Dermatology | Dr. Rzan
1
PRURITUS
OBJECTIVES
to define pruritus
to classify its causes
Definition:
PRURITUS: Itching= Unpleasant sensation that provokes the desire for
scratching.
Scratching: Is the action taken in response to itching.
Itching= sensation
Scratching=action
P. is the commonest dermatologic complaint.
It is not a diagnosis.
P. is a symptom that may be caused by many conditions.
Dermatology | Dr. Rzan
2
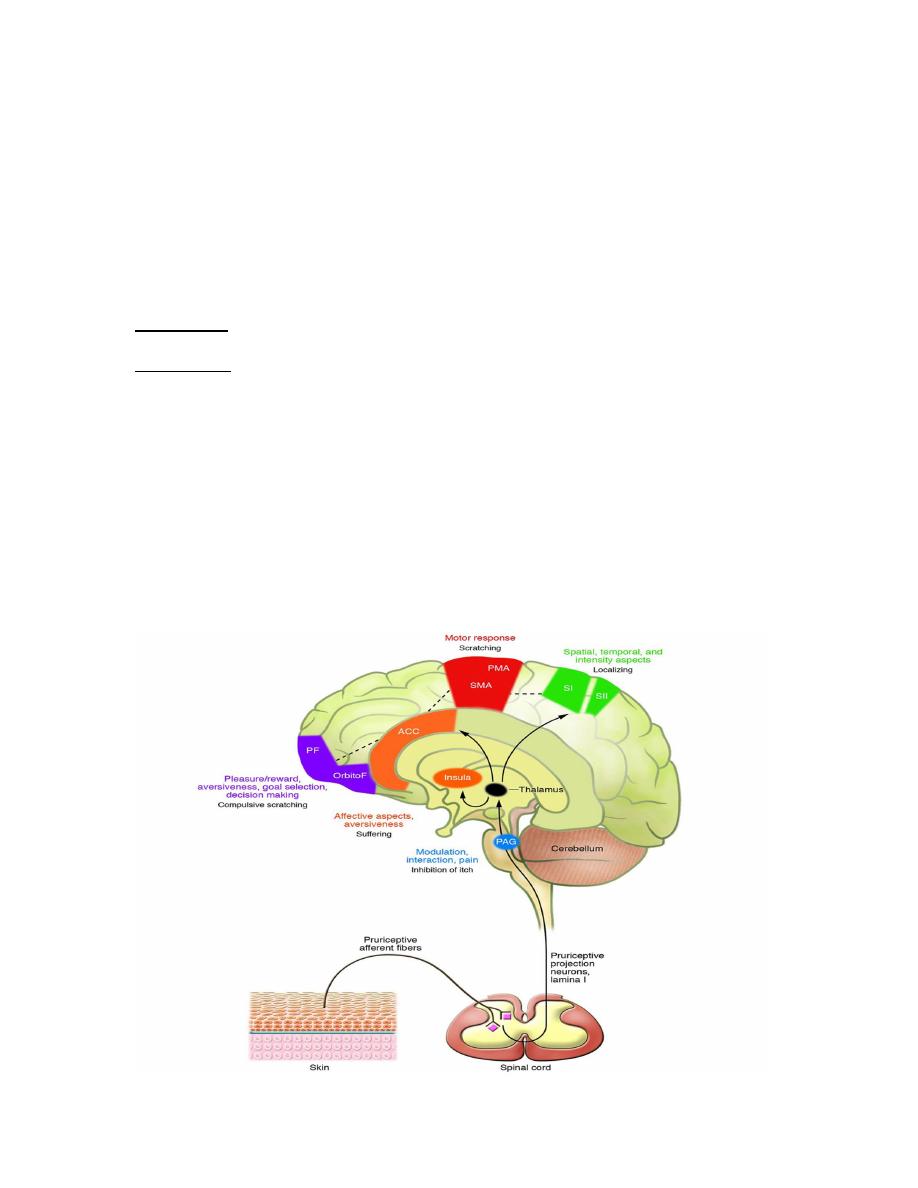
Itch pathway
Mediators: mainly; histamine from mast cell.
Other mediators: vasoactive chemicals like serotonin, bradykinin.
Itch nerve ending are lie very close to dermo-epidermal junction.
Itching sensation is transmitted via C fibers(slow conduction speed)
through spino-thalamic tract to the thalamus & on to a cortical
representation
How to analyze itching?
Site
Duration
Onset
Diurnal variation
Severity
Precipitating factors
Aggravating factors.
Alleviating factors.
Associated features.
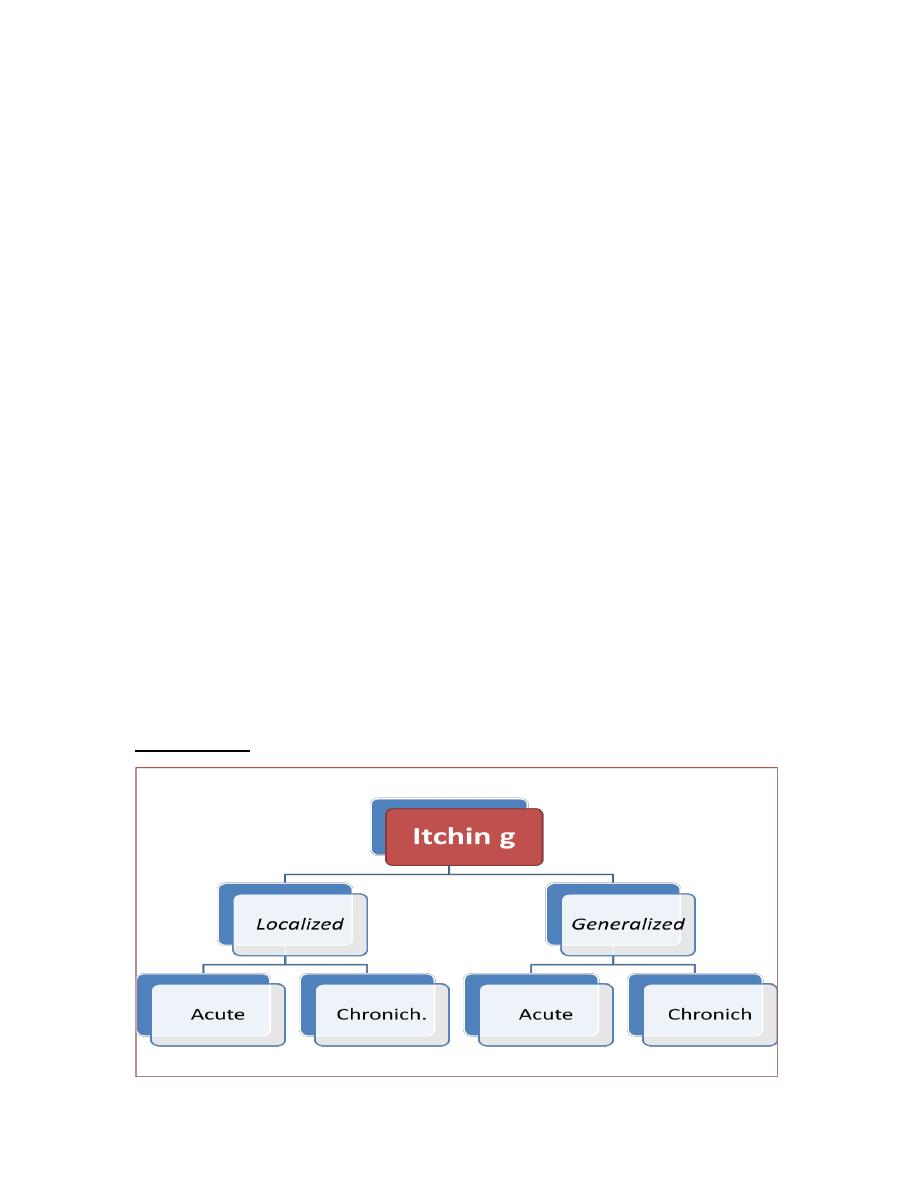
Classification
Dermatology | Dr. Rzan
3
Generalized Pruritus
Acute Generalized pruritus
1. Wide spread urticarial
2. Scabies.
3. Acute allergic contact dermatitis.
4. Drug eruption.
5. Pediculosis corporis.
6. Acute erupted lichen planus.
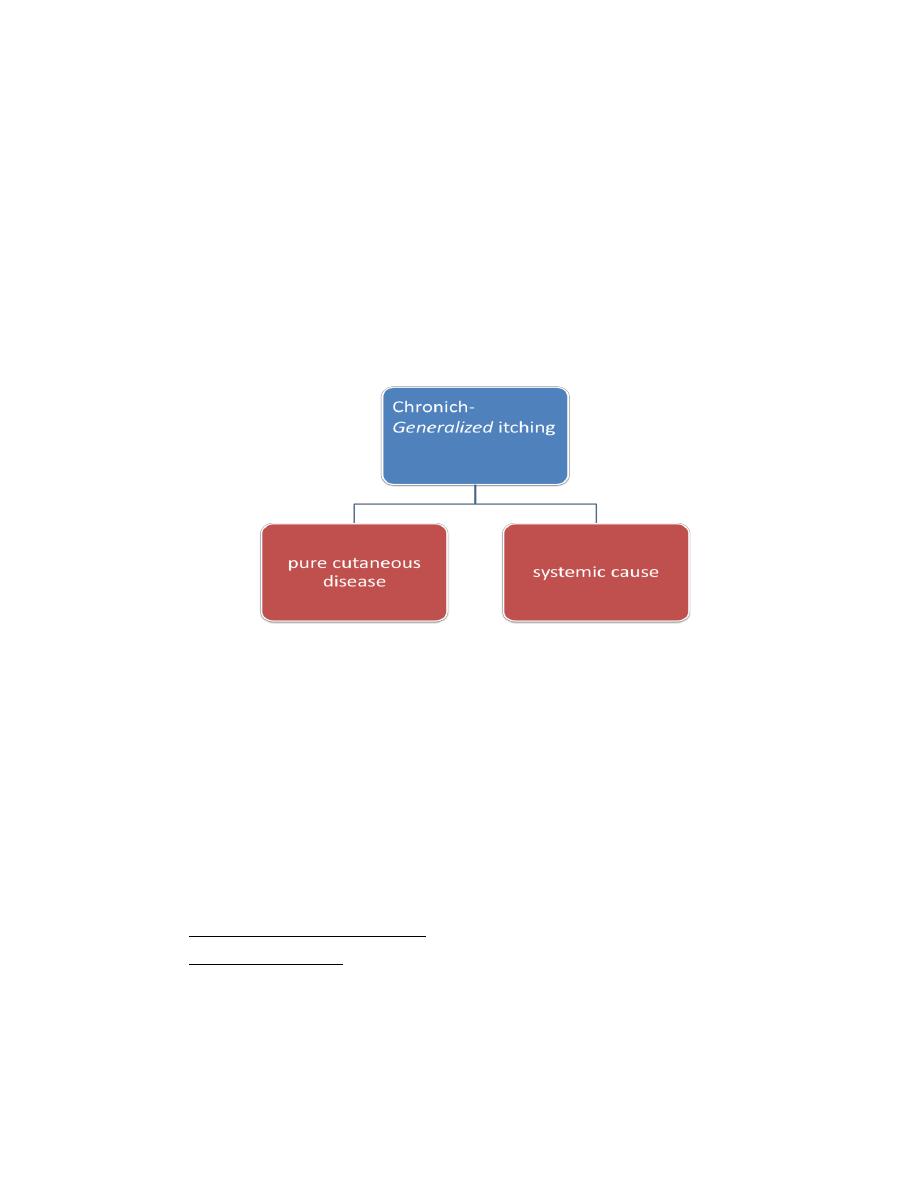
Pure cutaneous causes of chronic generalized itching
1. Atopic dermatitis.
2. Seborhoic dermatitis.
3. Senile pruritus.
4. Dry skin.
5. Dermatitis herpitiformis.
6. Cutaneous T cell lymphoma (Mycosis fungoides).
Systemic causes
1. Neuro-psychogenic pruritus
2. Endocrine disease;
A-Hyper thyroidism & Hypothyroidism;
B-D.M.
C-Pregnancy; (Obstetric Cholestasis.).

Dermatology | Dr. Rzan
4
3. Liver disease;
a- Cholestatic jaundice;
b-Primary Biliary Cirrhosis.
C-Chronic active hepatitis (HBV & HCV).
4. Renal disease;
-Chronic renal failure
5. Blood disease;
a-Polycythaemia rubra vera.
b-Iron deficiency anaemia;
c-Leukaemia; lymphoma, Myeloma.
6. Malignancy;
a-Hodgkin's disease;
b-Carcinoma; Ca. breast, bronchus, stomach & pancreas.
7. HIV
Localized chronic itching
1. Lichen planus.
2. Chronic contact dermatitis.
3. Nurodermatitis
4. Pomphylax
5. Discoid eczema
6. Varicose dermatitis.
7. Asteatotic eczema.
8. Lichen sclerosus it atrophicus.
9. Paget disease.
Localized –acute itching
1. Insect bite
2. Acute contact dermatitis.
3. Photodermatitis
4. Fixed drug eruption.
5. Pediculosis pubis& capitis.

Dermatology | Dr. Rzan
5
6. Worm infestation (Oxyuriasis).
Diagnosis
Mainly clinical
Simple Investigations.
Sophisticated Investigations.
According to the suspected cause.
Tr
eatment
A-General measures:
1. Reassure
2. Explain the condition.
3. Treat the primary underlying cause.
4. Avoid aggravating factors (scratching).
5. Gentle skin care.
B-Topical measures:
1. Topical Emollients agent on skin.
2. Topical antihistamine.
3. Topical CS (have potent anti-pruritic effect).
4. Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus.
5. Other therapies to decrease itching include Topical menthol 1%,
camphor.
C-systemic therapies
1. Systemic H1 blocking anti histamines (either sedative or not).
2. Systemic CS (short course small dose).
D-Others:
Phototherapy: UVB & PUVA.
