د. ساجدة فسلجة 14\2\2018
عدد الاوراق ( 5 ) م\2\موصل lec: 1THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
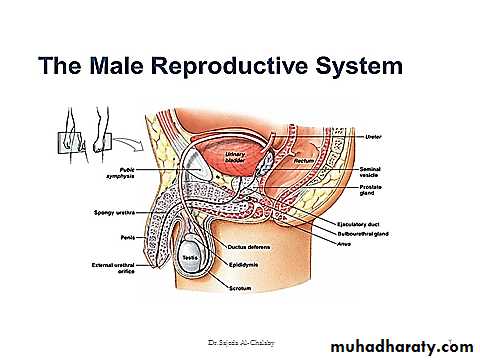
The male reproductive system consist of the paired testis , the reproductive tract & the external genitalia .
ANATOMY
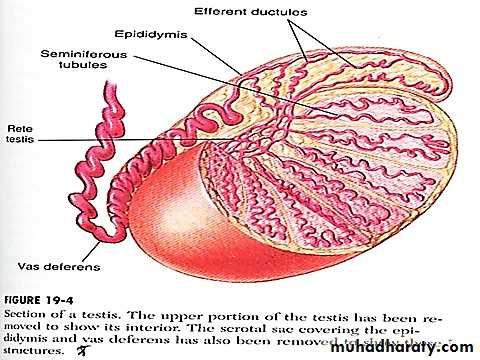
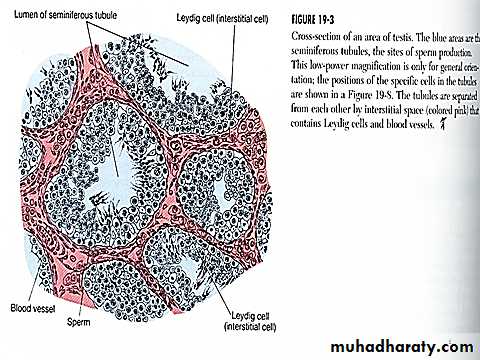
The testis composed of 900 coiled seminiferous tubules each average more than 5 meters length in which the sperms are formed . between the seminiferous tubules are interstitial cells of Leydig for synthesis of testosterone . the sperms pass from the seminiferous tubules to the epididymis which is coiled about 6 meters length this leads to the vas deferens which enlarges into the ampulla before entering into the prostate gland . the seminal vesicles are two , one located on each side of the prostate , empties into the prostatic end of the ampulla & the contents from the ampulla & the seminal vesicles pass into the ejaculatory duct leading to the urethra .The testis serve three main functions :
1 . production of gametes .2 . secretion of hormones that cause differentiation of the brain & reproductive tract during fetal & neonatal development maintain the structure & function of the reproductive tract , promote development of secondary sex characters.
3 . feedback regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary hormone secretion
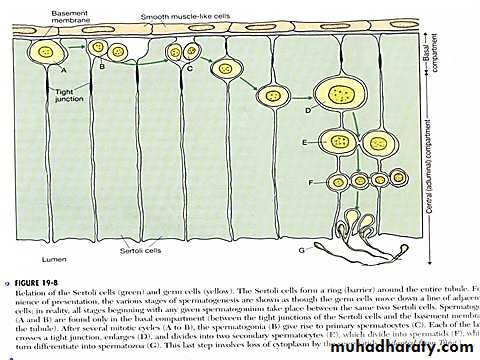
The seminiferous tubules lined with Sertoli cells & spermatogonia , the sertoli cells are linked by tight junctional complexes to form the sertoli cell barrier which limits the movement of fluid & nutrients between the interstitial space of the testis & the lumen of the seminiferous tubules . lipid-soluble substances such as steroids , are able to traverse the barrier & enter the lumen of the seminiferous tubules . the barrier prevent the penetration of the immunoglobulins that might interfere with the development of the spermatozoa .
Sertoli cells have many functions :
provision of nutrients to germ cells .synthesis of multiple proteins that are secreted into the luminal fluid including ceruloplasmin , acidic glycoprotein , & transferring .
synthesis of estrogen .
production of androgen – binding protein ABP .
phagocytosis of damaged germ cells .
synthesis & secretion of inhibin .
secrete during embryonic life (MIS) which causes female duct system to regress.
INHIBIN
Is a protein that selectively inhibits the synthesis & secretion of FSH by the pituitary gonadotropes .Androgen Binding Protein
Is protein that binds androgens . it is found both in the luminal fluid & the plasma . ABP is concentrated in the luminal fluid & in the epididymis & its role is to carry testosterone within the sertoli cells & from the testis to the epididymis inorder to maintain high testosterone concentrations .Estrogen
The principal estrogens in the plasma of adult males are estradiol & estrone . only 10% -20% of the circulating estrogens are synthesized by Sertoli cells in the testis . the remainder originate through the extragonadal conversion of testosterone & androstenedione .Interstitial cells of leydig
The principal function of leydig cells is to produce androgens . Leydig cells begin to secrete androgens during the 7th week of fetal life in response to hCG which is produced by the placenta . during childhood when gonadotropin secretion is low , the Leydig cells regress . when plasma LH levels rise again at puberty , the Leydig cells differentiate again & secrete steroid .Androgen
Androgenic steroid hormones , are the male sex hormones . their functions are :
differentiation of the male reproductive tract & brain during fetal life .
stimulation of the testis descend during the last three months of gestation .
stimulation , maturation & maintenance of reproductive tract .
maintenance of spermatogenesis in adult testis .
negative feedback regulation of LH secretion by the pituitary .
Androgens also stimulate development of male secondary sex characters including :
Growth of facial , chest , axillary & pubic hair as well as hair recession & balding .Hypertrophy of the laryngeal mucosa causing enlargement of the larynx & deeping of the voice .
Development of increased musculature due to increased protein deposition & nitrogen retension .
Enhancement of linear growth through stimulation of bone growth .
Androgens are very potent anabolic hormones that accelerate metabolism .
Increase thickness of skin over the entire body & increase the rate of sebaceous glands results in acne .Increase the total quantity of bone matrix & cause calcium retension ,it causes narrowing of pelvic outlet , & causes funnel- like shape pelvis & increase strength of pelvis for load-bearing .
Testosterone increase RBC count so adult male have 700,000 RBC more than in female .
Testosterone cause sodium reabsorption from kidney tubules .
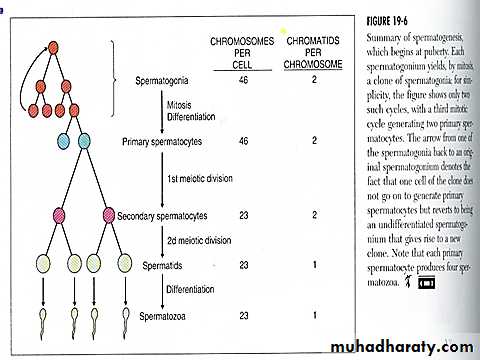
Spermatogenesis
the seminiferous tubules contain large number of germ cells called spermatogonia located in 2-3 layers . in the first stage of spermatogenesis , type A spermatogonia divide four times to form 16 more differentiated cells called type B spermatogonia , at this stage spermatogonia migrate centrally among the Sertoli cells .for a period of 24 days , each spermatogonium that crosses the barrier into the Sertoli cell layer becomes by mitosis a large primary spermatocyte , at the end of the 24 days each primary spermatocyte divide to form two secondary spermatocytes , this division is called the first meiotic division . in this process each of the 46 chromosomes become two chromatids so each secondary spermatocyte have 23 chromosomes.
within 2-3 days a second meiotic division occur in which the two chromatids in each of the 23 chromosomes split apart forming 2 sets of 23 chromosomes , one set passing into one daughter spermatid . the importance of these meiotic divisions is that the eventual sperm that fertilizes the ovum provide one half of the genetic material to the fertilized ovum & the ovum will provide the other half .these stages from spermatogonia to spermatid are androgen independent
during the next few weeks after meiosis each spermatid is nursed & reshaped by its Sertoli cell chang into a sperm by losing some of its cytoplasm , formation of a compact head , formation of a tail , maturation of spermatid to spermatozoa depends on androgen acting on Sertoli cells .
the entire period of spermatogenesis takes 74 days .
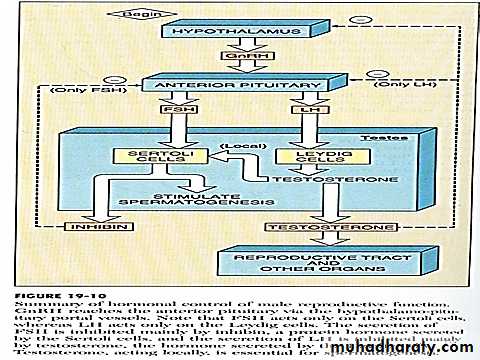
Hormonal factors that stimulate spermatogenesis
LH secreted by anterior pituitary stimulate Leydig cells to secrete testosterone .testosterone secreted by Leydig cells is essential for growth & division of germinal cells in forming sperm
FSH also secreted by the anterior pituitary stimulate secretion of Sertoli cells & without this stimulation spermiogenesis not occur in addition it promotes production of ABP .
estrogens formed by Sertoli cells essential for spermiogenesis , ABP is important for sperm maturation .
GH promotes early division of spermatogonia & its absence results in deficient or absent spermatogenesis .
Prolactin it may potentiate the stimulatory effect of LH on Leydig cells & of testosterone on many of its target cells .
Formation of sperm
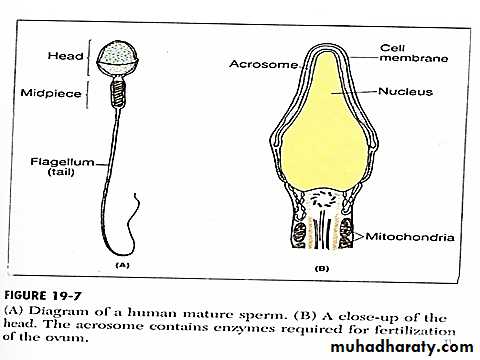
The sperm composed of head & tail , the head composed of condensed nucleus with only a thin cytoplasmic cell membrane layer around its surface . on the outside of the anterior 2/3 of the head is a thick cap called the acrosome , this contains a number of enzymes including hyaluronidase which has a powerfull proteolytic enzymes , these enzymes play important roles in allowing the sperm to fertilize the ovum . the tail of the sperm called flagellum , flagellar movement of the tail provides motility for the sperm , normal sperm moves in a velocity of 1-4 mm/ mint .Acrosome reaction
The acrosome enzymes hyaluronidase & proteolytic enzymes realsed open pathways for passage of sperm head through the zona pellucida withen 30 mints so fertilization occur .Why does only one sperm enter the oocyte ?
only a few sperm get as far as the zona pellucida so that it might be 10 ,20 or 30 mints before second sperm arrives .
within few mints after the first sperm penetrate the zona pellucida Ca+2 diffuses through the oocyte membrane & cause realse of cortical granules that prevent binding of additional sperm .
the oocyte membrane after its fusion with sperm is believed to be elecetrically depolarized .
MATURATION OF SPERM IN EPIDIDYMIS
The sperm after its formation in the seminiferous tubules pass into the epididymis , they remain for 18-24 hours & become capable of motility , although in the epididymal fluid there is an inhibitory proteins which prevent sperm motility until after ejaculation . after ejaculation the sperm become motile & capable of fertilizing the ovum , this process called maturation . from Sertoli cells & epididymis there a fluid ejaculated with the sperm contains estrogens & testosterone this is essential for maturation . the adult testis forms about 120 million /day sperms , small quantity of them are stored in the epididymis while large quantity stored in vas deferens .Capacitation of spermatozoa
Several changes believed to occur that activate the sperm for final process of fertilization , these changes are :the uterine & fallopian tube fluids wash away the inhibitory factors that suppress sperm motility .
the sperm deposited in female genital tract loses much cholesterol so the membrane at the head of sperm become weak .
the membrane of sperm head becomes more permeable to Ca+2 & Ca+2 enters the sperm giving it powerfull motion , without capacitation the sperm can not fertilize the ovum .
The mature sperm is capable of movement in a straight line , its activity increase with increasing temperature , also increase in neutral & alkaline medium & decrease in acidic medium . average PH of semen is 7.5 the sperm remain in the female genital tract for 1-2 days .
Semen
The fluid that ejaculated at the time of orgasm contains sperms & secretion of seminal vesicles , prostate & cowpers gland . normal semen volume 2.5-5 ml . sperm count 20 million /ml . activity 50% progressive movement . 60 % normal sperms .
Function of the prostate gland
The prostate gland secrets thin milky fluid (30 % of total volume ) contains citrate ion , calcium ion , phosphate ion , clotting enzymes & fibrinolysin . prostatic fluid is alkaline & helps to neutralize the acidity of the vaginal secretion & of the vas defernsFunction of the seminal vesicles
The secretion of seminal vesicles form 60 % of total volume , is mucoid contain fructose , citric acid , & other nutrients , also prostaglandins & fibrinogen . prostaglandins are believed to aid fertilization by :by reacting with cervical mucus making it more receptive to sperm movement .
causing reverse peristalitic contraction of uterus & fallopian tubes to move the sperm towared the ovaries .