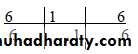Indices of periodontal diseases
Index for measurement of Gingivitis:1.Gingival index of Löe and Silness (1963)
Selection of teeth and scoring:
The scored teeth :16,12,24,36,32and 44.
The examination done by blunt probe. The Each of four surfaces of the tooth near the gingival margin is scored.
Criteria
0 : No inflammation.
1 : Mild inflammation, slight change in color, slight odema, no bleeding on probing.
2 : Moderate inflammation, moderate glazing, redness, bleeding on probing.
3 :Severe inflammation, marked redness and hypertrophy, ulceration, tendency to spontaneous bleeding.
II.WHO System (1977)
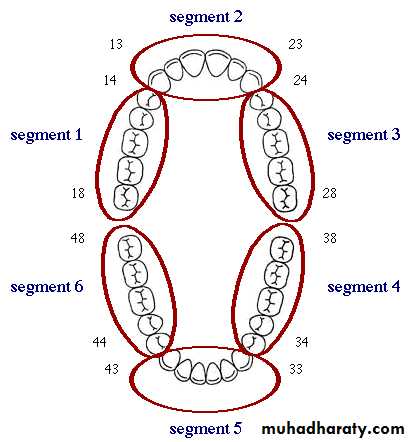
This is a simple prevalence index . the teeth are not dried and no probe is used.Selection of teeth and scoring: The mouth is scored in 6 segments: Anterior and right and left posterior in each jaw. All surface are examined each segment is scored as one unit. The maximum score for an individual is 6.
Criteria of WHO System :
0: there is no or only minor alteration in gingival colour and form, and no bleeding after digital palpation.
1: there is a marked change on colour ,bleeding on firm digital palpation and marked general loss of stippling .
Indices for measurement of periodontal destructions (loss of attachment ):
Loss of attachment is usually signified by pocketing , but pocketing may occur without loss of attachment when there is hyperplasia or swelling of the gingiva .There may be loss of attachment due to past disease but no pocketing in a currently well – cured gingiva .
The destruction of bone is the most important criteria for assessing the severity of periodontal disease.
Bone loss measure by:
Loss of attachment,radiographic evaluation
gingival recession
Assessment of tooth mobility.
Ramfjord periodontal disease index (Gingival sulcus measurement)
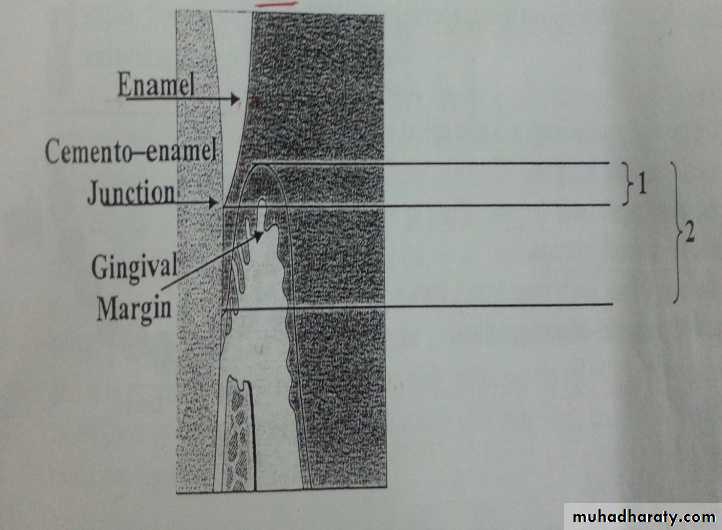
Selection of teeth and scoring:The indexed teeth are 16,21,24,36,41 and 44. The four surfaces of each tooth are examined . The examination done by narrow graduated periodontal probe (Michigan O ).Use the cemento – enamel junction as baseline from which to measure the loss of attachment.
The score for an individual is the total score divided by the number of teeth examined. No replacement of missing teeth .
If gingival margin is on enamel:
Measure distance from gingival margin to CEJ.Measure distance from gingival margin to the base of the pocket (when the pocket is apical to CEJ).
Loss of attachment = 2-1
Pocket depth = 2
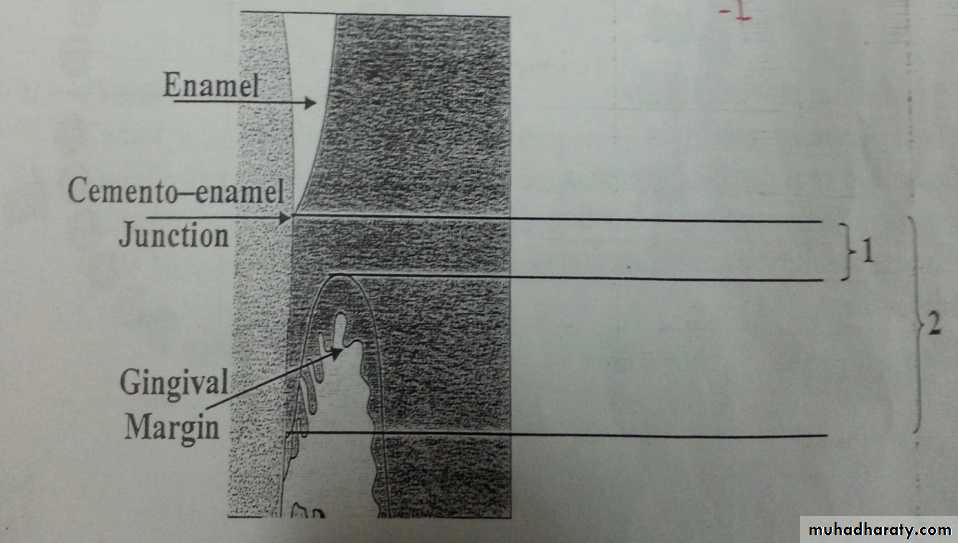
B. If gingival margin is on cementum:
1- Measure distance from CEJ to gingival margin (minus score).2- Measure distance from CEJ to bottom of pocket.
Loss of attachment = 2
Pocket depth = 1+2
Ramfjord periodontal disease index ( pocket depth )
Selection of teeth and scoring:The indexed teeth are 16,21,24,36,41 and 44. The four surfaces of each tooth are examined. The score for an individual is the total score divided by the number of teeth examined. No replacement of missing teeth.
Criteria :
4 : if the base of pocket is up 3mm apical to CEJ .5 : if the base of pocket is 3-6 mm apical to CEJ .
6 : if the base of pocket is more than 6 mm apical to CEJ.
Ramfjord periodontal disease index (Mobility of the teeth):
Selection of teeth and scoring:The indexed teeth are 16,21,24,36,41 and 44. The four surfaces of each tooth are examined. The score for an individual is the total score divided by the number of teeth examined. No replacement of missing teeth.
Criteria :
M0 : physiological movement only.
M1 : slightly increase mobility .
9
Community Periodontal Index of Treatment Needs (CPITN) – (1982) :
Selection of teeth and scoring:The mouth is divided into 6 sections (sextant): Anterior and right and left posterior in each jaw.
The indexed teeth are 17,16,11,26,27,37,36,31,46 and 47.
specified indexed teeth in each sextant are measured ;if they are absent the remaining teeth present are examined .The score of the worst indexed tooth in each sextant is recorded.
Treatment need :
Treatment need in a sextant is only recorded when:2 or more teeth are present in that sextant.
not indicated for extraction.
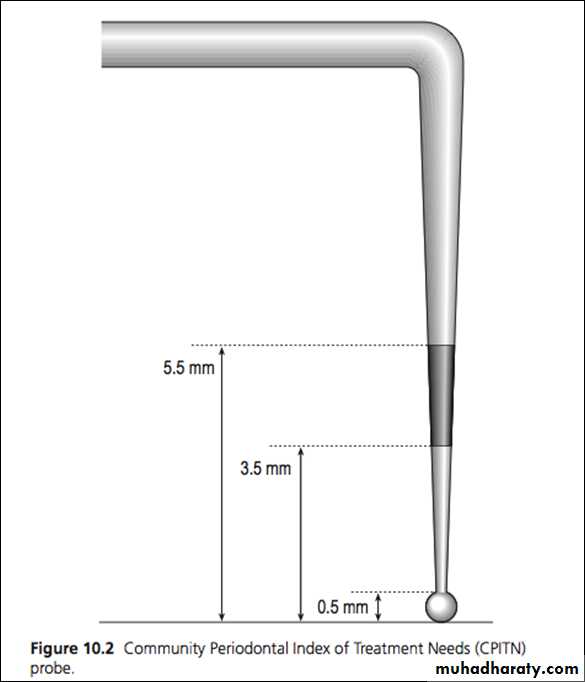
WHO probe
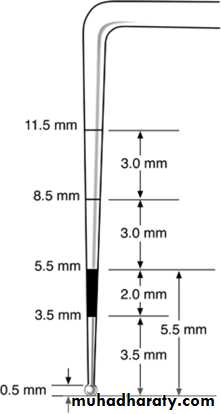
A special designed light weight explorer (probe) is used with a small ball tip of 0.5 mm in diameter It is a colour coded probe . The explorer is black coloured for 2 mm , called black zone , starting from 3.5 mm away from the tip of the ball ; i.e., it is black coloured coded from 3.5 mm to 5.5 mm from tip of the ball . This probe is known as WHO probe .CPI probe
Amore recent probe is used in this index which is called CPI probe ,and it is similar to the WHO probe . The only difference is that CPI probe contains, in addition to the black area , two graduations of 3 mm each ; i.e.; 8.5 mm and 11.5 mm from the tip of the ball.criteria
0: No periodontal disease.1:Bleeding on probing.
2: supra-sub –gingival Calculus with plaque seen or felt by probing.
3: Pathological pocket 4 – 5 mm.
4: Pathological pocket 6 mm or more.
X: When only 1 tooth or no tooth are present.
Treatment need:
0 : No need for treatment.
1 : Personal plaque control +(oral hygiene instruction - OHI).
2 : Professional cleaning (scaling and polishing) + OHI
3 : Professional cleaning (scaling and polishing) +OHI
4 : complex treatment : Deep scaling , root planning, surgical procedure.
Malocclusion index:
Angle's Classification:
Class I: malocclusion in which the lower first permanent molar is within one half cusp width of its correct relationship to the upper first permanent molar . This arch relationship is some time called “ neutron – occlusion “.
Class II : The lower arch is at least one –half cusp width posterior to the correct relationship with the upper arch ,judged by the first molar relationship. This arch relationship is some time called “ disto- occlusion
Class II is divided according to the inclination of the upper central incisors :
Division 1 : The upper central incisors are proclined or the average inclination so that there is an increase in over jet .
Division 2 : The upper central incisors are retroclined. The overjet is usually average but may be a little increased .Sometime the upper lateral incisors are proclined , mesially inclined and mesiolabially rotated.
Class III: The lower arch is at least one –half cusp width too far forward in relationship with the upper arch ,judged by the first molar relationship. This arch relationship is some time called “ mesio - occlusion “.