Lec:
علوم سلوكيةDr.Safeyya Alchalabi
Psychology of learning
Thinking
How people think?
Thinking (cognition):
Refers to mental activities that occur in the brain when processing, organizing, understanding, or communicating information to others.
Thought can be conceived as a language of the mind
Mental imagery
Mental images are representations for objects or events used in mental activity.
Mental images are interacted with in similar ways as physical objects.
Mental images are processed in the brain slightly differently than actual objects
Actual images (eyesvisual cortexother cortical areas).
Mental images (cortical areas associated with stored knowledge send info to visual cortex).
Concepts
are ideas that represent a class or category of objects, events, or activities.
Concepts
are used to interact and organized information without having to think about or process every specific example of the category .
can represent different levels of objects and events
can be well-defined based on strict criteria (formal), or fussy, based on personal experience (nature).
are represented by prototypes, best examples of the defining characteristics (vary according to personal experience, knowledge, and culture).
are an important tool in problem solving.
Problem solving and decision making
Thinking and behaving in certain ways to reach a goal
Can involve different strategies, logical methods (convergent thinking)
Trial and error
Trying one solution after another until one works
Algorithms
Specific, step-by-step procedures for solving certain problems
Always result in correct solution if there is one
heuristics
simple rules intended to apply to many situations
educated guesses based on prior experience
generally faster than algorithms but will not always lead to correct solution
Insight
When solution seems to appear in a flash (“aha!” moments)
Usually based on reorganization of information
Problems with problem solving
Solutions to problems are not always apparent
Problems can be caused by three common barriers
Functional fixedness
Only thinking about objects in terms of their typical uses
Mental set
A tendency to persist in using problem-solving patterns that have worked in the past
Confirmation bias
A tendency to search for evidence that fits your beliefs while ignoring evidence to the contrary
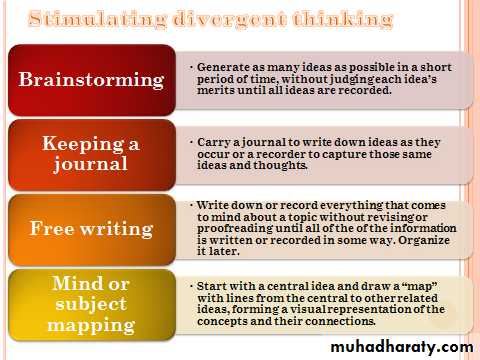
Creativity
Consist of new ways of combining ideas or behavior
Typically the result of divergent thinking
Less prone to common barriers of problem solving
Can be stimulated