Obstetric procedures
تسلسل 18المرحلة الرابعة
نسائية
د.شيماء
العدد13
12\4\2018
Caesarean section
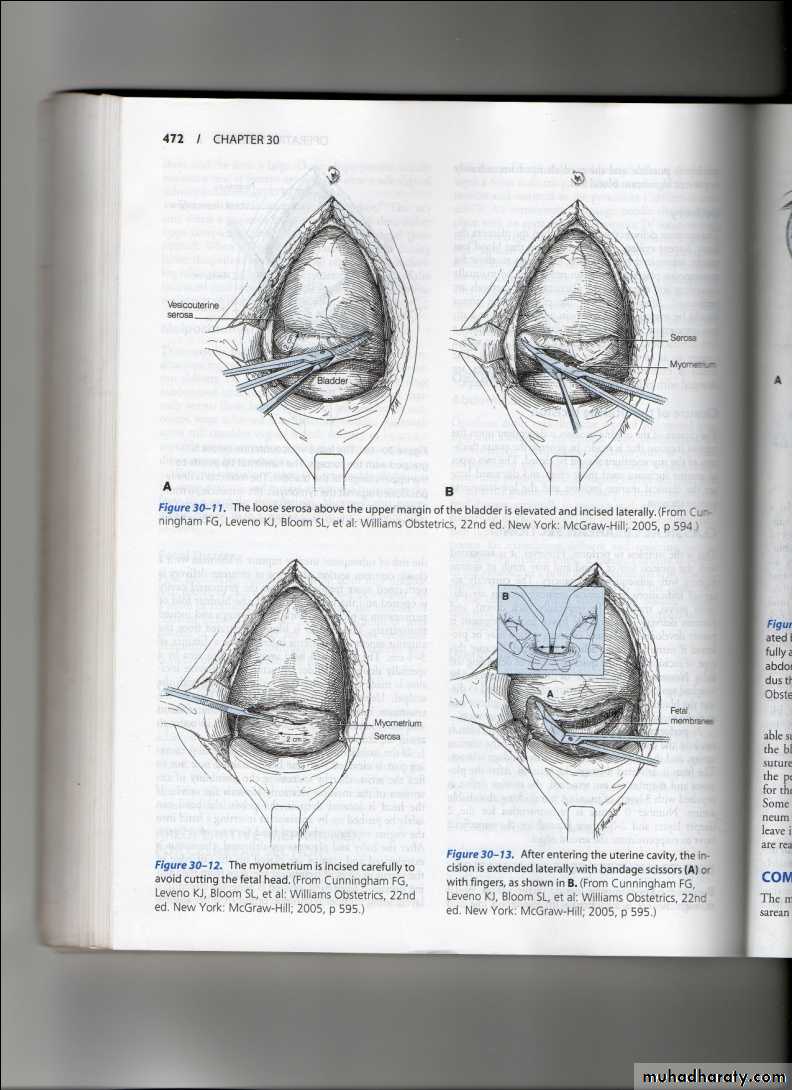
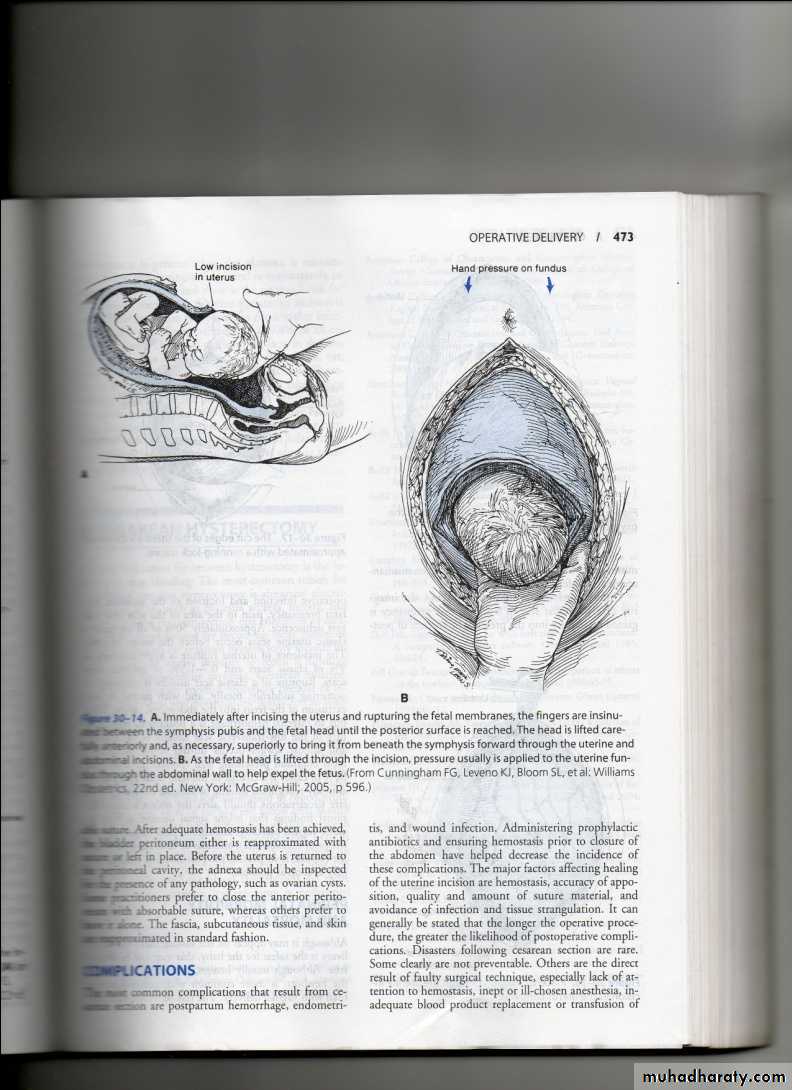
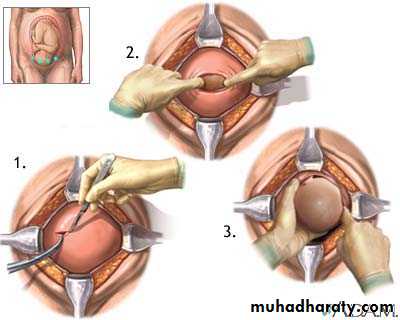
Is the operation that is performed to the delivery of a fetus,placenta & membrane through an abdominal & uterine incisions.Types of C.S.
Classified according to the site of uterine incisions:Lower segment C.S.
Transverse incision in the lower uterine segment .
Advantage : reduced chance of rupture .
reduced risk of bleeding ,peritonitis
paralytic ileus and bowel adhesion.
.
Upper segment (Classical C.S) :
Vertical incision in the lower segment (low vertical incision).
Indications
• Obstructed labour, malpresentation, malposition, multiple gestation• Foetal distress/ prolapsed cord
• Maternal medical conditions
• Obstetric complications
5.Previous uterine surgery : Classical C.S. /Previous 2 C.S./ Previous myomectomy (Full thickness ) .
Indications of Classical c\s
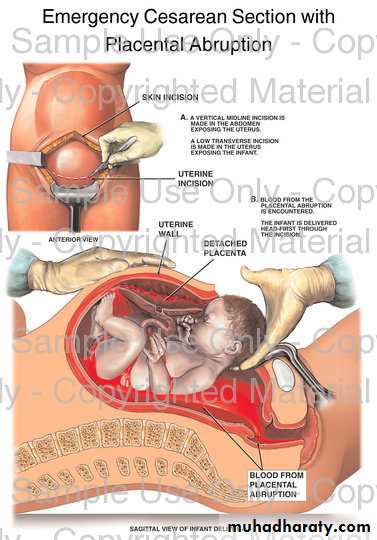
• Preterm labour• Placenta previa- abruptio
• PROM, poor lower segment& transvers lie
• Transvers lie with back inferior
• Large cervical fibroid
• Sever adhesion in lower segment
• Post mortem cs
Cesarean hysterectomy
Preparation for C.S. :
Left lat. Position .
Empty the stomach and antacid .
Thrombo prophylaxis .
Prophylactic antibiotics .
Catheterization .
Skin preparation : shaving , iodine , chrorhexidine .
Skin incision :
Low transverse suprapubic incision .(more cosmotic , less dehiscence and hernia ).Midline or paramedian incision better exposure .
The skin wound is about 15 cm in length
vvvvvvvvvvvgj0p
Risk of C. S. :Maternal risk
Mortality after C.S. is 5-10X after normal vaginal delivery .Risk is more after emergency than elective C.S..
Immediate complications :
• Anasthesia , aspiation (Mendelson’s syndrome)
• Haemorrhage (blood transfusion and shock)
• Injury to adjacent organs .
• Infection .
• Post operative ileus .
• Pulmonary embolism .
• Remote : Rupture in pregnancy &labour , Placenta previa,
• Intestinal obstruction and hernia, Risk of repeated C.S.
Perinatal morbidity &mortality
• Risk of anasthesia .
• Respiratory problems (transient tachypnea)
• Intracranial haemorrhage (difficult delivery)
• Prematurity ( inaccurate date ).
• Fetal laceration is reported at rate 0.2-0.4%
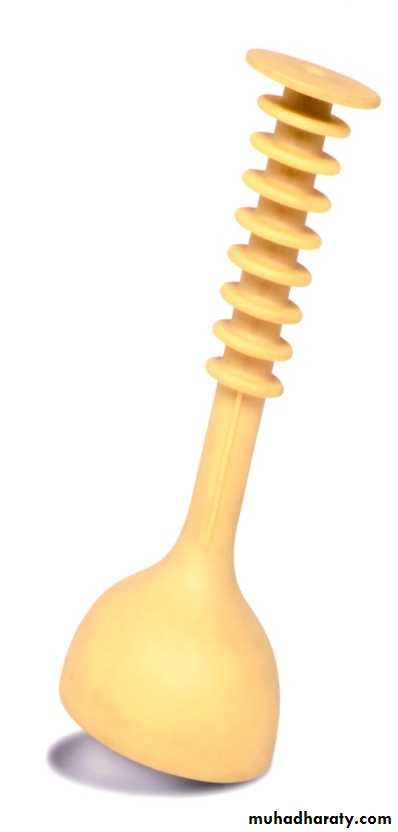
Operative vaginal delivery or Assisted Vaginal Delivery:
Instrumental vaginal deliveryVaccum (ventose) & Forceps
assisted vaginal delivery :- delivery of a baby vaginally using an instrument for assistanc when spontaneous vaginal delivery does not occur within a reasonable time.
Indication for assisted delivery:
Maternal Indication :1. Maternal distress during 2nd stage .
2. Prolonged 2nd stage .
3. Cardiopulmonary or vascular disease to
reduce the stress of the 2nd stage of labour .
4. Vaginal birth after previous lower segment
C.S. to reduce the stress on the scar .
5. Significant vaginal bleeding .
Fetal Indications :
• 1. Malposition of the fetal head (OP, OT)
• 2. Fetal distress ( bradycardia or deceleration )
• and cord prolapse .
• 3. Preterm baby (1500 – 2500 Kg )
• 4. Vaginal delivery of breech : forceps for after coming head to avoid traction on the trunk and the cervical spine and produce controlled flexion of the head .
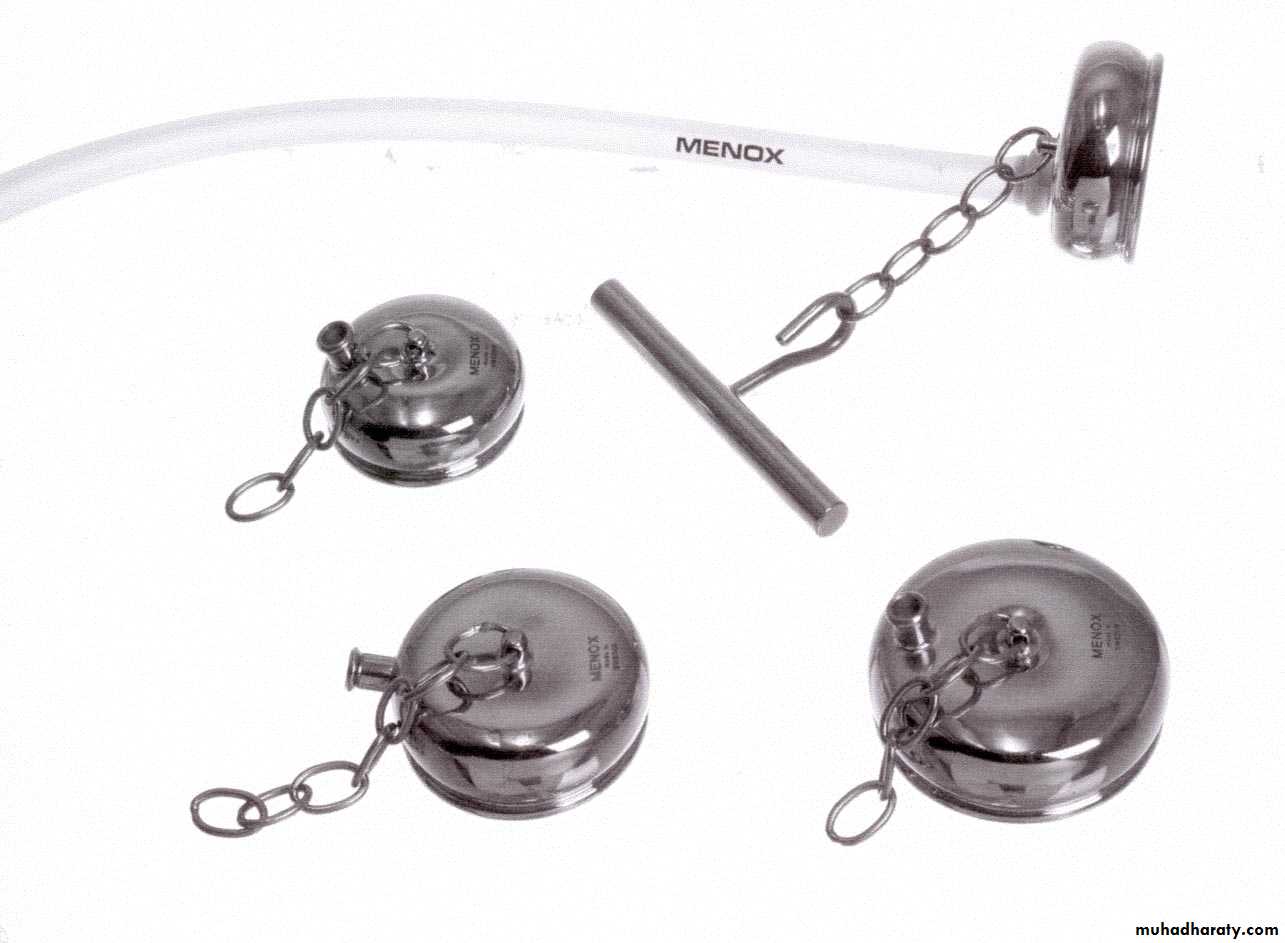
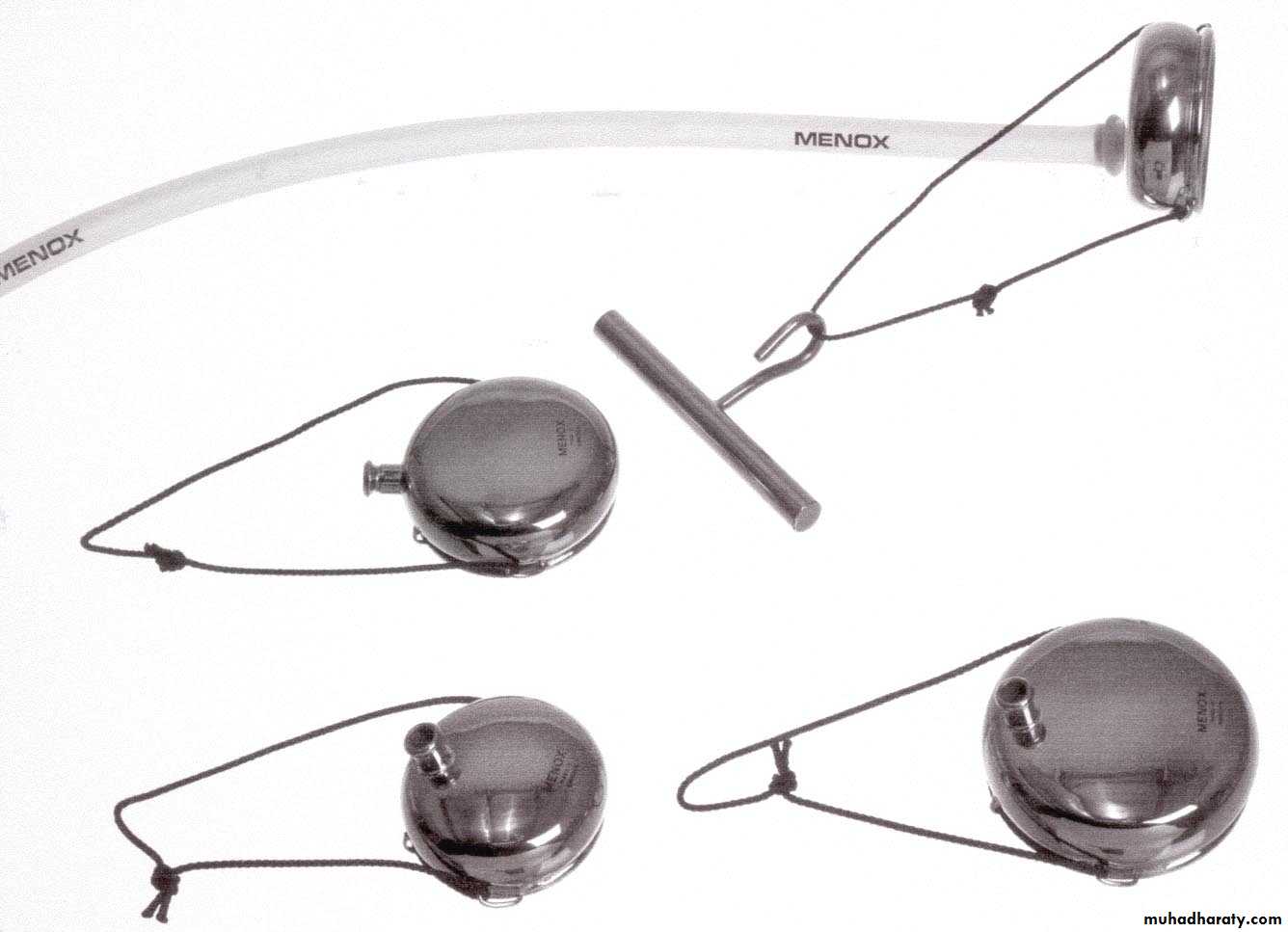
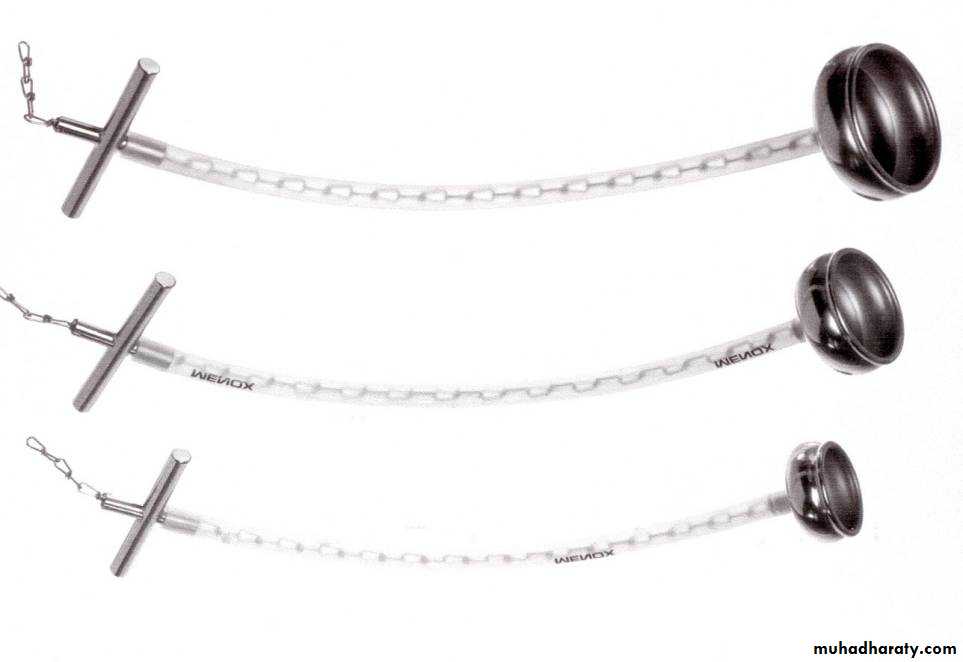
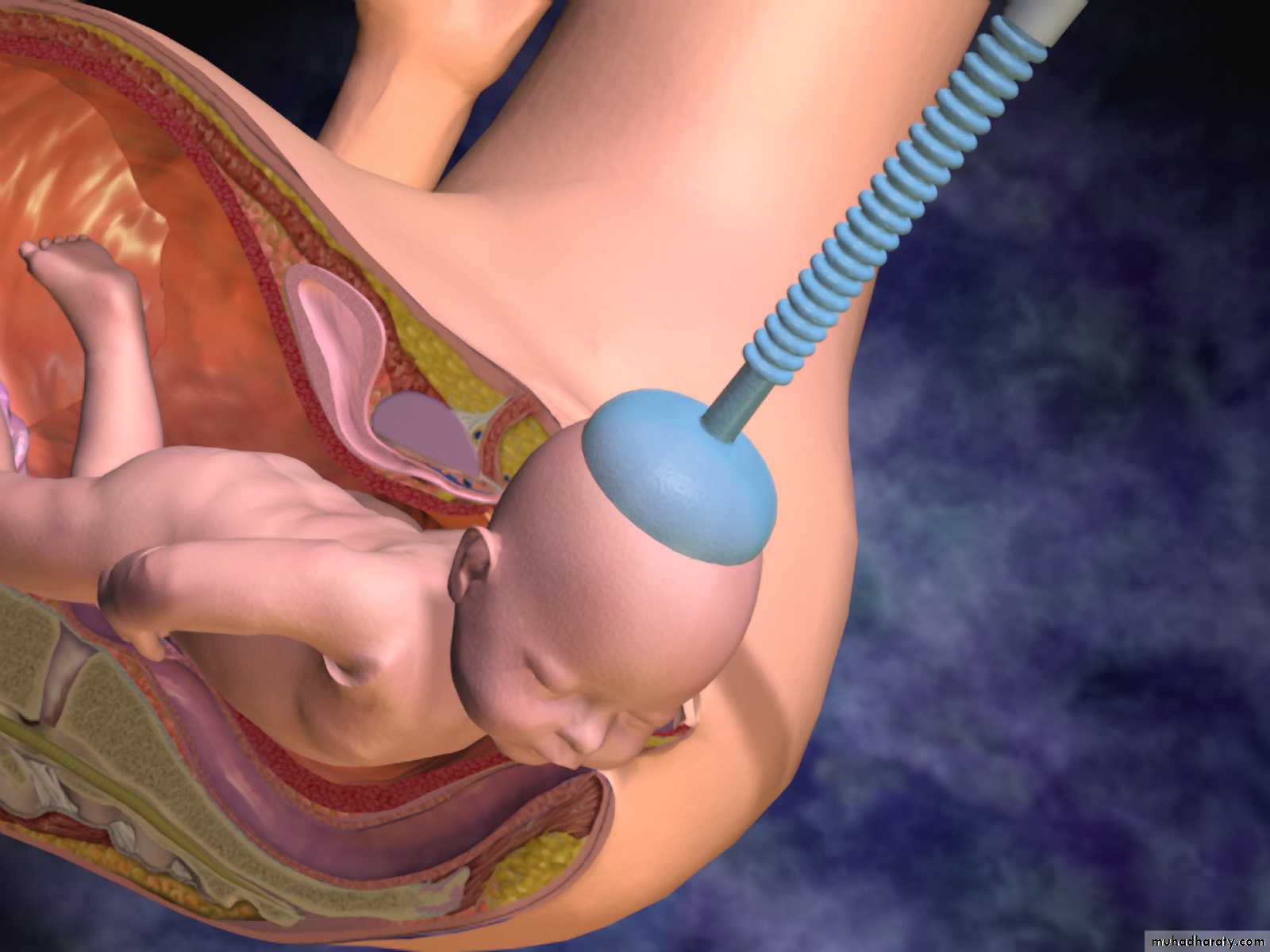
Ventouse delivery
The vacuum extractor works by allowing the external traction force applied to fetal scalp to be transmitted to the head.Types of vacuum: 1.Rigid vaccum: O’neil Bird Malmstrom
2.Soft vacuum: Funnel cause less fetal injury ,higher failure rate .mushroom Ring
Indications and contraindications for delivery with the ventouse
IndicationsDelay in the second stage
Fetal distress in the second stage
Maternal conditions requiring a short second stage
Contraindications
Face presentation
Gestation less than 34 weeks
Marked active bleeding from a fetal blood sampling site
Prerequisites for delivery with the ventouse
Dilatation of the cervix and full engagement of the headCo-operation of the patient
Good contractions should be present
The cup should be reapplied no more than twice.
If failure with the correctly placed ventouse occurs despite good traction, the forceps should not be tried as well
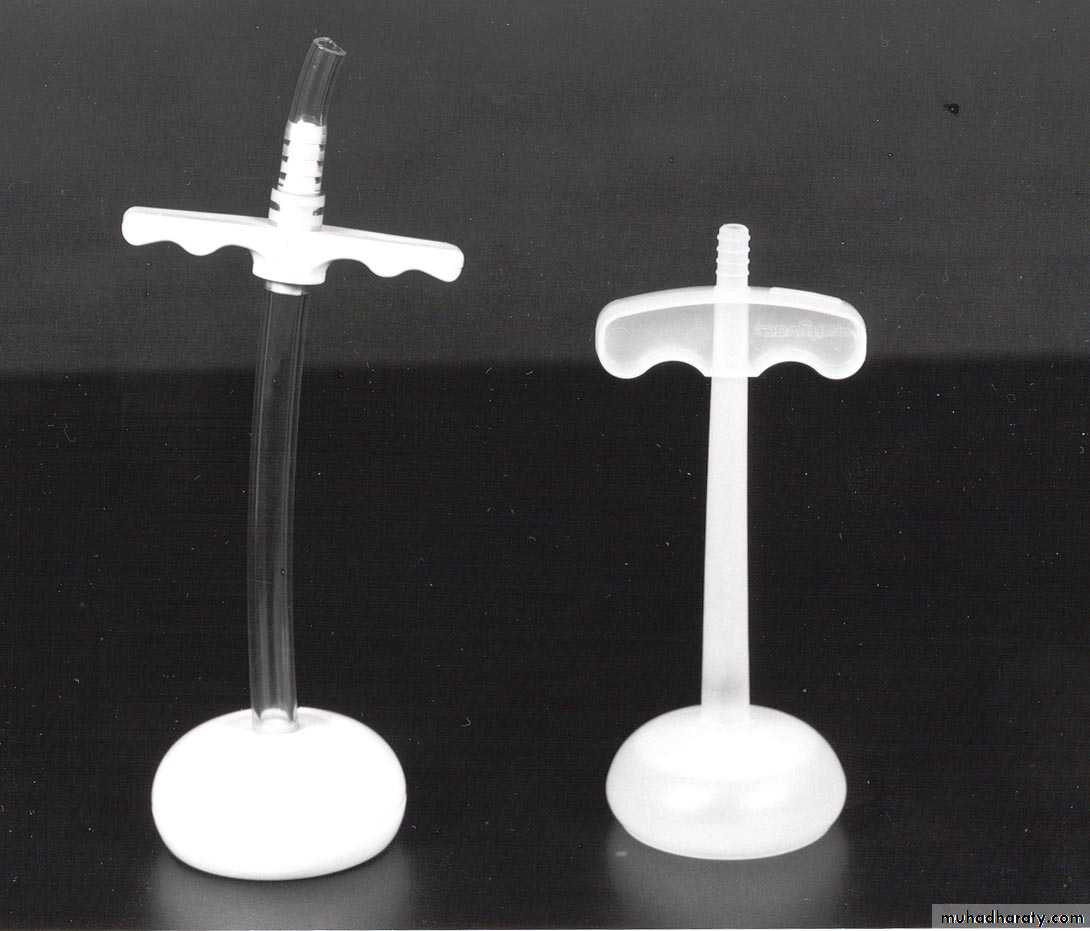
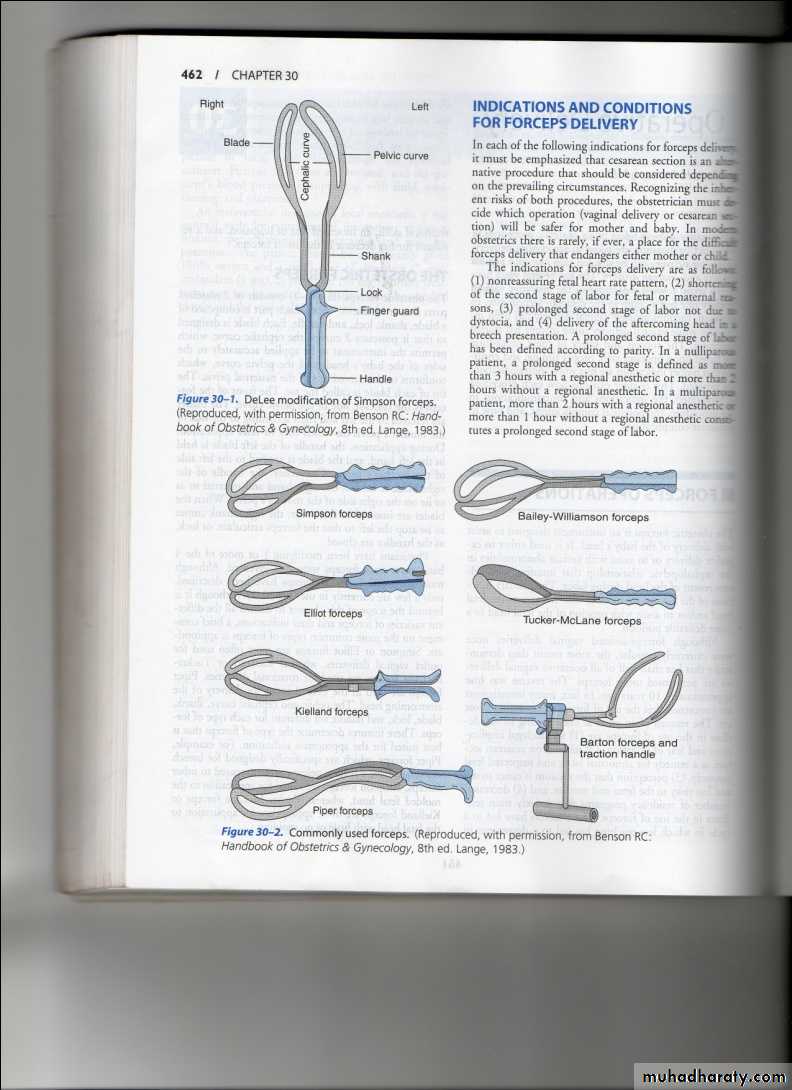
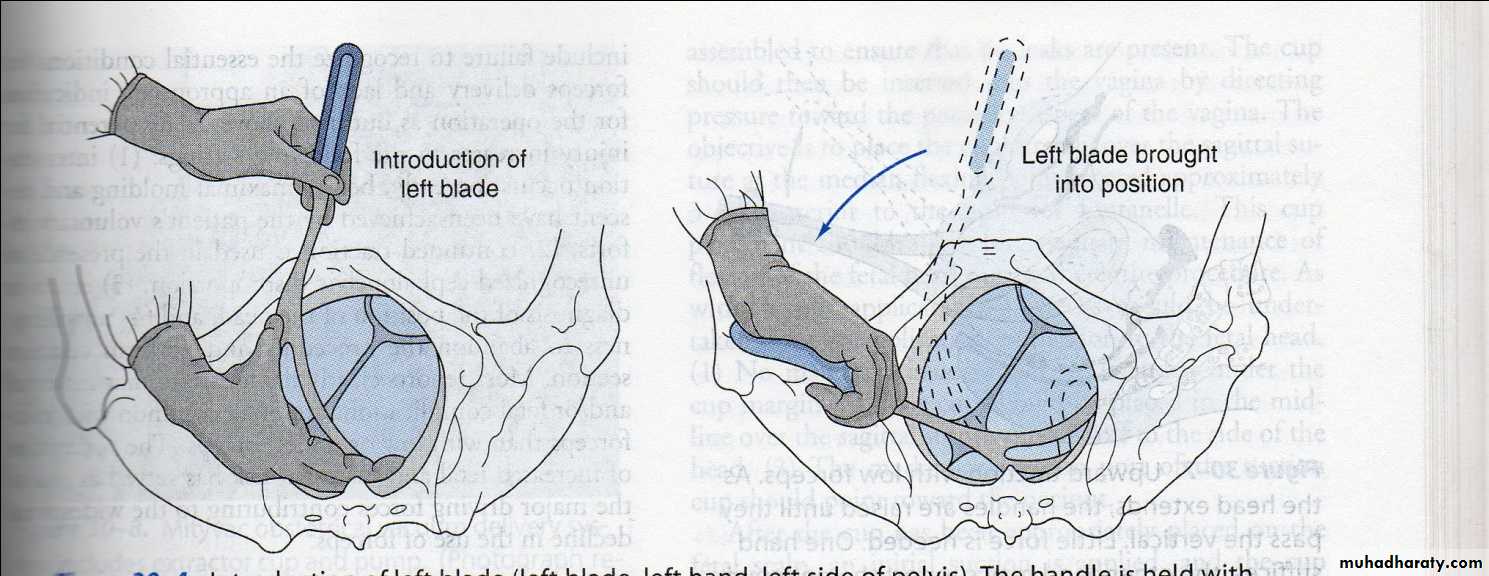
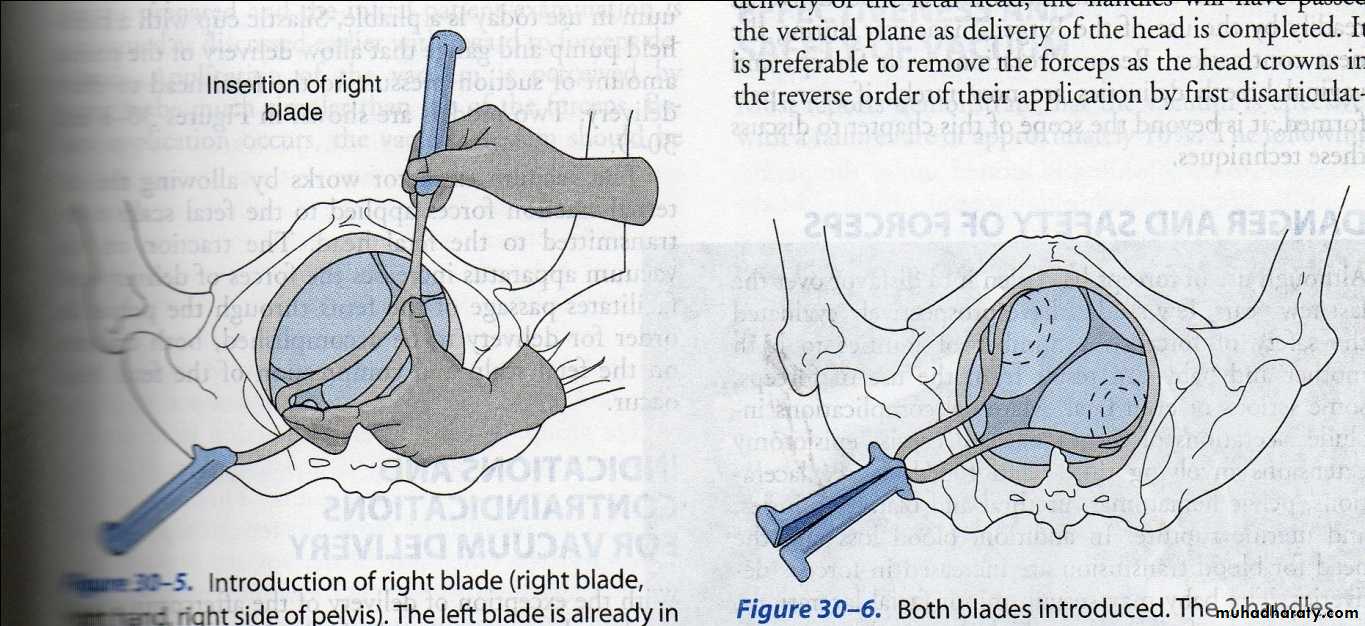
Forceps delivery
Types of obstetric forcepsShort curved forceps
Long curved forceps
.
Kielland’s forceps
-
preparations for forceps :
1. Engaged head .2. Position and attitude of the head .
3. Clinically adequate pelvis (mid ,outlet )
4. Empty bladder .
5. Ruptured membrane .
6. Cervix is fully dilated .
7. Appropriate anaesthesia (vacuum without )
8. Experience of the doctor .
9. Well informed patient .
10. working equipment .
Complication of assisted delivery :
Maternal complication : is more common with forceps than vacuum .
Soft tissue injuries
Fetal complication :
With forceps : 1. Transient facial marks.2. Facial palsy .
3. Fracture of skull or facial bones .
4. Sever cervical cord damage .
With vacuum :
• 1. Scalp injury . 6. Fracture of skull .
• 2. Cephalhaematoma . 7. Neonatal jaundice
3. Subgleal haematoma . 8. Retinal haemorrhage
4. Intracranial haemorrhage .. 9. Brachial plexus
5. Tentorial tears . 10. cerebral palsy .
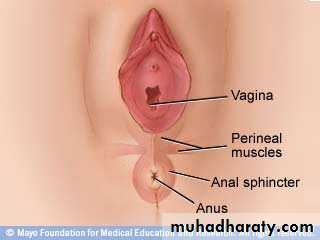
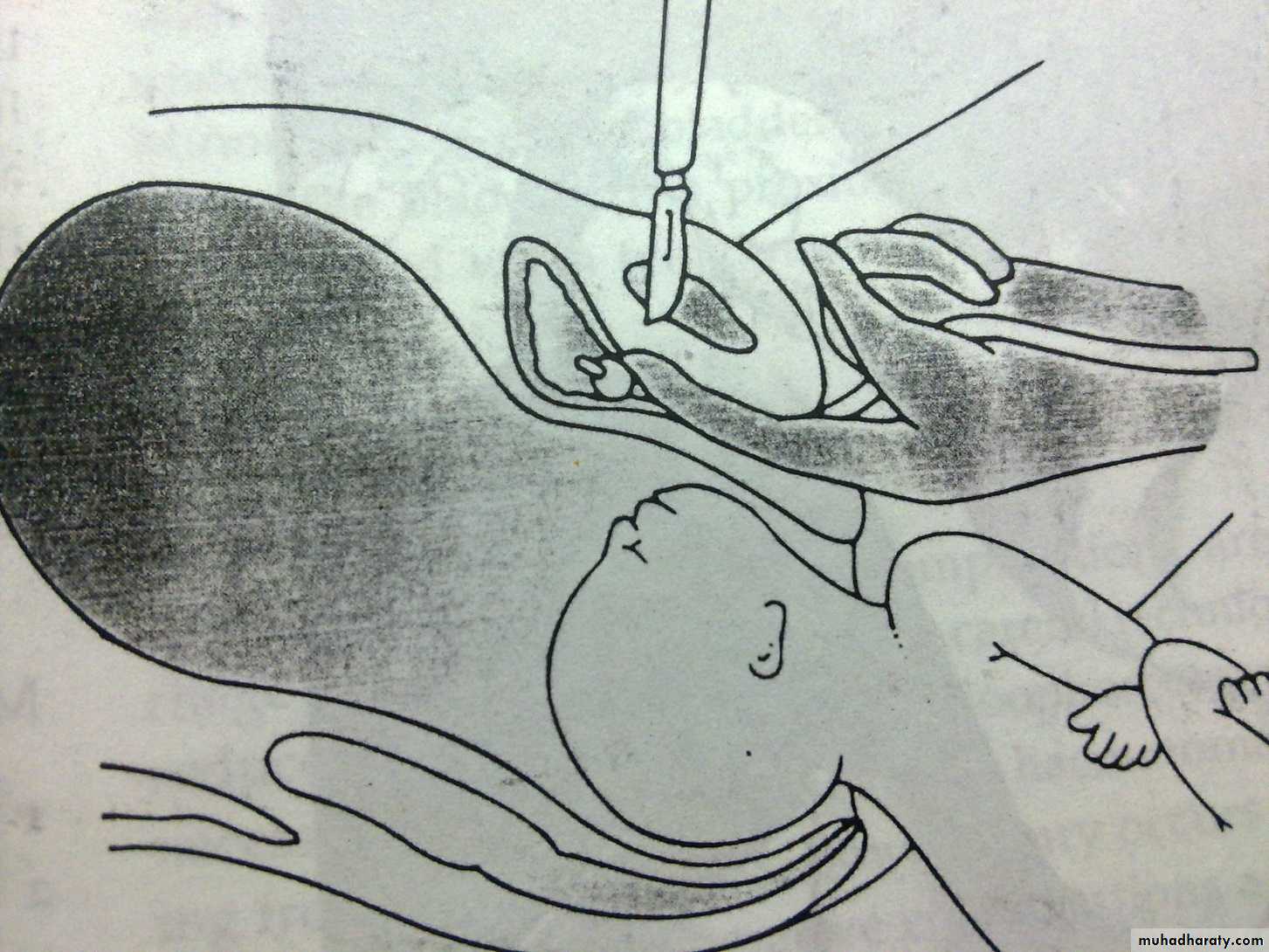
EPISIOTOMY
Episiotomy is an intentional surgical incision of the perineum to increas the soft tissue outlet dimensions to help with childbirth.Indications of episiotomy
tears with bleeding appear.fetal distress
to facilitates instrumental vaginal deliveries
If the delivery process is delayed and it is thought to be due to rigid perineum.
. Whenever there are vaginal manipulations needed such as in some assisted breech deliveries
and in cases of shoulder dystocia an episiotomy may be useful.
Those women who had a previous pelvic floor or perineal surgery may also benefit by an episiotomy.
Types of episiotomy:
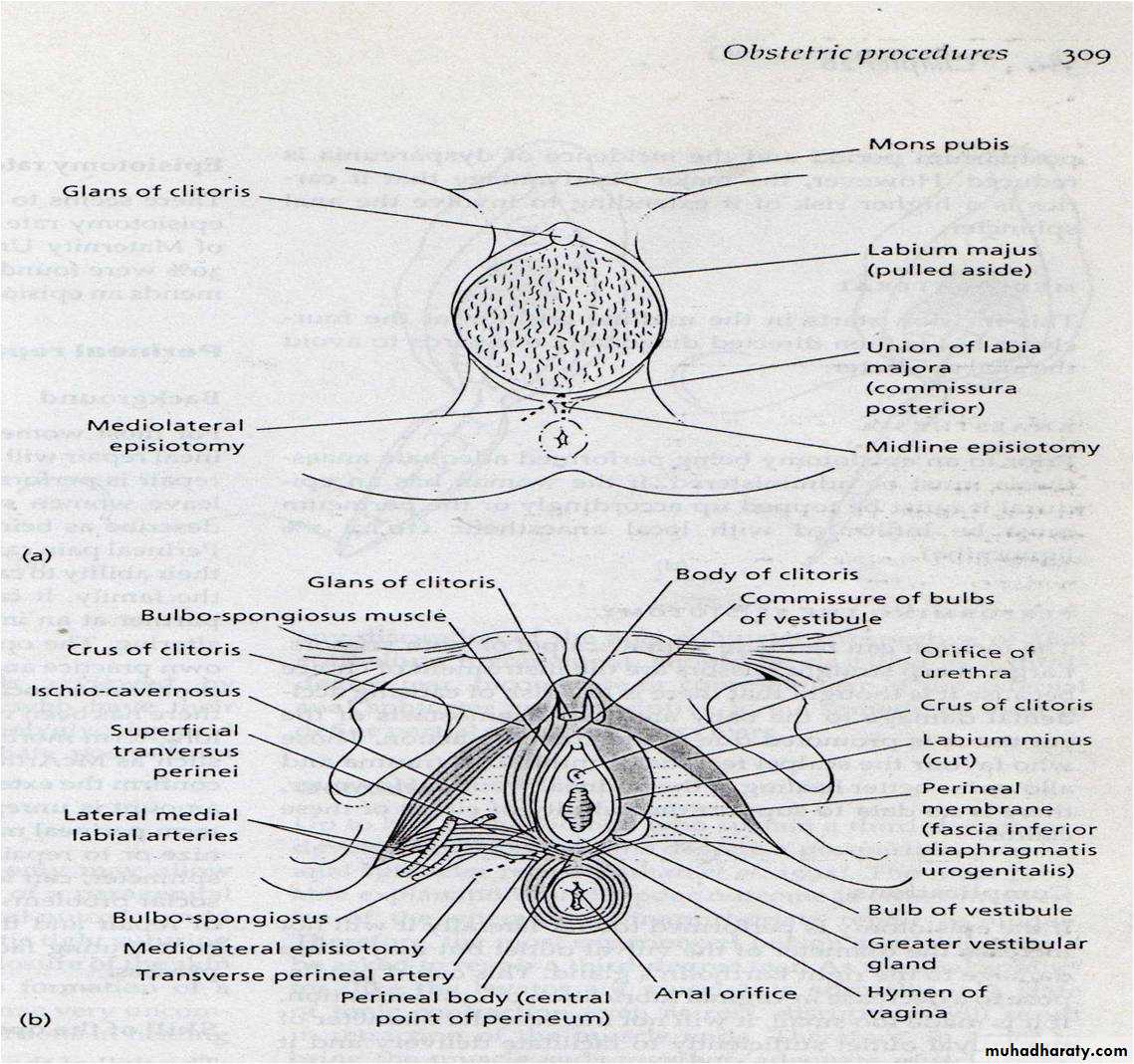
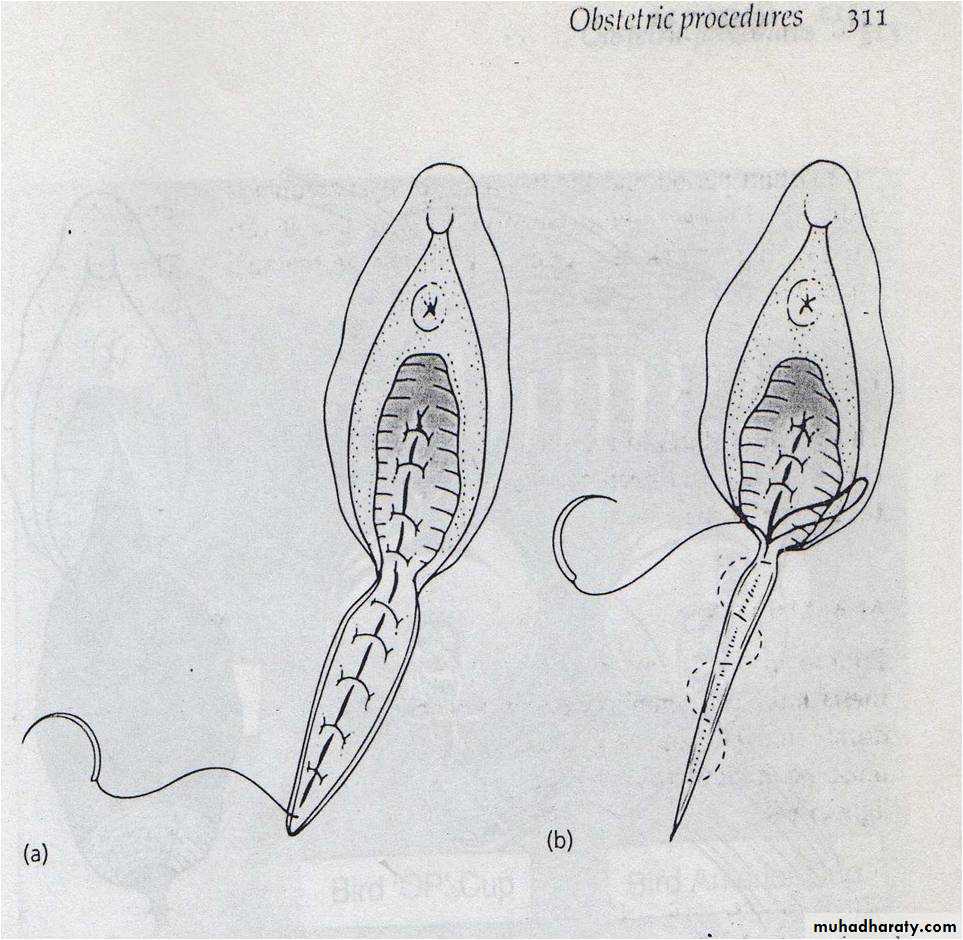
Midline episiotomy :vertical incision towards the anus , less blood loss ,easier repair ,quicker healing , less pain in the postpartum period ,less dysparunia.-risk of extension to the anus.
Medio lateral episiotomy : start at midline then
laterally to avoid the anal sphinctor .
Lateral episiotomy .
Complication:1.Difficult repair.2.heavy bleeding.3.extention to the anus.4.infection.5.pain and dyspareunia.6.weak point in the perinium-tear.7.Dryness from injury to bartholine gland.
After care:1.analgesia,oral or suppositories.2.prophylactic antibiotics.3.washing with water and soap.4.hot sitz bath.
Symphysiotomy
Considered in cases of cephalo-pelvic disproportion with vertex presentation & living fetusIndicated for traped aftercoming head& shoulder dystortia
Destructive operations
Required when the fetus is dead
1-crainiotomy
2-perforation of after-coming head
3-decapitation