Introduction to Endodontic
The word Endodontic means the branch of Dentistry That specializes in dealing with the cause, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of diseases of the pulp and the periapical tissues that surround the root of the tooth.What Is Endodontics?
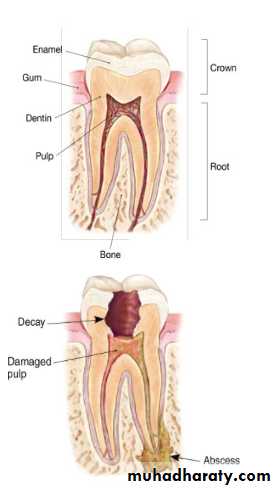
Physical IrritationMost generally brought on by extensive decay.
Trauma
Blow to a tooth or Jaw.
Causes of pulpal Nerve Damage
Pain when biting downPain when chewing.
Sensitive with hot or cold beverages.
Facial swelling.
Signs and Symptoms of pulpal Nerve Damage
Endodontic Diagnosis
Subjective Examination
• Chief complaint• Character and duration of pain
• Painful stimuli
• Sensitivity to biting and pressure.
Objective Examination
• Periodontal conditions surrounding the tooth in question• Extent of decay
• Presence of an extensive restoration
• Tooth mobility
• Swelling or discoloration
• Pulp exposure.
Percussion tests
Used to determine whether the inflammatory process has extended into the peiapical tissues.Completed by the dentist tapping on the incsal or occlusal surfac of the tooth in question with the mouth mirror hanle held paralle to the axis of the tooth.
Diagnostic test
Palpation tests.
Used to determine whether the inflammatory process has extended into the periapical tissues.
The dentist applies firm pressure to the mucosa above the apex of the root.
Diagnostic tests-cont.d
Thermal sensitivity
Necrotic pulp will not respond to cold or hotCold test.
Ice ,dry ice, or ethyl chloride used to determine the response of tooth to cold .
Heat test.
Piece of gutta-percha or instrument handle heated and applied to surface of the tooth.
Diagnostic tests-Cont’d
Diagnostic tests-Cont’dElectric pulp testing.
Delivers a small electrical stimulus to the pulp
Factors that may influence reading:
Teeth wit extensive restoration
Teeth with more than one canal
Failing pulp can produce a variety of responses
Control teeth may not respond as anticipated.
Moisture on the tooth during testing.
Batteries in the tester may be weak.
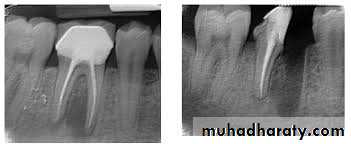
Usually four Photographs can be taken during An Endodontic procedures>
• Initial RadiographDiagnostic
2. Working length Radiograph
Used to determine the length of the canal
3.Final instrumentation radiograph(Master Cone)
Taken with the final size file /files/
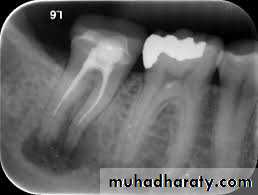
4.Final radiograph (Root canal after Obturation)
Taken after the tooth has been temporized.
5. Recall Radiograph.
Taken at evaluation
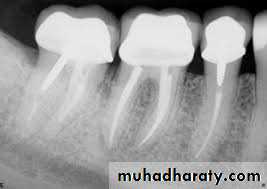
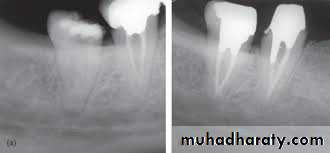
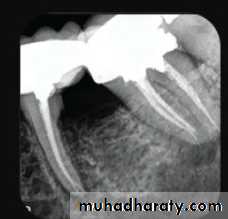
Rdiographs in Endodontics
Show 4-5 mm beyond the apex of the tooth and the surrounding bone or pathologicPresent an accurate image of the tooth without elongation or fore-shortening
Exhibit good contrast so all pertinent structures are readily identifiable.
Requirments of Endodontic Films
1
Diagnostic Conclusions
1.Normal Pulp
There are no subjective symptoms or objective signs. The tooth responds normally to sensory stimuli, and a healthy layer of dentin surrounding the pulp.2. Pulpitis
The pulp tissues have become inflamed.
3. Reversible pulpitis
The pulp is irritated, and the patient is experiencing pain to thermal stimuli.
4. Irreversible pulpitis.
The tooth will display symptoms of lingering pain.
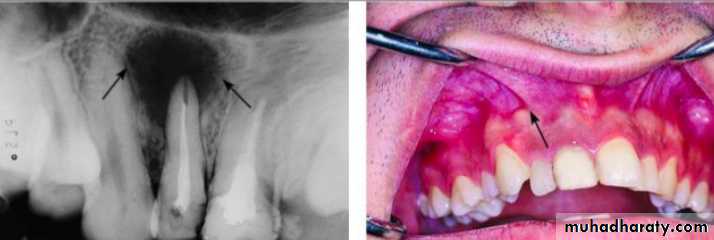
5. Periradicular abscess
An Inflammatory reaction to pulpal infection that can be chronic or have rapid onset with pain, tenderness of the tooth to pressure, pus formation, and swelling of the tissues.
6. Periodontal abscess.
An inflammatory reaction frequently caused by bacteria entrapped in the periodontal sulcus .A patient will experience rapid onset, pain, tenderness of the tooth to pressure , pus formation, and swelling.
7. Periradicular cyst
A cyst that develops at or near the root of a necrotic tooth. These types of cysts develop as an inflammatory response to pulpal infection and necrosis of the pulp.8. Pulp fibrosis
The decrease of living cells within the pulp causing fibrous tissue to take over the canal.
9. Necrotic tooth
Referred to as non vital. Used to described a tooth that describe a tooth that does not respond to sensory stimulus.Endodontic Procedures
1.Pulp CappingA covering of calcium hydroxide is placed over an exposed or nearly exposed pulp to encourage the formation of irritated dentin at the site of injury.
2. Indirect pulp capping
Is indicated when a thin partition of dentin is still intact.
3. Direct pulp capping
Is indicated when the pulp has been slightly exposed.
5.Pulpotomy
Involves the removed of the coronal portion of an exposed vital pulp.
Completed to preserve the vitality of the remaining portion of the pulp within the root of the tooth
This procedure is commonly indicated for vital primary teeth, teeth deep carious lesions, and emergency situations.
6. Pulpoctomy
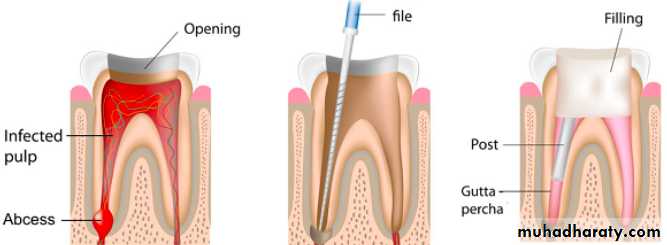
Referred to as root canal therapy;Procedure involves the complete removal of the dental pulp
Endodontic Explorer
Endodontic spoon excavatorHeadstrom files/Broaches
Endodontic files
• Manual files
• Rotary Instruments (gates-Glidden bur, Pesso reamer, Lentulo spiral, Rotary files)
Rubber stops
Paper points
Spreaders
Sluggers
Glick NO.1
Millimeter ruler
Instruments and Accessories for Endodontic Procedures
Sodium Hypochloride
Hydrogen PeroxideChlohyxodine
Irrigation Solutions
Gutta-percha pointsAugenol
Formocresol Root canal sealer
Medicaments and Dental Materials in Endodontics
Medicaments and Dental Materials in Endodontics
Anesthesia and pain control
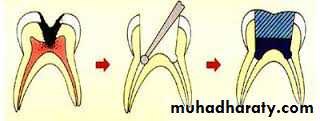
Isolation and disinfection of the siteAccess preparation Debridement and shaping the canal
Obturation
Overview of Root Canal Therapy
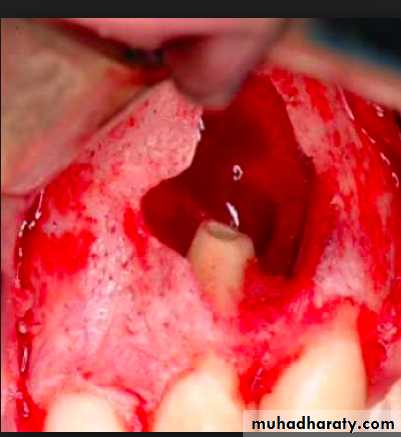
7- Surgical endodontic
Indication for surgical intervention
Endodontic failure caused by persistent infection, severely curved roots ,perforation of the canal, pulp stones, or accessory canals that cannot be treated.Exploratory surgery
To determine why healing has not occurred
Biopsy