
Urinary System
Dr. Ahmed Maher
Dr. Ahmed Manhal
Presentation Map
Kidney (cortex &
medulla).
Nephron.
Duct system.
Juxtaglomerular
apparatus.
Ureter, bladder &
urethra.
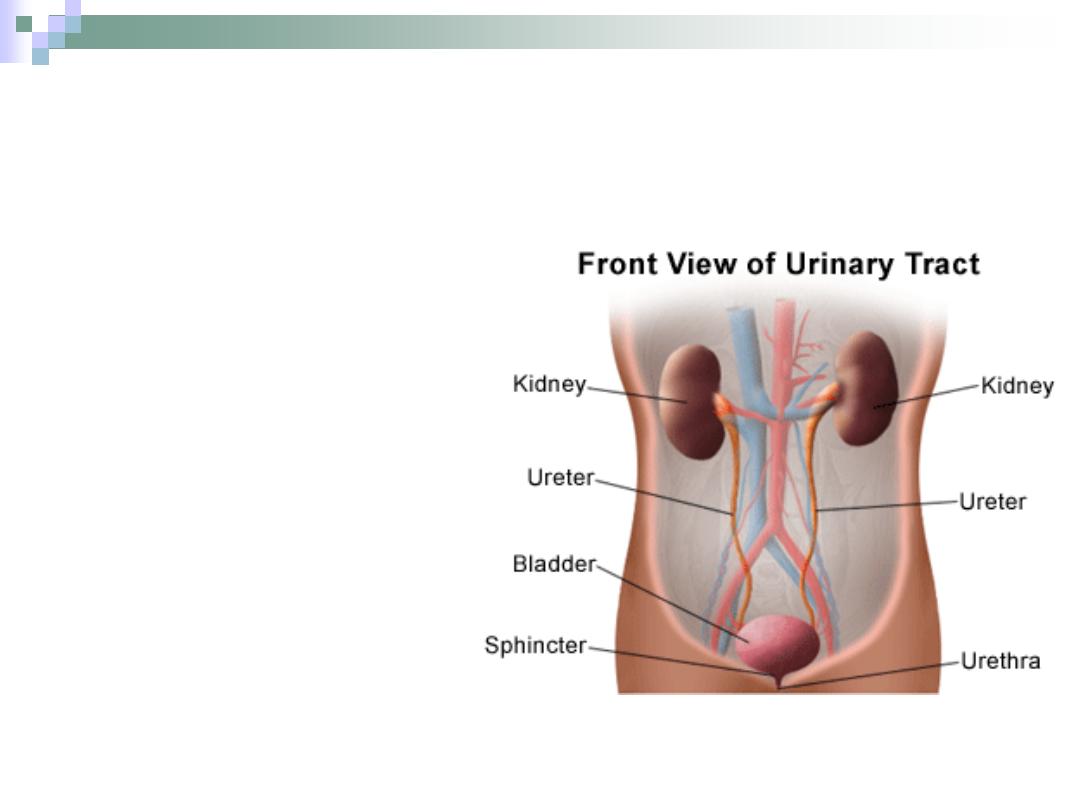
Definition & General Structure
The system which
eliminates waste products
of the body and maintains
fluid/salt balance.
It consists of paired
kidneys & ureters and
unpaired urinary bladder
and urethra.
Most of the functions are
preformed in the kidneys.
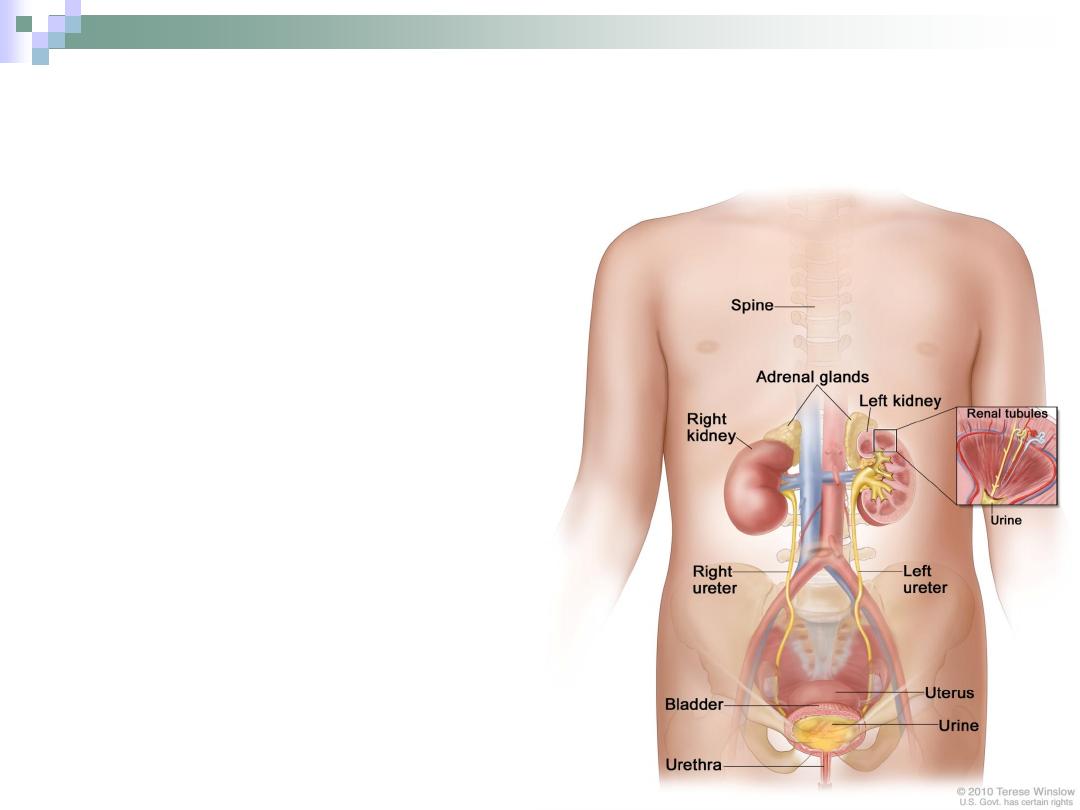
The Kidney
Two reddish bean shape
structures each one is
surrounded by a thick
C.T. capsule.
Located in the abdominal
cavity.
The right kidney is
pushed downwards by
the liver, so the left one is
1-2 cms higher.
It’s divided to outer cortex
and inner medulla.
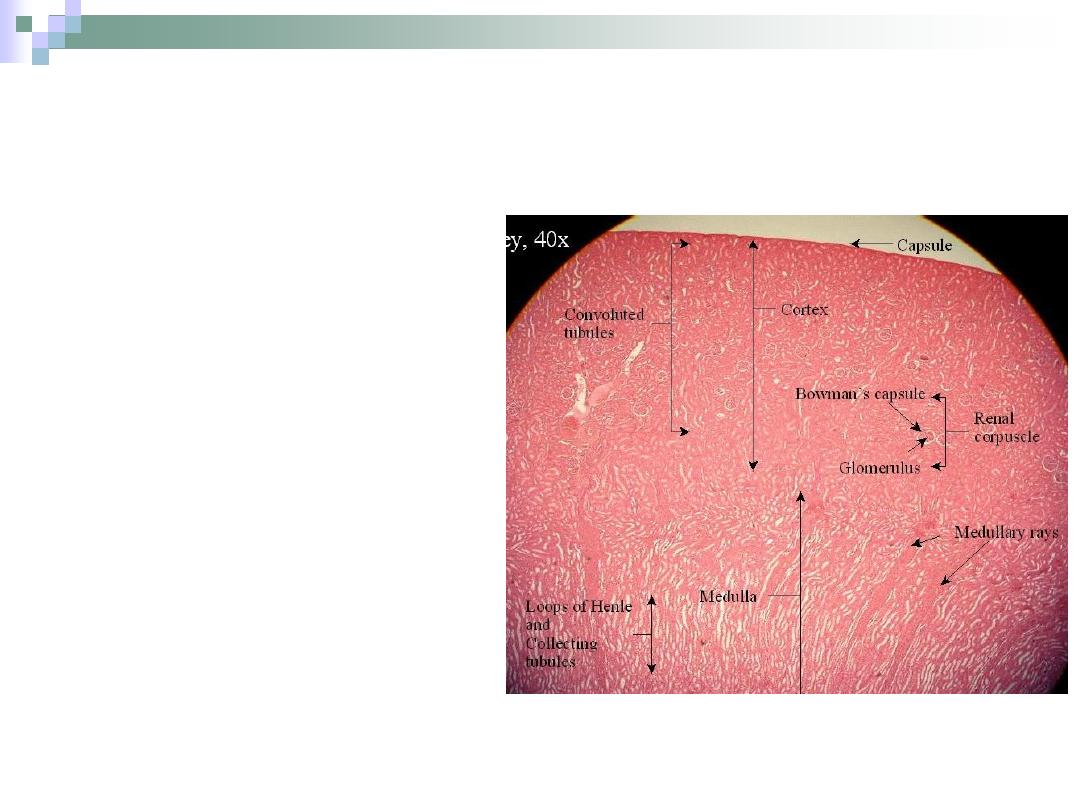
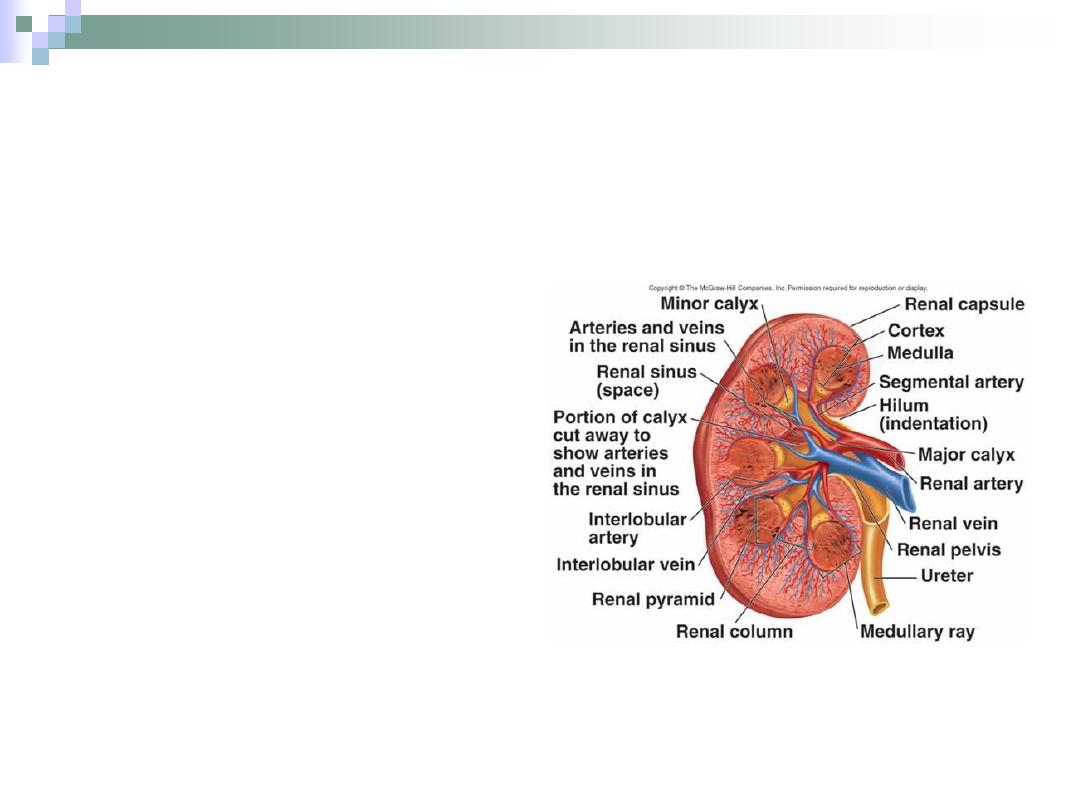
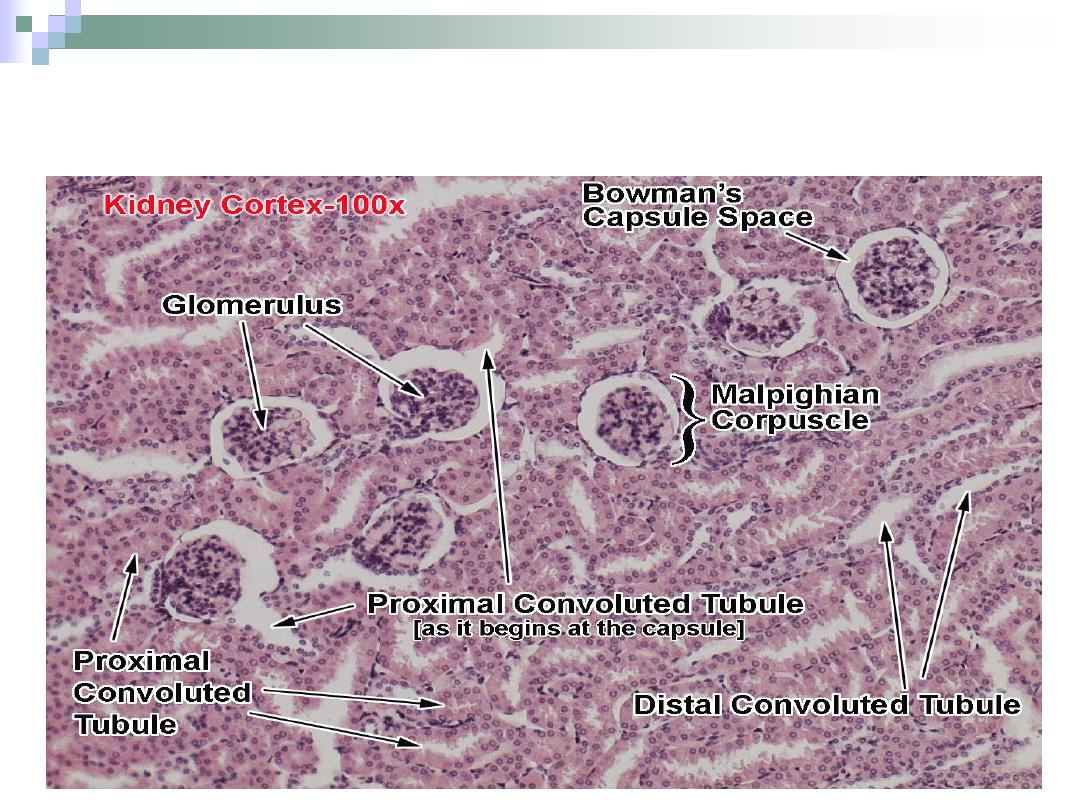
The Cortex
Dark brown granular
appearance.
5 mm thick.
Contains glomeruli &
convoluted tubules.
Medullary rays; coming from
medulla, are recognized here.
Between two rays is a region
called cortical labyrinth.
The medullary ray and its
surrounding cortical labyrinth
form the LOBULE.
Renal Cortex
The Medulla
Organized as multiple
medullary pyramids with
the base towards the
cortex.
Each pyramid and its
associated “cap” of
cortical tissue is known
as LOBE.
Contains Henle’s loop,
collecting tubules and
ducts.
Renal Medulla
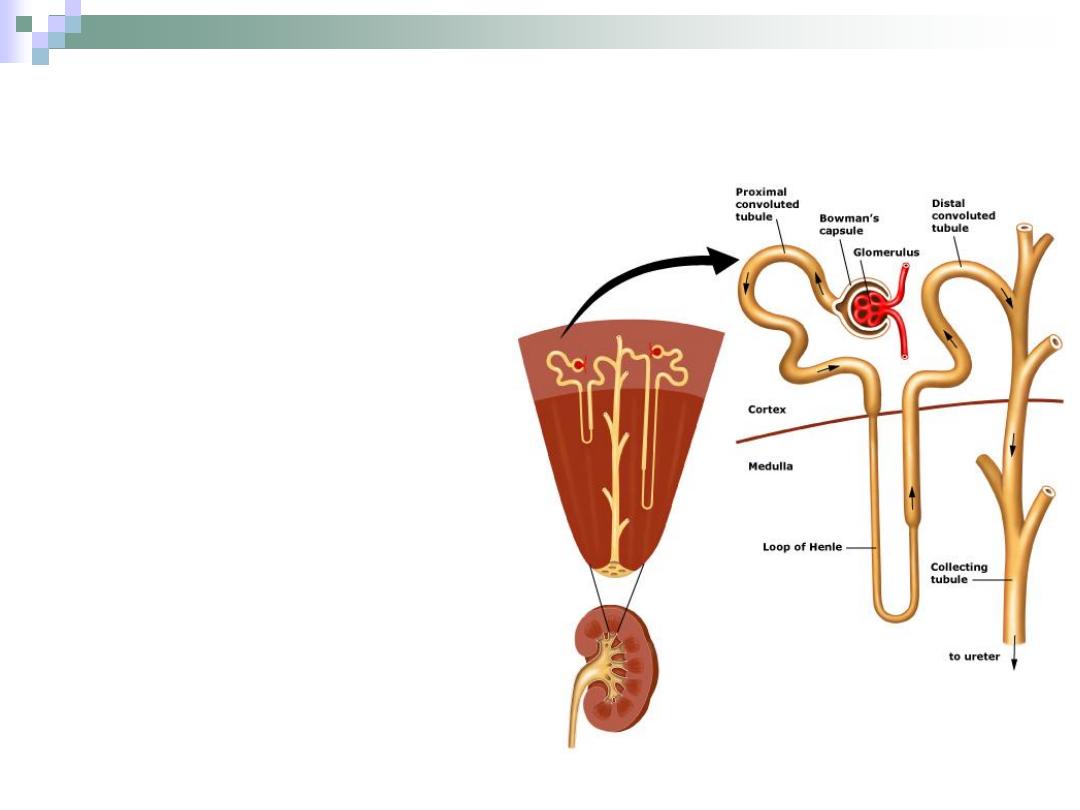
The Nephron
It’s the structure
responsible for urine
formation.
Consists of the renal
corpuscle, proximal
convoluted tubule,
Henle’s loop and distal
convoluted tubule.
There are two types of
nephrons: cortical &
juxtamedullary nephrons.
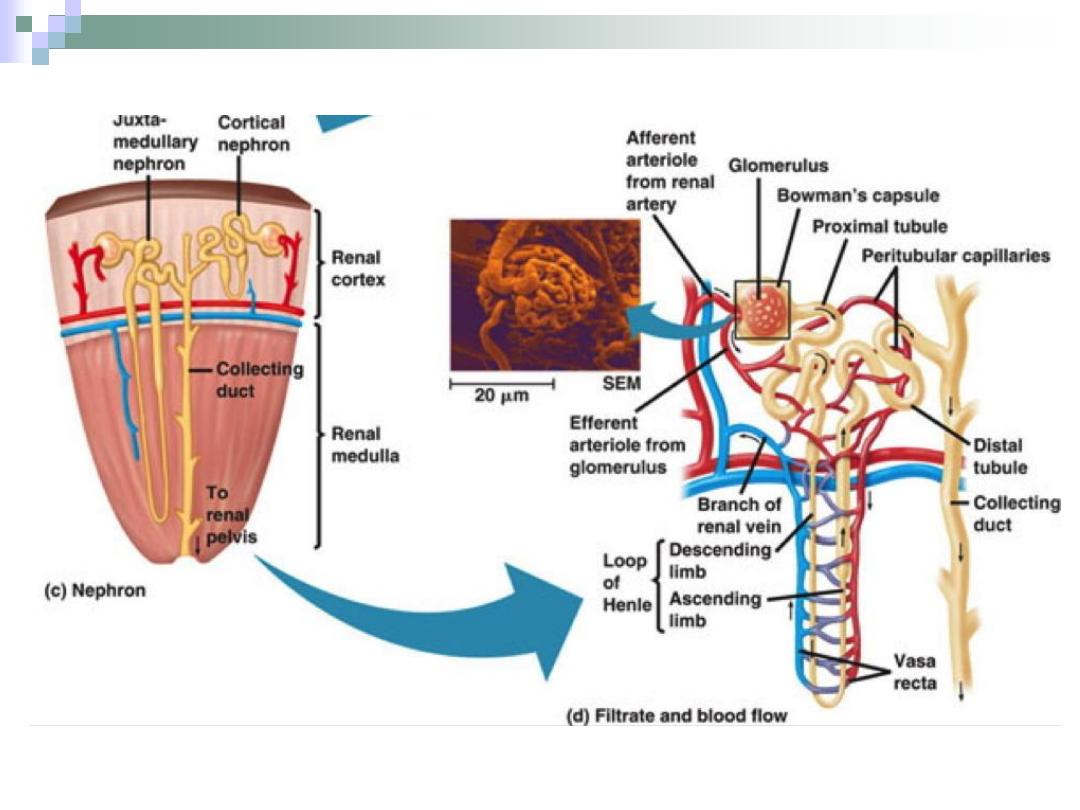
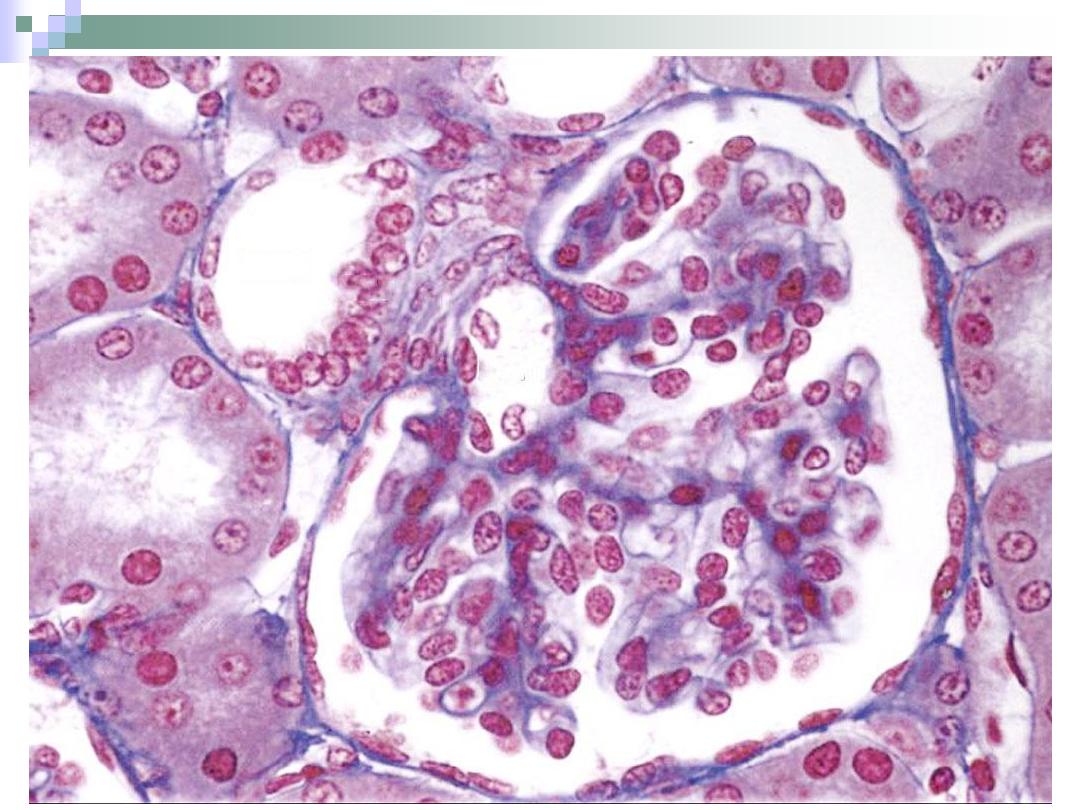
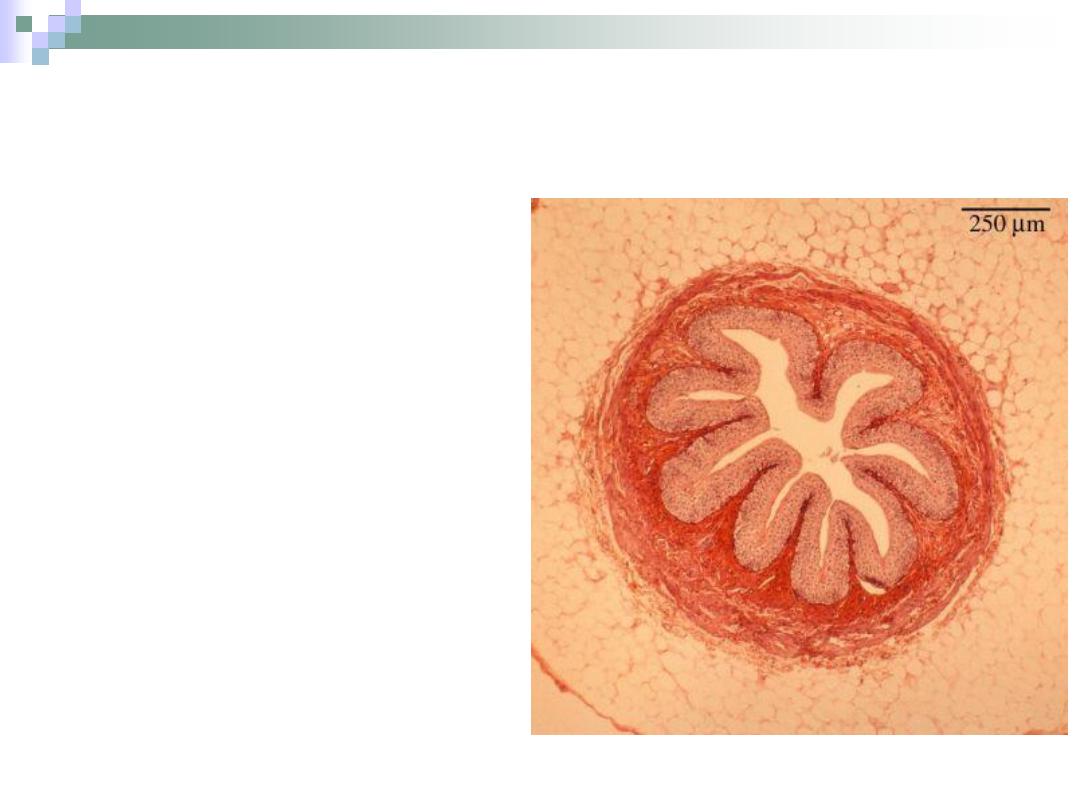
The Renal Corpuscle
The point at which the
nephron starts.
All renal corpuscles
lie within the renal
cortex.
It consists of
Bowman’s capsule
and the glomerulus.
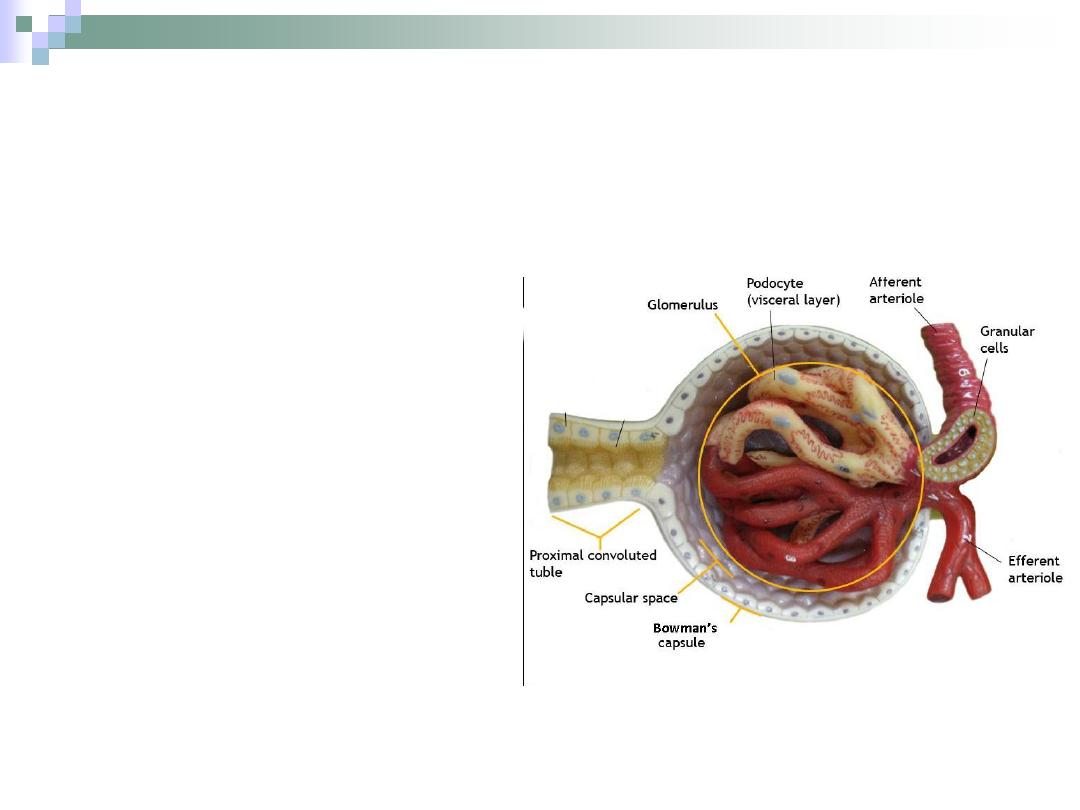
Bowman’s Capsule
The part of renal
corpuscle than envelopes
the glomerulus.
It consists of two layers.
Outer parietal layer.
Inner visceral layer.
Between these two layers
is the urinary space.
The Glomerulus
The capillary bed
found within
Bowman’s capsule of
the renal corpuscle.
It begins with afferent
arteriole and forms
efferent arteriole.
The process of
filtration takes place
in the glomerulus.
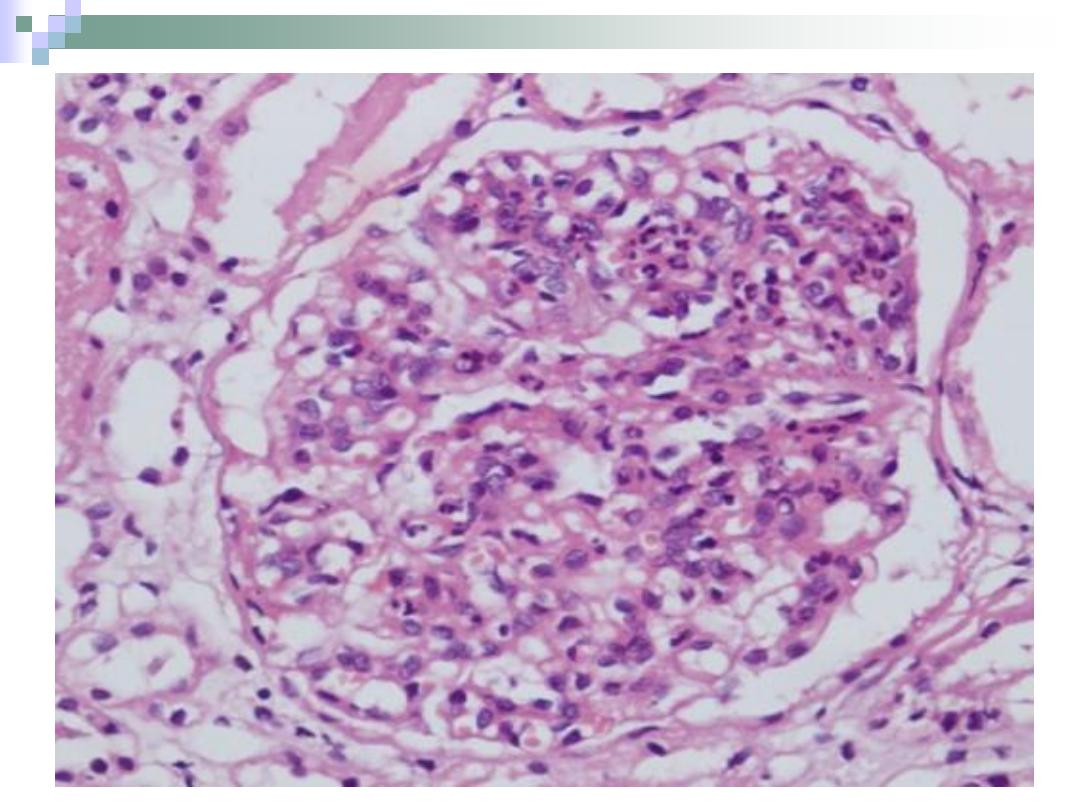
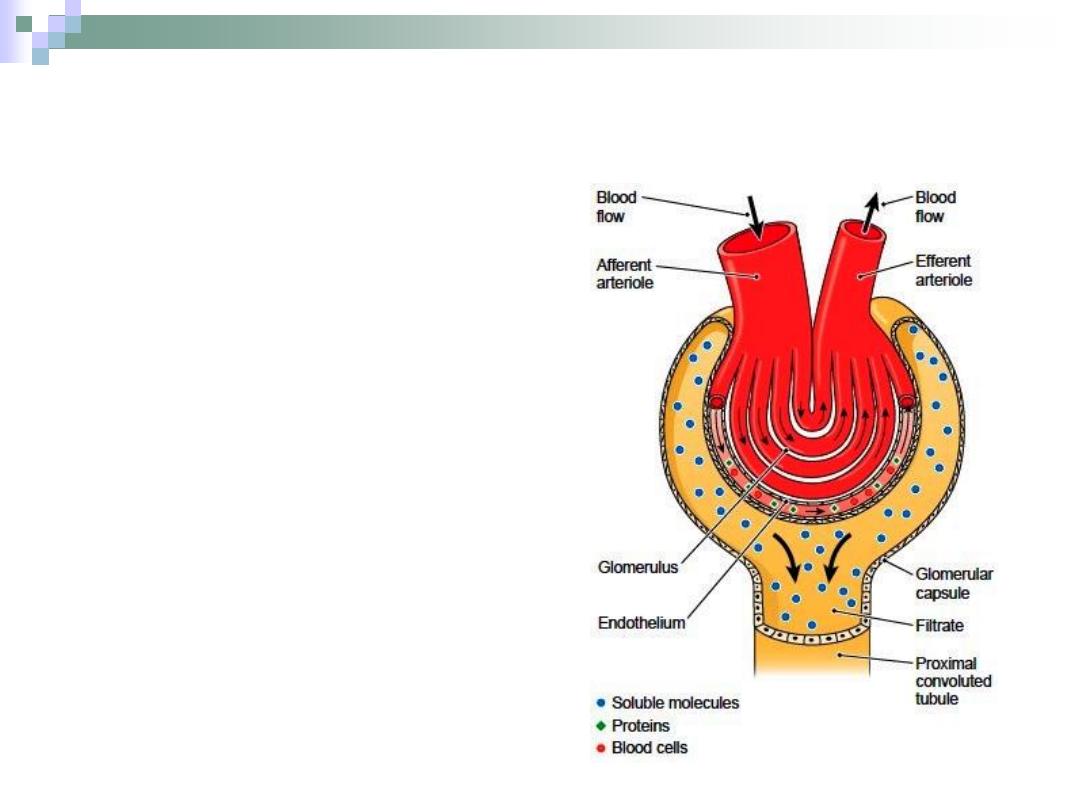
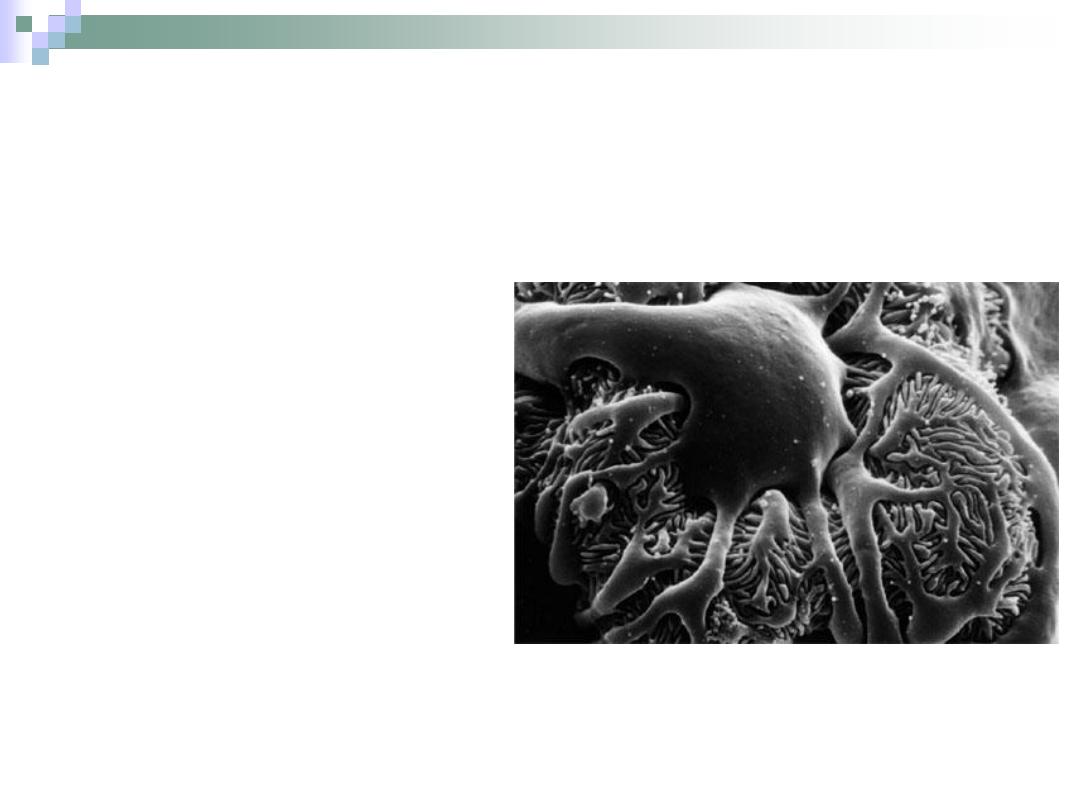
Filtration Mechanism
Movement of fluid from
vascular glomerulus
across the filtration
barrier into the urinary
space.
The endothelium,
basement membrane &
podocytes prevent
formed elements of blood
and other molecules from
passing with the filtrate.
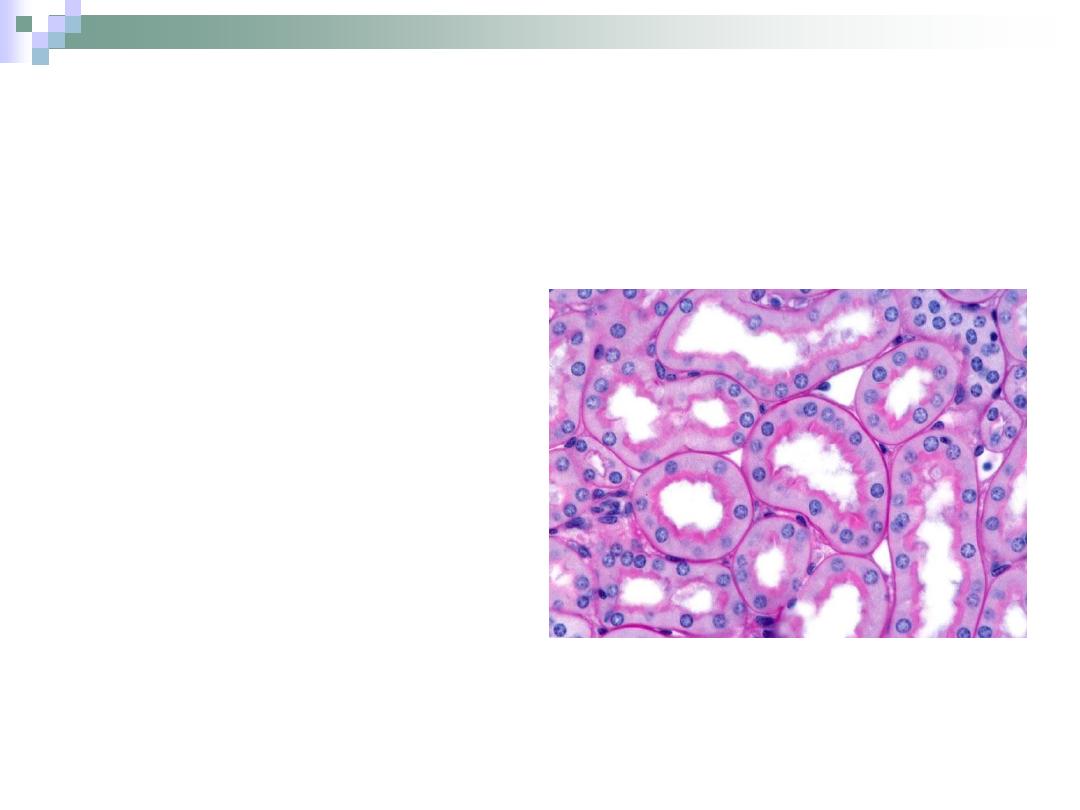
The Proximal Convoluted Tubule
PCT is longer & wider
than DCT.
Cuboidal \ truncated
pyramid cells.
Acidophilic cytoplasm.
The cells form brush
border on the apex.
The apical part of the
cells contain canaliculi
that increase the
absorbance potency of
the cell.
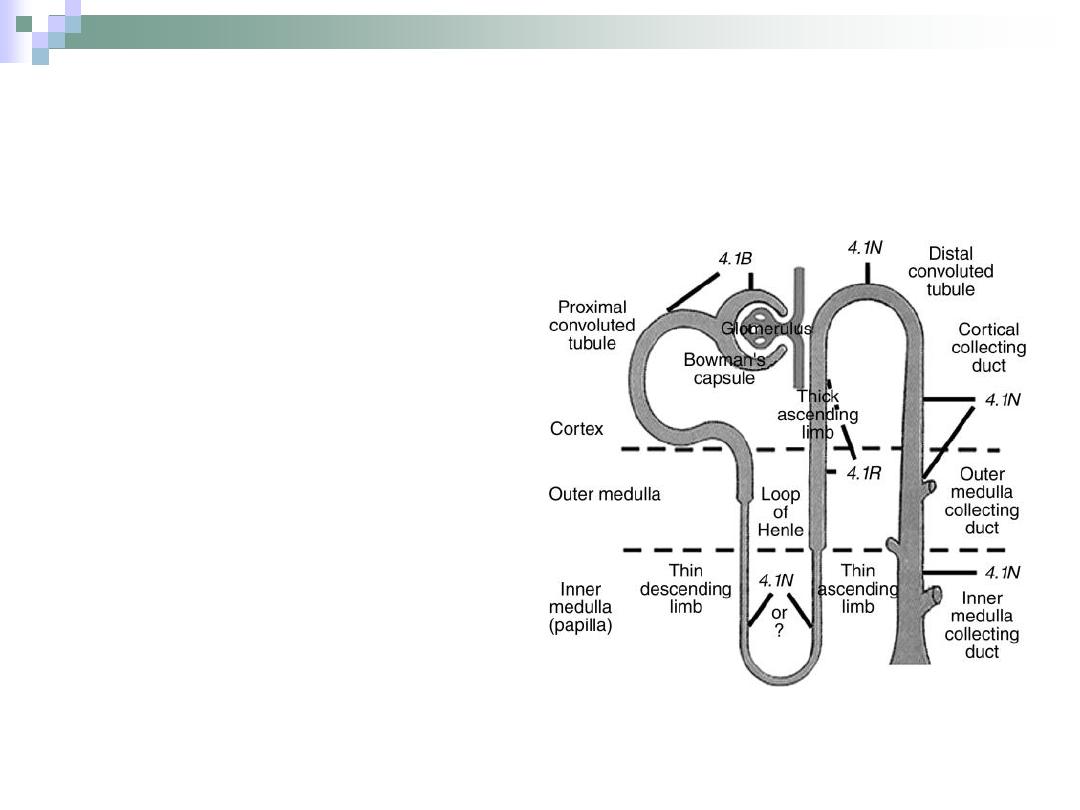
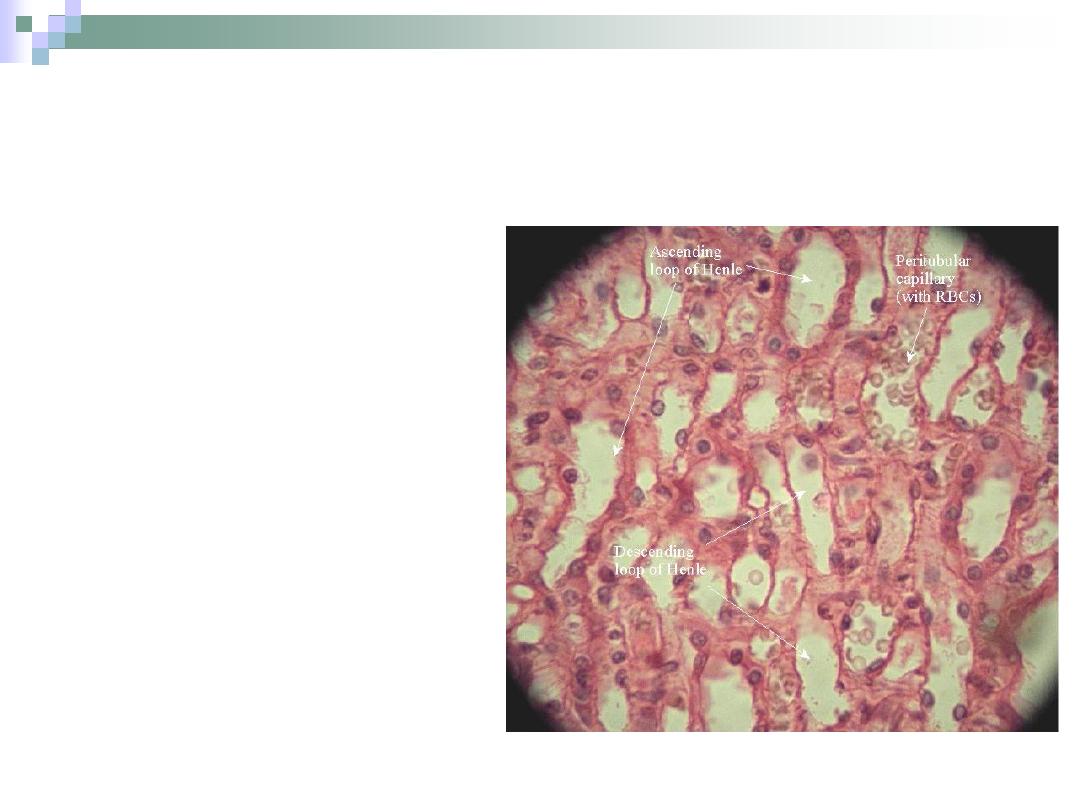
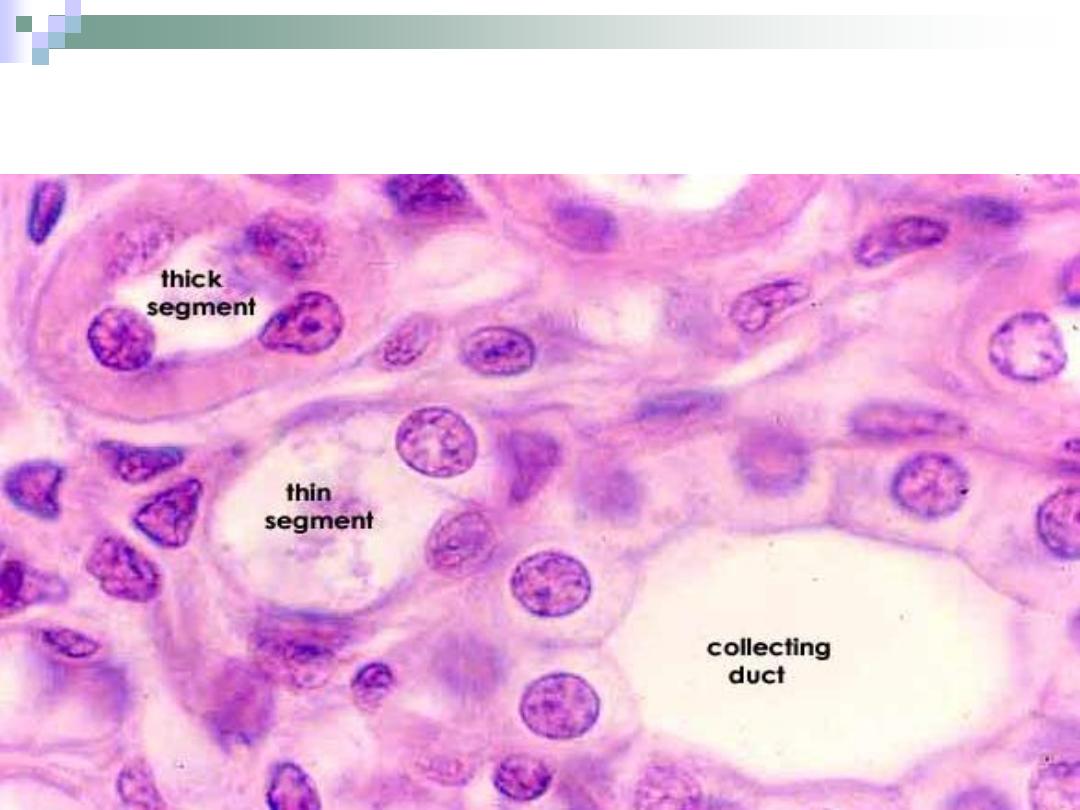
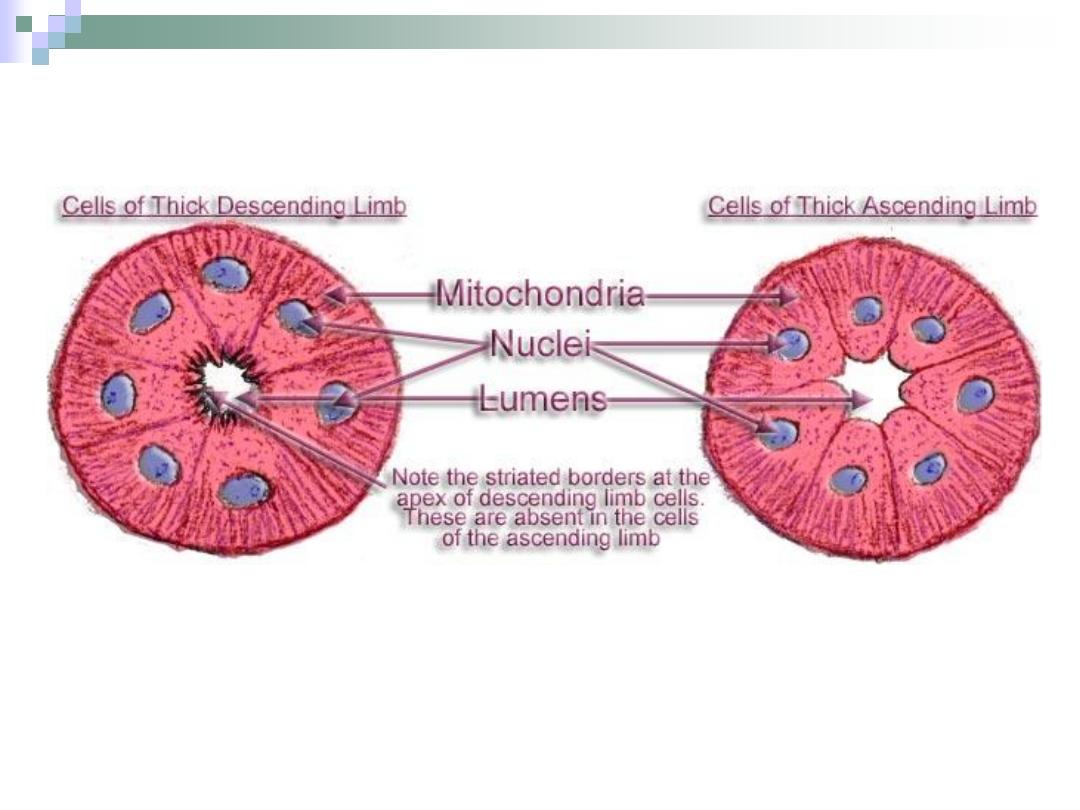
Henle’s Loop
“U” shaped structure that lies
within the medulla.
Responsible for water
retention.
Begins at the end of PCT &
ends at the beginning of DCT.
Consists of:
1.
Thick descending arm.
2.
Thin descending arm.
3.
Thin ascending arm.
4.
Thick ascending arm.
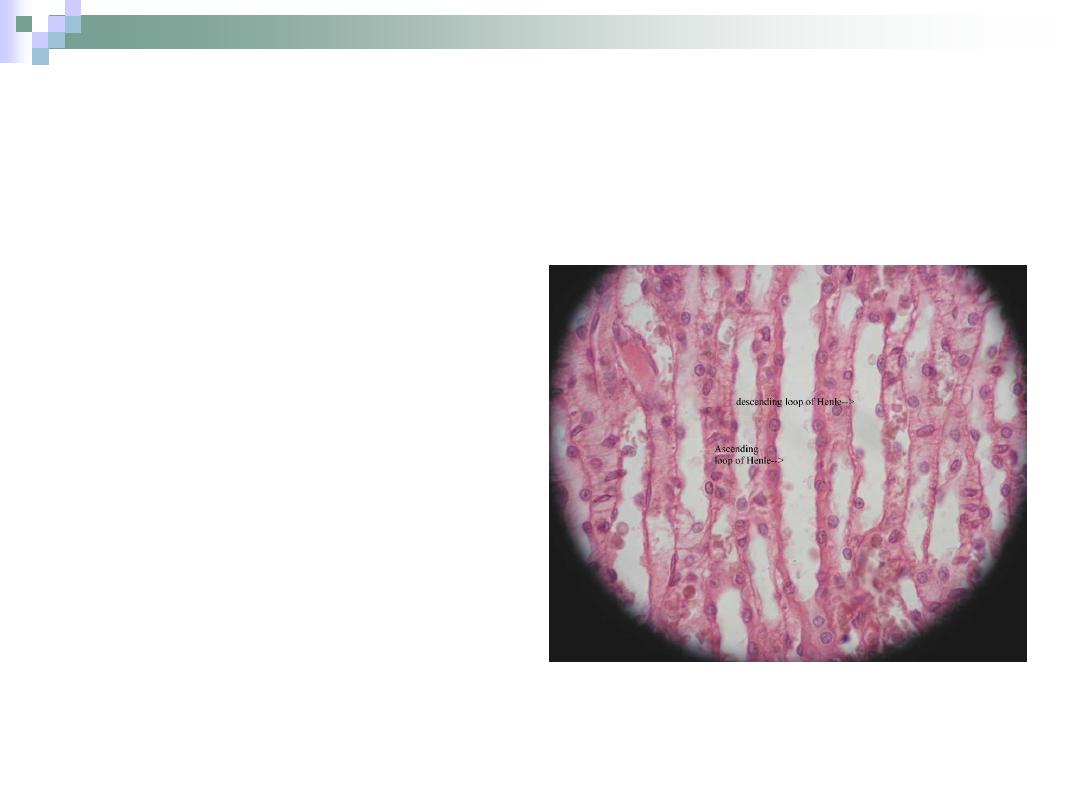
The Descending Arm
The thick arm is
similar to PCT.
It narrows to form
the thin arm.
The thin arm is lined
with simple
squamous
epithelium;
therefore, it has a
wide lumen.
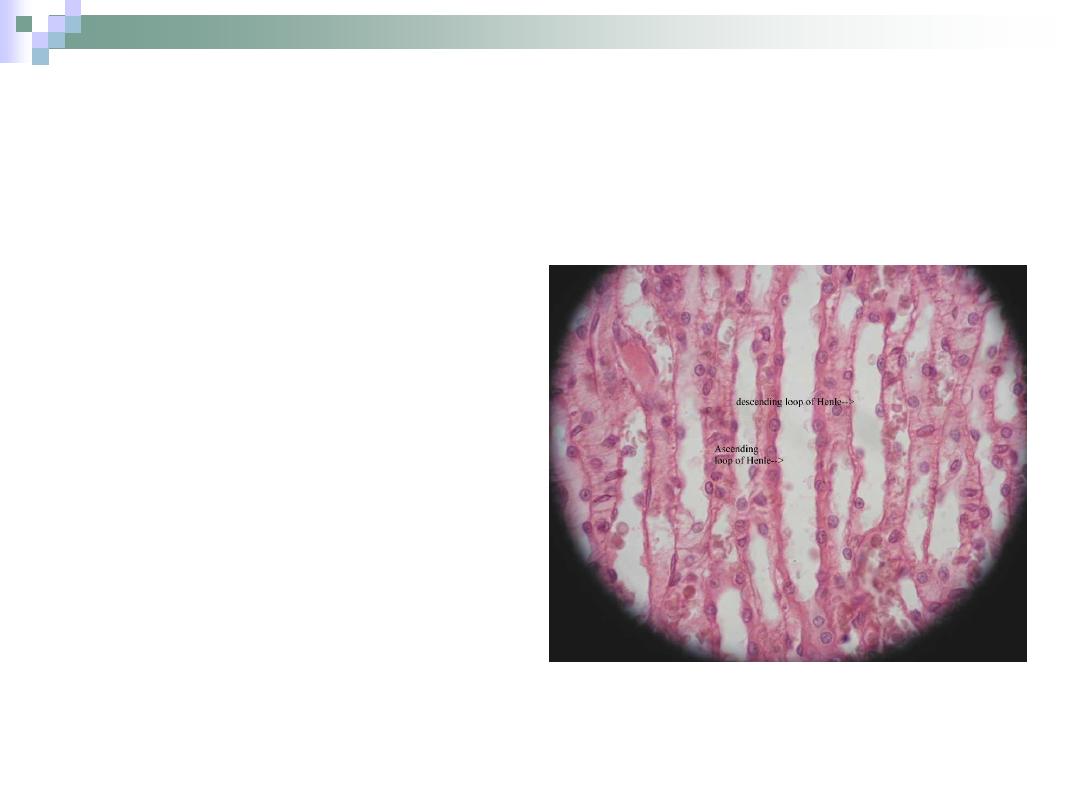
The Ascending Arm
The thin arm is only found
in juxtamedullary
nephrons and it’s similar
in structure to the thin
descending arm.
The thick arm is similar in
structure to the DCT.
Responsible for sodium &
chloride absorption from
urine.
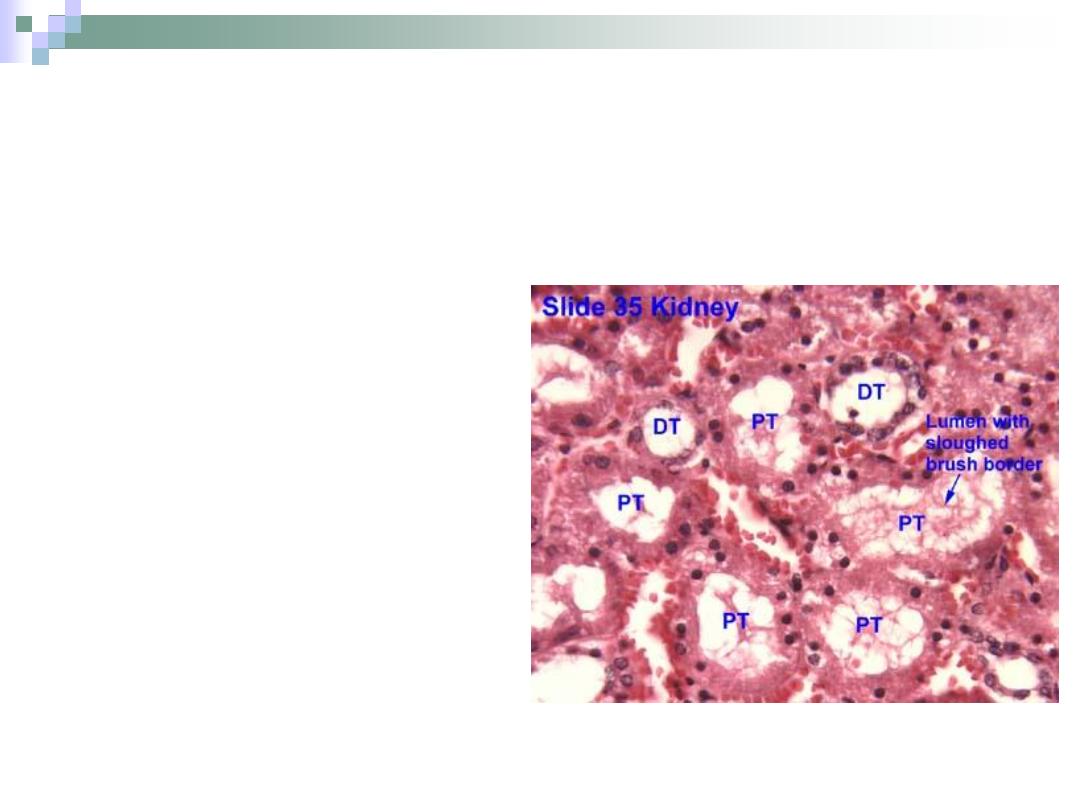
The Distal Convoluted Tubule
Lies within the cortex.
Tortuous course with
simple cuboidal
epithelium lining.
Has no brush borders
in the apices of the
cells.
No canaliculi.
Responsible for ion
transportation.
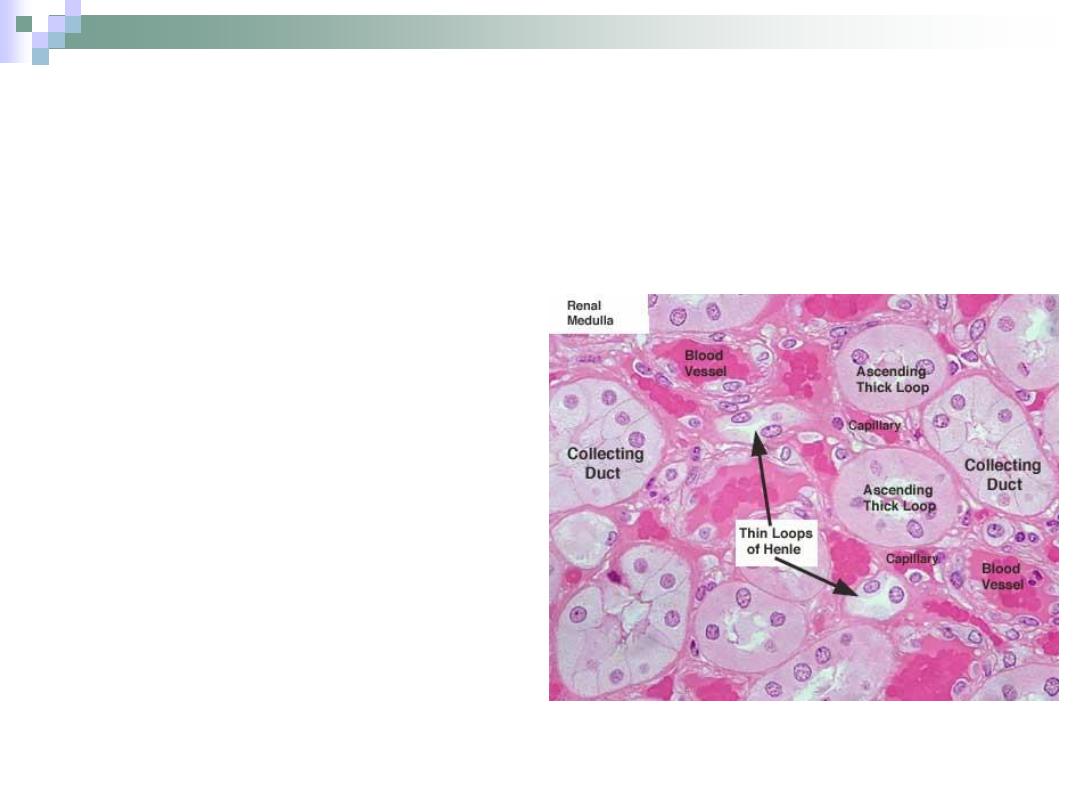
Collecting Tubules & Ducts
The collecting tubule
begins at the end of DCT.
Collecting tubules join
each other to form
collecting ducts.
The collecting ducts form
the papillary ducts near
the tips of medullary
pyramids.
The lining begins as
simple cuboidal and ends
as simple columnar.
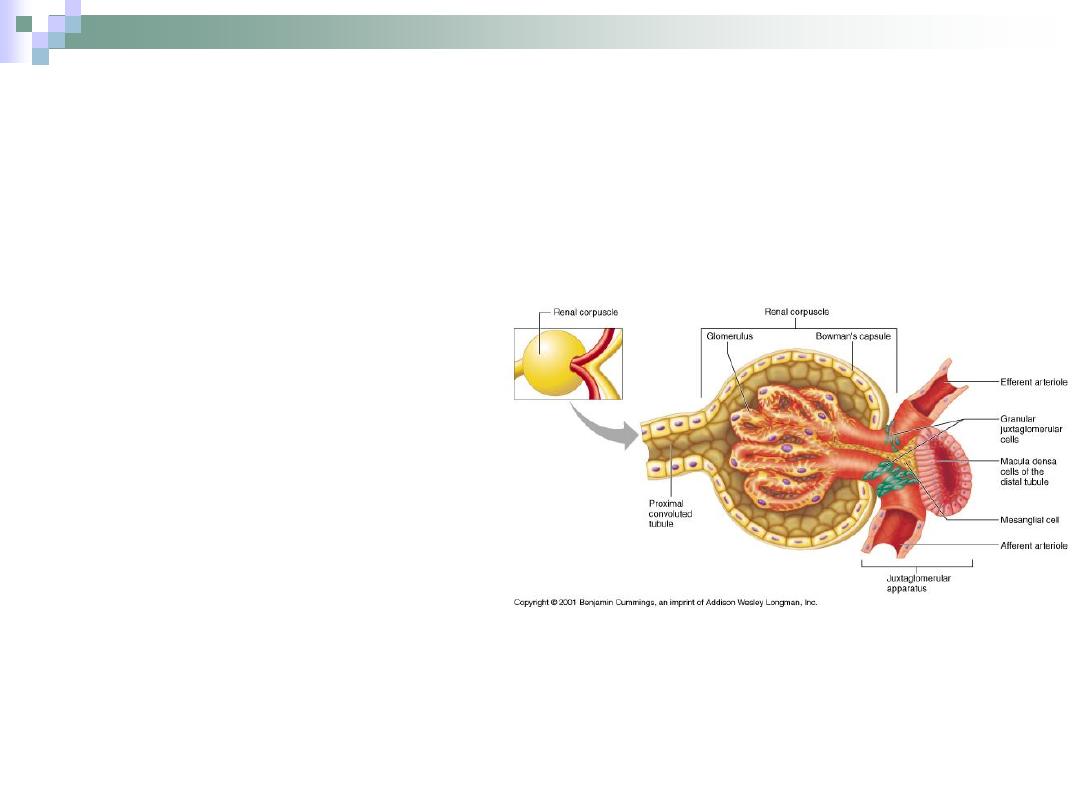
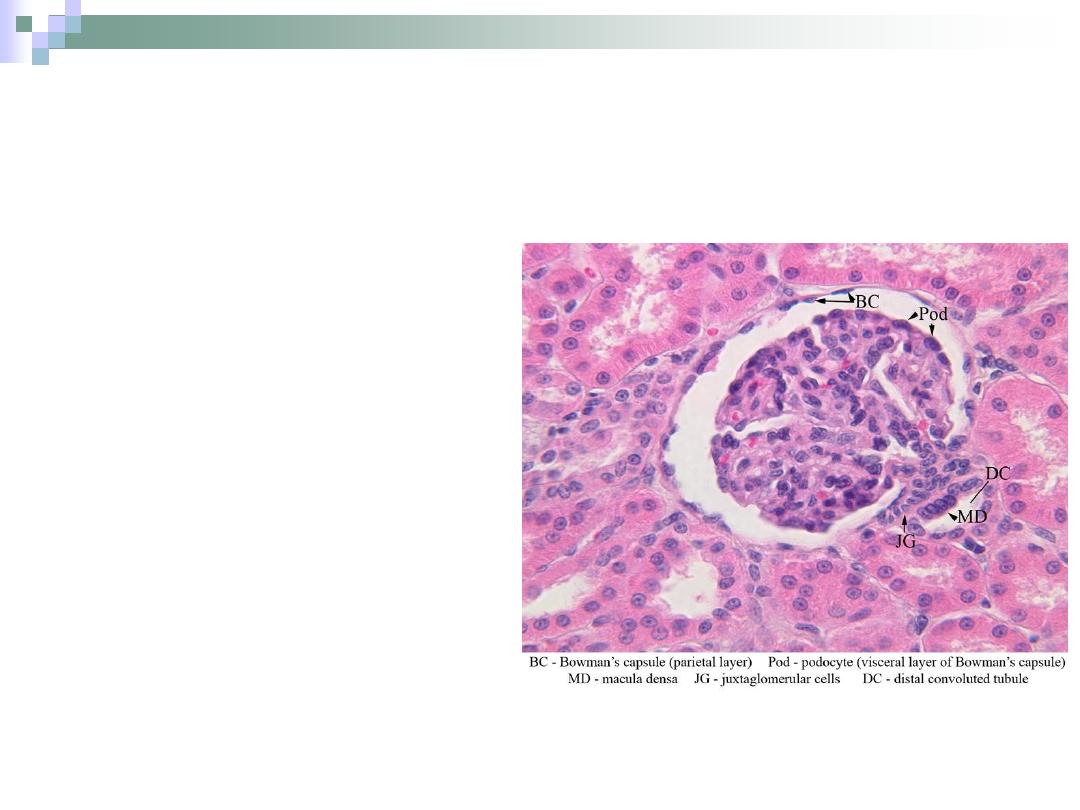
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
Consists of
1.
macula densa of
DCT.
2.
Juxtaglomerular cells
3.
Lacis cells
(extraglomerular
mesangial cells).
This apparatus
participates in controlling
blood pressure through
some hormones
secretions.
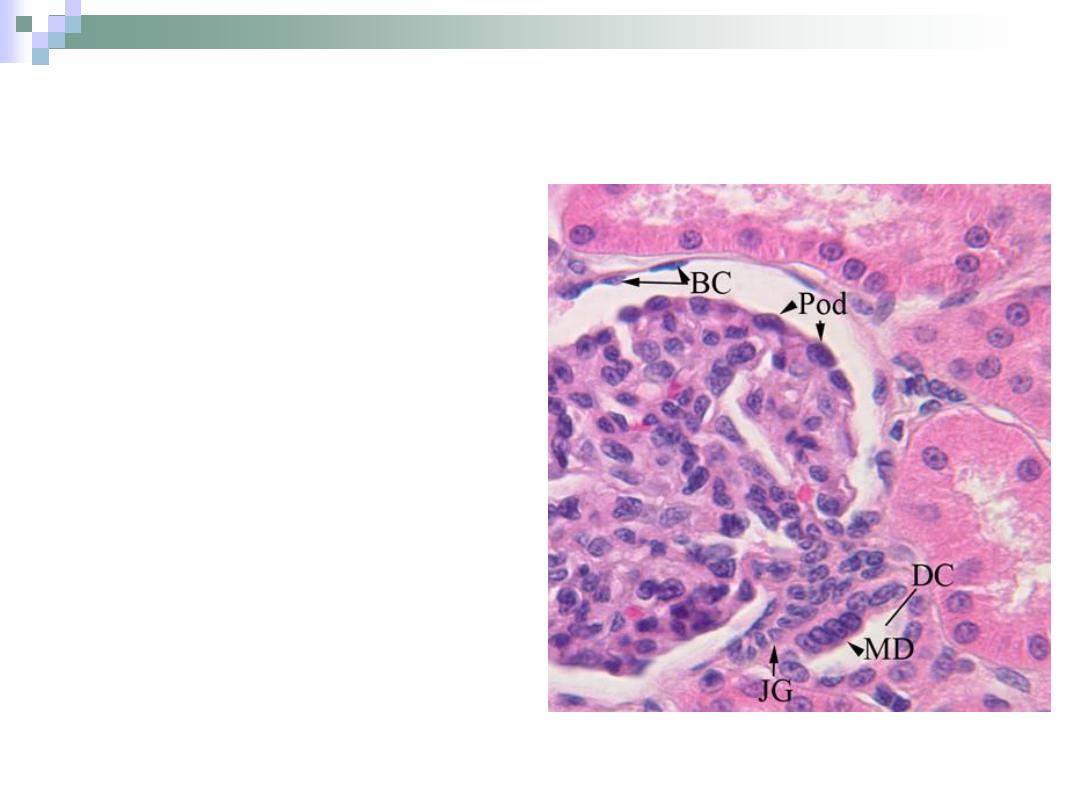
Macula Densa
Formed by DCT when it
approaches the
glomerulus.
Have a columnar (instead
of cuboidal) cells which
are densely packed
together.
It secretes the hormone
renin which takes a part
in blood pressure control.
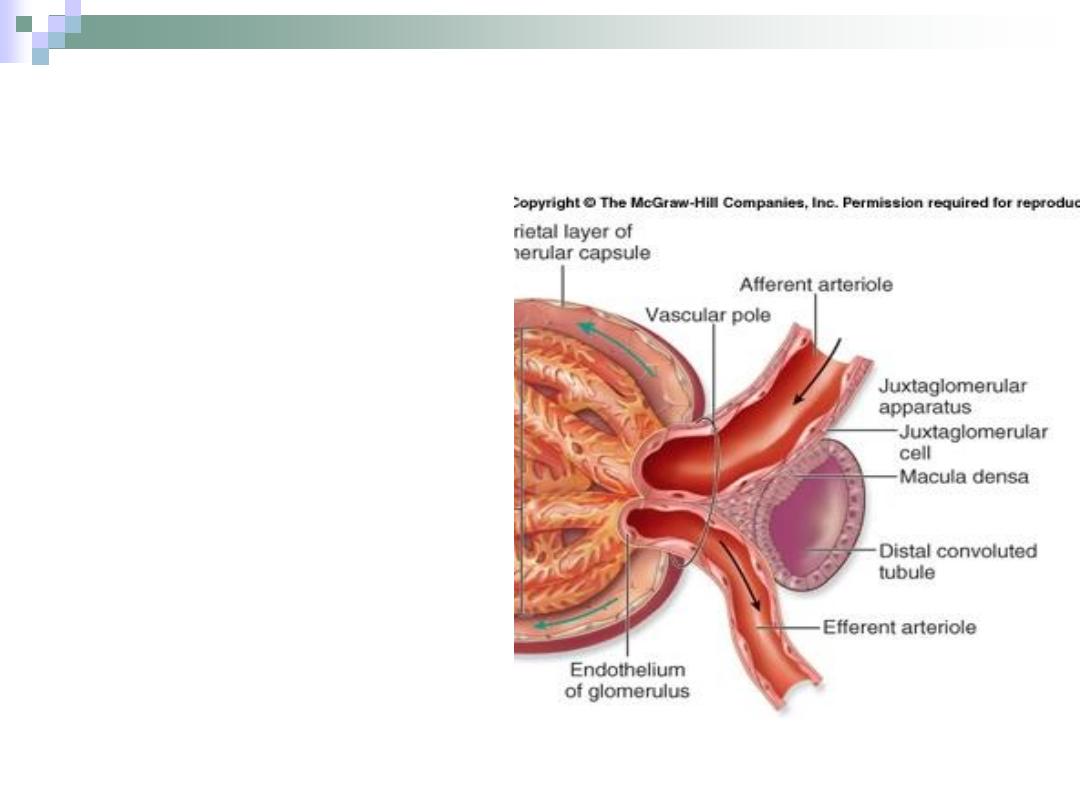
Juxtaglomerular Cells
Formed by tunica
media of the afferent
arteriole.
Have round nuclei.
Also takes a part in
blood pressure
control.
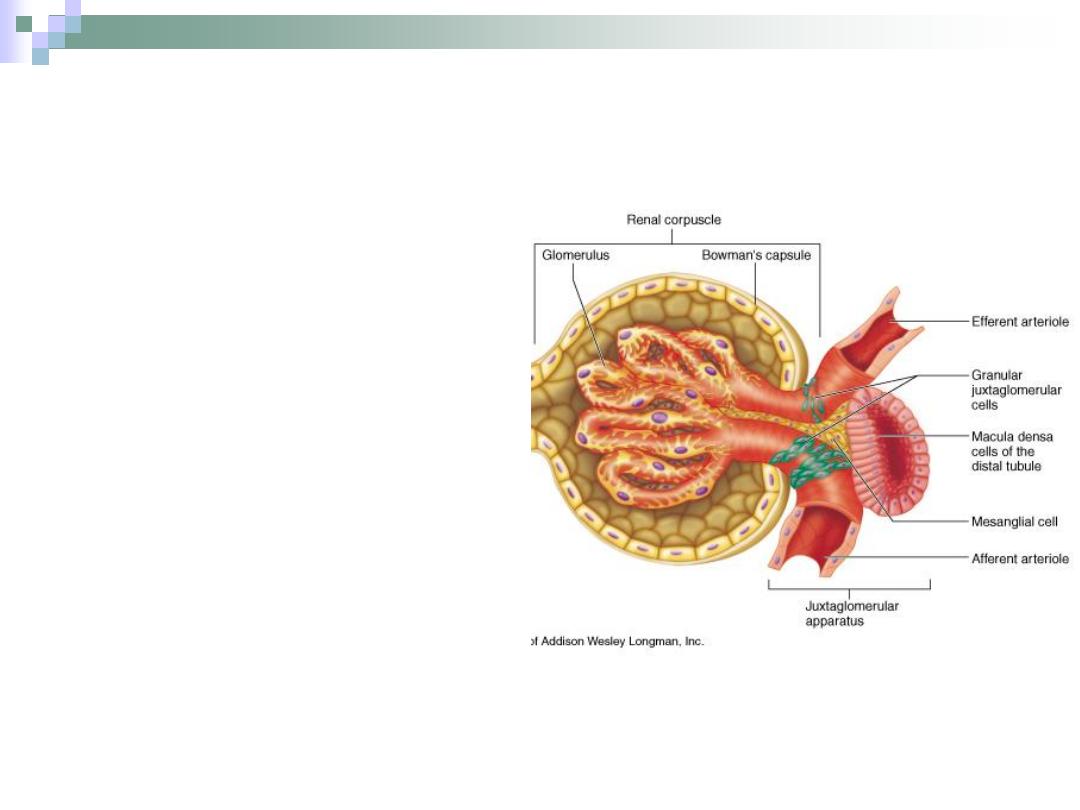
Lacis Cells
Bounded by:
1.
Afferent & efferent
arterioles.
2.
Macula densa.
3.
Glomerulus.
The function of these
cells isn’t well defined
yet.
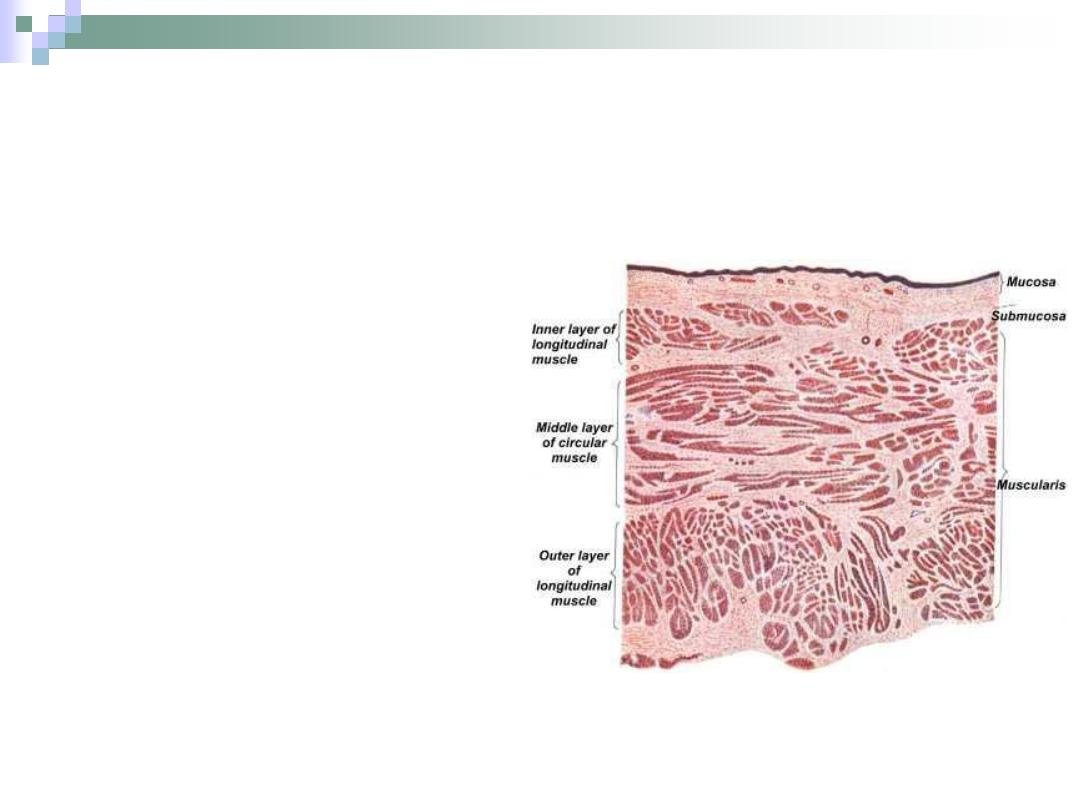
The Ureter
Composed of:
1.
folded mucus
membrane.
Transitional
epithelium.
Lamina propria.
2.
Smooth muscle coat.
3.
Fibro-elastic
adventitia.
There is no sub
mucosa.
Urinary Bladder
Composed of the
same layers of ureter,
but the muscular layer
is much thicker.
It stores urine until its
excreted outside the
body.
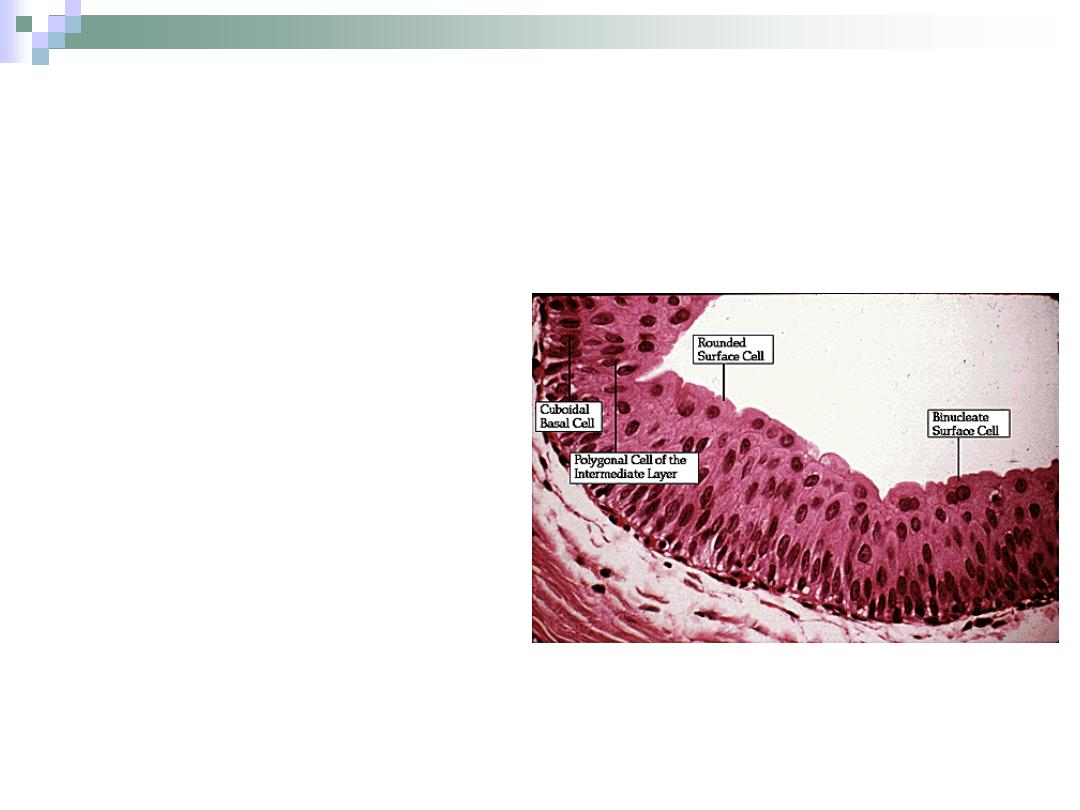
Transitional Epithelium
It has the ability to:
1.
Stretch and yet maintain
a strong barrier that
prevents diffusion of
urine components.
2.
Change the number of
layers.
3.
Change the shape of
cells.
Outer cells are umbrella
shape.
Mid layers cells are polygonal
in shape.
When stretched, the cells
become squamus in shape
and the number of layers is
decreased.
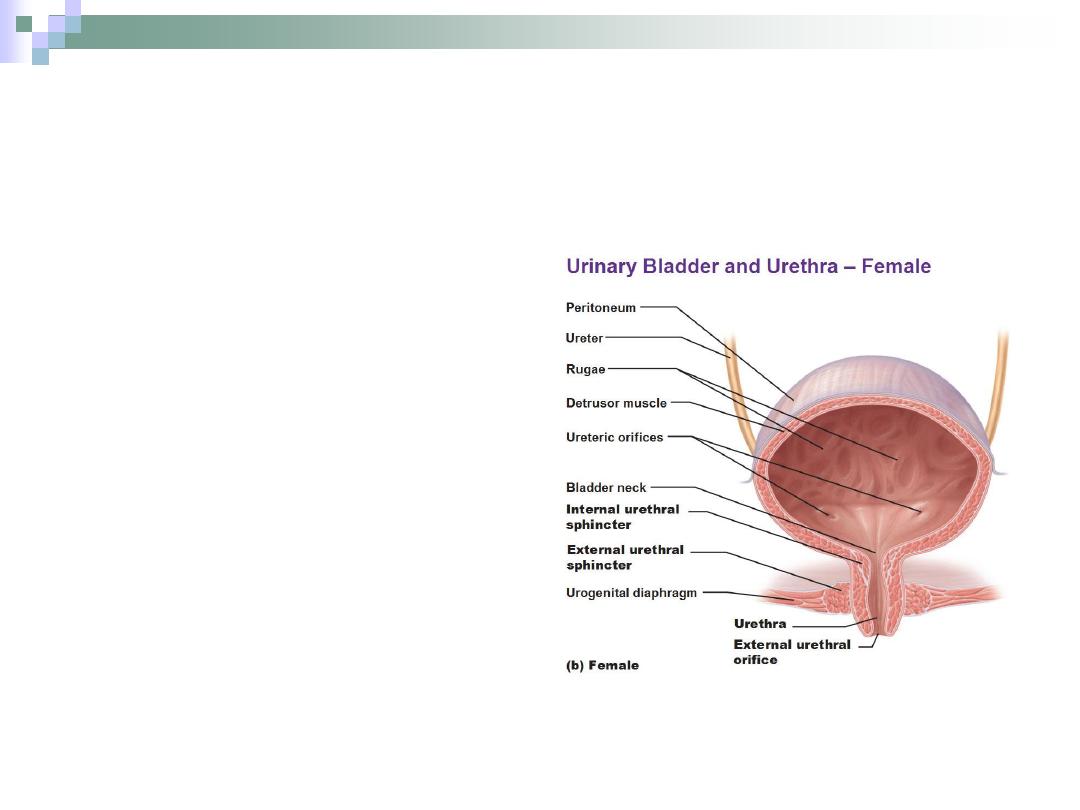
Urethra
The last part of the
urinary system.
It passes from the
bladder to the
exterior.
Composed of:
1.
Mucosa.
2.
Sub mucosa.
3.
Muscular coat.
4.
Adventitia.

Thank You
