
Medicine
Dr.Abdullah Alyouzbaki
1
Liver cirrhosis
Real Case
• 54 yrs old post menopausal lady with Hx of upper
abdominal colic and ascites , loss of appetite.
• PMHx:HT
• O/E depressed , mild pallor , no stigma of CLD , ascites.
• Did EGD: varieces grdae 1-2 ,
• EUS fibroscan: cirrhotic liver.
• US: normal Liver ( size and shape) , prominent portal vein ,
splenomegaly.
• CT abdomen: moderate ascites , splenomegaly ,normal
looking portal vein , Rt adexial mass
• Hepatitis screen:-ve.
• Is this pt had cirrhosis??
Cirrhosis
Hepatic necrosis and degeneration combined with hepatic
regeneration and fibrosis leading to Nodular formation
CAUSES OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS
-Infections:post hepatitic cirrhosis(B,D,C).
-Toxins:Alcohol.
-Cholestatic liver disease:PBC,PSC…
-Autoimmune diseases:autoimmune hepatitis.
-Vascular disorders: cardiac cirrhosis,Veno occlusive disease
2
-Metabolic and genetic :Wilson disease
,hemochromatosis,alpha 1- antitrypsin deficiency.
-Non alcoholic steato hepatitis(NASH).
-Cryptogenic.
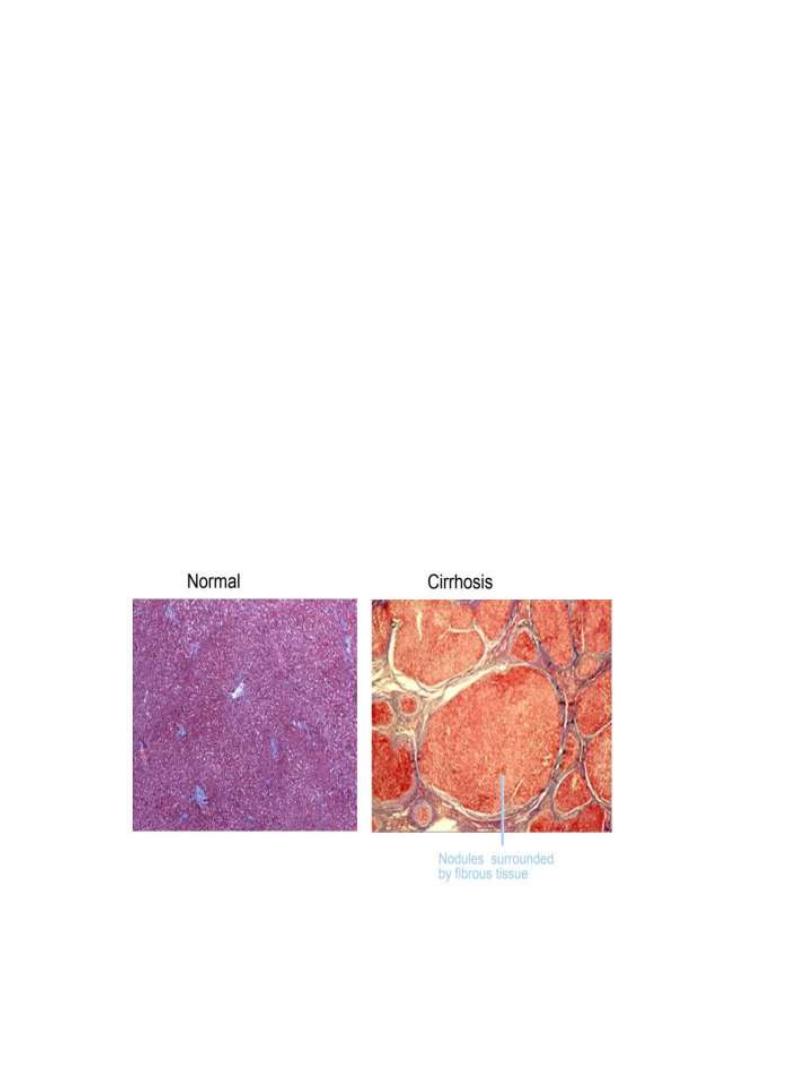
Pathology of cirrhosis
• nodularity(regenerating nodules).
• fibrosis(deposition of dense fibrous septa)
• fragmentation of sample.
• abnormal liver architecture
• Hepatocyte abnormalities : pleomorphism, dysplasia,
hyperplasia
• Gross pathology : irregular surface ,yellowish colour , small
, firm
3
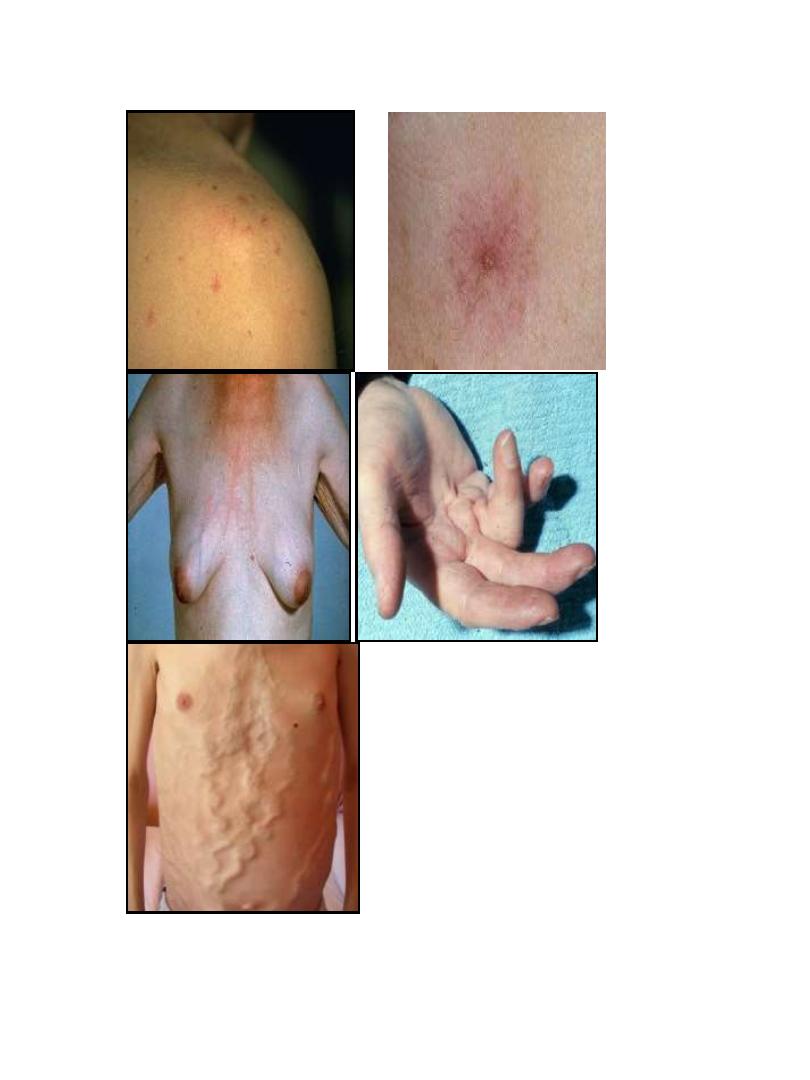
CLINICAL FEATURES
•
Hepatomegaly (although liver may also be small)
•
Jaundice
•
Ascites
•
Circulatory changes – Spider telangiectasia, palmar
erythema, cyanosis
•
Endocrine changes – Loss of libido, hair loss
–
Men: gynaecomastia, testicular atrophy, impotence
–
Women: breast atrophy, irregular menses,
amenorrhoea
•
Haemorrhagic tendency – Bruises, purpura, epistaxis,
menorrhagia
•
Portal hypertension
– Splenomegaly, collateral vessels, variceal bleeding, fetor
hepaticus
• Hepatic (portosystemic) encephalopathy
• Other features
– Pigmentation, digital clubbing
4

5
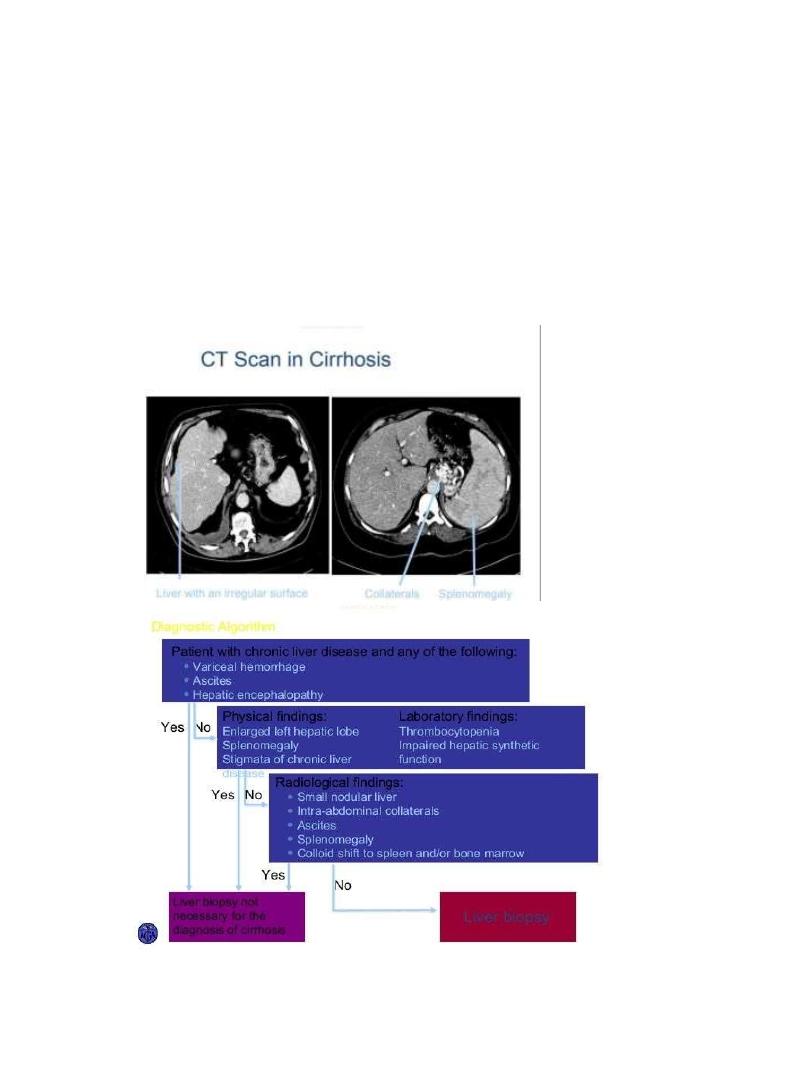
Diagnosis of cirrhosis
• clinical + laboratory+ radiologic + fibroscan +/liver biopsy.
In Whom Should We Suspect Cirrhosis?
• Any patient with chronic liver disease
• Chronic abnormal aminotransferases and/or alkaline
phosphatase
• Physical exam findings
• Stigmata of chronic liver disease (muscle wasting, vascular
spiders, palmar erythema)
• Palpable left lobe of the liver
• Small liver span
• Splenomegaly
• Signs of decompensation (jaundice, ascites, asterixis)
• Laboratory
• Liver insufficiency
6
• Low albumin (< 3.8 g/dL)
• Prolonged prothrombin time (INR > 1.3)
• High bilirubin (> 1.5 mg/dL)
• Portal hypertension
• Low platelet count (< 140 x1000/µl)
• AST / ALT ratio > 1
CT Scan in Cirrhosis
7
Management of cirrhosis
•
Specific treatment in some pre cirrhotic lesions: wilson
disease : penicillamine. hemochromatosis : phlebotomy.
antiviral drugs for chronic viral hepatitis.
•
in established cirrhosis---treatment of complications.
•
screening for hepatocellular carcinoma
•
liver transplantation
•
maintenance of nutrition
CHILD-PUGH CLASSIFICATION OF PROGNOSIS IN
CIRRHOSIS
MELD SCORE
• MELD = 3.8(SERUM BILIRUBIN – G/DL)+11.2
IN INR + 9.6 IN SERUM CREATININE – MG/DL+ 6.4

8
PORTAL HYPERTENSION
•
Definition:it is an increase in portal venous pressure.
•
-normal portal pressure:5-10mmHg.
•
-portal hypertension;>12mmHg
•
-normal portal blood flow:1-1.5L/minute
•
- increased resistance to portal blood flow +hyperdynamic
circulation-----formation of porto systemic collaterals that
diver blood to systemic circulation bypassing the liver
CAUSES OF PORTAL HYPERTENSION
ACCORDING TO SITE OF ABNORMALITY
•
Extrahepatic post-sinusoidal: Budd-Chiari syndrome
•
Intrahepatic post-sinusoidal: Veno-occlusive disease
•
Sinusoidal:
-Cirrhosis
-Cystic liver disease
-Partial nodular transformation of the liver -Metastatic
malignant disease
•
Intrahepatic pre-sinusoidal: Schistosomiasis, Sarcoidosis,
Congenital hepatic fibrosis, Vinyl chloride, Drugs.
•
Extrahepatic pre-sinusoidal: Portal vein thrombosis due to
sepsis* (umbilical, portal pyaemia) or procoagulopathy
(thrombotic diseases, oral contraceptives, pregnancy), or
secondary to cirrhosis , Abdominal trauma, including
surgery, Malignant disease of pancreas or liver,
Pancreatitis, Congenital
9
Clinical complications of PHT
•
VARICES:esophageal,gastric,anorectal,retroper itoneal.
•
portal hypertensive gastropathy and colopathy.
•
caput medusae
•
ascites
•
congestive splenomegaly
•
hepatic encephalopathy
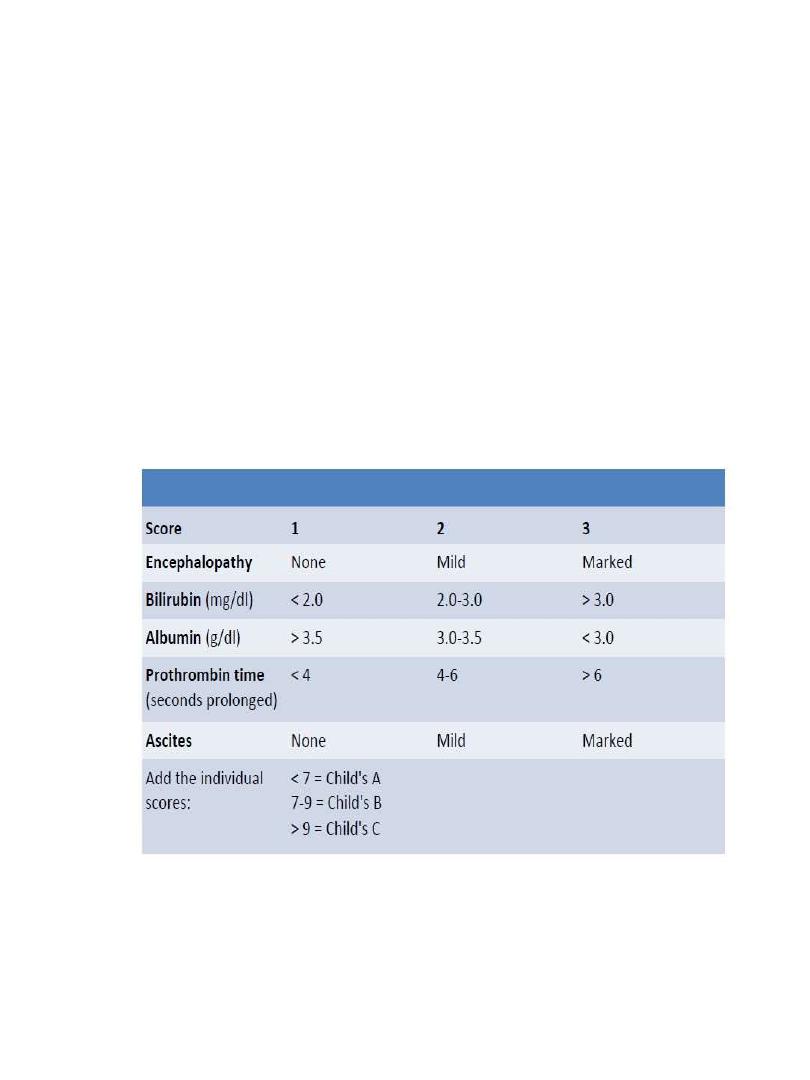
Varices Increase in Diameter Progressively
10
Treatment of portal hypertension
• treatment of complications : variceal bleeding ,,, ascites…
• endoscopic procedures : sclerotherapy +band ligation +
prophylactic propranolol
Treatment of Acute Variceal Hemorrhage
• General Management:
Iv acess and fluid resuscitation
Do not overtransfuse (hemoglobin ~ 8 g/dL)
Antibiotic prophylaxis
• Specific therapy:
Pharmacological therapy: terlipressin, somatostatin and
analogues, vasopressin + nitroglycerin
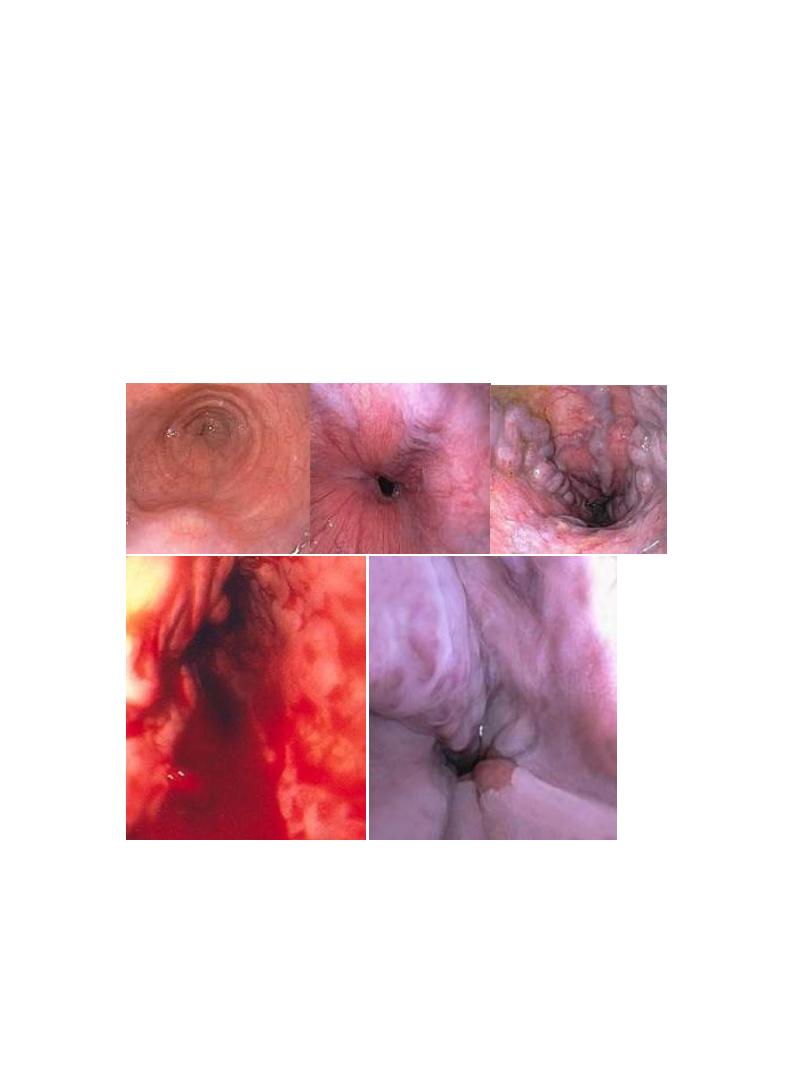
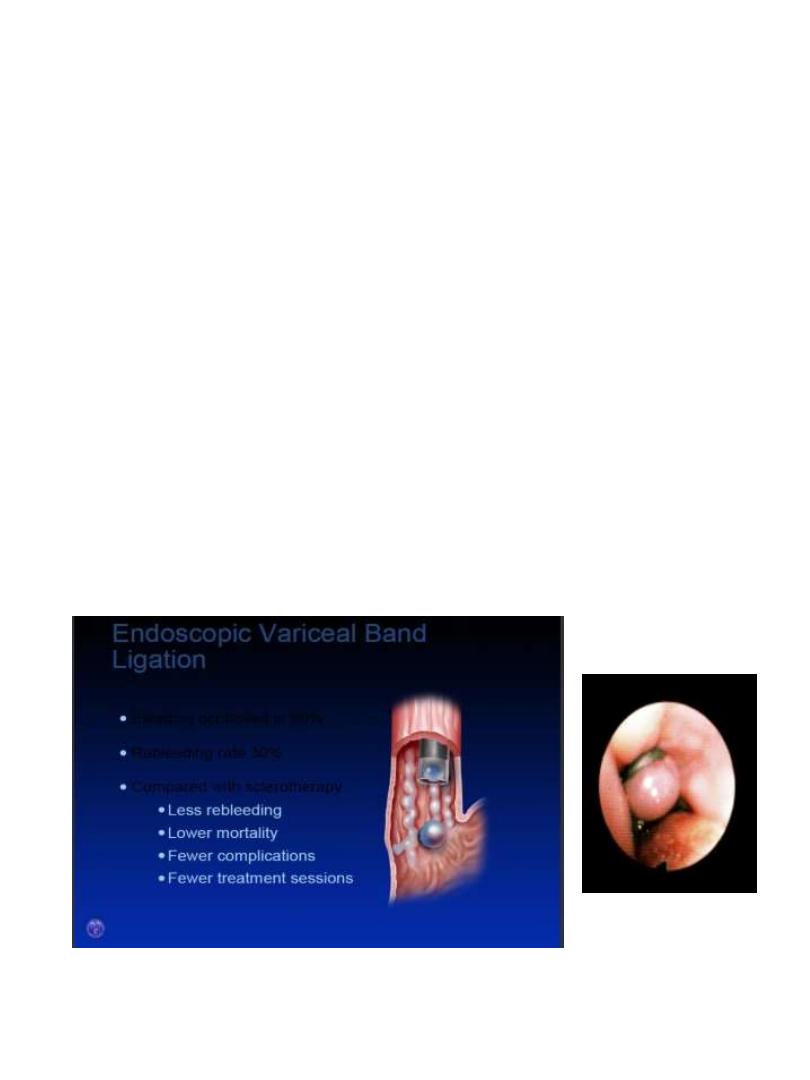
• Endoscopic therapy: ligation, sclerotherapy
• Shunt therapy: TIPS, surgical shunt
11
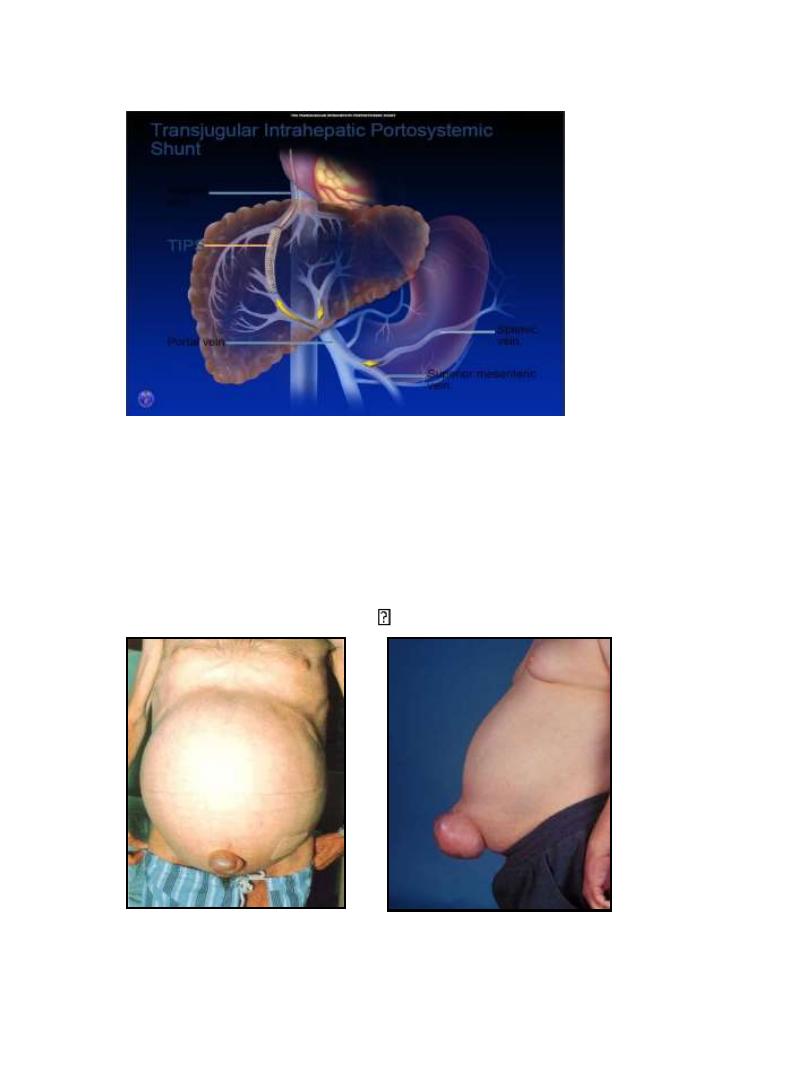
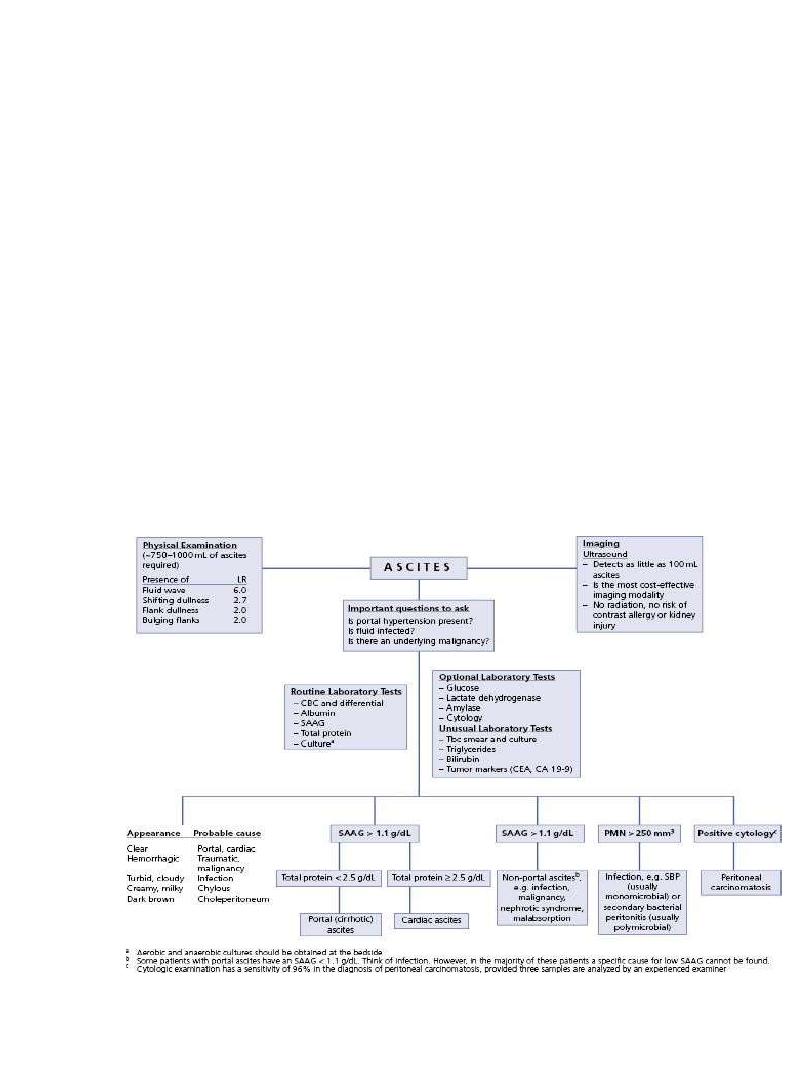
Ascites
• Ascites responsive to diuretics in the absence of infection
and renal dysfunction:
Sodium restriction: Effective in 10-20% of cases
• Diuretics: Should be spironolactone-based A progressive
schedule (spironolactone
furosemide) .
12
Management of Uncomplicated Ascites
• Diuretic Therapy Dosage : Spironolactone 100400
mg/day,Furosemide (40-160 mg/d) ·
• Side effects: Renal dysfunction, hyponatremia,
hyperkalemia, encephalopathy, gynecomastia
Early Diagnosis of SBP
• Diagnostic paracentesis:
1. If symptoms / signs of SBP occur
2. Unexplained encephalopathy and / or renal dysfunction
3. At any hospital admission
• Diagnosis based on ascitic fluid PMN count >250/mm3
13
Treatment of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
• Recommended antibiotics for initial empiric therapy: i.v.
cefotaxime, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid,oral nofloxacin
(uncomplicated SBP)
• avoid aminoglycosides
• Minimum duration: 5 days
• Re-evaluation if ascitic fluid PMN count has not decreased
by at least 25% after 2 days of treatment
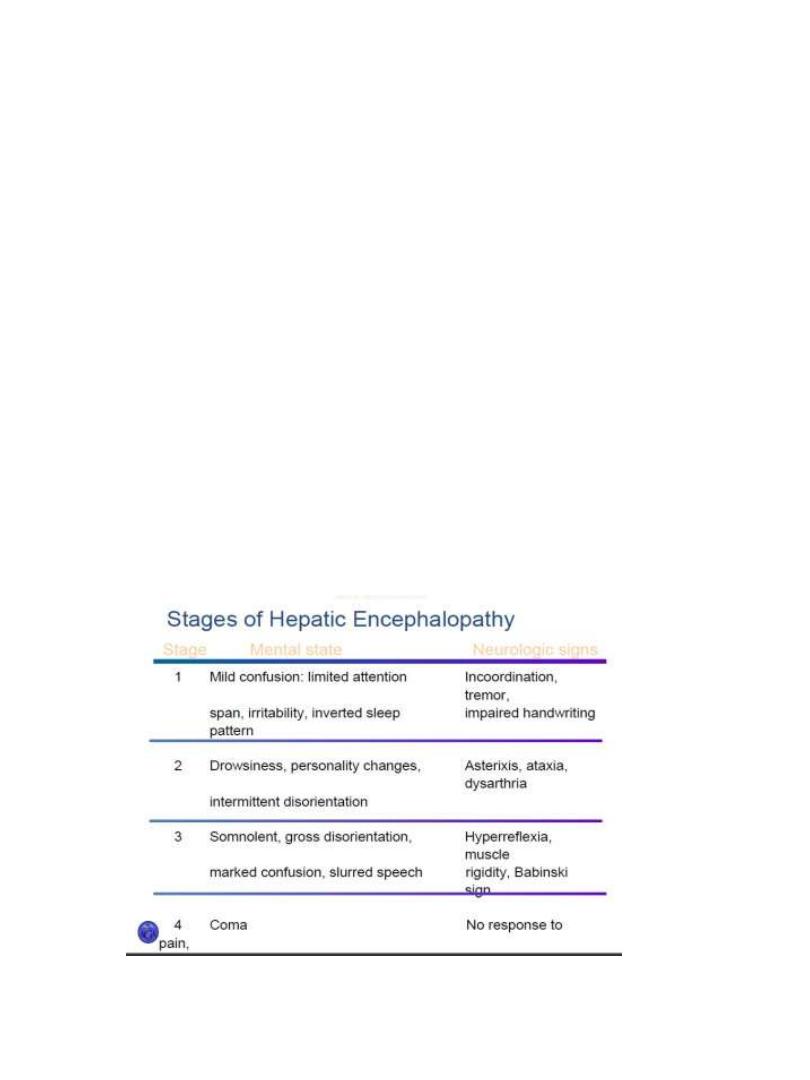
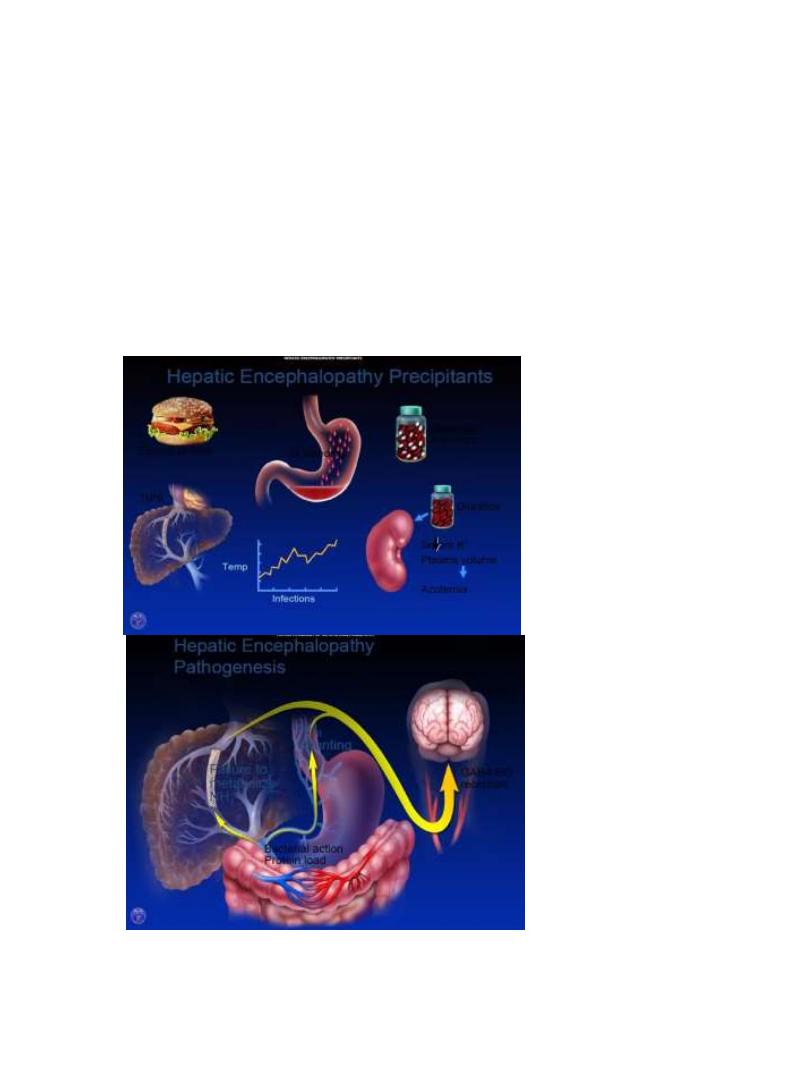
Type C Hepatic Encephalopathy is the Encephalopathy of
Cirrhosis
• Neuropsychiatric complication of cirrhosis Results from
spontaneous or surgical / radiological portal-systemic
shunt + chronic liver failure
• Failure to metabolize neurotoxic substances
14
Hepatic Encephalopathy Is A Clinical diagnosis
• Clinical findings and history important
• Ammonia levels are unreliable
• Ammonia has poor correlation with diagnosis
• Measurement of ammonia not necessary
• Number connection test
• Slow dominant rhythm on EEG

15
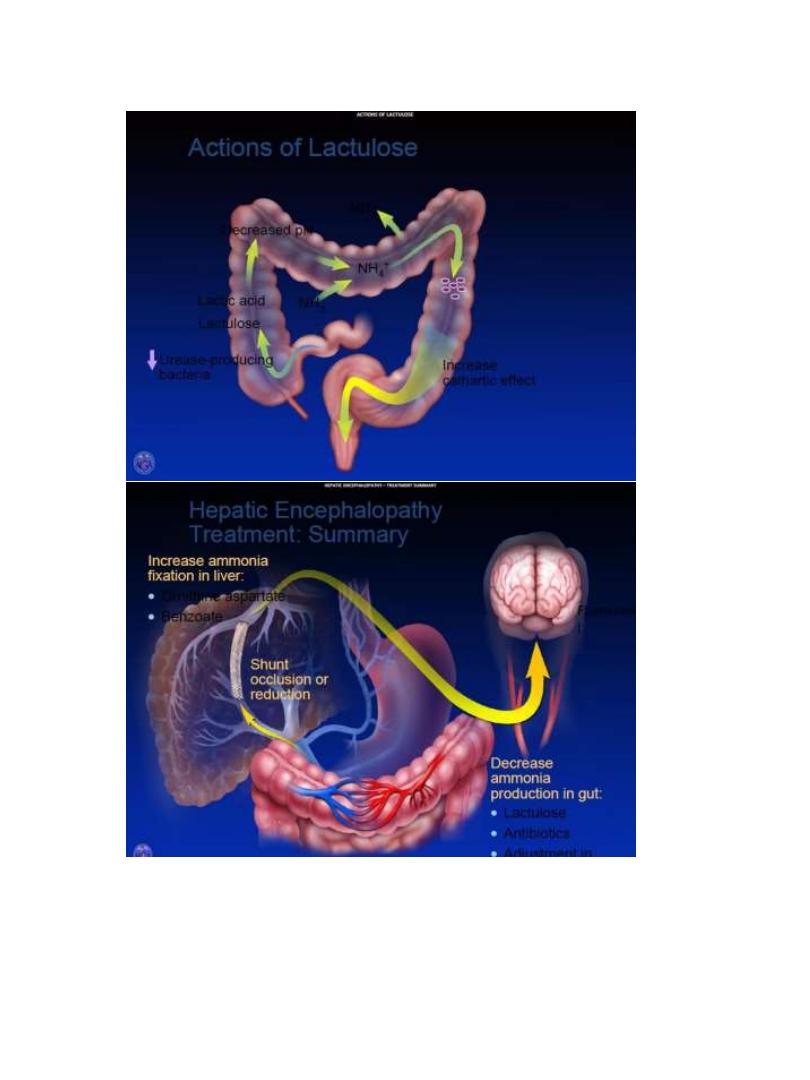
Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy
• Identify and treat precipitating factor: Infection, GI
hemorrhage, Prerenal azotemia , Sedatives, Constipation.
• Lactulose (adjust to 2-3 bowel movements /day)
• Protein restriction, short-term (if at all)
16
