
The Cytoskeleton and Cell Movement –Related Parts
Microfilaments, Centrioles, Cilia, Flagella
If we see an amoeba under the microscope and how its move ?
Its cytoplasm seems to flow or stream alternating between a watery condition (fluid –
state) and a firm jelly like condition (jell-state).this fluid –Gel action or called
cytoplasmic streaming move the animal from place to places, it push out projections
called pseudopodia or false feet .
There are white blood cells in man
'
s blood that can move in this way.
Microfilaments
:
Made up of protein actin and myosin within the cell cytoplasm.
Are thought to contract in much the same way as our muscle do to move our bones .its
function:
1-These sub –microscopic cell muscles leave and pull and support the cytoplasm.
2-they act as a sort of cell skeleton (cytoskeleton).
Microtubules and Centrioles:
Are found in animal cells but not in plant cells.
They are extremely small tubules (microtubules) located in the cytoplasm near
the nucleus ,as pairs structures in non dividing cell(centrosome containing two
centrioles that lie at right angle to each other). During cell division, microtubules
form spindle fibers, which assist the movement of chromosomes.
By electron microscope it show that in cross section they are a bundle of microtubules
arrange as 3 in a circle of 9 9this called the 9+0 pattern) and no doublet in the center.
When the cell begin undergo division ,one of the pairs moves around to the opposite site
of the nucleus from the other centriole .Fibers spread out from each centriole towered the
center of the cell and in some way act to move the chromosomes in cell division (mitosis
or meiosis).
Its function :1-organize the spindle apparatus on which chromosomes move during
mitosis or meiosis.
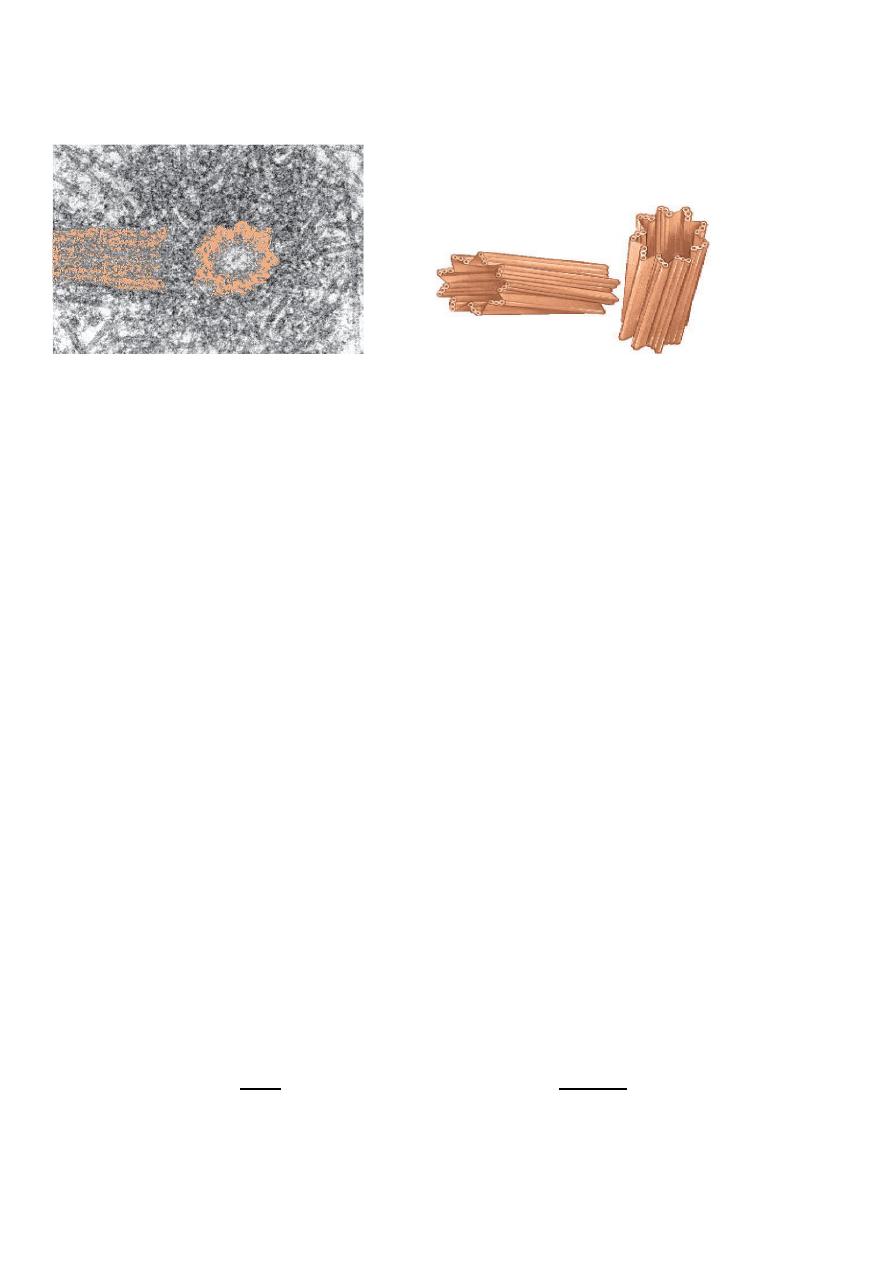
2-neede to make cilia and flagella
Cillia
:
Are hair like projection from cell membranes. They move like oars of a rowing
boat ,driving fluids across the surface of the membrane.
Cilia are found lining the oviduct ,drive the fluid in which eggs are transported
.They also found lining the trachea ,move the slimy mucous that traps dust
particles in the air we breathe in and prevents dust getting into our lungs.
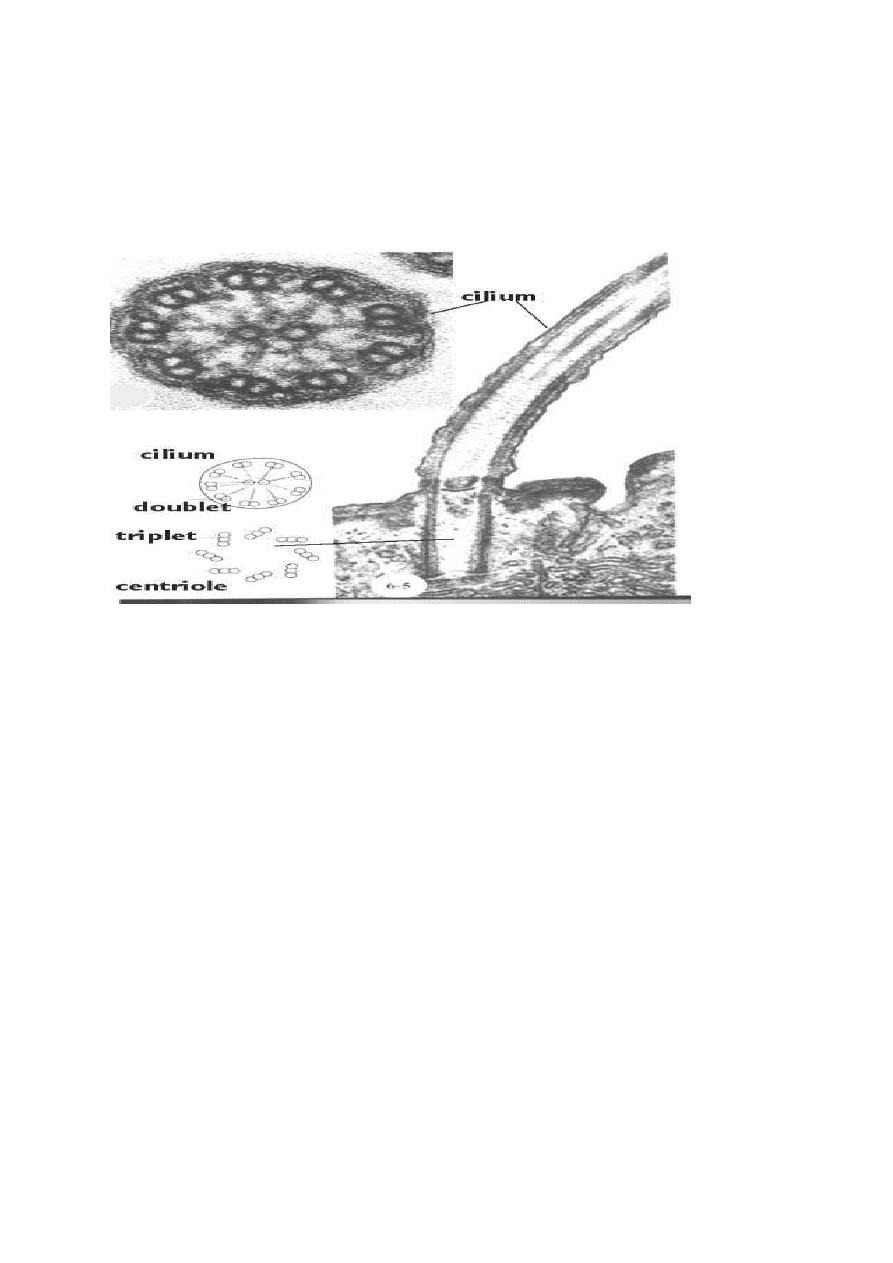
Both cilia and flagella have the same basic structures which are
composed of doubles of microtubules arranged as 2 in a circle of 9 and
doublet in the center (this called the 9+2 pattern).
A cilium is about 20
times shorter than a flagellum but both have Motor molecules, powered
by ATP, allow the microtubules in cilia and flagella to interact
and bend, and thereby move.
Each cilium or flagellum grows out from ,and remains attached to a
basal body in the cytoplasm.
Flagella
:
Are similar to cilia but they are longer and lash a boat like whips to drive an
animal or a cell through a liquid .The tail of the sperm whip like flagellum.
Cilia Flagella
1- Smaller ,many hair like larger ,single whip like
2-found in apical surface facing lumen found in the position to locomotive
Or cavity e.g epithelium tissue ,trachea cell e.g. sperm, bacteria
3-move fluid to transport or passed the cell locomotion for the cell drive the cell
through the fluid
Structure of cilia and flagella
Transport between cells and their surroundings
Cells are grouped together to form tissues , where the membrane of one cell touches
that of another ,they tend to join specializations ‟structure” that form intracellular
junction within a tissue of multi cellular organism.
The epithelial cells, and
sometimes the muscle and nerve cells, of a tissue are connected by cell junctions.
These junctions help a tissue perform its particular function.
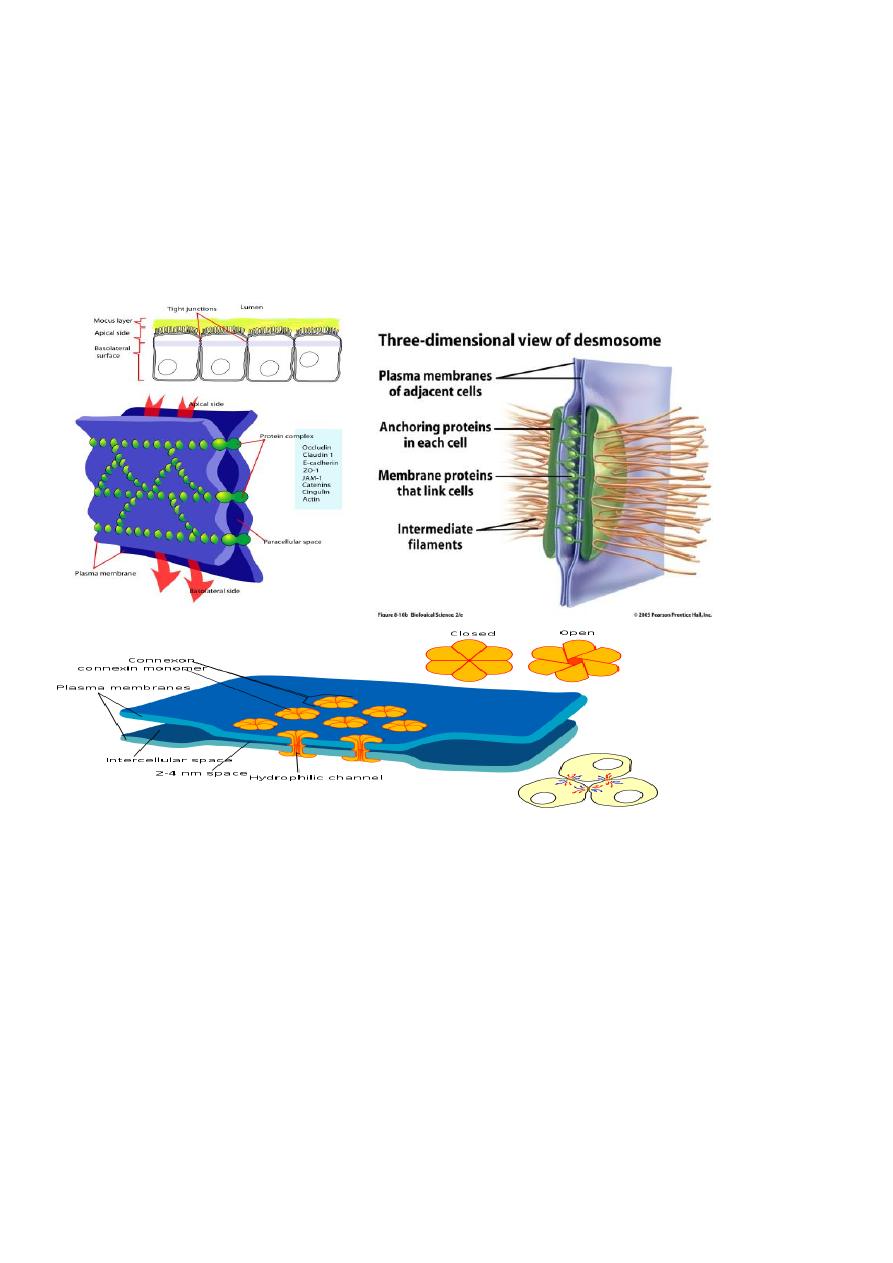
Cell junction are of different sorts: (F1)
1-Tight junction 2-Desmosomes 3-Gap junction
1-Tight junction (by tight junction protein):
Are protein from each membrane fuse together .Their function:

1- They hold cells together, allow epithelial cells to form a layer that covers the
surface of organs and lines body cavities.
2- They block the movement of integral membrane proteins allowing the specialized
function of each surface.
3- They prevent the passage of molecules and ions through the space between cells
,while material must enter the cells by diffusion or active transport in order to pass
through the tissue. . The layer of cells becomes an impermeable barrier because
adjacent plasma membrane proteins join, producing a ( zipperlike fastening ). In
the stomach and intestines, digestive secretions do not leak between the cells into
the body. In the kidneys, the urine stays within kidney tubules because epithelial
cells are joined by tight junctions.
2-Desmosomes:(by intracellular thin filaments)
Cell to cell Links by means of thin filaments ,its made up by:
1-Desmosome core : extracellular space between two cell membrane.
2-Desmosome plaque: thick layer of dense material ,just between the plasma
membrane.
3-Desmocollins: filaments and granules of glycoprotein found inside core which bind
p.m. together.
So In This Junction keep cells anchored to one another, but the layer of cells can still
bend and stretch.
Adhesion junctions are common in tissues subject to mechanical
stress. They allow the skin, for example, to stretch and bend in response to mechanical
stress.
Gap junction: (by membrane channels protein)
The cells are joined by means of protein channels between the membranes across
which substances such as salts ,sugars ,amino acids ,vitamins and water may be
transported.
So in this junction the two closely opposite membranes are separated by 20-40
ₒ
A
space or gap.
Their functions:
1-it lend strength to the cell.
2-allows small molecules and ions to pass between them.
E.g skin ,cardiac and smooth muscle and all virtually tissues of the body exept motile
cell type(sperm ,blood cells).see Figure
Movement across cell membrane:
Cell membrane are semi permeable or selectively permeable,(small, non charged ,lipid
soluble molecule can pass through the pores whilst other large and small molecules
cannot).So cell membrane have a very important job because they must prevent
poisons from entering the cell but allow foods, water, and oxygen to enter. The
method of passing through cell membranes can be as:
1-Endocytosis 2- exocytosis 3-Diffusion 4-Osmosis
5-Active and facilitative transport

1-Endocytosis: as active ways = vesicle transport ,need energy)
Large molecules or other materials can enter the cell by endocytosis ,such as protein,
lipids, liquids solids---.
A- Liquids can be packaged into a vacuole or vesicle which is then taken into the cell
.This called "Cell drinking " Pinocytosis. In this process ,small invagination of the
cell membrane form and entrap extracellular fluid ,anything solves in the fluid
,pinocytosis vesicle pinch off from the cell surface → fuse with the lysosome to be
digested inside them.
The cycle: small invagination form (fluid ,entrap)→inside pinocytosis vesicle+
primary lysosome →pinolysosome → fluid digestion.
B- Solid can also be taken in this way ,called Cell eating Phagocytosis .It's the method
used by white blood cells when they eat up microbes (bacteria) that may invade our
bodies ,it's done by phagocytes cells such as macrophage and neutrophils. In this
process ,pseudopodia extension from cell membrane of phagocytic cell surrounding
the bacteria and fuse together forming vesicle called phagosome ,then phagosome fuse
with primary lysosome to form phagolysosome ,where bacteria is broken down.
The cycle :pseudopodia from phagocyte cell (bacteria)→inside phagosome +
lysosome → phagolysosome →bacteria broken.
C- Receptor mediated endocytosis(RME):these receptors for main substances such as
hormones are located in the cell membrane ,so special coated pits are lined with
receptor protein that bind with specific material, filled with it to form vesicle to
transport the material.
The cycle :special coated pits lined with receptor protein integral protein of p.m.
hormones bind → filled in receptor protein → coated pits formed vesicle →material
transport. see Figure
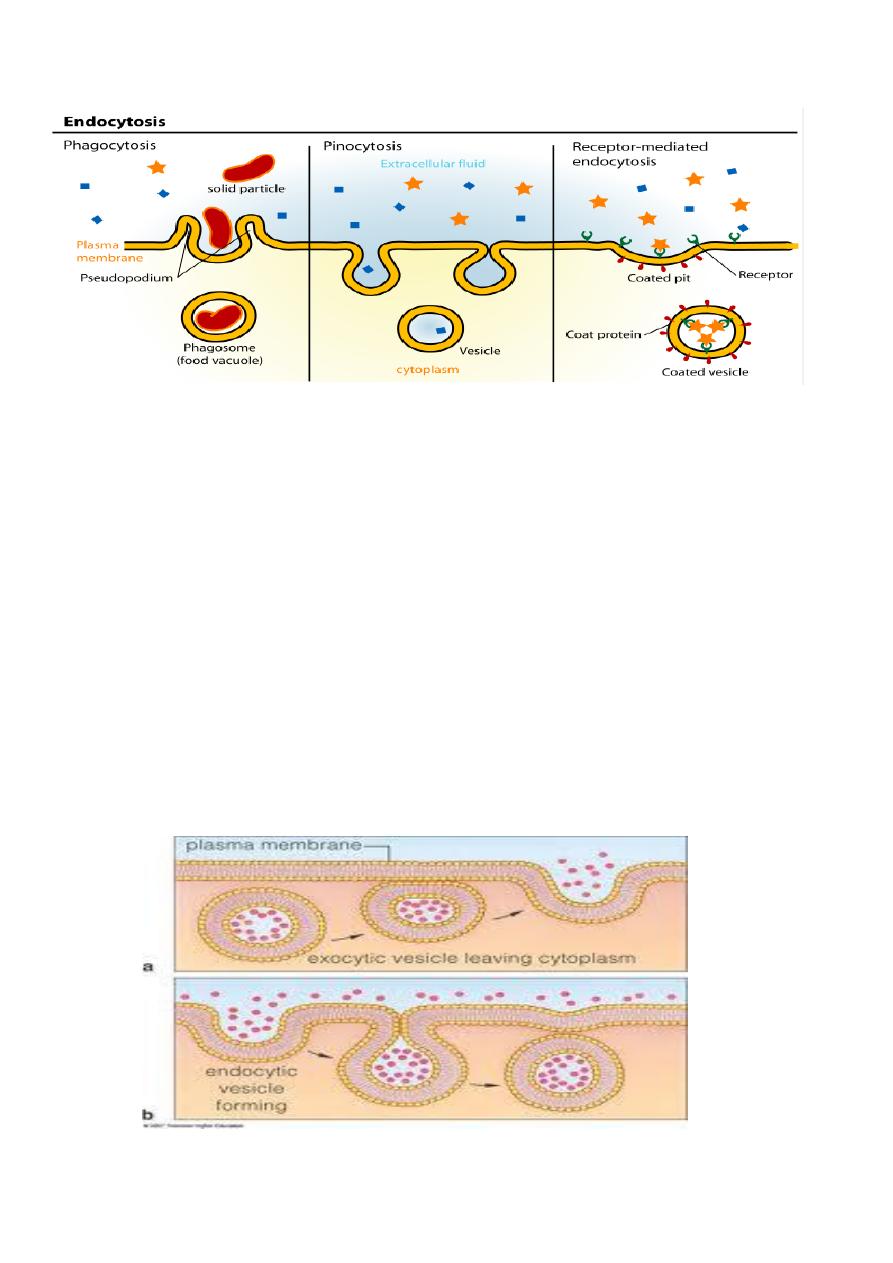
2-Exocytosis: (as active ways = vesicle transport ,need energy)
Many substances that may be exit from a cell ,e.g. the secretion produced by Golgi
apparatus need to leave a cell to do their job .Exocytosis is reverse of endocytosis
.These secretions or enzymes are packaged into vacuoles and then moved towards the
cell membrane where they are discharged, So the cellular product are secreted into
extracellular environment. Atypical example the stored product from the secretory
cells ,such as exocrine gland in pancreas and salivary gland .Finally large molecules
(proteins ,nucleic acids ,poly peptides and poly saccharides are not carried by
transport protein but it needs exocytosis or endocytosis. See Figure

3.Diffusion :(passive ways = not need energy)
Its occurs in many day to day situation ,as perfume molecules or bad smell will diffuse
through the atmosphere of a room and colored dyes added to water will diffuse
throughout the water ,all of them move molecules from area of high concentration to
an area of lower concentration ,so this movement is called "Movement down a
diffusion gradient" or "Concentration gradient" .Water and oxygen molecules
seen to be able to diffuse back and forth across cell membranes, because membranes
are semi permeable or selective permeable.
4-Osmosis: (passive ways = not need energy)
This is the diffusion of water across selectively permeable membrane ,from an area of
high concentration of water to area of low concentration of water only the water
molecules are able to cross the membrane .
.The water is able to pass through the membrane and there by dilute the salty or
sugary solution on other side. As the water accumulates on the solution side of the
membrane ,it produces pressure called "Osmotic pressure". The effect of osmosis
depend upon the deference on concentration between the solution on either side of the
membrane ,.
When we give blood or other body fluids to patients we must be very
careful that the osmotic concentration is correct. Osmotic pressure controls water
movement in our bodies. For example, in the small and large intestines, osmotic
pressure allows us to absorb the water in food and drink. In the kidneys, osmotic
pressure controls water absorption as well.
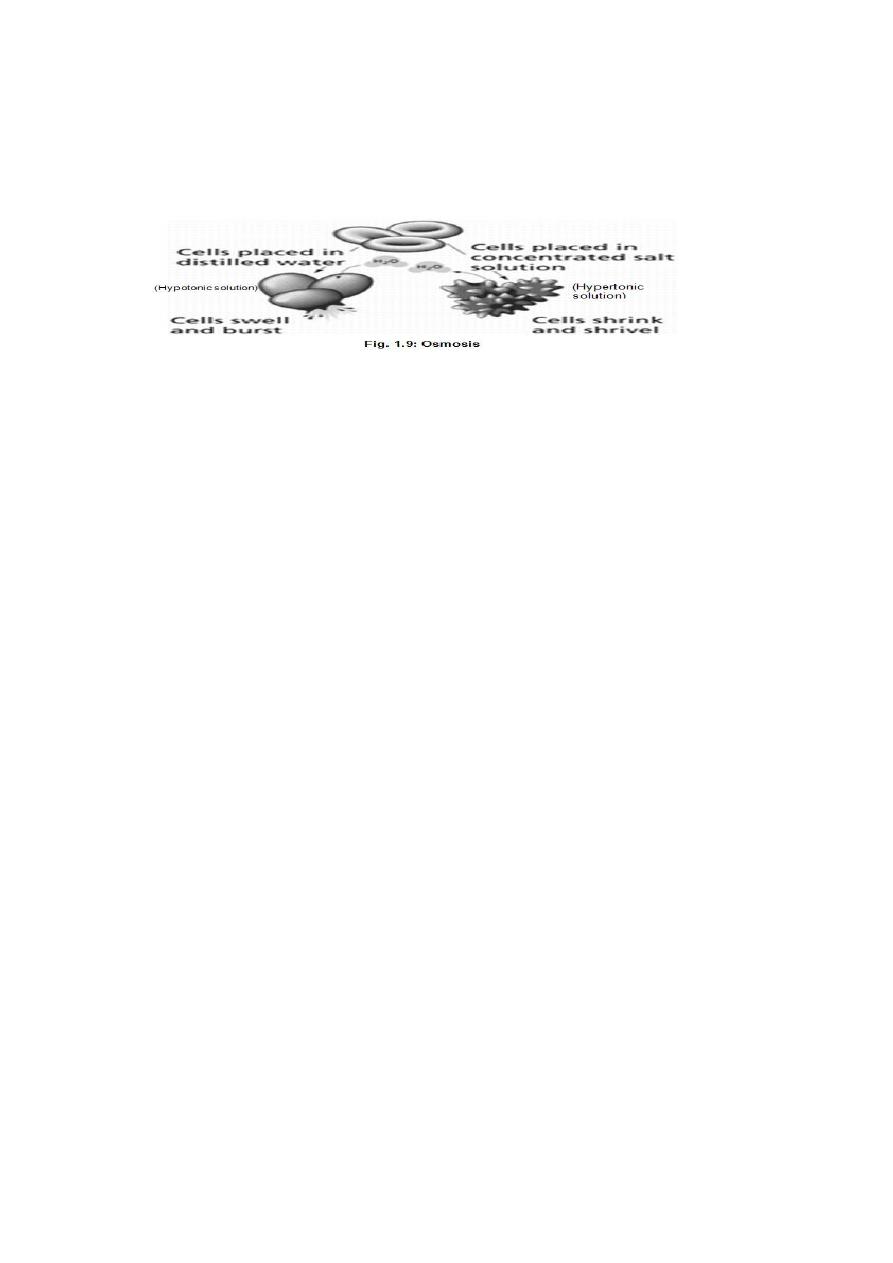
Tonicity. The arrows indicate the movement of water.
Isotonic solution :solution are equal strength to our body fluids ,cause neither
shrinking nor swelling of cells and tissues .A 0.9% solution of normal saline (or
NaCl) is isotonic with our R.B.C.
Hypotonic solution : solution contain less dissolved material and more water than the
body fluids .This water passes into the cells by osmosis and causes then to swell up
and burst. A solution of salt weaker than 0.9 % is hypotonic to R.B.C. cause
haemolysis (swelling and burst).
Hypertonic solution :solution contain more dissolved material and less water than the
body fluids ,water leaves the cells by osmosis and causes then to shrink .A 10%
solution of NaCl is hypertonic to R.B.C. and will cause them to shrink because of
withdrawal of water.
So ,the strength of a solution in relationship to osmosis called "Tonicity".
5-Active transport : (as active ways, need energy)
That chemicals and water tend to move against concentration gradient ,which uses
energy to pump materials into the cell.
Cells that accumulate and store materials use this transport method .e.g. the thyroid
gland cells collect iodine from the blood ,. Sodium (Na+) is sometimes almost
completely withdrawn from urine by cells lining kidney tubules
+
so that water follows
by osmosis if this didn’t occur we would be in constant danger of dehydration because
of water loss by kidneys (kidney cells have a large number of mitochondria to
produced energy ).
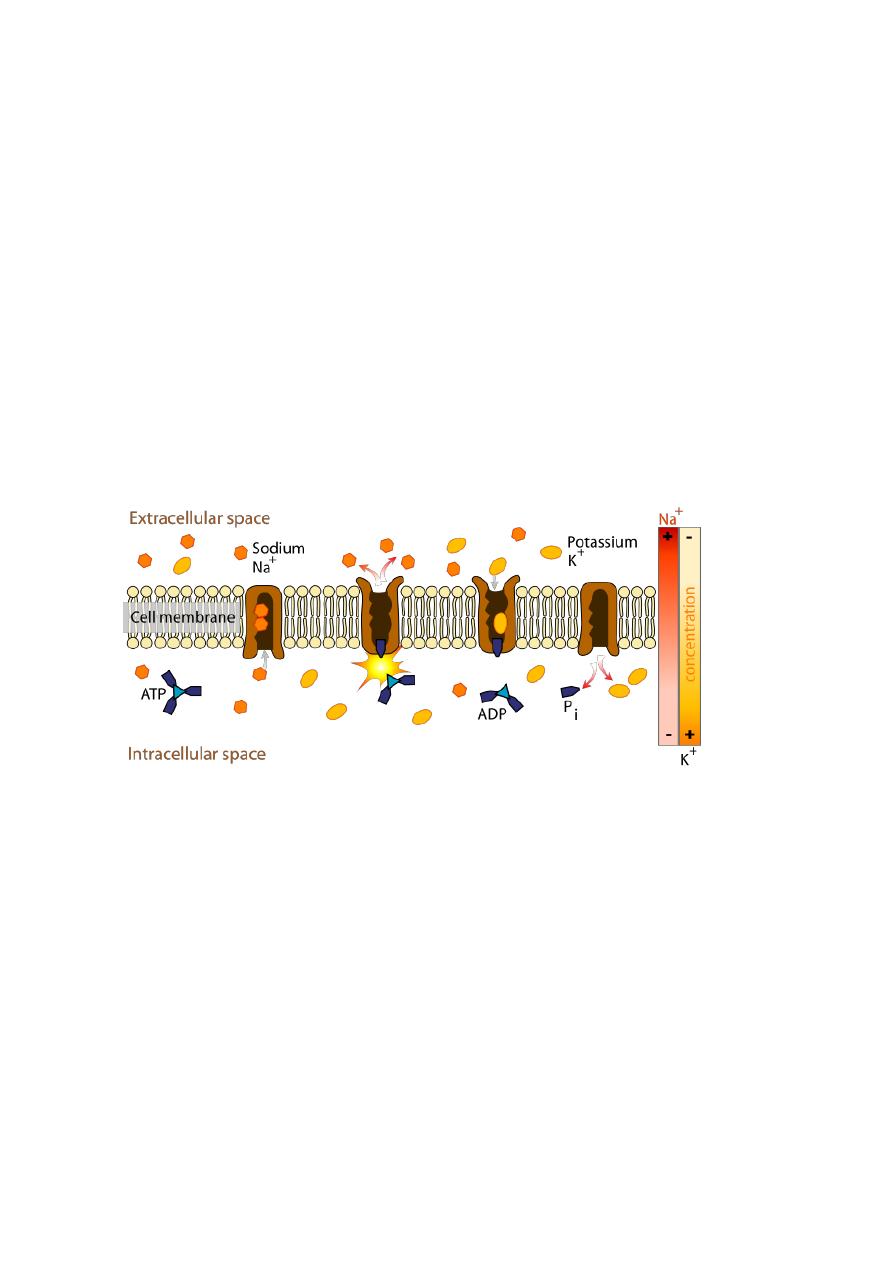
Active transport requires a protein carrier and the use of cellular
energy obtained from the breakdown of ATP. When ATP is broken down, energy is
released. In this case, the energy is used to carry out active transport. Proteins
involved in active transport often are called pumps. Just as a water pump uses energy
to move water against the force of gravity, energy is used to move substances
against their concentration gradients. One type of pump active in all cells moves
sodium ions (Na+) to the outside and potassium ions (K+) to inside the cell ( see Fig.).
This type of pump is especially associated with nerve and muscle cells.
6-Facilitated transport (as passive ways, not need energy)
Is faster diffusion ,take place along special protein pathways in the cell membrane
across which chemicals can pass quickly .In this transport the integral protein in p.m.
helps the movement of glucose ,amino acids and nucleotides into the cell quicker than
would be expected for normal diffusion processes with its concentration gradient, so
no need energy.
Two types of integral protein need:
1-Channel protein :form a water filled pore or channels in the membrane ,to allow
charged substances like ions to diffuse across the membrane.
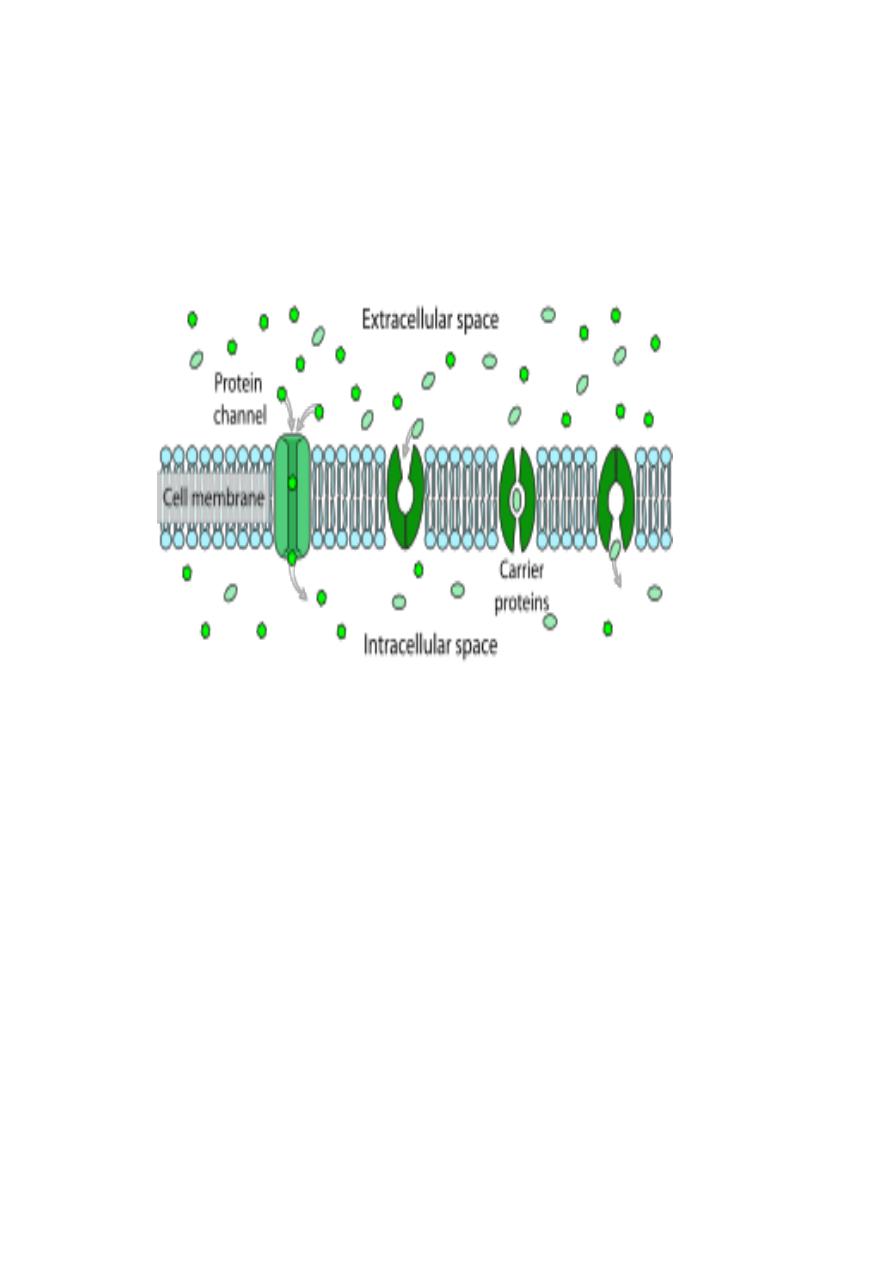
2-Carrier proteins :have binding site for specific substance as a solute .which only
bind where is high concentration and be released where is lower concentration .as in
"glucose carrier "
Diabetes type 2 results when cells lack a sufficient number of
glucose transporters..
