Embryology
Facial development:The face develops from tissues surrounding the oral pit during 4th, 5th, 6th and 7th week of prenatal life.
Fourth week:
At 4th week gestation, the oral pit is surrounding by five masses of tissues (processes):
1: frontal process: the frontal process of brain bulge forward and laterally to dominate the facial area.
2: left and right maxillary processes: two small wedge shape tissue developed below frontal process on the bilateral side of oral pit.
3: left and right mandibular processes (arch): they are lay beneath the maxillary process and in this week they are separated medially.
The most important event in this week of gestation is the starting heart beet, that it lays beneath the oral pit and it conceders fastest growing organ.
Fifth week:
1: three structures appeared in this week on bilateral sides:Nasal placodes, medial and lateral nasal processes.
The frontal process grows to form frontonasal process. The nostrils become deepen and the median and lateral nasal processes become more prominent.
2: the eyes become prominent on both side of face.
3: the two mandibular processes unite and loss there constriction on midline.
Sixth week: Many events occur in this week include:
1: the face is broadening due to lateral expand of brain.
2: the eye and maxillary process come to the front of face that present on the lateral sides of face in fifth week.
3: the maxillary processes and mandibular processes come in contact lead to widening of the mouth opening.
4: Two medial nasal processes grow down to form middle part of upper lip.
5: the lateral and medial nasal processes formed nasal pit.
6: the upper lip composed of two medial nasal processes medially and two maxillary processes laterally. The fusion of maxillary and medial nasal processes formed nasal fin.
7: oronasal optic groove developed by fusion of lateral nasal process and maxillary process. Beneath this groove nasolacrimal duct developed.
8: The external auditory tubes develop from first pharyngeal clef.
9: six small hillocks, three from mandibular arch and three from hyoid arch, known as auricular hillocks.
Seventh week:
1: the face has more human appearance. The eyes come in front of face and more prominent.2: the auricular hillocks fused to form auricles.
3: the philtrum appeared by fusion of two medial nasal process.
4: the ridge around eye developed to eye lids.
Intraoral development during 7th and 8th week:
1: palatal development.2: tongue development.
3: thyroid gland development.
1: Palatal developed:
1: The medial nasal process give wedge shape structure grows posteriorly to form floor of nasal pit known as primary palate (future premaxill).
2: The two maxillary processes give palatine shelves that grow to form posterior surface of mouth to pharynx.
3: The tongue act as a mold elevate palatine shelves to its final position by process called palatine shelves elevation.
4: After reach to the final position, the palatine shelves closure occurs.
5: the fusion of primary palate and two palatine shelves well form the palate that binned superiorly the nasal septum between two nasal pits.
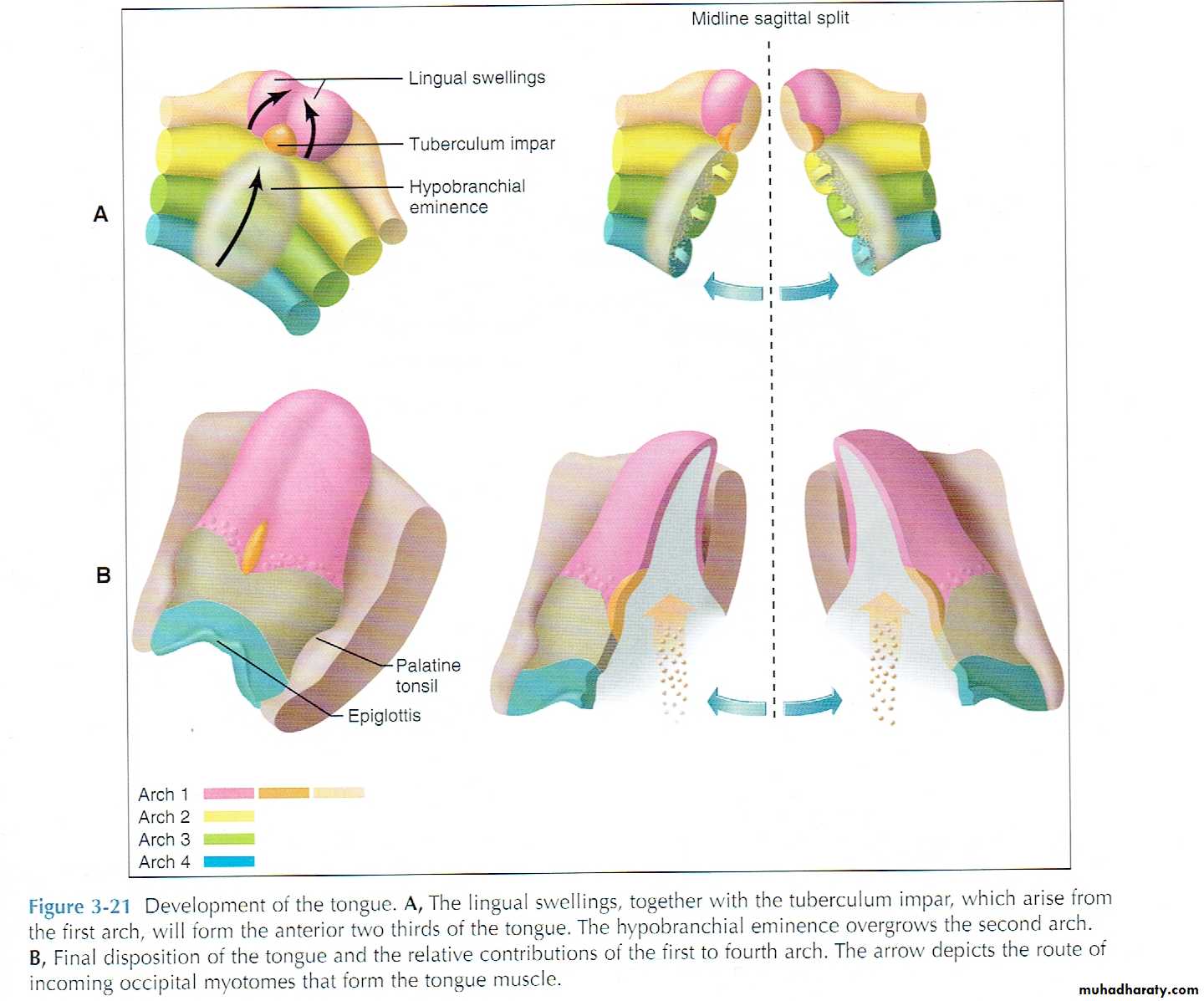
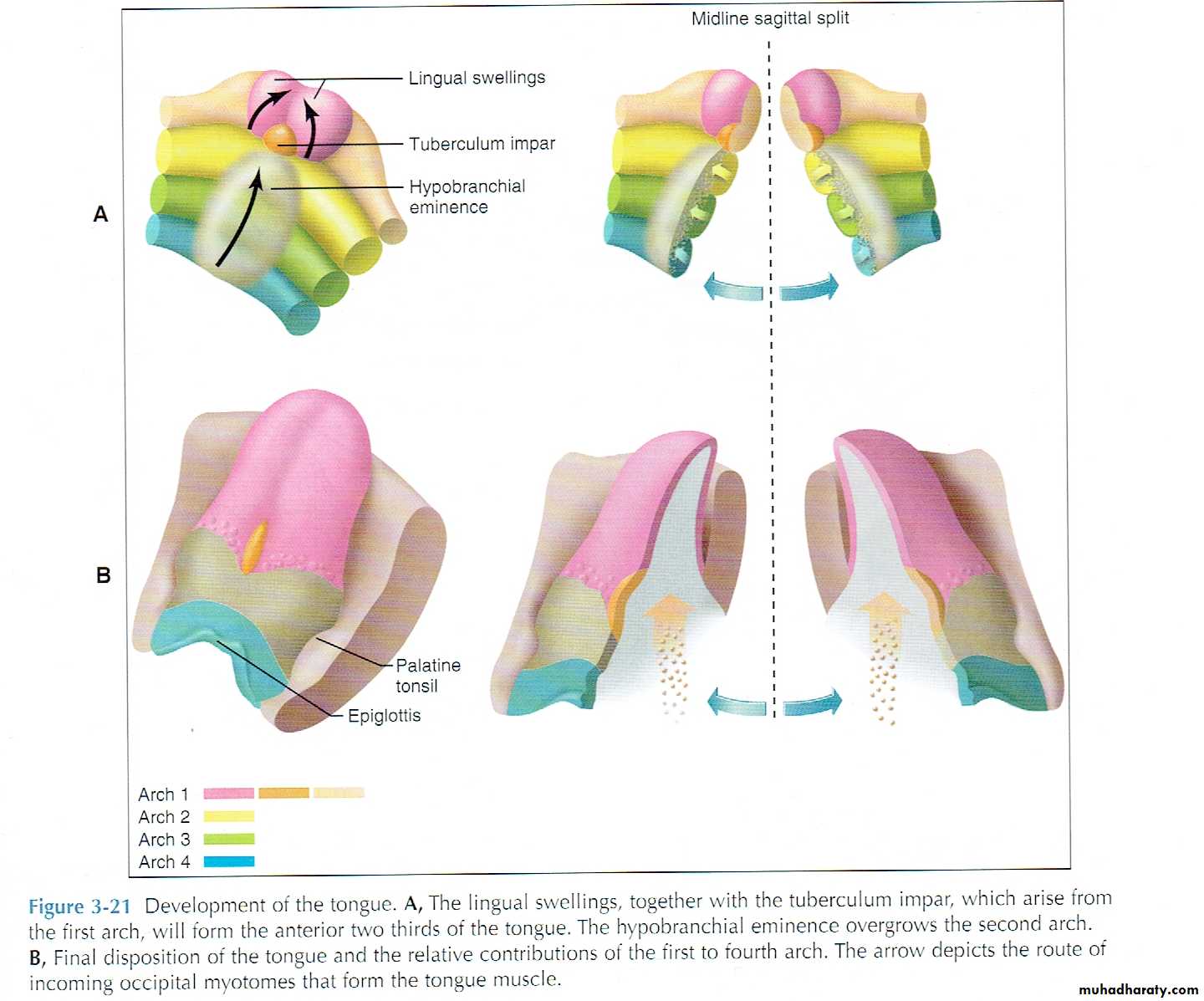
2: Tongue development:
1: the first pharyngeal arch formed anterior (movable) body of tongue by forming the central structure known as tuberculum impar and two lateral lingual swelling.2: the second, third and fourth pharyngeal arches formed posterior (immovable) base of the tongue.
The second arch gives the capula and the 3rd and 4th give the hypobronchial eminence. The capula disappear and eminence over grow to produce posterior third of tongue.
These three parts grow rapidly and merge. The anterior part separates from posterior part by V shape groove called terminal sulcus.
3: U shape sulcus develops around tongue and separates it from the jaw to allow free movement.
3: Thyroid gland development:
1: the thyroid gland developed from foramen cecum which is an epithelial proliferation on the surface of tongue at the junction of base and body.2: the cells from foramen cecum migrate through midline of pharynx to the level of laryngeal cartilage in front of trachea.
3: during this migration, the gland remains attached to tongue by thyroglossal duct which later disappear and become solid.
Developmental abnormalities:
1: Thyroid gland:
A: thyroglossal cyst: is a blind pocket lined with gland epithelium appears as a swelling on lateral surface of neck.
B: thyroglossal fistula: it is similar to the cyst but it has opening on the surface of neck.
C: Aberrant thyroid tissue: it is a part of thyroid epithelium remains on the area of foramen cecum.
2: tongue:
A: ankyloglossia (tongue tie): The lingual frenulum’s that bind tongue to the flour of mouth extend to the tip of tongue and limit its movement.
B: bifid tongue: (snack tongue): failure of union of two lingual swelling of tongue.
3: Developmental malformation: facial cleft:
They classified according to the position and extension to the unilateral and bilateral and to the complete and incomplete cleft.
Cleft lip:
1: midline cleft lip: it is in complete union of two medial nasal processes lead to incomplete philtrum formation and can be extend to the premaxilla and involve nasal cavity.
2: lateral cleft lip: (uni or bilateral) Incomplete merge of medial nasal process with maxillary process result in cleft formation in labial fin area.
3: oblique facial cleft: incomplete formation of lacrimal duct formation due to incomplete fusion of maxillary process with lateral nasal process.
Cleft palate:
Causes:
Cleft palate occur due to fail migration of palatine shelves to meet each other’s or to meet premaxilla either due to insufficient mesenchymal tissues or due to disturbance of mechanism of shelves elevation or the epithelial lining not breakdown that prevent merge of tissues.
Types:
1: incomplete unilateral cleft palate. Occur between premaxilla and maxillary process but not reach to the end of palate.
2: incomplete bilateral cleft palate: similar to first one but it involves both side of premaxilla.
3: unilateral complete cleft palate:
4: bilateral complete cleft palate:
These two types reach to the distal end of palate and can involve uvula.
Cleft of mandible:
The two mandibular process show early constriction on the midline but early beating of hear cause pressure on mandible that lead to separation of two processes in 4th week. It is rare condition.