Cyclic Antidepressants Toxicity
Dr. Shamil AL-NuaimiCyclic Antidepressants Toxicity
CAs were first used in the 1950s to treat clinical depression.
The first report of the adverse effects of tricyclic overdose came within 2 years of their clinical use.
uses
In pediatric :enuresis,
obsessive-compulsive disorder,
attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder,
school phobia,
separation anxiety
In adults :
depression,
neuralgic pain,
chronic pain,
migraine prophylaxis .
Pathophysiology
The CAs are well absorbed orally and undergo significant first-pass metabolism in the liver.
They have a large volume of distribution and have long half-lives that generally exceed 24 hours.
After the CAs are metabolized in the liver via glucuronic acid conjugation, they are then excreted through the kidneys.
Toxic effects of tricyclics
Toxic effects of tricyclics are results of their 4 main pharmacologic properties:Inhibition of norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake at nerve terminals
Anticholinergic action
Direct alpha-adrenergic blockade
Membrane stabilizing effect on the myocardium by blocking the cardiac myocyte fast sodium channels
Mechanism of toxicity
Seizure :by increasing biogenic amines such as norepinephrine and serotonin at nerve terminalsAltered mental status :is mainly attributed to anticholinergic and antihistaminergic properties of CAs.
Hypotension :mainly a result of the well-recognized anti–alpha-adrenergic effect of the CAs
The effects of CA overdose on the cvs
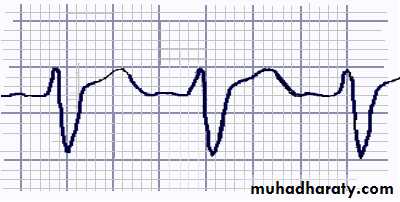
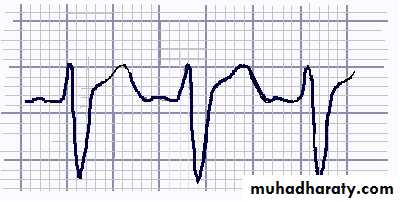
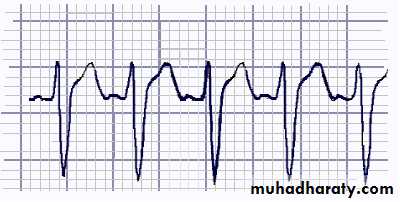
CAs, like the class IA antiarrhythmics, decrease the sodium influx through the fast sodium channels and consequently decrease the slope of phase 0, leading to the widened QRS complex that is typically seen on ECGs of CA poisoned individuals.Frequency:
Antidepressants are the third leading cause of toxic exposures in 2004 after analgesics and sedatives.The CA most frequently ingested in CA toxicity is amitriptyline, followed by doxepin and nortriptyline.
Amitriptyline exposure is associated with the most number of deaths among the various CAs.
Mortality/Morbidity: Fatality before reaching a healthcare facility occurs in approximately 70% of patients attempting suicide with CAs.
Only 2-3% of CA overdoses that reach a healthcare facility result in death.
Sex: the incidence of CA exposure is greater in women than in men because women are at a higher risk for suicide attempts.
symptoms
Onset of symptoms typically occurs within 2 hours of ingestion, which corresponds to the peak CA serum level, which may range from 2-12 hours.sypmtoms
CardiovascularPalpitation
Chest pain
Hypotension
CNS
Convulsion
Decrease mental status
Respiratory depression
Drowsiness
Coma
Peripheral autonomic system
Dry mouthDry skin
Urinary retention
Blurred vision
Anticholinergic Syndrome
Anticholinergic Syndrome:
Hot as hell
Blind as a bat
Red as a beet
Dry as a bone
Mad as a hatter
A sensitive indicator for ingestion, but poor predictor for toxicity.
PhysicalPhysical findings are usually consistent with the anticholinergic toxidrome and quinidine-like cardiotoxicity:
Tachycardia
Hypotension and orthostasis
Fever
Altered mental status
Ileus
Absent bowel sounds
Rigidity
Dry skin and mucous membranes
Mydriasis
Lab Studies
Studies have shown that serum CA level does not correlate well with severity of CA toxicity and is a poor predictor of clinical outcome.Because multisubstance ingestion is common, routine screening for other potentially treatable toxins is recommended (eg, acetaminophen). Request for the other serum toxicologic levels should be guided based on the clinical picture (eg, acidosis: aspirin, ethylene glycol, methanol)
Check electrolytes, BUN, creatinine, and anion gap.
CBC
Alcohol level
ABG for evaluation of acidosis or hypoxia
Imaging Studies
A chest radiograph should be obtained in cases of suspected aspiration or when respiratory symptoms are noted, and it may be used to rule out other causes of fever, tachycardia, and altered mental statusOther Tests
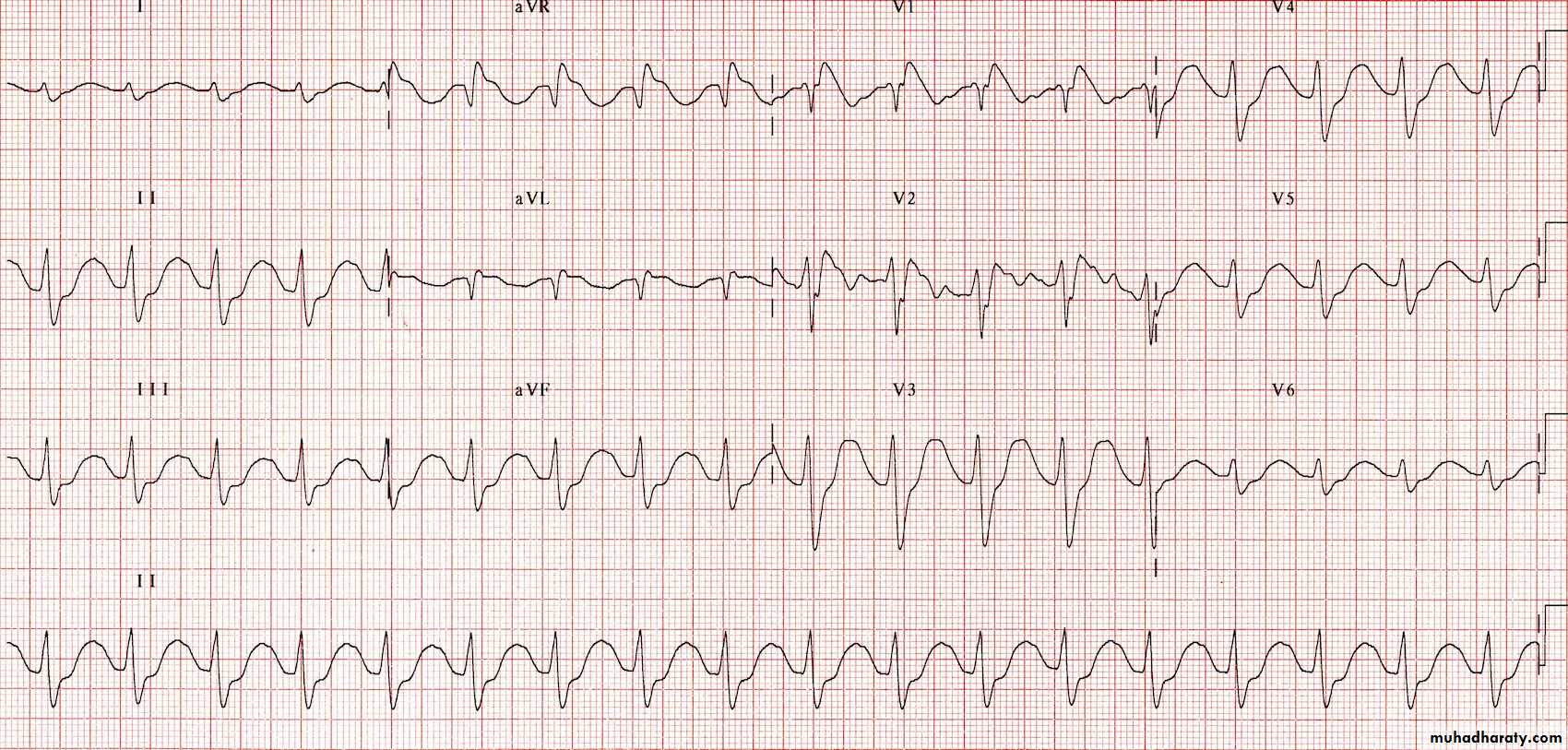
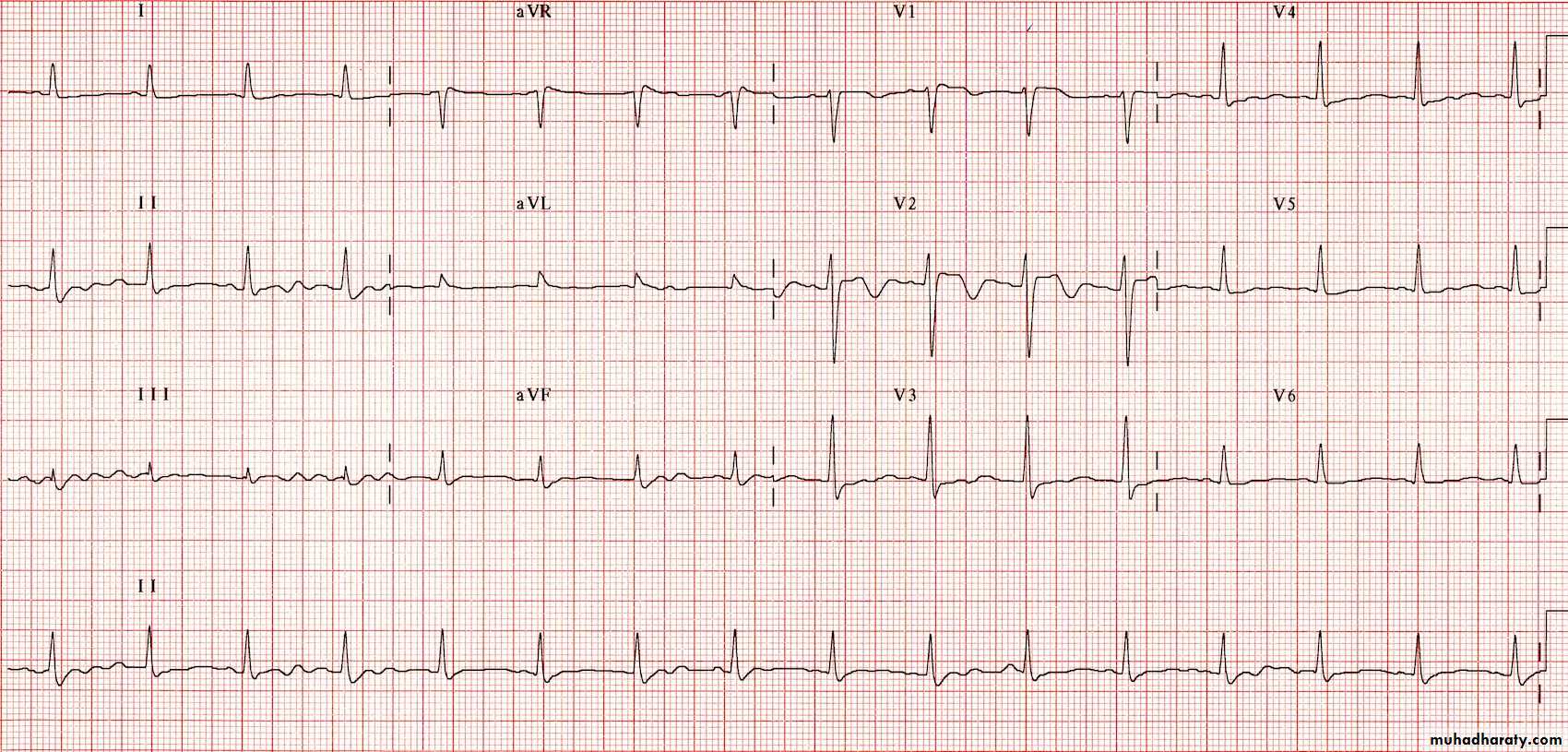
ECG - Sinus tachycardia is the most common ECG finding in CA toxicity.Measurement of limb-leads QRS duration can be used to assess severity of CA exposure. QRS interval of greater than 100 msec is the basis for treatment with bicarbonate (alkalinization).
Patients with QRS less than 100 msec are unlikely to develop seizures and arrhythmias.
Those with QRS greater than 100 msec have up to a 34% chance of developing seizures and up to a 14% chance of developing a life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia.
With QRS complex greater than 160 msec, chances for ventricular arrhythmias increase to 50%.
The greatest risk of seizures and arrhythmias occurs within the first 6-8 hours of CA ingestion.
For all patients with possible cyclic antidepressant toxicity :
airway protection,
ventilation and
oxygenation,
intravenous fluids,
cardiac monitoring, and
obtaining ECGs are all essential measures
Treatment
Airway: Endotracheal intubation may be necessary in patients who present with seizures or who are in a comatose state for airway protection.Hypotension
Normal saline intravenous fluids are indicated for CA-induced hypotension.
For hypotension refractory to intravenous saline, vasopressors, such as norepinephrine, with alpha-agonist effect, may be used.
GI decontamination: Once the patient is stabilized, activated charcoal can be considered.
Intravenous sodium bicarbonateSerum alkalinization with intravenous sodium bicarbonate has been the mainstay of therapy in CA-induced cardiovascular toxicity. Prolonged QRS is most often the indication for serum alkalinization in CA toxicity.
Serum AlkalinizationIndications
HypotensionECG abnormalities
QRS prolongation
arrhythmias
Seizures
CNS depression requiring intubation
not a strict indication
HA
H+ +A-
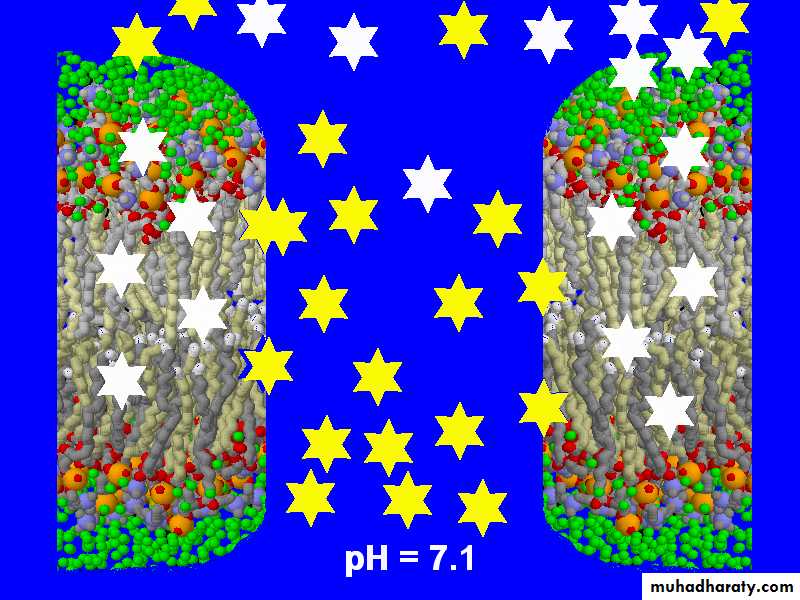
Drugs and Receptors can be considered to be weak acids or bases.
Equilibrium influenced by external pHThe balance of the equilibrium can be expressed by pKa
The pKa is the pH where [ionised] = [non-ionised]
Henderson-Hasselbach
For basic compounds:pH = pKa + log (non-ionised/ionised)
ionised/non-ionised = 10 (pKa – pH)
HA
H+ +A-
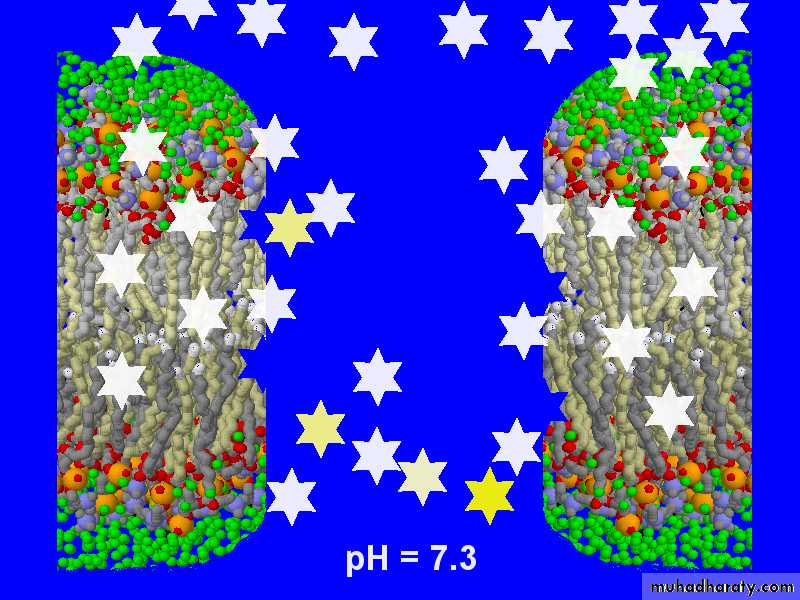
TCA: pH = 7.1
TCA: pH= 7.3
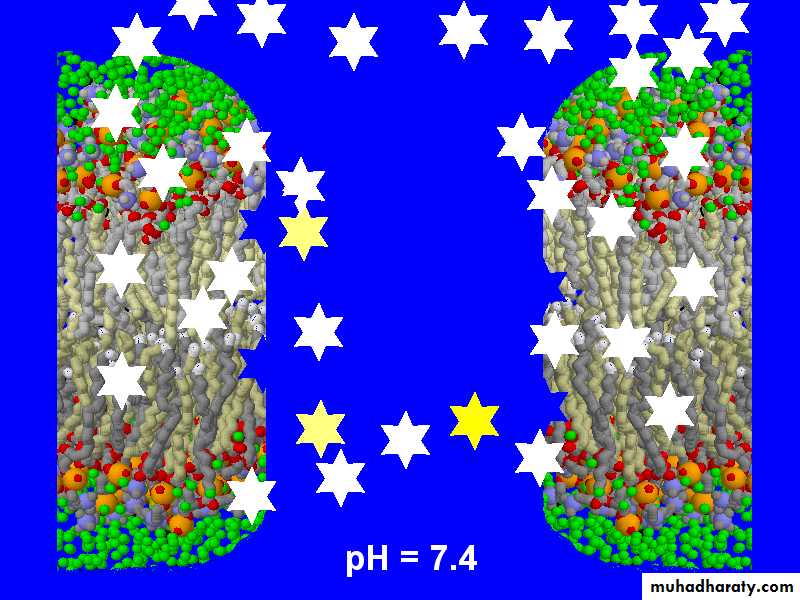
200 mEq bicarbonateTCA: pH =7.4
200 mEq bicarbonateBenzodiazepines
The seizures in CA toxicity are usually self-limited. The treatment of choice for prolonged or recurrent seizures in cyclic antidepressant toxicity is a benzodiazepine.Most CA-induced seizures are usually brief and resolve prior to the administration of anticonvulsants.
General anesthesia should be reserved for patients in status epilepticus who are unresponsive to the standard treatment regimen
Further Inpatient Care:
Level of conscious and ECG changes at presentation are the most sensitive clinical predictors of serious complications.
CA toxicity typically lasts 24-48 hours following a significant overdose. However, case reports exist demonstrating prolonged CA toxicity as long as 4-5 days. Amitriptyline is the drug most commonly implicated in these cases.
Consider ICU admission for any ECG changes.
Medical/Legal Pitfalls:
Use of physostigmine in CA poisoning has been associated with complete heart block, asystole, and hypotension.Ipecac syrup is not recommended as the procedure in GI decontamination because of the possibility that patients experience sudden neurologic deterioration (eg, lethargy, seizures) and aspirate.
Use of type IA and IC antidysrhythmics or other sodium channel blockade agents may exacerbate toxic effects of CAs on the myocardium.
Use of flumazenil for reversal of benzodiazepines overdose with concomitant CAs exposure can precipitate seizures
Serum AlkalinizationMonitoring Parameters
Don’t hang the bag and walk awayMonitor serum pH every hour until within range, then back off
Monitor potassium closely
Monitor serial ECG’s