation occurring during the growth period but may be idiopathic.
The deformity involves fullness of the face
Deviation of the chin to the affected side
An elongated mandible
Flatness of the face on the unaffected side. (The side to which the ramus is short causes muscles to appear fuller; the muscles on the unaffected side are stretched so that side appears flatter.) Mandibular deviation causes malocclusion.
Diagnosis is based on a history of progressive facial asymmetry during the growth period
X-ray evidence of condylar deformity and antegonial notching (a depression in the inferior border of the mandible just anterior to the angle of the mandible),
frequently, a causative history.
Treatment consists of surgical shortening of the unaffected side of the mandible or lengthening of the affected side.
Presurgical orthodontic therapy helps optimize results.
Disease of the TemporoMandibular Joint (TMJ)
Infection( specific, non specific infection)
Acute, chronic
Viral, bacterial, fungal
Origin
Ear
Direct injury
Systemic spread
Disease of the TemporoMandibular Joint (TMJ)
Traumatic injury to the joint
Traumatic arthritis
Acute subluxation
Chronic subluxation
Dislocation
Acute, chronic
Anterior, posterior, medial , lateral
Tearing of the disk
Damage to the condyle
# condyle
Infection
Still’s disease (Systemic-Onset Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis) is a disorder characterized by inflammation with high fever spikes, fatigue, salmon-colored rash and/or arthritis. Though there have been several theories regarding the cause(s) of Still's disease, the cause is not yet known. Many symptoms of Still's disease are often treatable with anti-inflammatory drugs)
Ankylosis of the Temporomandibular join
Disease of the TemporoMandibular Joint (TMJ)
Limitation of Mouth openingExtra capsular causes
# zygoma
Coronoid bone hyperplasia ( enlargement)
Scar tissue due to burn of the skin of the face
Neurogenic causes
Myogenic causes ( scar tissue in the muscles of mastication, myositis ossificans due to injury)
Psychogenic causes (hysterical condition)
Submucous fibrosis
Inferior Dental block
Haematoma
Low grade infection
Wisdom tooth removal (oedema , swelling and trismus)
Tetanus
Intra capsular causes
Ankylosis of the TMJ
Fibrous Ankylosis
Bonny ankylosis
Disease of the TemporoMandibular Joint (TMJ)
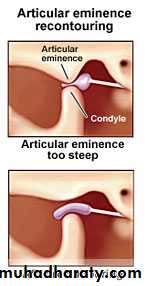
Functional Disturbances of the jointDisease of the TemporoMandibular Joint (TMJ)
OsteophytePannus formation
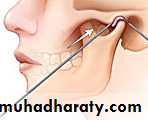
Arthrocentesis (is the irrigation of the joint.)
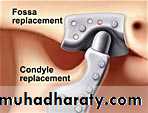
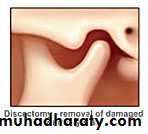
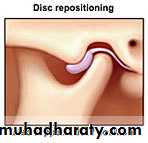
Arthroplasty refers to all types of open surgery for TMJ, including disk repositioning, discectomy, and joint replacement
Disk repositioning is used when the protective cartilage disk has slipped out of place inside the TMJ
A discectomy is performed when the disk providing padding and protection to the TMJ has deteriorated or become damaged
TMJ replacement
Disease of the TemporoMandibular Joint (TMJ)
MALIGNANT TUMORSOsteogenic sarcoma
Chondrosarcoma
Synovial cell sarcoma
Synovial fibrosarcoma
Multiple myeloma
Lymphoma
Aggressive fibromatosis
Disease of the TemporoMandibular Joint (TMJ)
BENIGN TUMORS AND LESIONSOsteoma
Osteochondroma
Chondroma
Chondroblastoma
Giant cell granuloma
Giant cell tumor
Neurofibroma
Hemangioma
Arteriovenous malformation
Synovial chondromatosis
Osteochondrosis dissecans
Villonodular synovitis
Ganglion cyst