د.منى زهير
Lec.8Ninth week to birth ( third month to birth ) or called the fetal period:
This period is characterized by:
rapid growth of the body.maturation of organ systems.
The age is indicated as the crown-rump (C.R.) length and the crown-heel (C.H.) length which is the measurement from the vertex of the skull to the heel (the standing height), it is expressed in centimeters.
During fetal period the growth in length is mainly during the 3rd, 4th and 5th months, while the increase in weight is mainly during the last two months of gestation.
One of the main characteristic changes occur during the fetal period is the relative slowdown in the growth of the head compared to the rest of the body. So:
In the 3rd month, the head is about 1/3 of the C.R. length.
By the 5th month it is about 1/3 of the C.H. length.
At birth it is about 1/4 of the C.H. length.
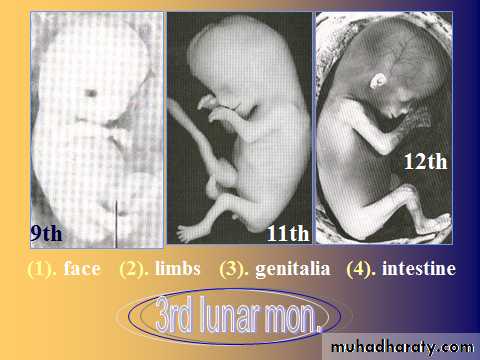
External Features During the third month:
The face becomes more human looking, the eyes initially lie on the sides, now they become on the anterior Aspect and the ears are on the lateral Sides.
Limbs are well formed and the primary ossification centers appear in long bones and skull.
External genitalia develop and the sex of the fetus can be determined by the 12 week.
By the end of the 12 week, the intestinal loops will drawn into the abdominal cavity,
Movements (Muscular activity) begin but not recognized by mother.
External feature during the fourth and fifth months :
The fetus lengthens rapidly and at the end of the fifth month, the C.R. length is 15 cm.
The weight increase little and at the end of the fifth month, the weight is less than 500 gm. .The head hair and eyebrows appear and the skin is covered by fine hair called lanugo hair.
During the 5th month, the movements of the fetus are recognized by the mother.
External feature during the sixth month :
The skin of the fetus is reddish and has a wrinkled appearance due to the lack of the underlying connective tissue.
A fetus born during the sixth month has a great difficulty to survive although several organ system are able to function, the respiratory system and CNS are not well differentiated.
External feature during the seventh month :
when the fetus is 28 weeks (7 months) it is able to survive but with difficulty.
External feature during the last two months :
The fetus obtains well-rounded contours as the result of the deposition of subcutaneous fat.
Weight increase greatly.
At the end of the ninth month or at the time of birth (full term) :
The skin is covered by whitish fatty substance called vernix caseosa which is secreted by the sebaceous glands.
Sexual characteristics are pronounced , and the testes should be in scrotum.
The skull has the largest circumference of all parts of the body.
C.R. length of the fetus is 36 cm and C.H. length is 50 cm. .
The weight is about 3000 – 3500 gm. .
Time of birth :
Expected date of delivery :
It is calculated as 266 days or 38 weeks after fertilization. the obstetrician calculates the time of birth as 280 days or 40 weeks from the first day of the last menstrual bleeding or period , this method is accurate in woman with regular 28 days menstrual periods.
The delivery date counts by submitting three calendar months from the onset of the last menstrual period and then adding a year and one week (or adding one week and nine months to the onset of last menstrual period).
In general most fetuses are born within 10-14 days of the calculated delivery date. if they are born earlier, they are referred as preterm babies, if later they are referred as post term babies.
If the fetus born at the expected date, but lighter in weight of normal (less than 2000 gm.) this referred as small for date (i.e. full term but low weight baby).
If the fetus born at the expected date, but heavier in weight of normal (more than 4500 gm.) this referred as large for date (i.e. full term but heavy weight baby).
Factors causing fetal growth retardation or intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) or small for date :
Maternal malnutrition.
Multiple pregnancy (twins).
Placental insufficiency : placental dysfunction (like in intravillous coagulation infarction) leads to fetal growth retardation.
Impaired uteroplacental blood flow : like in severe maternal hypotension or maternal renal disease.
Heavy smoking and alcohol.
Genetics and chromosomal abnormalities.
Maternal infection {e.g. rubella , cytomegalovirus (CMV) , toxoplasmosis}.
(Note : Diabetic mother may deliver large for date baby).
The age of the fetus can be determined by :
Estimating the time of fertilization.
Estimating the onset of last menstrual period.
Ultrasound :
By measurement of
C.R. length
C.H length
Biparietal diameter(BPD)
femur length
foot size.
By external features.