
Refractive Errors
The optical power of the eye is attributed to the cornea ( 43 Diopter ) and the
Lens ( 15 Diopter ).
Emmetropia is the refractive state in which parallel rays of light from a
distant object are brought to focus on the retina .
Ametropia refers to the absence of emmetropia.
▪65% of the population have refraction of 0.00 to +0.75 and can therefore
regarded emmetropic,
In axial ametropia, the eyeball is either unusually long (myopia) or short
(hyperopia).
In refractive ametropia, the length of the eye is statistically normal, but the
refractive power of the eye is abnormal: excessive in myopia or inadequate
in hyperopia. Aphakia is an example of extreme refractive hyperopia.
An ametropic eye requires either a diverging or a converging lens to focus a
distant object on the retina.
Myopia
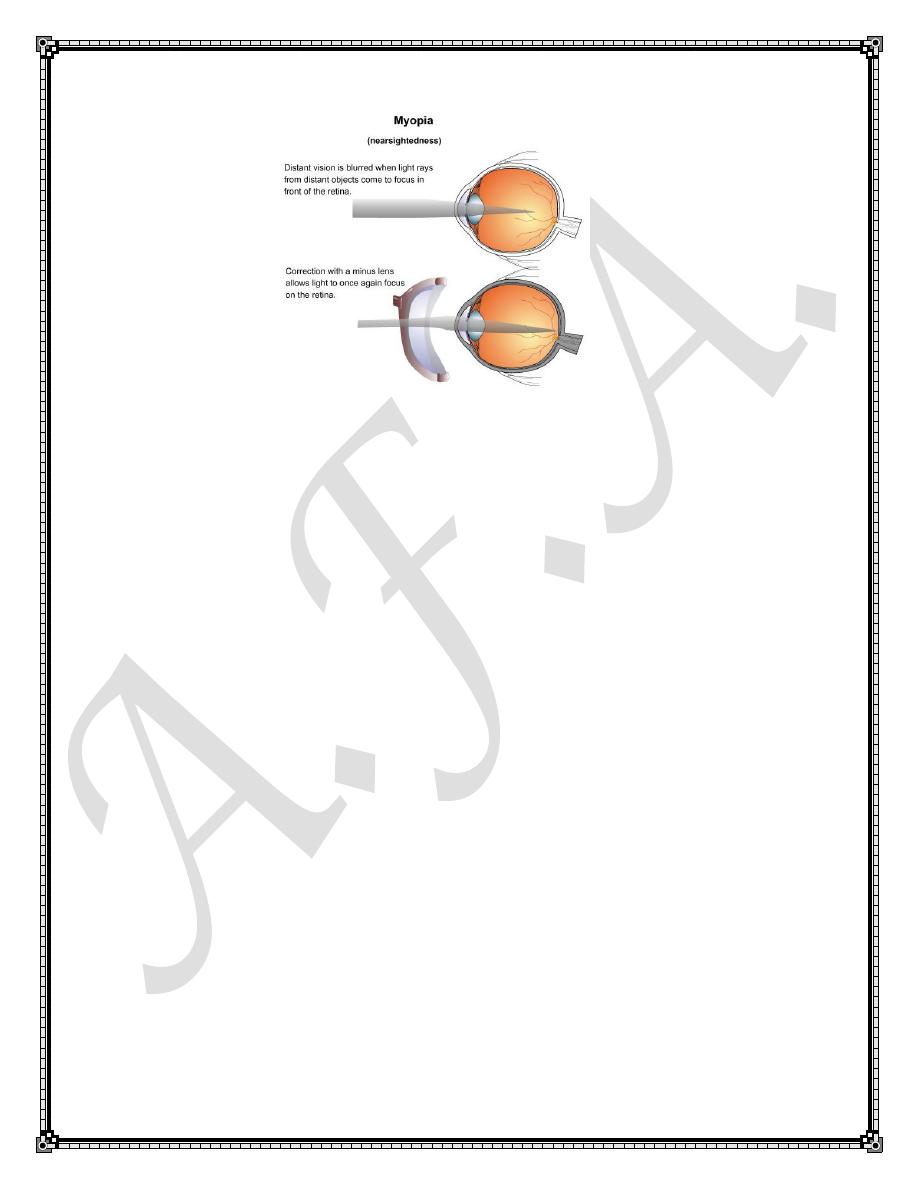
The myopic eye possesses too much optical power for its axial length. In
myopia light rays from an object at infinity converge too soon and thus focus
in front of the retina .The main symptom is blurring of vision especially for
far.
Myopic eyes tend to be large with deep anterior chamber
Aetiology :
1.Axial Myopia :
2.Refractive Myopia :e.g nuclear sclerosis and keratoconus .
According to the degree of refractive error (measured in Diopter), myopia
can be classified into:
1.Simple myopia (5-6 D)
2.Pathologic myopia ( more than 6D):-associated with progressive
excessive elongation of the globe often followed by degenerative changes
involving the sclera, choroid, Bruches membrane ,RPE and the sensory
retina .
Signs of pathological Myopia include:
1. Tilted optic disc and peripapillary atrophy.
2. Chorioretinal atrophy involving the posterior pole and / or the retinal
periphery .
3.Macular changes
4.Retinal detachment .
5.Cataract and lens subluxation.
6.increased prevalence of primary open angle Glaucoma.
7.Posterior staphyloma which is an out bulging of the thinned sclera at the
site of exit of the optic nerve.

Treatment:-
Patients with pathological myopia should have their Fundi routinely
examined with well dilated pupils and their visual symptoms taken seriously.
Optical correction include
1.Concave (minus lenses)
2.contact lenses
3.Radial Keratotomy (old almost obsolete procedure).
4.Clear lens extraction :gives very good visual results but small
risk of retinal detachment.
5.Photorefractive procedures: PRK and LASIK the procedure
performed with excimer Laser which can accurately ablate corneal tissue to
an exact depth with minimal distruption of the surrounding tissue.Ablasion
of the central cornea 10 micrometers can correct 1D myopia. 6 - 12 Ds of
myopia can be corrected with this procedure.
6. Intraocular Collamer lens implantation (ICL) can correct up to
-17.0 Diopters of myopia.
Hyperopia:
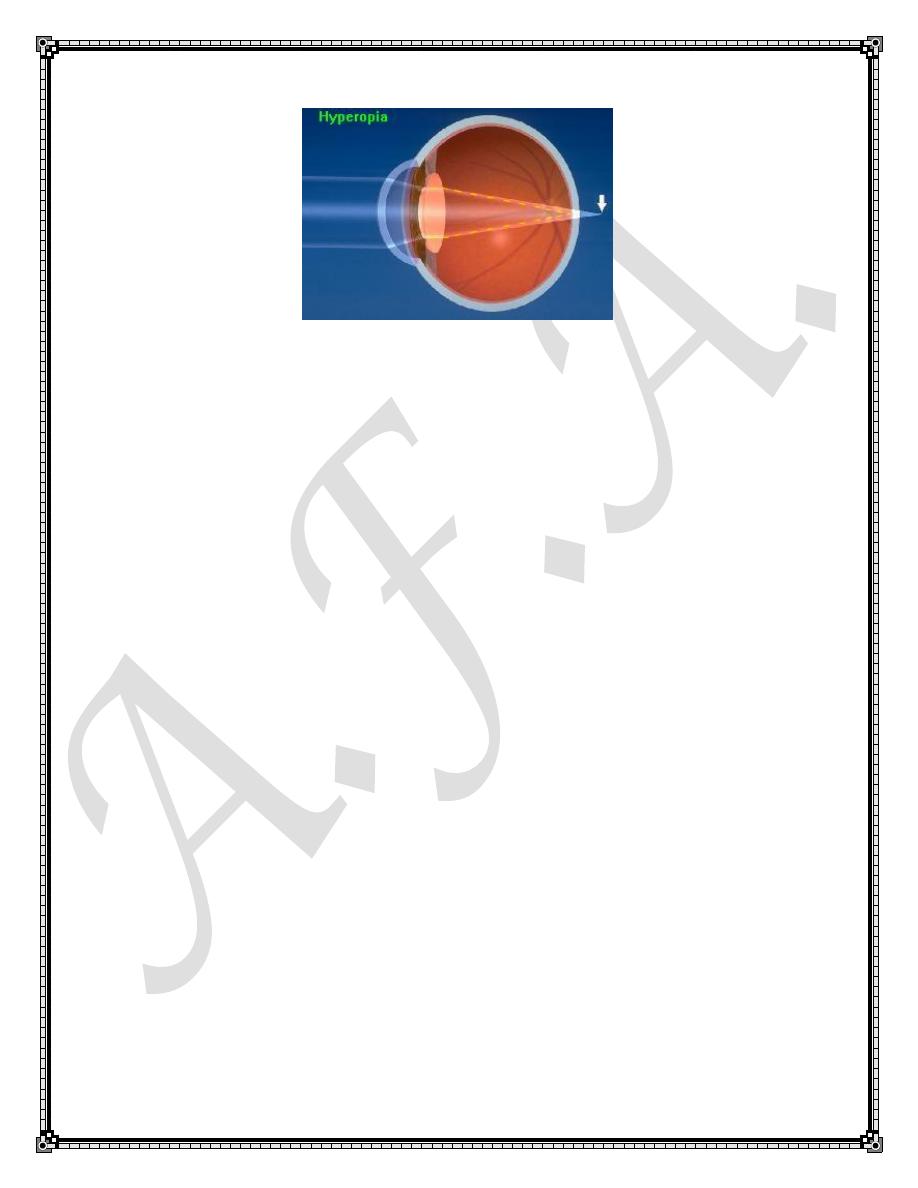
The Hyperopic eye does not possess enough optical power for its axial
length .
In hyperopia ,an object at infinity focuses behind the retina .
Accommodation :
In order to bring the images of nearer and nearer objects to focus on the
retina ,the optical power of the eye has to increase .This process is called
accommodation which usually occur in synergism with convergence and
pupillary miosis. Children usually have high ability to accommodate and this
in turn play a rule in development of some kinds of strabismus.
Aetiology:
1. Axial Hypermetropia.
2. Refractive Hypermetropia: e.g. when the cornea is flatter than normal for
that particular eye(curvature hypermetropia) which may be congenital
(cornea plana) or acquired (trauma to the cornea with subsequent scar
formation ).
Hypermetropia can be classified into:-
a. Total hypermetropia: is the amount of hypermetropia after all
accommodation is suspended (using cycloplegic drops e.g. atropine or
cyclopentolate).determination of total Hypermetropia is important in
management of children with strabismus.
b.Manifest Hypermetropia: is the strongest convex lens accepted for clear
distant vision.
c.Latent Hypermetropia:is the difference between total and manifest
hypermetropia.
At birth 90-95% of new born eyes are hypermetropic to the extent of 2.5-3D
because they have a short axial length .Thus , in the absence of strabismus
such children rarely need spectacles .
Clinical Features:
Blurring of vision esp. for near and symptom of eye strain like headache and
ocular pain due to excessive accommodation however some patients might
be almost asymptomatic especially in low degrees of hyperopia .
Hyperopic eyes tend to be bit smaller in size with shallower anterior
chamber than emmetropic eyes.
Excessive accommodation may result in excessive convergence and
esotropia
Treatment : after determination of the degree of R.E. , treatment options
include:
1.Convex (plus) lenses to bring the image from behind the retina a new
focus on it.
2. Contact lenses
3. Photorefractive Keratectomy(PRK) and LASIK can correct
hypermetropia by ablating the corneal periphery.LASIK can correct up to 6
Diopters.
Astigmatism
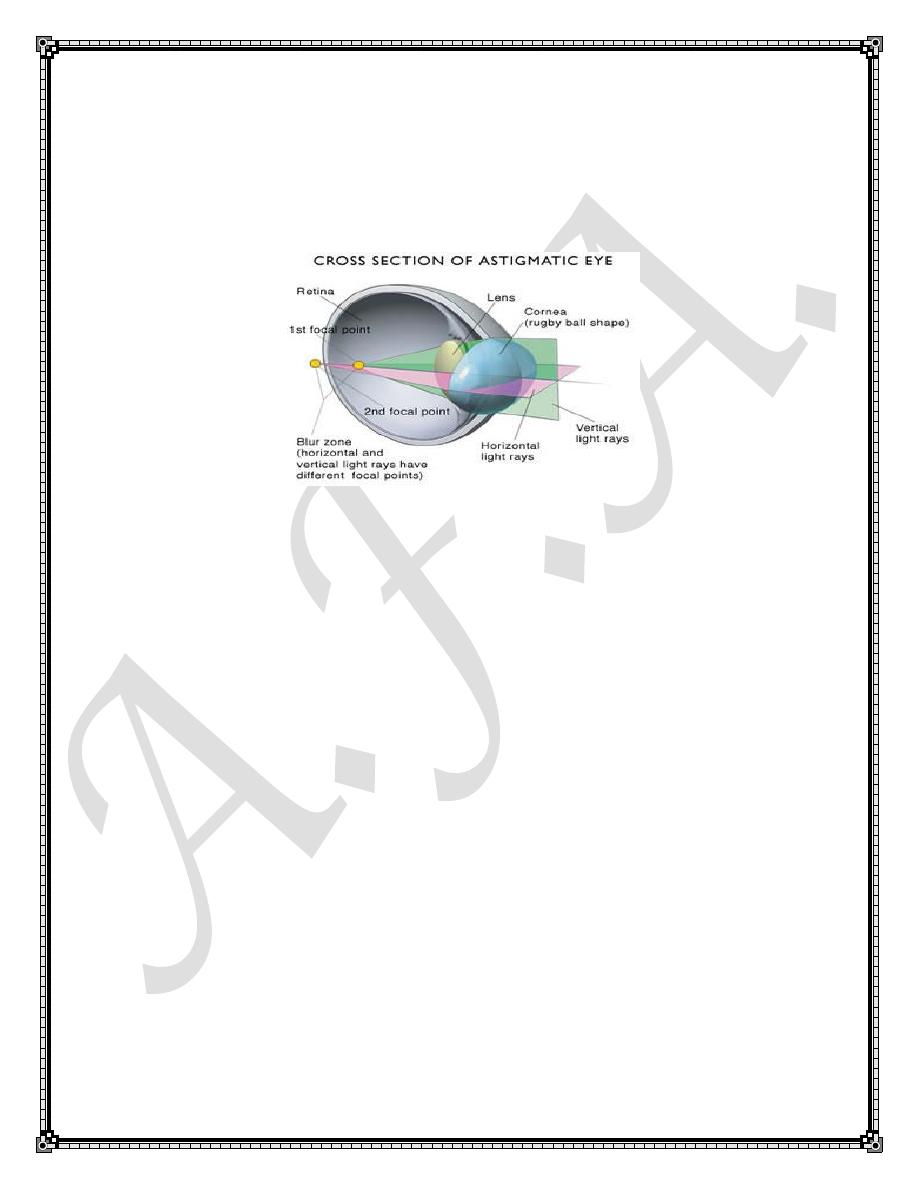
In astigmatism, variations in the curvature of the cornea or lens at
different meridians prevent the light rays from focusing to a single point i.e.
the refractive power of the eye varies in different meridians and a focus line
rather than point is formed .
Types of Astigmatism:
1) Regular Astigmatism :
the tow principal meridians are at right angle to each other and is correctable
with cylindrical spectacle lenses. it is further subdivided into:-
▪Simple myopic: one line focus lies on the retina and the other lies in front
of the retina.
▪Simple Hypermetropic: one line focus lies on the retina and the other lies
behind of the retina.
▪Compound Myopic: Rays in all meridians come to focus in front of the
retina.
▪Compound hypermetropic: Rays in all meridians come to focus behind of
the retina.
▪Mixed: one line focus lies in front of the retina and the other lies behind
the retina.
2) Irregular astigmatism:
If the orientation of the principal meridians changes from point to point
across the pupil,
Or if the amount of astigmatism changes from one point to another, the
condition is Known as irregular astigmatism. Cylindrical lenses can do little
to improve Vision in these cases, although rigid contact lenses may be
useful.

Treatment:-
1. Cylindrical lenses
2. Soft contact lense may be used if astigmatic error is less than 2D, while
rigid contact lenses may be used for higher degrees.
3. Photorefractive surgery weather PRK or LASIK.
4. Advanced Keratoconus may benefit from intrastromsl corneal rings or
even corneal grafting.
Presbyopia
Is an age related process represents loss of the eye to its ability to
accommodate for near objects . It usually manifest around the age of 40 .
Plus lenses are used to deal with this condition.
