
Lecture No.2-11 by Hussein J. AbdulHussein
Advanced Calculus II Al Muthanna University, College of Science
1
EVEN FUNCTION AND ODD FUNCTION
(a) Even Function
A function
f(x) is said to be even (or symmetric) function if , , f(−x) = f(x)
The graph of such a function is symmetrical with respect to y-axis
[f(x)axis ] Here y – axis
is a mirror for the reflection of the curve
The area under such a curve from
− π to π is double the area from 0 to π
∴ ∫
f (x)dx = 2 ∫ f (x)dx
π
0
π
− π
A function is called odd (or skew symmetric) function if
f(−x) = −f(x)
Here the area under the curve from
− π to π is zero.
∫ f (x)dx = 0
π
− π
Expansion of an even function
a
0
=
1
π
∫
f (x)dx =
2
π
∫ f (x)dx
π
0
π
− π
a
n
=
1
π
∫
f (x) cos nx dx =
2
π
∫ f (x) cos nx dx
π
0
π
− π
As
f(x) and cos nx are both even function, therefore, the product of f(x) ∙ cos nx is also an
even function
b
n
=
1
π
∫
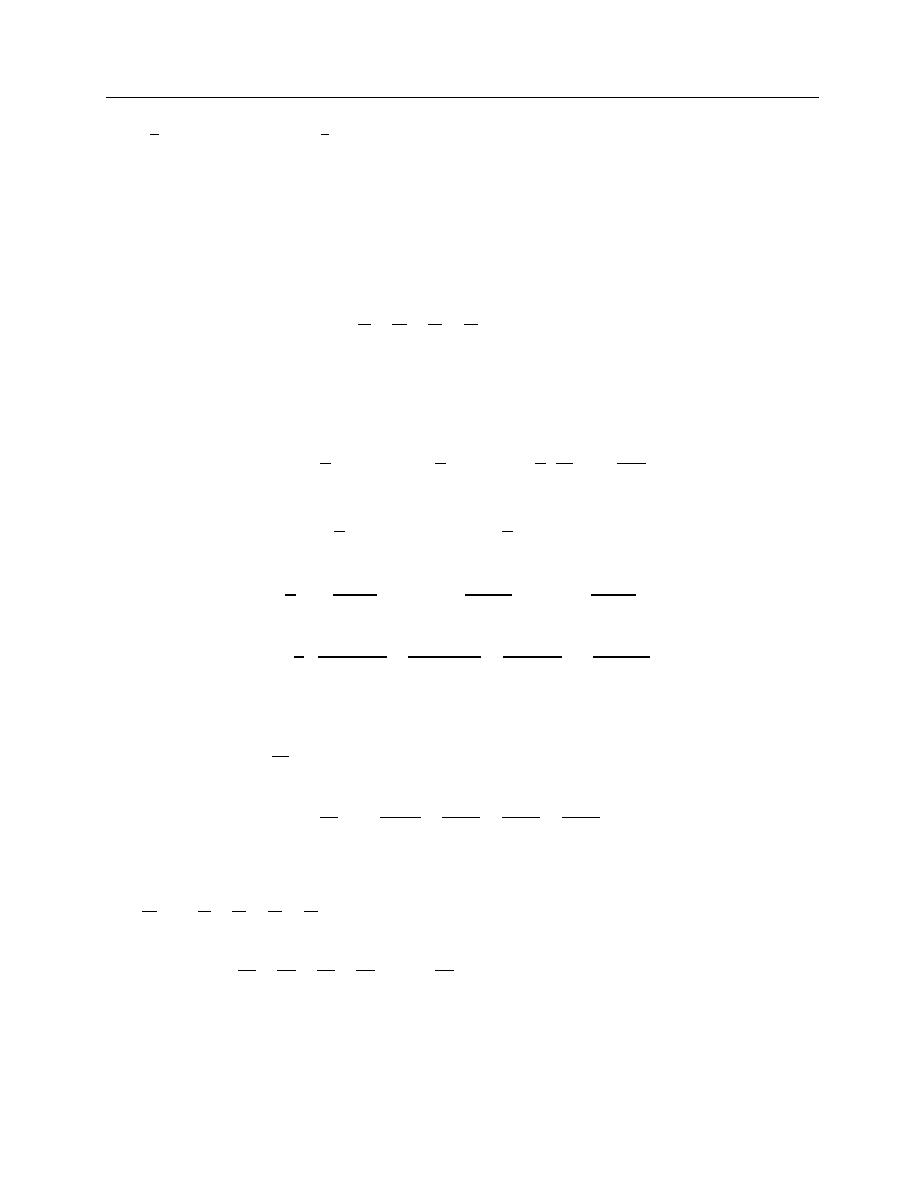
f (x) sin nx dx = 0
π
− π
As is an odd function so
f(x) is also an odd function We need not to calculate b
n
It saves our lab
our a lot The series of the even function will contain only cosine terms
Expansion of an odd function:
a
0
=
1
π
∫
f (x)dx = 0
π
− π
a
n
=
1
π
∫ f (x) cos nx dx = 0
π
− π
[f(x) cos nx is odd function ]
Lecture No.2-11 by Hussein J. AbdulHussein
Advanced Calculus II Al Muthanna University, College of Science
2
b
n
=
1
π
∫
f (x) sin nx dx =
2
π
∫ f (x) sin nx dx
π
0
π
− π
,
[f(x) cos nx is odd function ]
The series of the odd function will contain only sine terms. The function shown below neither odd
nor even so it contains both sine and cosine terms Fourier Series
Example 9. Find the Fourier series expansion of the periodic function of period
2π
f(x) = x
2
. −π ≤ x ≤ π
Hence find the sum of the series
1
1
2
−
1
2
2
+
1
3
2
−
1
4
2
+ ⋯
Solution
f(x) = x
2
. −π ≤ x ≤ π
This is an even function
∴ b
n
= 0
a
0
=
2
π
∫ f (x)dx =
2
π
∫ x
2
dx =
2
π
[
x
3
3
]
0
π
π
0
π
0
=
2π
2
3
a
n
=
2
π
∫ f (x) cos nx dx =
2
π
∫ x
2
cos nx dx
π
0
π
0
=
2
π
[x
2
[
sin nx
n
] − (2x) [−
cos nx
n
2
] + (2) [−
sin nx
n
3
]]
0
π
=
2
π
[
π
2
sin nπ
n
+
2π cos nπ
n
2
−
2 sin nπ
n
3
] =
4(−1)
n
n
2
Fourier Series is
f(x) =
a
0
2
+ a
1
cos x + a
2
cos 2x + a
3
cos 3x + ⋯ + a
n
cos nx + ⋯
x
2
=
π
2
3
− 4 [
cos x
1
2
−
cos 2
2
2
+
cos 3
3
2
−
cos 4
4
2
+ ⋯ ]
On putting
x = 0 . we have
0 =
π
2
3
− 4 [
1
1
2
−
1
2
2
+
1
3
2
−
1
4
2
+ ⋯ ]
⇒
1
1
2
−
1
2
2
+
1
3
2
−
1
4
2
+ ⋯ =
π
2
3
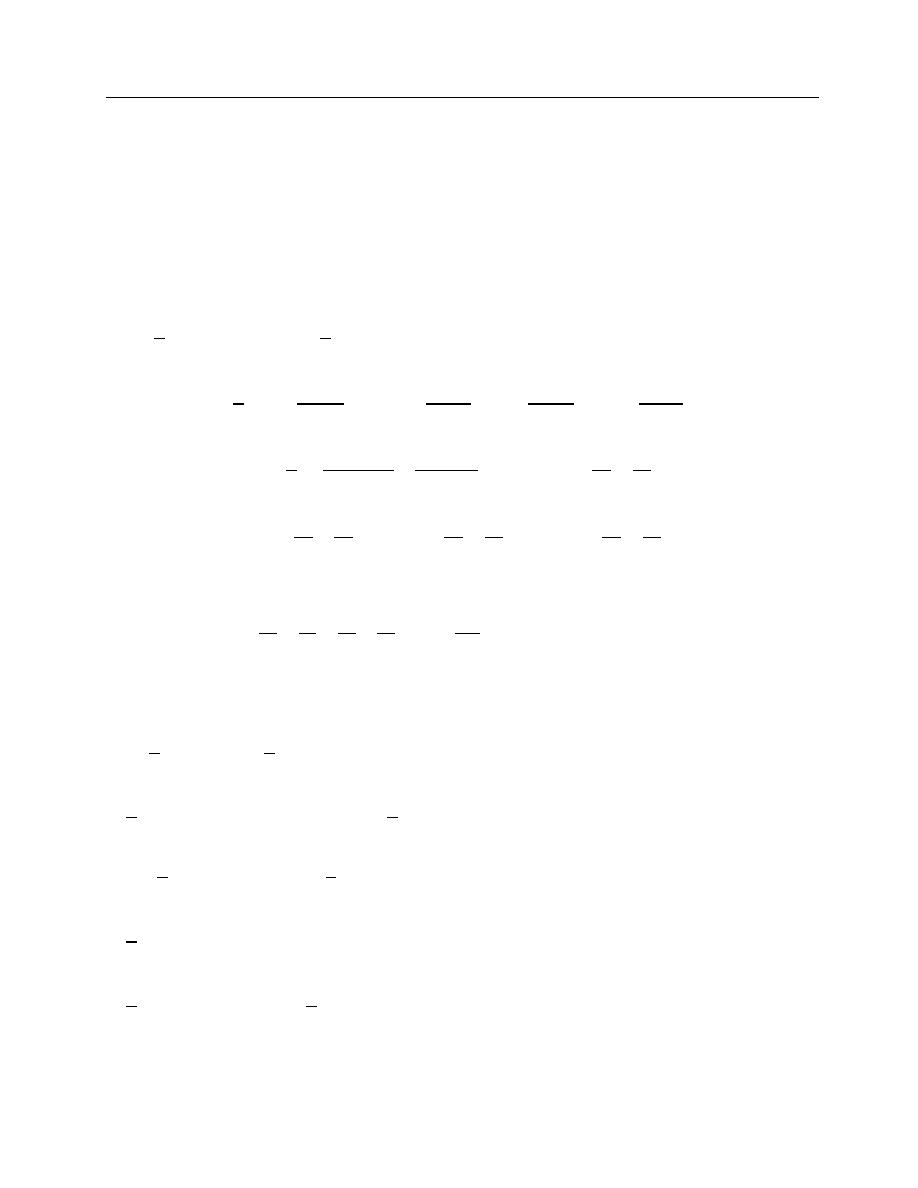
Lecture No.2-11 by Hussein J. AbdulHussein
Advanced Calculus II Al Muthanna University, College of Science
3
Example 10. Obtain a Fourier expression for
f(x) = x
3
. −π < x < π
Solution.
f(x) = x
3
is odd function
∴ a
0
= 0 and a
n
= 0
b
n
=
2
π
∫ f (x) sin nx dx =
2
π
∫ x
3
sin nx dx = [∫ uv = uv
1
− uv
2
+ u
′′
v
3
− u
′′′
v
4
+ ⋯
π
0
π
0
]
=
2
π
[x
3
[−
cos nx
n
] − 3x
2
[−
sin nx
n
2
] + 6x [
cos nx
n
3
] − 6 [−
sin nx
n
4
]]
0
π
=
2
π
[−
π
3
cos nπ
n
+
π cos nπ
n
3
] = 2(−1)
n
[−
π
2
3
+
6
n
3
]
∴ x
3
= 2 [− [−
π
2
1
+
6
1
3
] sin x + [−
π
2
2
+
6
2
3
] sin 2x − [−
π
2
3
+
6
3
3
] sin 3x + ⋯ ]
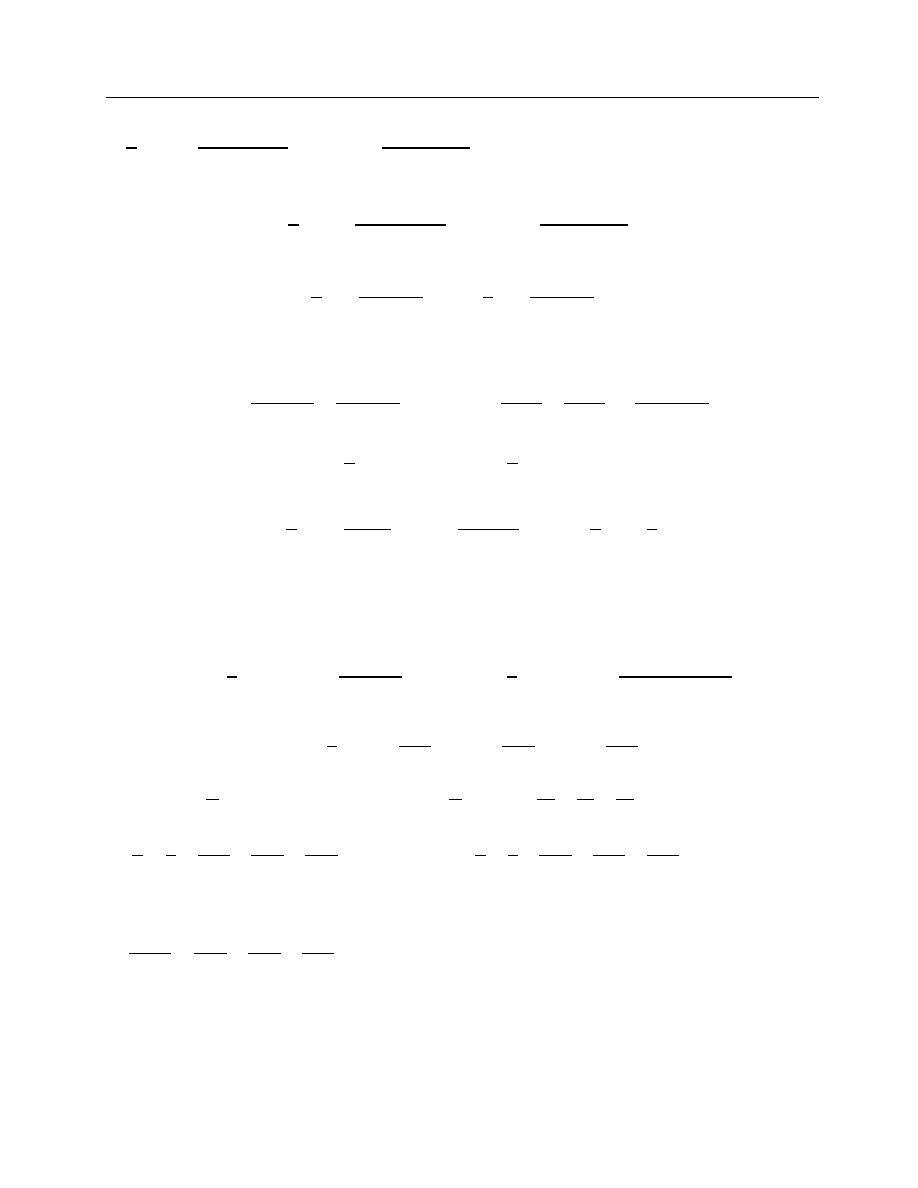
Example 11. Expand the function
f(x) = x sin x. as a Fourier series in the interval−π ≤ x ≤ π
Hence deduce that
1
1∙3
−
1
3∙5
+
1
5∙7
−
1
7∙9
+ ⋯ =
π−2
4
Solution.
f(x) = x sin x.
a
0
=
2
π
∫ f (x)dx =
2
π
∫ x sin x dx
π
0
π
0
(Here x sin x is an even function )
=
2
π
[x(− cos x) − (1)(− sin x)]
0
π
=
2
π
(π) = 2
a
n
=
2
π
∫ f (x) cos nx dx =
2
π
∫ x sin x cos nx dx
π
0
π
0
=
1
π
∫ x {sin(n + 1)x − sin(n − 1)x} dx
π
0
=
1
π
∫ x sin(n + 1)xdx −
1
π
∫ x sin(n − 1)x dx
π
0
π
0
Lecture No.2-11 by Hussein J. AbdulHussein
Advanced Calculus II Al Muthanna University, College of Science
4
=
1
π
[x (−
cos(n + 1)x
n + 1
)
0
π
− (1) {−
sin(n + 1)x
(n + 1)
2
}]
0
π
−
1
π
[x (−
cos(n − 1)x
n − 1
)
0
π
− (1) {−
sin(n − 1)x
(n − 1)
2
}]
0
π
=
1
π
[−π
(−1)
n+1
n + 1
+ 0] −
1
π
[−π
(−1)
n−1
n − 1
− 0]
= −
(−1)
n+1
n + 1
+
(−1)
n−1
n − 1
= (−1)
n+1
[
1
n + 1
+
1
n − 1
] =
2(−1)
n+1
n
2
− 1
a
1
=
2
π
∫ x sin xcos xdx
π
0
=
1
π
∫ x sin2x dx
π
0
=
1
π
[x (−
cos 2x
2
) − (1) (
− sin 2x
4
)]
0
π
= [−
π
2
] = −
1
2
b
n
= 0 [As x sin x sin nx is an odd function]
Hence
f(x) = 1 −
1
2
cos x + 2 ∑
(−1)
n+1
n
2
− 1
∞
n=2
cos nx = 1 −
1
2
cos x + 2 ∑
(−1)
n+1
(n − 1)(n + 1)
∞
n=2
cos nx
x sin x = 1 + 2[−
1
4
cos x −
1
1 ∙ 3
cos 2x +
1
2 ∙ 4
cos 3x −
1
3 ∙ 5
cos 4x + ⋯]
Putting
x =
π
2
. we get
π
2
= 1 + 2 {
1
1∙3
−
1
3∙5
+
1
5∙7
− ⋯ }
or
π
4
=
1
2
+
1
1 ∙ 3
−
1
3 ∙ 5
+
1
5 ∙ 7
− ⋯ ⇒
π
4
−
1
2
+
1
1 ∙ 3
−
1
3 ∙ 5
+
1
5 ∙ 7
− ⋯
⇒
π − 2
4
=
1
1 ∙ 3
−
1
3 ∙ 5
+
1
5 ∙ 7
− ⋯

Lecture No.2-11 by Hussein J. AbdulHussein
Advanced Calculus II Al Muthanna University, College of Science
5
Example 12. Find the Fourier Series expansion for the function
f(x) = x cos x. −π < x < π
Solution Since
x cos x. is an odd function therefore, a
0
= a
n
= 0
Let
x cos x = ∑ b
n
sin bx . where
b
n
=
2
π
∫ x cos x sin nx dx
π
0
=
1
π
∫ x {sin(n + 1) x + sin(n − 1)x} dx
π
0
=
1
π
∫ x sin (n + 1)x dx
π
0
+
1
π
∫ x + sin(n − 1)x dx
π
0
=
1
π
[x (−
cos(n + 1)x
n + 1
) +
sin(n + 1)x
(n + 1)
2
]
0
π
+
1
π
[x (−x
cos(n − 1)x
n − 1
) +
sin(n − 1)x
(n − 1)
2
]
0
π
=
1
π
[π {
cos(n + 1)π
n + 1
−
cos(n − 1)π
n − 1
}]
⇒ b
n
= {−
(−1)
n+1
n + 1
+
(−1)
n−1
n − 1
} . n ≠ 1
b
n
= −(−1)
n+1
[
1
n + 1
+
1
n − 1
]
= − {
1
n + 1
+
1
n − 1
} =
−2n
n
2
− 1
. If n is odd; n ≠ 1
But b
n
= {
1
n + 1
+
1
n − 1
} =
2n
n
2
− 1
. If n is even ; n ≠ 1
If n = 1. then b
1
=
2
π
∫ x cos x sin nx dx
π
0
=
1
π
∫ x sin 2x dx
π
0
∴ cos x = b
1
sin x + b
2
sin 2x + b
3
sin x + ⋯
= −
1
2
sin x +
4 sin 2x
2
2
− 1
−
6 sin 3x
3
2
− 1
+ ⋯
