Traumatic Injuries to the Teeth
Dr Nizar Al ChaarLondon University
Traumatic Injuries to the Teeth
A trauma (injury) to the tooth/teeth and/or periodontium (gums, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone), and nearby soft tissues such as the lips, tongue.Definition:
Traumatic Injuries to the TeethTypes
• Tooth Avulsion• Root fractures
• Crown fractures
• Crown-Root fractures
• Tooth luxation
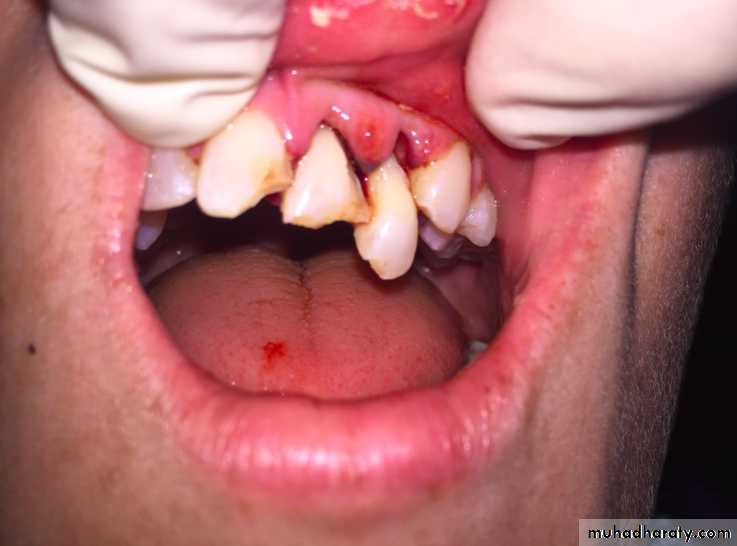
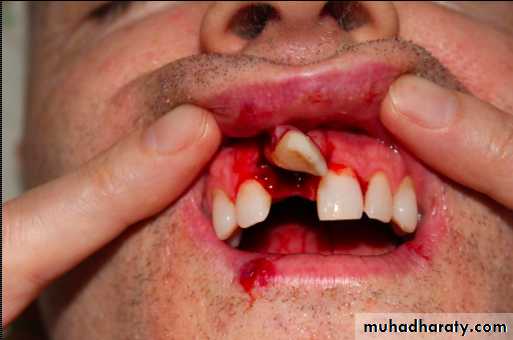
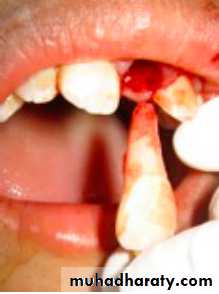
1-Tooth Avulsion
Definition:
Is a Complete displacement of tooth out of socket, The periodontal ligament is severed and fracture of the alveolus may occur.
Avulsed Permanent Teeth
Incidence- 0.5% to 16% of treatment InjuriesMain Etiologic factors: - Fights and A Knocked out tooth
- Sports injuries
- Automobile accidents
Avulsed Permanent Teeth
Maxillary Central Incisor- Most commonlyavulsed tooth
Mandibular Teeth- Seldom affected
Most frequently involves a
single tooth
Most Common age-7 to 11
Permanent incisors erupting
Loosely structured PDL
Avulsed Permanent Teeth
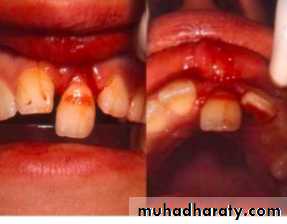
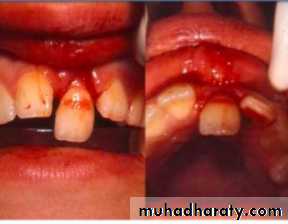
Associated injuries-Fracture of alveolarSocket wall
Management of avulsed tooth
Periodontal ligament responsesPulpal prognosis/Endodontic Rationale
Treatment regimen
Follow up Period
Management Avulsed Permanent Teeth
Associated injuries-Fracture of alveolar socket wall
- Injuries to the lips and gingiva
Management of the Avulsed Permanent Tooth
What tissue should be our primary concern?-Pulp?
Management of the Avulsed Permanent Tooth
What tissue should be our primary concern?-Pulp?
-Socket?
Management of the Permanent Avulsed Tooth
What tissue should be our primary concern?-Pulp?
-Socket ?
-PDL?
Management of the Avulsed Permanent Tooth
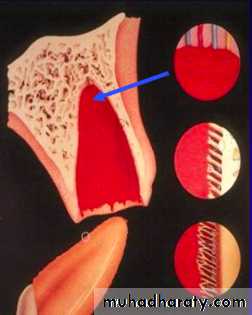
Ultimate goalPDL healing without root resorption.
Most critical factor-Maintaining an intact and viable PDL on the root surface
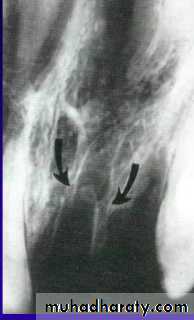
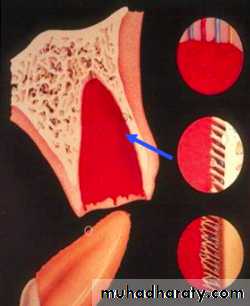
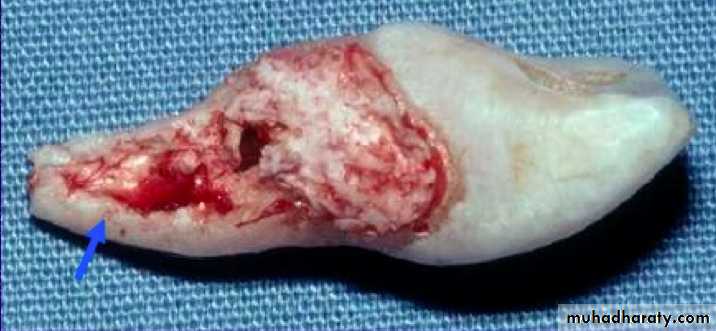
Periodontal Ligament Responses
Surface ResorptionSuperhacial resorption cavities
Mainly in cementum
Complete repair of PDL
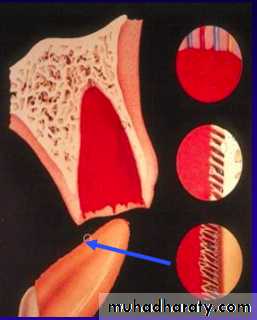
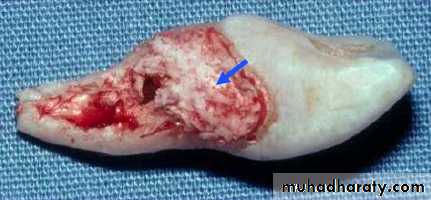
Periodontal Ligament Responses
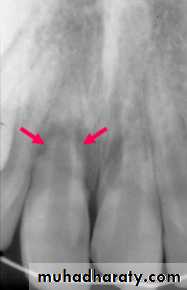
Replacement Resorption(Ankylosis)
Direct union of bone and root
Resorption of root
Replacement with bone
Direct result of loss of vital PDL
Periodontal Ligament Responses
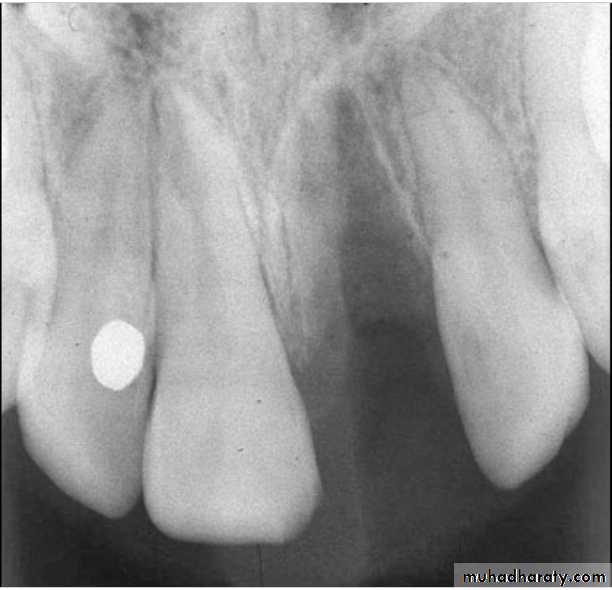
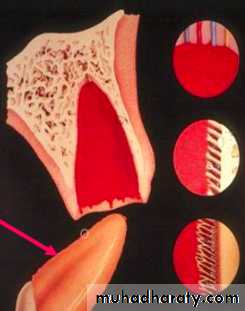
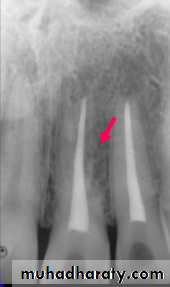
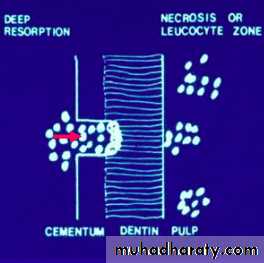
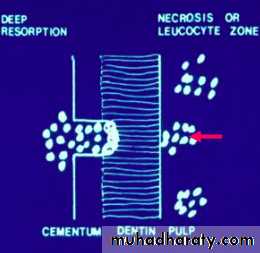
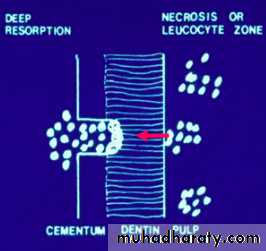
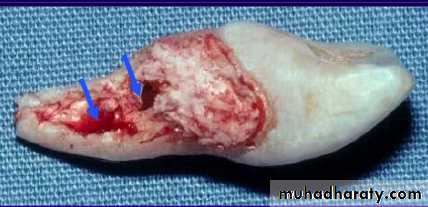
Inflammatory Resorption-Resorption of cementum and dentin
-Inflammatory reaction in the periodontal
ligament
Etiology
Infamatory resorption
-Surface resorption of cementum
exposing dental tubuless
Etiology
Infamatory resorption-Surface resorption of cementum
exposing dental tubuless
-Pulp necrosis
Etiology
Infamatory resorptionSurface resorption of cementum
exposing dental tubules
Pulp necrosis
Toxic products from the pulp provoke
an inflammatory response in the PDL
Periodontal ligament Responses
Surface resorptionPeriodontal ligament Responses
Surface resorptionReplacement resorption(Ankylosis)
Periodontal ligament Responses
Surface resorption
Replacement resorption(Ankylosis)
Infammatory resorption
Treatment considerations
Success of treatment depend onExtra oral time
Extra oral environment
Root surface manipulation
Management of the socket
Stabilization
Extra oral time
The shorter Time the better prognosis*-<30min 10% resorption
- > 90min 90% resorption
*depending on storage medium
Extra oral environment
teeth that are protected in physiologically ideal media can be re -implanted within 15min to one hour after accident with good prognosis.HBSS (Hank’s balanced salt solution),
Milk have proposed for avulsed teeth.
Viaspan
Eagle’s
Ascorbic acid
-Water
Dry
-Saliva
-Saline solution
Extra oral environment
Taper water Poor resultDry
Saliva Good protection
Saline for 2 hrs
Milk as a storage medium
Storage media-milk vs .salivaPhysiologic osmolality
Markedly fewer bacteria than saliva
Readily available
Storage for 2hrs –periodontal healing
Almost as good as immediate replantation
Storage for 6hrs
-Saliva extensive replacement resorption
Milk healing almost as good as
immediate replant
Cell Cultural Media
Eagle’s MediumHank’s Balanced salt solution
Hank’s Balanced salt solution
Proper PH and Osmolality
Reconstitutes depleted cellular metabolities
Washes toxic breakdown products from the root surface
Organ Transplant Storage Media
Viaspan- Dramatically prolongs the storage of human organs
- Expensive
- Not readily available
- Complete healing after 6 and 12 hrs.
- Good for extended storage period (72hrs and 96 hrs.)
Recommended Storage Media
1- Socket (Immediate replantation)
2- Cell culture medium
3-Milk
4-Physiologic saline
5- Saliva
Replant Contraindication
ImmunosuppressionExtensive periodontal disease
Caries avulsed tooth/teeth
Alveolus fracture
Crowding of avulsed tooth
Primary tooth avulsion
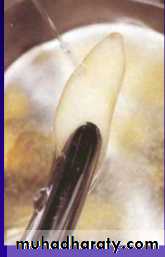
Root Surface Manipulation
Rinse The rootAttempt to retain PDL cell viability
1-Do not curette root surface
2- Avoid caustic chemicals
Extraoral dry time <1hr
-PDL healing is still possible
-Handling recommendations:
1- Keep root moist
2-Don’t handle root surface
3-Gentle debridement
Root Surface Manipulation
Extra oral dry time >1hr-Loss of PDL cell viability inevitable
-Treatment recommendations
1-Remove tissue tags
2-Soak in accepted dental fluoride solution
for 20 min
Fluoride Treatment
1.0-2.4% topical fluoride solution
-Sodium fluoride
-Stannous fluoride
20 minute sock
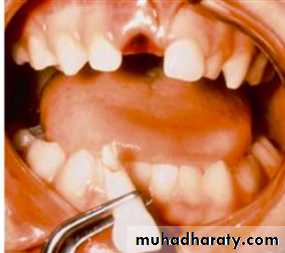
Management of the socket
Administration an AnesthesiaGentle saline rinse
Assess suitability for replant
1-Integrity of alveolus wall
2-Integrity of adjacent teeth
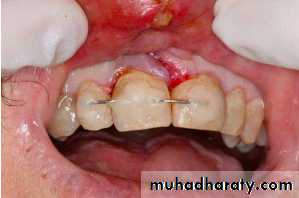
Replant using light digital pressure
Replant the tooth
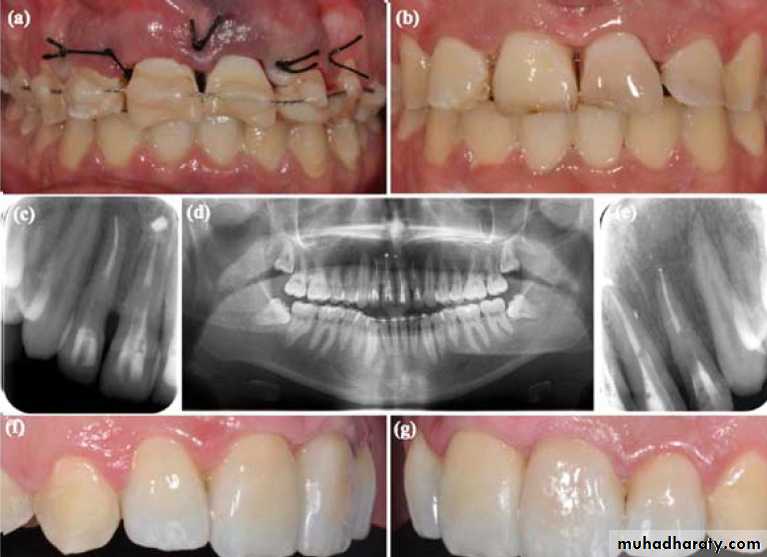
Gentle reinsertion of the tooth into the socket followStabilization
To immobilize the tooth with a semi- rigid splint for (7 -10) daysThe splint should not interfere with the patient’s capability to perform correct hygiene
It should allow a physiological movement of the tooth.
In cases of bone fracture, the tooth should be splinted for a longer period, (1 or 2 months), depending on the clinical situation. Rigid immobilization is constrain- dictated, except incases of root fracture
After the immobilization, a radiograph should be taken to verify the correct position of the tooth/teeth.
Stabilization
Types of splinting
• Acid-etched composite splinting
• Interdental wiring
• (Vacuum- formed plastic ) splint
• Arch bare splint
More rigid and the longer the stabilization, the more root resorption, amyloses that can be expected
Acid-etched composite splinting
Pharmacologic treatment
Systemic antibiotic during the first week after re plantation. To prevents the development of root resorption.The administration of systemic antibiotic
Refer the patient to a physician within 48 hours for a tetanus booster if the avulsed tooth contacted soil or if the status of the tetanus coverage is uncertain.
Endodontic treatment
• Tooth with open apex (divergent apex)and less than one hour extra oral dry time:
-Replant in an attempt to revitalize the pulp
-Recall patient every 3-4 weeks for evidence of pathosis
-If pathosis is not ,thoroughly clean and fill the canal calcium hydroxide ( Apexification procedure)
B. Tooth with open apex (divergent apex) and greater than one hour extra oral dry time:
Thoroughly clean and fill canal with calcium hydroxide
Recall the patient in 6-8 weeks
Because of poor prognosis, consider alternative treatment
Options.
Endodontic treatment
C. Tooth with partially to completely closed apex and less than one hour extra oral dry time.• Biomechanical clean the root canal system in 7-14 days.
• Medicate the canal with calcium hydroxide for as long as practical, usually 6-12 moths.
• Then ,obturate canal with gutta percha and sealer unless complications are apparent.
D. Tooth with partially to completely closed apex and greater than one hour extra oral dry time.
• Perform root canal therapy either intraorally or exteraorally.
• Prior to replantation, remove tissue tags from the root surface and sock the tooth in an accepted denatl fluoride solution.
Restoration of the avulsed tooth
Recommended Temporary Restoration ,For open or partially open apex
Recommended permanent Restoration ,immediately after final obturation
Patient Instructions
Soft food for 1 weekBrush with soft bristle
Rinse with chlorhexidine o.1% to prevent plaque accumulation
Additional Considerations
Avulsed primary teeth should not be replantedSplint removal and clinical and radiographic control after 2 weeks.Clinical and radiographic control after 4 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, 1 year and then yearly thereafter.
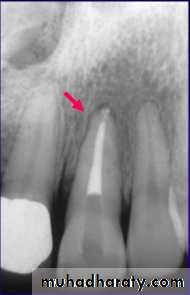
Inflammatory resorption, replacement resorption ankylosis and tooth submergence are potential complications when avulsed tooth are replanted
References:
• Essential of traumatic injuries of teeth2nd edition .J O. Andreasen and F.M Andreasen.• Pathway of pulp 6th edition Stephen Cohen. Richard C Burns.
• Endodontics 5th edition Ingle.Bakland
• Principles and Practice of Endodontics 2nd edition Walton .Torabinajad