Obstetrics injuries
These include;1~Rupture of uterus
2~Cervical tears
3~Vaginal tears
4~Haematoma of vulva
5~Perineal tears
6~Trauma to the pelvic joints and nerves
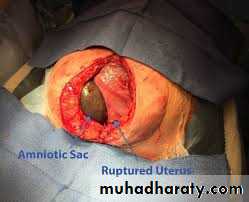
Rupture of uterus
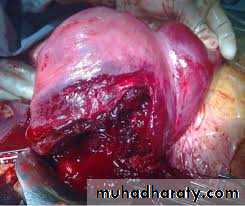
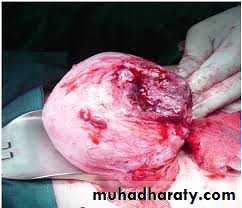
It's define as disruption of the continuity of the pregnant uterus.It's an obstetrics emergency.
incidence
about 1:4000, 95% of cases occur in multipara particularly grand multipara.Rupture occurs at junction of upper & lower segment or at site near the point of uterine vesseles .
Bleeding may occur into peritoneal cavity or may track down between bladder& upper vagina
Types
1~complete involving the whole uterine wall including the peritoneum .2~incomplete, not involving the peritoneal coat
Causes
1-during pregnancy
A-spontaneous
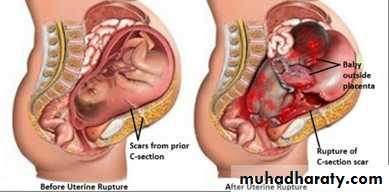
-rupture of a uterine scar eg. previous CS mainly upper segment CS, myomectomy, hysterotomy.
-abruptio placenta with severe concealed haemorrhage.
-rupture of a rudimentary horn at the 4th-5th month.
B -traumatic
-perforation during vaginal evacuation.
-external trauma
2-during labour
A-spontaneous-obstructed labour
-rupture of uterine scar
-grand multipara due to degeneration and overthining of the uterine muscle .
B-traumatic
-internal version-manual removal of placenta
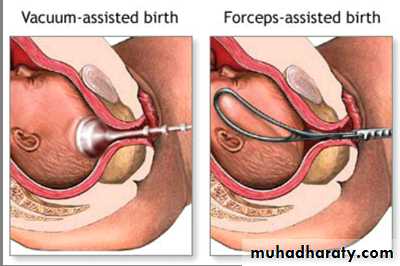
-instrumental delivery eg.forceps or ventous applications before full cervical dilatation.
C-improper use of oxytocin
Clinical pictures
A~impending ruptureBefore actual rupture, the following manifestations may be detected
~lower abdominal pain
~tender uterine scar
~vaginal spotting (minimal bleeding).
B~actual rupture
Symptoms
~sudden severe abdominal pain (it's differentiated from labour pain being continuous).
~if the patient was in labour, there is cessation of uterine contractions.
~shoulder pain on lying down due to irritation of the phrenic nerve by accumulating blood under diaphragm.
Signs
**General examination...patient may be in shock state. This may appears post partum in case of traumatic rupture uterus
.
**Abdominal examination
...examine the scar of previous operation ....fetal parts are prominent and felt easy abdominally
...the presenting part recedes upwards
...abnormal fetal attitude and lie.
...FH sound usually undetected.
...in incomplete rupture, the fetous still inside the uterus with suprapubic painful tender swelling which is an accumulated blood in the vesico-uterine pouch
**Vaginal examination
...the presenting part recedes upwards.
...vaginal bleeding may be present.
...contracted pelvis may be detected.
Treatment
1-call for help2-blood transfusion and anti-shock measures (wide bore canula, iv crystalloid solution, oxygen )
3-immediate laparotomy
4-deliver the fetous & placenta
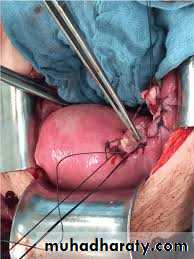
5-explore the rupture site.
...if it's amenable for repair & the patient didn't complete her family....repair is done.
...if it's not amenable for repair...hysterectomy is done.
6-exploration of the other viscera mainly the bladder .
7-internal iliac artery ligation may be needed in case of broad ligament hematoma.8-vaginal repair if there is slight extension of a cervical tear
preventive measures
##During pregnancy ;1-good antenatal care for assessment of pelvis, fetal size, presentation& position
2-planning for hospital delivery for a patient who has previous CS
3-training to midwifes to recognize high risk pregnancy & time of referal to hospital
##During labour ;
1-monitor the labour using partogram2-proper use of oxytocin
3-hard pressure on abdomen should be avoided to force delivery
4-early diagnosis of complications
5-exploration of the genital tract after difficult labour or instrumental delivery
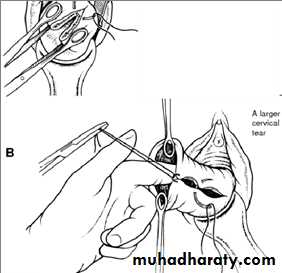
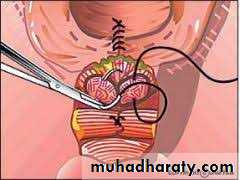
Cervical lacerations (tear )
Aetiology
1- ventous or breech extraction before full cervical dilation2-manual dilatation of cervix
3-improper use of oxytocin
4-precipitate labour
Clinical features
1-sever vaginal bleeding after delivery inspite of well contracted uterus .2-vaginal examination ;the tear can be felt
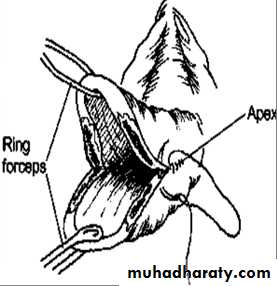
3-speculum exam; using a posterior wall self retaining speculm or vaginal retractor & 2ring forceps to grasp anterior & posterior lips of cervix . so the tear can be visualized
Treatment
Immediate repair: is carried out under general anaesthesia with good light exposure.Interrupted cut gut dexon or vicryl sutures are taken starting from above the apex of the tear to control bleeding from the retracted blood vessels.
Vaginal lacerations
CausesPrimary lacerations less common and caused by:
...Forceps application.
...Destructive operations.
...Vacuum extraction
Secondary lacerations:
more common and are due to extension from perineal or cervical tears
Management
**Immediate repair: Continuous locked cat gut sutures are taken starting from above the apex to control bleeding from the retracted blood vessels.**Tight pack: may be needed to control bleeding from a raw surface area.
**Foley's catheter should be inserted before packing and both are removed after 12-24 hours
Hematoma of genital tract
A.Vulval (Infra-Levator) Haematoma
Causes:*Traumatic due to:
...incomplete haemostasis during repair of episiotomy or tear
...Direct trauma as kick or falling down
*Spontaneous: due to rupture of a varicose vein
Clinical picture
The haematoma usually appears 12-48 hours after delivery.The collection of blood is limited by the levator ani above but laterally it may extend to fill the ischiorectal fossa reaching a volume of 500 ml or more.
There is a progressive enlarged, painful, tender, tense, bluish swelling at the vulva.
Manifestations of hypovolaemia (e.g. hypotension and rapid pulse) and anaemia may be present
B.Vaginal (Supra-Levator) Haematoma
Causes:Deep vaginal lacerations .
Clinical picture:
The blood is collected paravaginally above the levator ani muscle.
It may not be visible externally.
It may not be painful until reaching a large size.
Manifestations of hypovolaemia and anaemia may be present
Management:
**Small not-increasing haematoma (less than 5cm);
is managed conservatively as it usually resolves spontaneously.
Prophylactic antibiotic may be given to guard against secondary infection with analgesia with blood transfusion if patient anaemic
**Large increasing haematoma:
...It is incised longitudinally,...evacuation of the clotted blood,
...bleeding points are ligated,
...the gap is closed in layers
Broad ligament haematoma
Form in broad ligament, it may follow spontaneous vaginal delivery or CS.Causes
Upper vaginal, cervical or uterine tears which usually involve the vaginal or uterine artery.Clinical picture
**Hypovolaemia, anaemia or shock: is usually present due to large amount of internal haemorrhage.
**Swelling on one side of the uterus which increasing over a period of hours or days and may reach up to the lower pole of the kidney or even the diaphragm.
**The uterus is felt separate and deviated to the opposite side.
**Fever, ileus and unilateral leg oedema: may develop later
Treatment
*Small not-increasing haematoma:is managed conservatively as vulval haematoma
Antibiotics, blood transfusion may be required.
*Large increasing haematoma: Laparotomy,Evacuation of the blood clots,Securing haemostasis, bilateral internal artery ligation or hysterectomy may be indicated(rare).
Perineal lacerations
AnatomyThe perineal body is a pyramidal mass of tissues about 4´ 4 cm between the lower vagina anteriorly, the anal canal and lower rectum posteriorly
It is composed of the following layers respectively:
Skin.Superficial fascia
Perineal muscles;
external anal sphincter,
superficial and deep perinei muscles,
Aetiology
Lack of perineal elasticity:
Elderly primigravida.Excessive scarring from a previous operation as posterior colpoperineorrhaphy
Friability due to perineal oedema.
Marked perineal stretch allowing head extension before crowning
Macrosomic baby
Face to pubis delivery.
Forceps delivery.Narrow subpubic angle pushing the head backward
Rapid perineal stretch
Precipitate labour.
Rapid delivery of the after-coming head in breech presentation
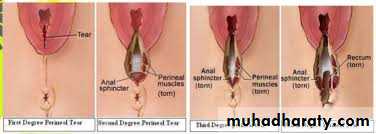
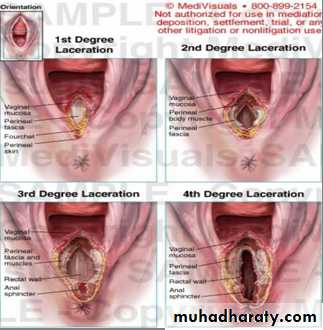
Degree
-First degree: involves the perineal skin, and the posterior vaginal wall.-Second degree: involves the previous structures + the muscles of the perineal body but not the external anal sphincter.
-Third degree: involves the previous structures + the external anal sphincter.
-Fourth degree: involves the previous structures + the anterior wall of the anal canal or rectum.
Complications
1-Postpartum haemorrhage.2-Puerperal infection
3-Incontinence of stool and flatus in unrepaired or imperfectly repaired 3rd or 4th degree tear.
4-Residual recto-vaginal fistula in imperfectly repaired 4th degree tear
5-Future genital prolapse
Treatment .
Any perineal tearshould be repaired
within 24 hours
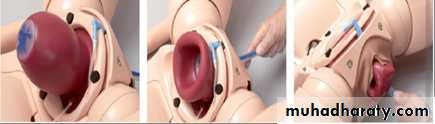
Uterine inversion
The body of the uterus becomes partially or completely turned out (inside out) after delivery of fetus
.it can be fatal if untreated.
There is descent of uterine fundus into cavity through cervix or even through vulva.
It's very rare.
Causes
Improper management of third stage of labour by pulling the umbilical cord or pressing on fundus while the uterus is not contracting & placenta has not yet separatedSymptoms & signs
*Pain*Shock out of all proportion to visible blood loss.inversion exerts traction on peritoneal structures which can elect a profound vasovagal response.
There is a risk of profuse bleeding due to uterine atony causing hypovolemic shock as well.
*appearance of uterine fundus at vulva sometimes
Treatment
1-immediate intravascular volume expansion with IV crystalloids2-immediate replace the uterus through cervix by manual compression by hand to avoid oedema of uterus which making replacement more difficult. If this fails, hydrostatic pressure works well
3-give oxytocin to encourage uterine contraction after replacement
4-surgical replacement rarely required.