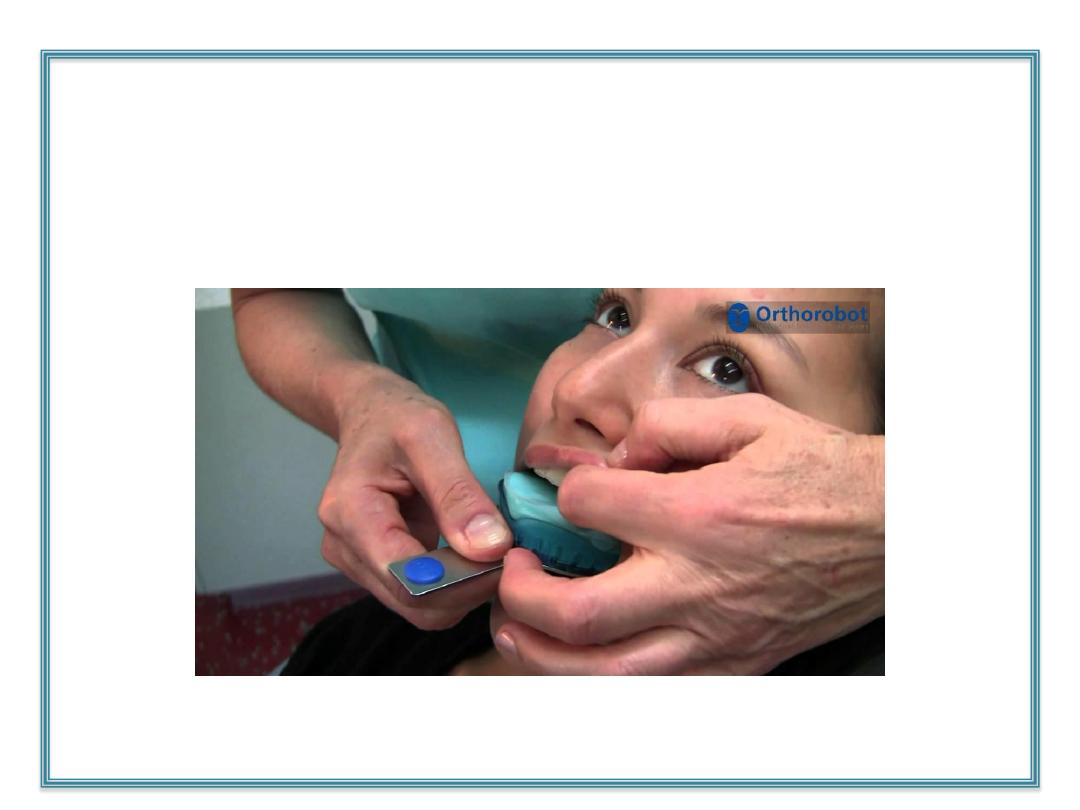
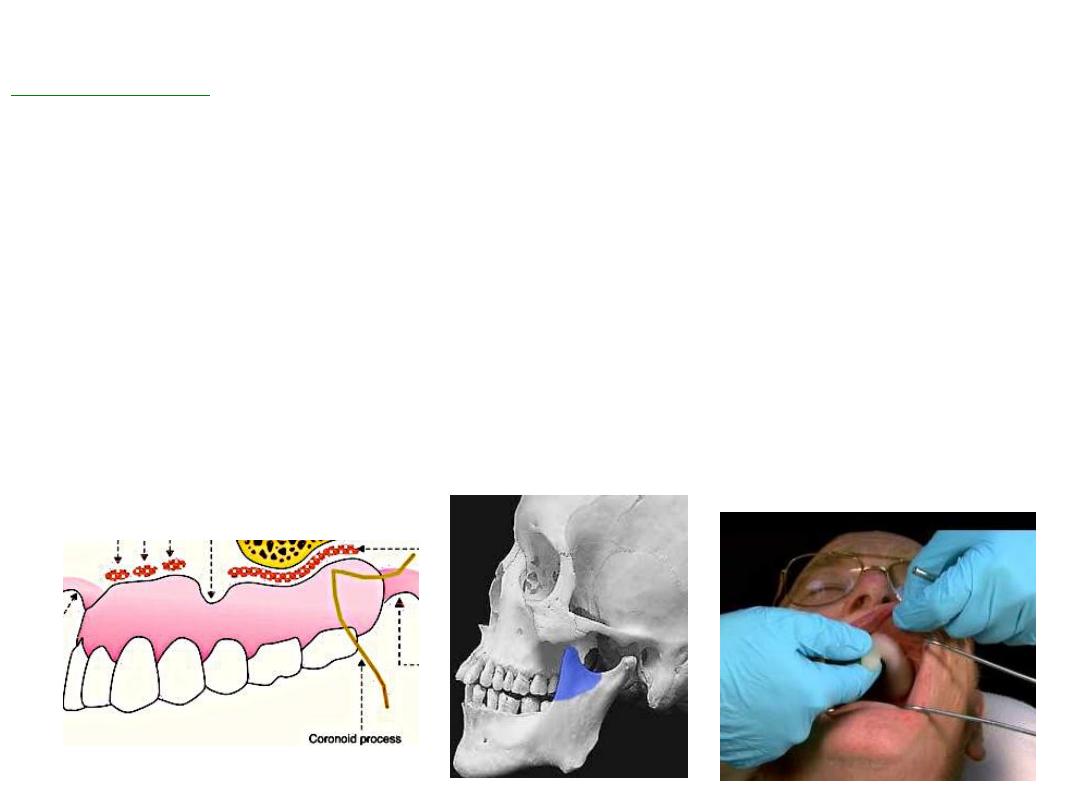
Impression of complete denture

Complete Denture Impressions
An
impression
: Record –ve form of tissue of oral cavity that make
up basal seal of denture.
•Most important step in complete denture
•Primary impression ….diagnostic ….tray
•Final impression…..final detail….master cast.

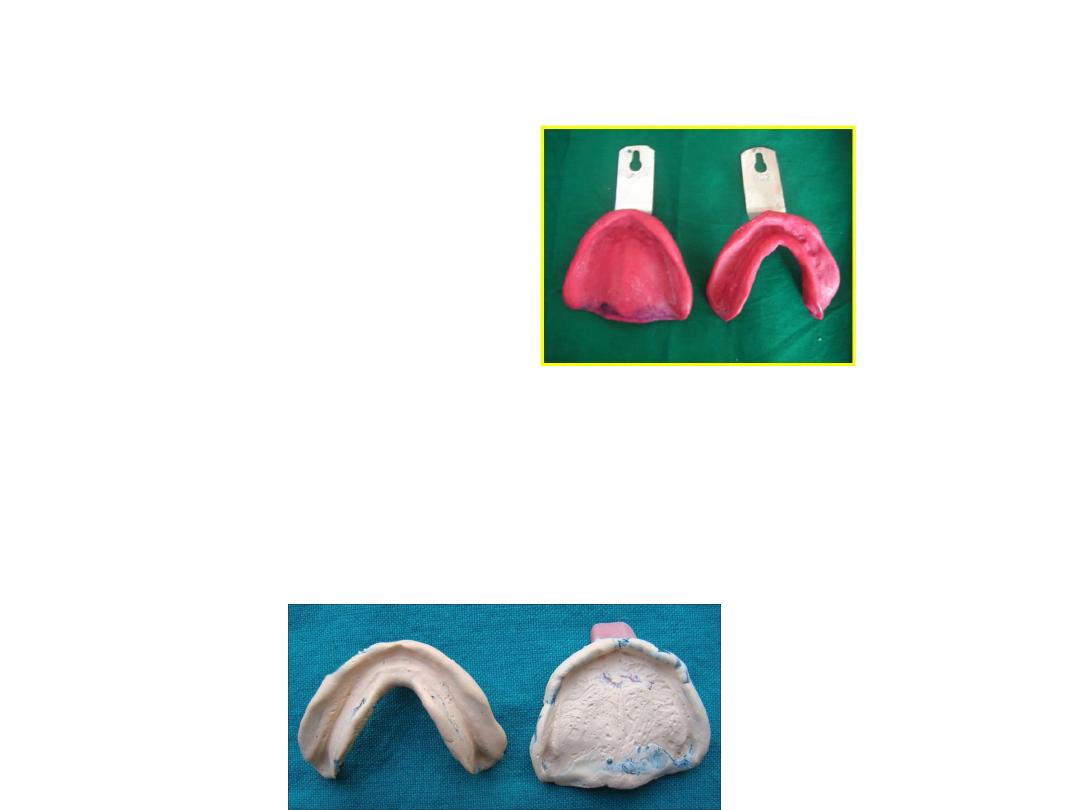
• Primary impression
: an impression of the edentulous mouth
which is made for purpose of producing a diagnostic cast upon
which custom tray will be fabricated.
• Final impression
: final detain…used for construction of master
cast ….upon which denture fabricated.
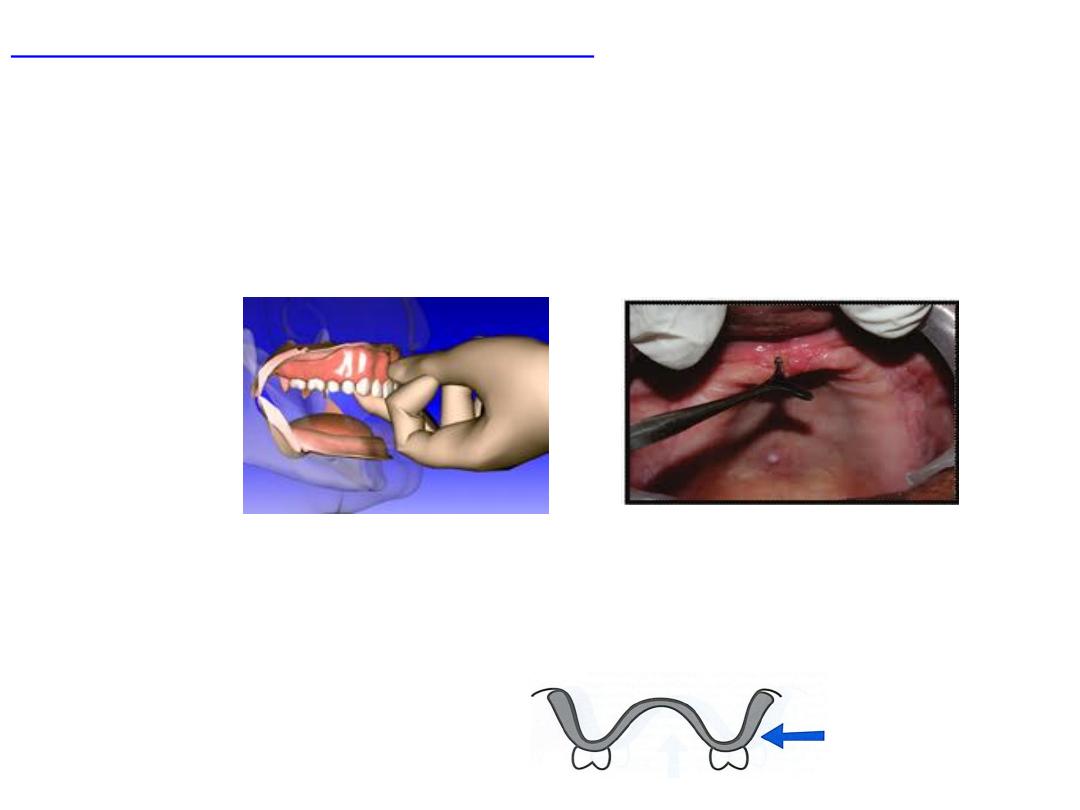
Objectives of C.D impression:
•Retention
: resist removal in direction opposite direction of its
insertion.
•What will happen to movable soft ridge…..in impression? Effect on
retention.
•Stability
: resist horizontal movement (quality final impression, flow
ability )…lack stability….gross soft tissue …bone change…
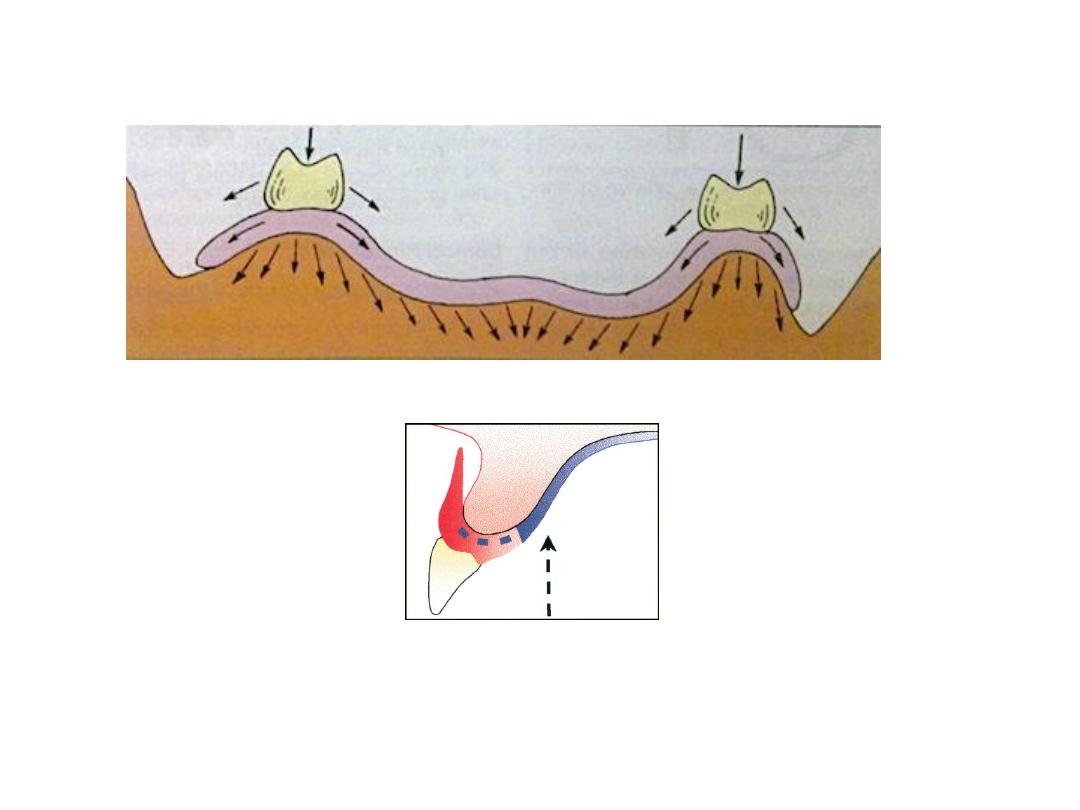
• Support
: vertical…basal seat…. Snow shoe.
• Esthetic
: good impression…good esthetic (border thickness ..lip
facial contour).
• Preservation of the residual ridge
: occlusion..interocclusal
distance…centric relation…impression technique…impression
materials.

Classification
1-
dep.on theories of imp
A. passive-minimal
B. functional-pressure
C. selective pressure
2-
dep.on the position of the mouth while making the impression
A. open mouth
B. closed mouth
3-
dep.on the tray type
A.stock tray
B. custom tray
1.close fit
2.spaced
4-
dep.on the manipulation for border molding
Hand manipulation
Functional movement
Theories of impression:
The
forces
directed to the tissue during impression is directly
influenced by:
• The
viscosity
and
flow
of the impression material used.
• Type of impression
tray
made
• Force
extended upon the tray when the impression is being
made.
Passive or Mucostatic
• use oversized tray
• record tissue at rest and jaws in normal relaxed condition
• no border mold
• Retention is achieved through accurate tissue adaptation.(poor retention stability)
• poor peripheral seal
• short denture flange so less resistance to lat. forces
Advantages
:
Health and preservation of the tissue
Disadvantages
• Reduce coverage ….poor stress distribution
• Short flange…. irritation of tongue less lateral stability
• Lack border molding …..space….Food beneath the denture
• Flowable material used
Pressure or Functional
Under pressure resemble under mastication
Heavy material like impression compound used
•use close fit tray
•imp.comp …special tray with occlusion rim
•record tissue at pressure
•Close mouth technique
•border are molded
•Good peripheral seal
•Better retention and support
•rapid R.R resorption
•Tissue ischemia
•Pressure on sharp spiny ridge
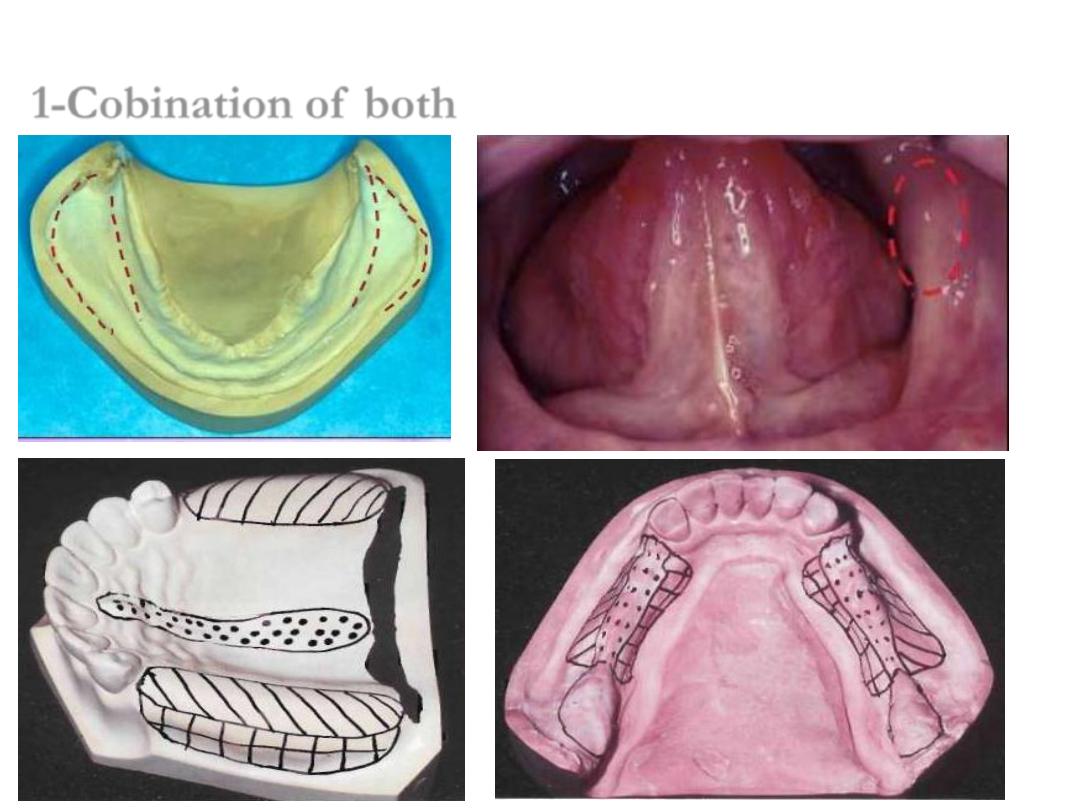
Selective pressure:
Combines both pressure non pressure techniques.
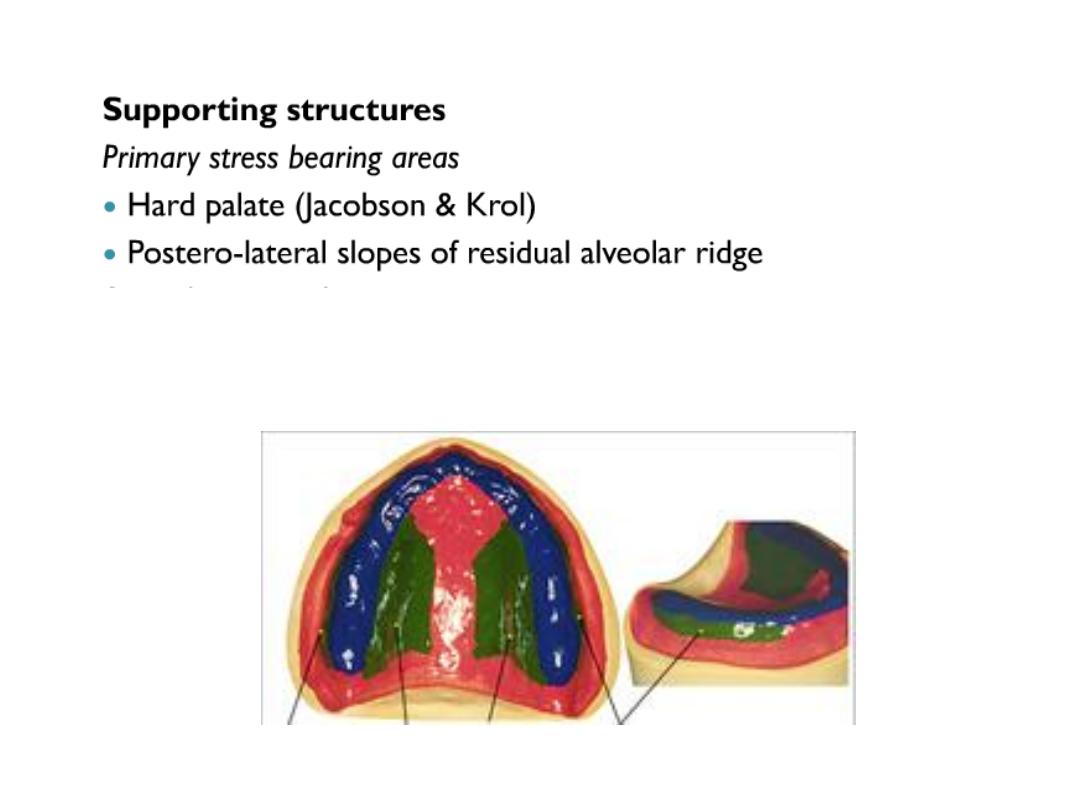
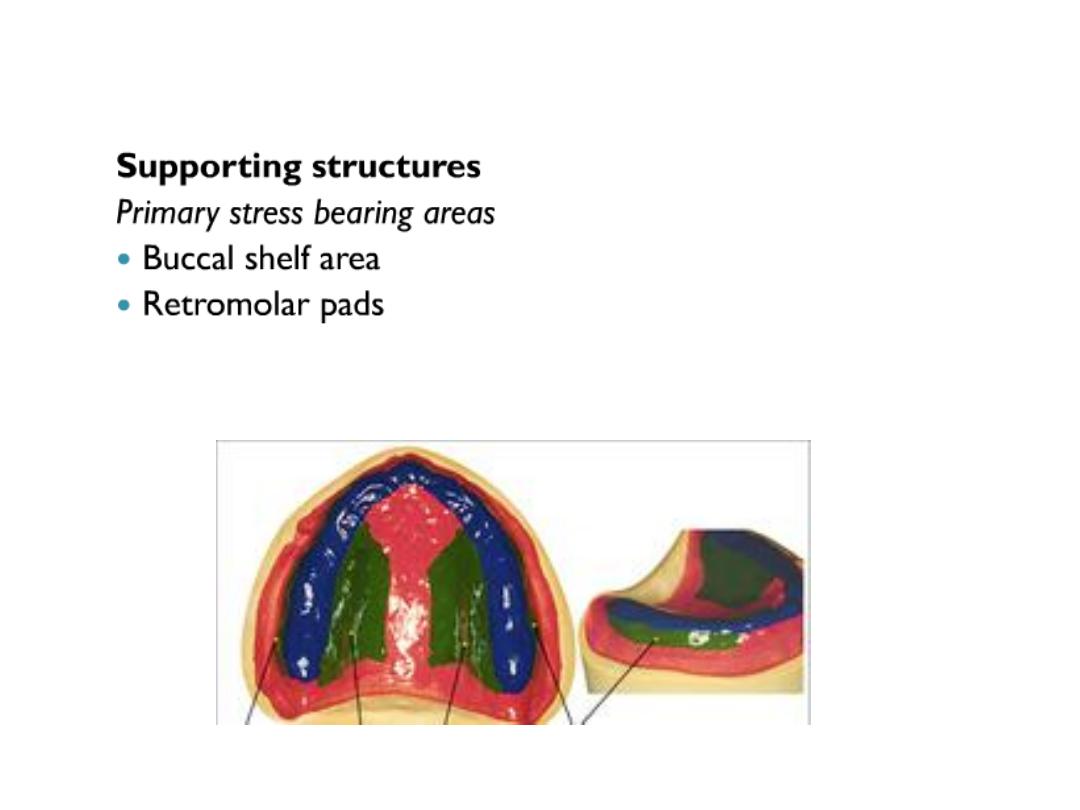
Basal seal area are divided into
•Primary stress bearing area
•Secondary stress bearing area
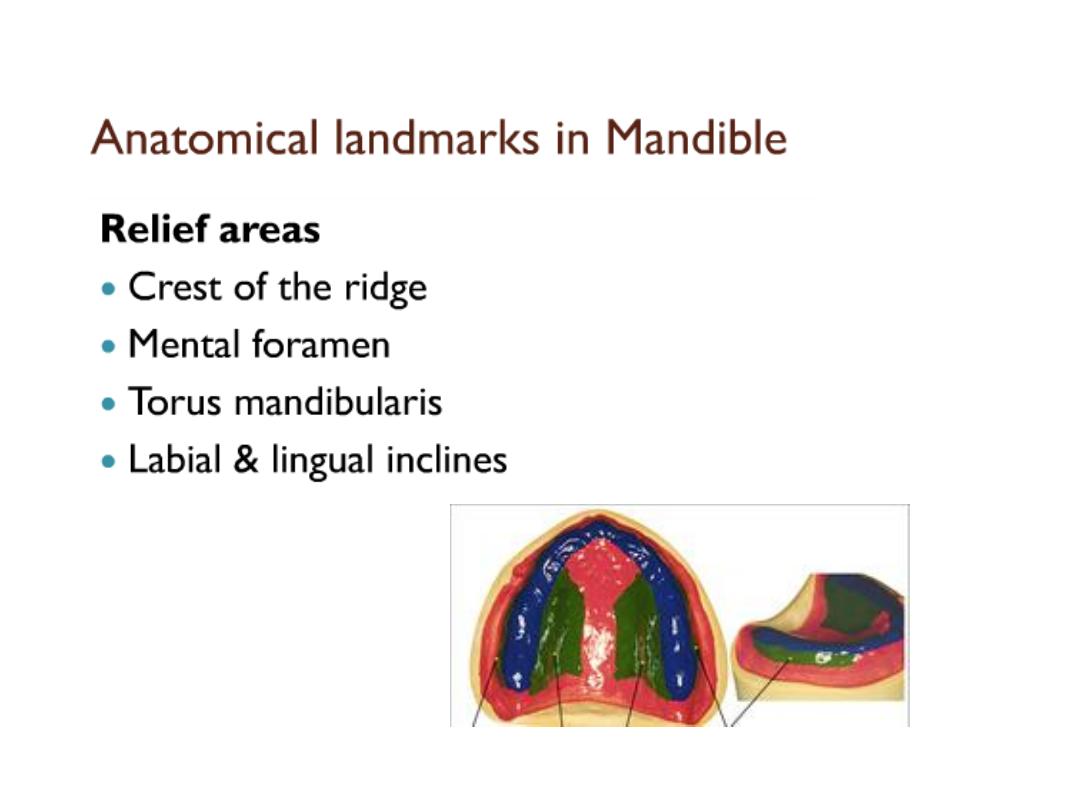
•Relief area
This is achieved by design of sp.tray in which non stress bearing area are relieved and
stress on stress bearing area.
Advantages
Physiological function of tissue of basal seats
Disadvantages
:
Some recorded impossible to record area with varying pressure.
Excess pressure …bone lose
Selective Pressure
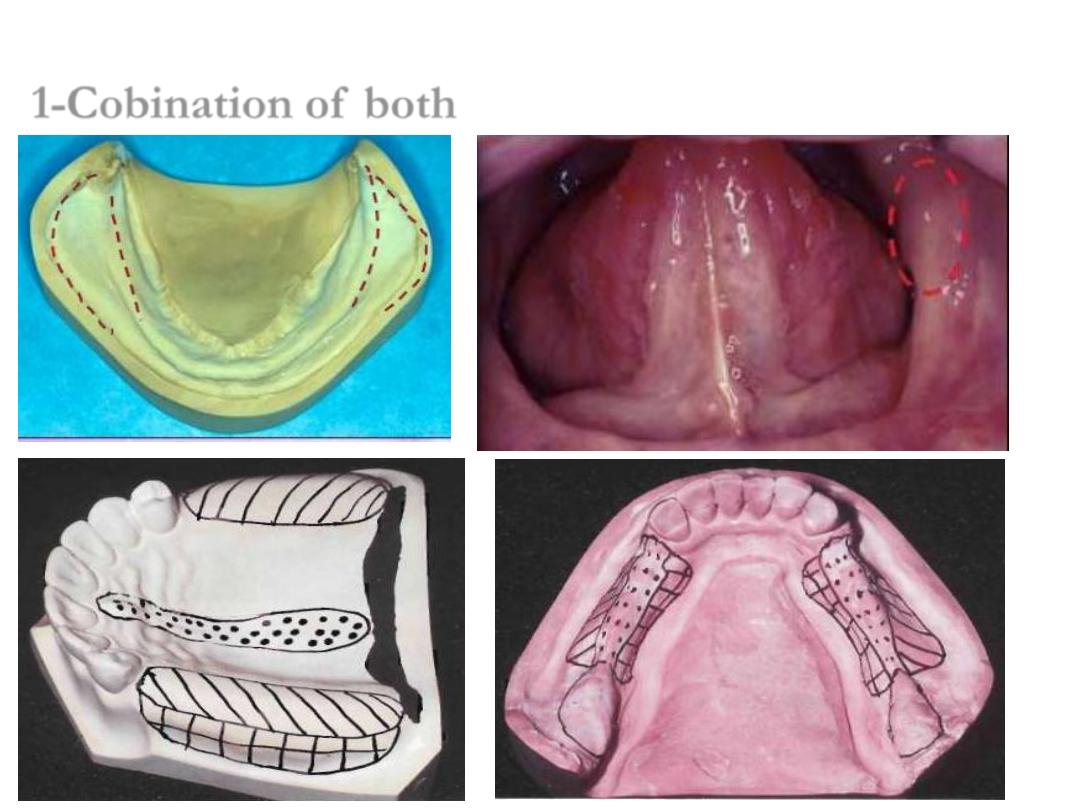
1-Cobination of both

Open mouth:
•Imp. Tray held by
dentist
while pt. mouth is open
•Limit tissue
recorded ,……when mouth open limit the extend of imp. Material ….
peripheral border.
•Allows better
observation
of the tray position and flow of material while lip cheeks
are border molded.
•Muscle movement
easier
•When mand. Literally or protruded …there will b e
clearance
between ramus and
mand. For good record.
Closed mouth:
•When mouth closed
tissue more relaxed
…good extension of material to recorded.
•Tongue
confined …cannot move …
material flow
to recorded
mylohyoid
ridge easier
•Occlusal rim
on tray to allow pt. to close on it.
•Pt. will do borer molding by (closing sucking grimcing swallowing)..
active molding
•Pressure by pt. during record….will be transmitted to denture …so once stress
release
tissue will rebound
this will effect denture seal
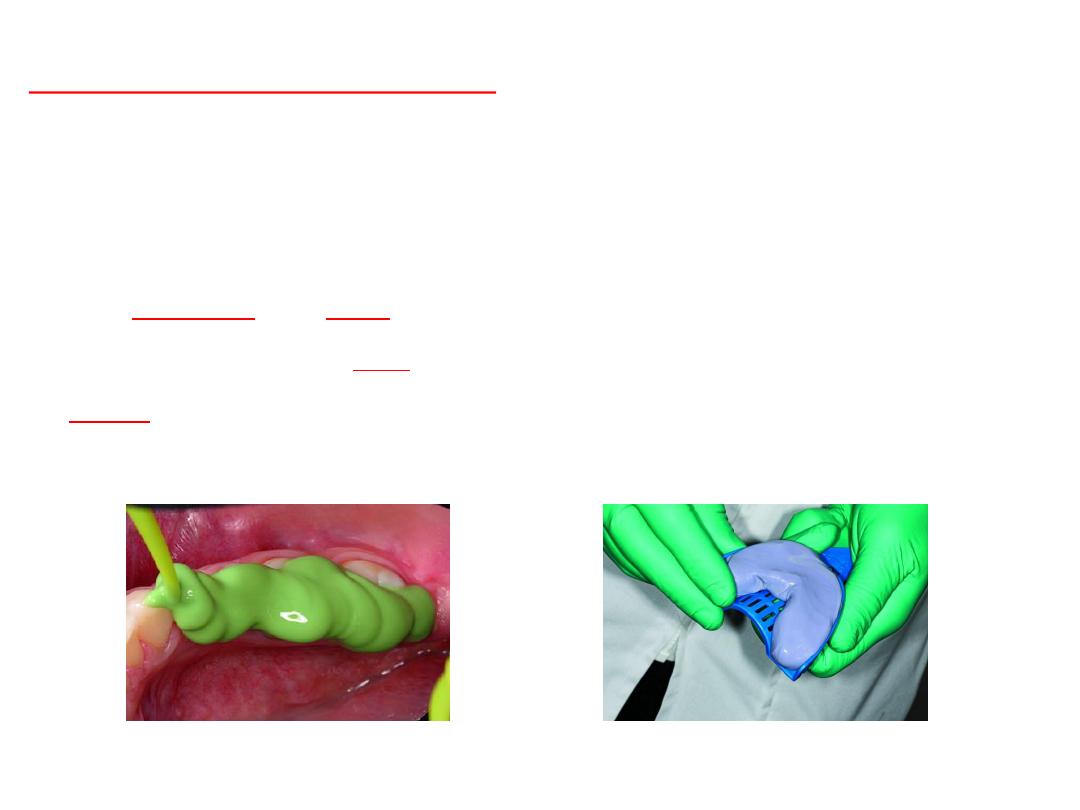
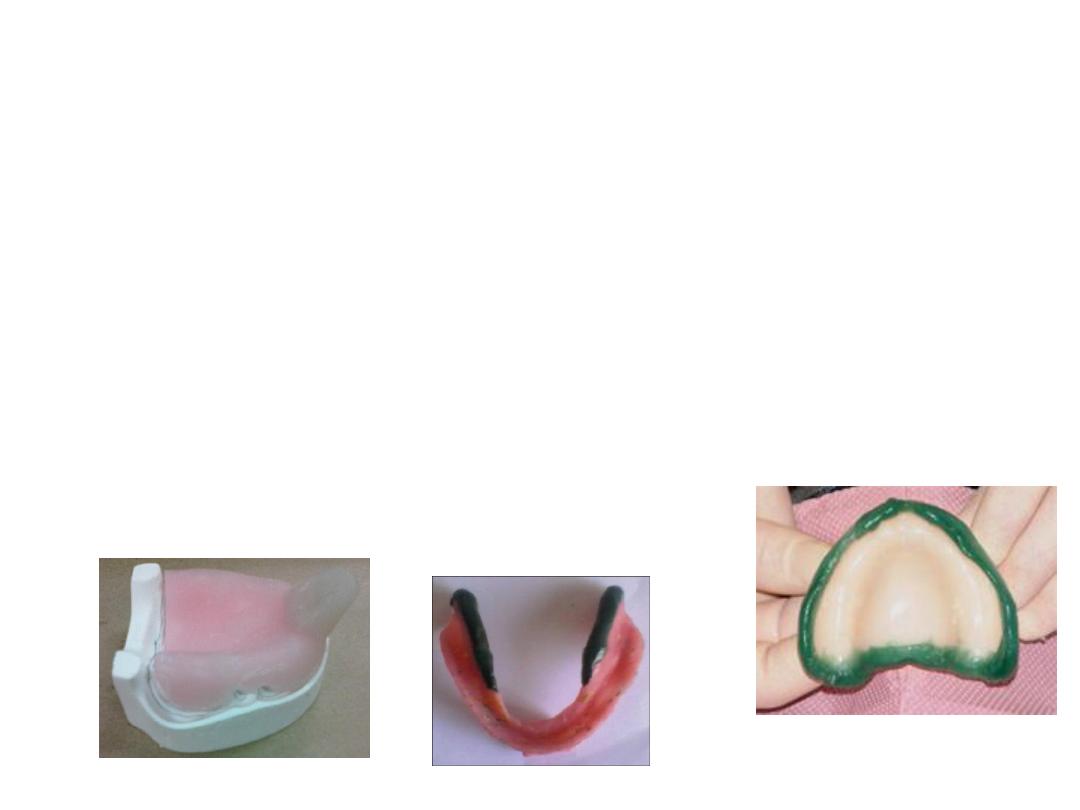
Primary imp.
•Alginate
…perforated tray
•Compound
….plain tray
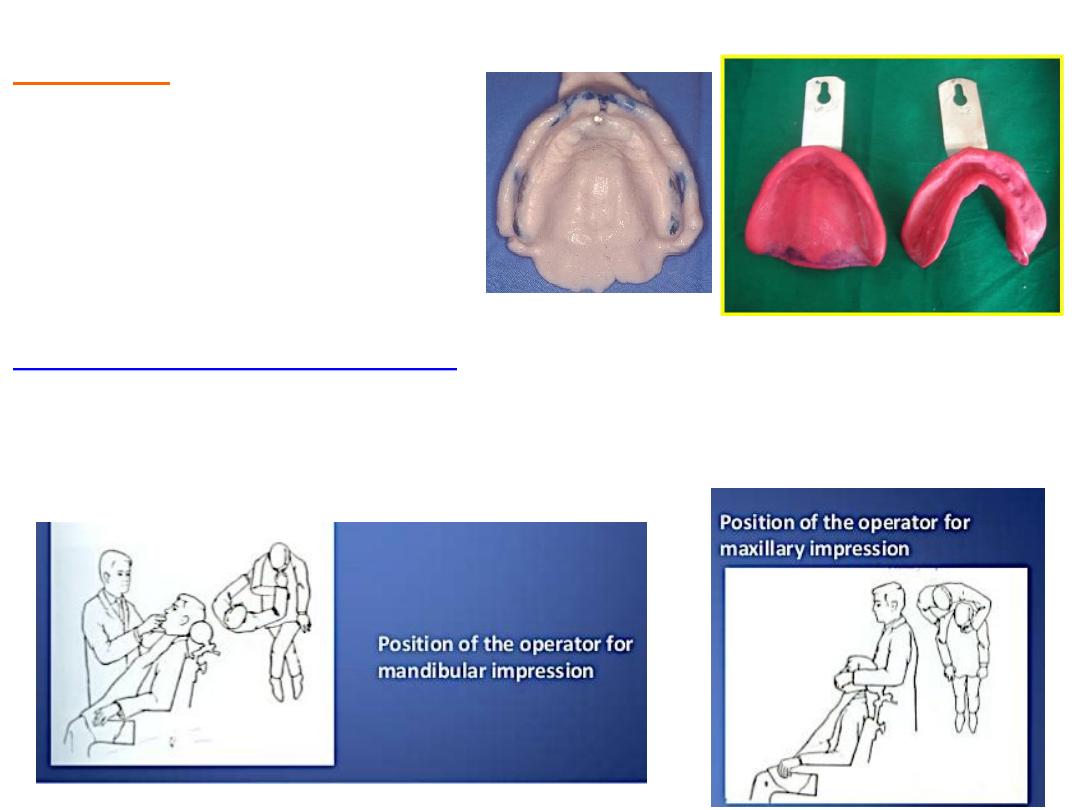
Position of dental chair….
•Lower…pt. mouth with level of operator shoulder….dentist in front right side
•Upper…pt. mouth with level of operator elbow…chair tilted back little. dentist right
little behind.
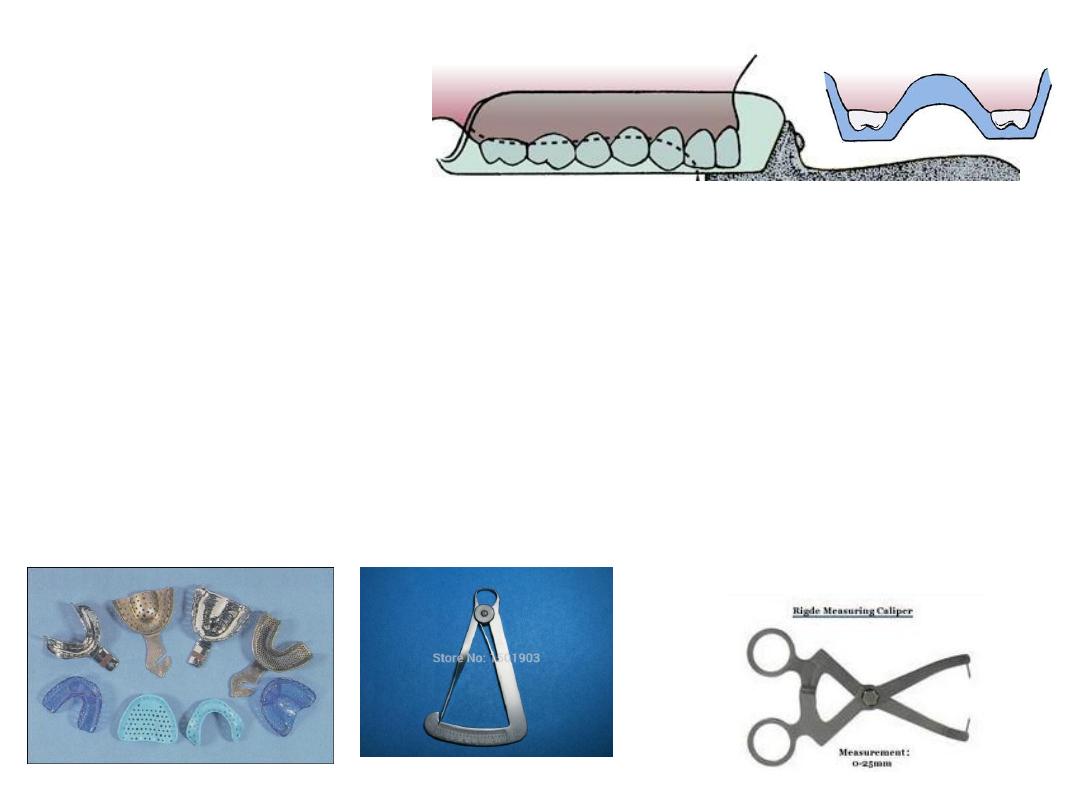
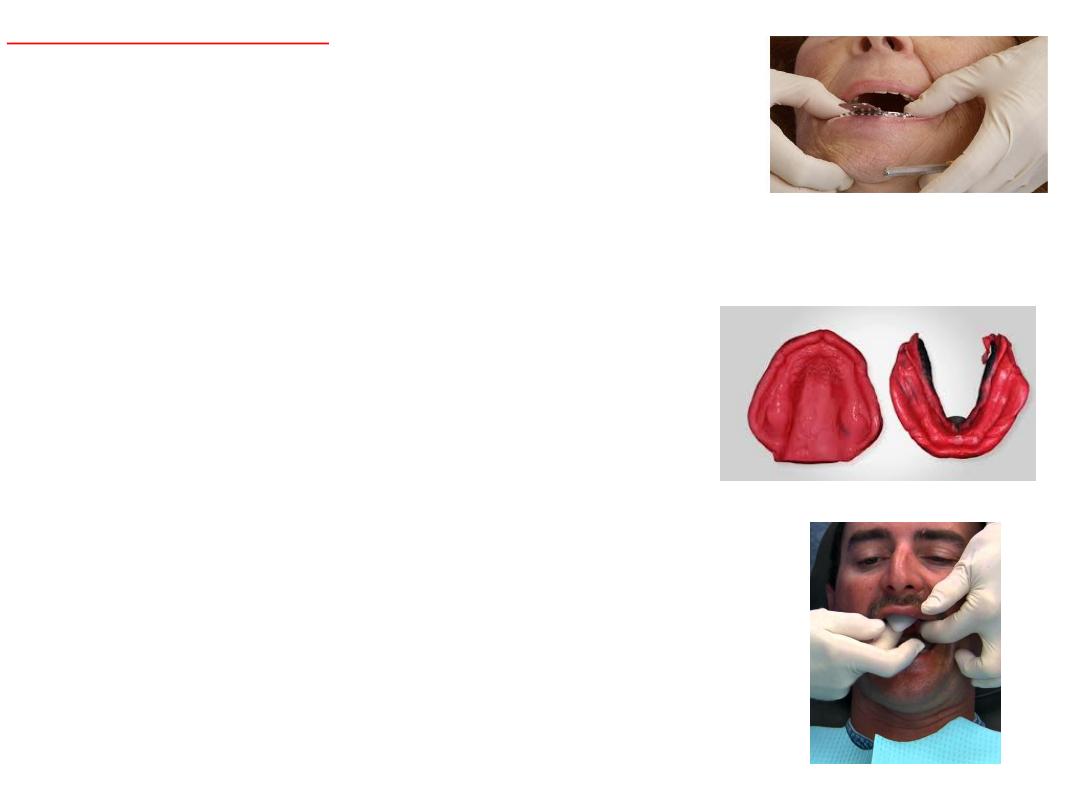
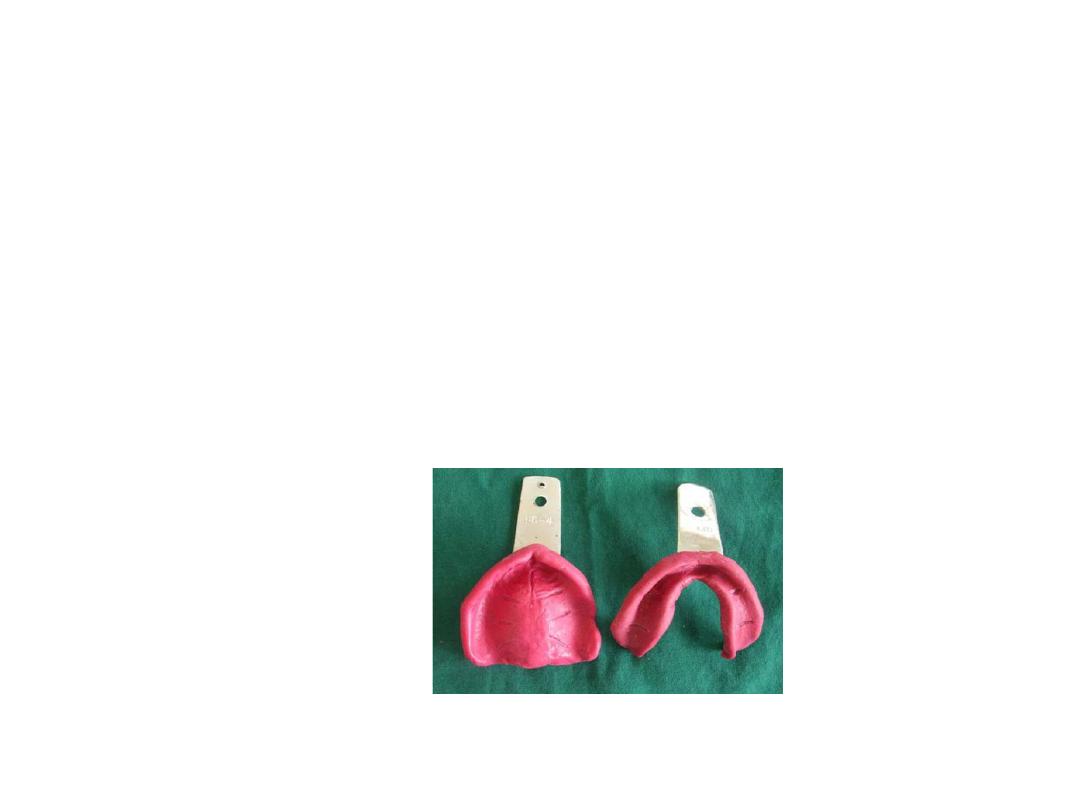
Selection of stock tray:
• Oversize providing
3mm space
flange should not impinge on frenal.
Selection of lower tray:
• Calipers
to measure arch width .(for lower tip of caliper on lingual
aspect of ridge right left below retromolar pads.
• Pt. asked to rise tongue to check
tongue space.
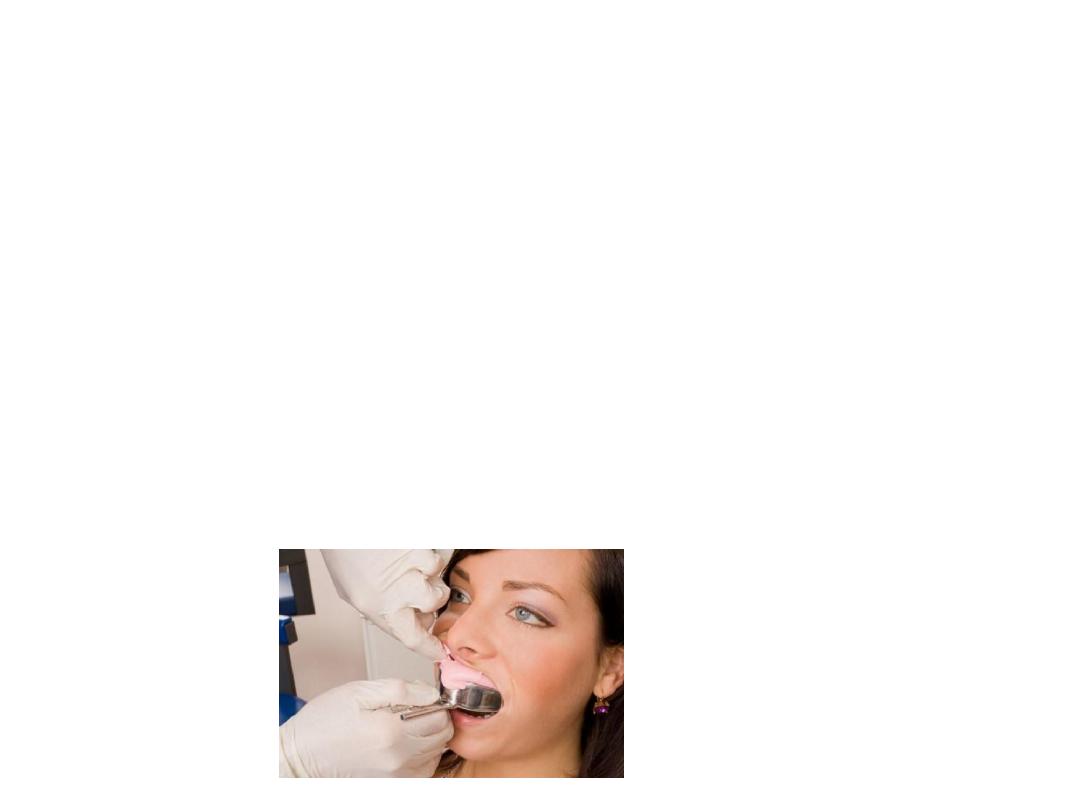
Selection of the upper tray:
•Tip of caliper on buccal vestibule in tuberosity region….then on tray.
•2-3 mm space for material
Sequence of making impression :
upper
or
lower?
•Discomfort…anaxiety…reflex.
•Salivation when foreign body in mouth ….activation

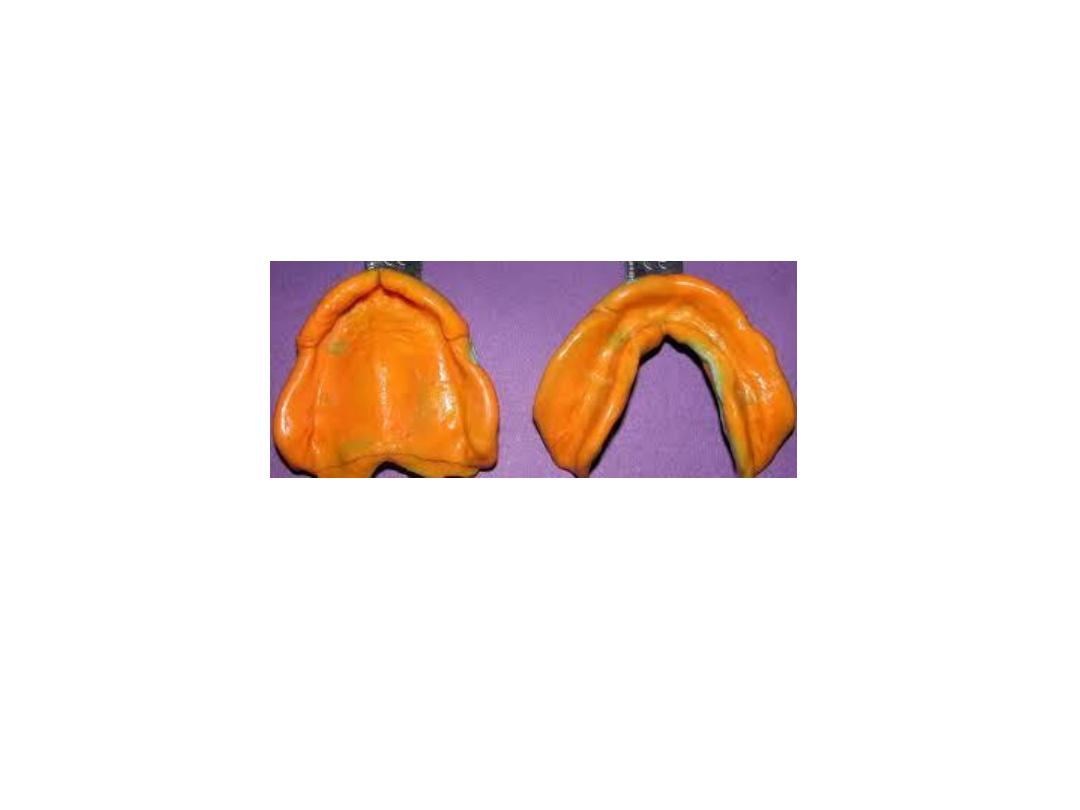
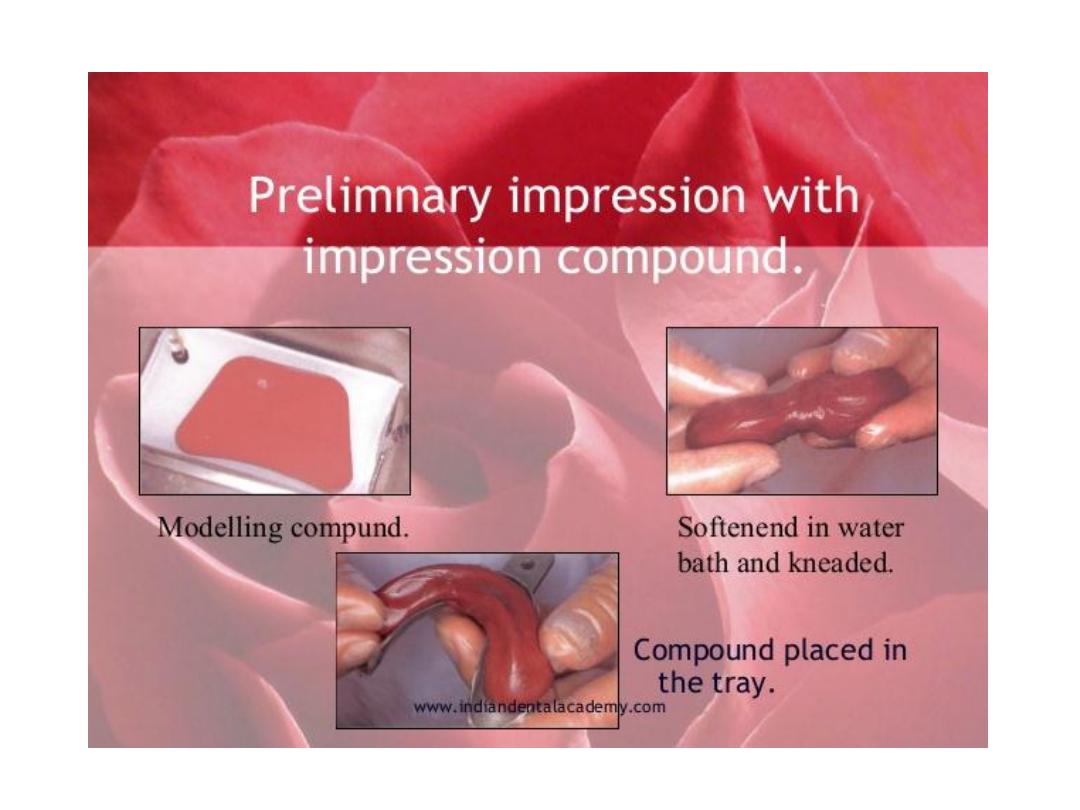
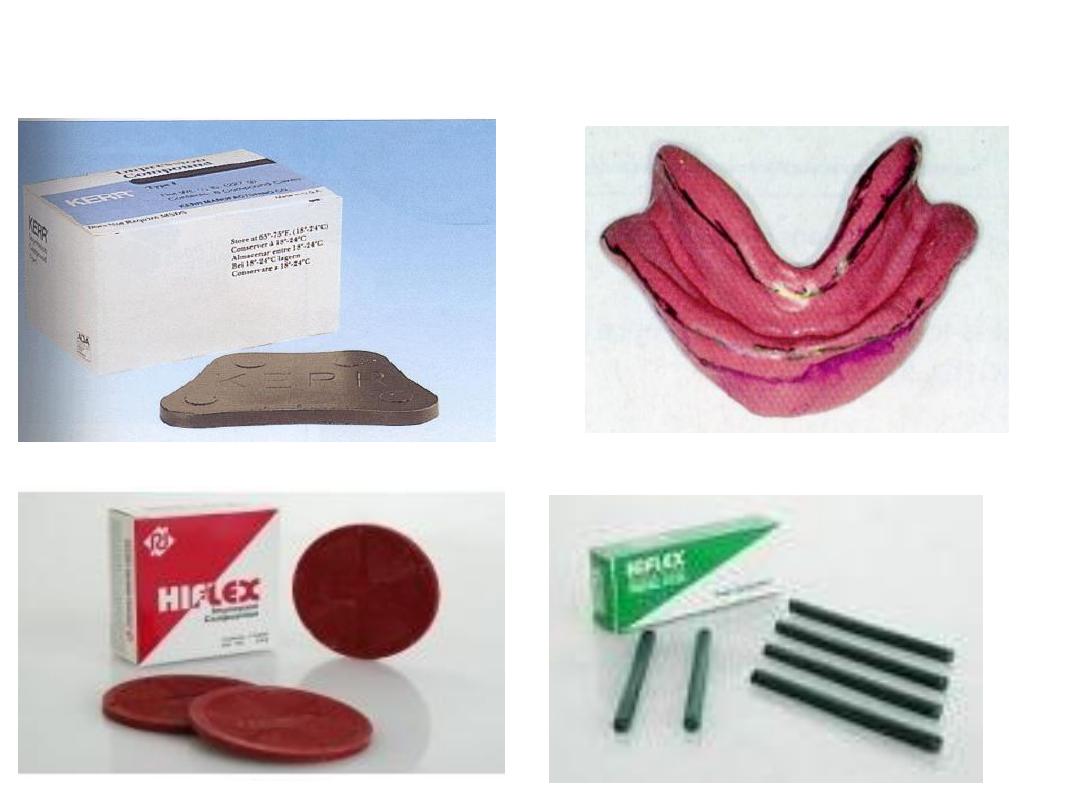
Primary imp….compound:
adv.
Cost
.
easy
use…dimensional
stability
…….
disadv
.
viscosity
…
displace
tissue
. Not accurate
.
Soften
in water bath …kneaded
rolled
into ball on tray using tumb…spread adapt over
tray …approximate ridge contour.
Center
the tray using labial frenum as guide.
Apply pressure on molar
region then hold by finger
border molder
moving lips
cheeks…poured with plaster within 30 min

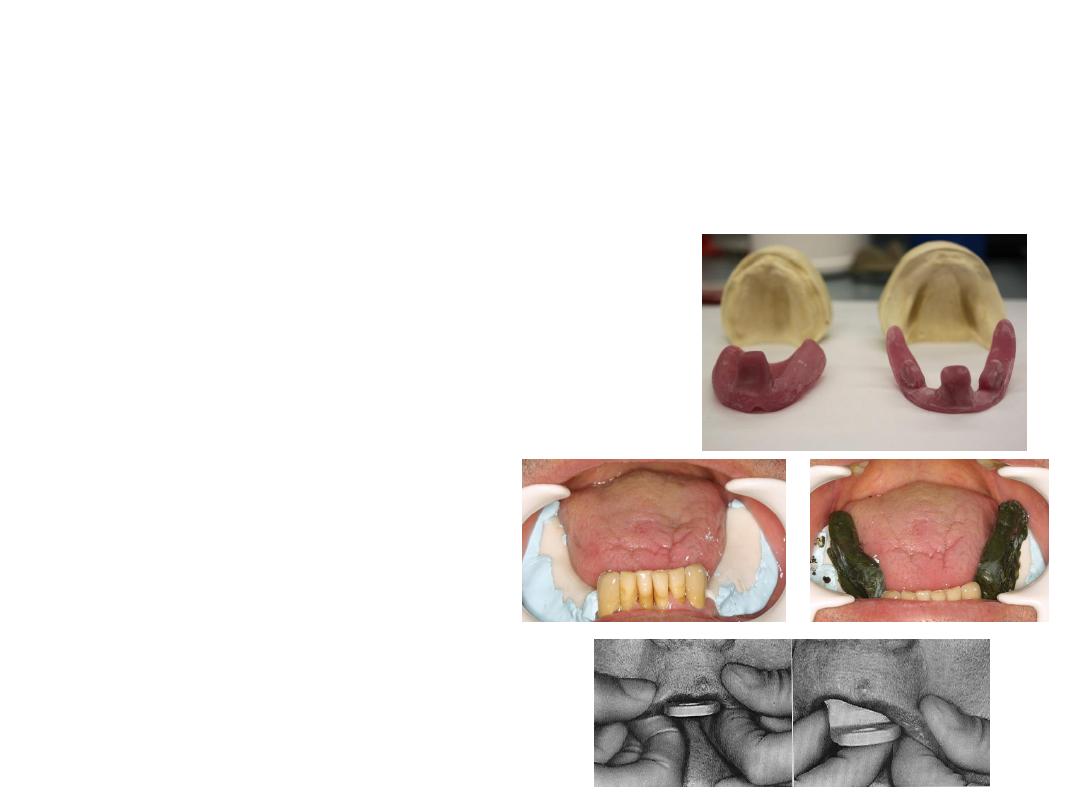
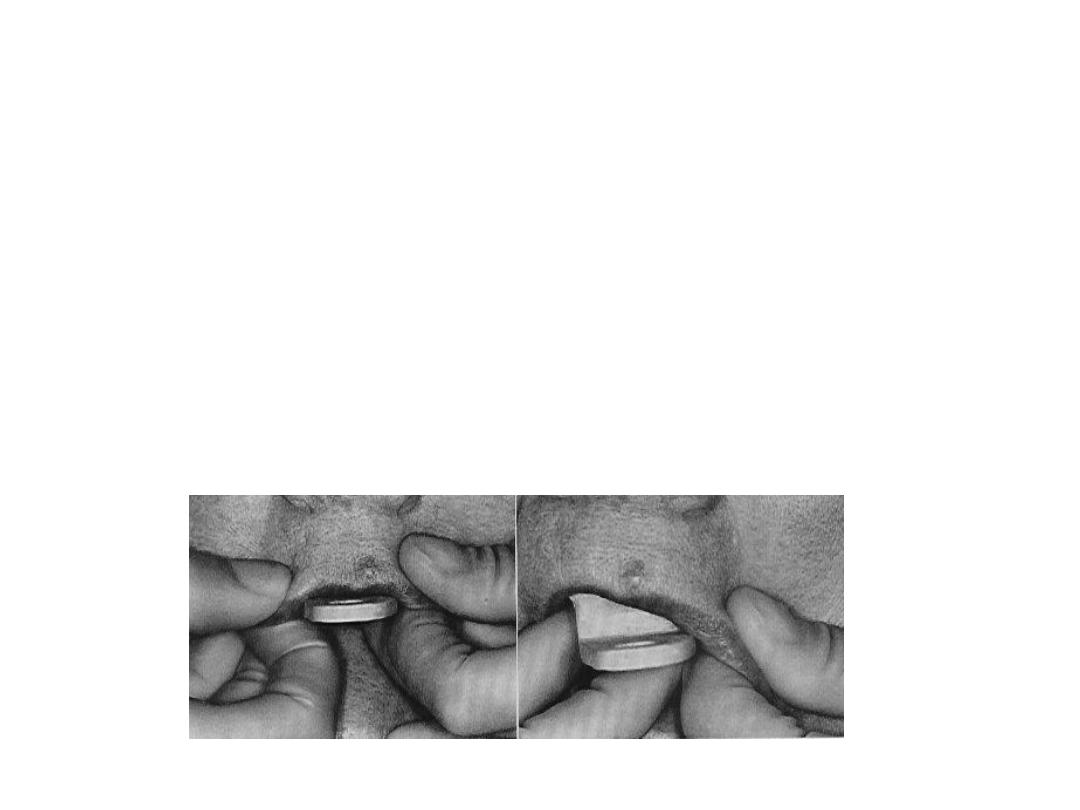
Mandibular imp.
•Same principle as maxillary imp. material rolled and rope shape
placed on tray …during border molding tongue moved for lingual
borders.
Final imp.
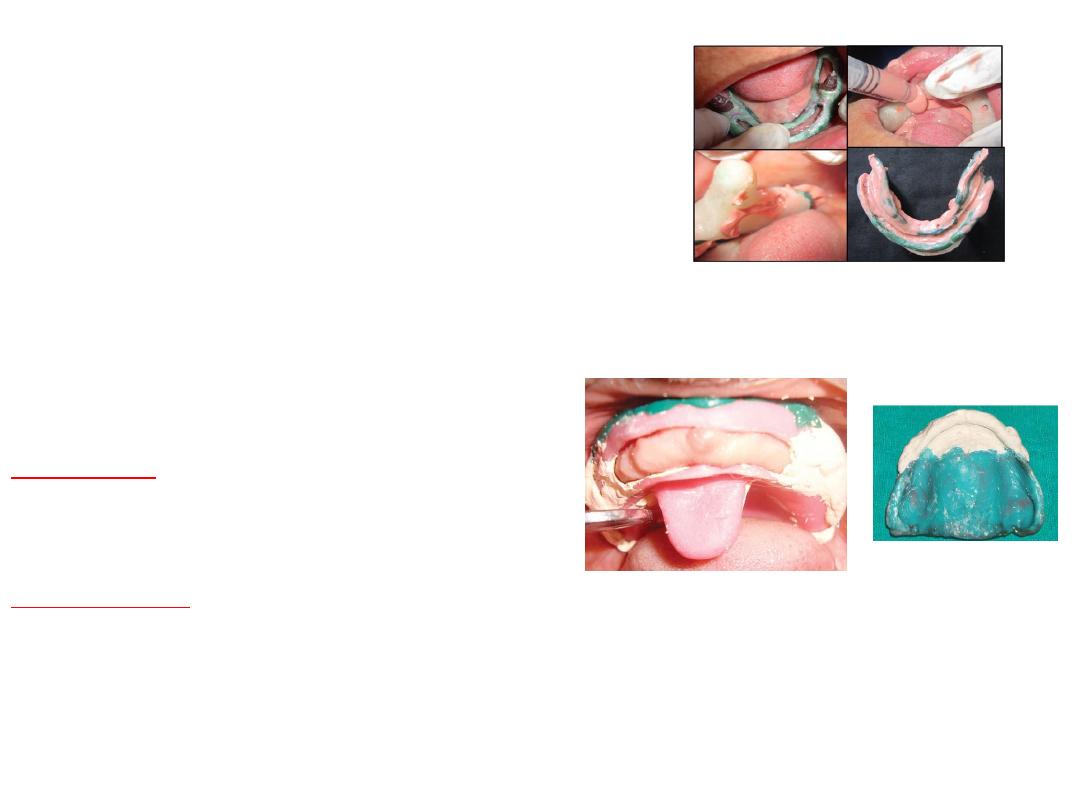
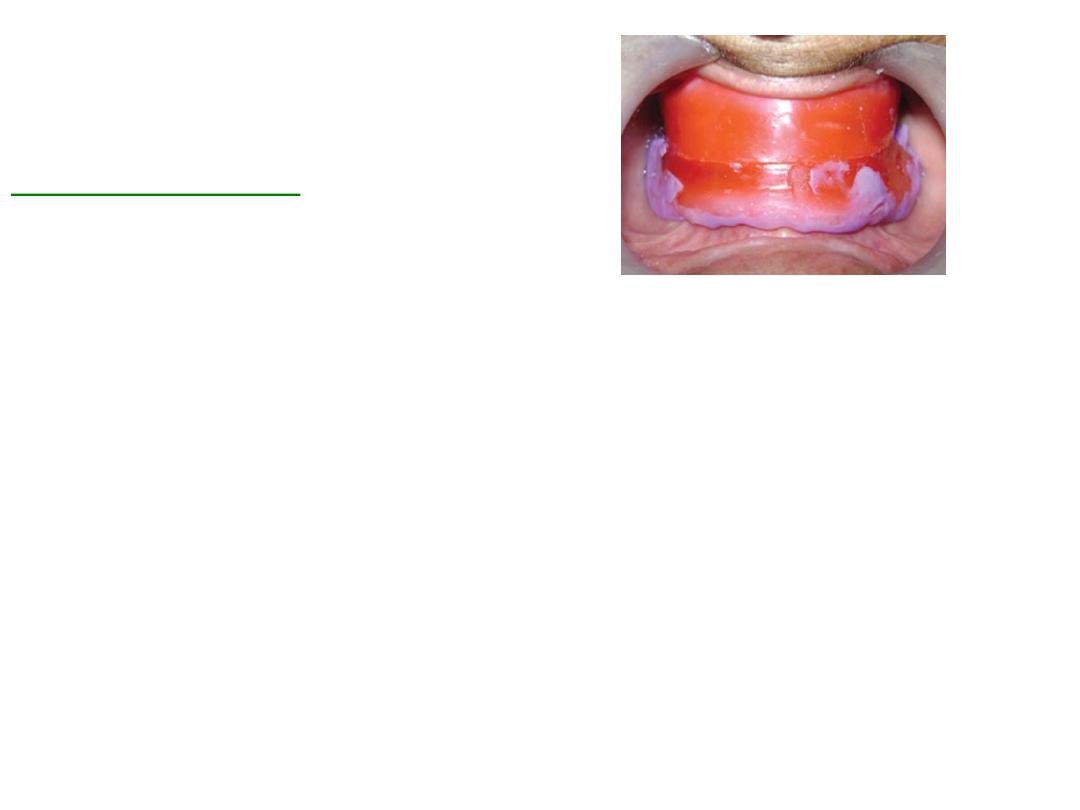
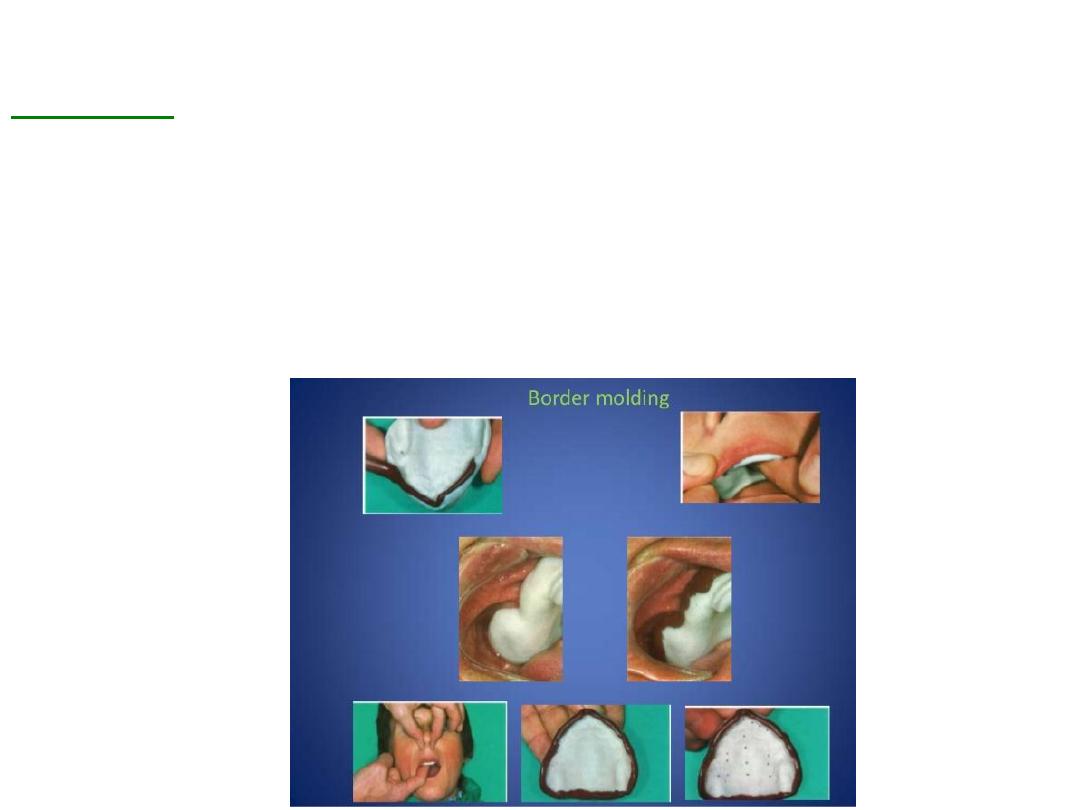
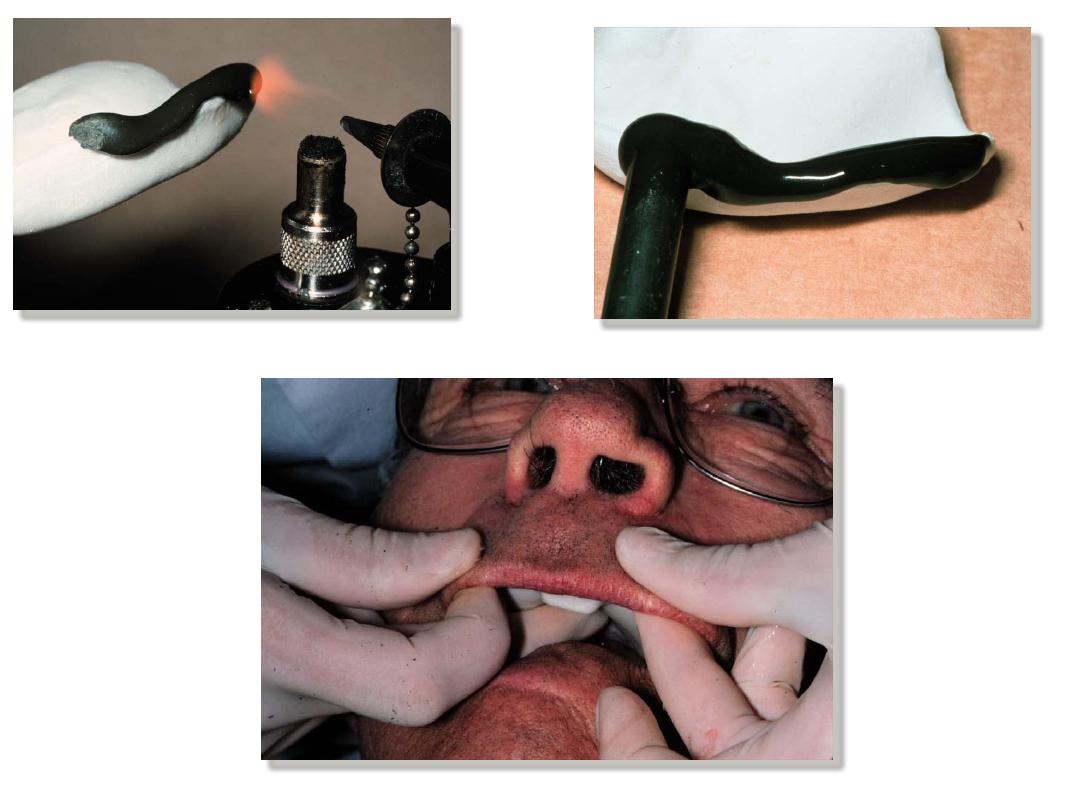
Border molding :
•Is the process by which the shape of the borders of the tray is made to
conform accurately to the contoured of the labial buccal vestibules
before making the final impression ….
also referred muscle trimming
.
•Done by manipulating tissue against moldable impression material that
are properly supported and controlled by the tray
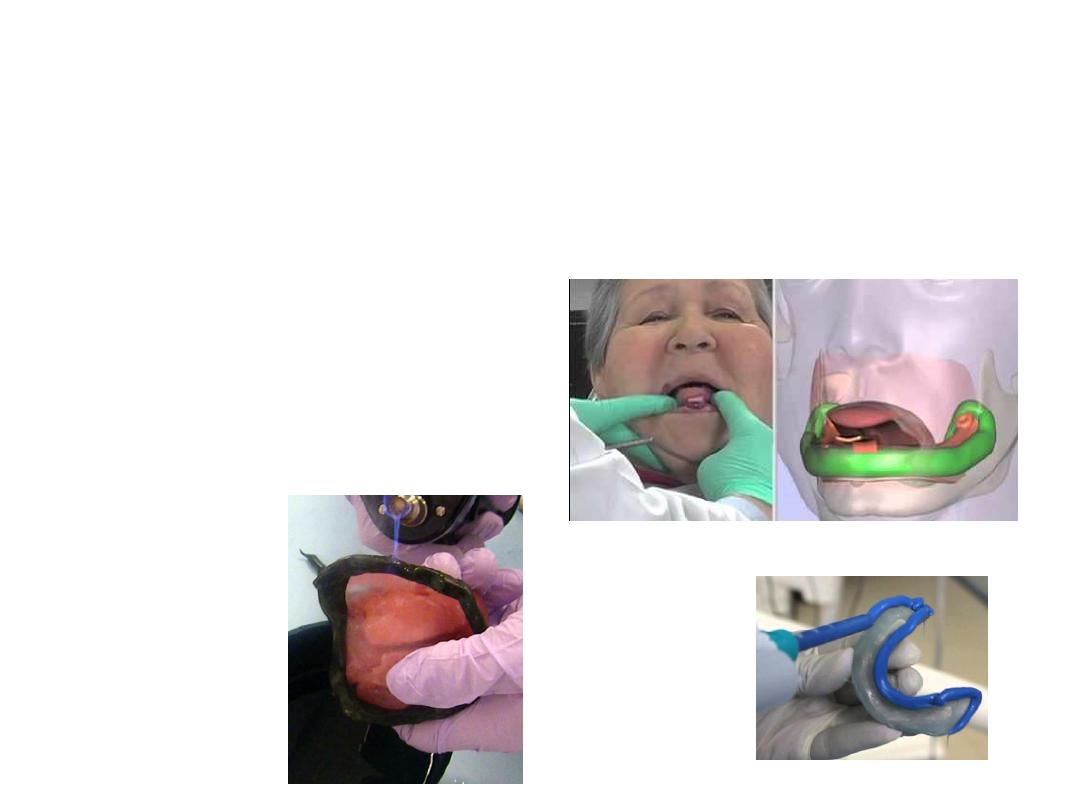
It is the only way to get ideal peripheral seal and cover the available
area of support.
Varity of materials have been used for border molding:
• Molding compound wax
• Auto polymerizing acrylic resin
• Elastomeric materials
• Heavy body putty type silicone
• Polyether.
General considerations:
• The custom tray should be stable and borders are
2mm
short.
• Uniform
thickness 2mm
• Handle
should not interfere with lip or movements
• Molding compound should be done for each area separately not all at
once .
• Control bulk and temperature of the molding compound.
• Too much pressure
…thin overextended flanges …while too
little pressure…excessively thick borders
• Tray should be
dried
before u put compound …better stick
• Also before reheating compound should be
dried
• Each section
molded separately
.
Movement for border molding:
Maxillary
:
• Labial border:
upper lip elevated then extended outward downward
and inward.
• Buccal border:
cheek is elevated and then pulled outward downward
and inward.
• Buccal frenum
is recorded by pulling the cheek backward and
forward.
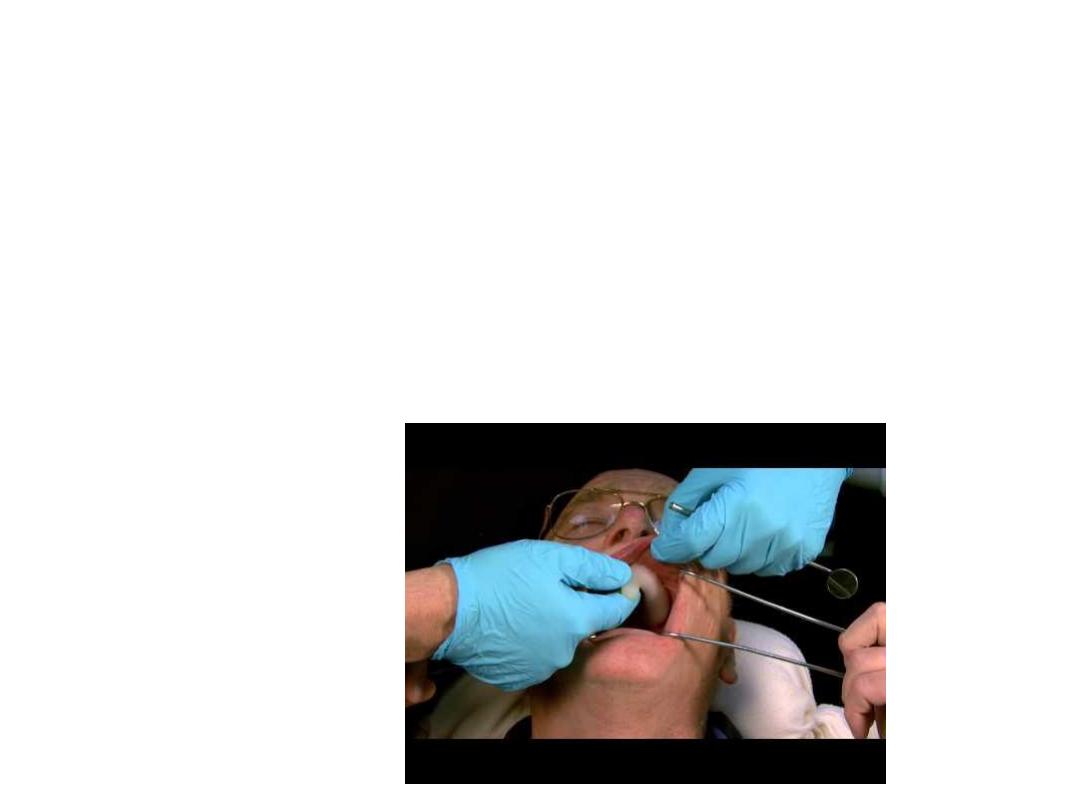
• The disto-buccal region
is recorded by pulling the cheek outward
downward inward fallowed by opening of the mouth widely and
moving the mandible from side to side.(when mouth widely
open coronoid process will come close to distal portion of max.
buccal sulcus.
• Thick flange
will cause will
interfere and pain
.
• Posterior palatal seal
area is molded by asking pt. To say ah
while refining area
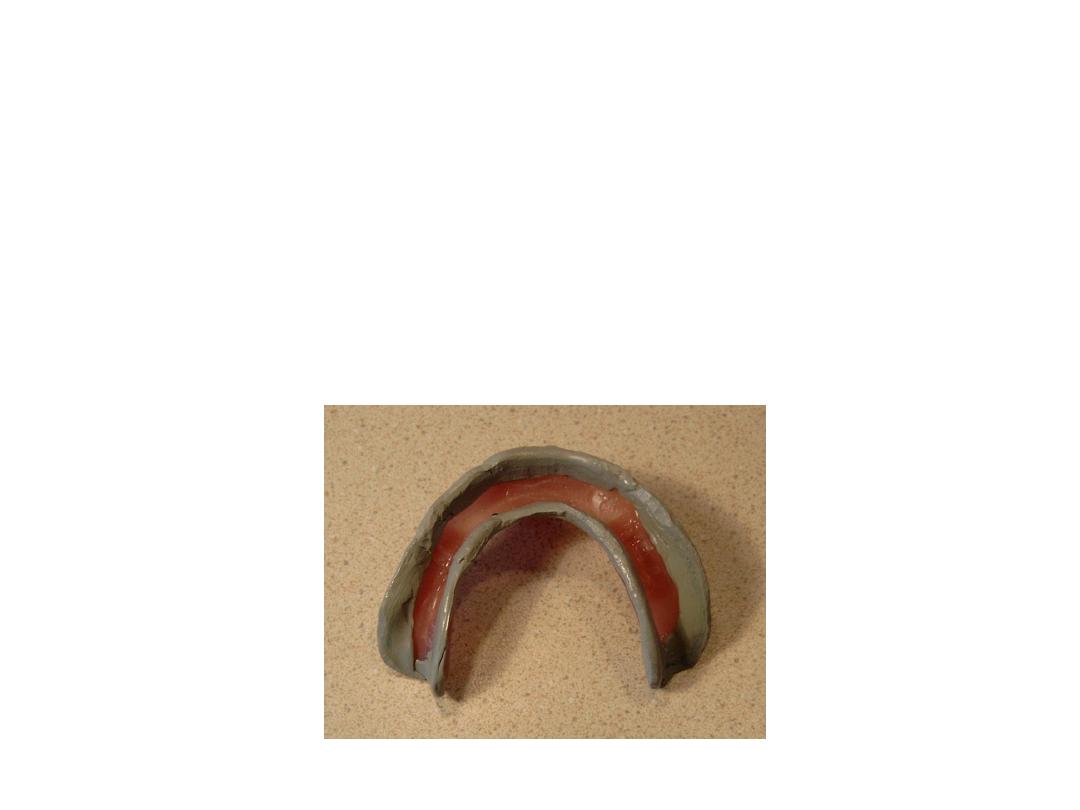

Mandibular
:
Recording labial buccal flanges:
•The
labial portion
is molded by moving the lip outward upward inward
•Buccal frenum
…moving cheek outward upward backwardand farward.
•Recording the
disto-buccal sulcus
…cheek should be well retracted and moved
upward and inward.
•To record action of masseter muscle
…pt. asked to willfully close his mouth
against resistance.

Recording the lingual flange:
• The
anterior lingual
border is molded by asking the pt to protrude his
tongue out and later to touch the anterior part of the palate.
• Mylohyoid area
is refined by asking pt. to move tongue forward to touch
the upper lip backward to touch posterior palate and laterally into the
cheeks.
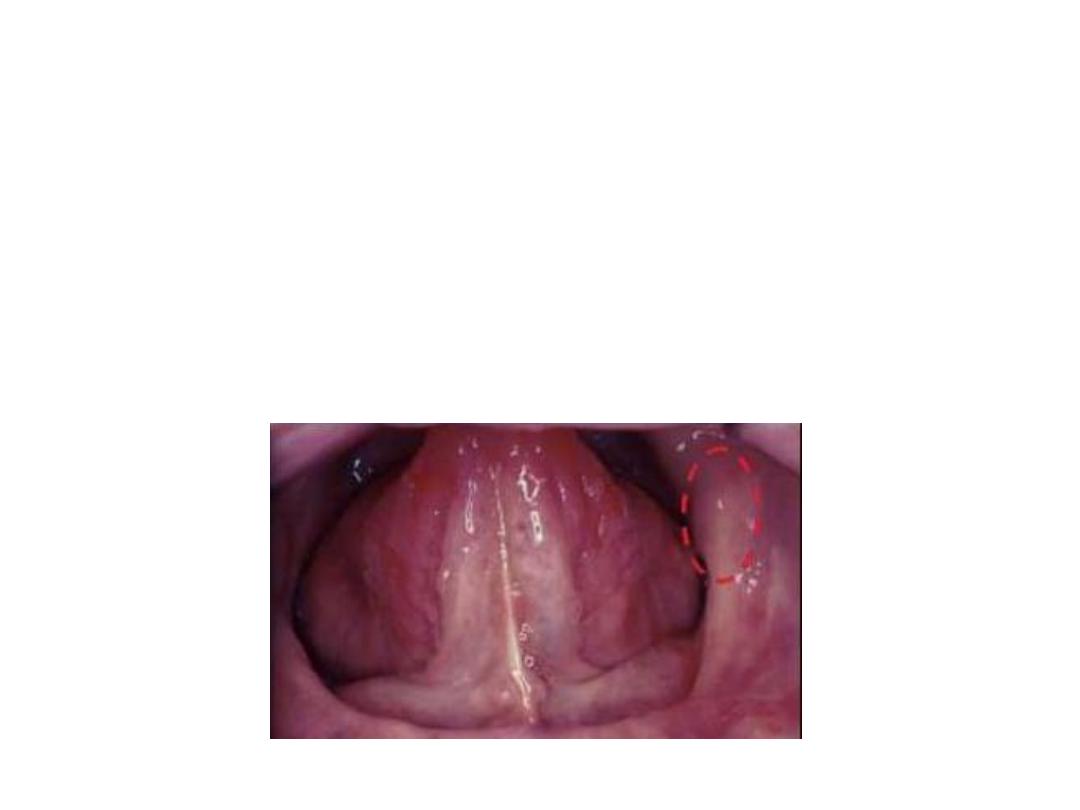
Retromylohyoid space:
the action of the retromylohiod should be recorded
by asking pt. to protrude the tongue perform lateral movement and close
forcefully against resistance.
Recording the retromolar pad:
• To record distal end of the tray the pt. asked to open mouth wide a notch
produced in the postero-medial end of the tray due to the action of the
ptrego-mandibular against raphe.
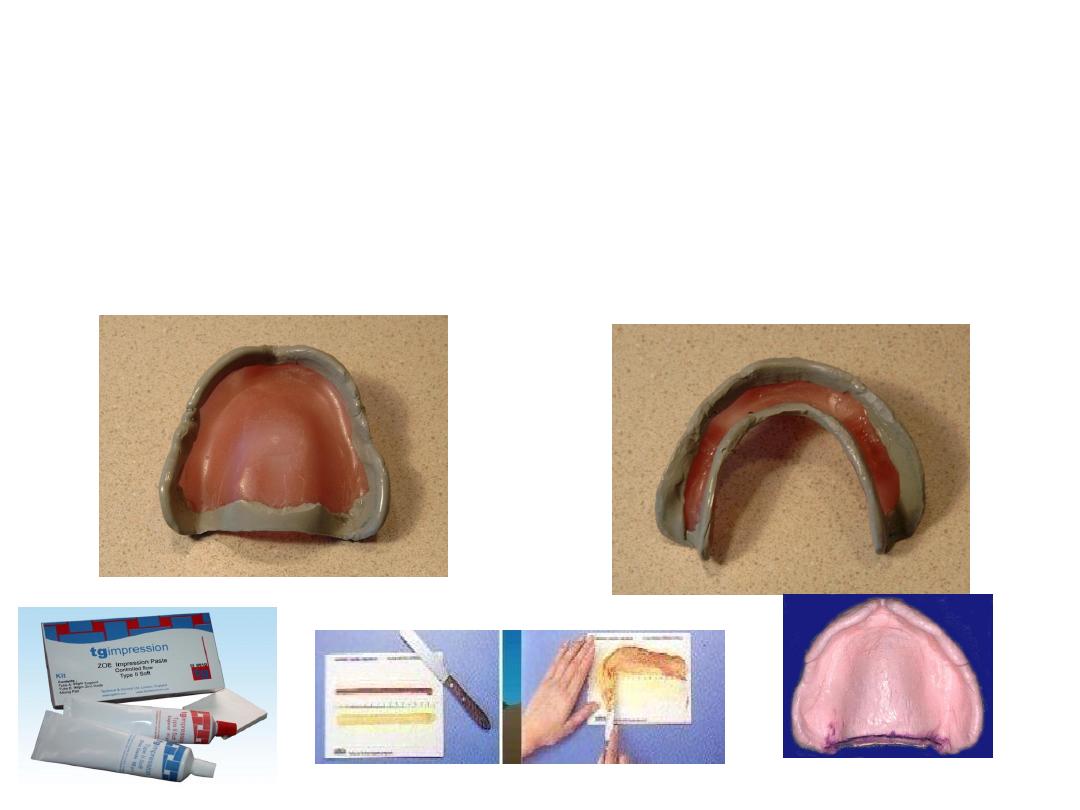
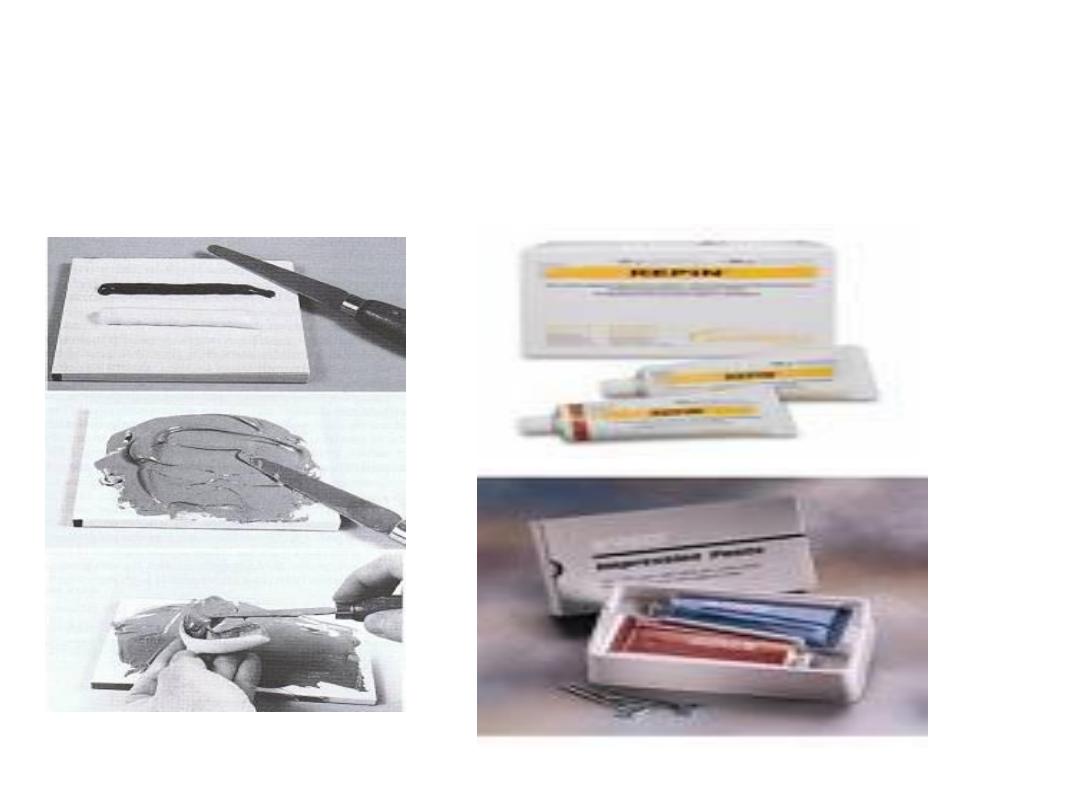
• Once border molding completed impression is taken by zinc
oxide euginol paste
Selective Pressure
1-Cobination of both


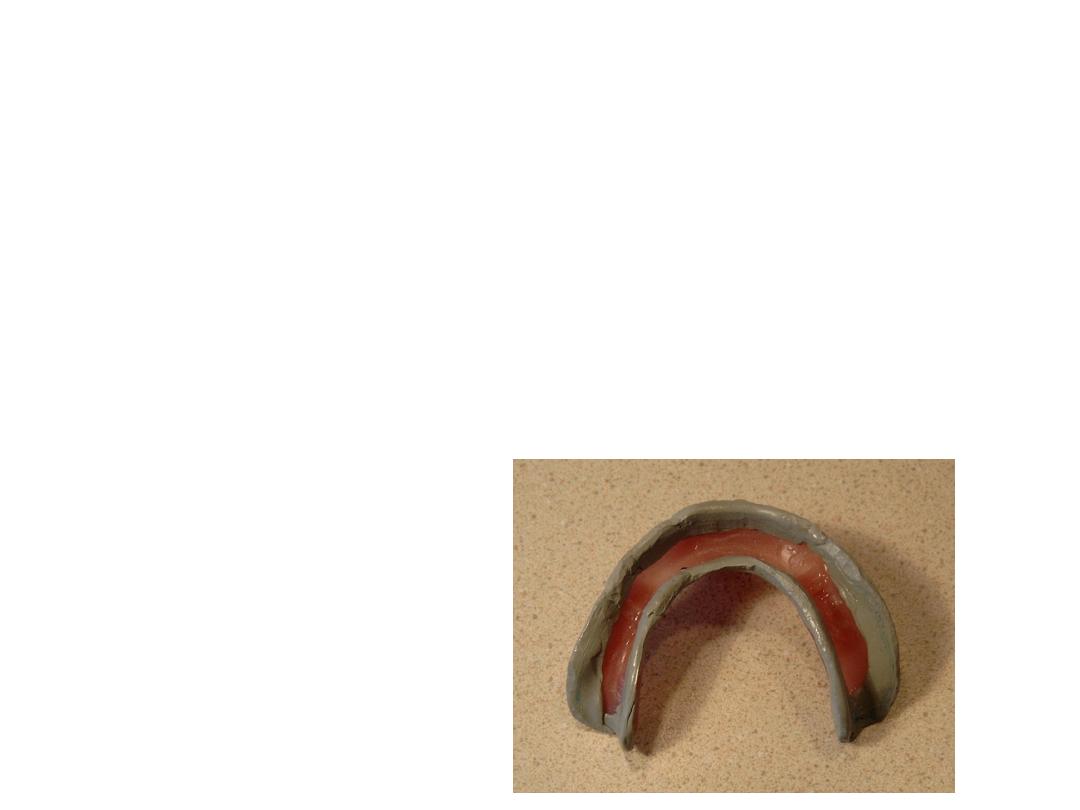
4- dep.on hand manipulation for function
movement( border moulding
)
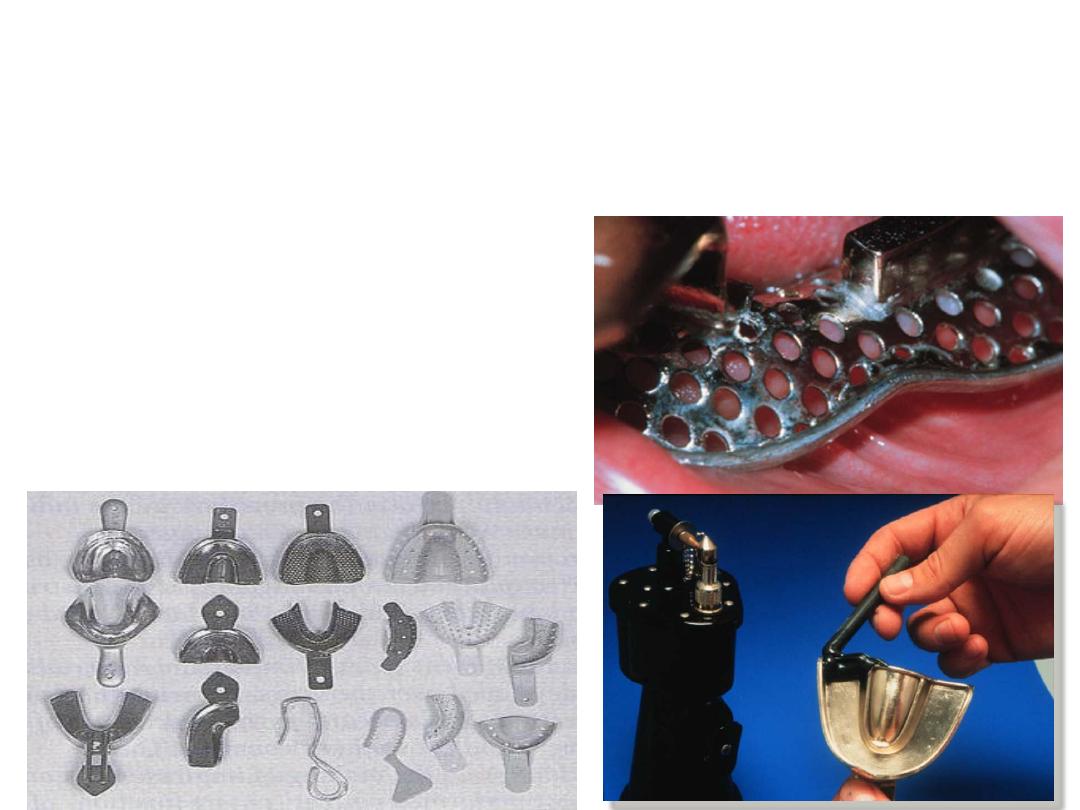
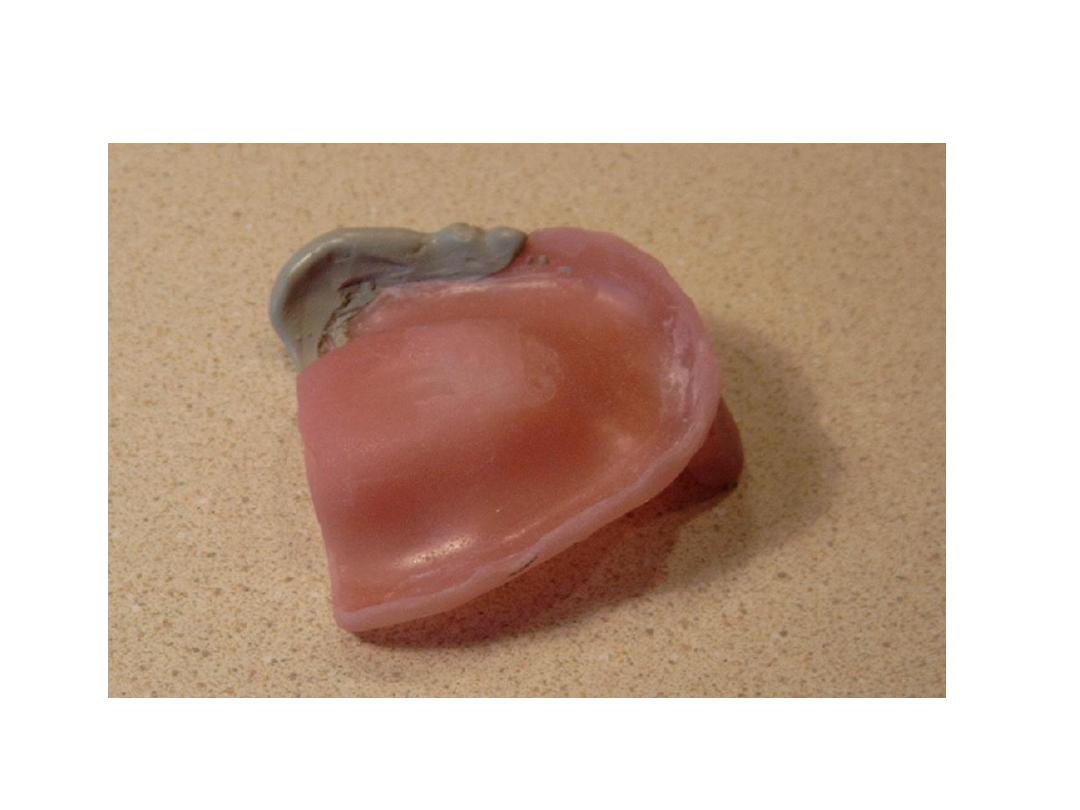
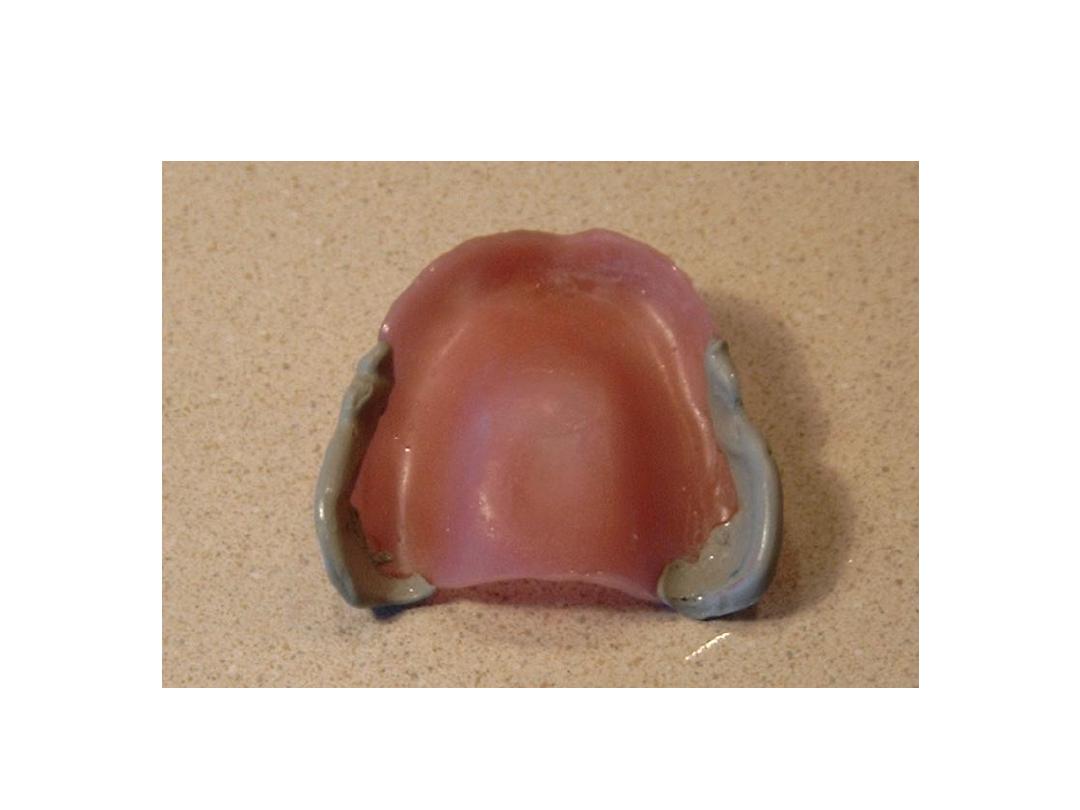
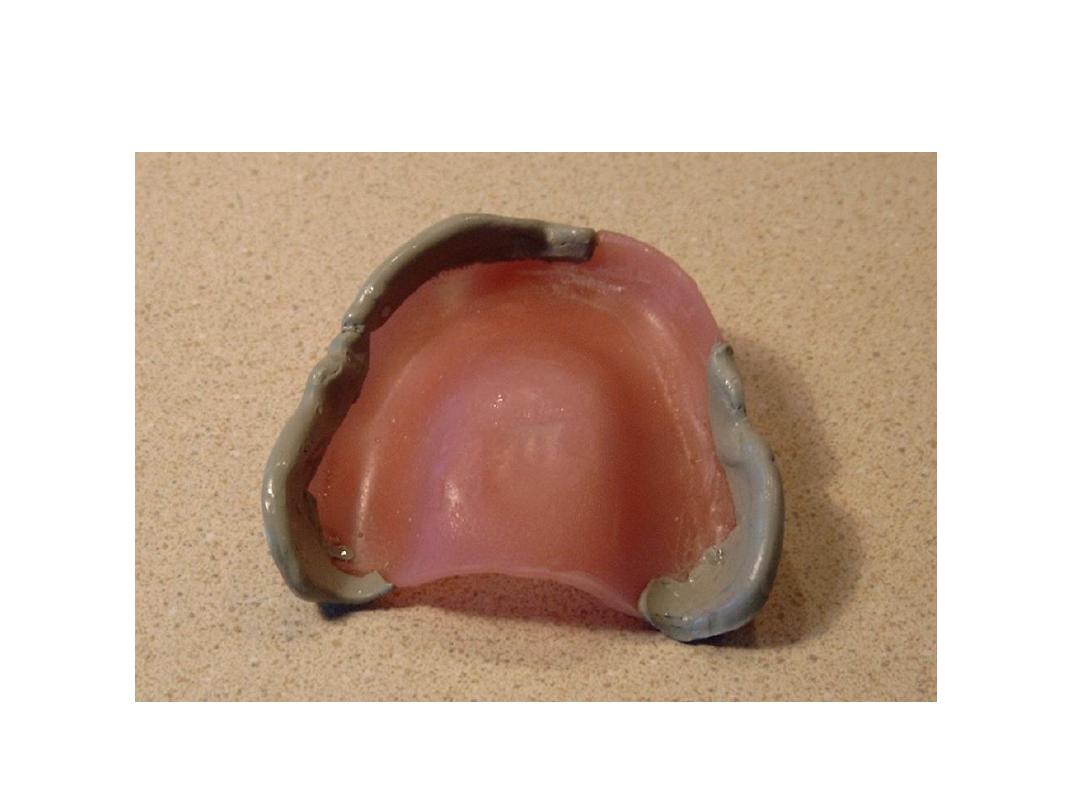
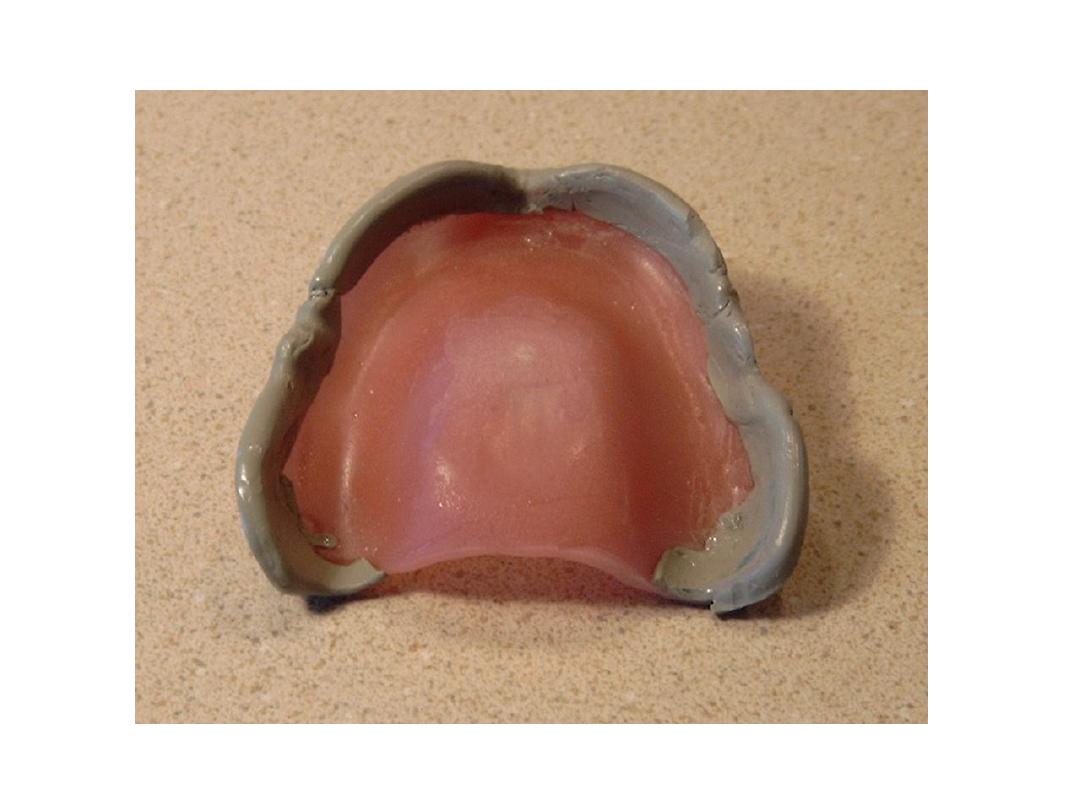
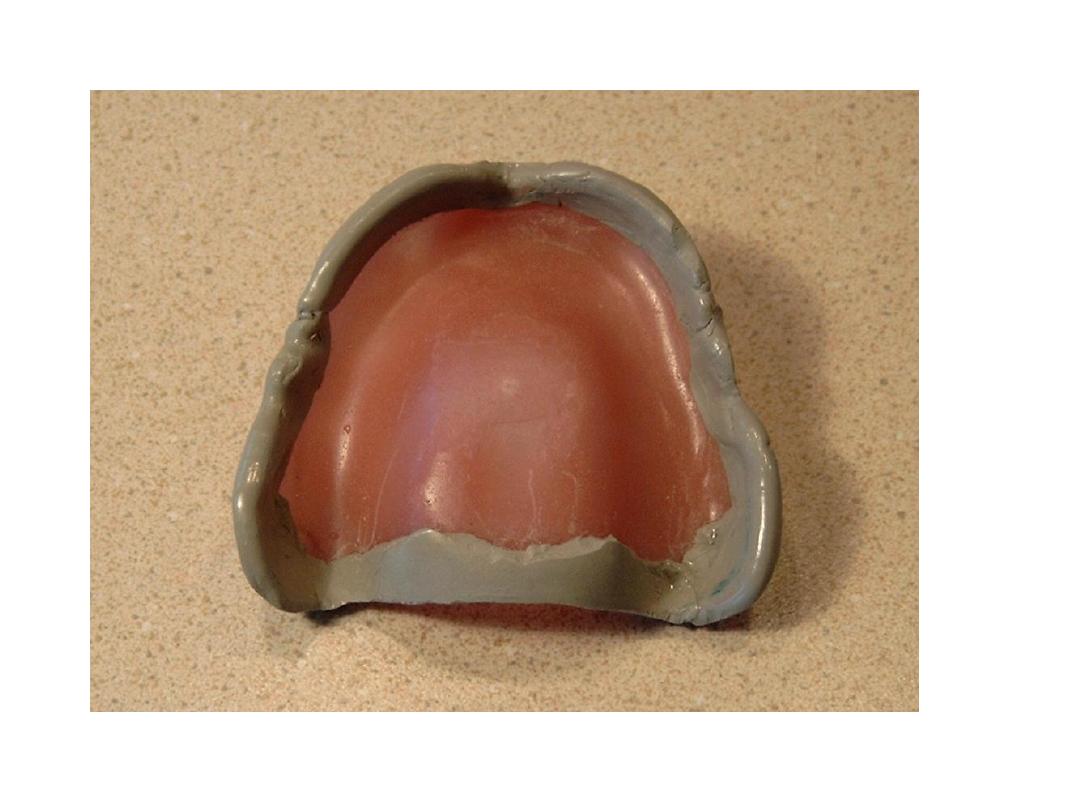
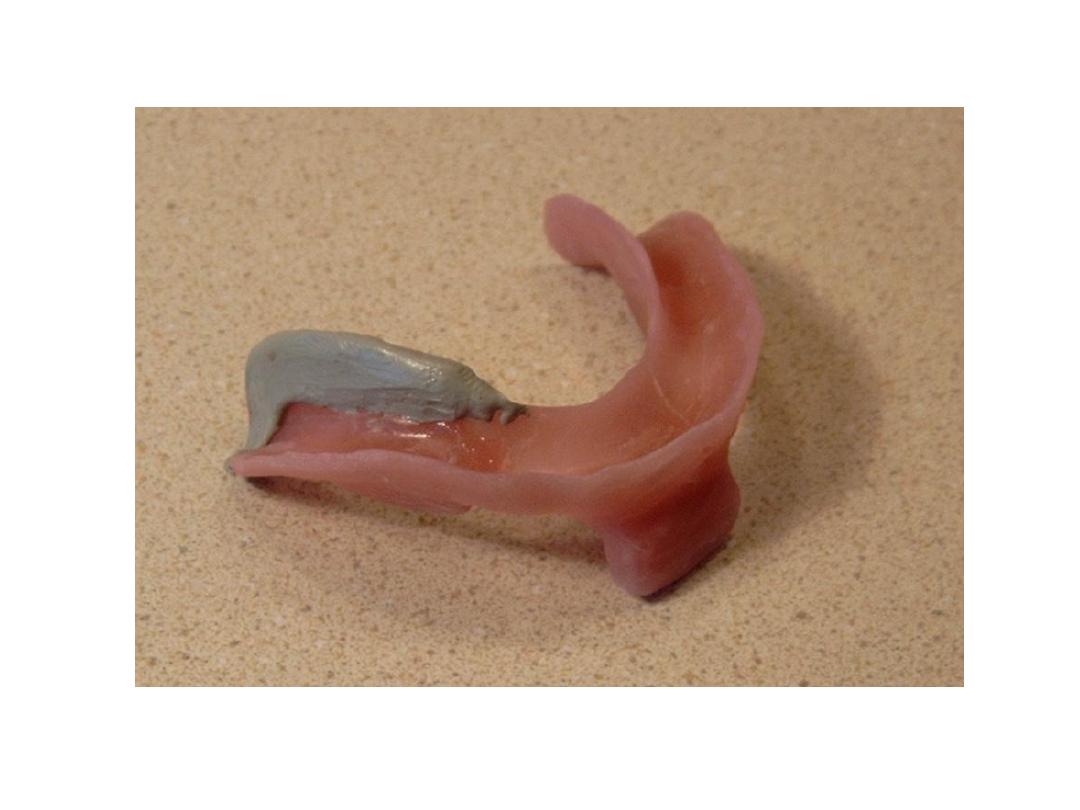
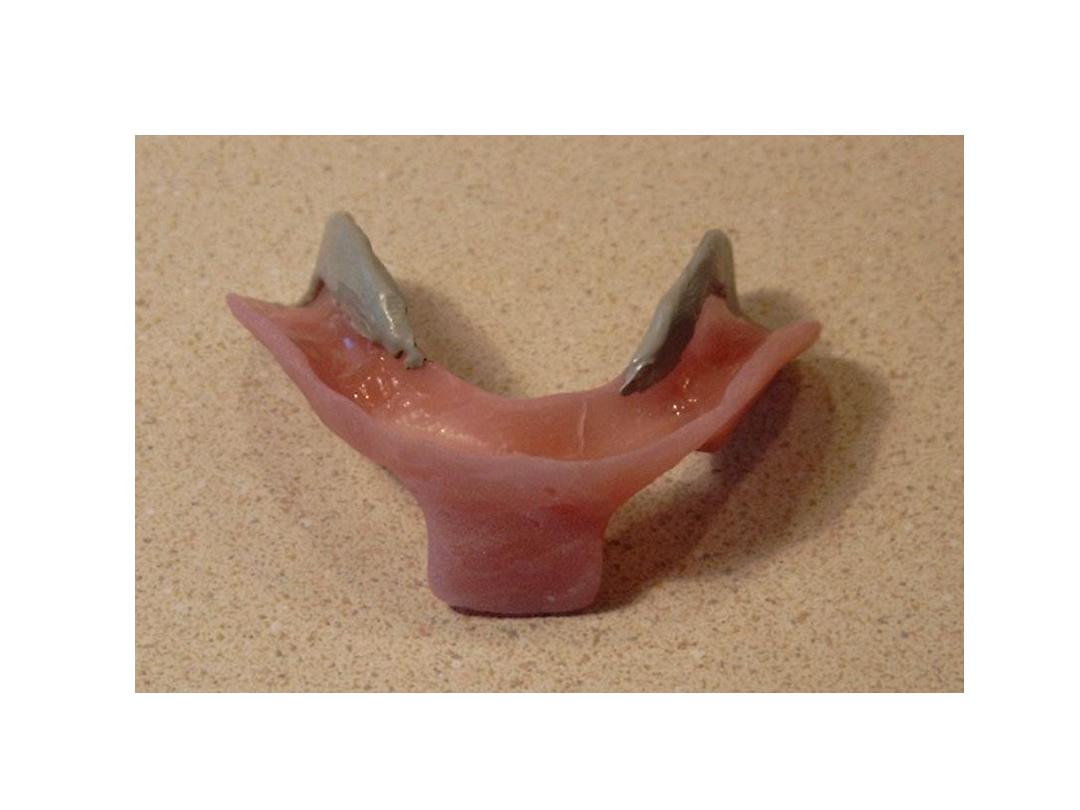
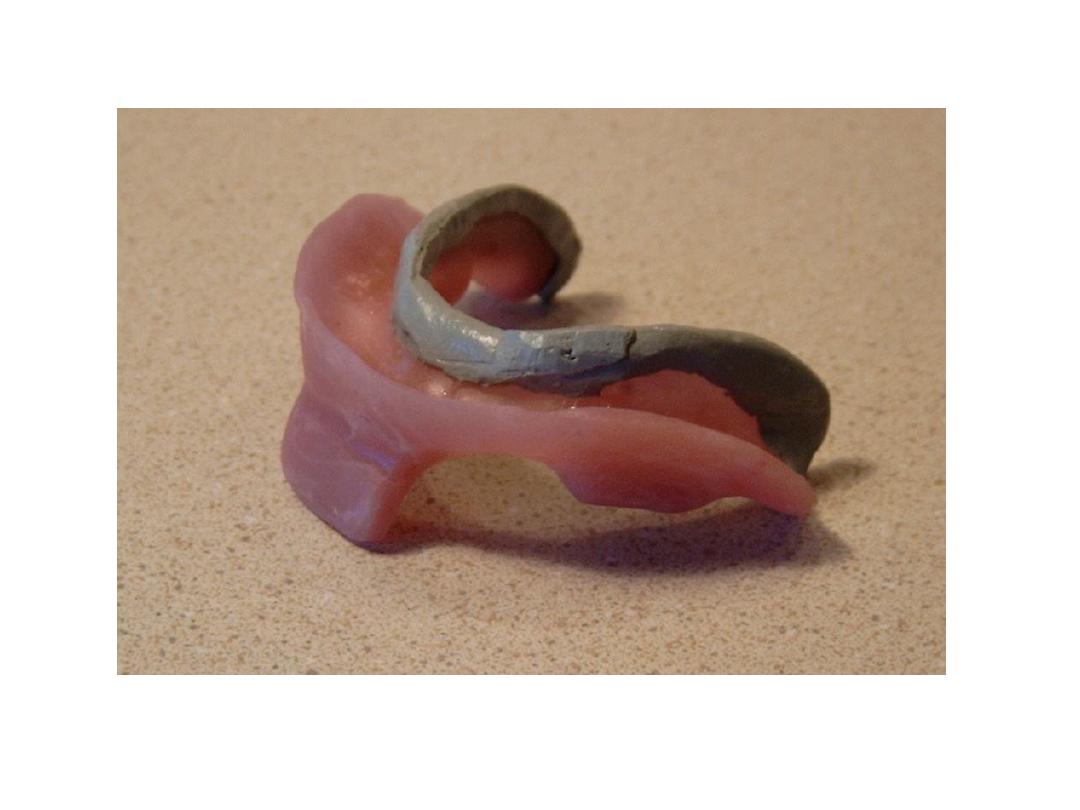

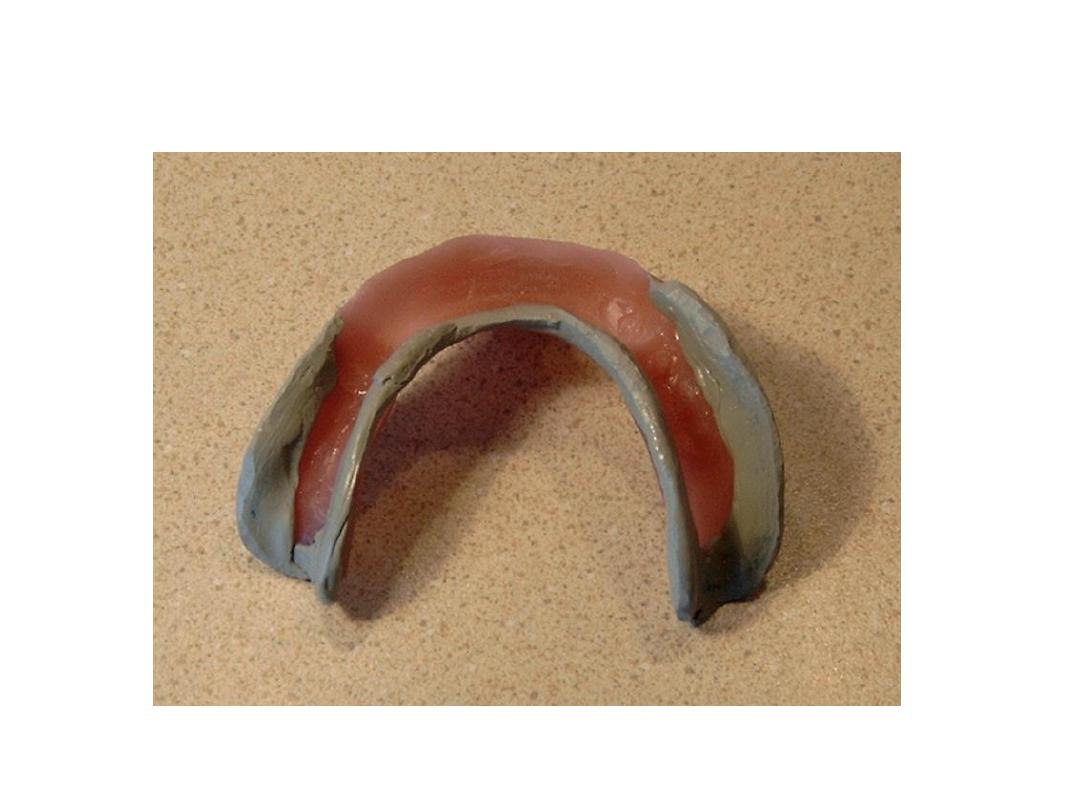

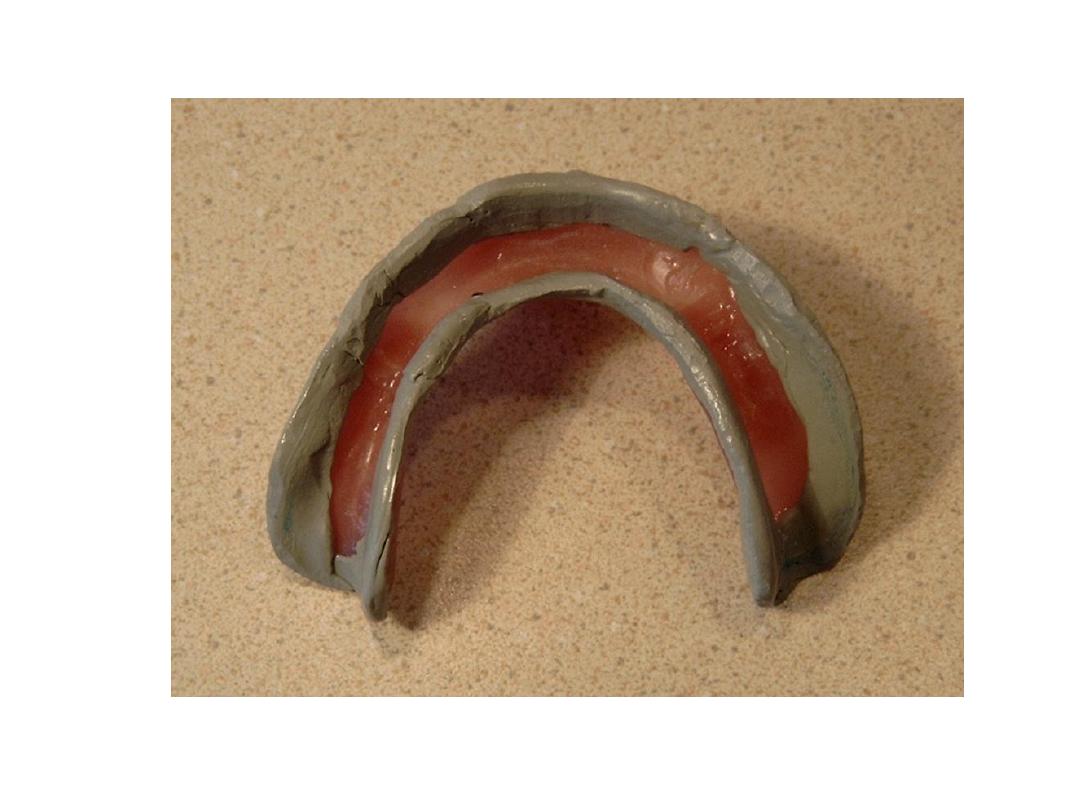
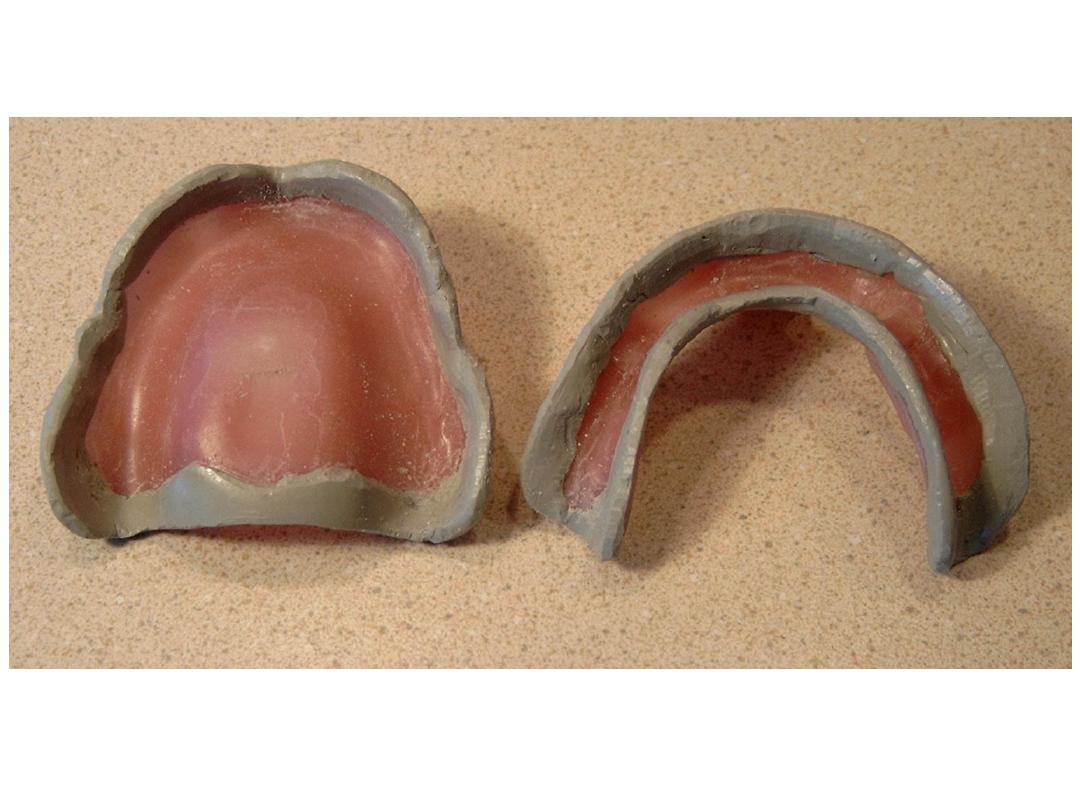

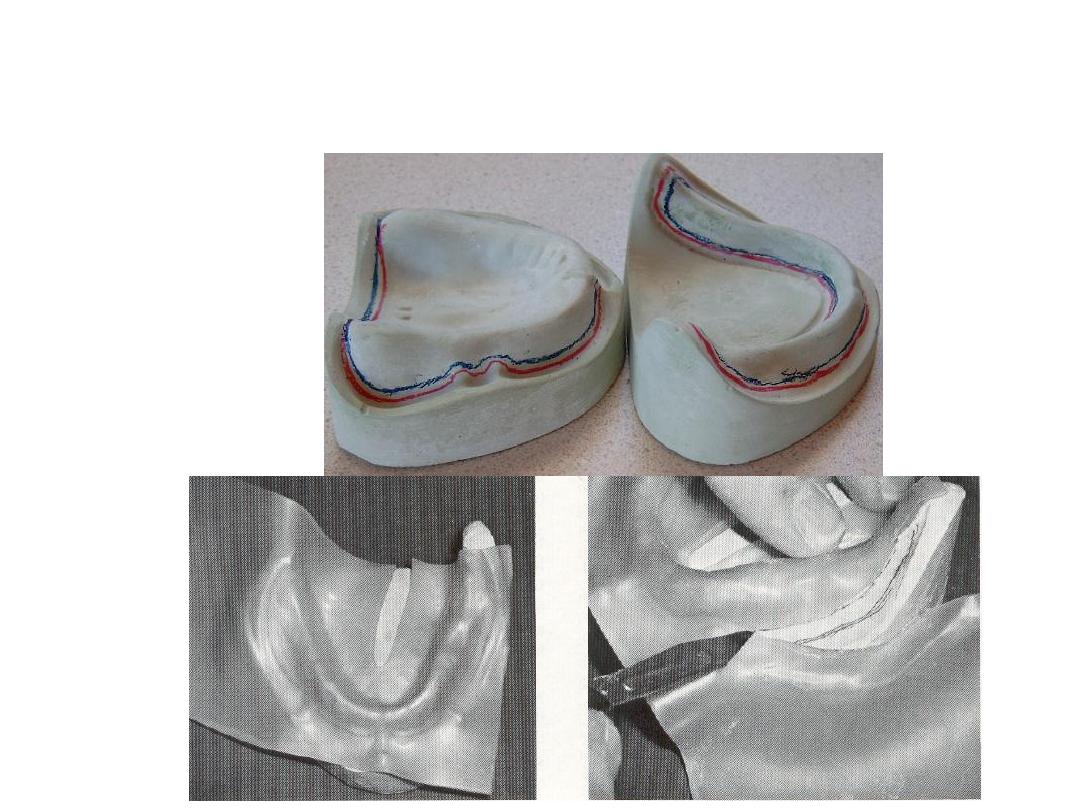
Primary impression
1-
From 2-5 mm clearance between the tray and the ridge
2-tray modification
3.Select according to
Imp.mat, state of edentulism
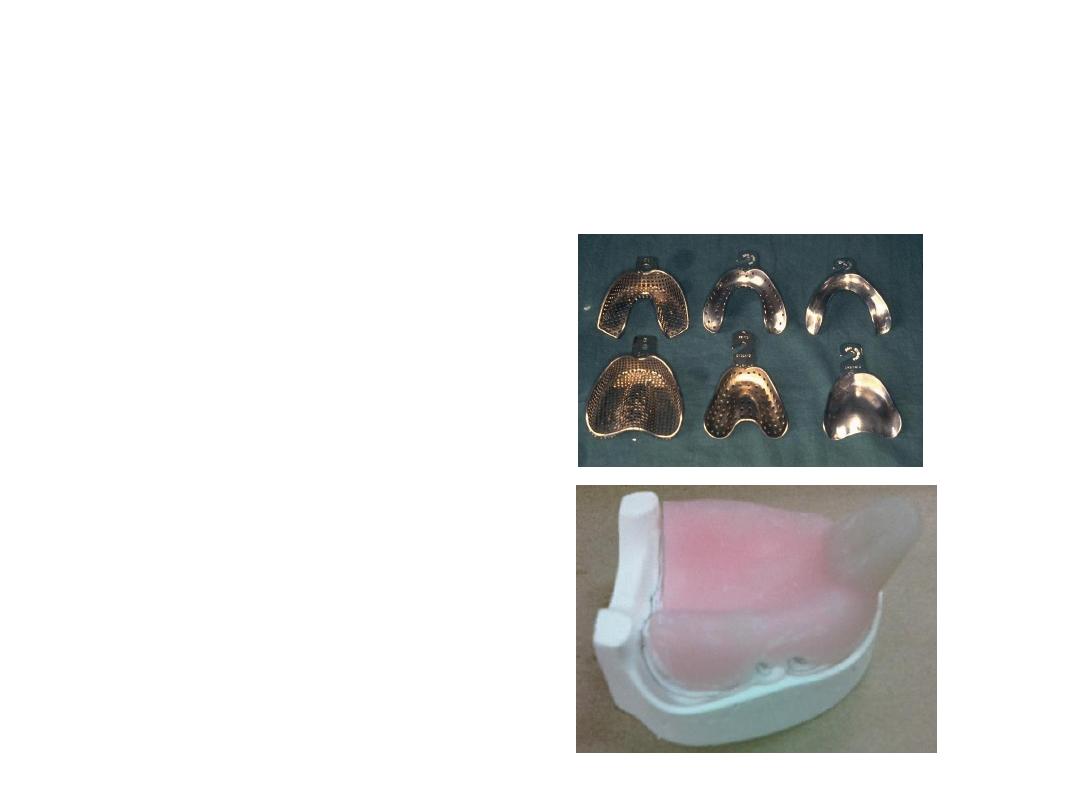
Type of trays
• 1-stock trays
• 2-special trays


Types of stock trays
1. Stainless steel trays.
2. Aluminum trays.
3. Plastic trays
.

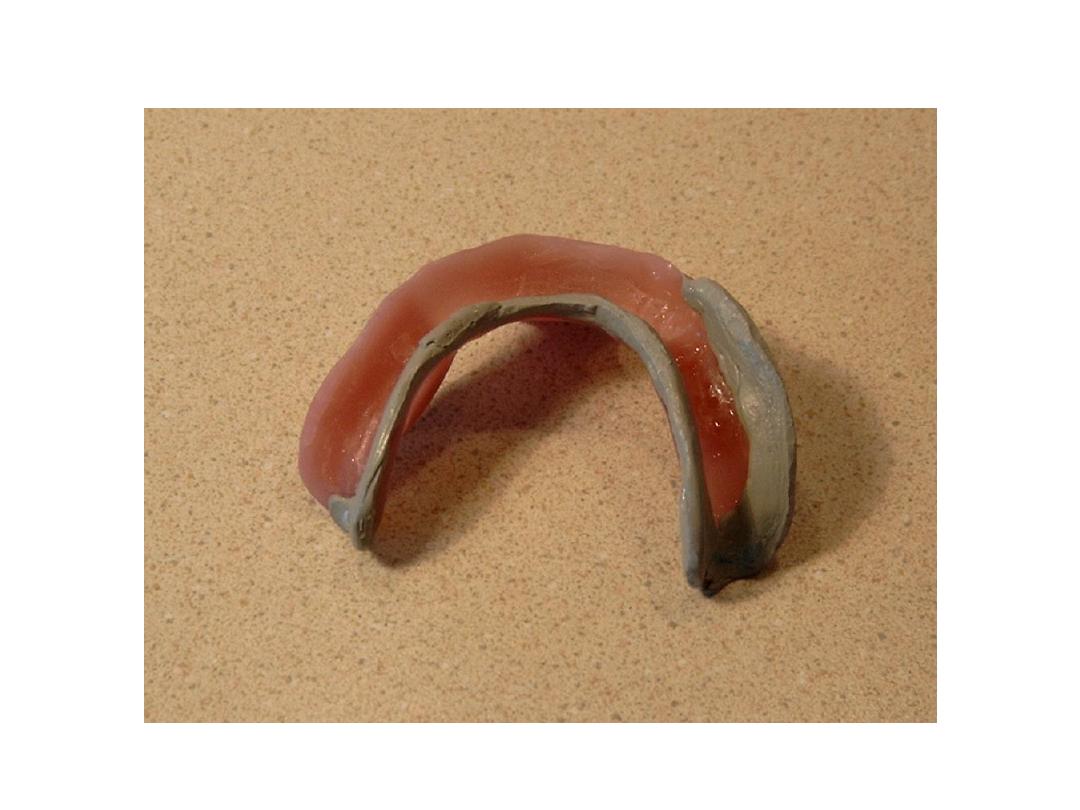
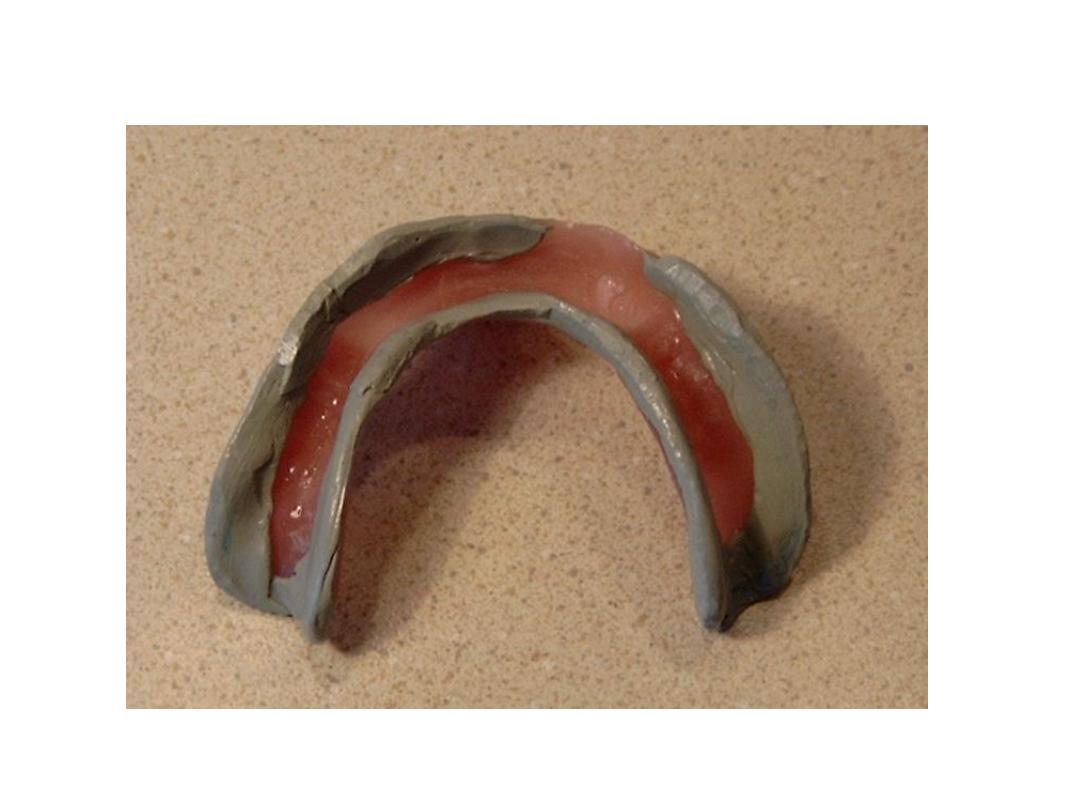
Final impression
Zinc Oxide Eugenol Paste
