Initial checks
1. Check the patients name
2. Look up the patients history
3. Read the date of the radiograph.
4. Look for markers
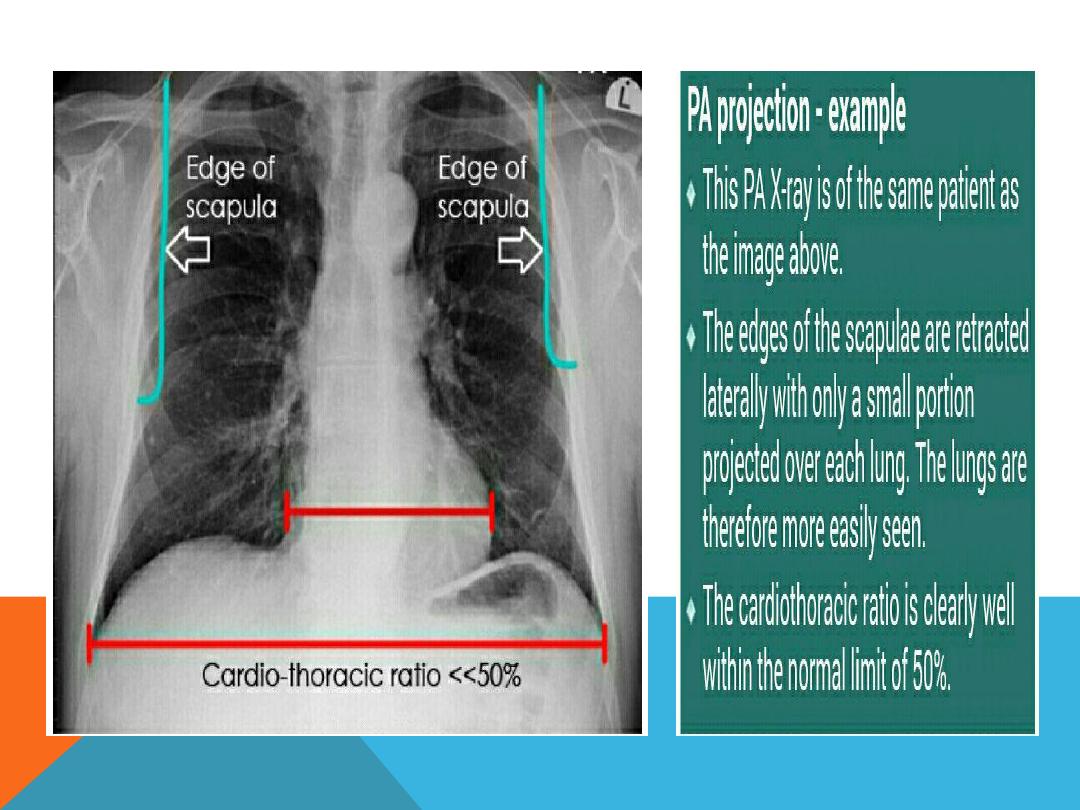
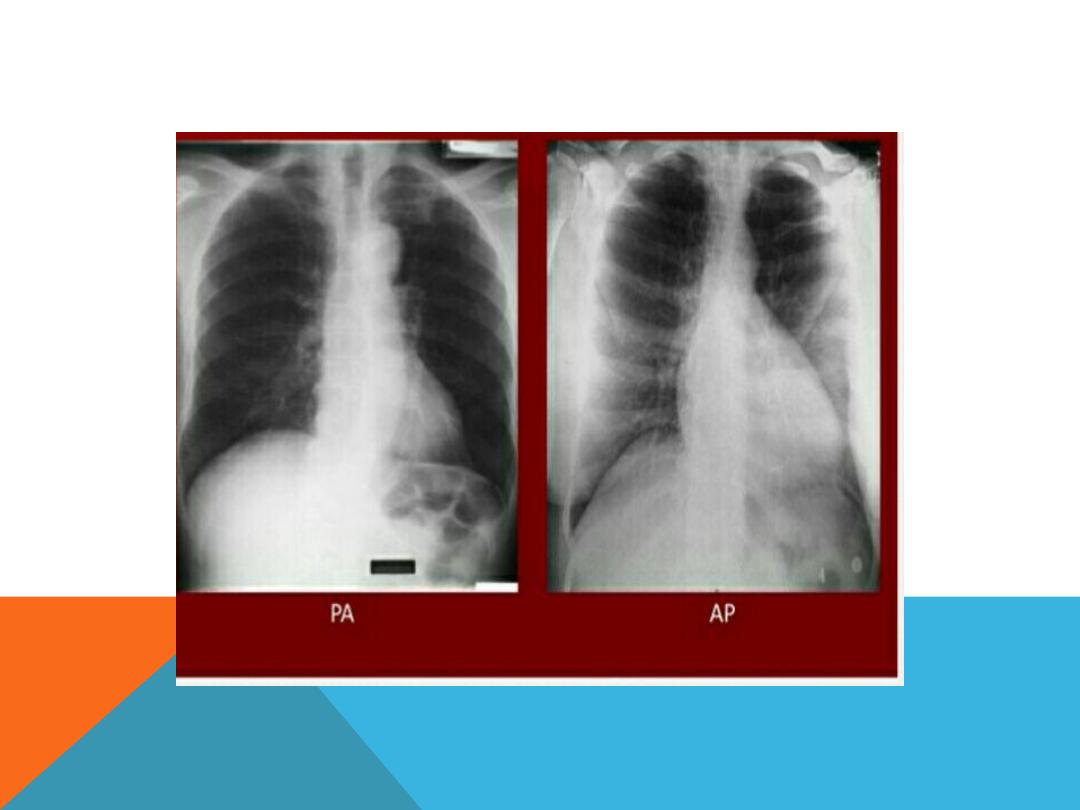
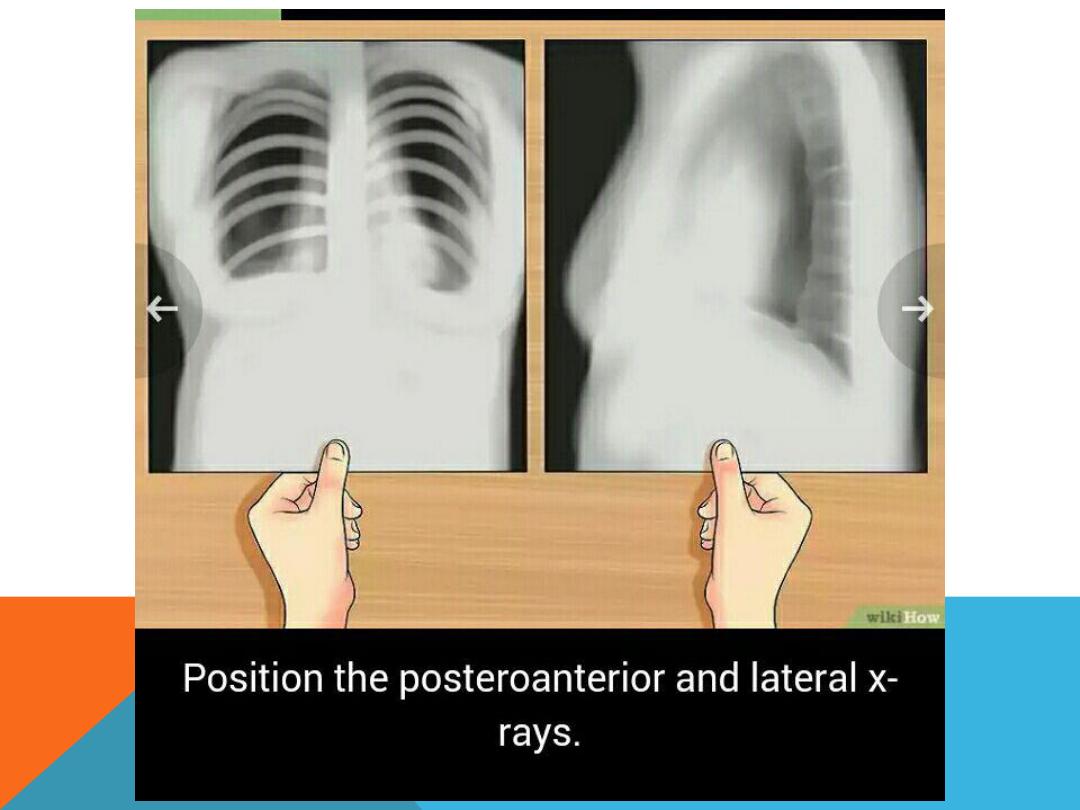
5. Position the postro -anterior and lateral view
6. Antro -posterior views taken in certain circumstances .
7. Check for any instrument insertions
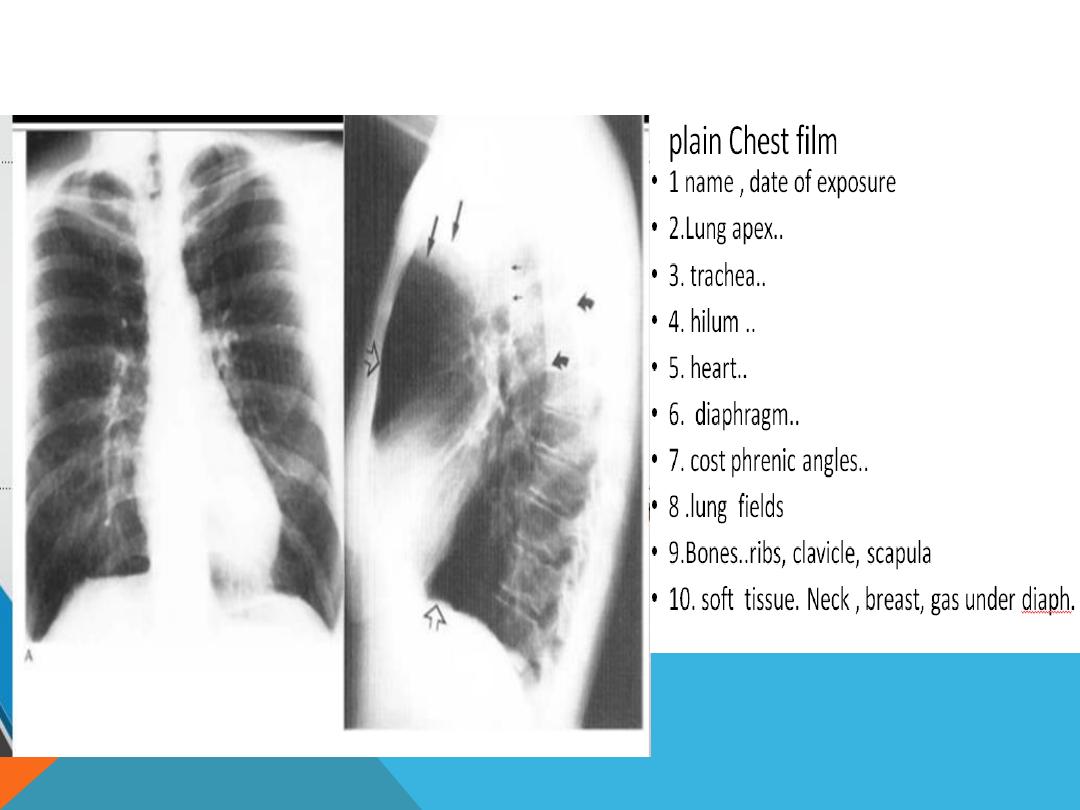
film quality
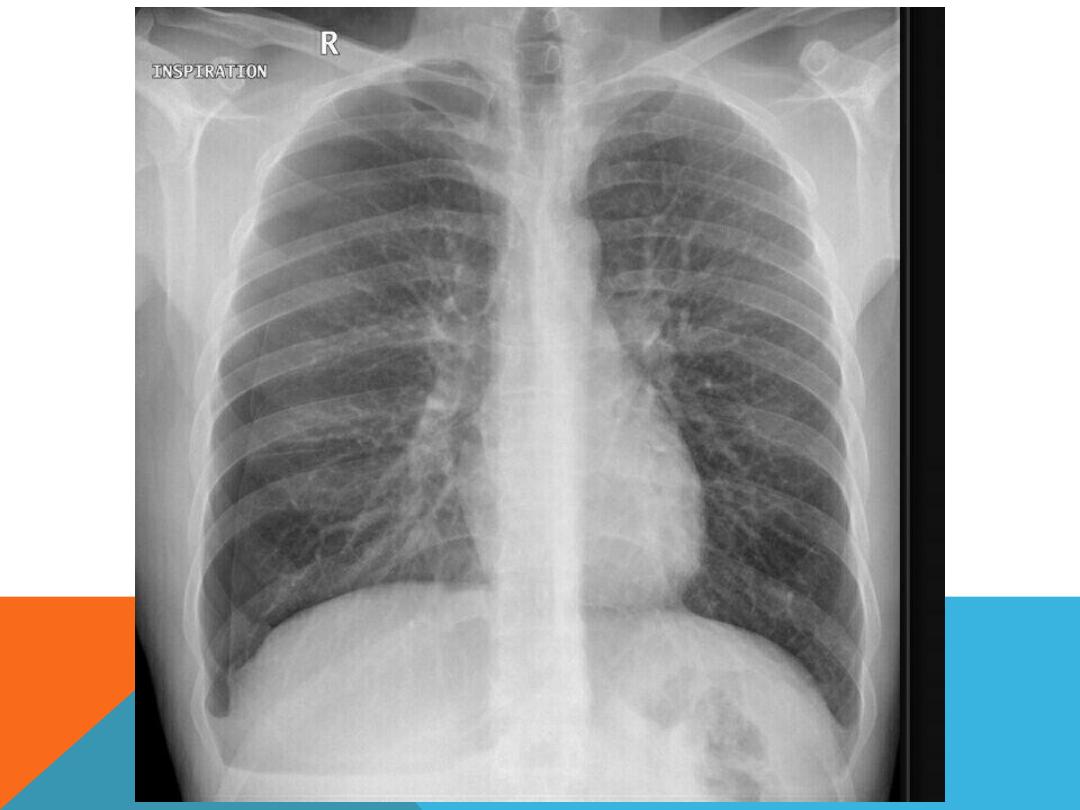
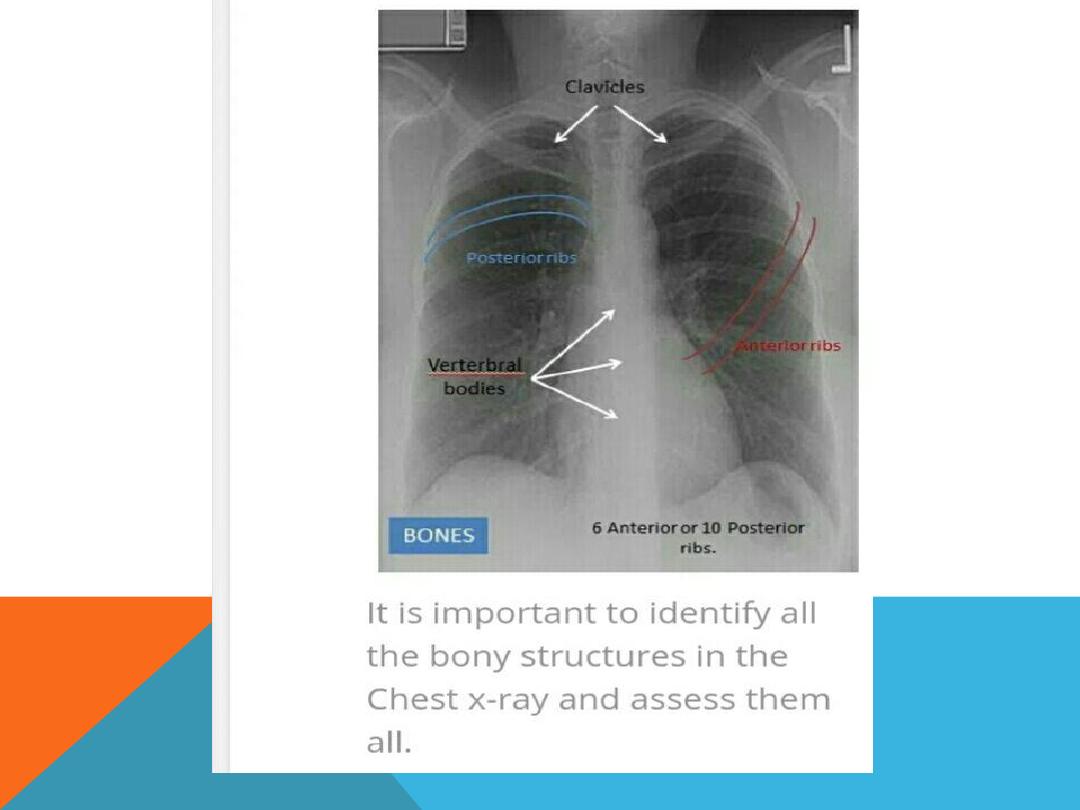
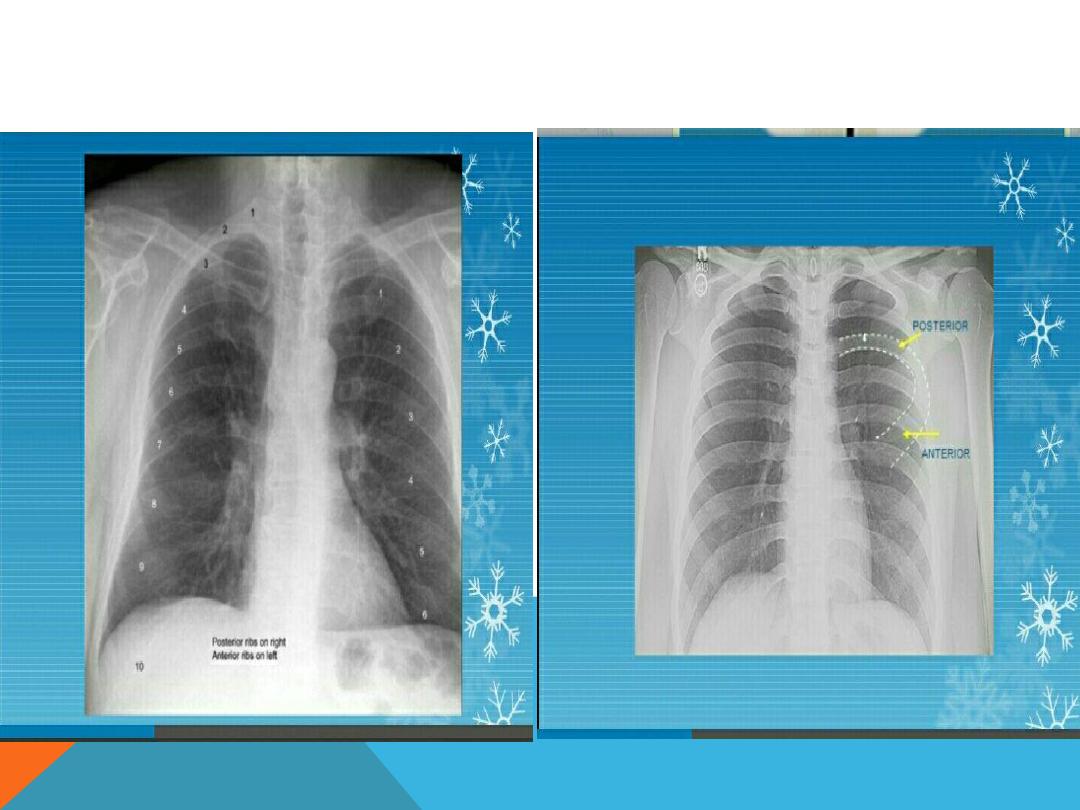
1. Is it taken under full inspiration ? U should be able to
see 10 posterior ribs and 6 anterior ribs.
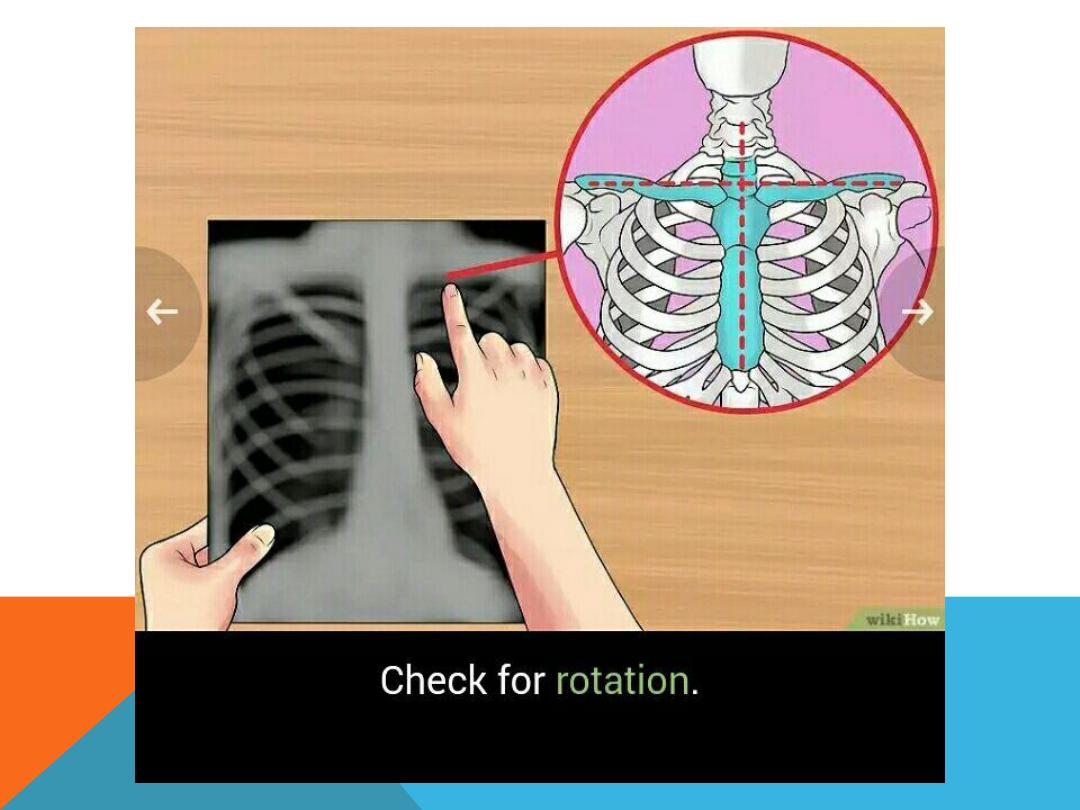
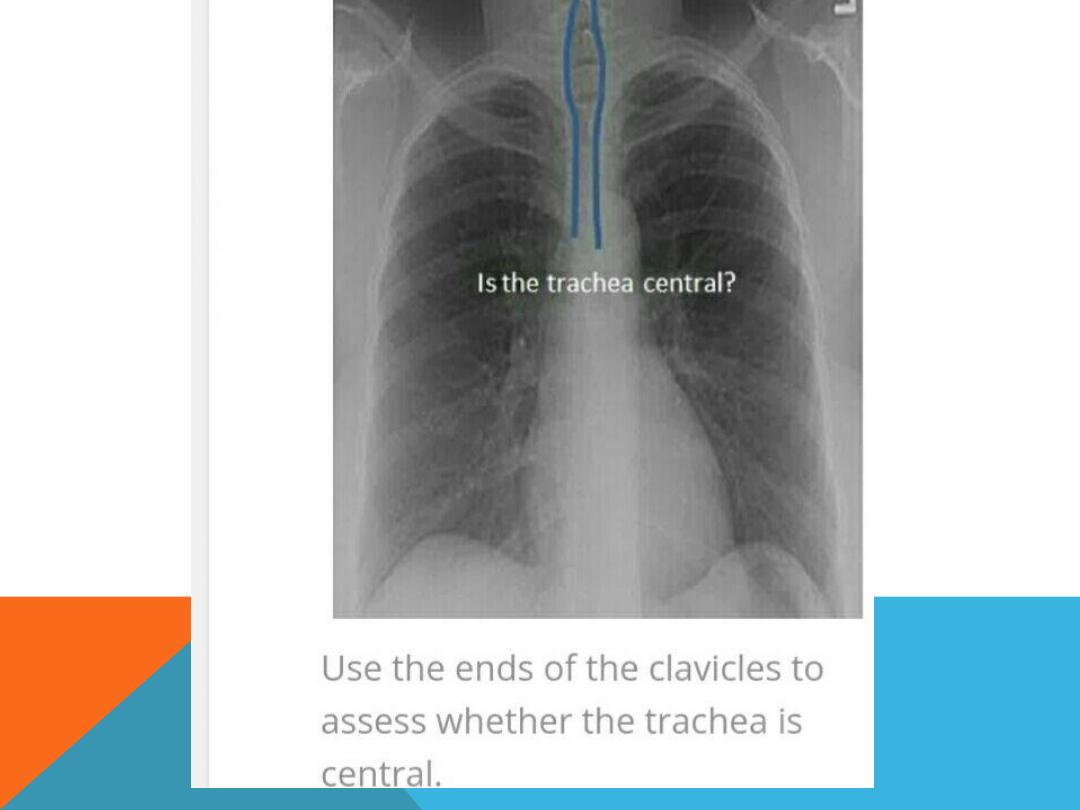
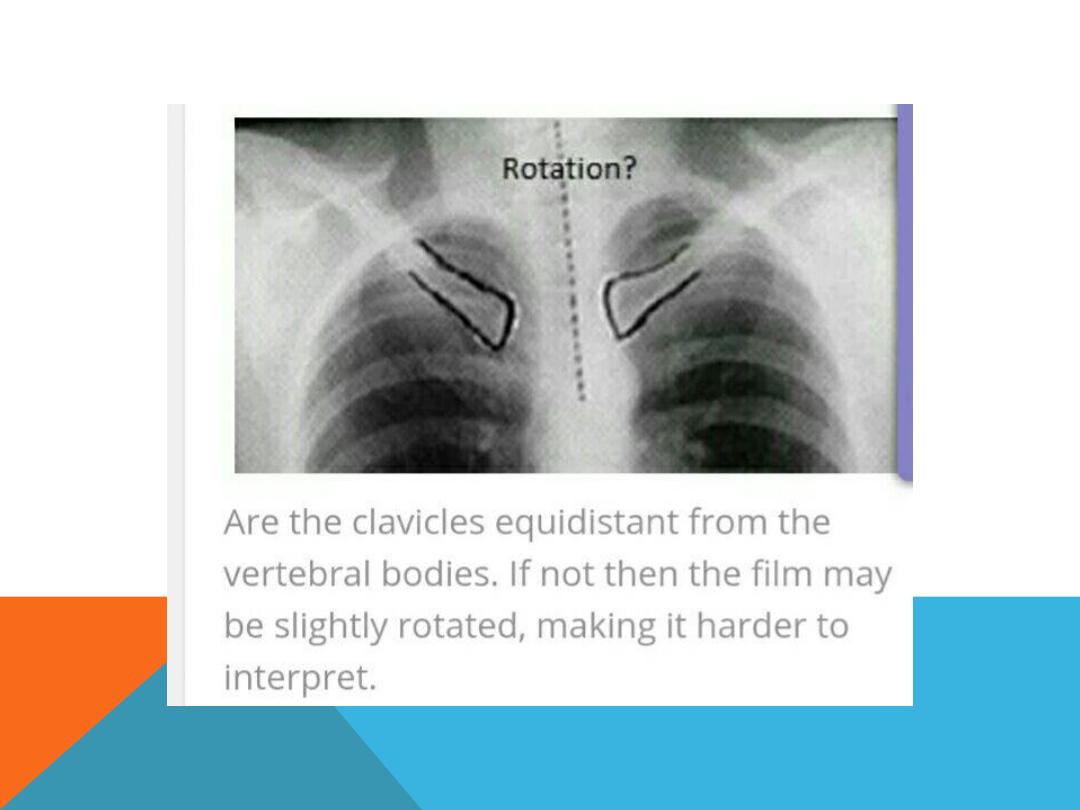
2. Check for rotation

CHECK PATIENTS NAME

LOOK UP THE PATIENTS HISTORY

LOOK FOR MARKERS
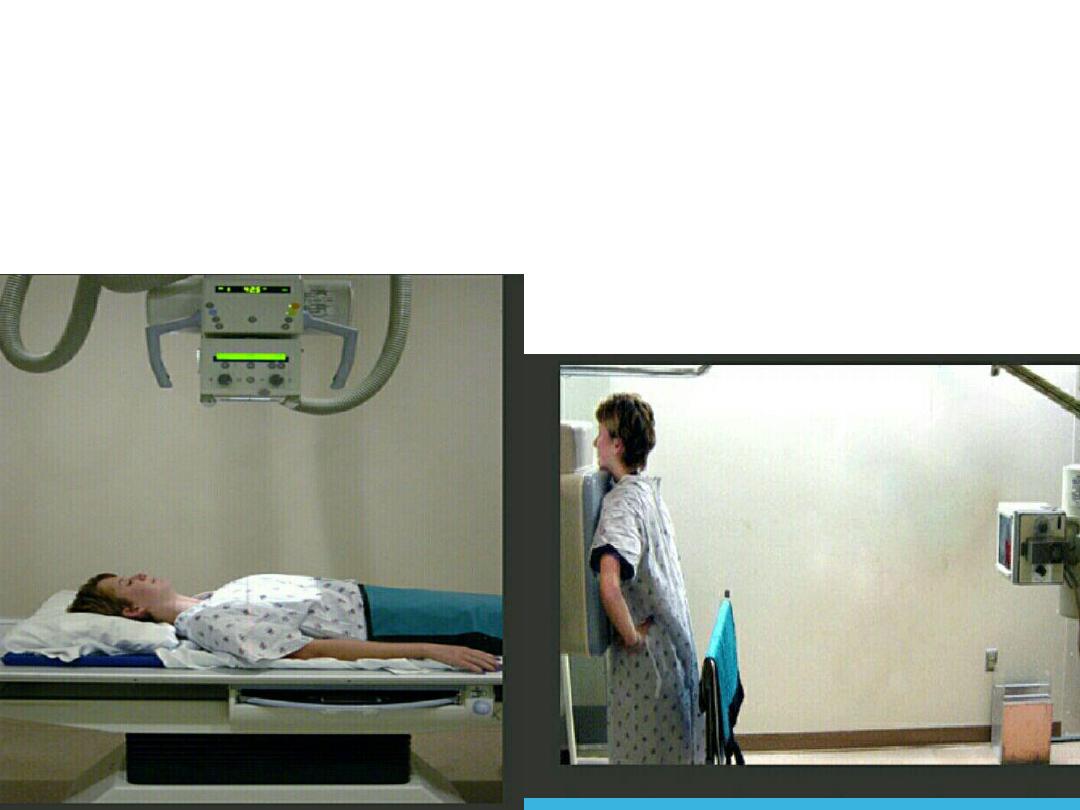
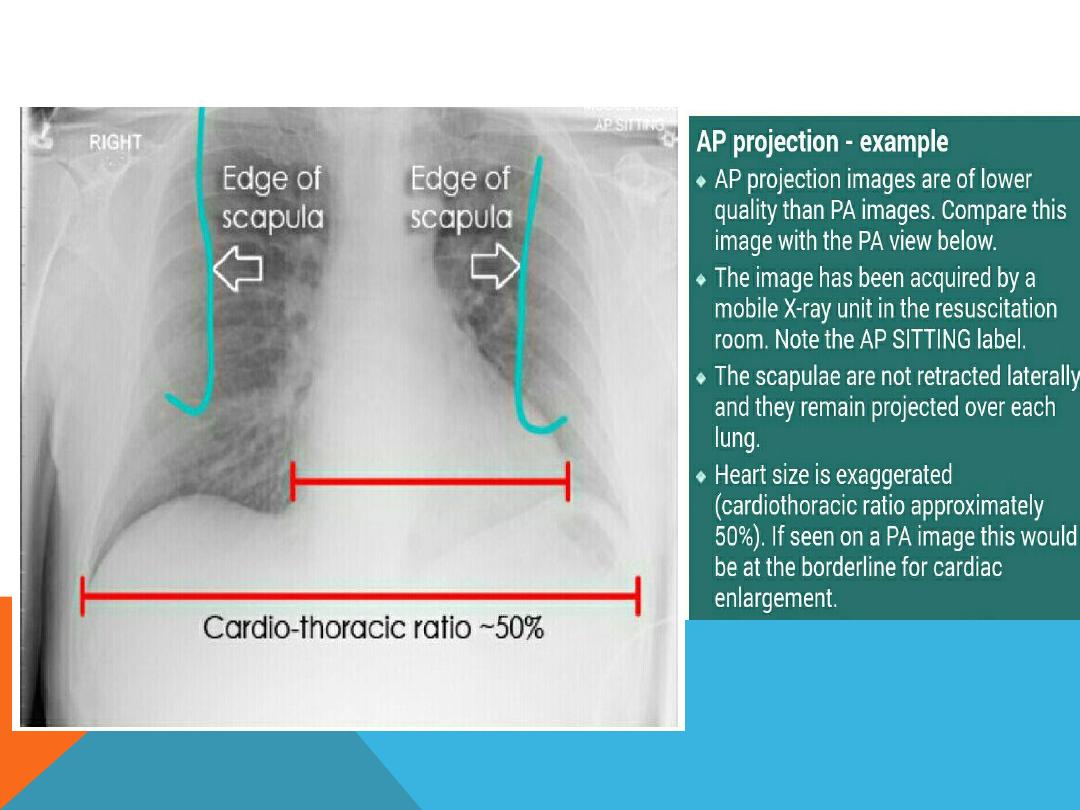
INDICATION OF AP VIEW
1. Severe illness
2. Pediatric s
diminish distance of x-ray beam result in more magnification of the heart
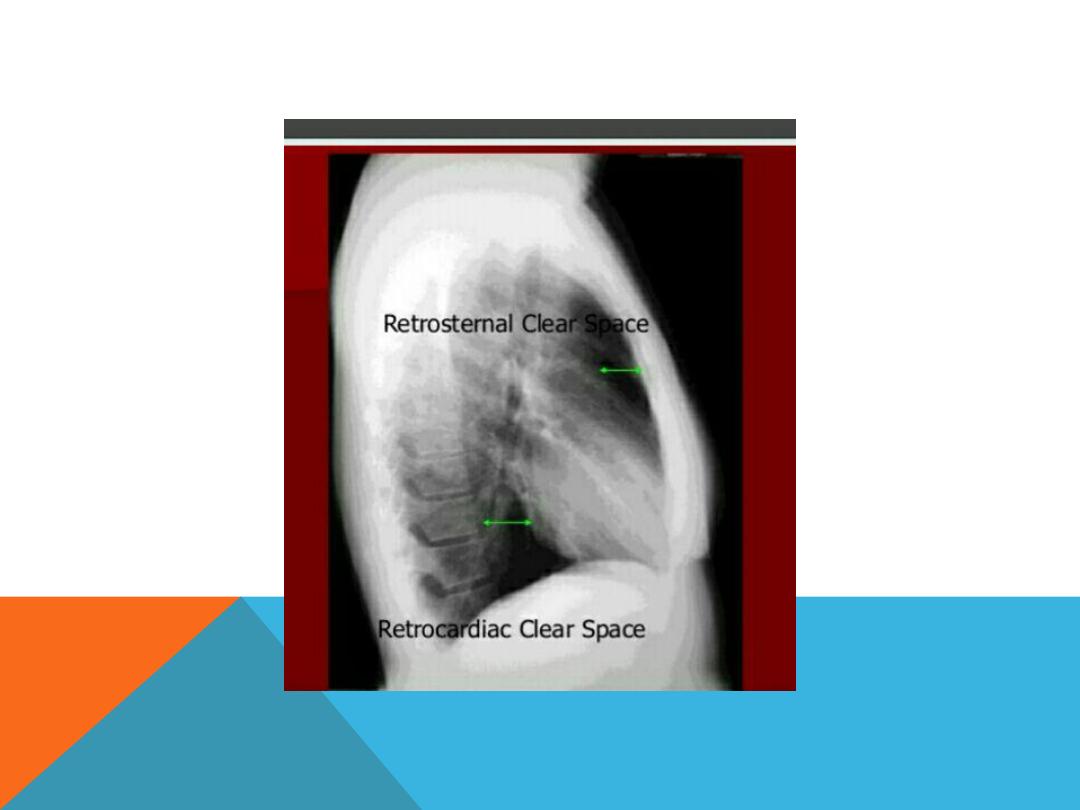
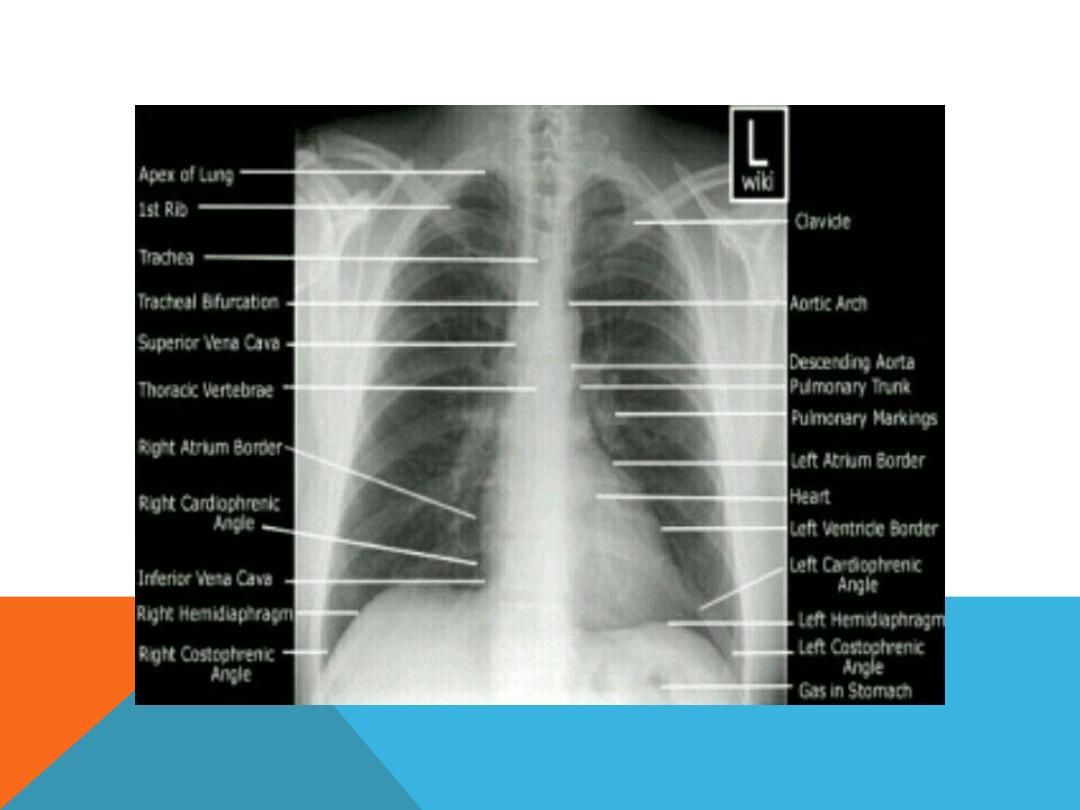
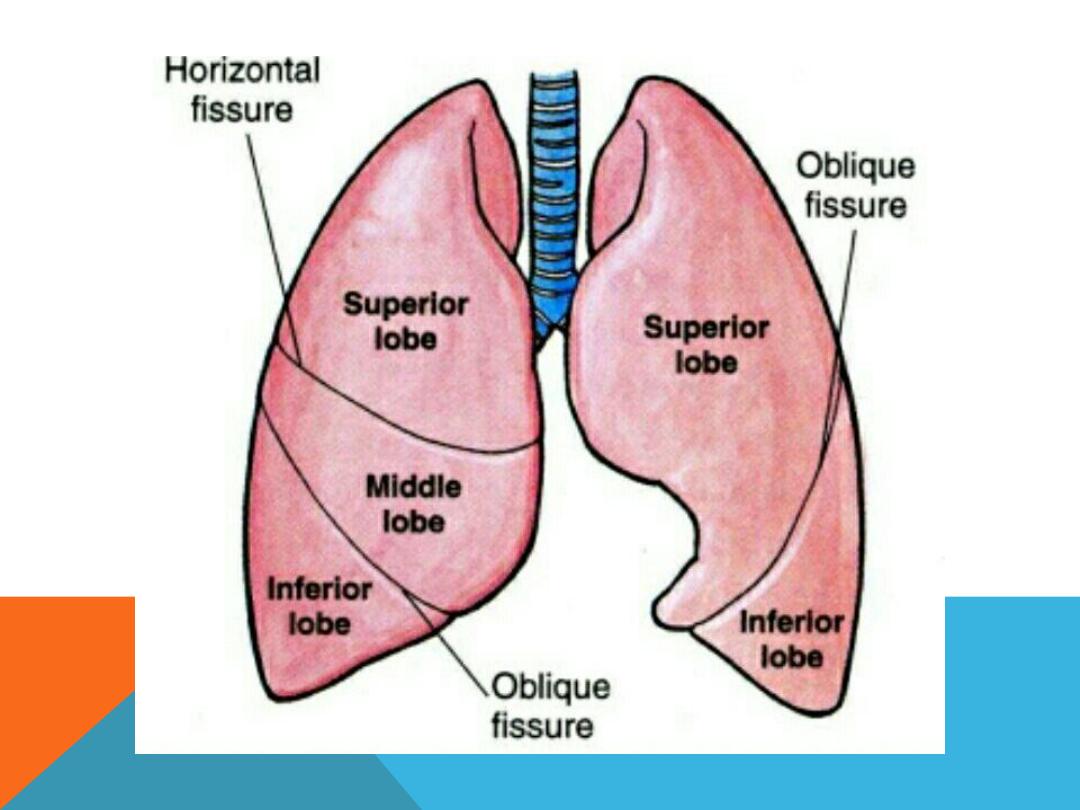
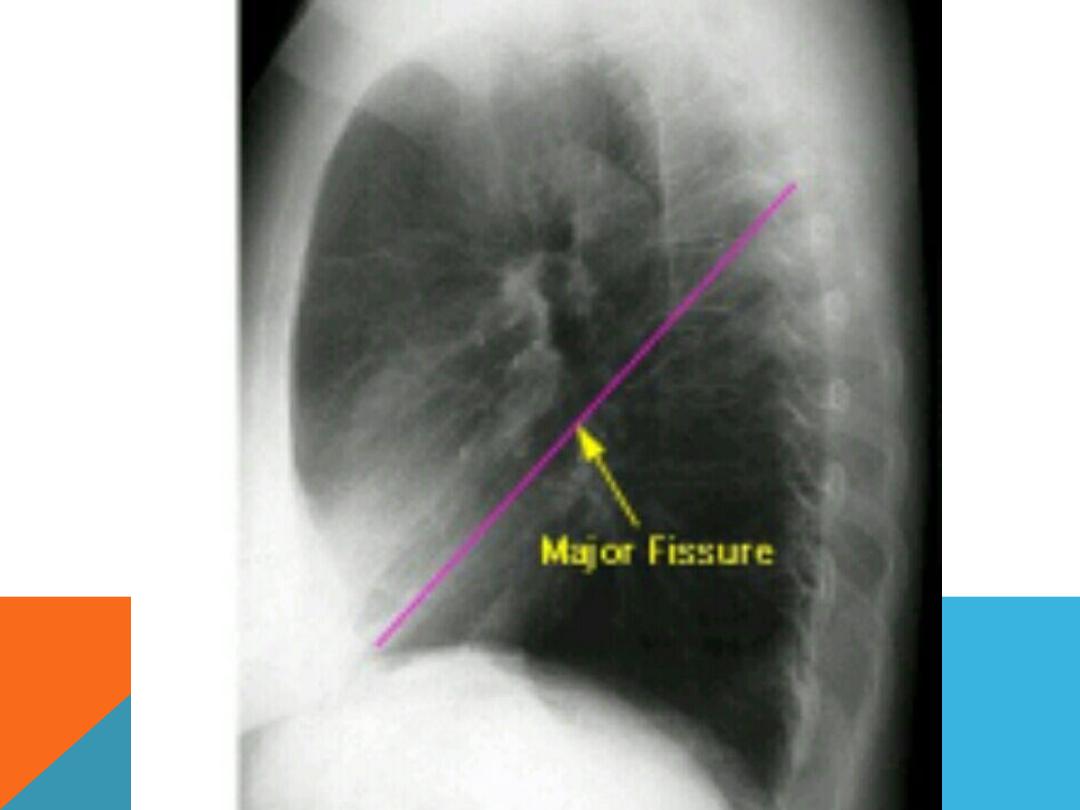
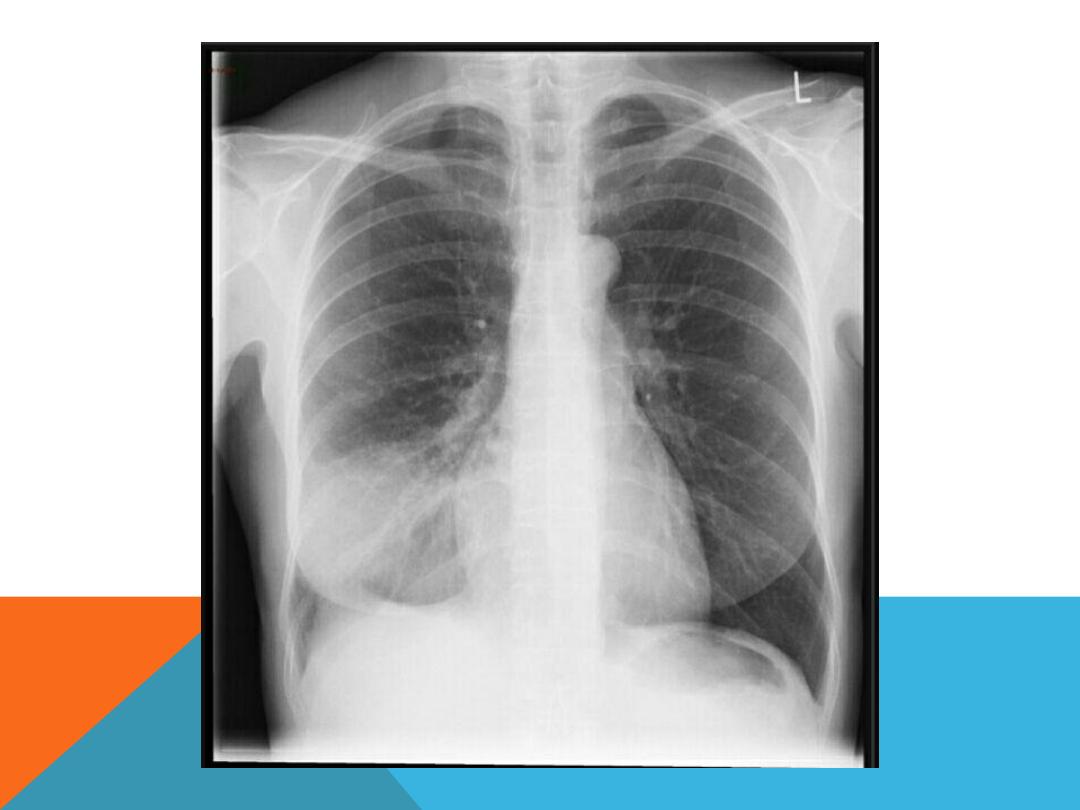
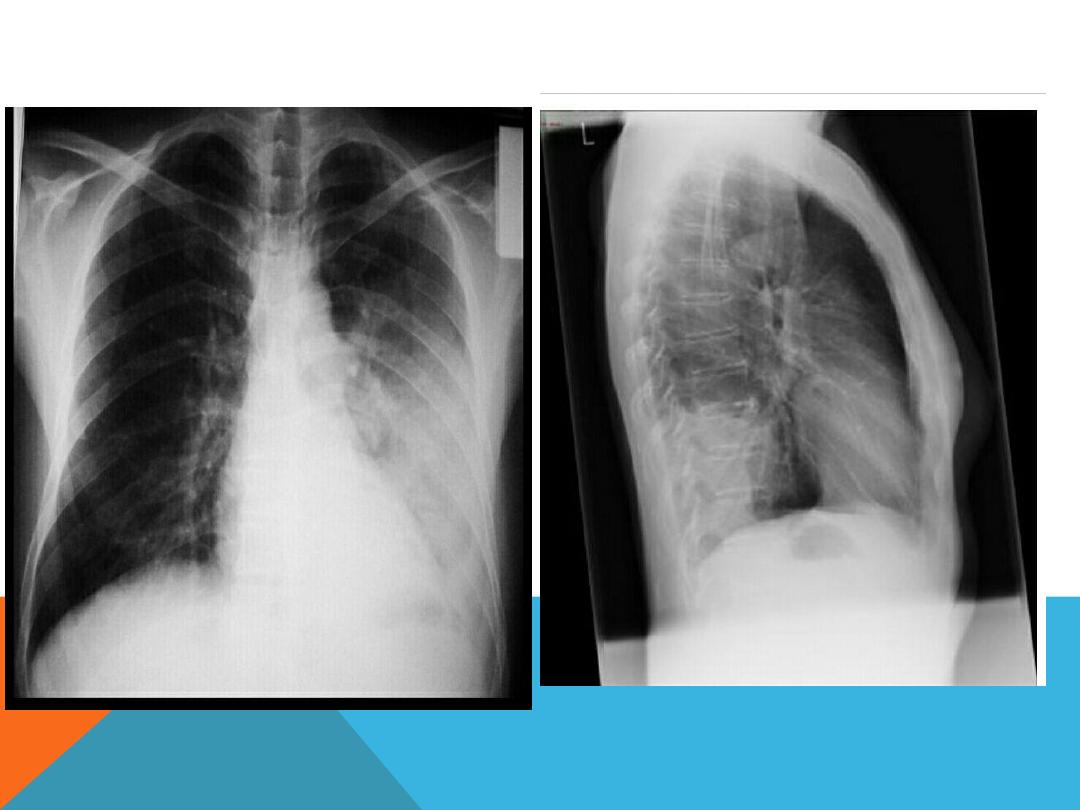
NORMAL CHEST PA AND LAT. VIEW
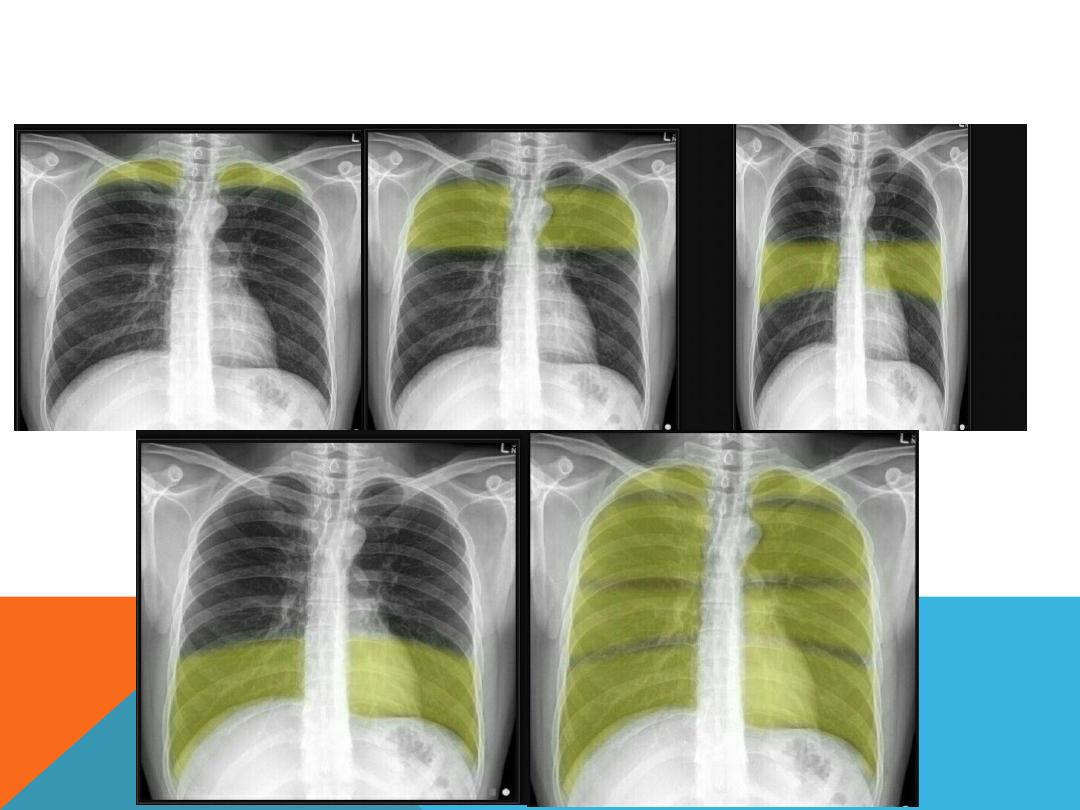
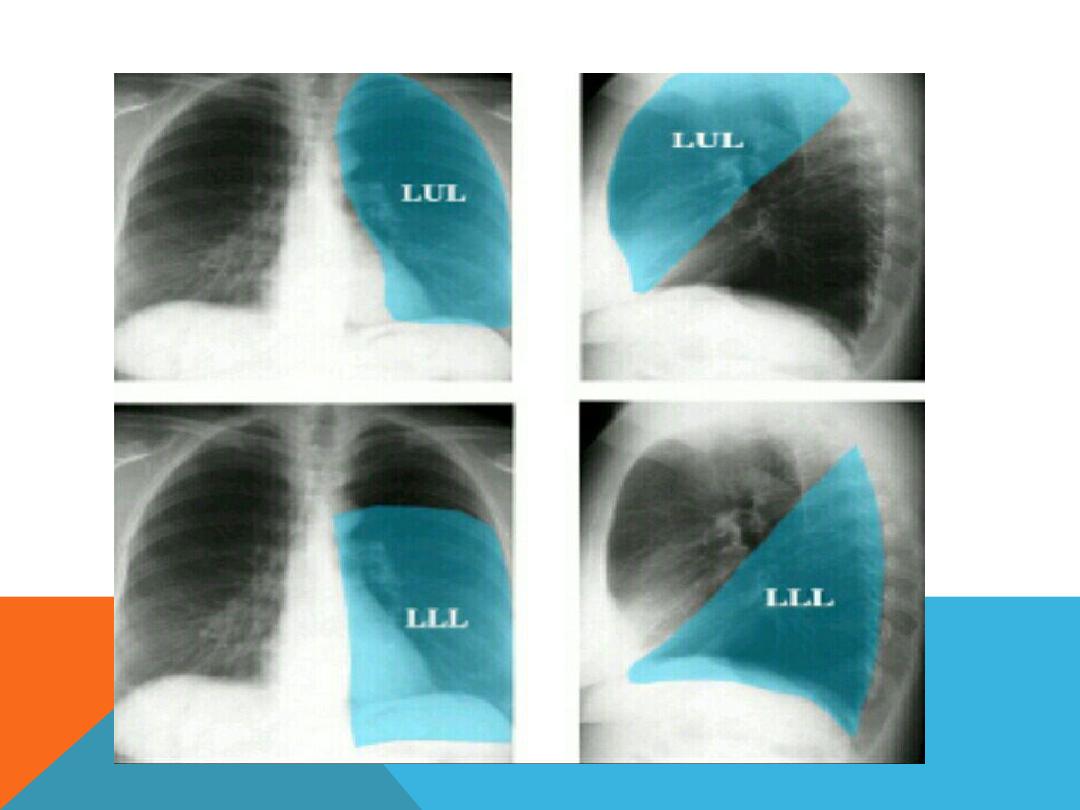
LUNG ZONE
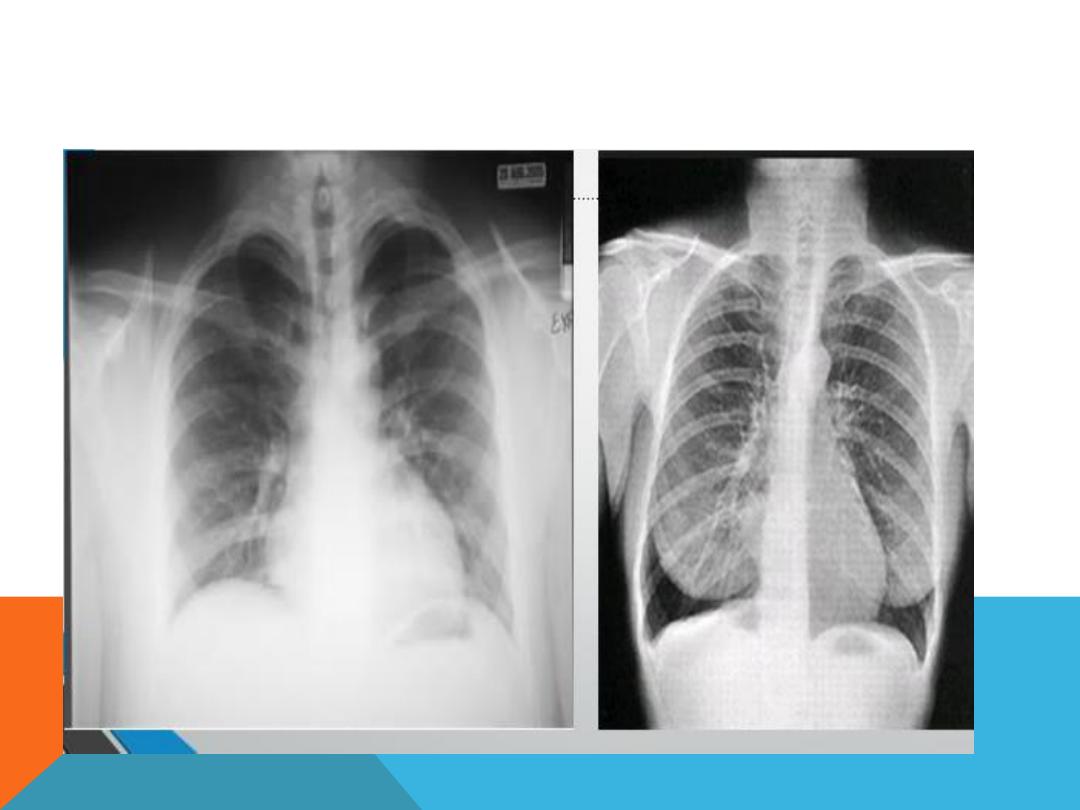
INSPIRATORY VS. EXPIRATORY FILMS

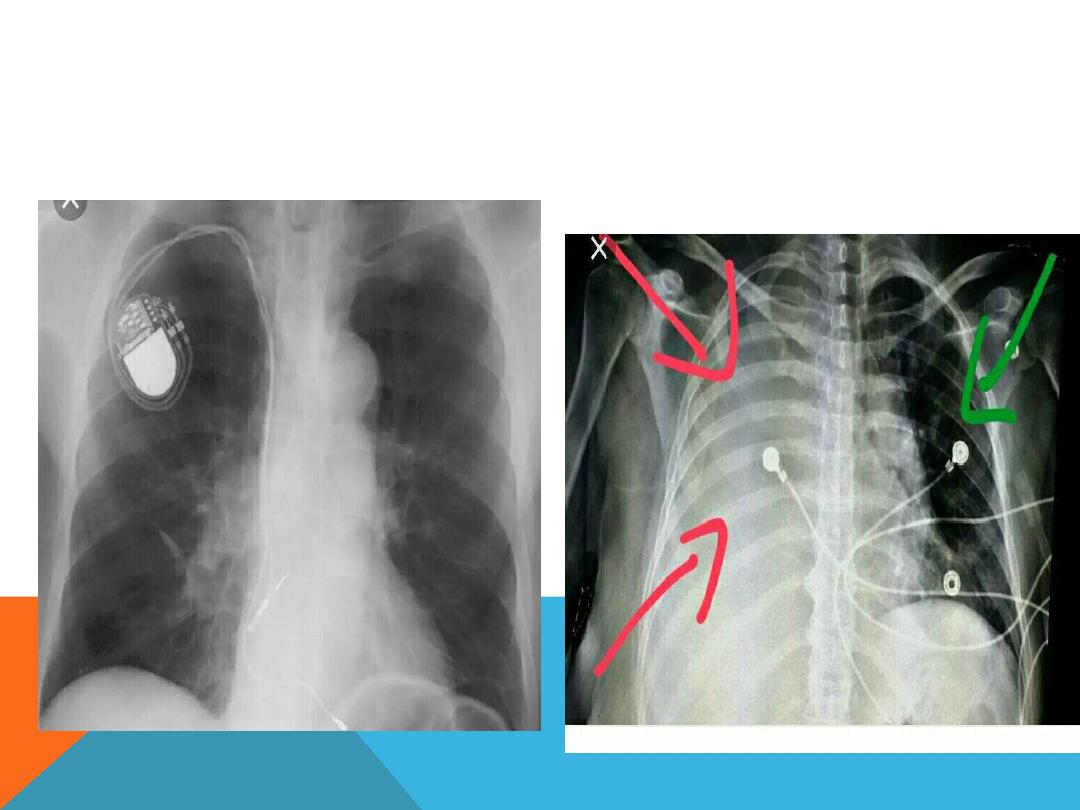
Check if there are any instrument

CHEST RADIOGRAPH TERMINOLOGY.
(RADIOLOGY LANGUAGE)
1.Silhouette sign
: Refers to loss of
normal borders between thoracic
structures , caused by an intra-thorasic
radio- opaque mass that touches the
border of the heart or aorta ex, in Rt.
middle lobe syndrome the Rt. heart
border is obscured

2. AIR SPACE OPACIFICATION (AIR SPACE FILLING )
Replacement of air in the alveoli by fluid or other materials …it has
an
ill-defined
border
except
when
it comes in
contact with a fissure .
Exudate …
consolidation
Transudate ….
pulmonary odema
Air bronchogram…
air filling the normal bronchi , being
made visible by the opacification of the near by
alveoli.
Pulmonary collapse . (atelectasis)
Nodular ,spherical opacities
Linear opacities.
Wide spread opacites
Cavitation
CONSOLIDATION( PNEUMONIA
)
Replacement of air in one or more acini by fluid
or solid material vol. of the lung is normal un
like collapse
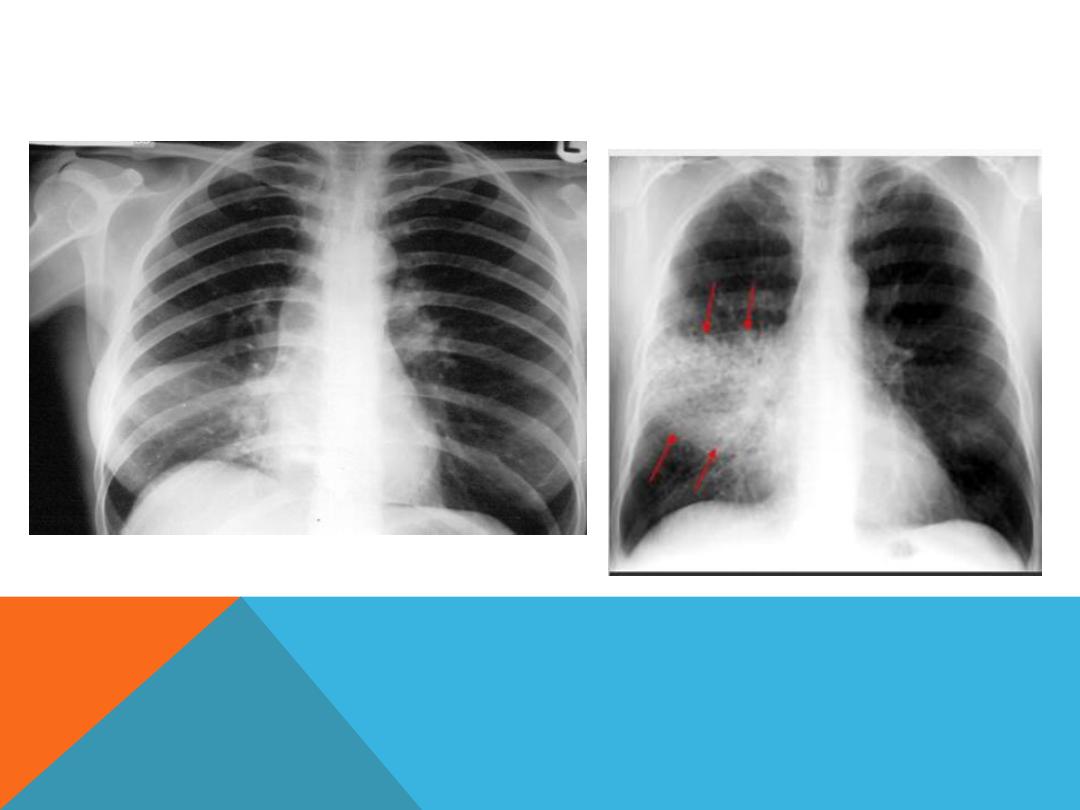
MIDDLE LOBE CONSOLIDATION
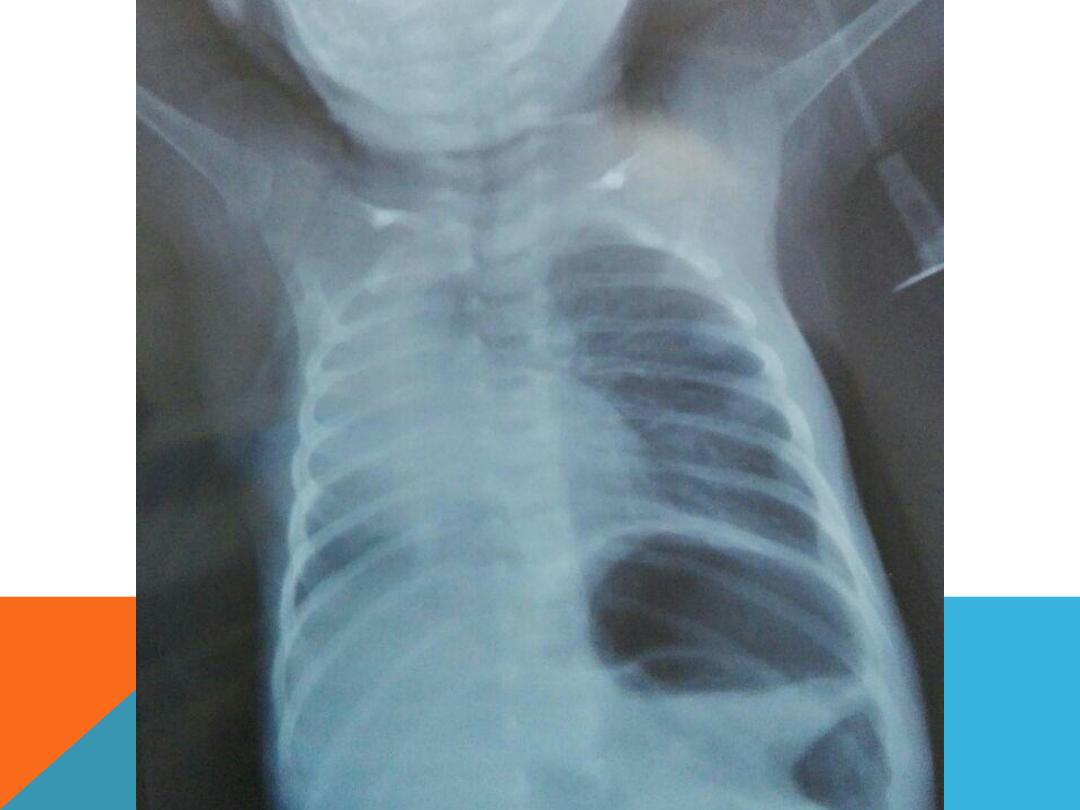
AIR BRONCHO GRAM : ARE FILLING BRONCHI WHICH
IS MADE VISIBLE BY THE OPACIFICATION OF THE
SURROUNDING ALVEOLI

DISEASE OF LUNG APEX
1.Pneumothorax
2.Pan coast tumor
3.bullae
4.Pulmonary TB
5.Upper lobe blood diversion reaching lung
apices ( pulmonary plethora )
6.Massive pleural effusion reaching lung
apices.

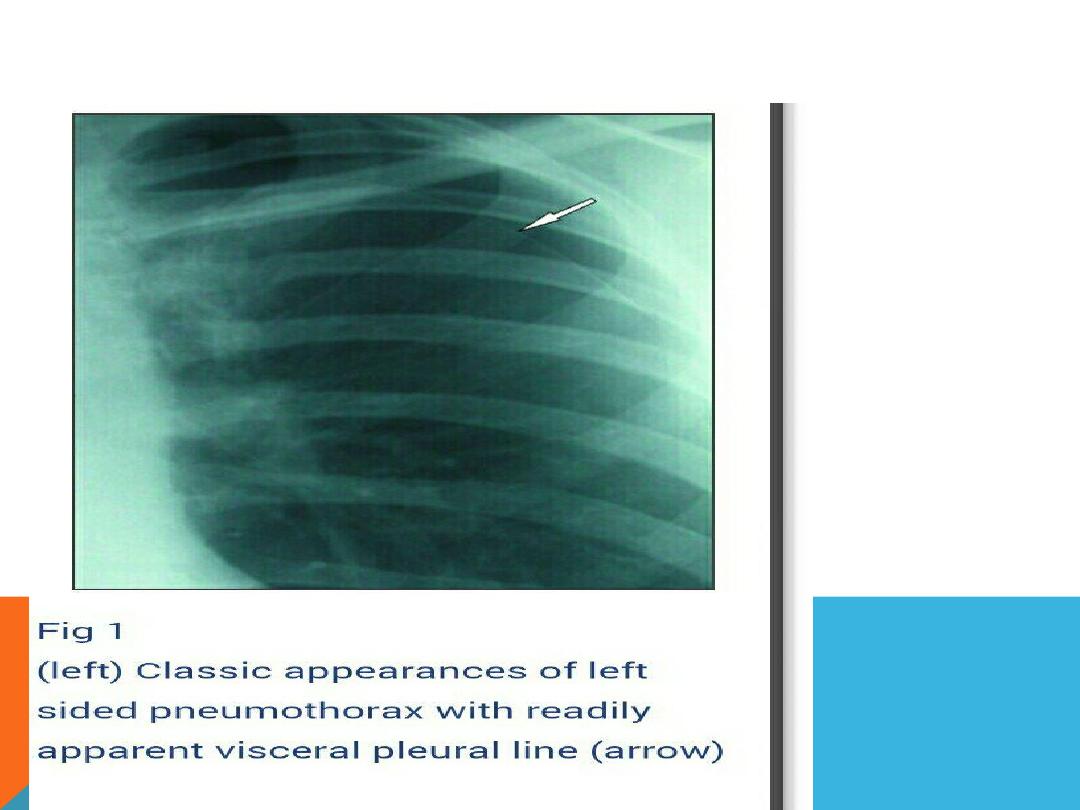
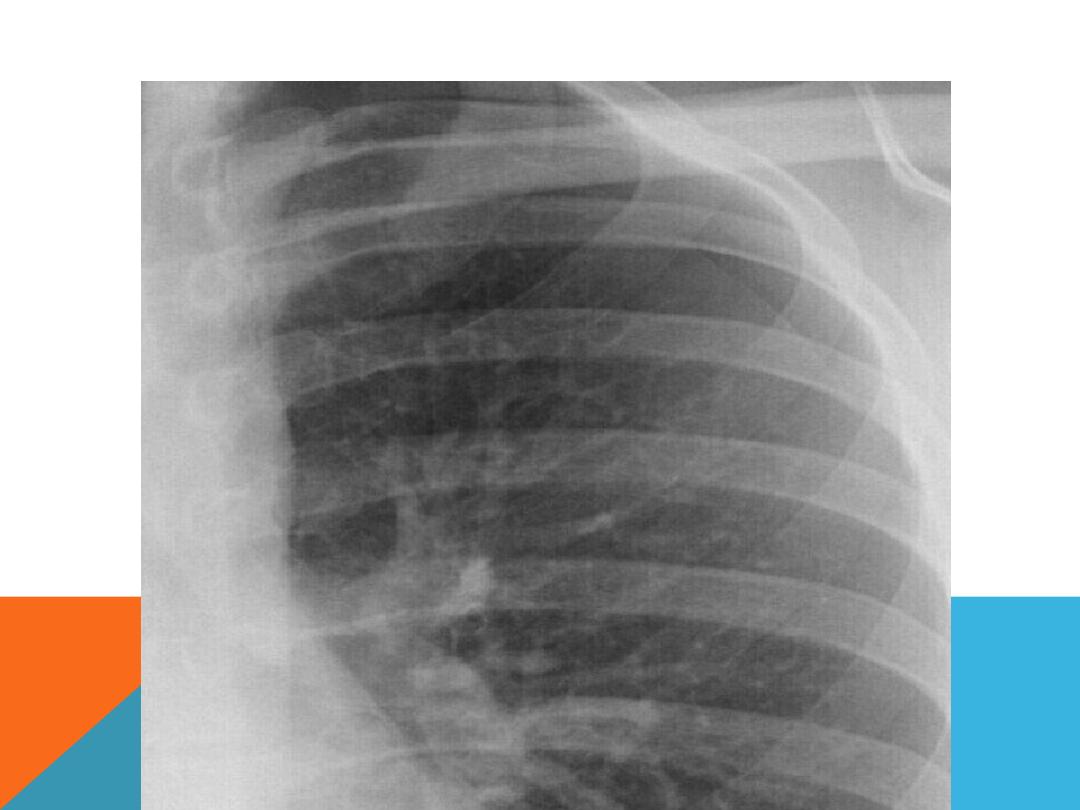
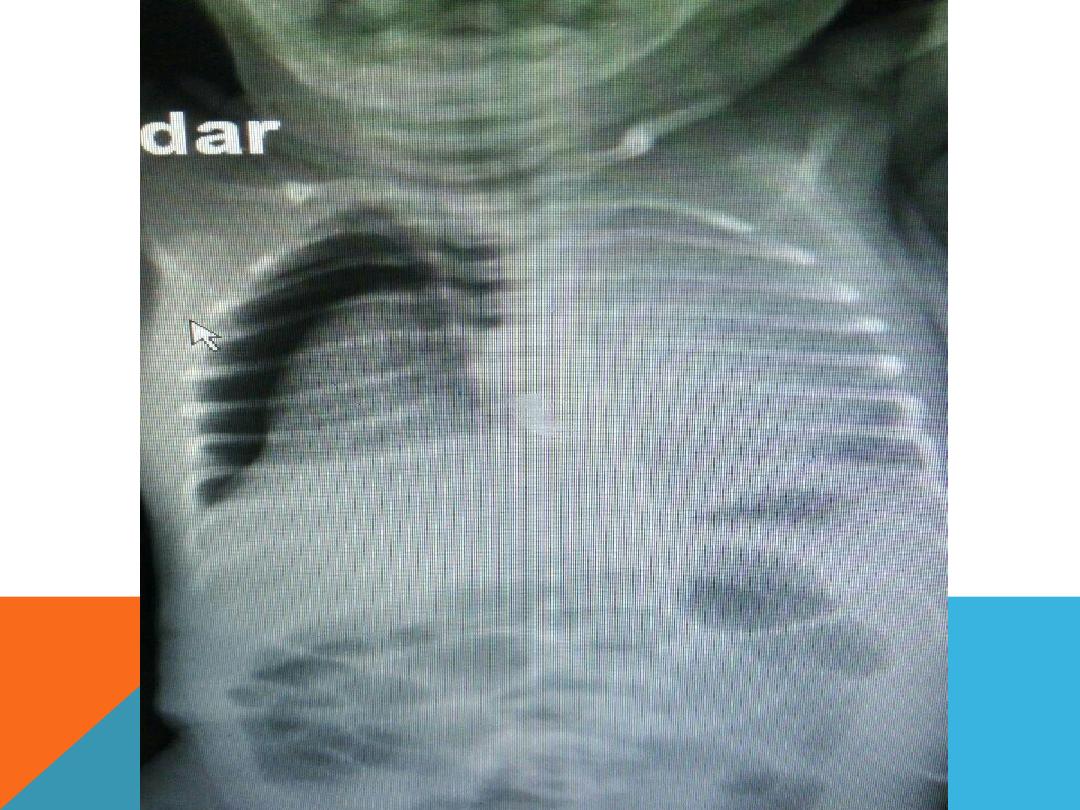
PNEUMOTHORAX ..SUDDEN ONSET DYSPNEA,
.CHEST PAIN
Causes
1.Chest trauma
2.Rupture air blister (bleb) …Tension
pneumothorax
3.lung disease .pneumonia , cystic
fibrosis ,chronic interstitial lung disease
Risks factors
:
male , smoker , age ,
genetics, mechanical ventilation ,previous
pneumothorax
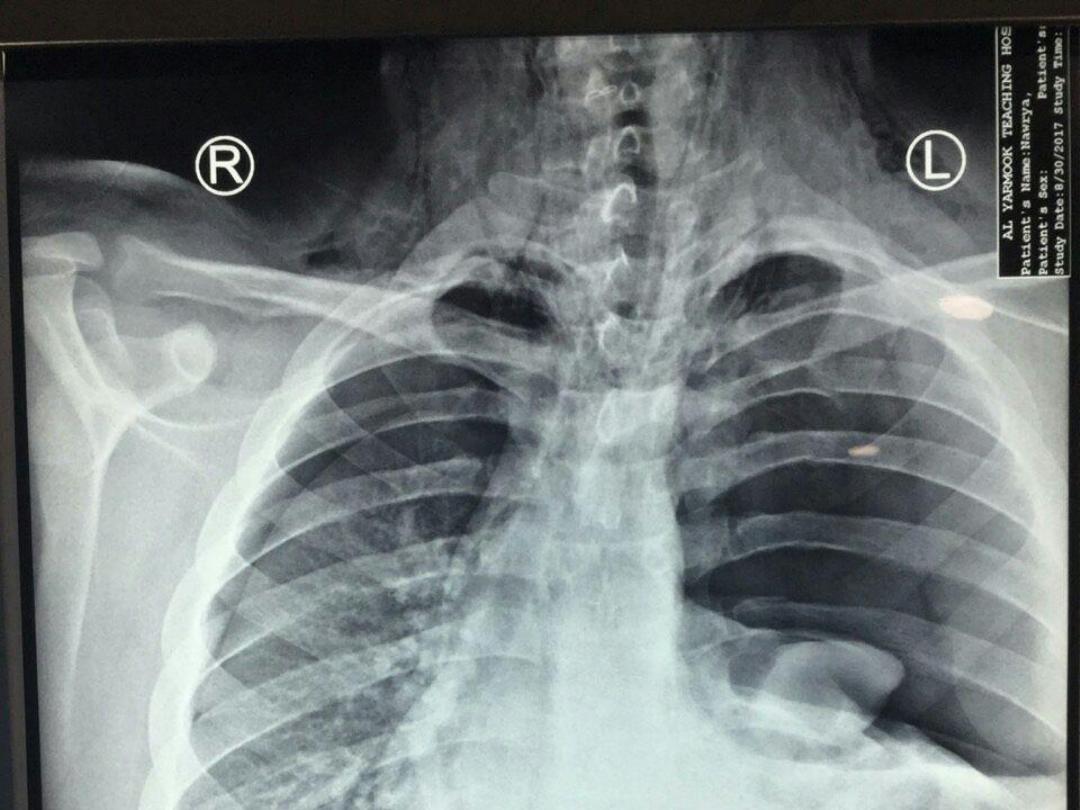

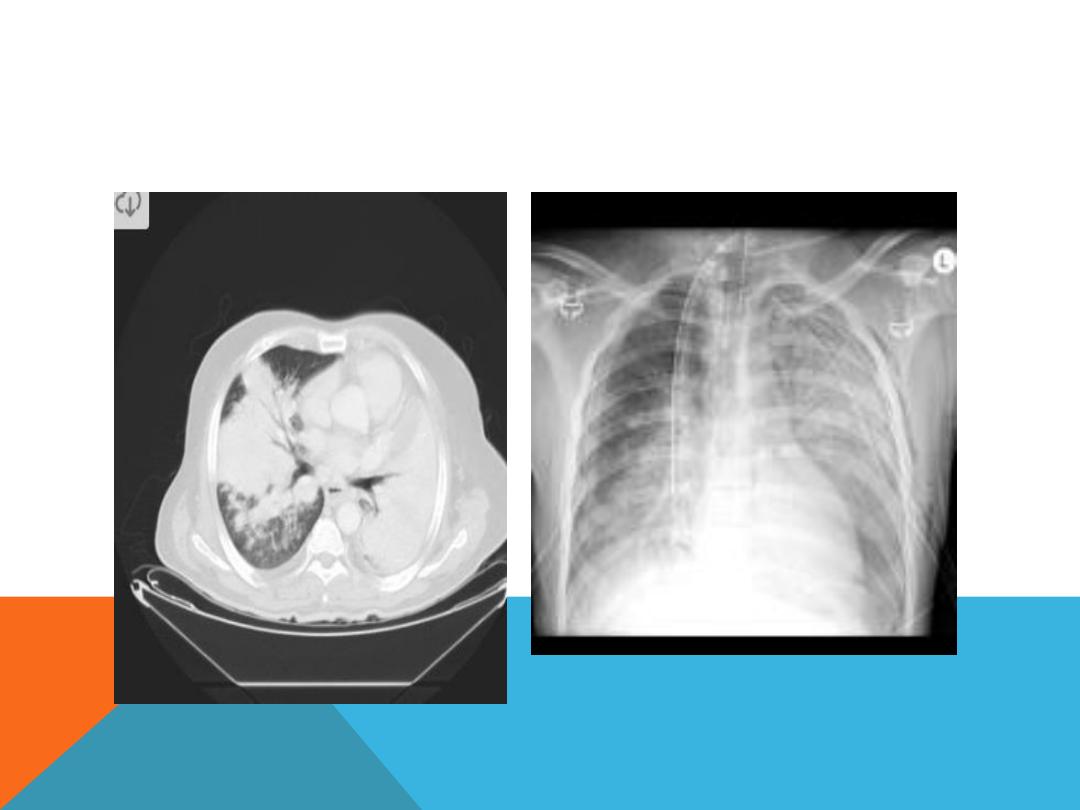
PAN COAST TUMOR ( SUP. SULCUS TUMOR)
Un common situation of primary
bronchogenic carcinoma arising in
the lung apex
Presenting as arm pain, shoulder pain
, Horner syndrome, chest symptoms
, wt. loss.
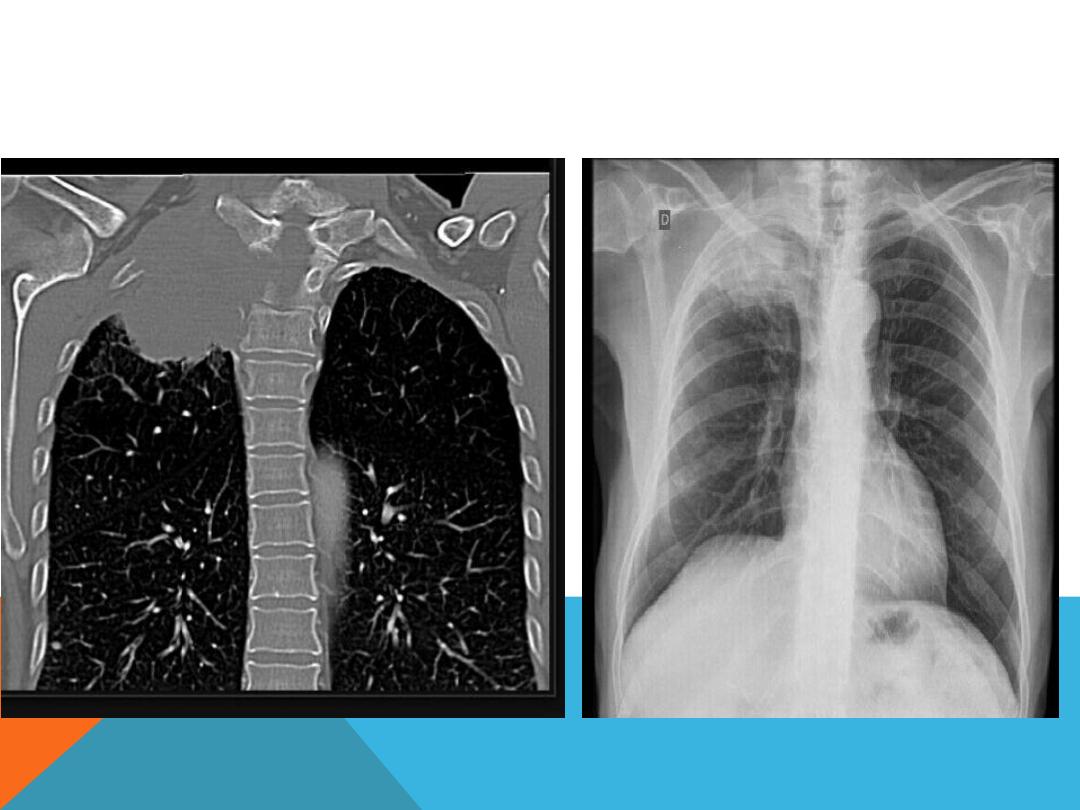
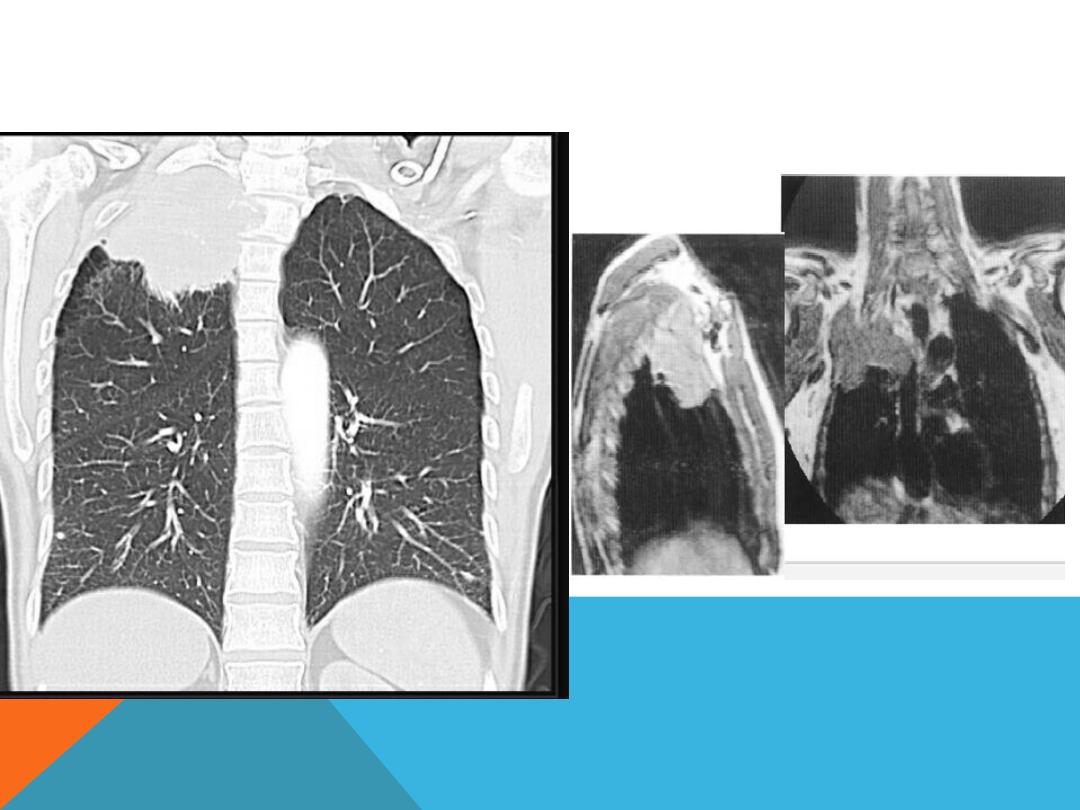
PAN COAST TUMOR

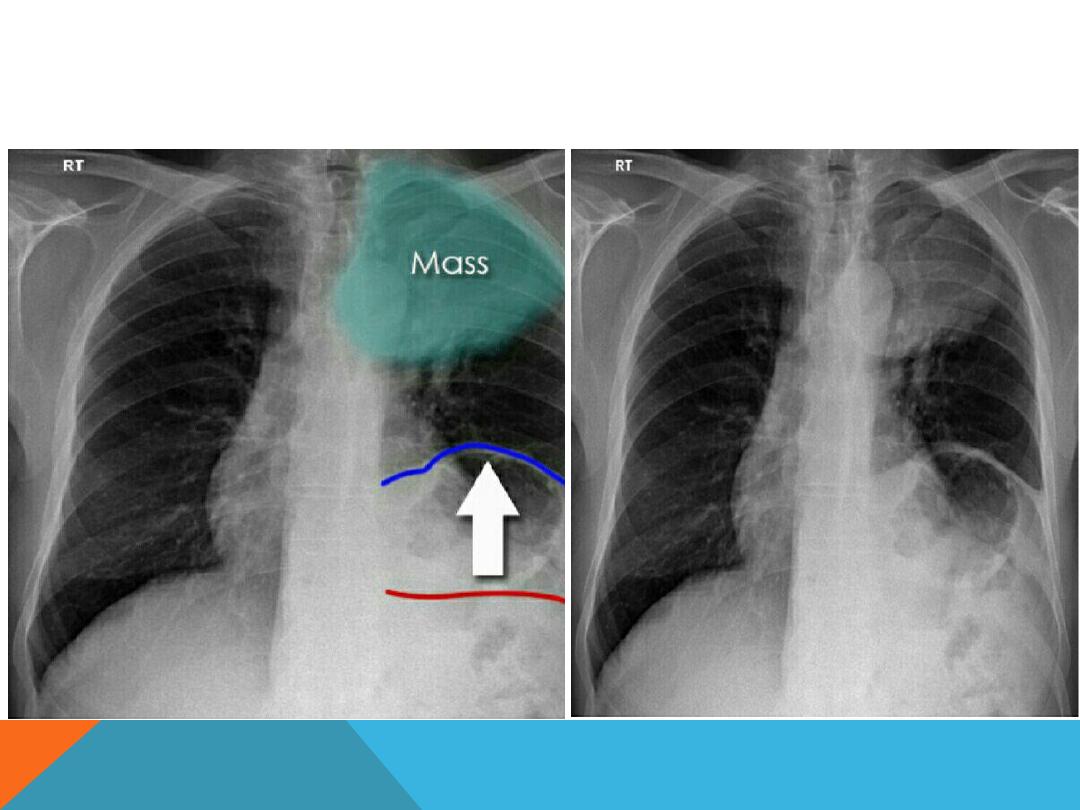
HILAR LUNG DISEASE
1. Enlargement
:
bilateral ..both are enlarged and
denser than normal …ex: primary TB , sarcoidosis ,
Mets. ( ca. breast ) , lymphoma , infection , pulmonary
arterial hypertension . ..When
asymmetric,
one hilum
appears larger than the other .
2. Displaced hilum :
abnormal positioned ,
pulled
to one
side . Indicating loss off volume in the affected side
..
or
pushed
to the other side : ex.. Massive pleural
effusion, emphysema or pneumothorax of the contra
lateral side
3. Normal positioned …it is formed by vessels and end
on bronchi
HILUM
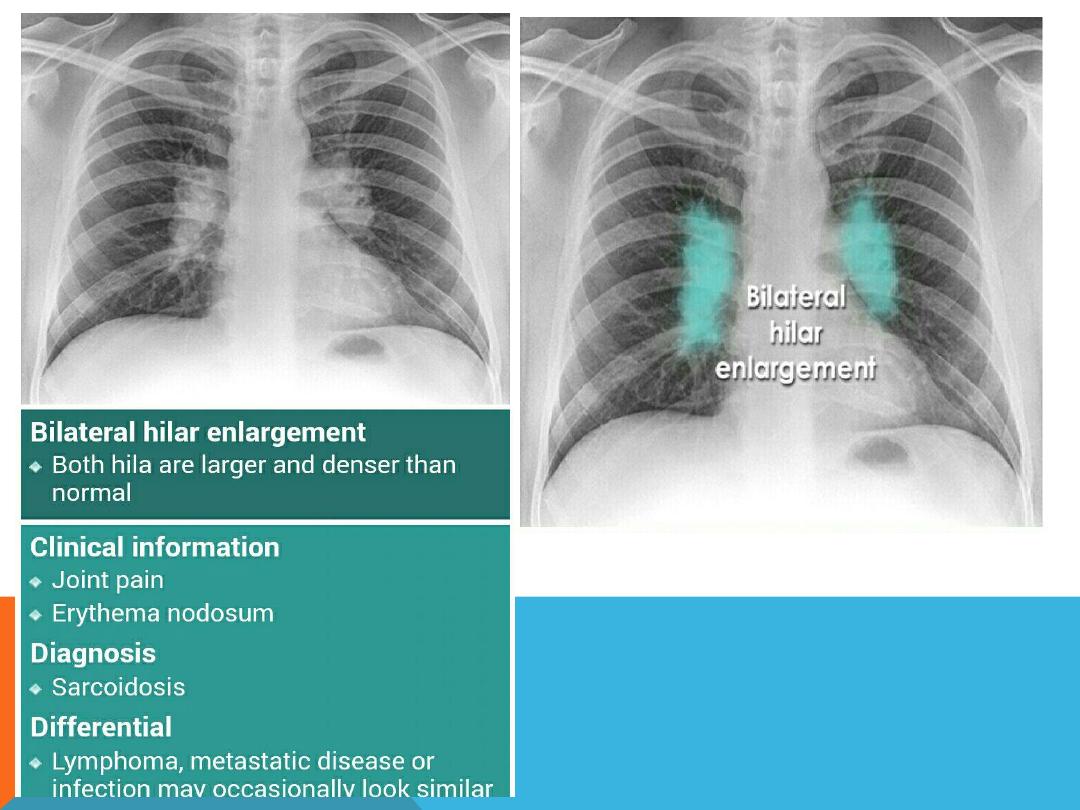
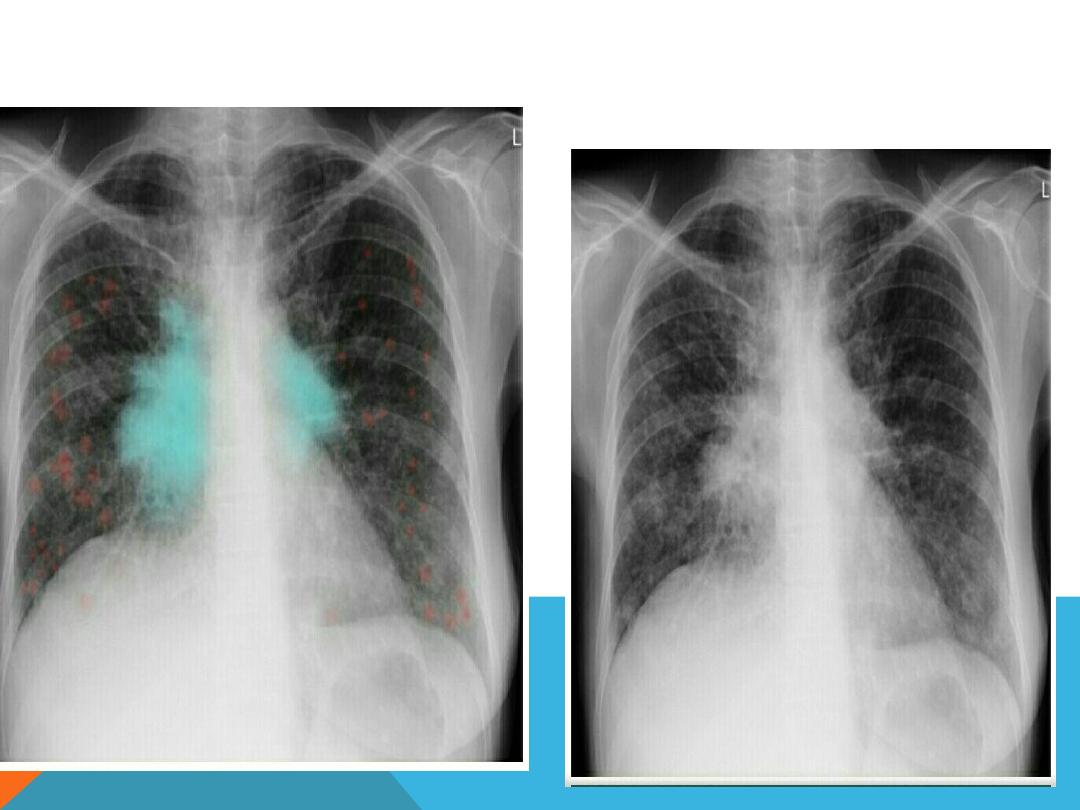
NON SYMMETRIC HILAR ENLARGEMENT
THE DIAPHRAGM
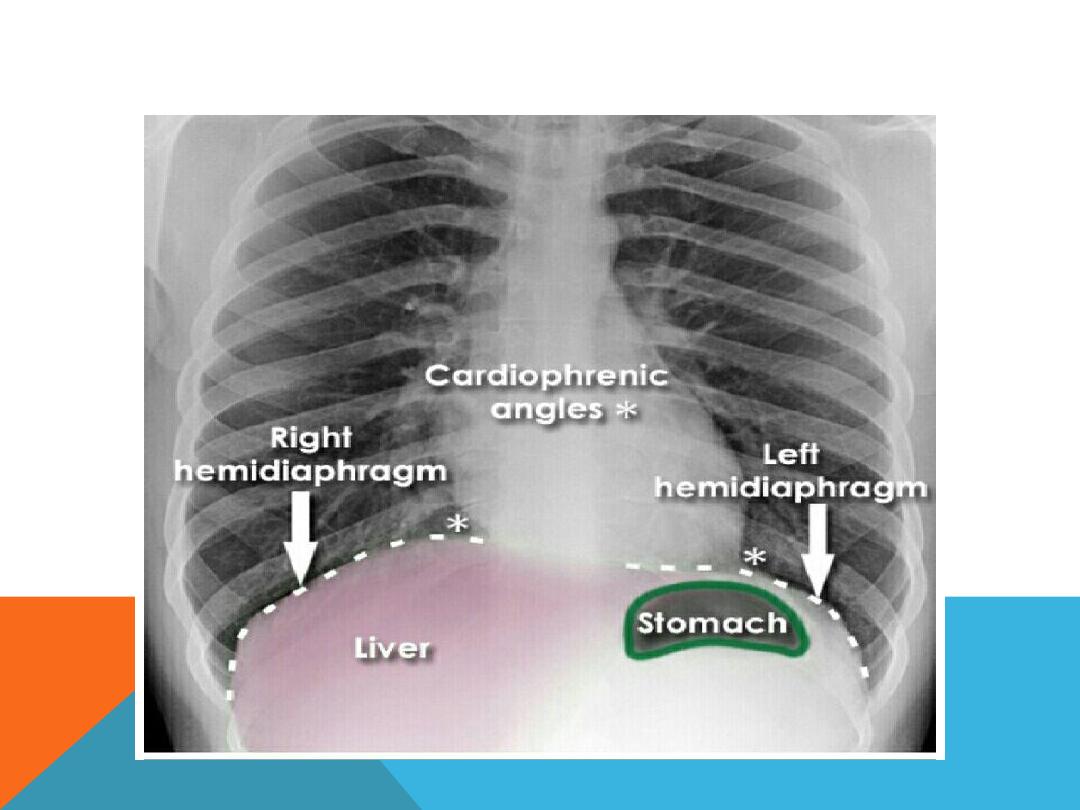
DIAPHRAGM
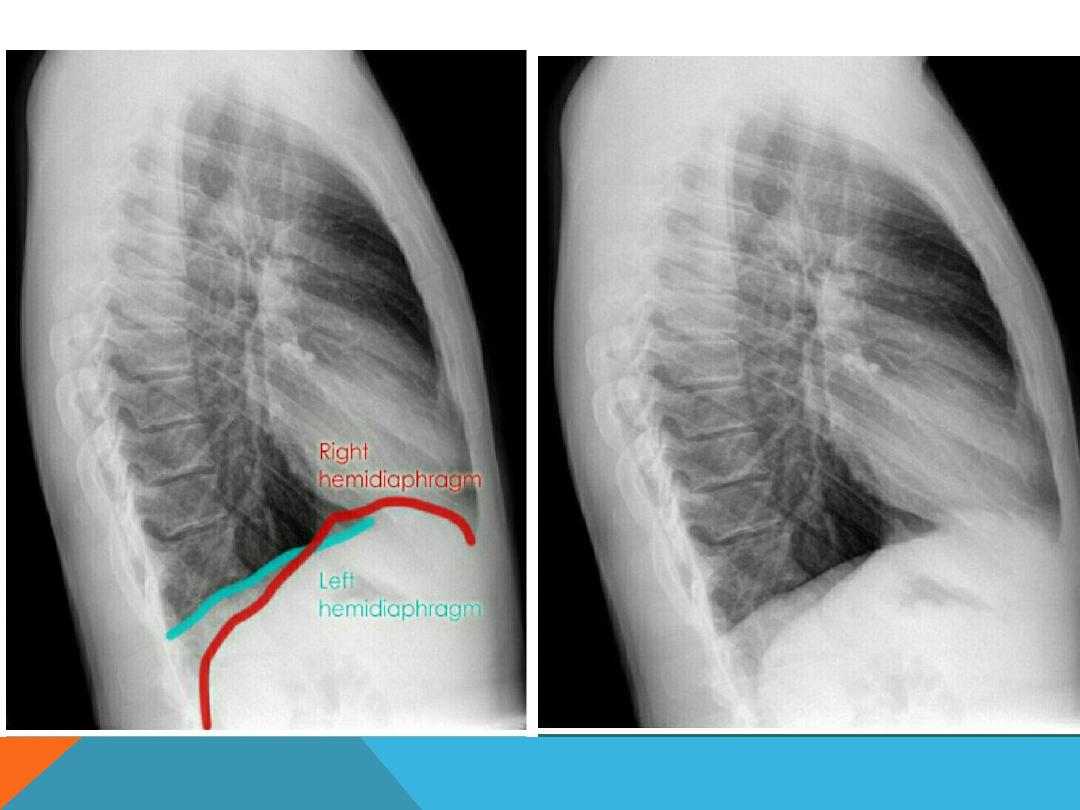
PHRENIC NERVE PULSY
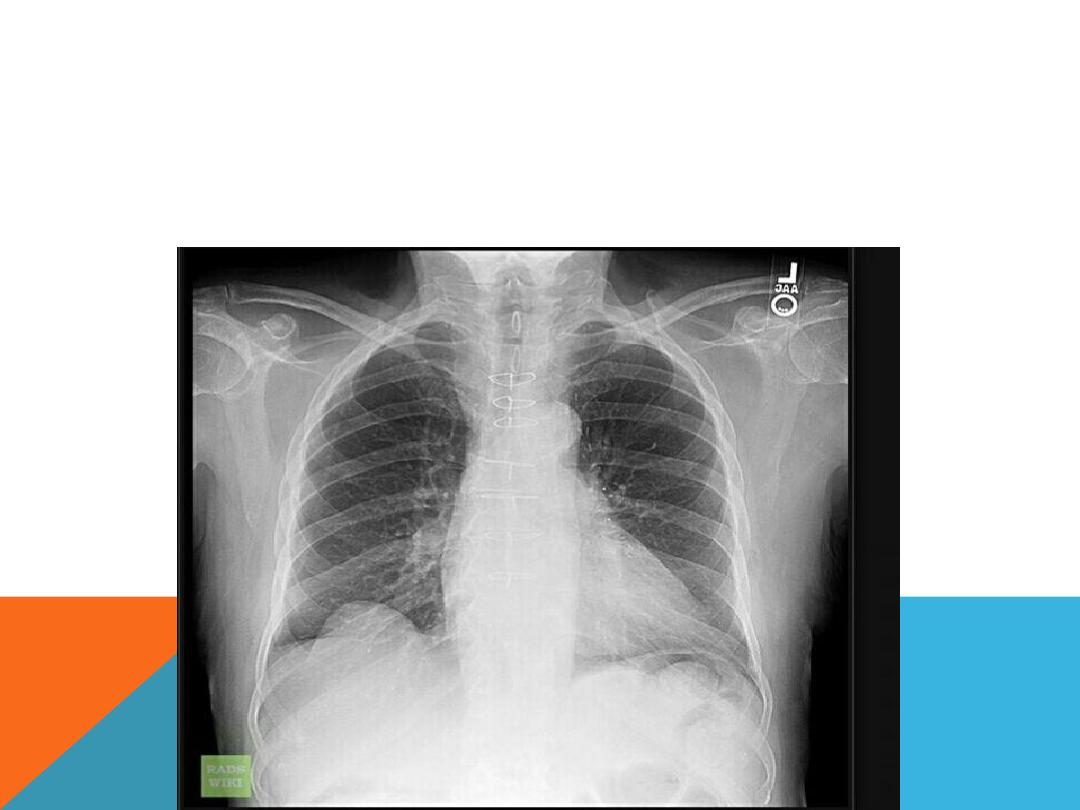
EVENT RATION OF THE DIAPHRAGM
Abnormal contour of the diaphragmatic dome, it
affect a segment of the hemi diaphragm
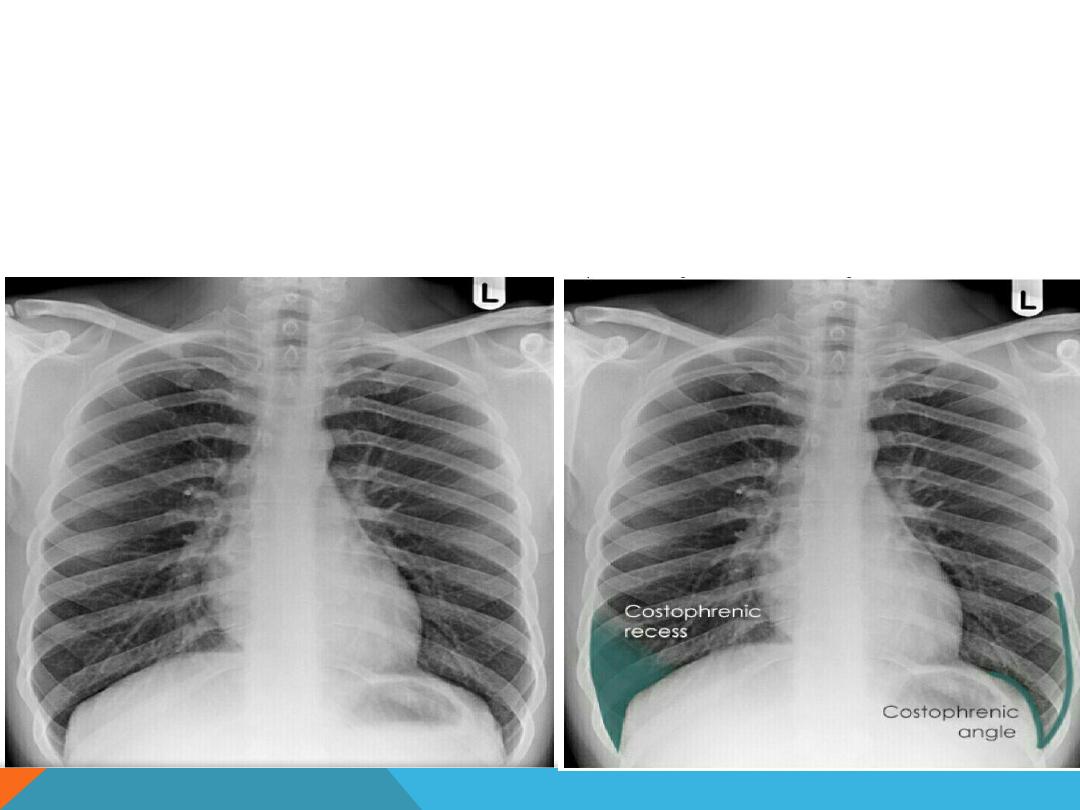
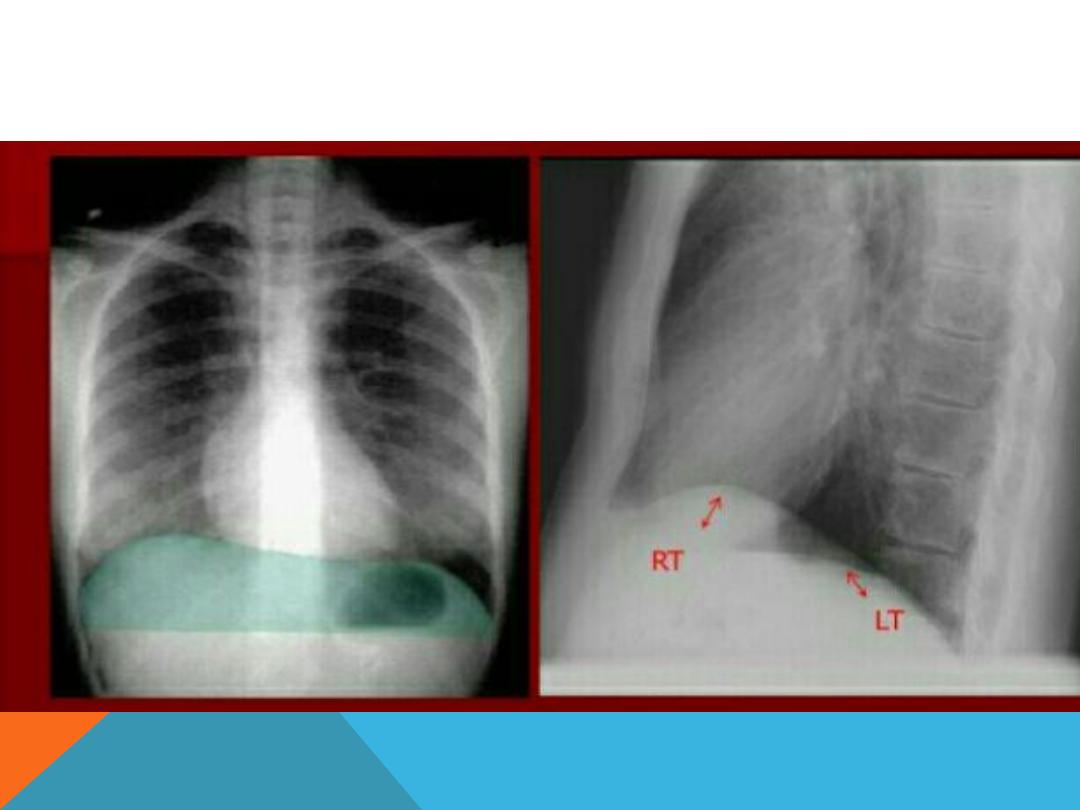
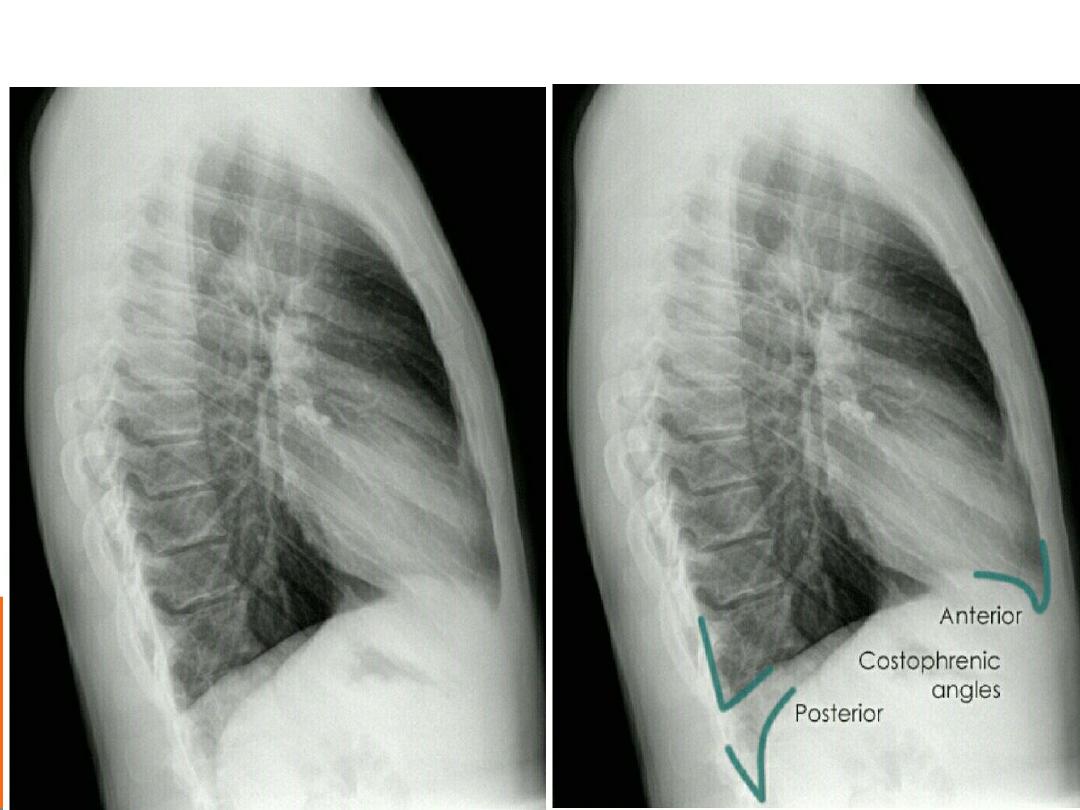
COSTO-PHRENIC ANGLES (RECESS )
Formed by the hemi diaphragms and
the chest wall
FULL INSPIRATION, PA, 10 POST. OR 6 ANT.
RIBS
SOFT TISSUE.. LT MASTECTOMY

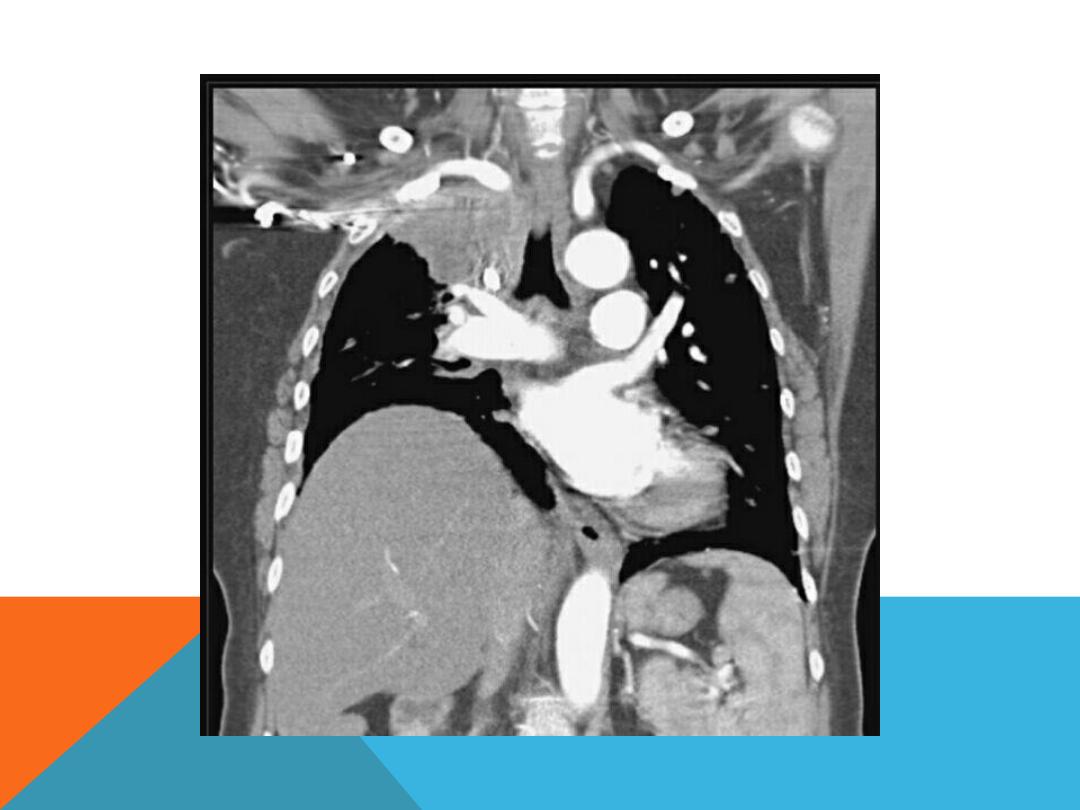
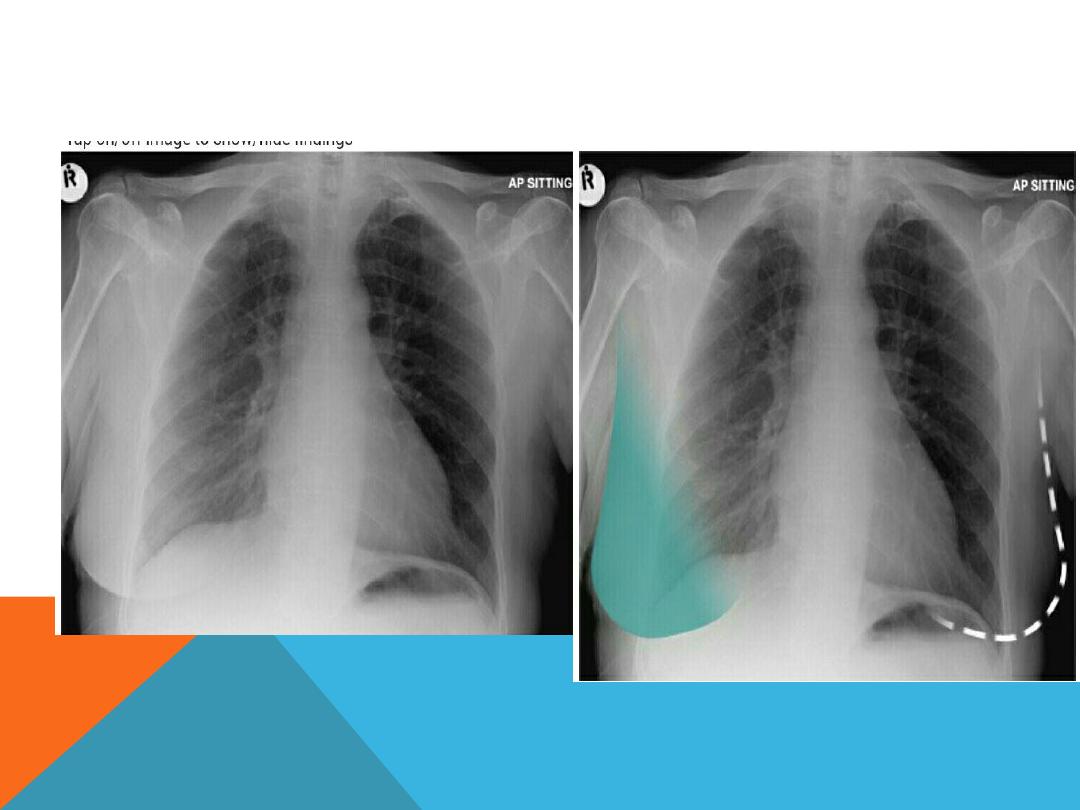
PLEURAL EFFUSION
Fluid accumulate in the pleural space .
History …
chronic hepatitis
,alcoholic induced pancreatitis,
trauma, malignancy ( lung,
breast , ovary , lymphoma,
adenocarcinoma ), heart failure
….
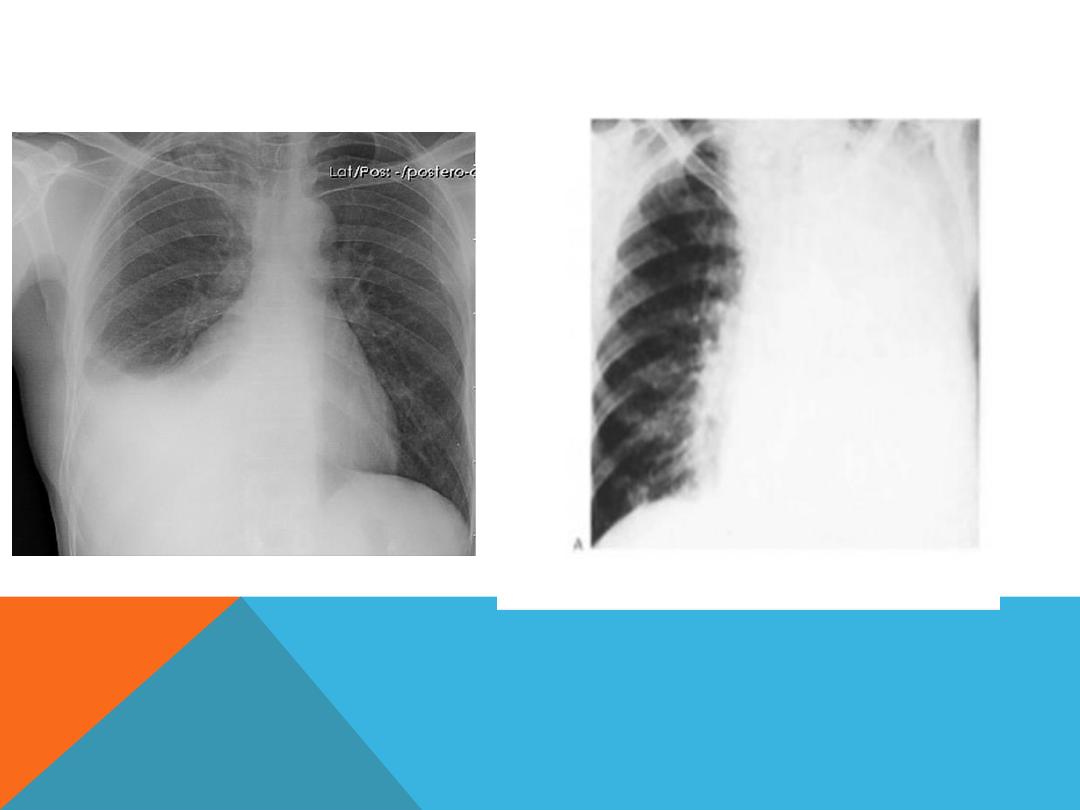
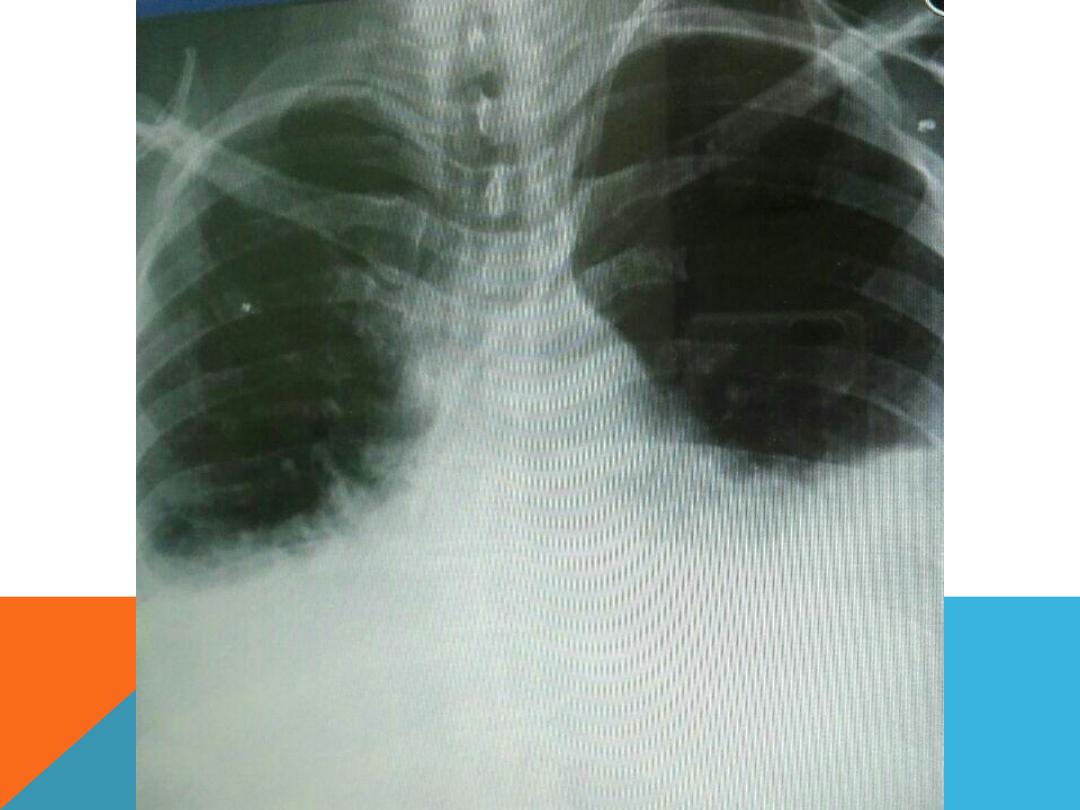
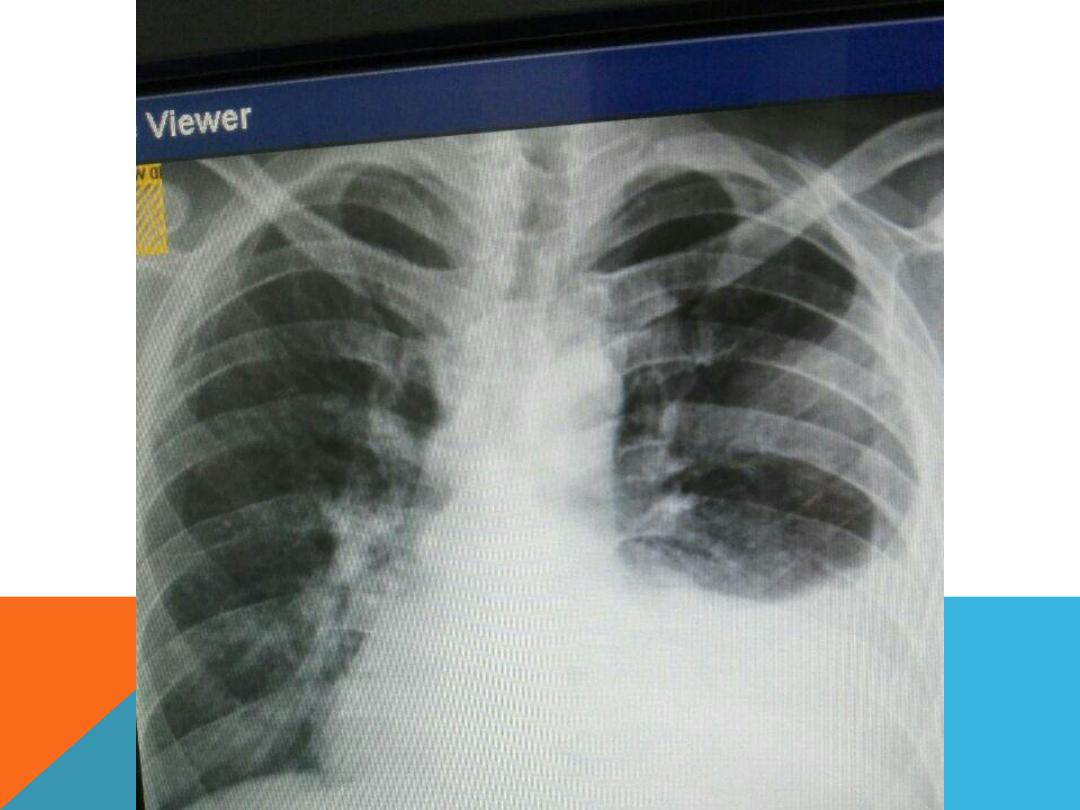
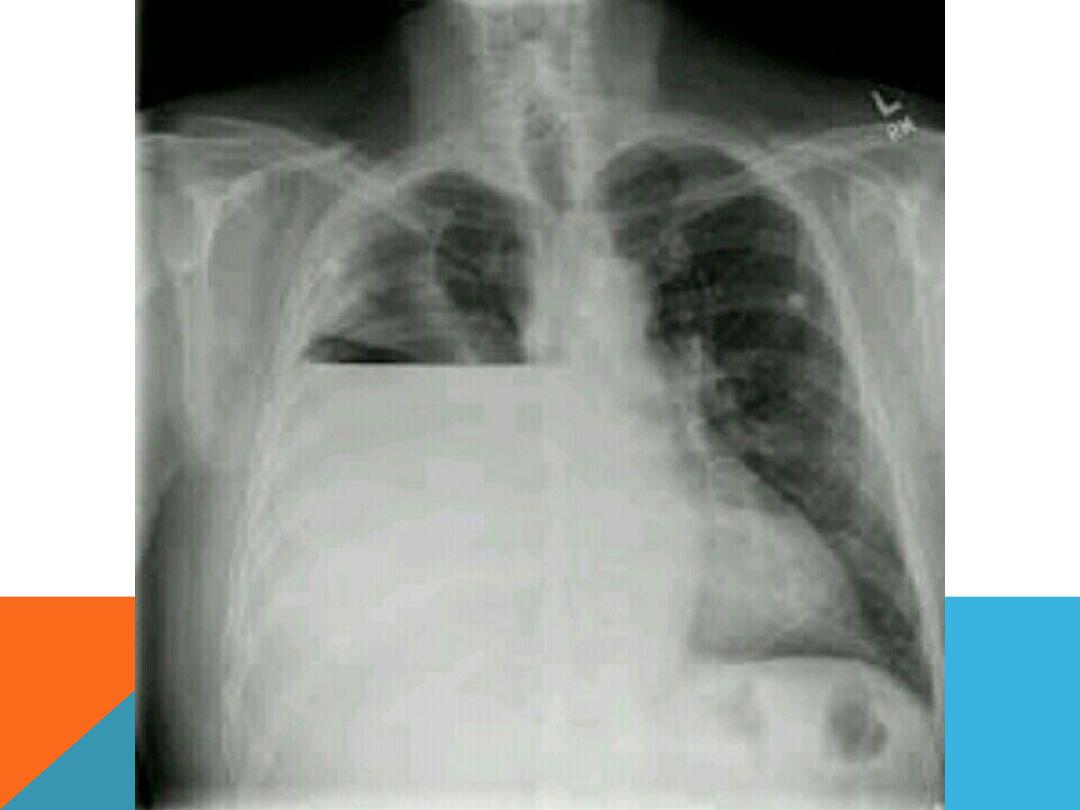


DEFUSE LUNG DISEASE
Miliary opacification
…
small opacities = 4
mm in size ex TB, sarcoidosis,
histeoplasmosis , Mets ( beast, thyroid ,
renal , colorectal, Ewing sarcoma ,osteo
sarcoma, chorionic carcinoma ) hyaline
membrane disease
Reticulonodular
…
even smaller in
diameter .. Ex collagen disease .
Pneumoconiosis,
Fungal infection ,sarcoidosis,, pulmonary
odema ,defuse interstitial pulmonary
fibrosis.

Honey comb opacification
..
end stage destruction of the
lung parenchyma following
advanced pulmonary fibrosis
..thin wall air cyst = about 4 mm
in size . There is an increase
risk of
tension pneumothorax
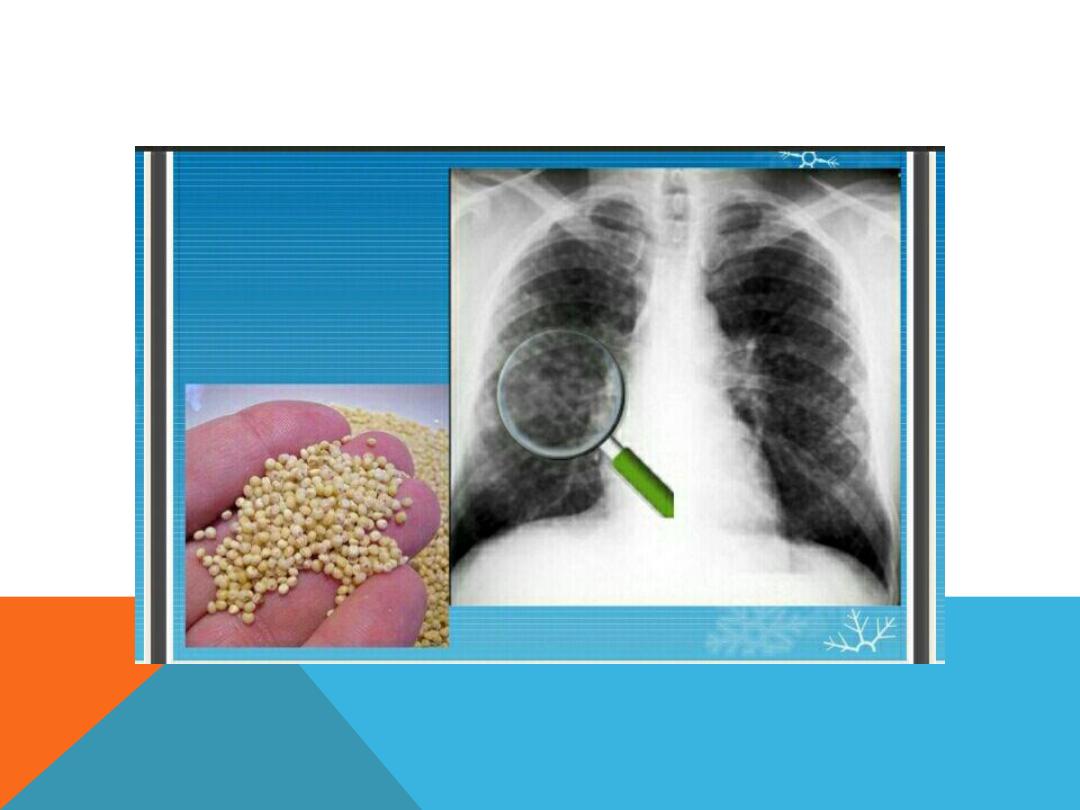
MILIARY OPACIFICATION
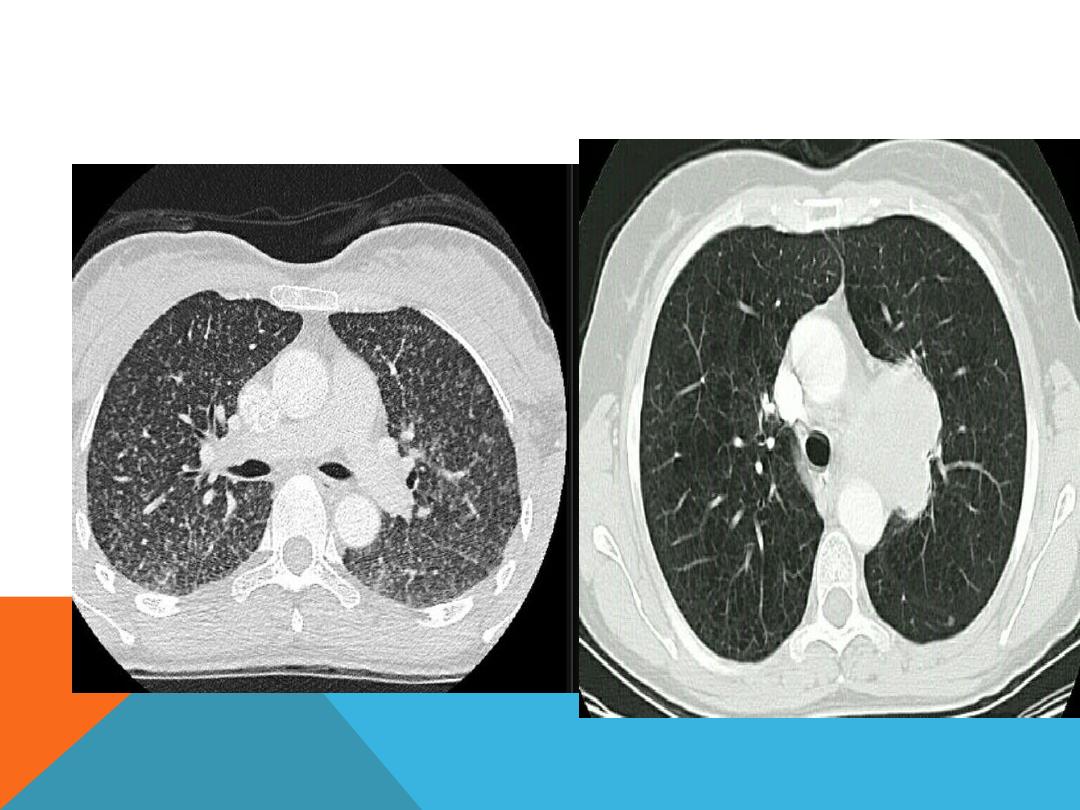
MILIARY + NORMAL CHEST
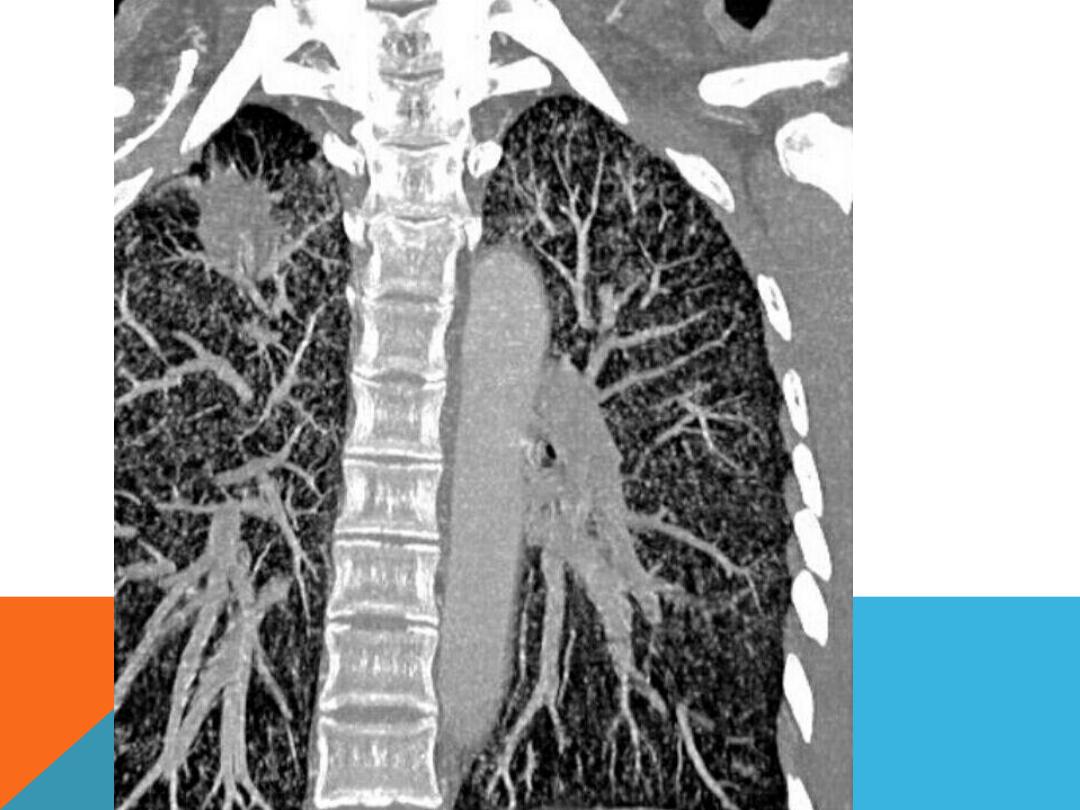
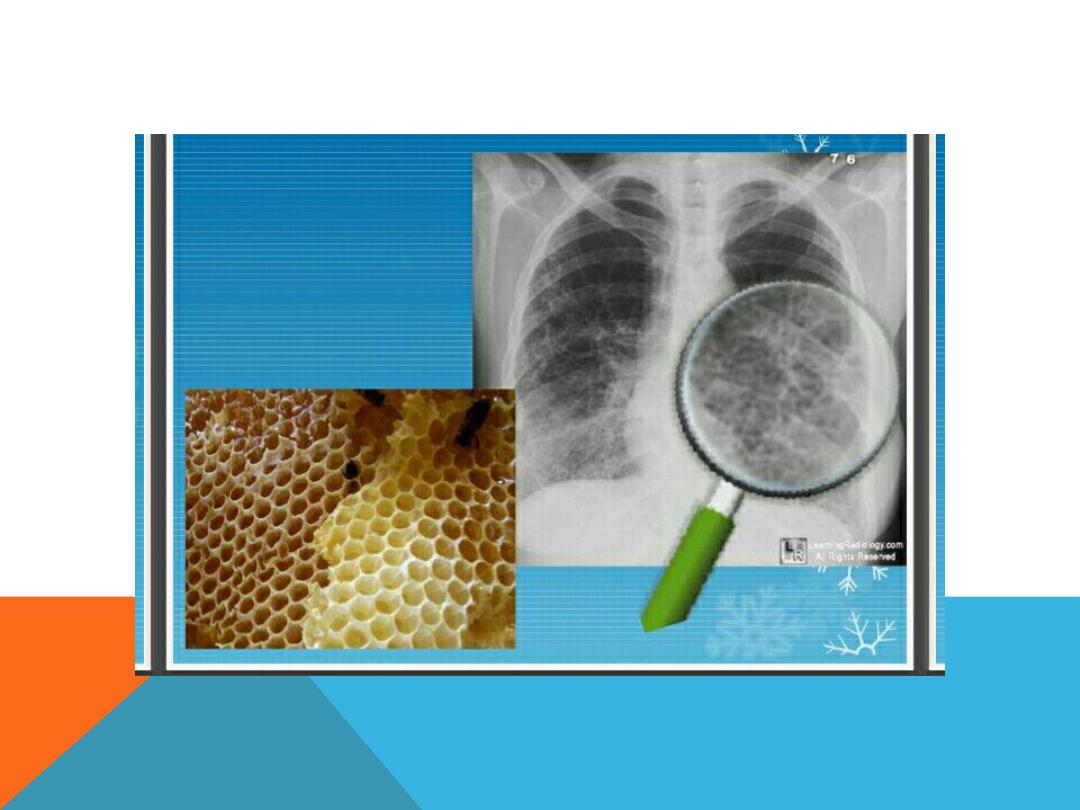
HONEY COMB OPACIFICATION

PULMONARY NODULES
A nodule is a coin mass about
3 cmm in size
Single
…
primary tumor
,Mets., lymphoma,
Hamartoma ,TB , abscess , hydatid
,granuloma.
Multiple
… Mets, lymphoma, hamartoma,
hydatid , granuloma

CAVITATING LESIONS AND CYSTS
cavity
..a gas – filled space
surrounded by a complete wall of
variable thickness
Ex.. TB , staph aureus cyst ,
carcinoma, abscess, bronchogenic
cyst , pneumatocele

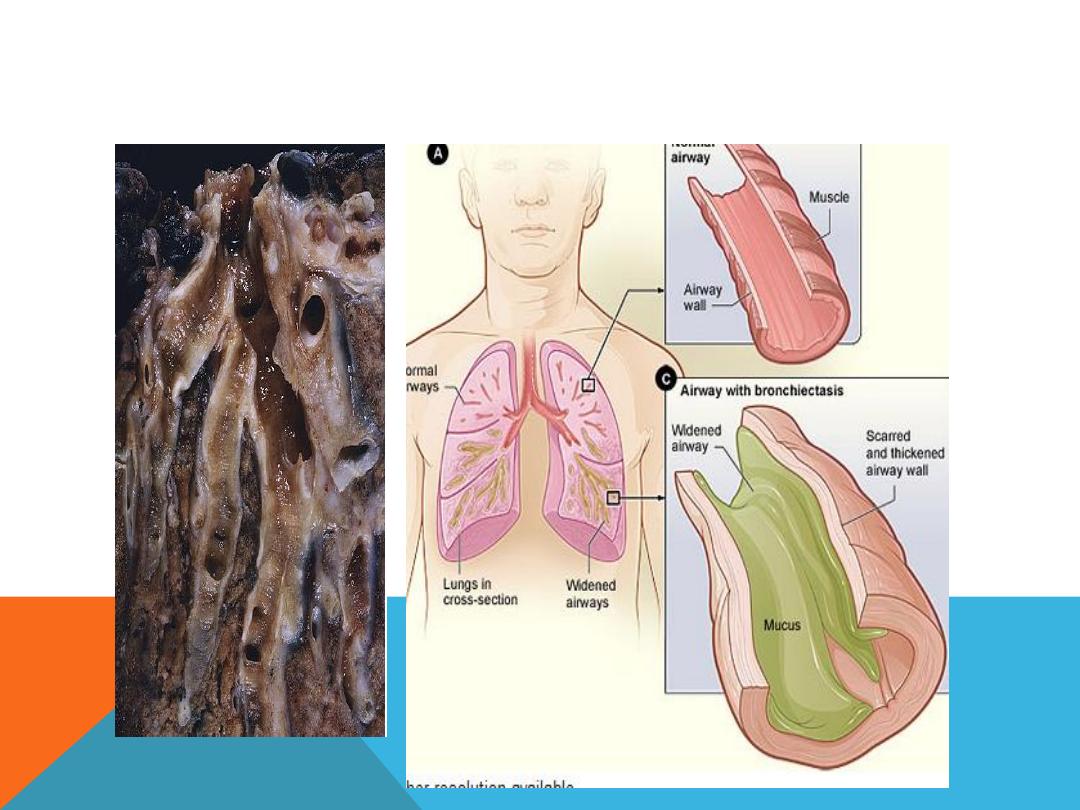
BRONCHIECTASIS
Permanent irreversible dilatation of the
bronchial trea
Recurrent chest infection …much sputum +
hemoptysis ( could be the only presenting
feature )
TB , staph aureus , klebdiella ,
Cystic fibrosis,
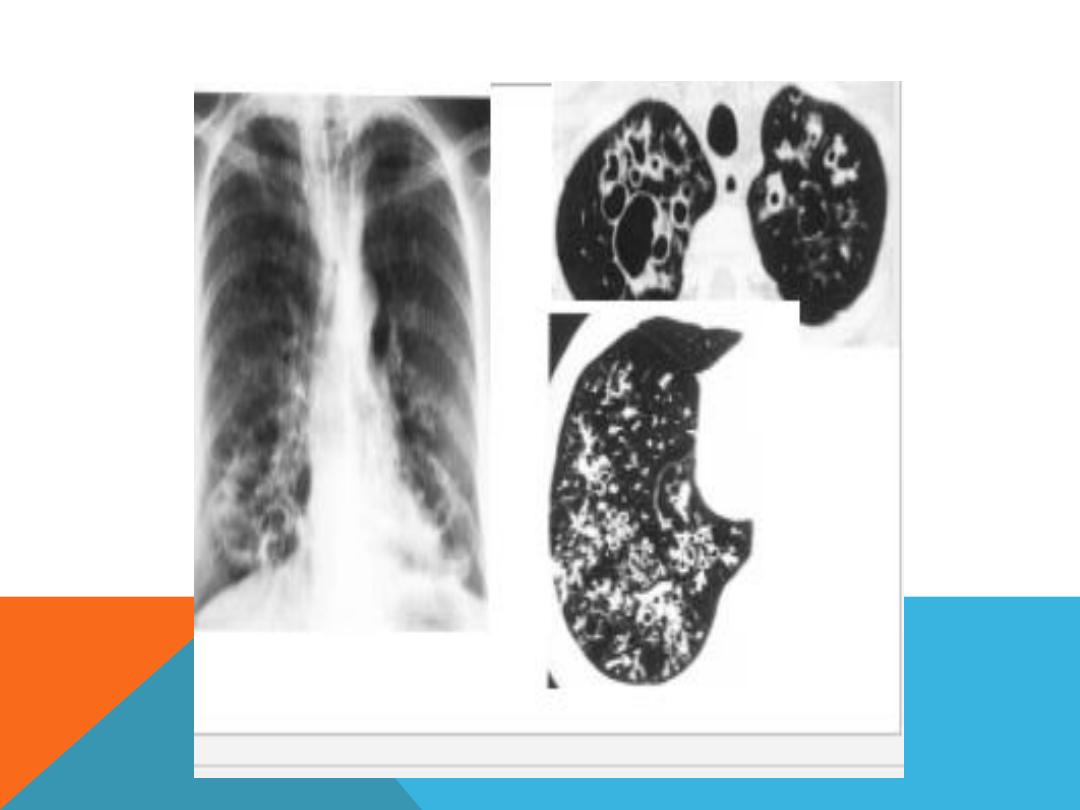
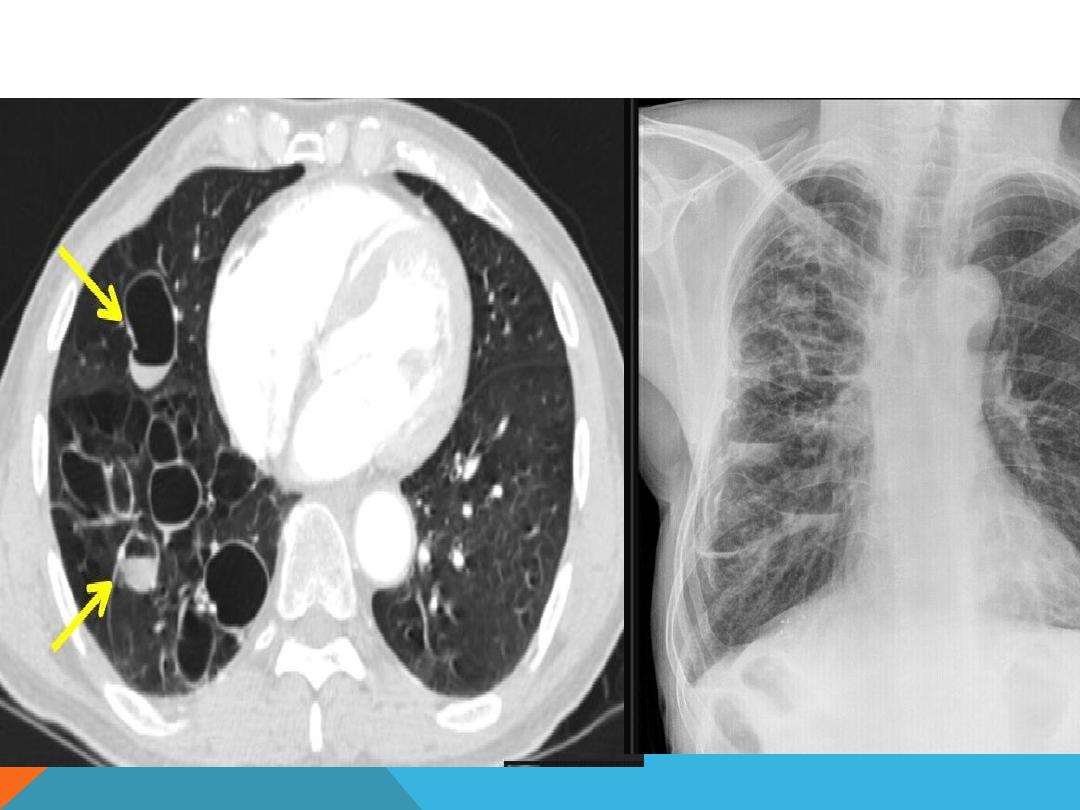
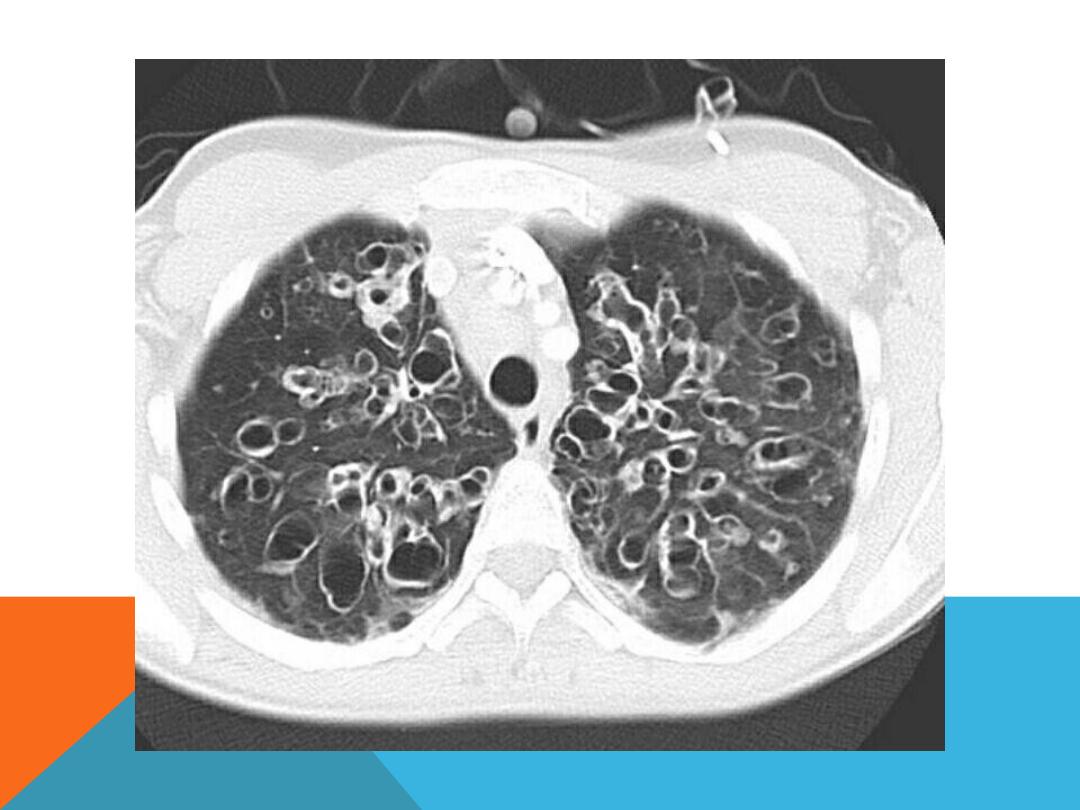

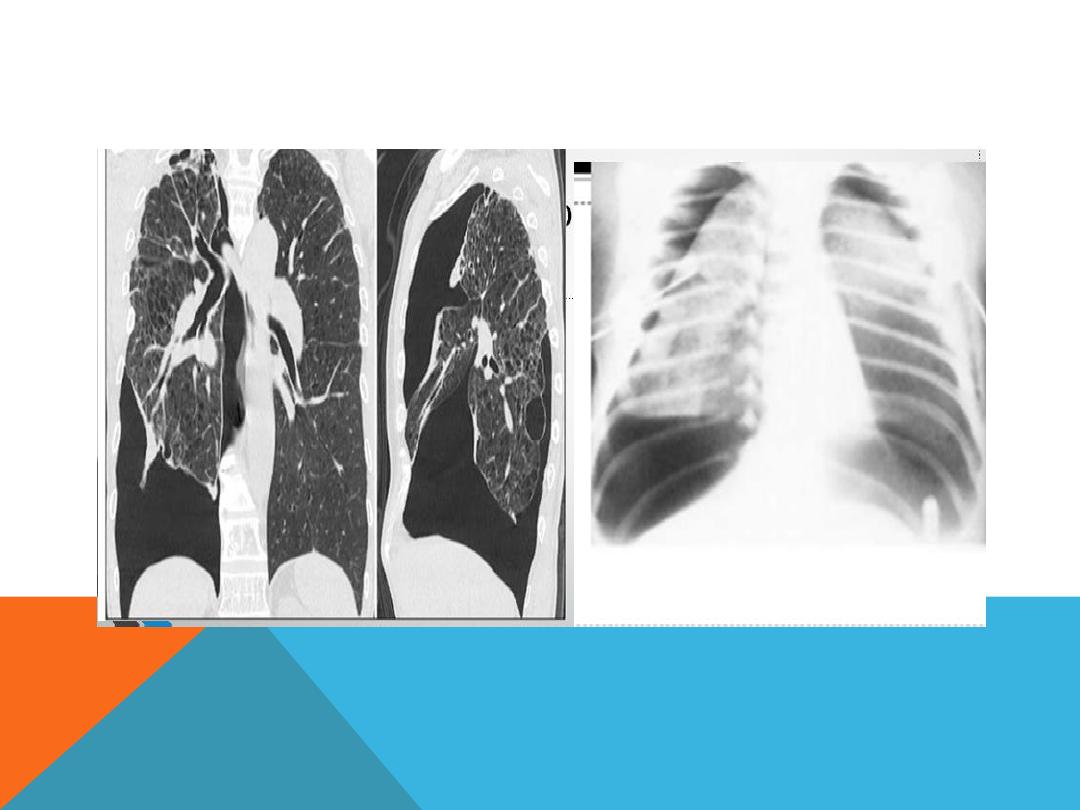
EMPHYSEMATOUS BULLAE
1. Air filled space ,
2. very thin wall which is not
clearly discriminated from the
adjacent normal lung tissue ,
3. big size 1cm and more in
diameter .
4. develop in
chronic irreversible
destruction of the lung
parenchyma

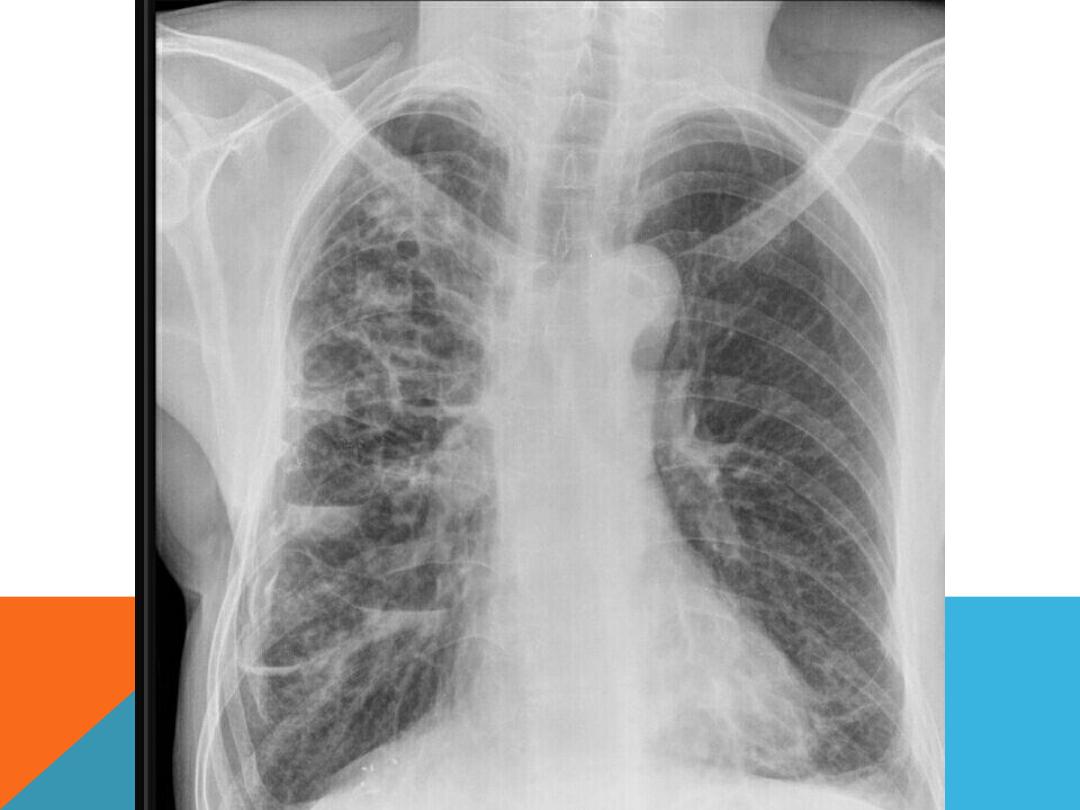
IMAGING EVALUATION ,
Enlarged lung
Depressed diaphragm
Mediastinal shift to the normal
side
More radiolucent than normal
lung.( more darkness on CXR ,
black on CT scan)

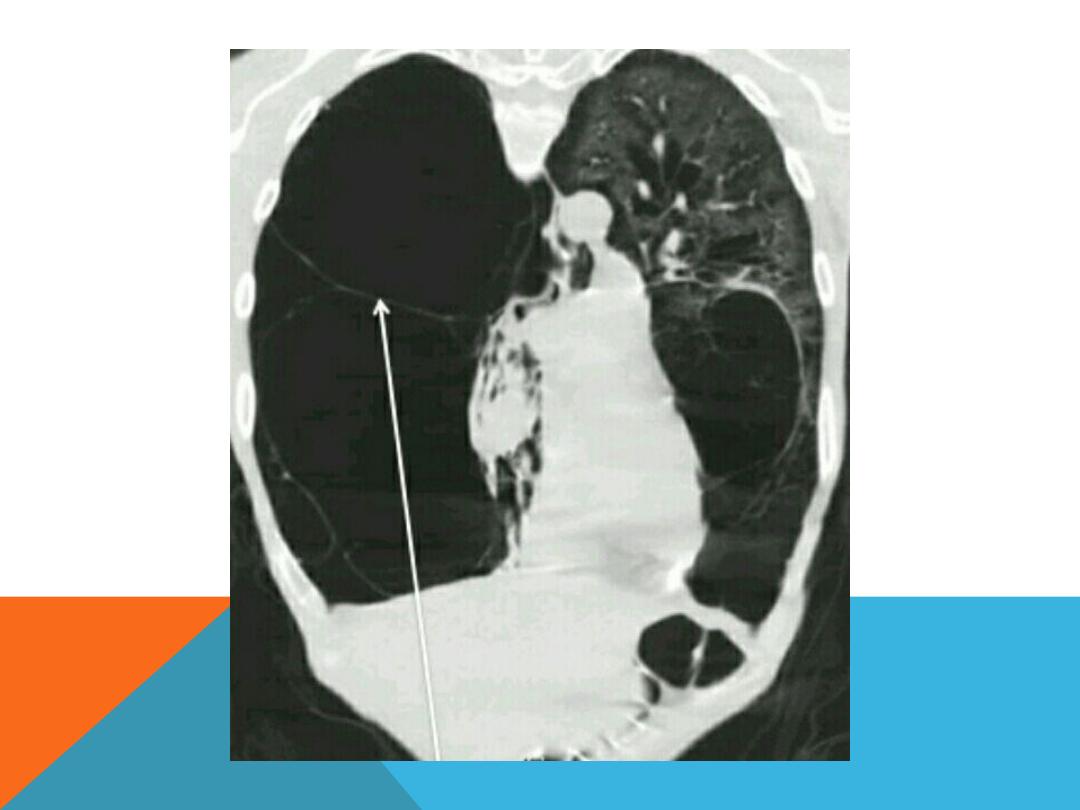
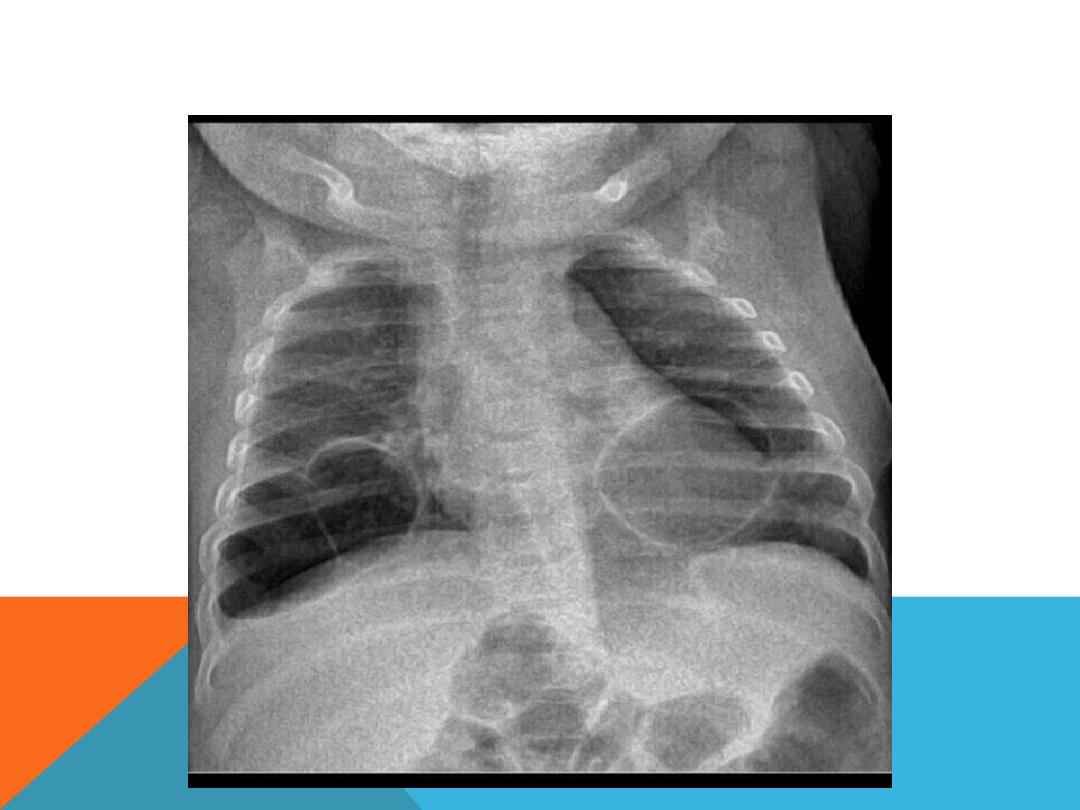
PNEUMATOCELE
similar imaging features to
bullae but it is
transient
in
acute pneumonia ; ex. Staph ,
klebsiella , strepto. H .
Influenzae they may contain
fluid, result from ventilating
induced injury in the neonate
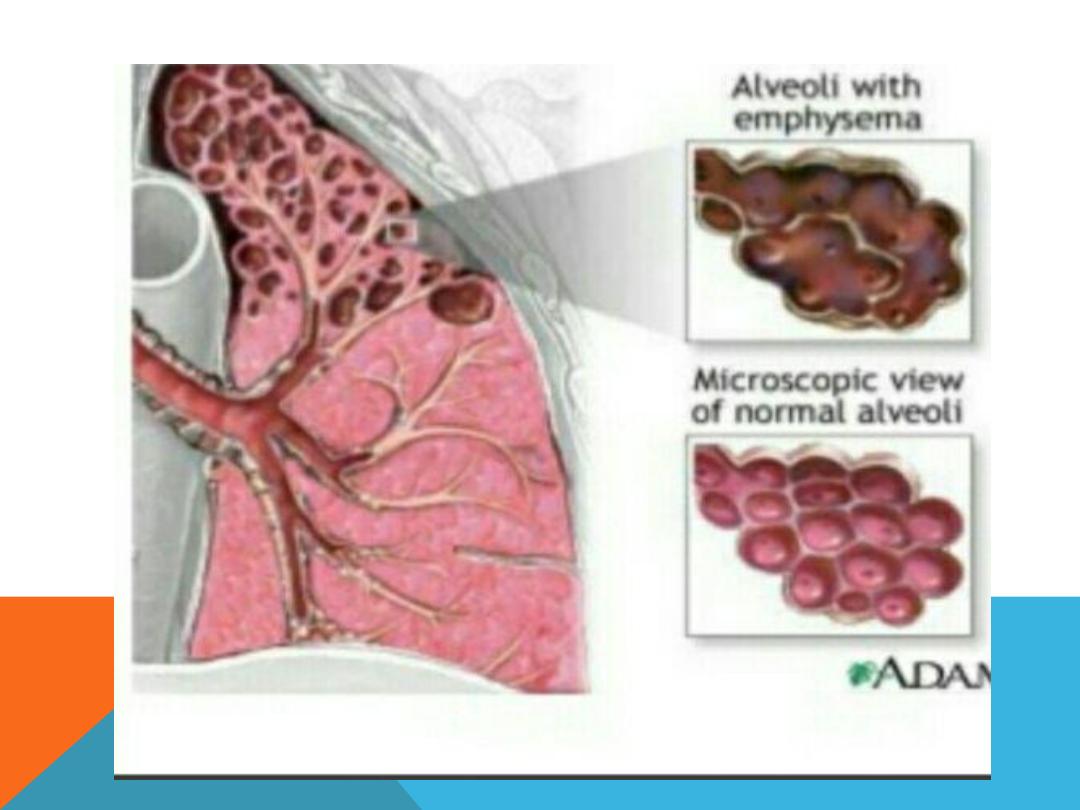
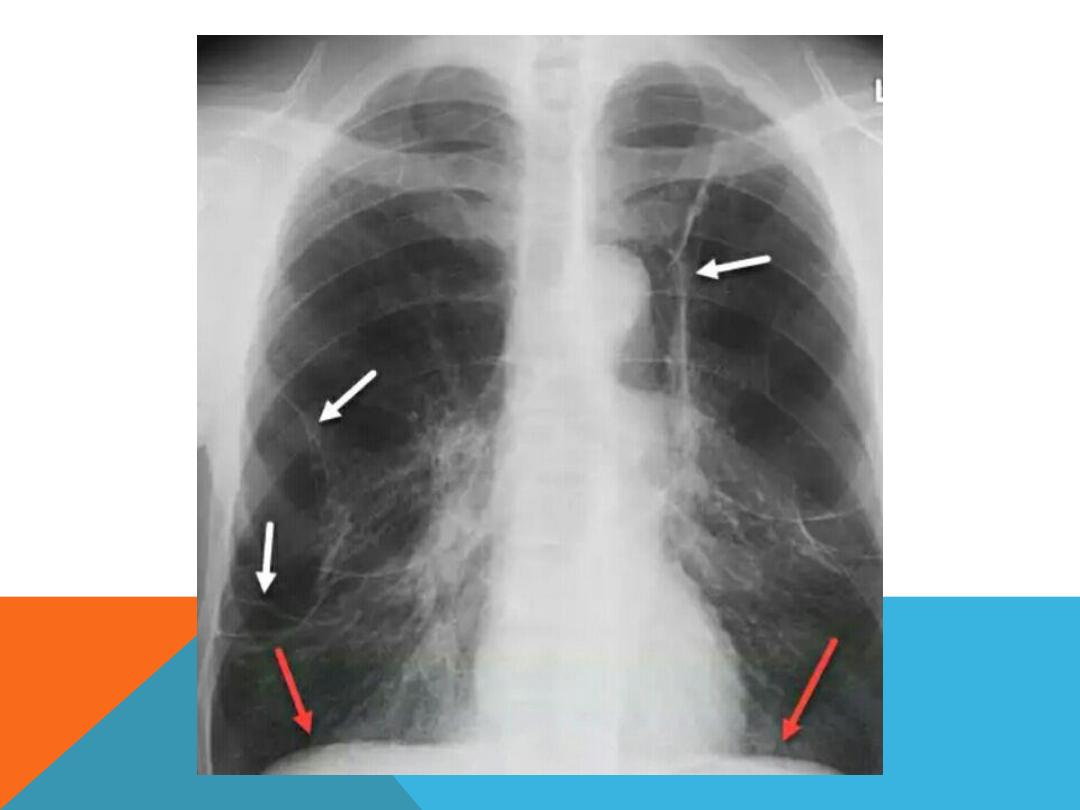
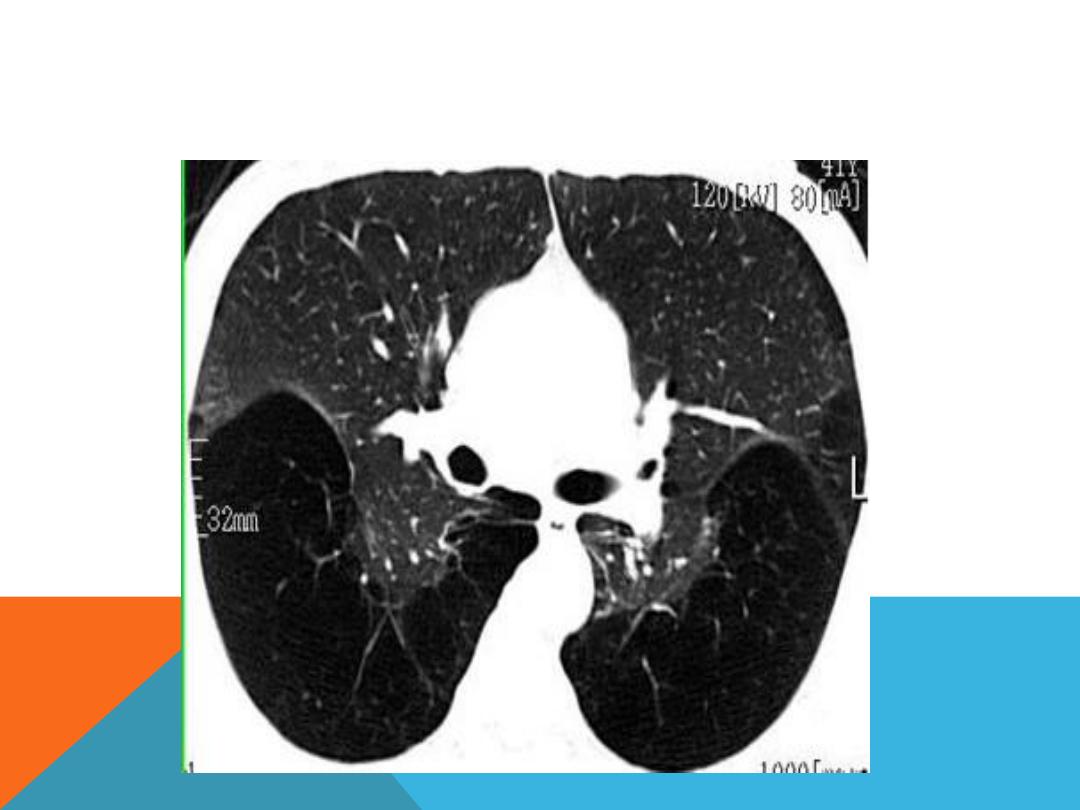
EMPHYSEMA
PNEUMATOCELE
PNEUMATOCELE WITH AIR FLUID LEVEL

LUNG COLLAPSE…. ATELECTASIS
1
mediastinal shift .
2.Rib crowding.
3. Loss of volume of the affected lung
lobe or segment .
4. Elevated diaphragm
5. Hyperinflation of the contra lateral lung
6. Tracheal deviation
7. Elevated hilum
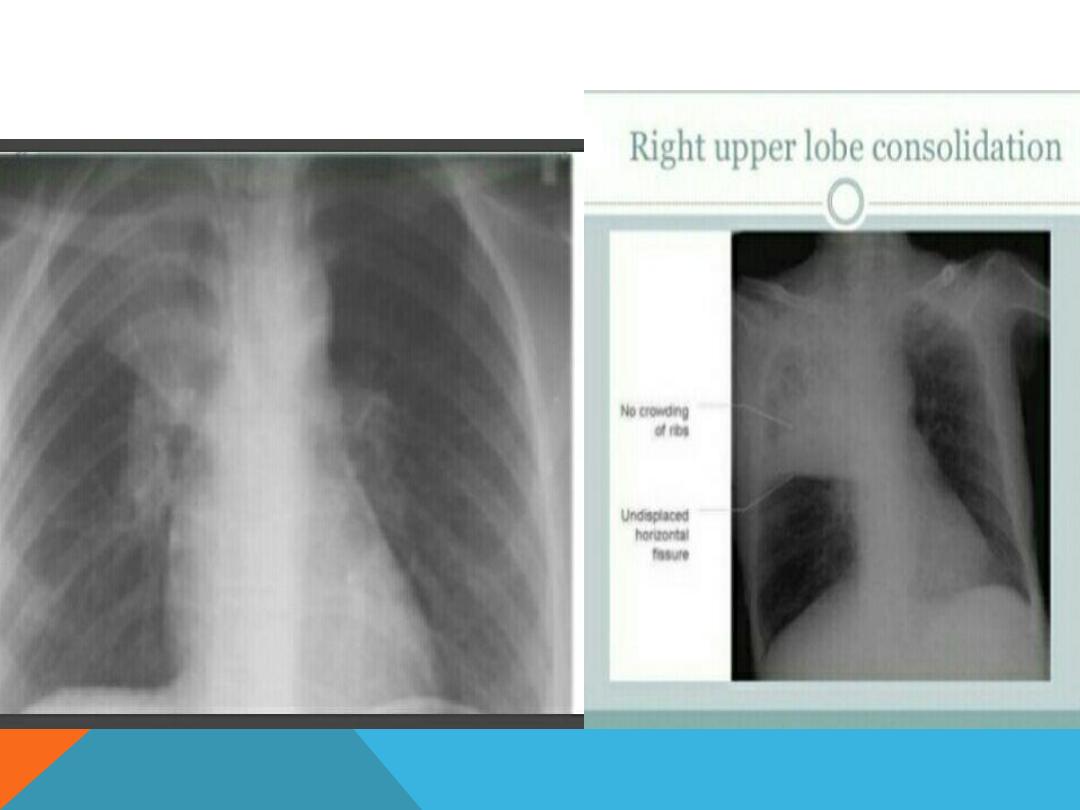
COLLAPSE…CONSOLIDATION
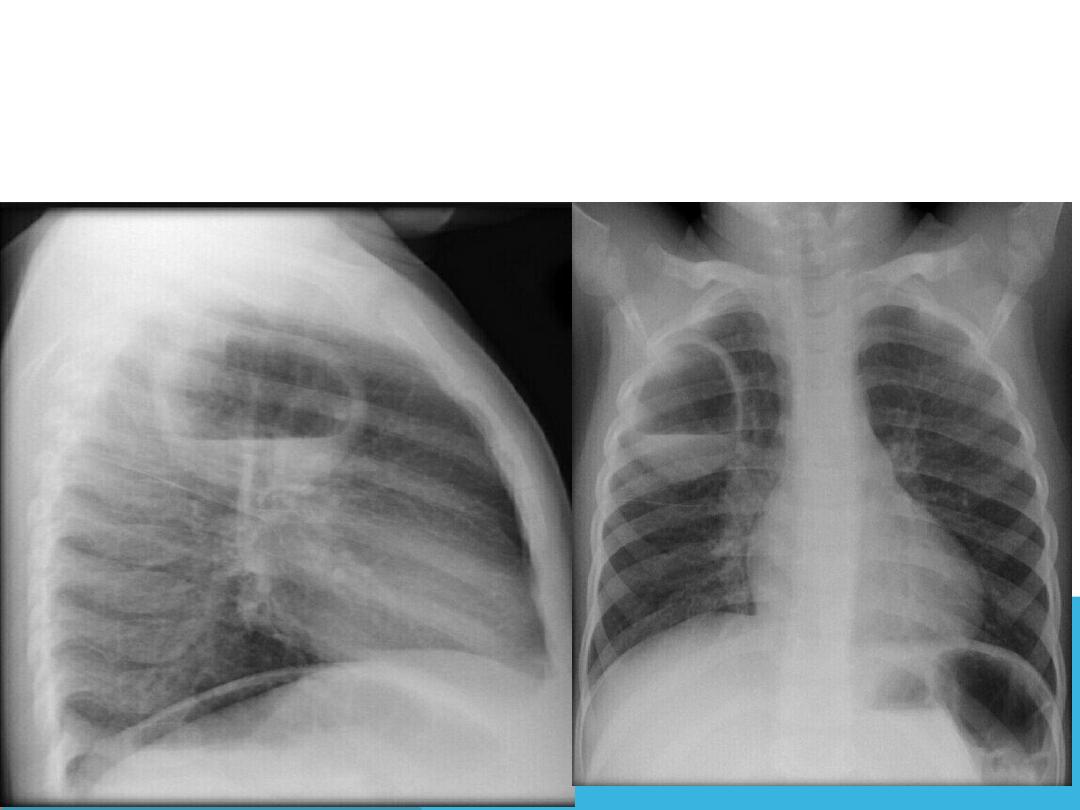
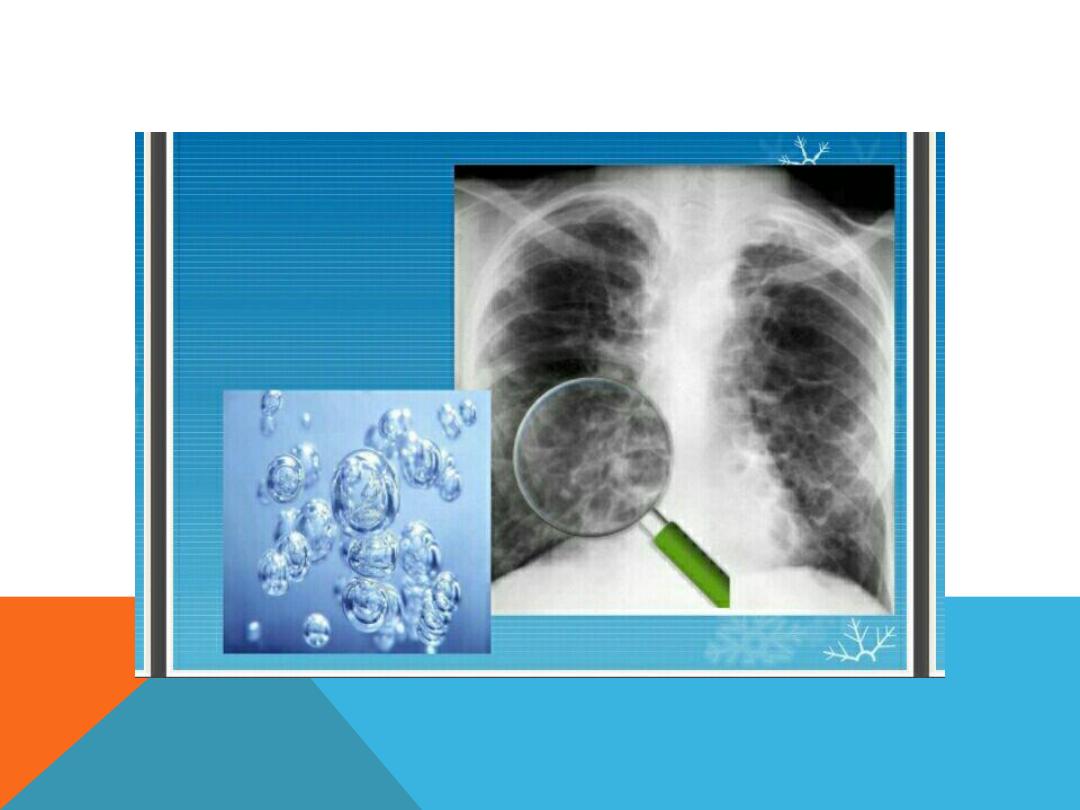
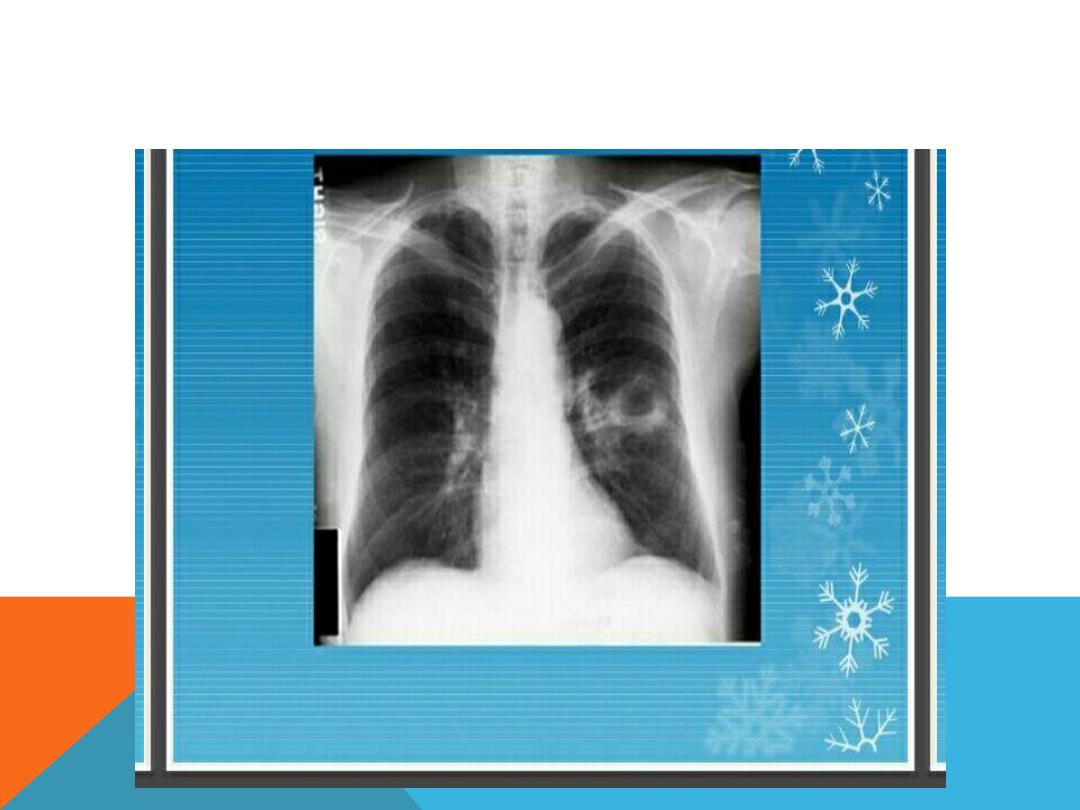
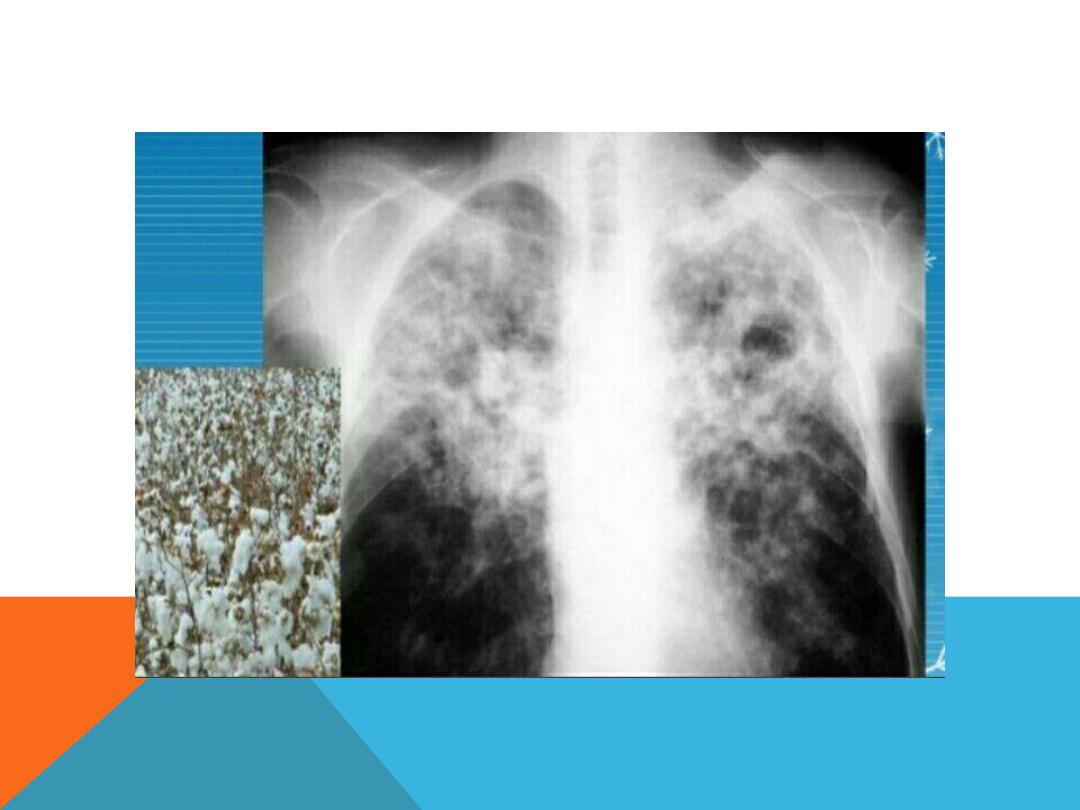
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS

Ultra sound
of the thorax is very useful in
the detection , characterization and
guided draining of pleural effusion
CT scan
..is more accurate in the early
detection of occult disease ,
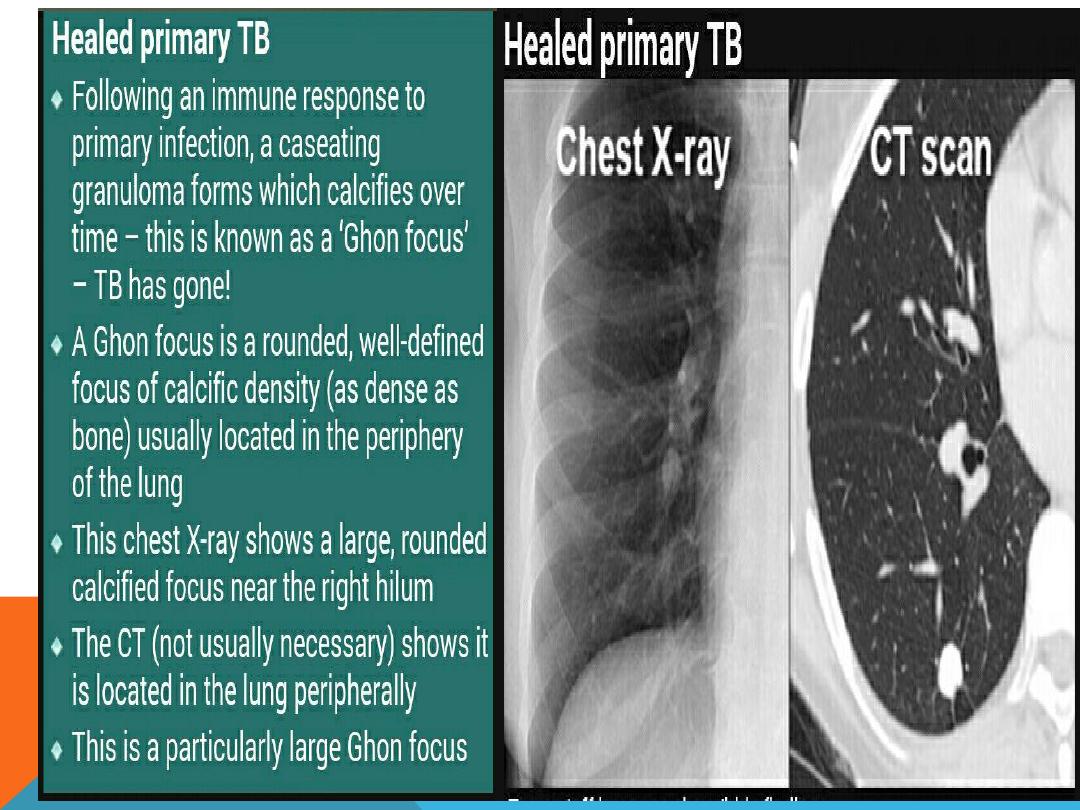
bronchiectasis , primary complex (ghon
focus + draining LN ,hilar and
mediastinal) ,cavitary lesions , fungal
balls ,calcifications , fibrosis. Miliary
distribution , tuberculoma,
bronchopneumonia , abscess, lobar
pneumonia
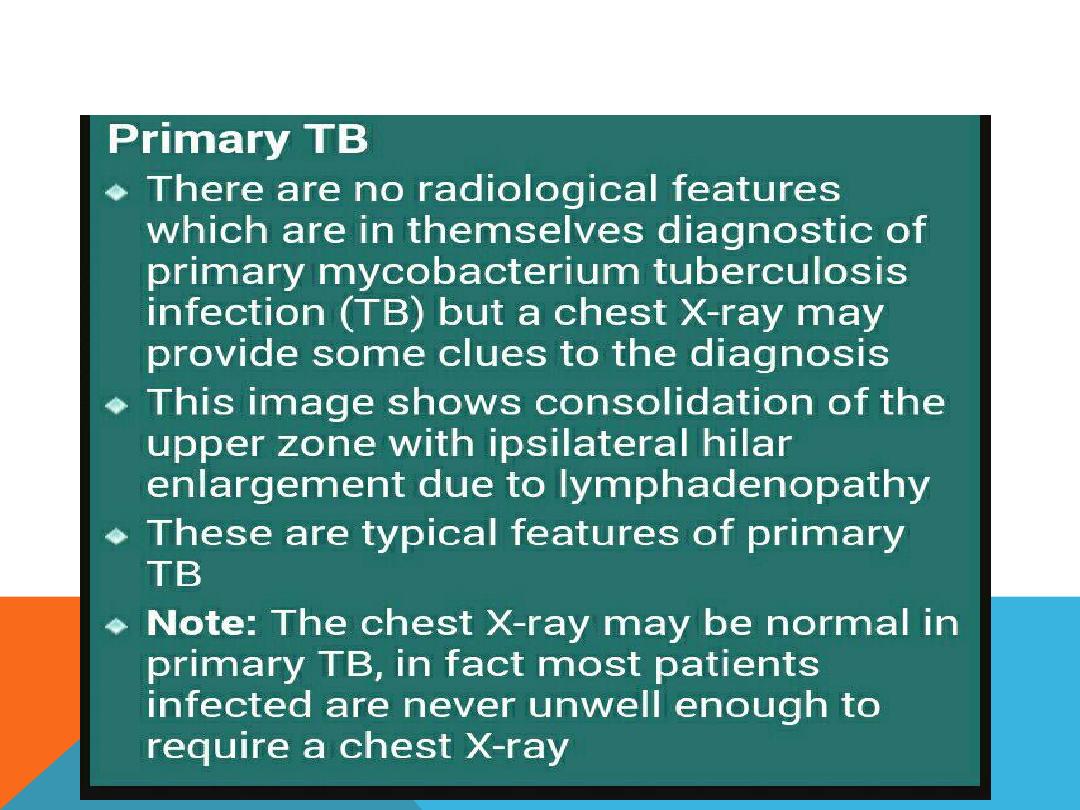
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
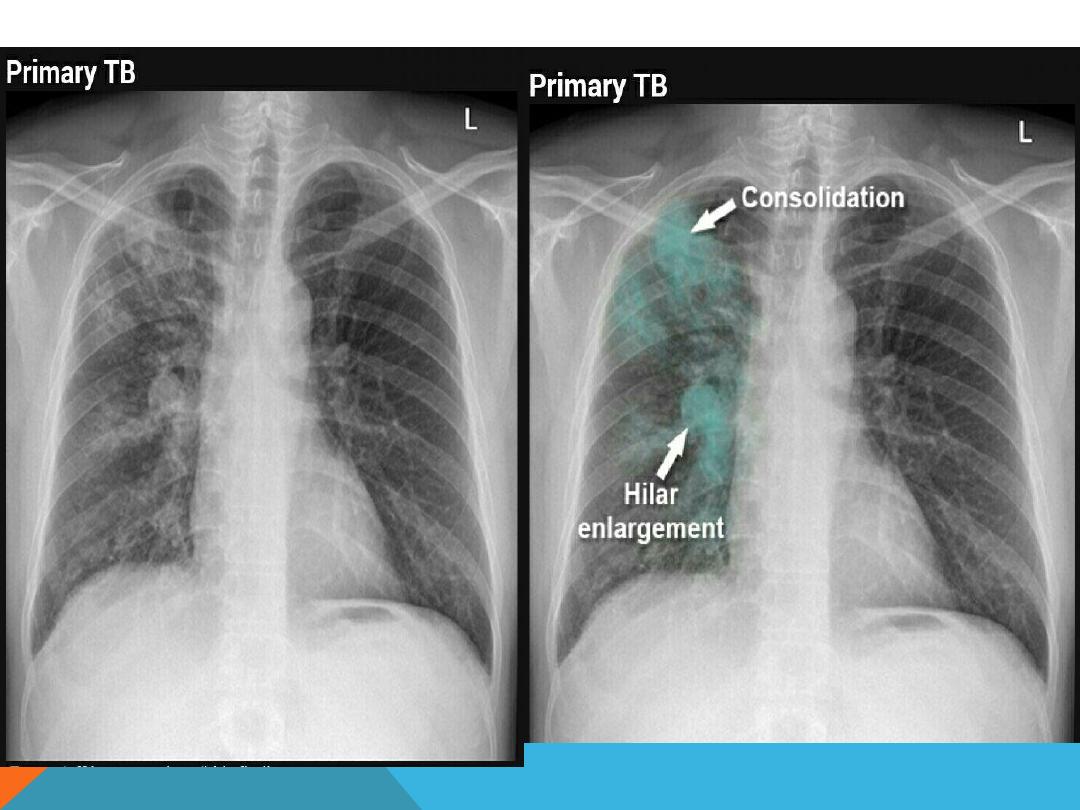
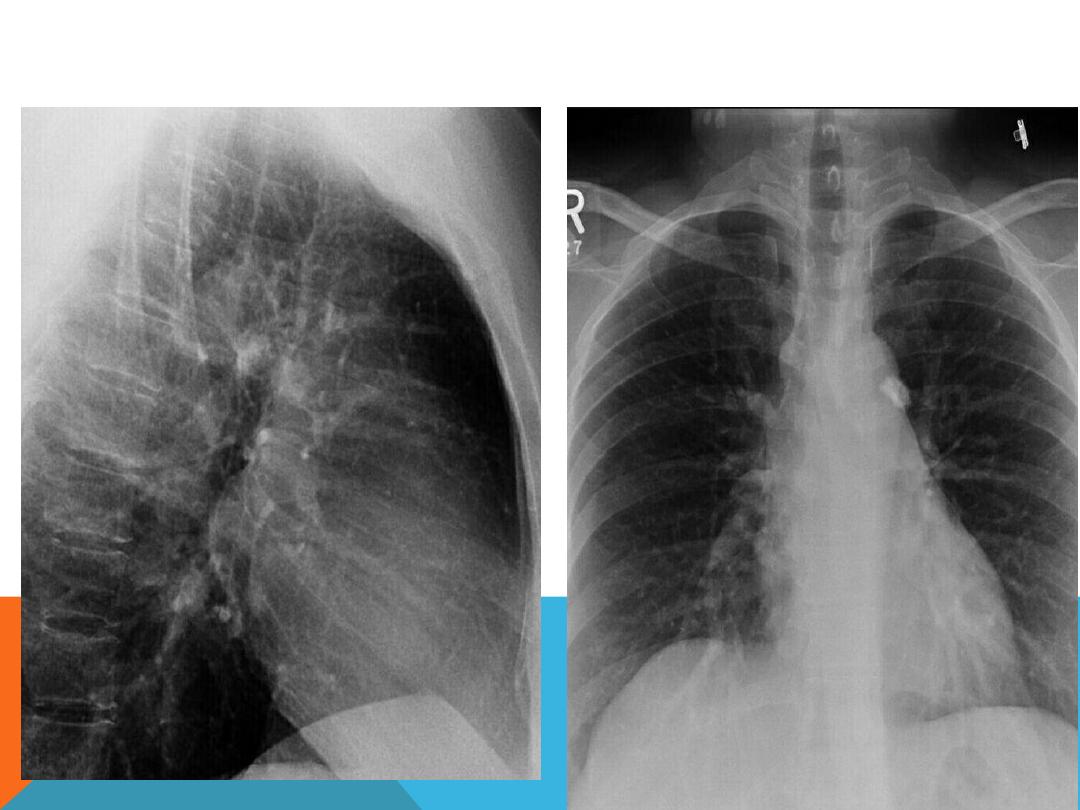
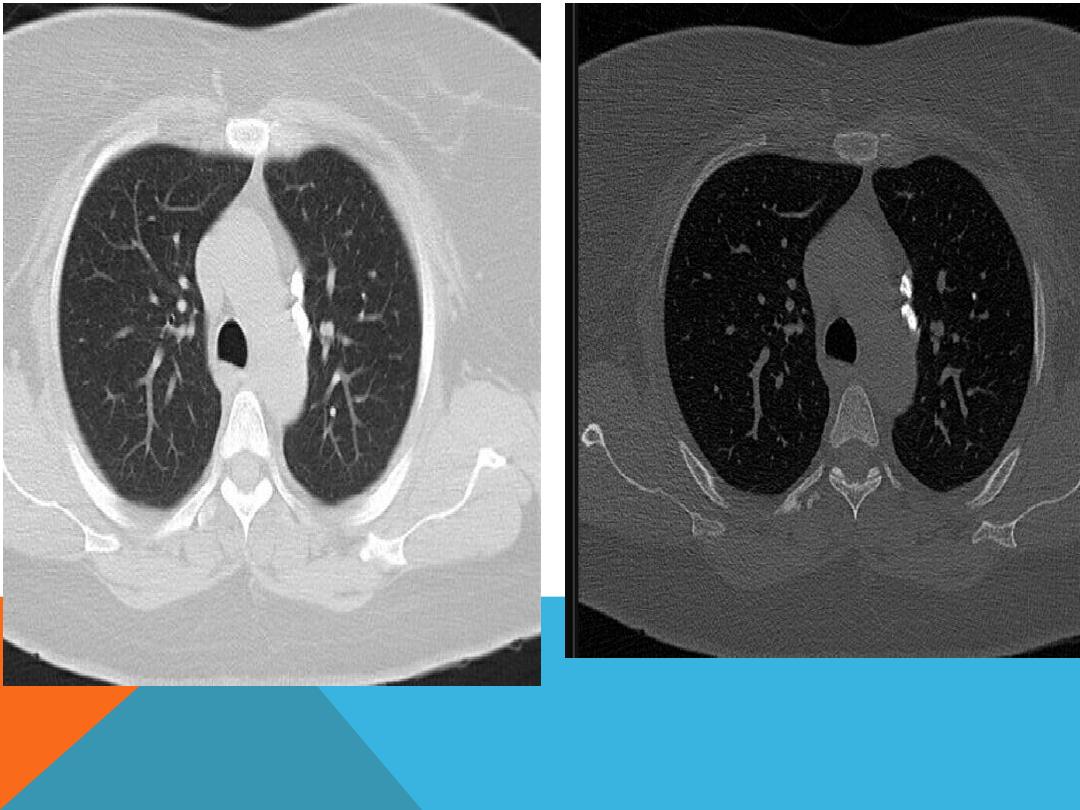

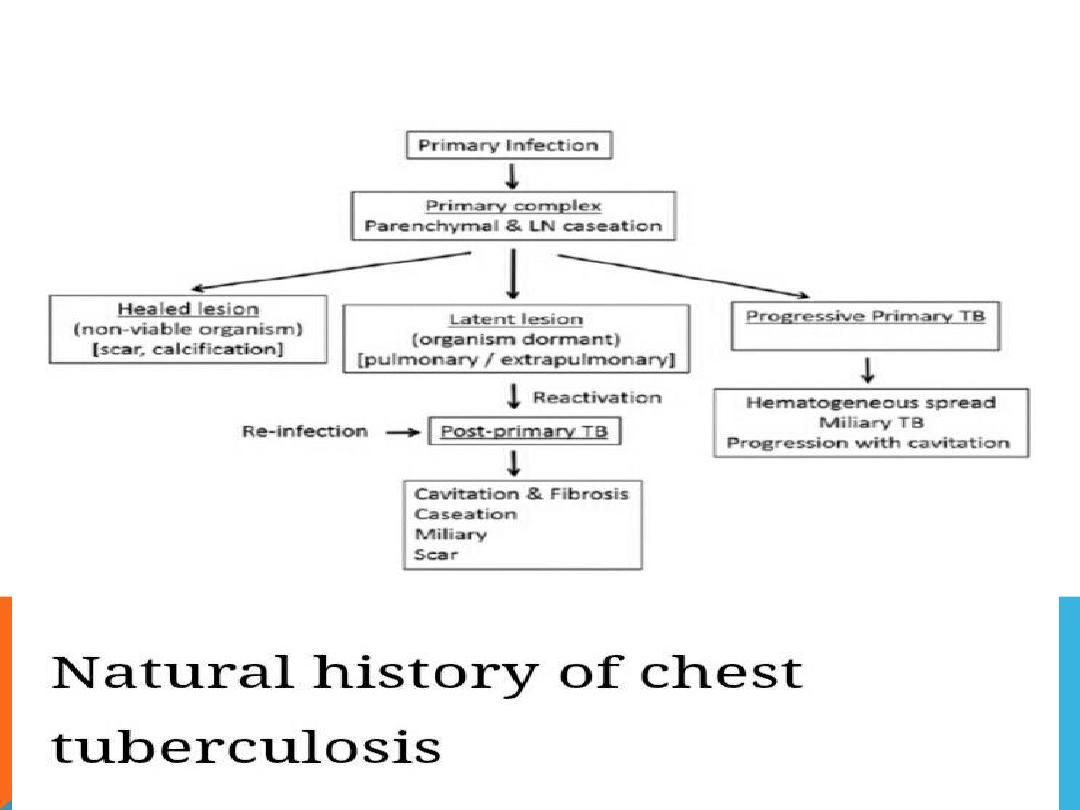
POST PRIMARY TB
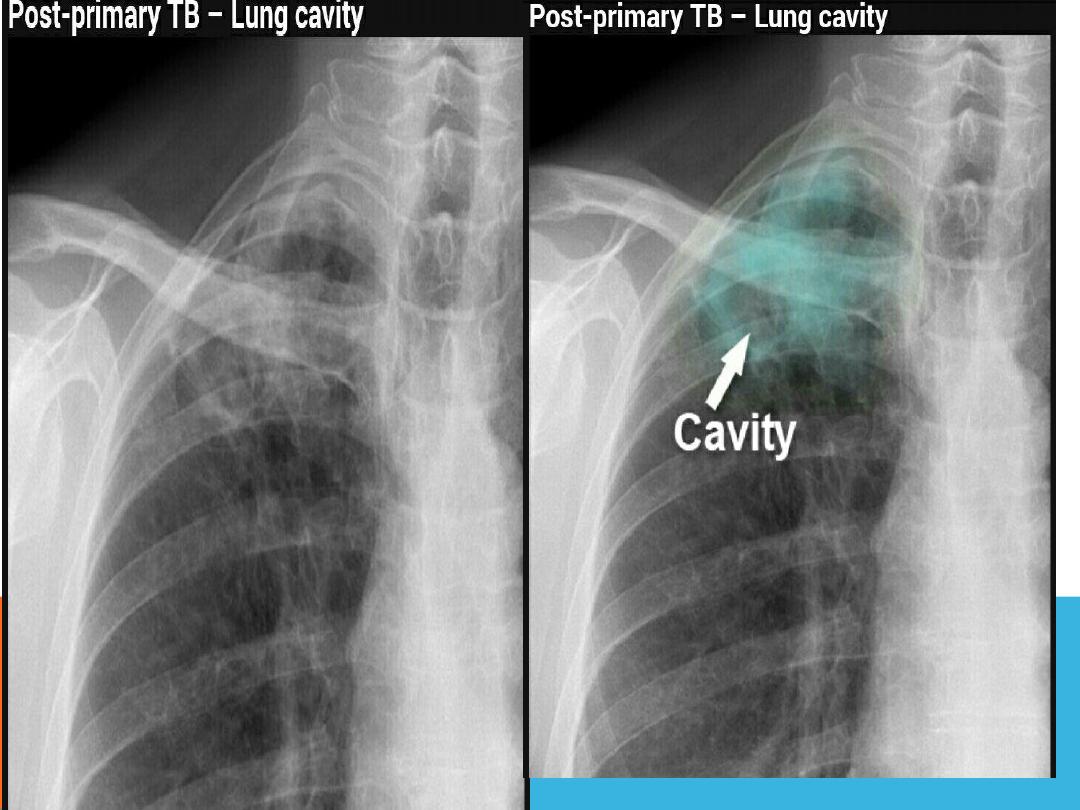
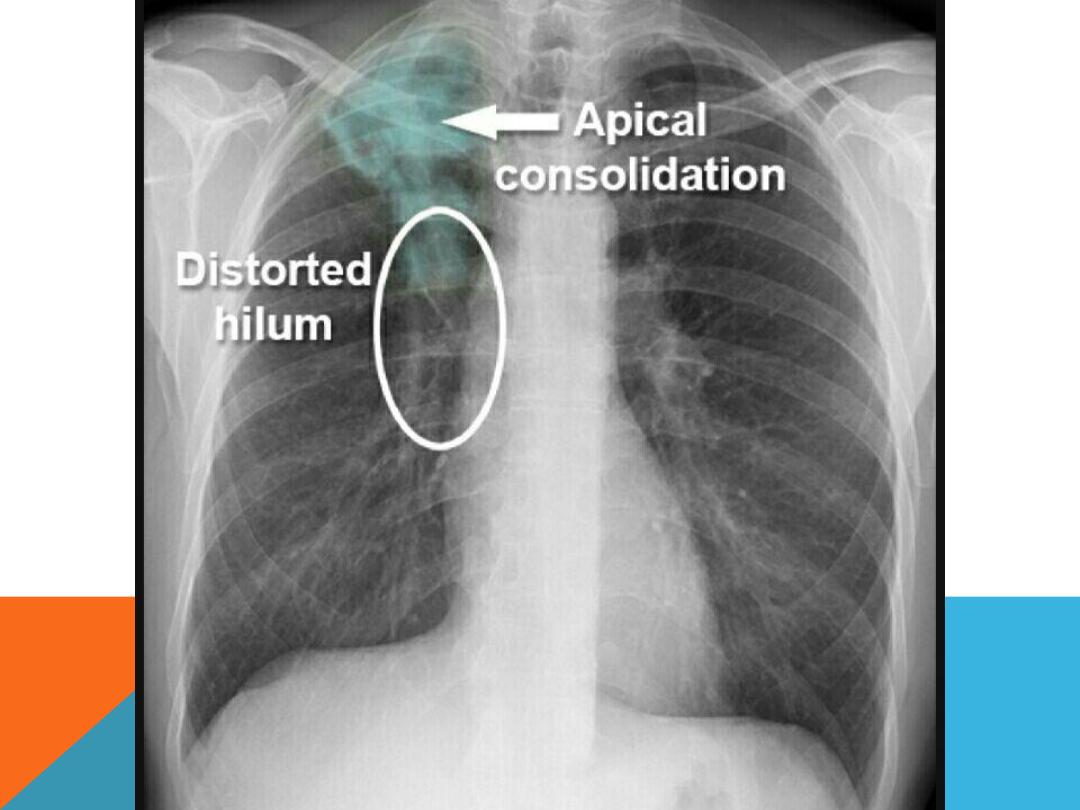
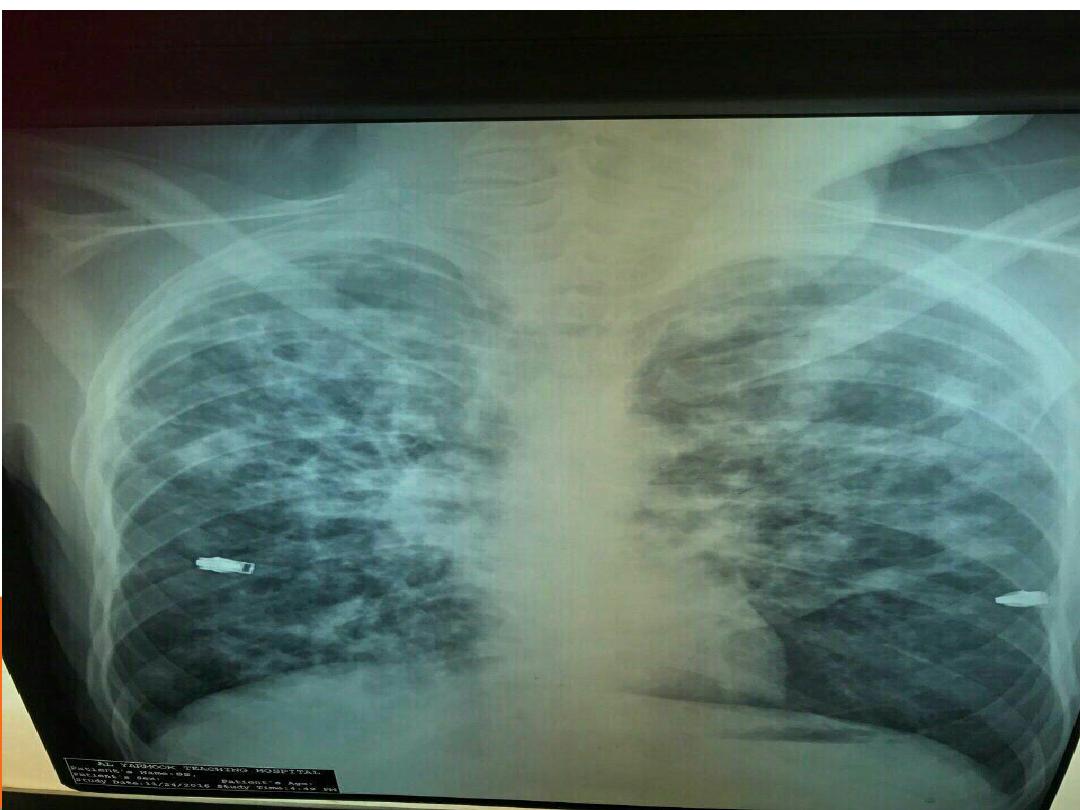
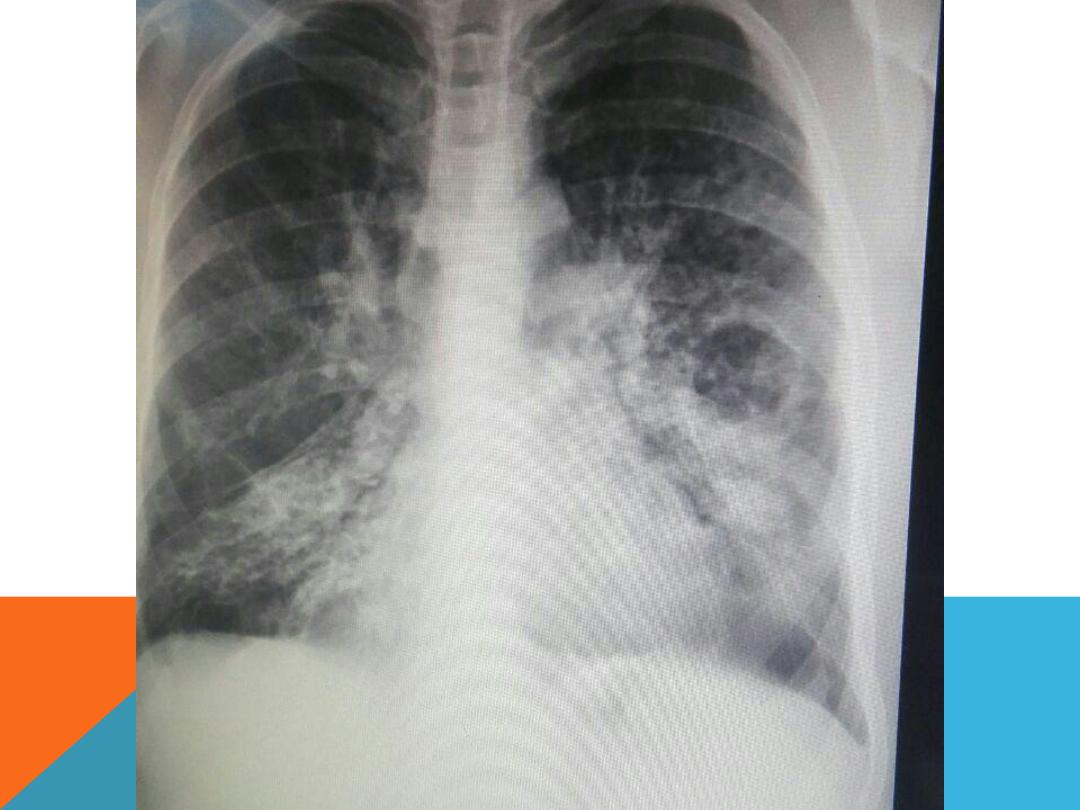
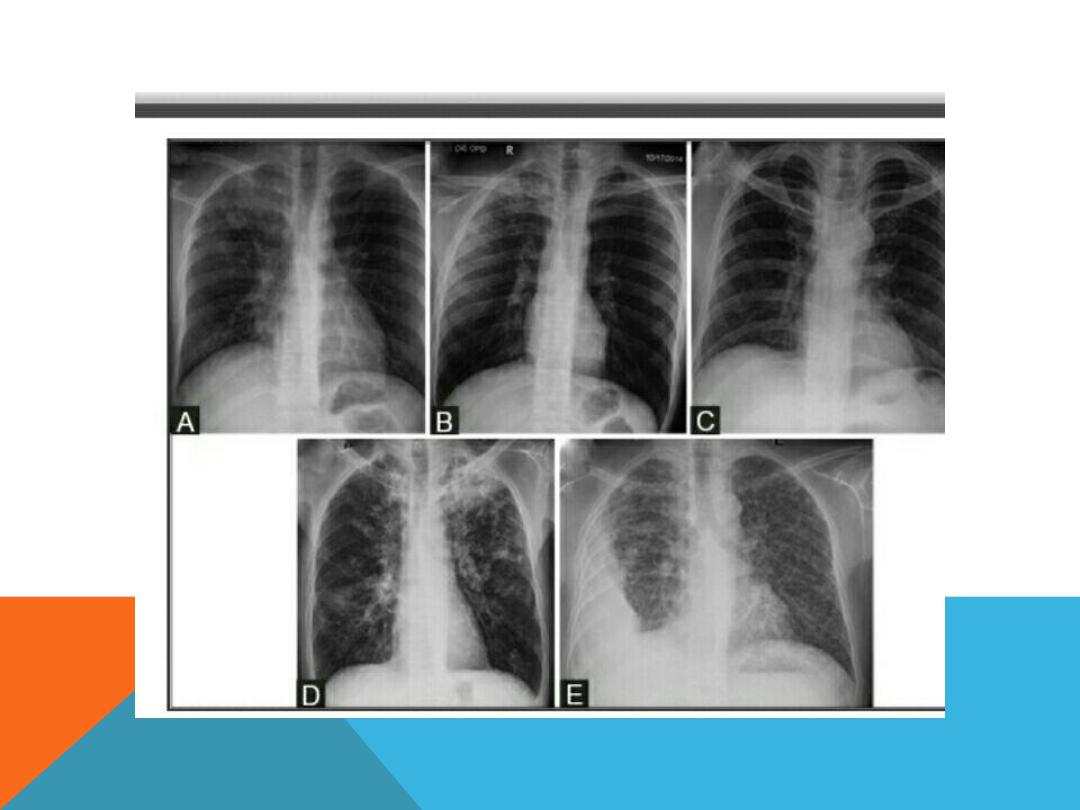
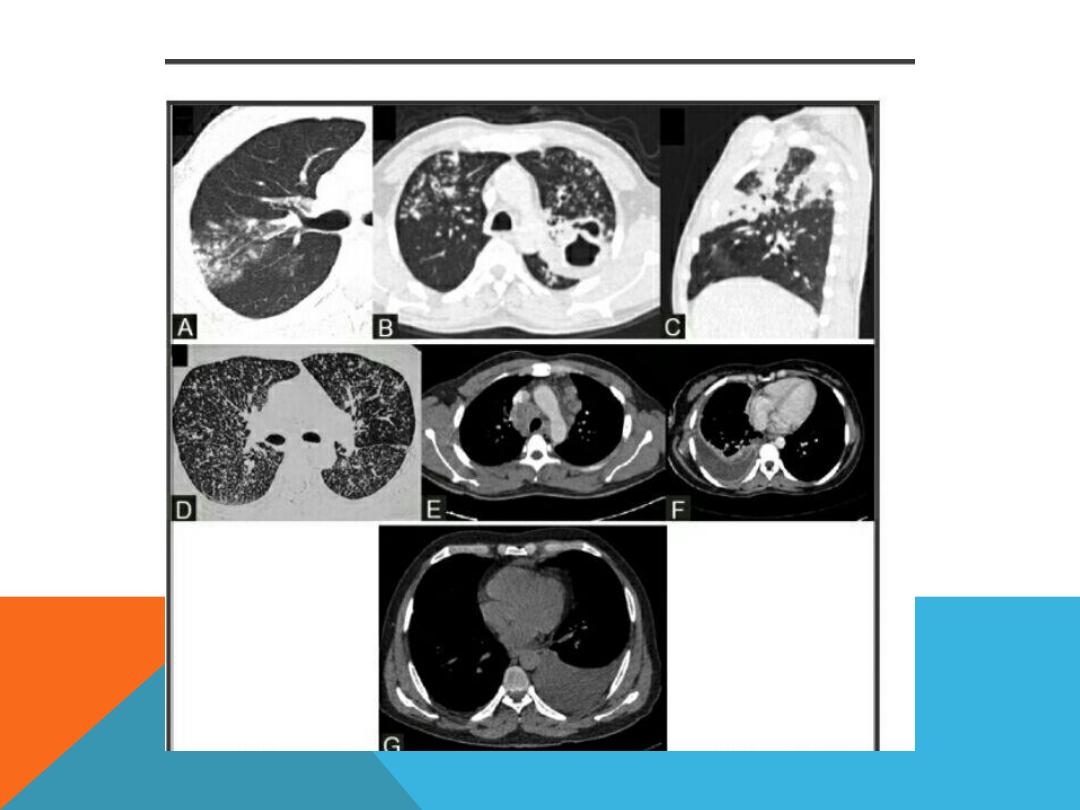
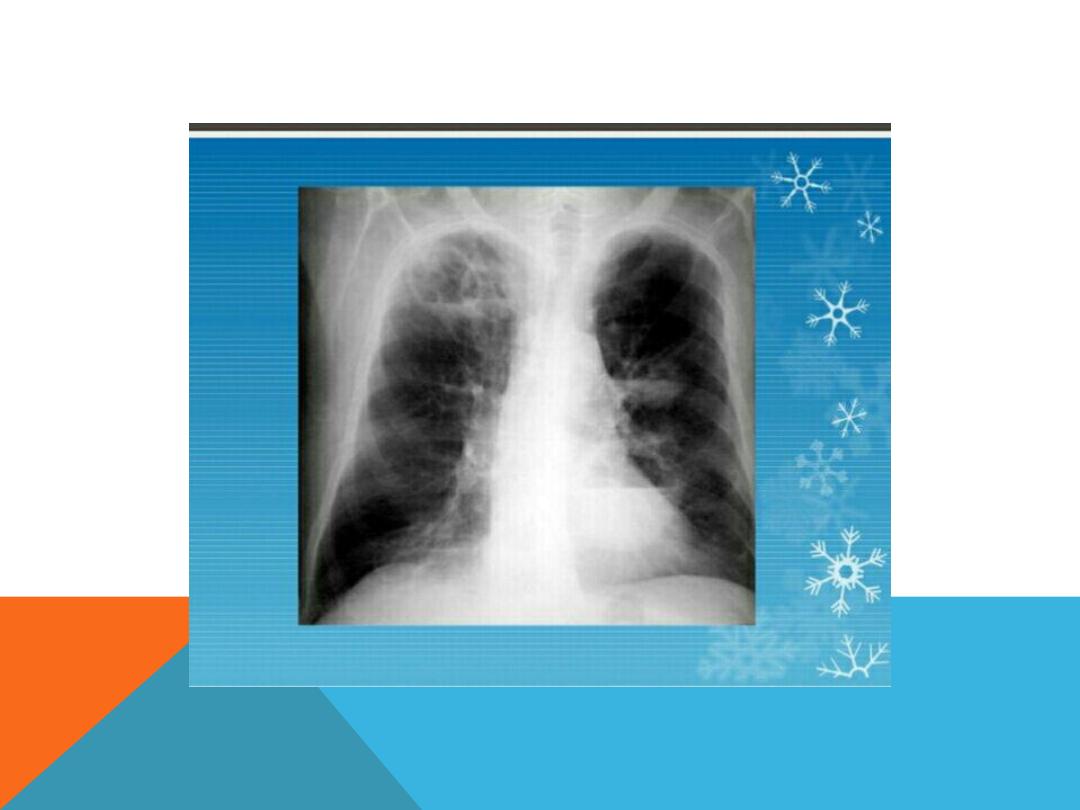

LESIONS ENCOUNTERED IN BOTH
PTB.
AND
POST PTB
.
miliary TB
Bronchopneumonia
Pleural effusion
Tuberculoma
Tracheo -broncheal LN enlargement .
Complications ..
fibrosis , scar
sarcoma

BRONCHO GENIC CARCINOMA
1.Hilar or peripheral mass
2.Multiple pulmonary nodules ( Mets)
3.Rib lesion
4.Pleural effusion
5.Review old x-ray
6.Doubling time .
7.Infiltrative ,ill-defined , speculate
margins , size greater than 3 cm
(mass)
8.Hx. …
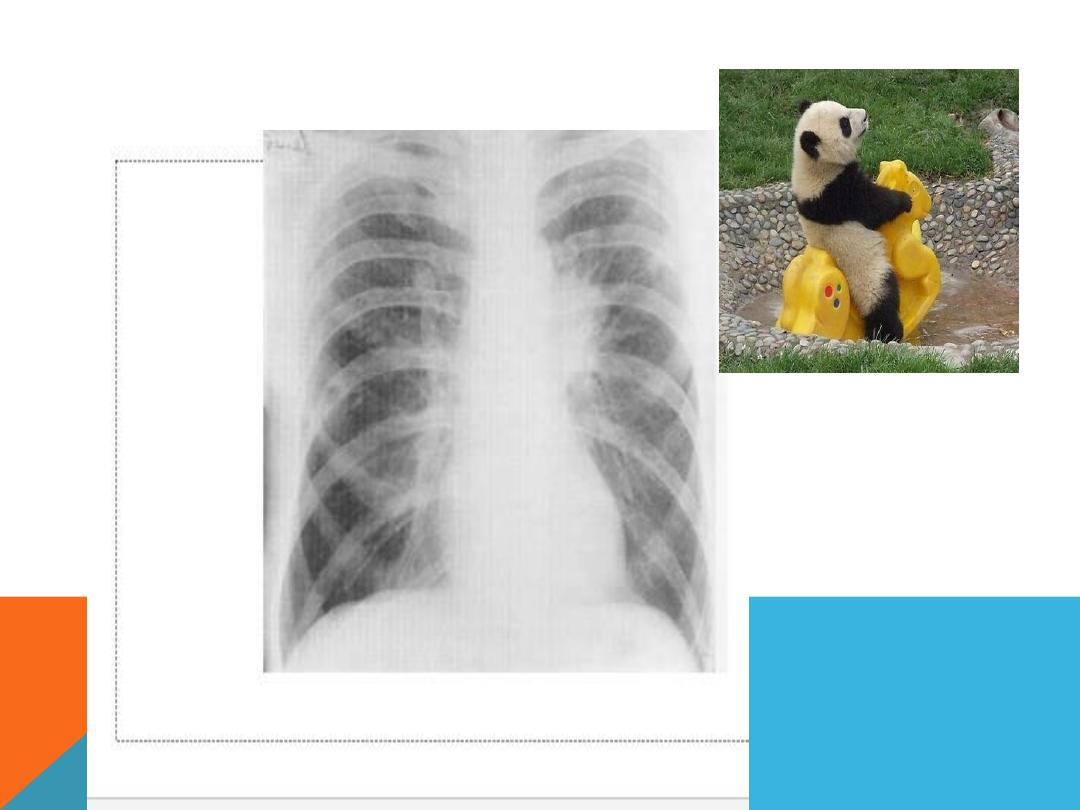
HILAR MASS
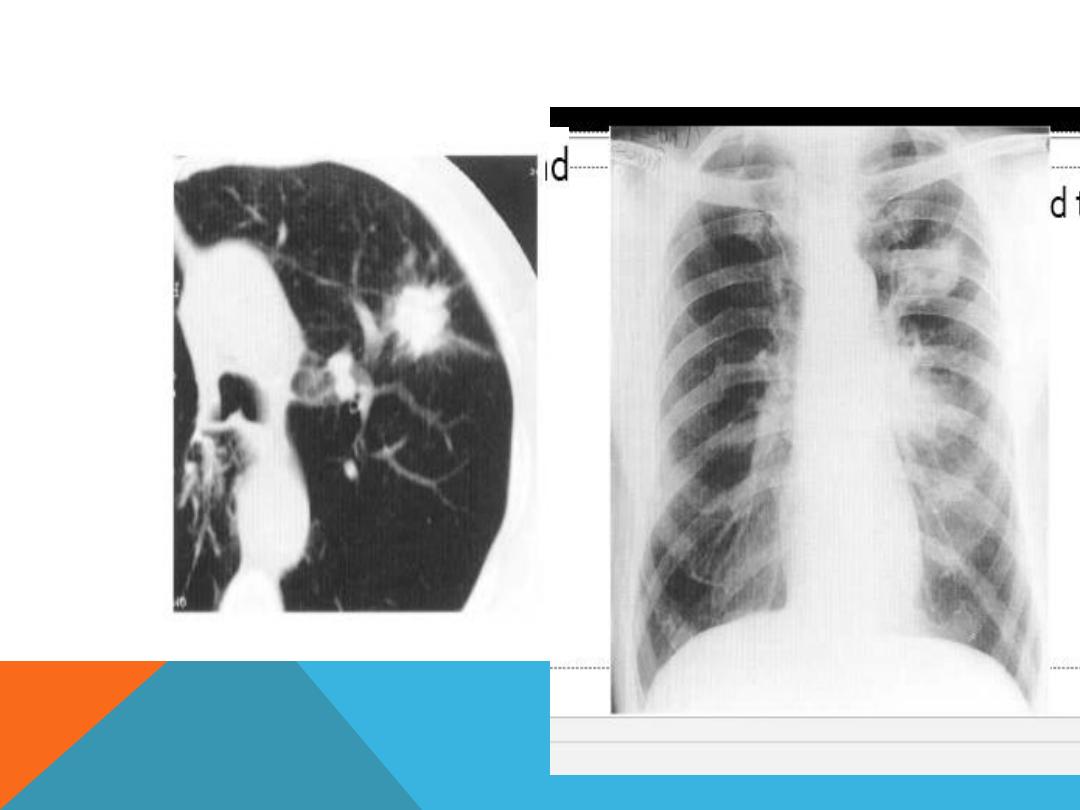
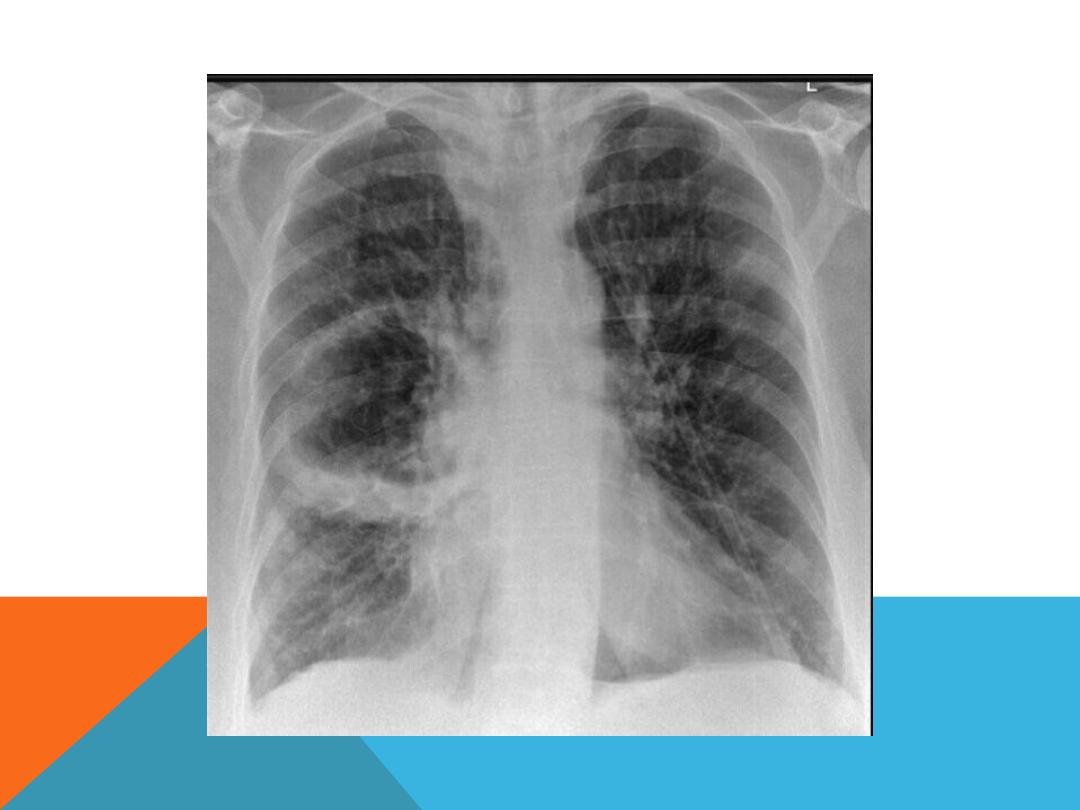
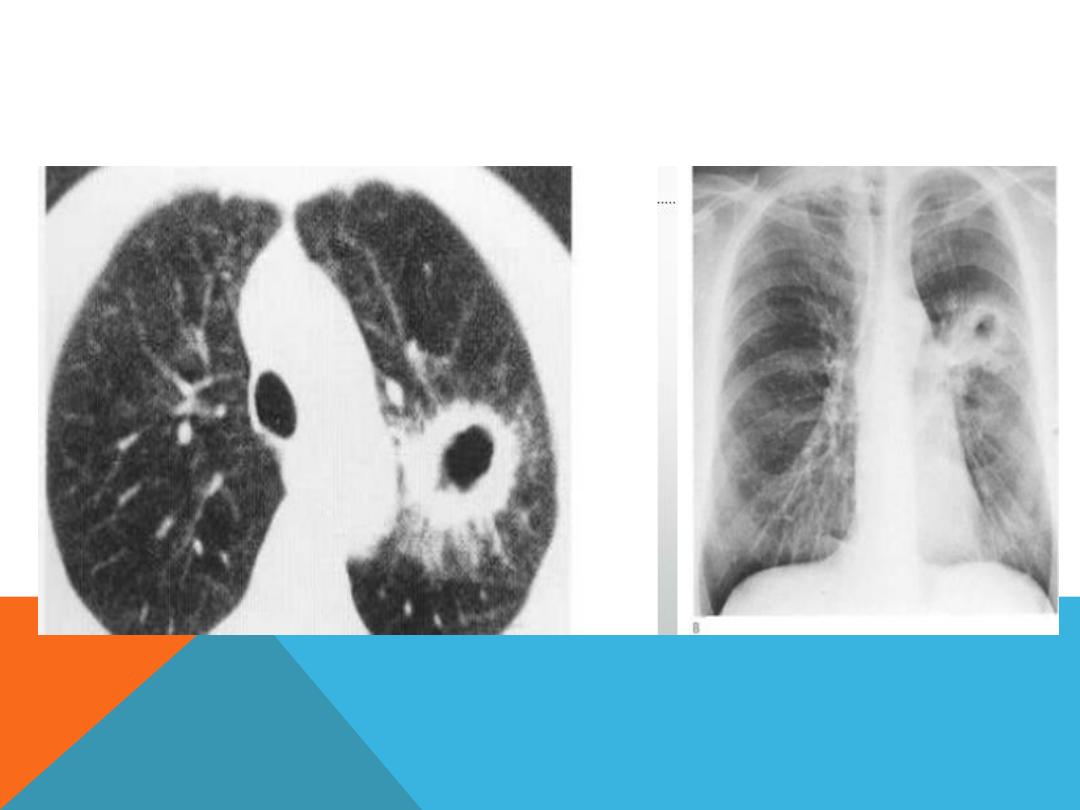
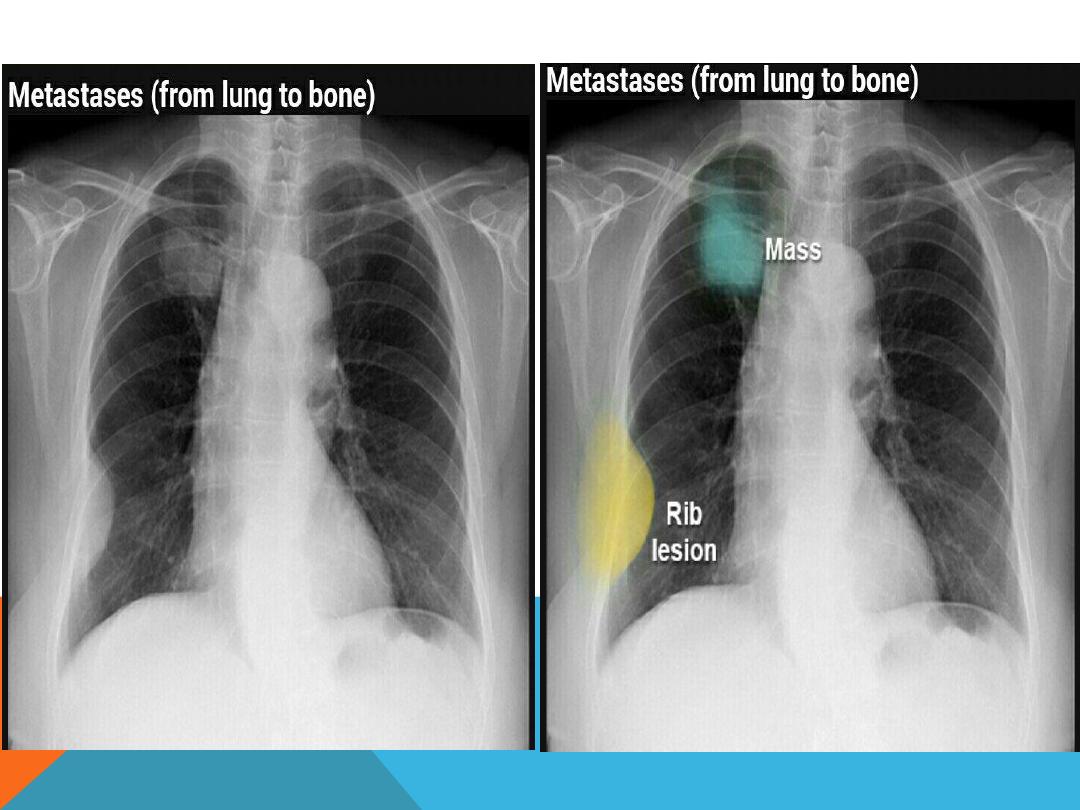
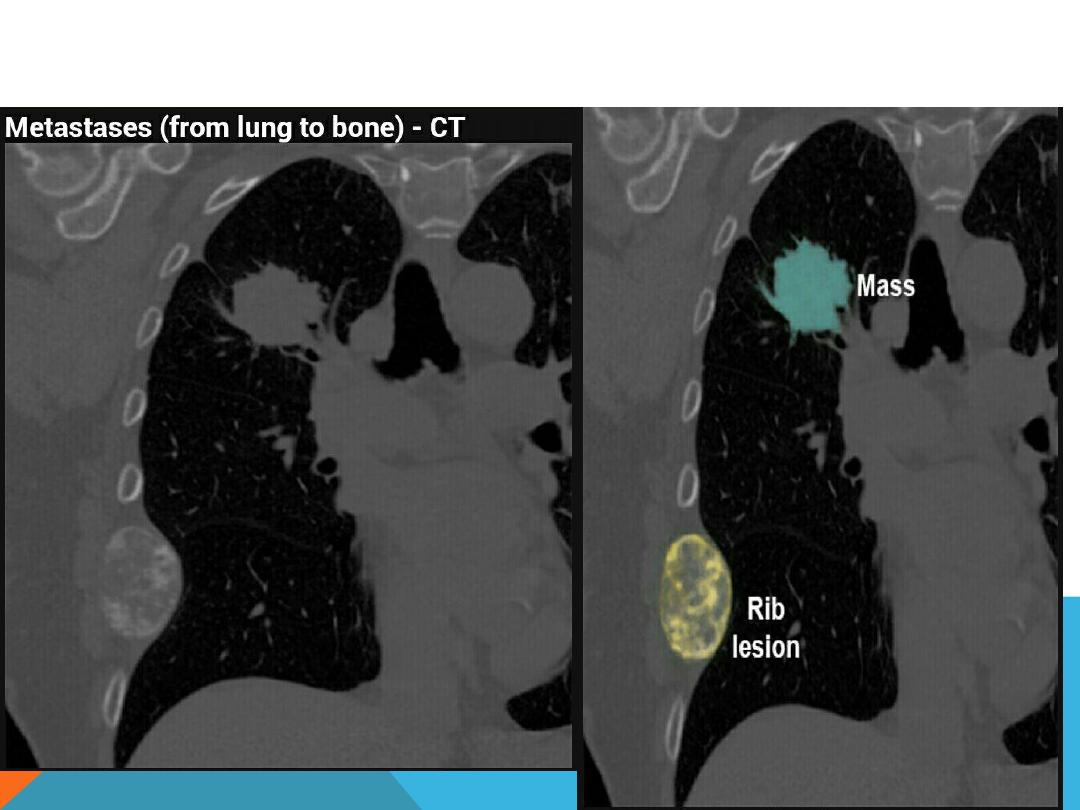
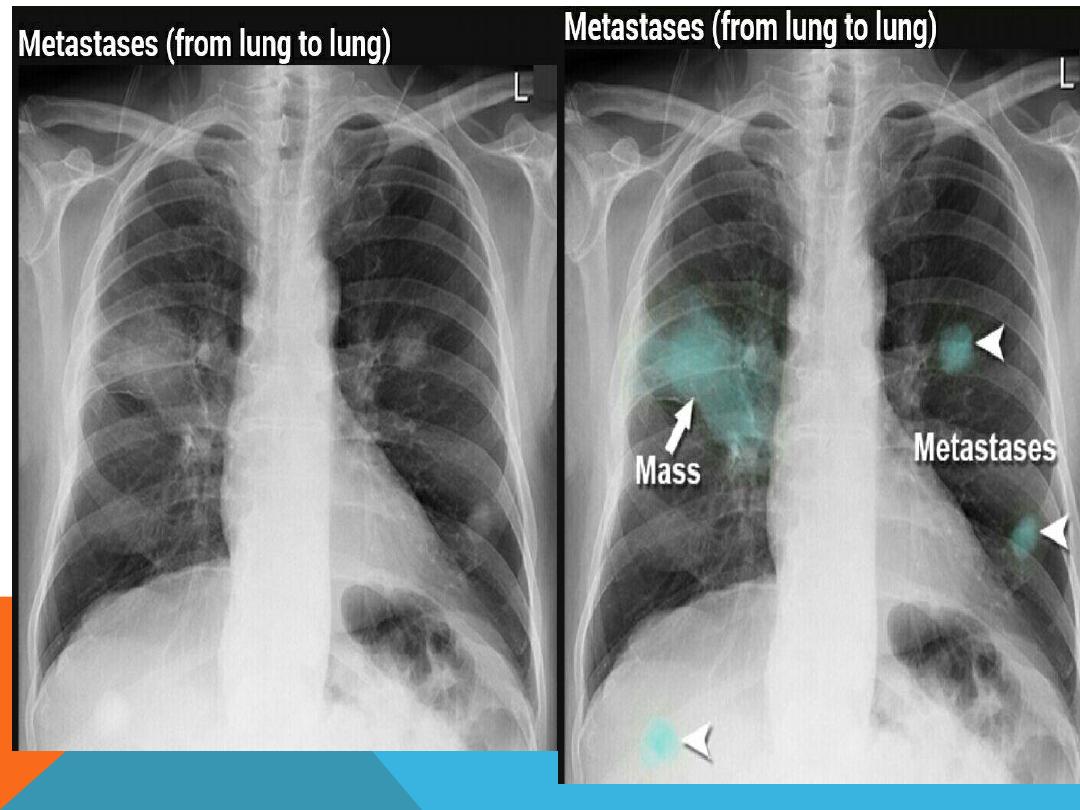

METASTATIC LUNG DISEASE
1.
multiple ,bilateral , non
symmetric ,variable size
pulmonary nodules
2.Single nodule .
3. Cavitary
4. Canon ball
5. Miliary
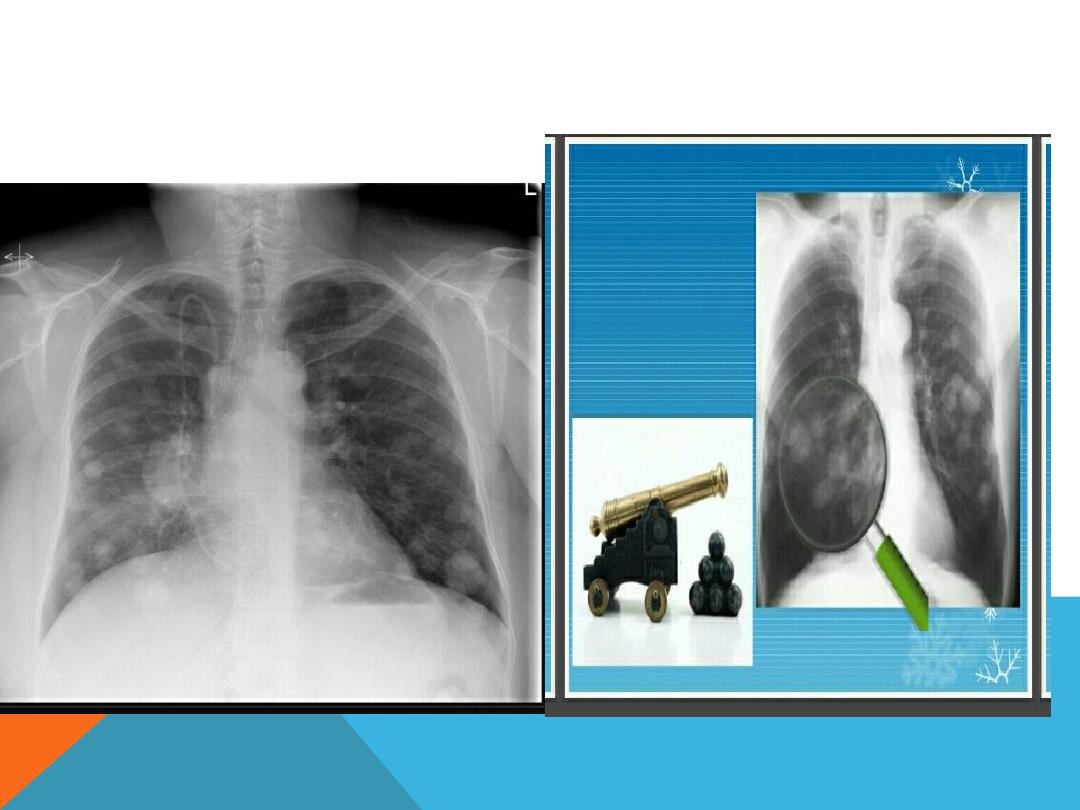
METASTATIC LUNG DISEASE