OPTIC NEUROPATHIES
Marwan Salah Salman MD.Signs of optic nerve dysfunction
Reduced visual acuity
Afferent pupillaryconduction defect
Dyschromatopsia
Diminished light
brightness sensitivity
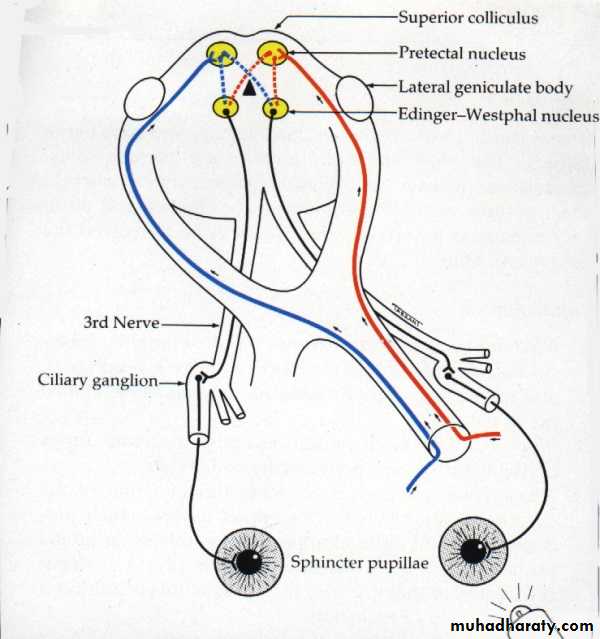
Applied anatomy of afferent conduction defect
Signs
Equal pupil size
Light reaction
- ipsilateral direct is absent or diminished
- consensual is normal
Near reflex is normal in both eyes
Total defect (no PL) = amaurotic pupil
Relative defect = Marcus Gunn pupil
Optic disc changes
Swelling in:
Papilloedema
Papillitis and neuroretinitis
AION
Atrophy
PostneuriticCompression
Hereditary optic atrophies
Optico-ciliary shunts
Optic nerve sheath meningiomaOccasionally optic nerve glioma
Classification of optic neuritis
Retrobulbar neuritis(normal disc)
Demyelination - most common
Sinus-related (ethmoiditis)
Lyme disease
Papillitis (hyperaemia and
oedema)
Viral infections and immunization
in children (bilateral)
Demyelination (uncommon)
Syphilis
Neuroretinitis (papillitis
and macular star)
Cat-scratch fever
Lyme disease
Syphilis
Non-arteritic AION
Presentation
Age - 45-65 years
Altitudinal field defect
Eventually bilateral in 30% (give aspirin)
Acute signs
Pale disc with diffuse or sectorial oedemaFew, small splinter-shaped haemorrhages
Late signs
Resolution of oedema and haemorrhagesOptic atrophy and variable visual loss
Superficial temporal arteritis
PresentationAge - 65-80 years
Scalp tenderness
Headache
Jaw claudication
Polymyalgia rheumatica
Superficial temporal arteritis
Acute visual loss
Special investigations
ESR - often > 60, but normal in 20%
C-reactive protein - always raised
Temporal artery biopsy
Arteritic AION
Affects about 25% of untreated patients with giant cell arteritisSevere acute visual loss
Treatment - steroids to protect fellow eye
Bilateral in 65% if untreated
Presentation
ON NON AION AIONPresentation
ON NON AION AION
20-40
40-6570-80
female
male=female
Female
Acute and progressive
Dramatic sudden onset
Dramatic sudden onset
Painful
painless
Painful
Ms symptoms
D,M H,T
Amaurosis fugax
Signs
Mild loss VA
Sever loss
Sever lossunilateral
Unilateral then other eye 30 %
Unilateral then other eye 65 %
RAPCD
RAPCD
RAPCD
Normal or papilitis pink
Disc swelling
Pale
Disc swelling
Chalky
Disprporttional to VA loss
Propotional to VA loss
Investigations
VF diffuse scotoma
Inferior altitudinal
Blood normal
ESR elevatedESR elevated
CRP markedly raised
FFA mild leakage
Moderate leakage
Sever leakage
VEP latency increase
Amplitude decrease
Amplitude decrease
MRI
Temporal artery biopsy
Done by Omar Abid ALsamrraeWith best wishes