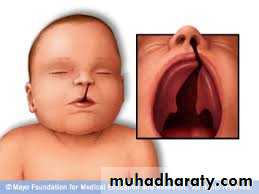
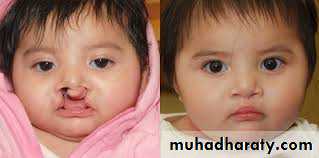
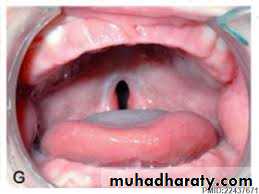
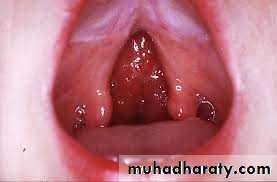
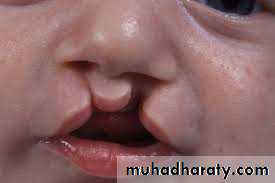
CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
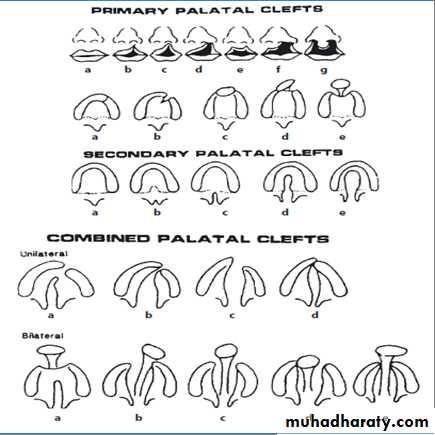
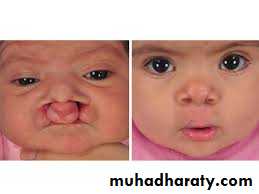
Clefting is deformity, in fusion of mid face skeleton with soft tissue, occurs in second month of pregnancy.Veau Classification - 1931
Veau Class I: isolated soft palate cleftVeau Class II: isolated hard and soft palate
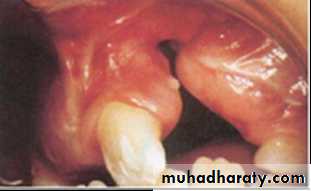
Veau Class III: unilateral CLAP
Veau Class IV: bilateral CLAP
ETIOLOGY
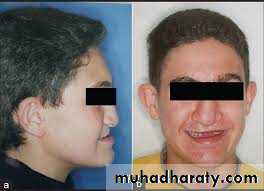
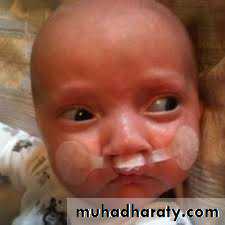
Clinical features of cleft patient
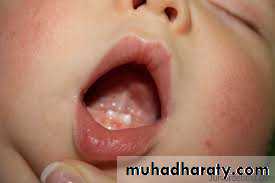
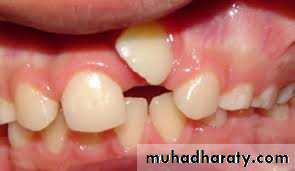
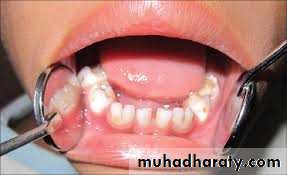
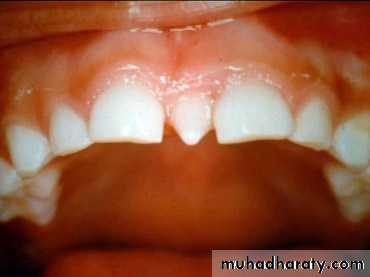
Natal or neonatal teeth.Congenitally missing teeth.Supernumerary teeth.Ectopic eruption of teeth.Anomalies in tooth morphology.Decreased periodontal support to permanent teeth erupting adjacent to cleft site.Protuberant and mobile premaxilla.
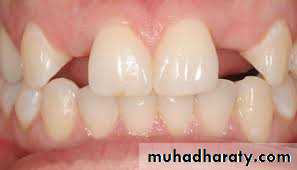
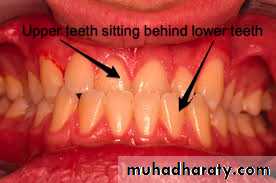
Anterior and posterior crossbite.Deficient maxilla
Presurgical infant orthopaedics
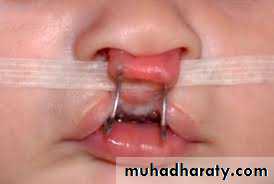
Taping– Effective in reducing the width of the cleft in a
nonsurgical manner
– Strip of hypoallergenic tape is placed with
tension across the cleft and secured to the
patient’s cheek
– Molds bony tissues by applying pressure to
protruding portions of the maxilla
– Must be worn 24 hours per day
Sometimes presurgical steps must be taken to improve surgical outcomes. When Series of plates to actively mould the alveolar segments into the desired position.
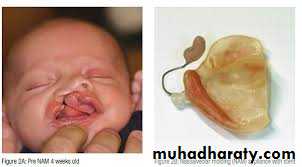
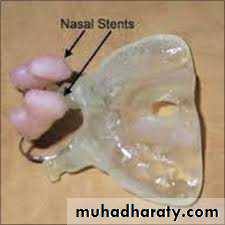
The nasoalveolar moulding appliance (NAM)
It consists of an intraoral moulding plate with nasal stents to mould the alveolar ridge and nasal cartilage concurrently. The objective of the presurgical NAM is to reduce the severity of the original cleft deformity and thereby enable the surgeon to achieve better repair of the alveolus, lip and nose. Use of the NAM technique has also eliminated surgical columella reconstruction and the resultant scar tissue in bilateral cleft lip and palate.Orthodontic treatment
deciduous dentitionTreat with expansion together with protraction headgear to develop the maxilla.
Mixed dentition
Timing of treatment closely related to timing of planed bone graft.. either before lateral incisor erupts (argued can effect maxillary growth), or before canine erupts.When root of canine 1/3 to ½ developed.
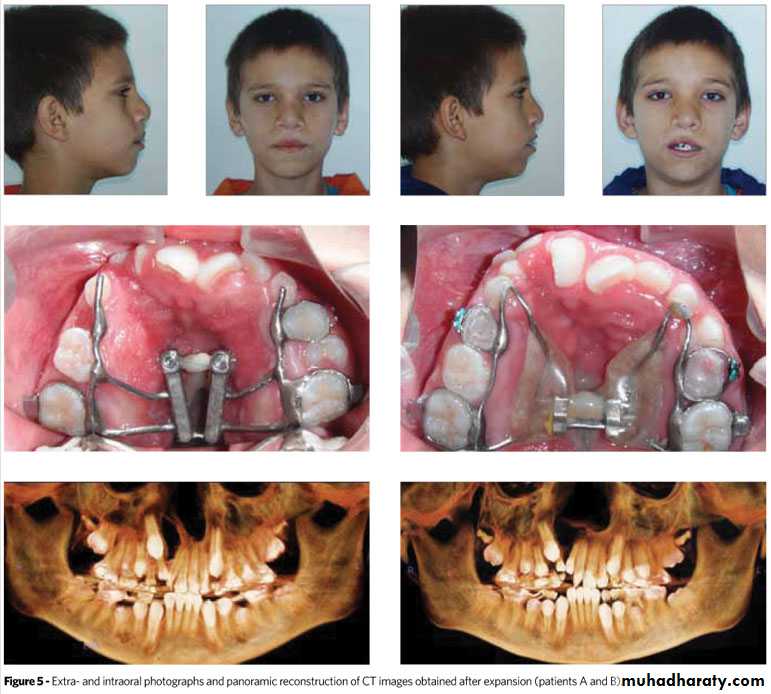
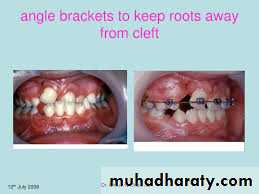
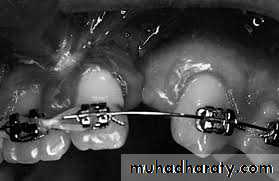
Orthodontic treatment involves expansion to develop favourable arch form, alignment ..care not to move roots into cleft defect.. correct root angulations' post grafting.
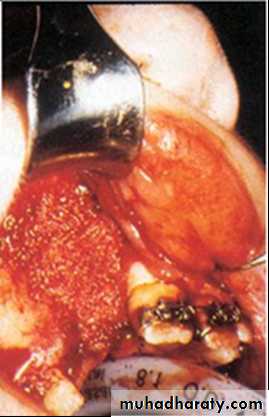
Alveolar bone grafting (ABG)
Provides continuity of alveolar ridge.Provides bone for canine to erupt.
Osseous support for adjacent teeth.
Majority of canines erupt spontaneously…others require surgical exposure often in combination with orthodontics.
The erupting teeth often appear to then stimulate the formation of new alveolar bone.
Permanent dentition
• Tooth movement to arrange the occlusion: Management of arches. Correction of individual tooth irregularity.Closure of spaces wherever possible.Planned space maintenance in areas of missing teeth for prosthetic replacement.
• Surgical orthodontics.
Greater chance of relapse in CLP patients because of the Surgical scar. Usually require a long term and mainly permanent retention.