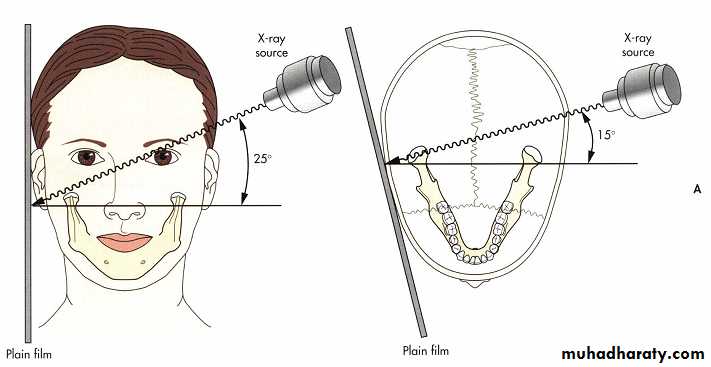
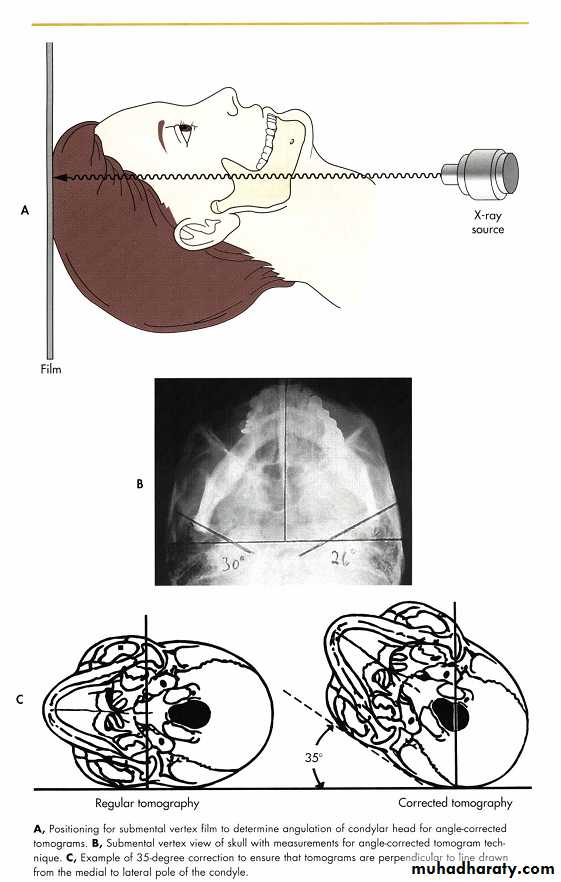
Imaging of the TMJ
RadiographTechnetium 99 (scanning the bone by injecting technetium- labeled phosphate complexes ). Higher activity is seen at sites of growth, inflammation, and neoplasm and areas where reactive bone is formed during reparative processes
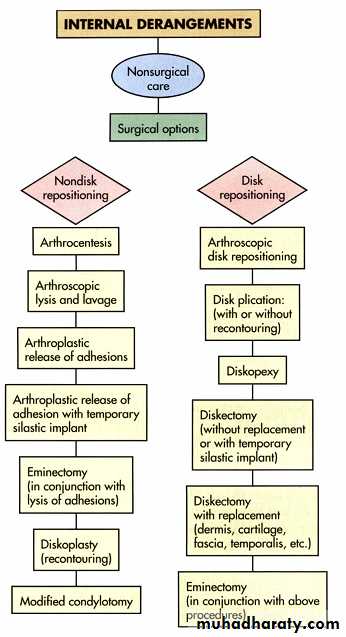
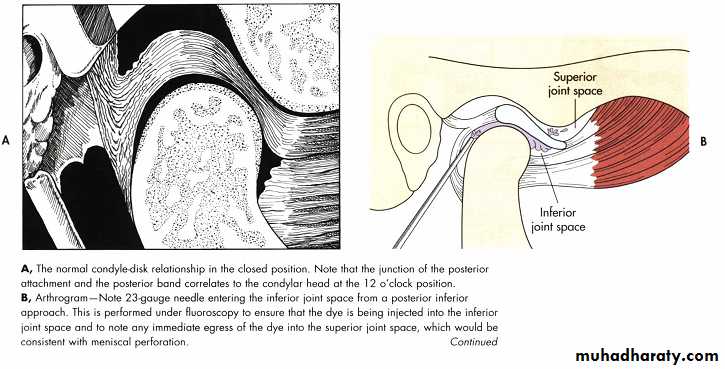
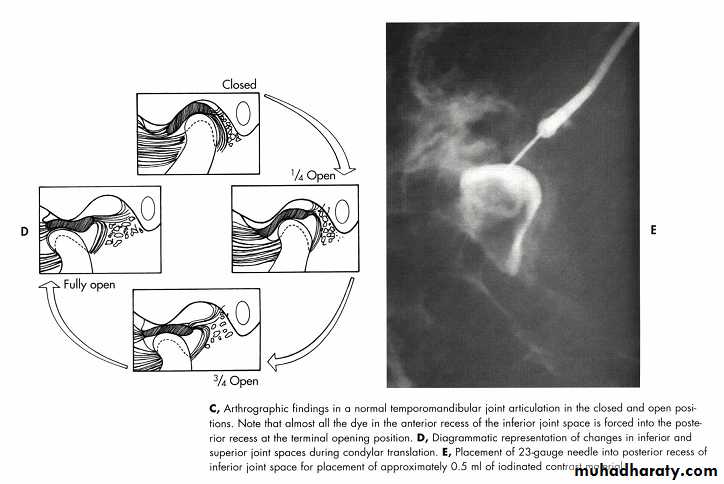
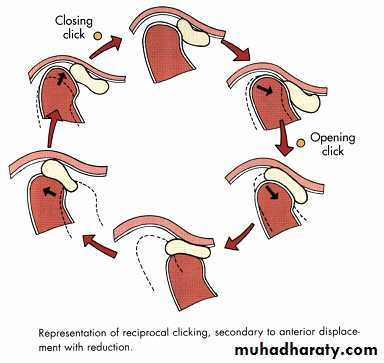
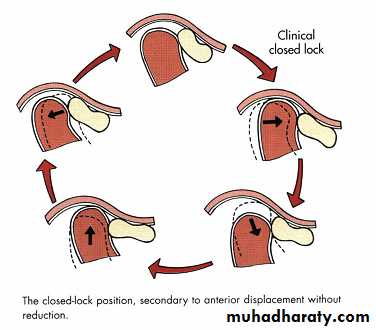
Arthrography ( injecting water soluble, iodinated contrast material into the inferior joint space under fluoroscopy, to show various stages of disk displacement with or with out reduction by a videotaped arthrofluoroscopic)
CT
MRI
Disadvantages of Arthrography
• Invasiveness• Pain (intra or postoperative)
• Risk of infection
• potential damage to
• disk
• capsule
• fibrocartilage
• Allergy to contrast material
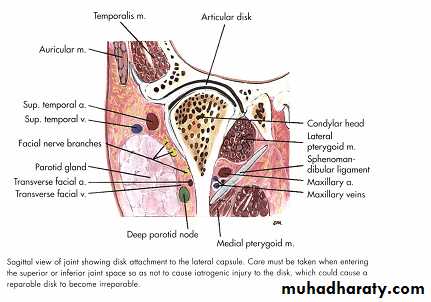
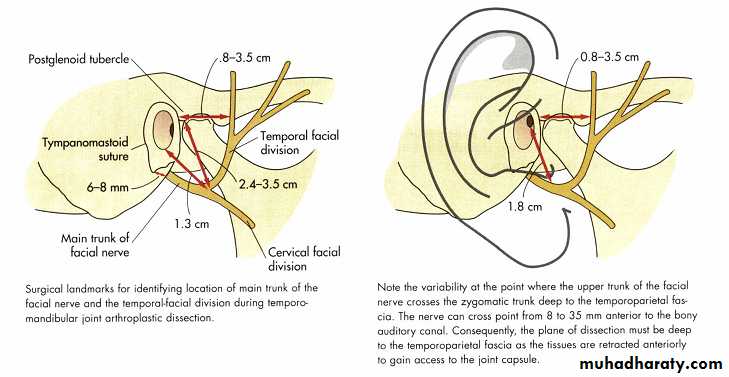
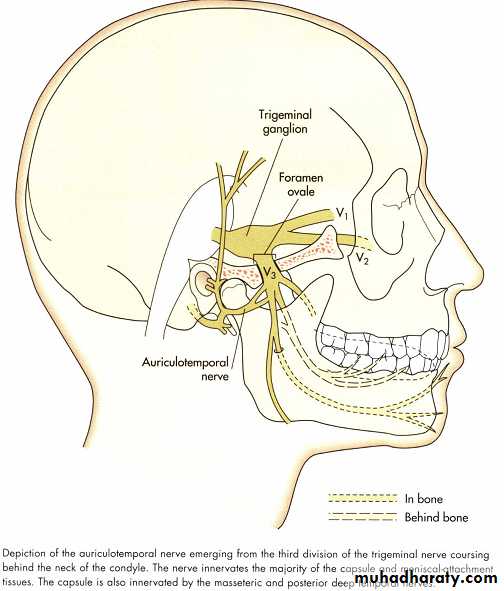
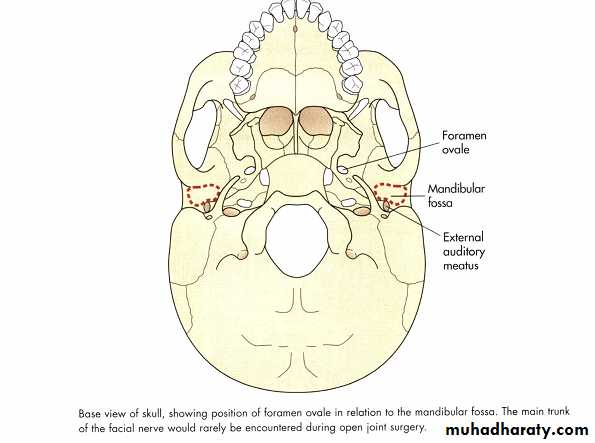
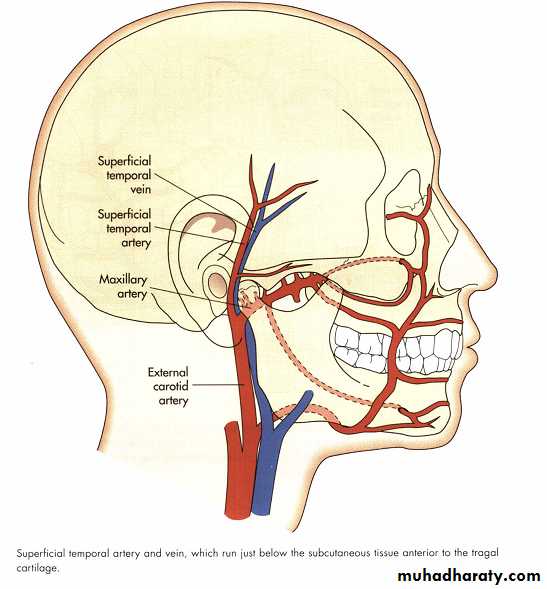
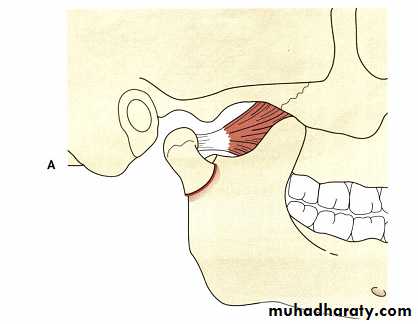
Applied anatomy
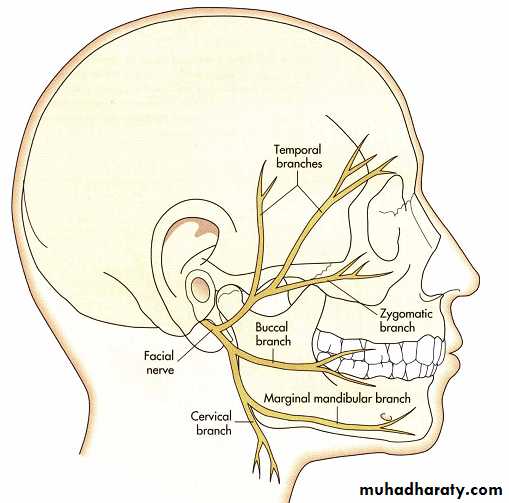
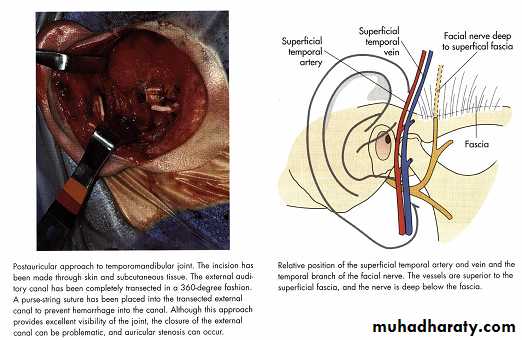
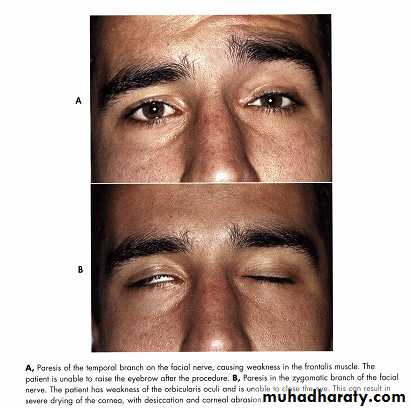
Facial nerveAuriculotemporal nerve
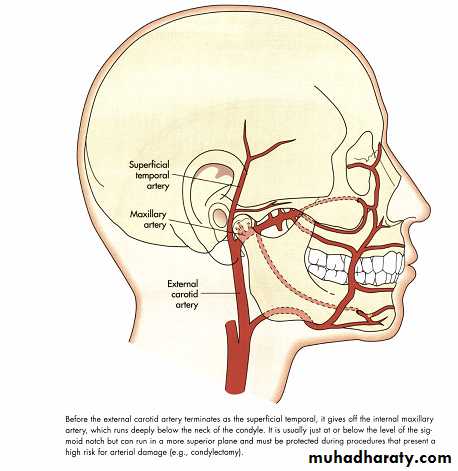
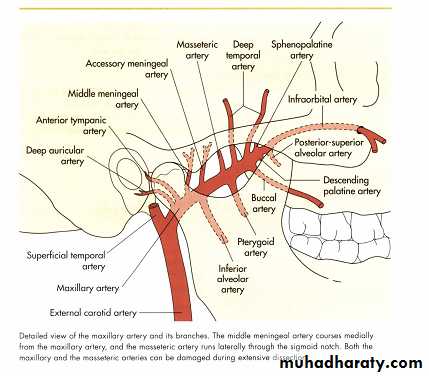
Vascular anatomy
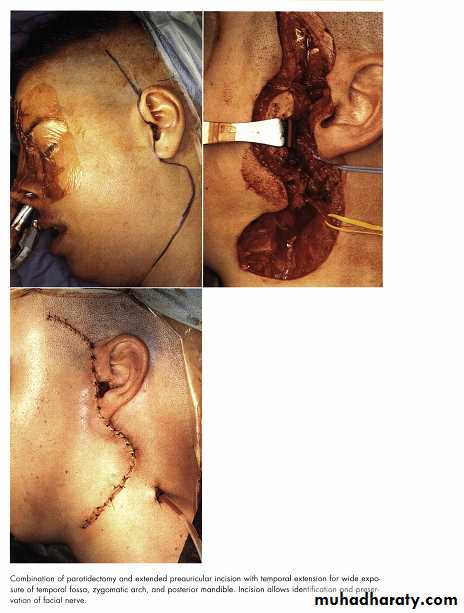
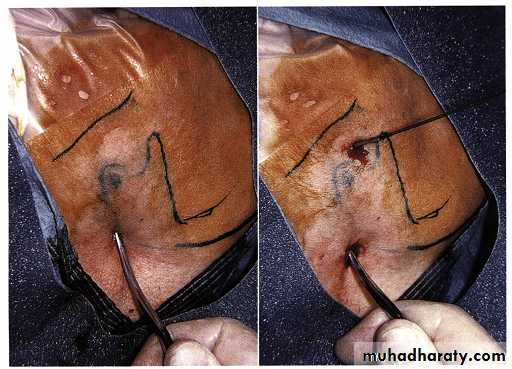
Rhytidectomy Approach
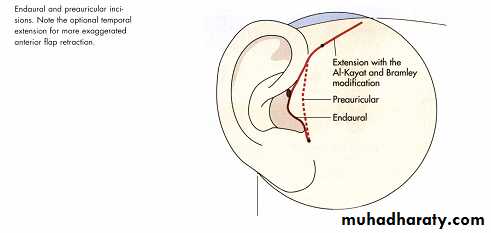
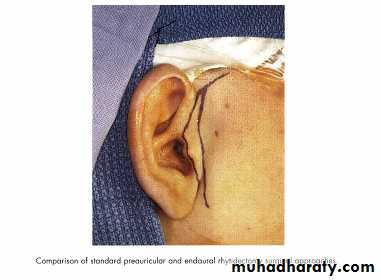
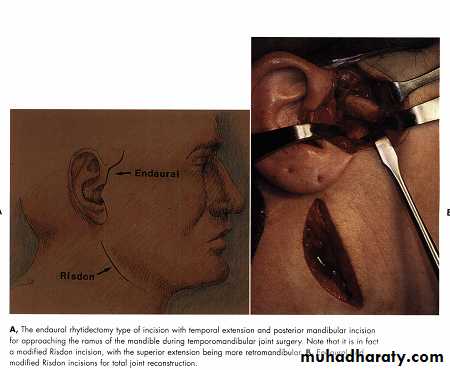
Preauricular ApproachEndaural Approach
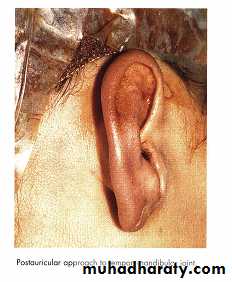
Postauricular approach
Submandibular Approach
(Retromandibular)
Intra Oral Approach
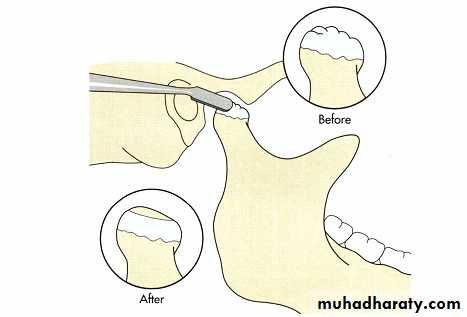
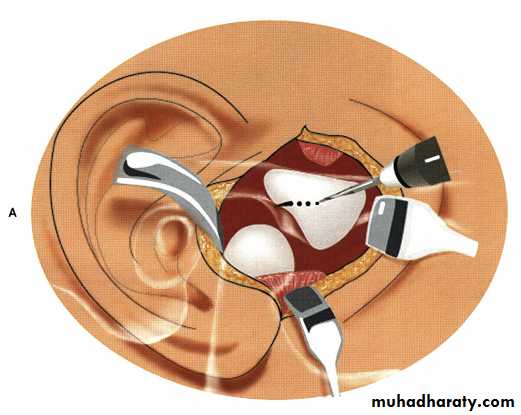
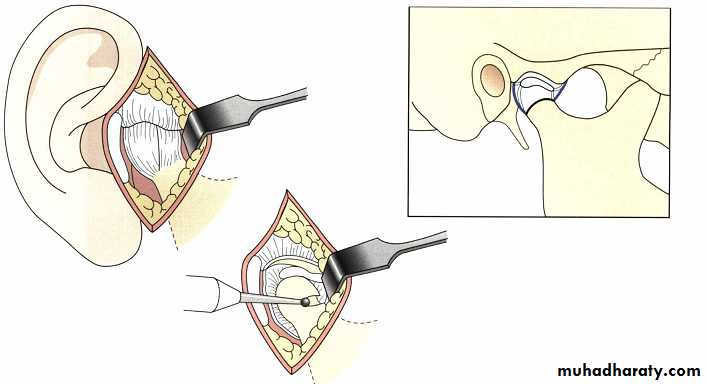
Bone file being used to contour the head of the condyle during condyloplasty procedure. Although this maneuver can sometimes be beneficial in removing osteophyte's, the fibrocartilage damaged during the procedure does not regenerate and further degenerative changes can occur secondary to the procedure
itself.
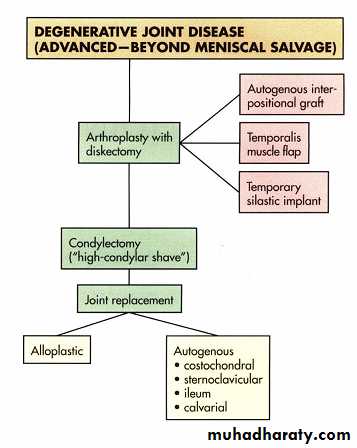
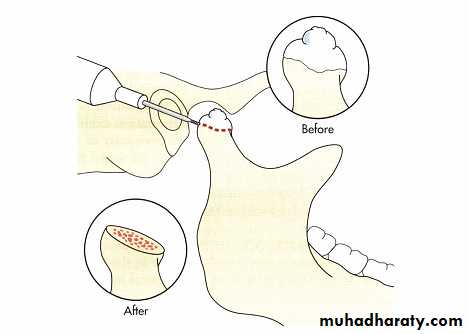
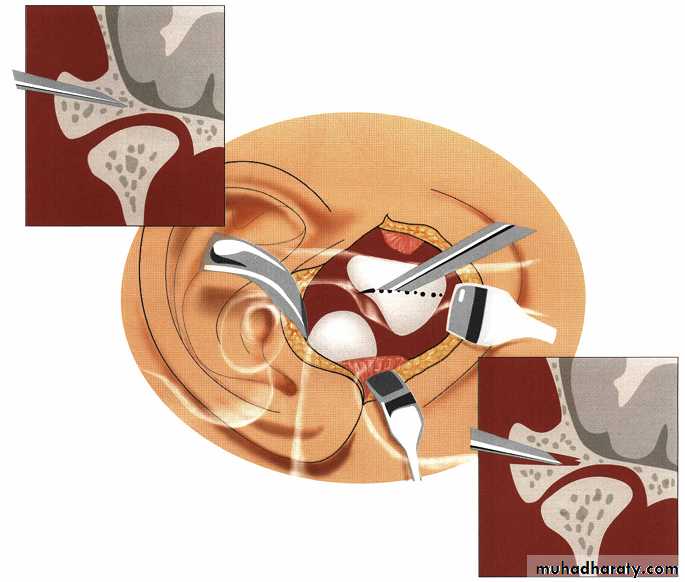
High condylar shave. A 1-mm fissure bur is used to remove a 3- to 4-mm section of the anterior-superior slope of the condyle. The cortical edges are then smoothed with a bone file. This maneuver often exposes underlying morrow in the condylar head and leads to progressive sclerosis and degeneration. (This procedure, in widespread use in the 1970s and early 1980s, involved a 2· to 4·mm resection of the anterior· superior slope of condyles that exhibited signs of degeneration, including sclerosis, breaking, subchondrol cysts, and osteophytes.
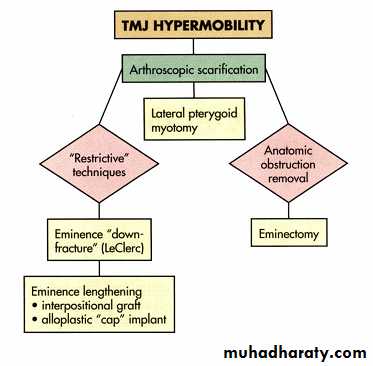
Eminoplasty-eminenectomy
A, Initiating osteotomy of articular eminence with 1-mm fissure bur. Approximately 90% of the cut is performed with the bur.
B, Completing eminectomy with osteotome. Note inferior angulation to ensure that the bony cut stays below the base of the skull.
B
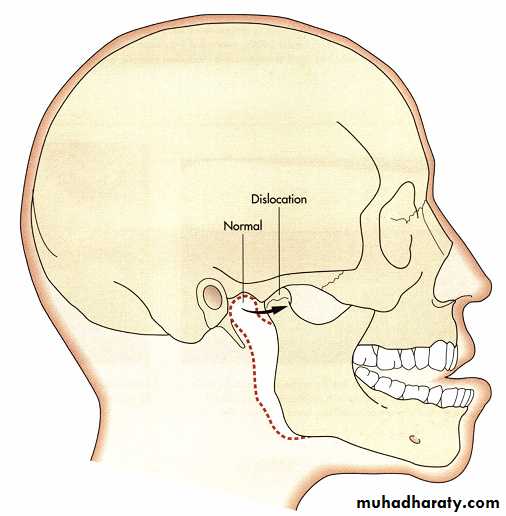
Autogenous or allogeneic bone or prosthetic implants have been used to lengthen the steepness of the articular eminence and thereby decrease the hypermobility of the condyle and prevent dislocation.
An alternative method to lengthen the articular eminence is the Doutrey procedure, in which the zygomatic arch is osteotomized and then fractured in an inferior position. It is subsequently secured
to the depth of the articular eminence to lengthen the slope of the anterior eminence.
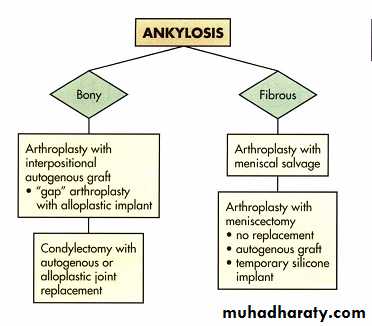
CONDYLECTOMY
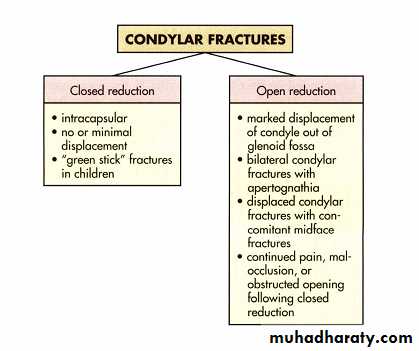
CONDYLOTOMY
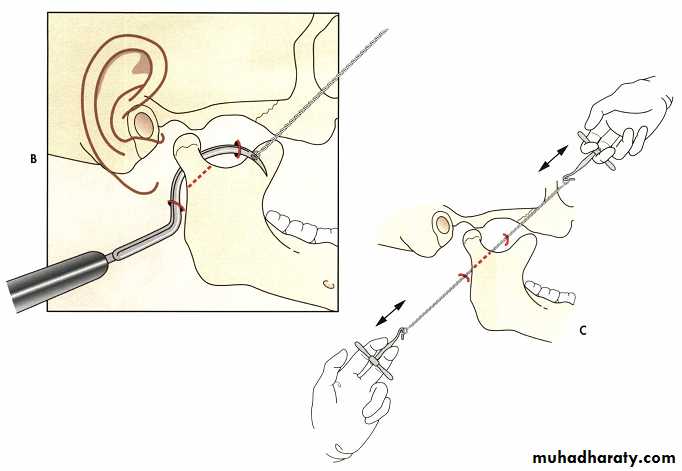
Costich needle is passed posterior to the ramus with the exit point in the coronoid notch