د.منى زهير
LEC. 6Trilaminar germ disc
Third week of development :
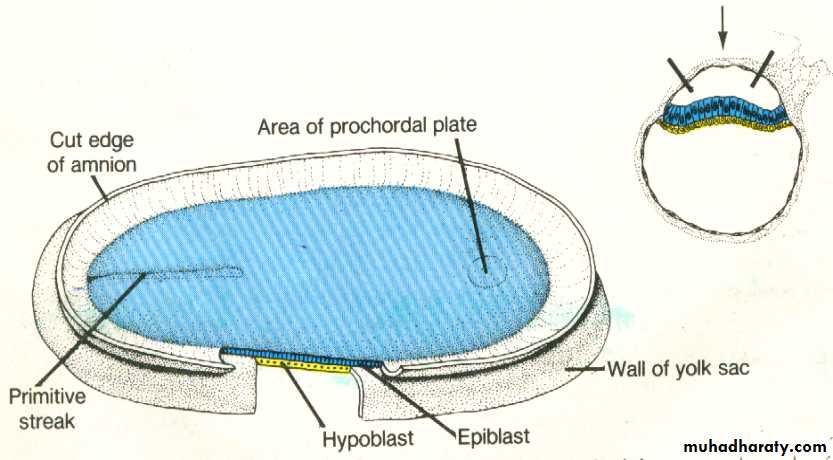
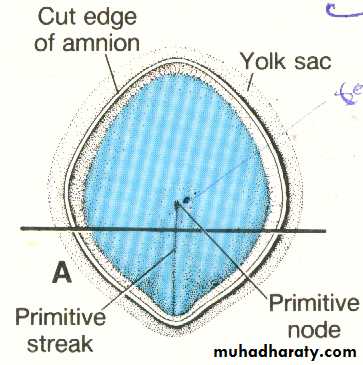
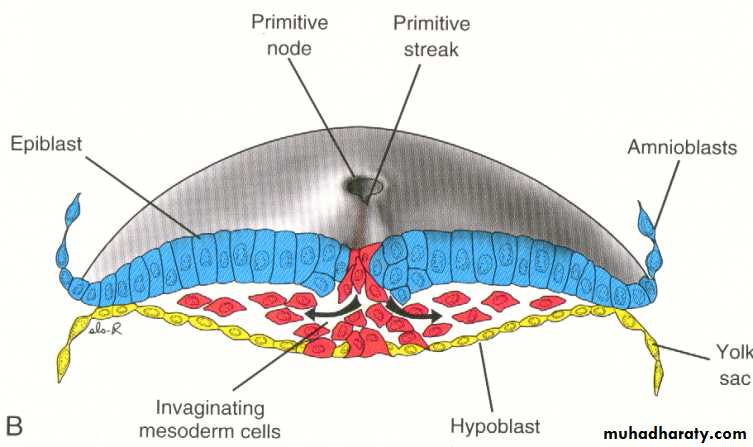
The most characteristic event occurring during the third week is gastrulation which is the process of establishment of the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm , and endoderm ) [these three layers known as trilaminar germ disc] gastrulation begins with the formation of the primitive streak on the surface of the epiblast as a narrow groove with elevated areas on either sides. The cephalic end of the streak which is called the primitive node consists of a small pit surrounded by elevated area.Note : after the formation of primitive Node it becomes possible to identify the craniocaudal axis of the embryo , it's dorsal and ventral surfaces and it's right and left sides.
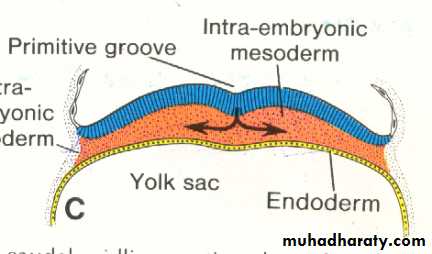
Epiblastic cells will migrate toward the primitive Streak and on arrival in the region of the streak , they invaginate detach from the epiblast and move beneath it , forming an intermediate cell layer , known as intraembryonic mesoderm (Or the third germ layer) some of the detached (or invaginated ) cells will displace most of the hypoblast , creating the embryonic endoderm . cells remaining in the epiblast will form the ectoderm.
The intraembryonic mesoderm will spread in lateral and cephalic directions establishing a contact with the extraembryonic directions , in the cephalic region , it move on each side of the prochordal plate to meet each other in front of this area forming the cardiogenic or heart forming plate.
Formation of notochord :
Cells invaginating in the primitive pit move forward in cephalic direction till reaching the prochordal plate forming a tube like process called notochordal process. the process then fuses with the underlying endoderm forming the notochordal plate , with further development , the cells of the plate proliferate and detach from the endoderm forming a solid cord of cells called the definitive notochord , which forms the basis for the axial skeleton , and it extends from the prochordal plate to the primitive node.at the primitive node , a small canal (the neurenteric canal) temporarily connects the amniotic and yolk sac cavities .
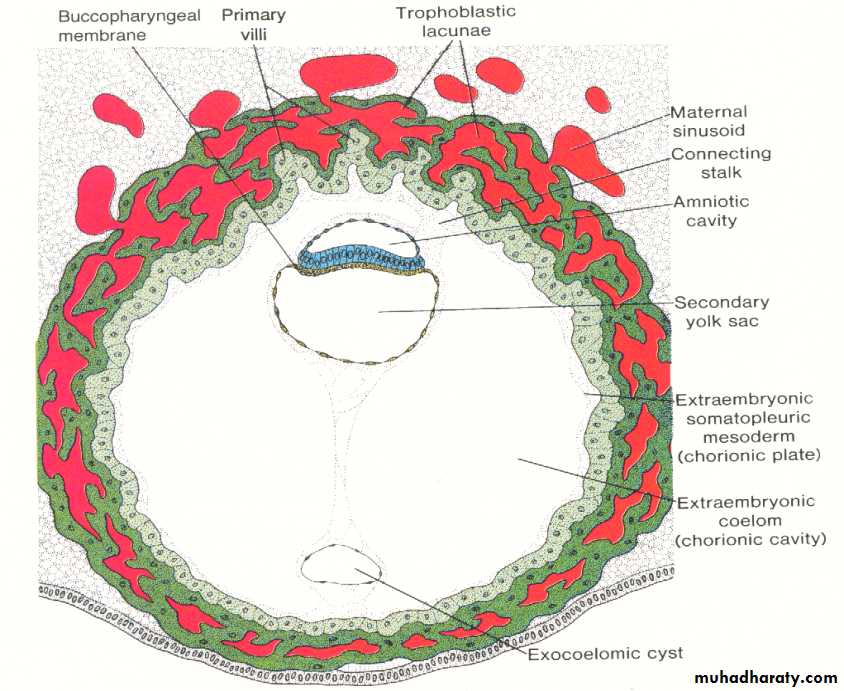
By the middle of the third week the mesoderm and notochord separate the endoderm and ectoderm entirely , except in the prochordal plate (cephalically ) and in the cloacal membrane ( caudally ). both regions consist of tightly adherent ectoderm and endoderm. with the appearance of cloacal membrane , the caudal wall of the yolk sac will form a small diverticulum which extends into the connecting stalk , known as allantois.
Growth of Germ Disc :
The initial germ disc is flat and circular , gradually becomes elongated with abroad cephalic and a narrow caudal ends. the growth and elongation of the cephalic part of the disc are caused by continuous migration of cells from the primitive streak in the cephalic direction.the process of migration and invagination of cells through primitive streak continue to the end of the fourth week , after that the primitive streak will decreases in size , degenerates and disappears. if remnants of the primitive Streak persist , at birth it will cause tumors in the sacrococcygeal regions (sacrococcygeal teratoma) these tumors contain tissues derived from the three germ layers.
formation of villi : ( further development of trophoblast )
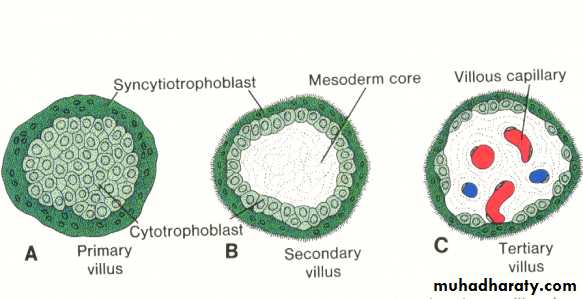
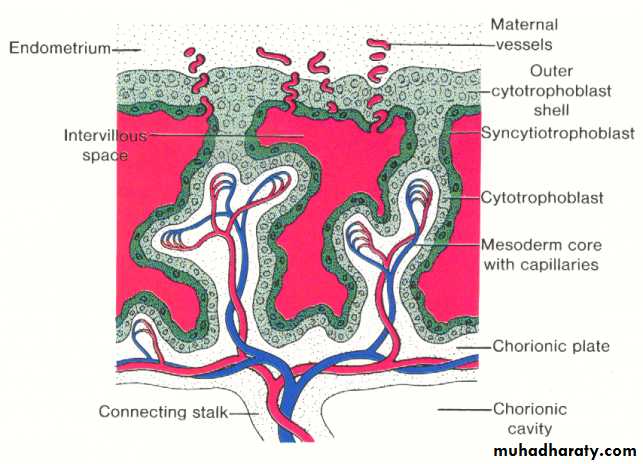
By the end of the second week , the primary stem villi have already been formed , consisting of a core of cytotrophoblast surrounded by syncytium. during the third week , the extra embryonic mesoderm invades or penetrates the cytotrophoblast of the primary villi forming the secondary villi , which consists of a core of mesoderm surrounded by alayer of cytotrophoblast which in turn surrounded by syncytium. by the end of the third week some of the mesodermal cells in the villus core differentiate into blood cells and vessels forming the villous capillary system and the villous now is known as the tertiary stem villus.The capillaries in the tertiary villi make contact with those developing in the chorionic plate and in the connecting stalk. these extra embryonic circulatory system vessels in turn establish contact with intra embryonic circulatory system , thus connecting the placenta and the embryo.
When the heart begins to beat in the fourth week of development , the villous system will be ready to supply the embryo proper with the necessary nutrients and oxygen.
With further development , the cytotrophoblast in the villi will penetrate into the syncytium until they reach the maternal endometrium and becoming in contact with the neighboring villous stem , forming the outer cytotrophoblastic shell which will surrounds the trophoblast entirely and attaches the chorionic sac firmly to the maternal endometrial tissue.