Anterior Cervical
Triangle
1

To describe boundaries & subdivisions of the
anterior cervical triangle
To list the contents of carotid, submandibular &
submental triangles
To describe the carotid sheath & its relations
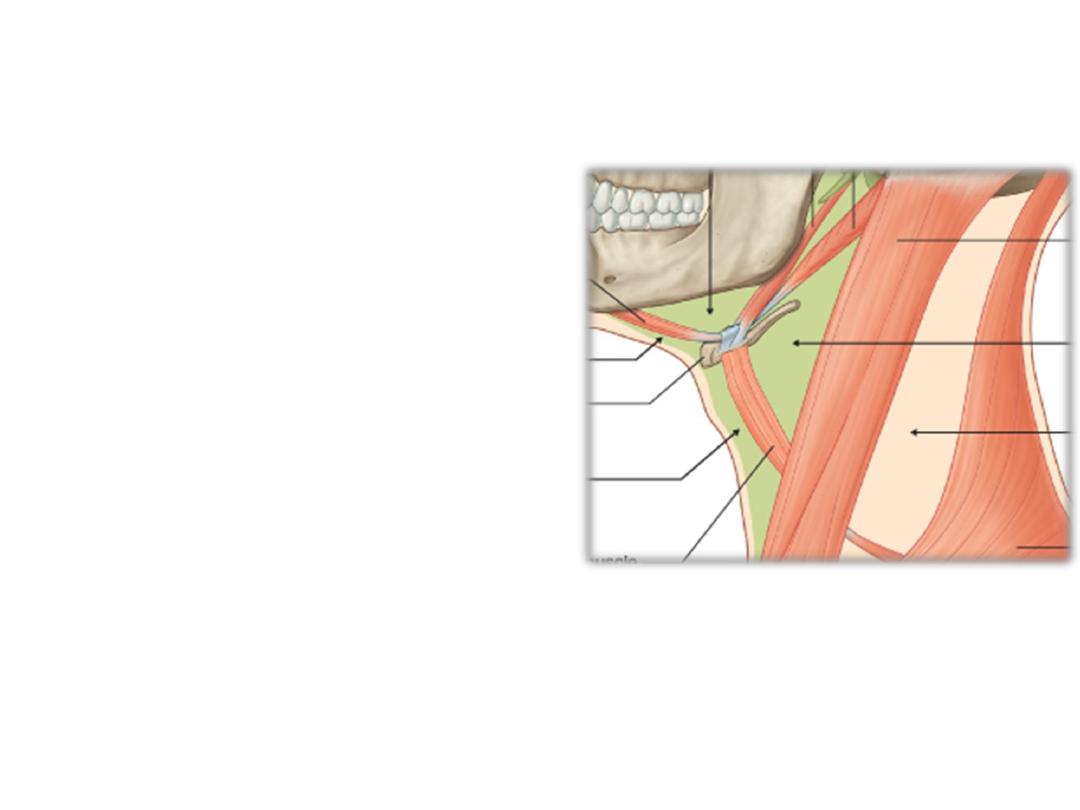
Anterior cervical triangle is divided into:
1) Carotid triangle
2) Submandibular triangle
3) Submental triangle
4) Muscular triangle
1
2
3
4
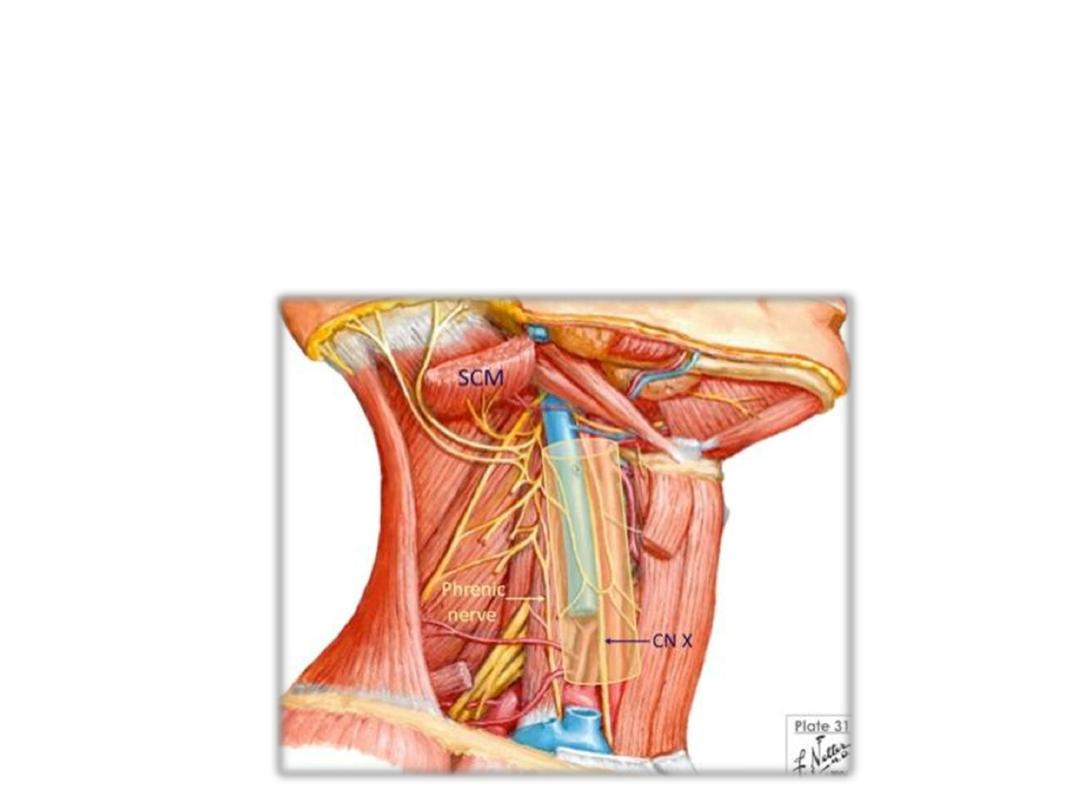
Carotid sheath:
• Upper attachment; margins of carotid canal
• Lower attachment: aortic arch
• Contents:
CCA & ICA
IJV
CN X
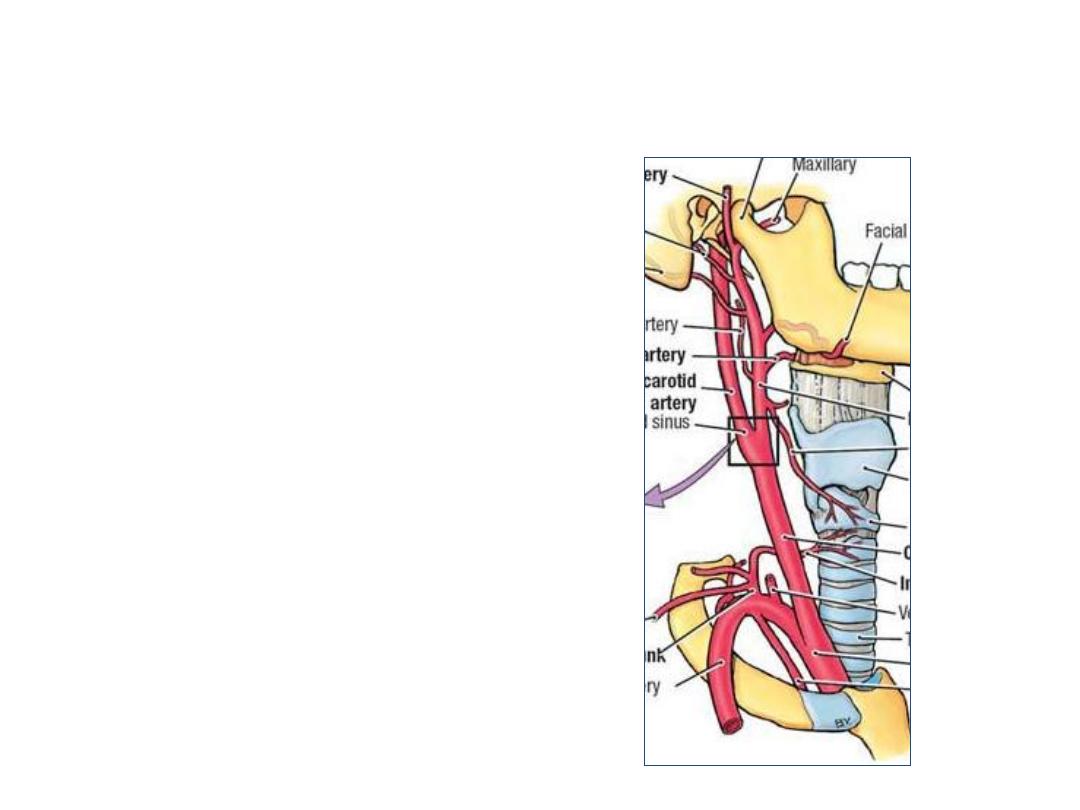
Carotid triangle:
Floored by hyoglossus, thyrohyoid, middle & inferior constrictors
Common carotid artery (CCA):
Arises from the brachiocephalic
trunk on the right & from aortic arch
on the left side
Ascends in the carotid sheath
with the IJV & vagus nerve
Ends at C3-4 by dividing into ECA
& ICA
Gives no branches (?!)
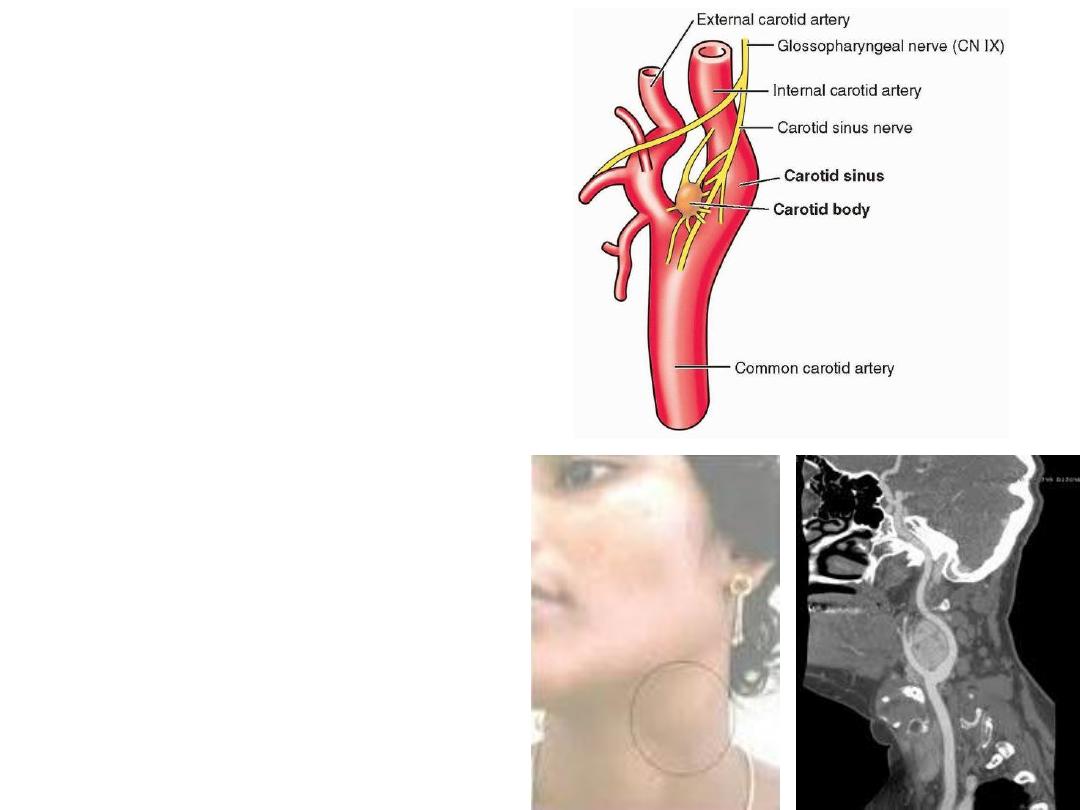
Carotid sinus:
-Dilatation at carotid bifurcation
-Contain baroreceptors
Carotid body:
-A mass of chemoreceptor cells in
the sinus
BOTH
are supplied by the sinu-
carotid branch of IX nerve
Carotid body tumor:
A pulsetile swelling on the side of
the neck
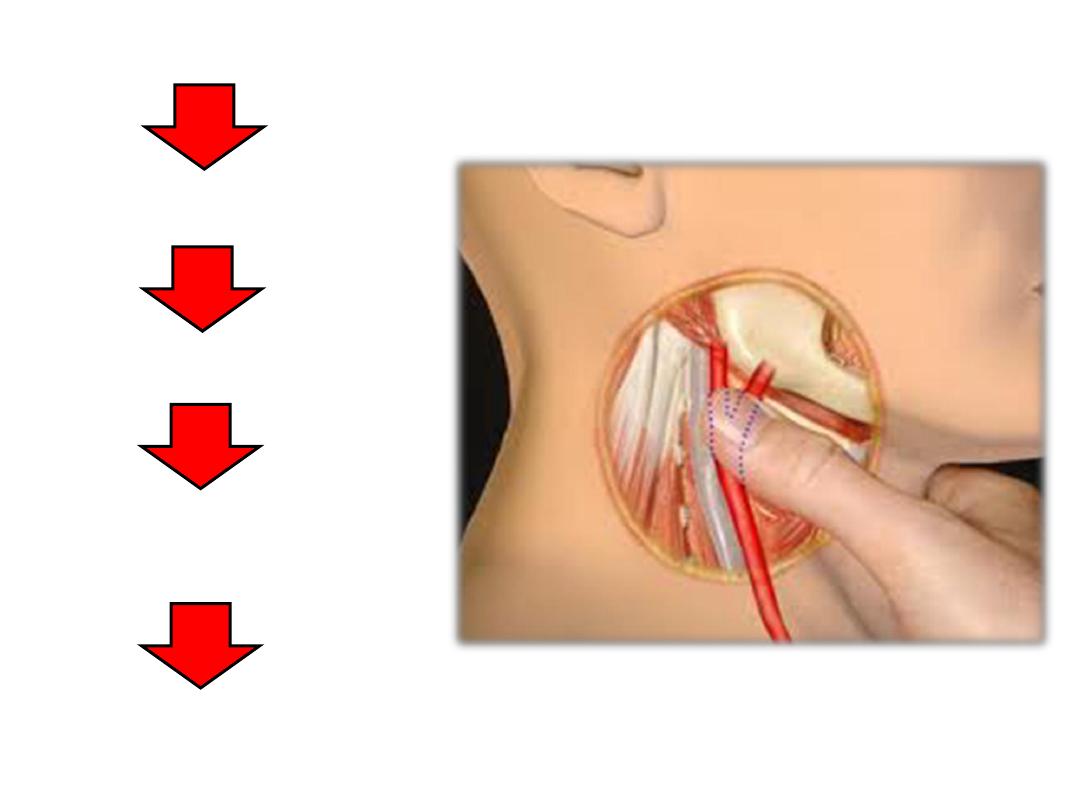
Carotid massage
Afferent by IX nerve
Medulla oblongata
Efferent by X nerve to
the cardiac plexus
Bradycardia
Hypotension
Carotid reflex
Internal carotid artery (ICA):
•Lies posterior to the ECA alongside the pharyngeal wall
•Enters the carotid canal (petrous bone) at skull base
•Passes inside cavernous sinus in the middle cranial fossa
•Ascends medial to the anterior clinoid process
•Supplies the brain & orbital structures
•It gives no branch in the neck
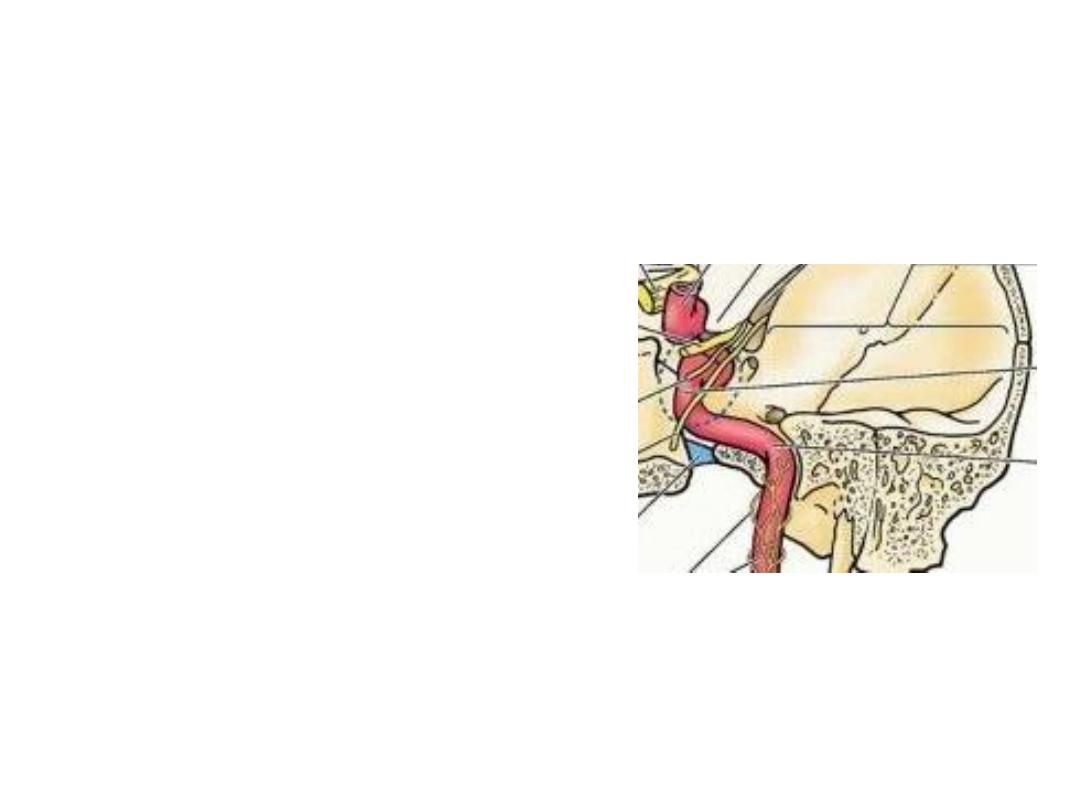
Bouthillier described seven segments for the internal carotid artery:
1. cervical segment
2. petrous segment
3. lacerum segment
4. cavernous segment
5. clinoid segment
6. ophthalmic (supraclinoid) segment
7. communicating (terminal) segment
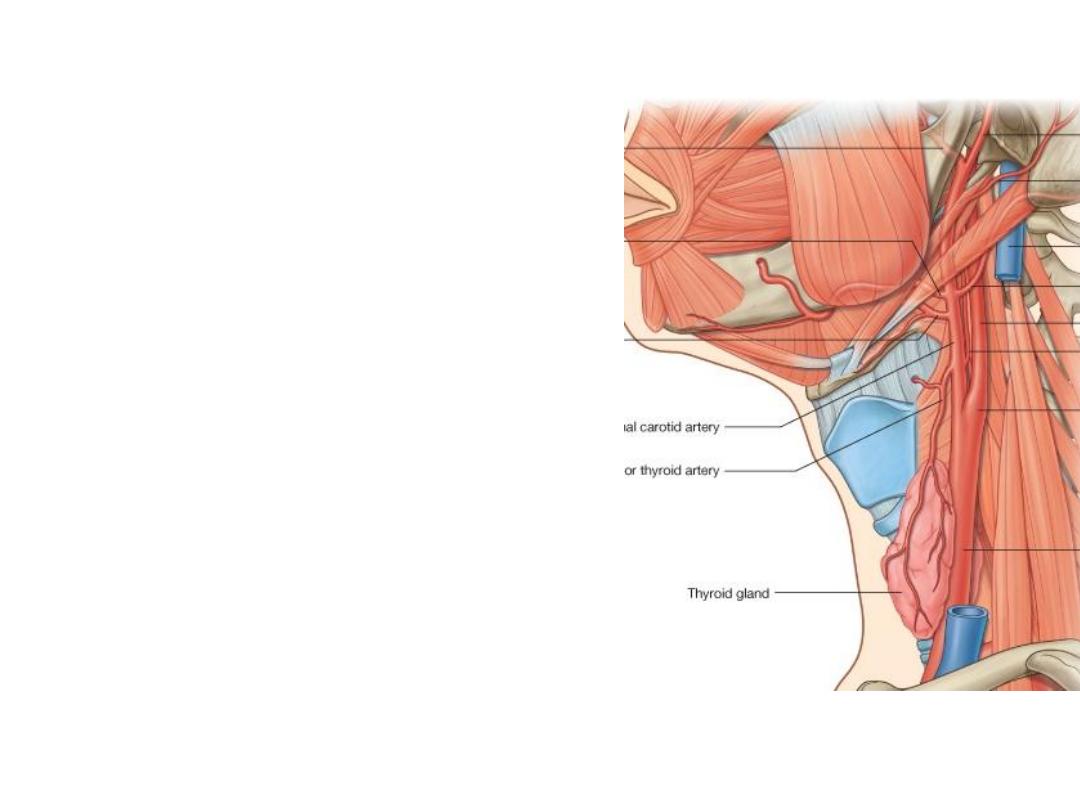
External carotid artery (ECA):
•Ascends anterior to ICA
•Passes deep to the posterior belly of
digastric
•It is the artery of head & neck giving 8
branches
•Ends behind the neck of the mandible by
dividing into its 2 terminal branches
Anterior branches:
1- Superior thyroid artery:
-Descends with the external laryngeal nerve
-Gives superior laryngeal artery to the larynx
-Enters the apex of thyroid lobe
-Supplies thyroid & parathyroid glands
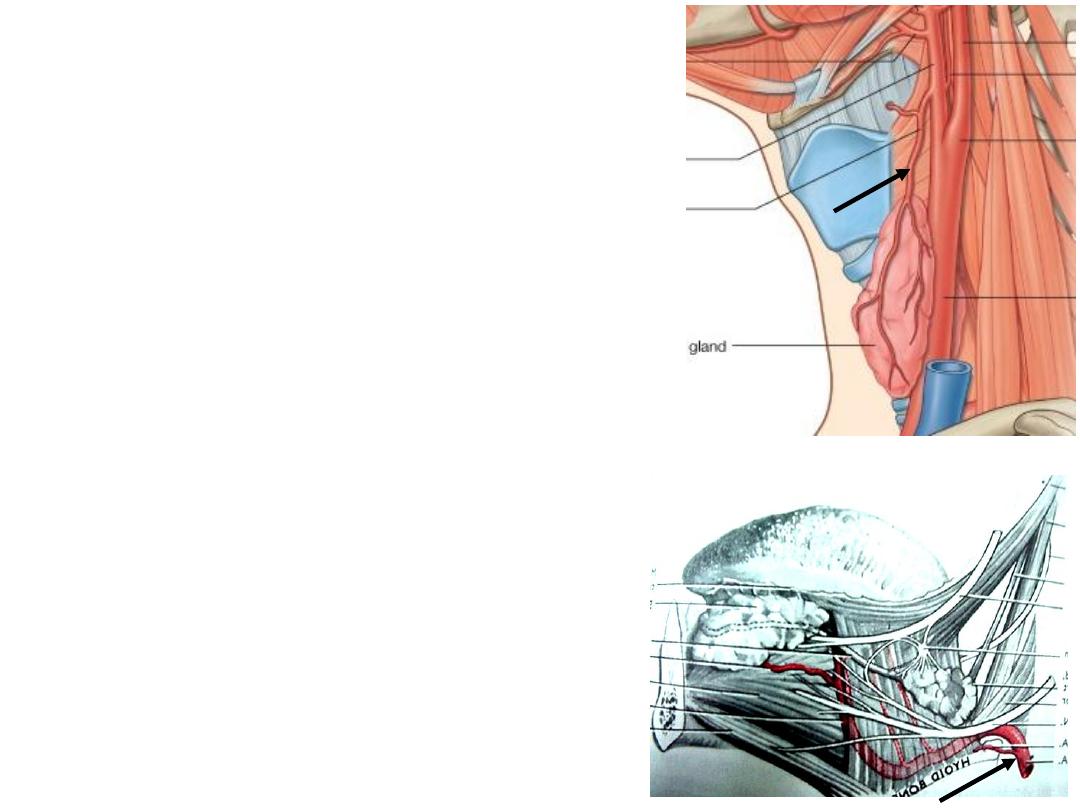
2- Lingual artery:
-Directed to the oral cavity after an upward loop
-XII nerve lies lateral to it
-Supplies the tongue & structures in the floor of
the mouth
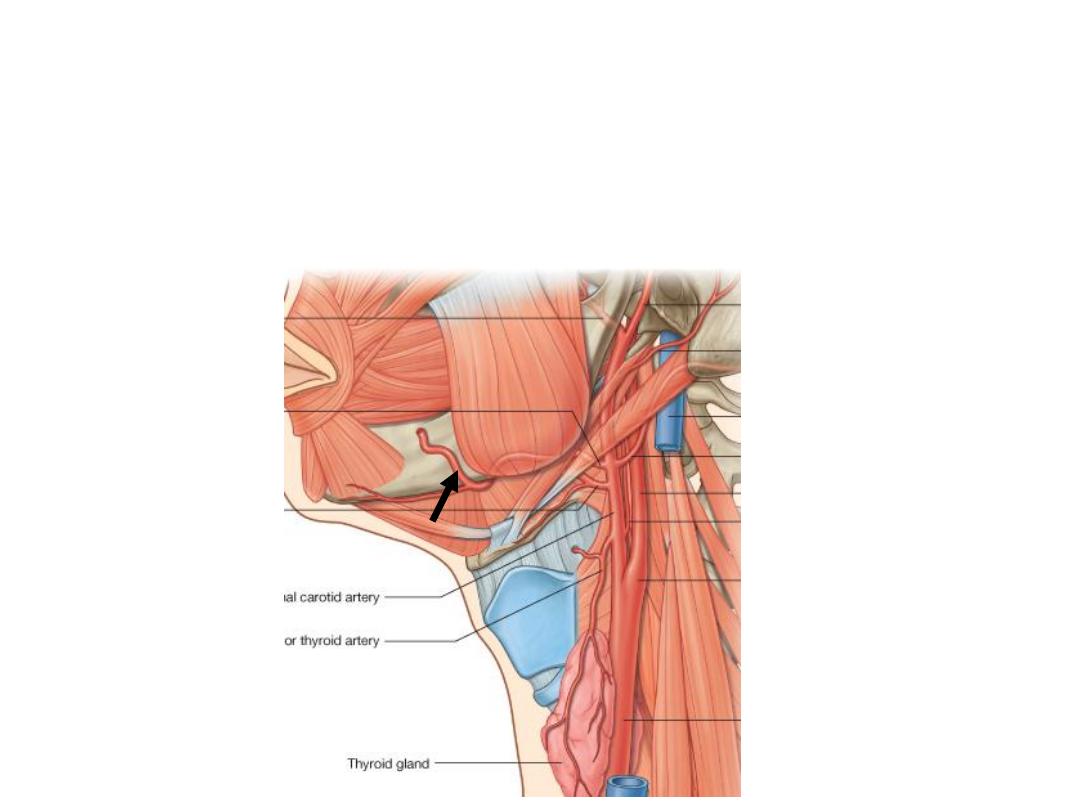
3- Facial artery:
-Crosses the submandibular triangle before reaching the face
-Supplies the tonsils, palate & submandibular gland
-Enters the face by turning below the lower border of the mandible
Posterior branches:
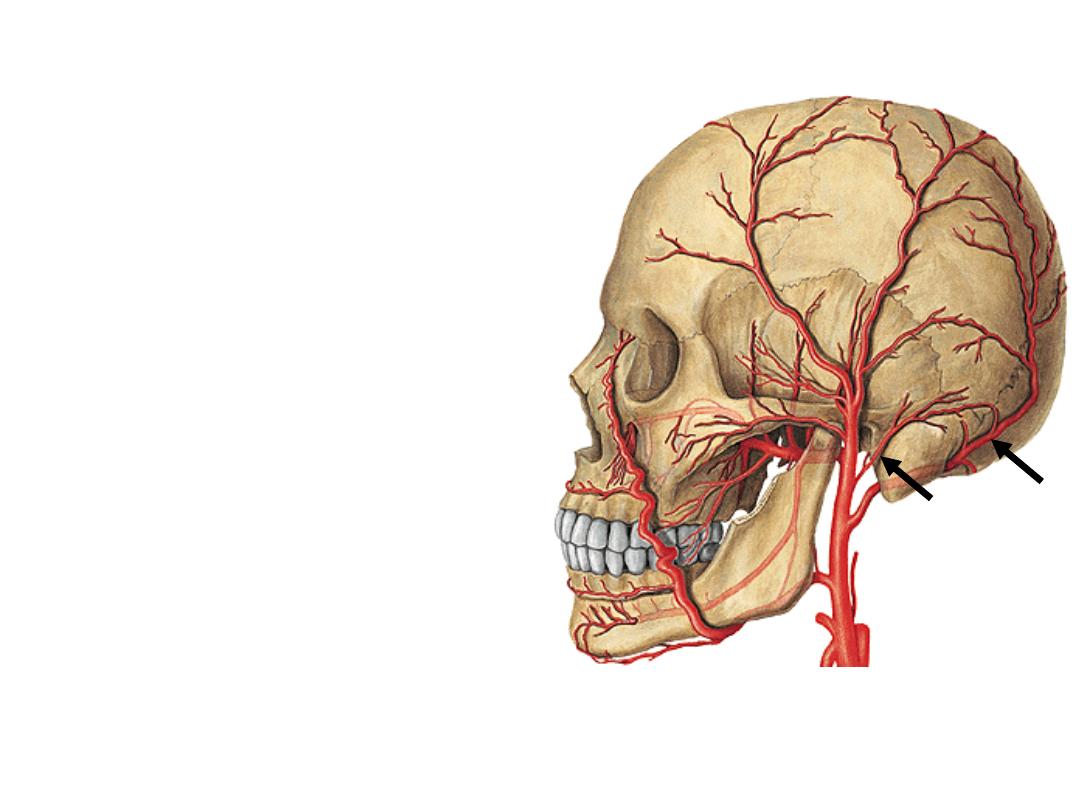
4- Occipital artery:
-Crosses the apex of posterior triangle
-Supplies the back of scalp
5- Posterior auricular artery:
-Lies superficial to the mastoid process
-Supplies the auricle
-Gives stylomastoid branch to the middle ear
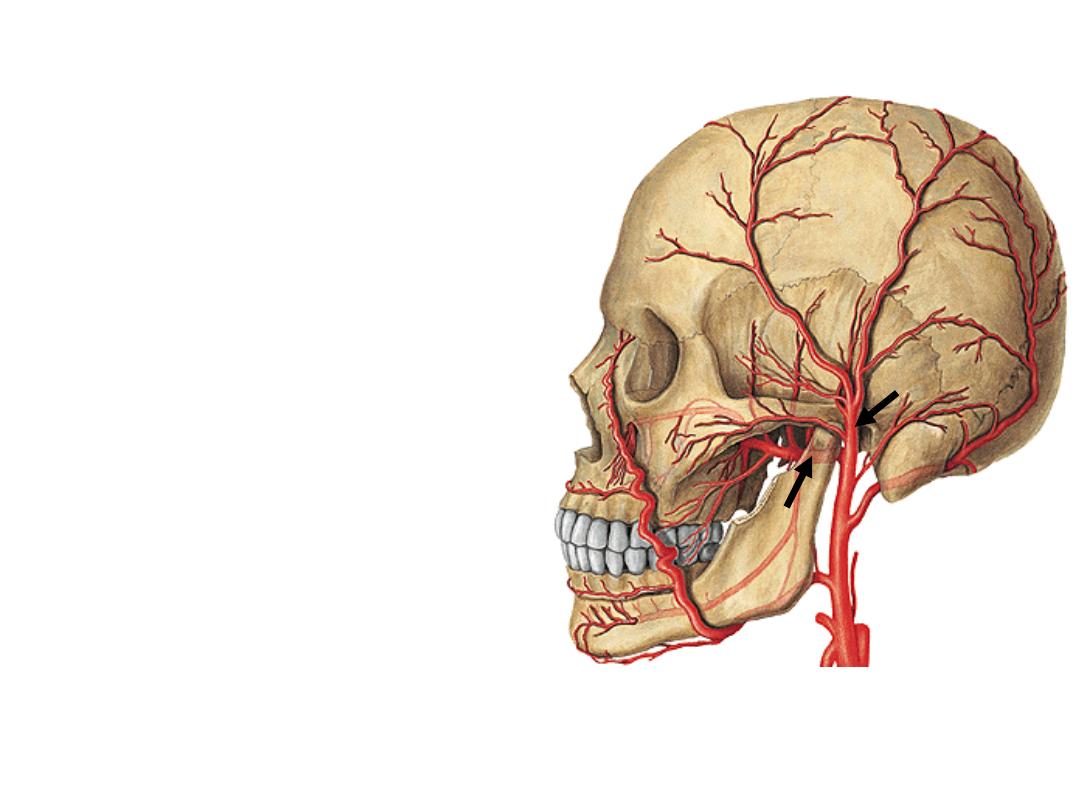
Medial branch:
6- Ascending pharyngeal artery:
•Ascends along pharyngeal wall
•Supplies the pharynx & tonsils
Terminal branches:
7- Superficial temporal artery:
Ascends upward to the temporal fossa
8- Maxillary artery:
Passes forward to the infratemporal fossa
Internal jugular vein (IJV):
Emerges from jugular foramen
Lies posterior to the carotid artery at
the skull base & lateral to it at the root
of the neck
The part of the carotid sheath
surrounding it is almost deficient
Ansa cervicalis & deep cervical
nodes are closely related to it
Ends by uniting with the subclavian
vein forming the brachiocephalic vein
Contains one pair of valves
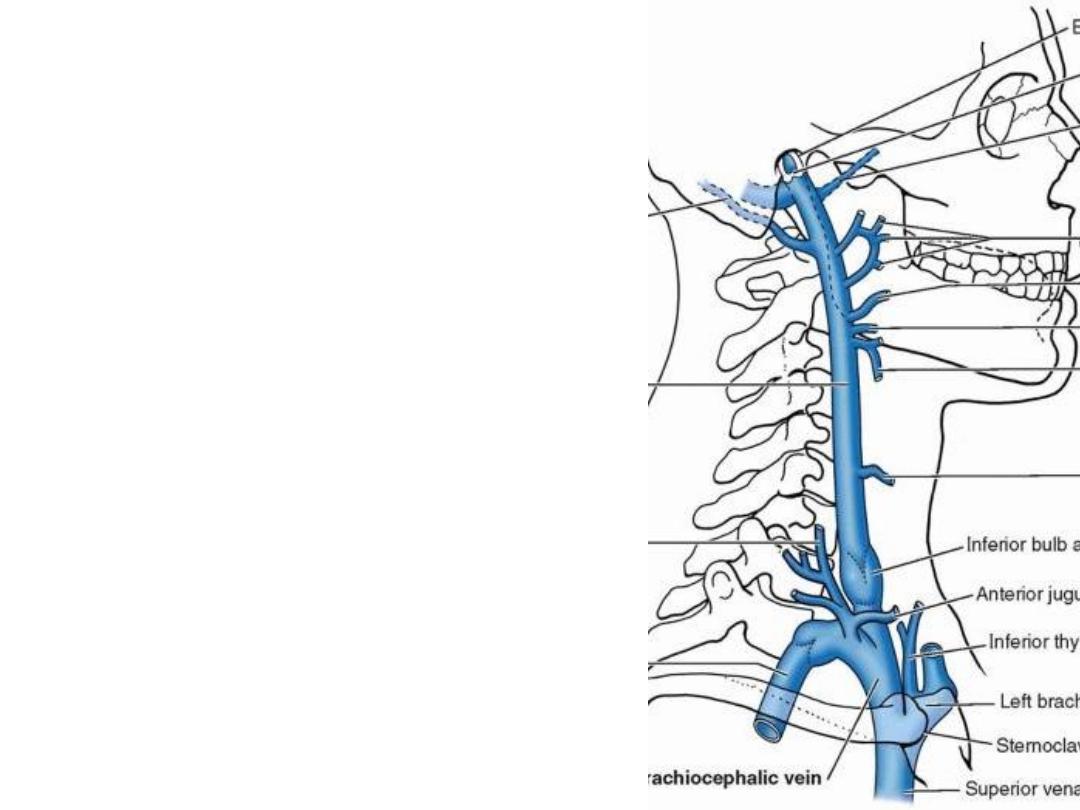
Tributaries:
1- Inferior petrosal sinus
2- Occipital veins
3- Thyroglossofacial veins
4- Pharyngeal veins
5- Middle thyroid vein
1
2
3
4
5
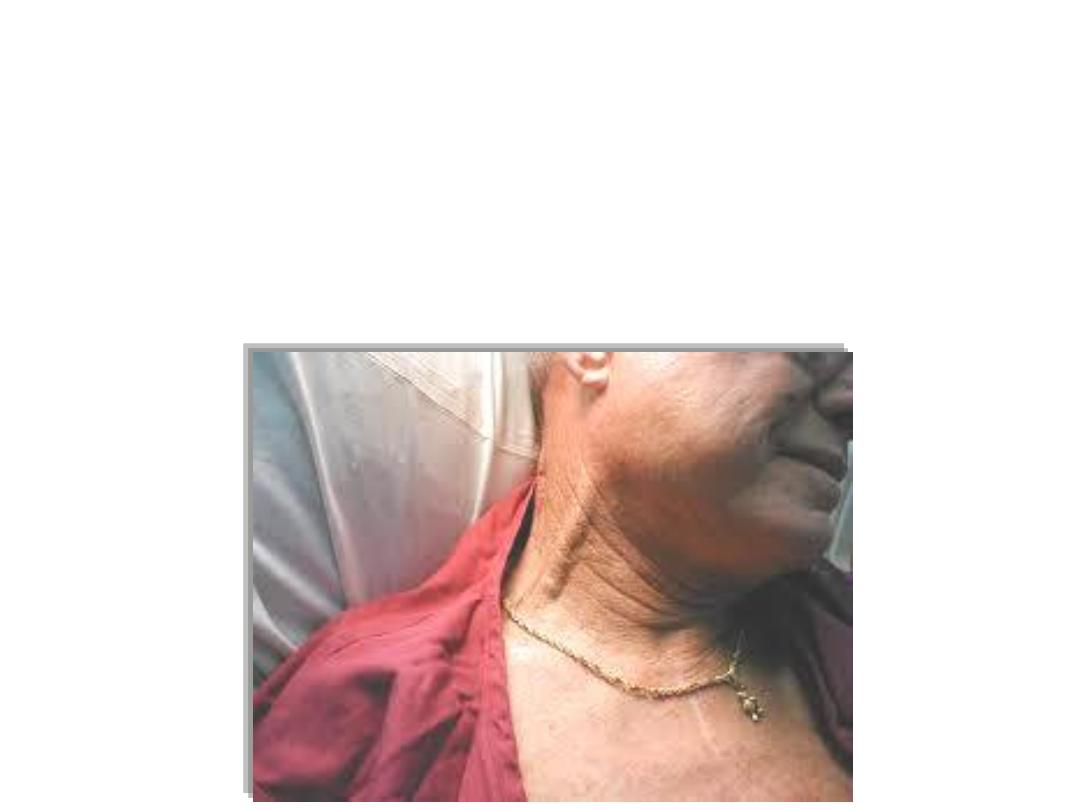
Case
A 55 years old heavy smoker man developed
heart failure
secondary
to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. When he was admitted to
hospital the physician started to examine his neck, he found
his neck
veins were severely distended & pulsating!
Why?
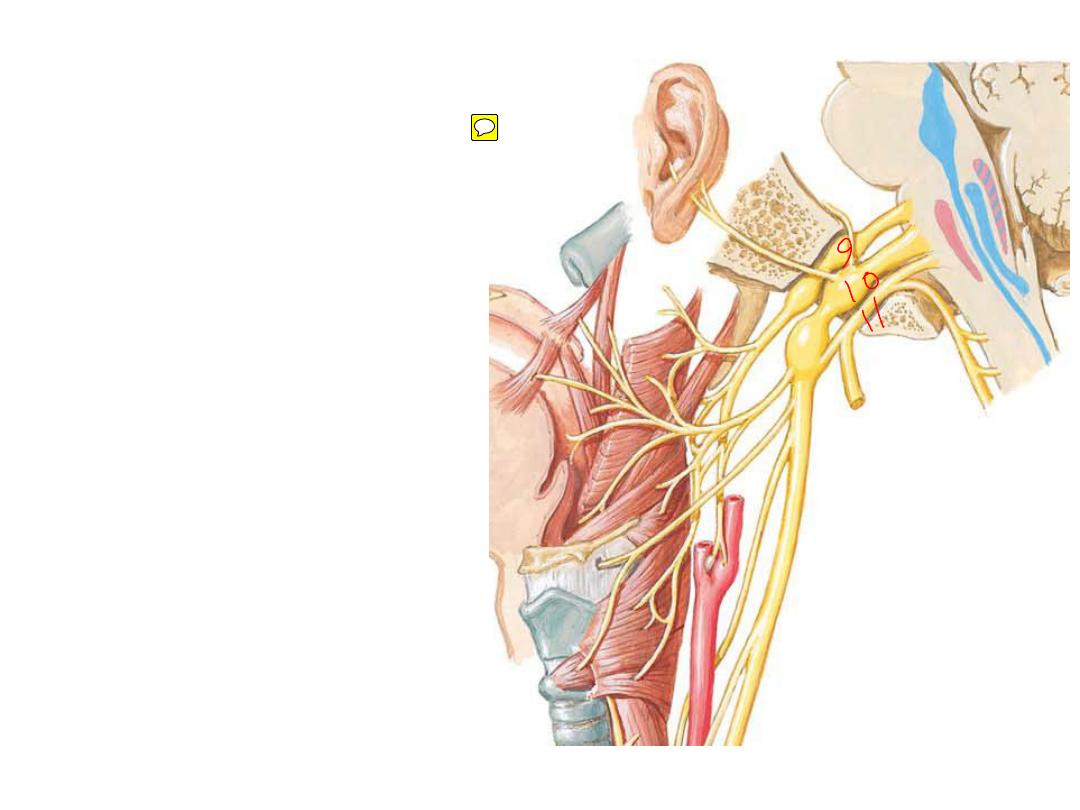
Vagus nerve:
•Leaves the jugular foramen &
descends in the carotid sheath
•Takes the cranial part of XI which
is distributed to pharyngeal &
laryngeal muscles
•Has two ganglia
•Contains
the
major
parasympathetic power in the
body (70%)
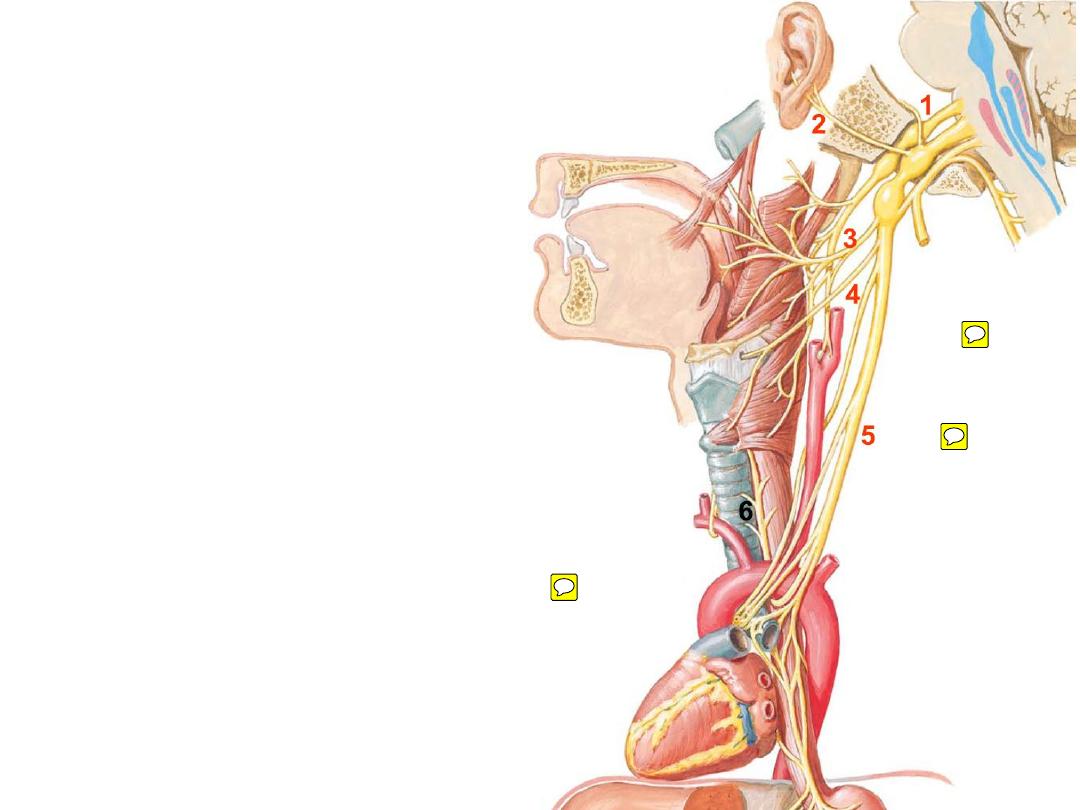
•Branches:
1- Meningeal; sensory
to the meninges
2- Auricular; sensory
to the external ear skin
3- Pharyngeal: motor
to muscles of the
pharynx & soft palate
4- Superior laryngeal; sensory & motor
to the
larynx
5- Cervical cardiac nerve; parasympathetic
to the cardiac plexuses in the thorax
6- Recurrent laryngeal; sensory & motor
to
the larynx
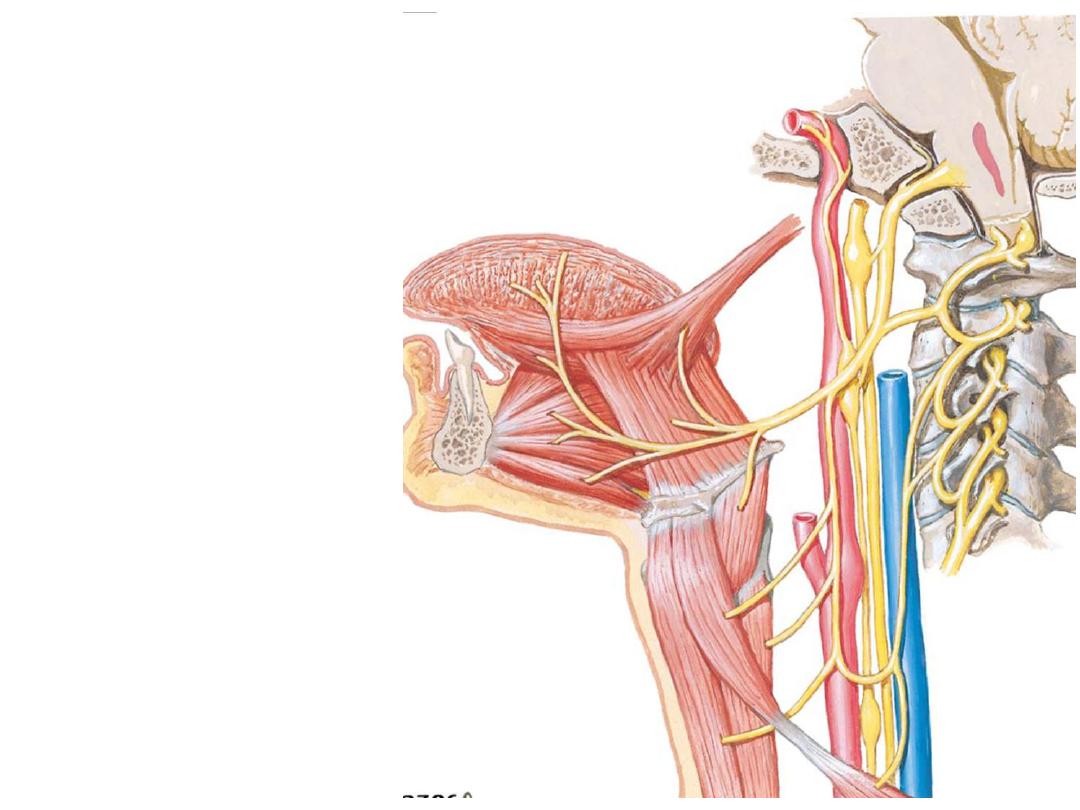
Hypoglossal nerve (XII):
Crosses lateral to the ECA in its
way to the floor of the mouth
Branches in the neck are of C1
origin:
-Ansa superior root
-Nerve to thyrohyoid
-Nerve to geniohyoid
Enters the floor of the mouth to
supply all tongue muscles except
palatoglossus
motor nerve
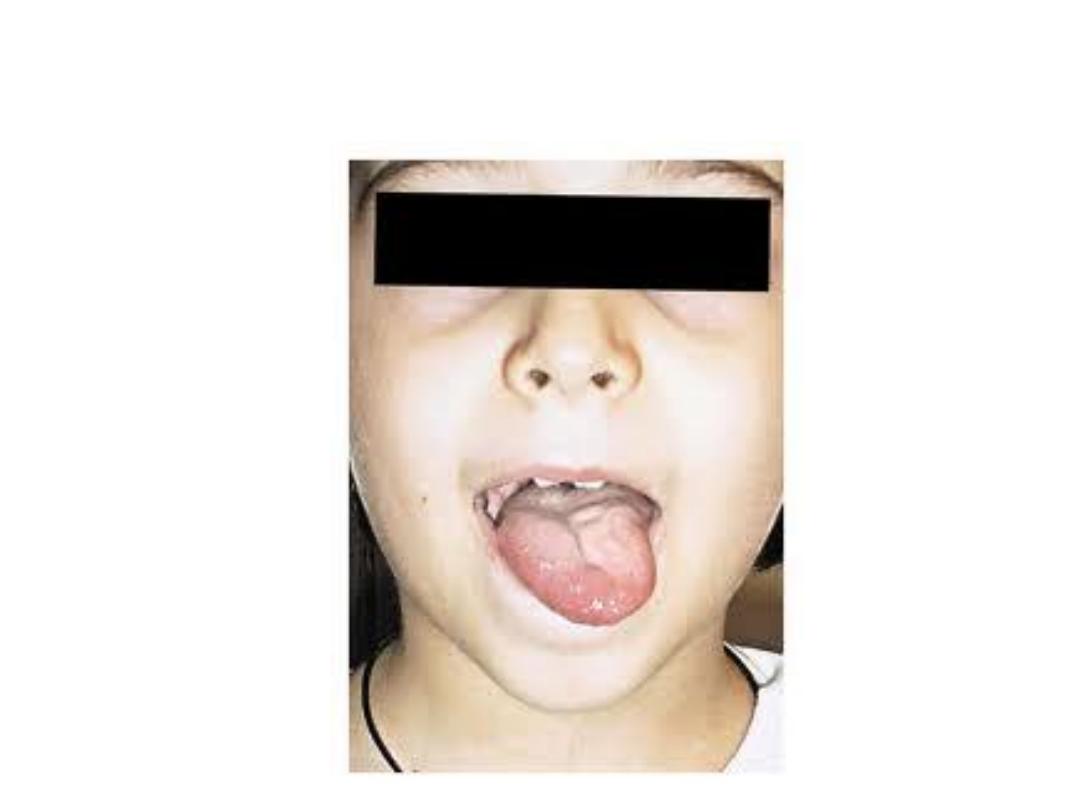
Hypoglossal nerve injury causes deviation of the tongue
to the .?. side
Nuclei
which
supply
striated
muscles through the lower four
cranial nerves (pharyngeal, laryngeal,
palatal & tongue muscles) receive
bilateral corticonuclear
supply
THEREFORE:
Lesions at nuclear levels & distally
(LMND)
markedly
affect
these
muscles
(Bulbar palsy)
Lesions above nuclear levels up to
the cortex (UMND)
minimally
affect
these muscles
(Pseudobulbar palsy)
Such lesions are often associated
with
pyramidal
tract
lesions
(hemiplegia)
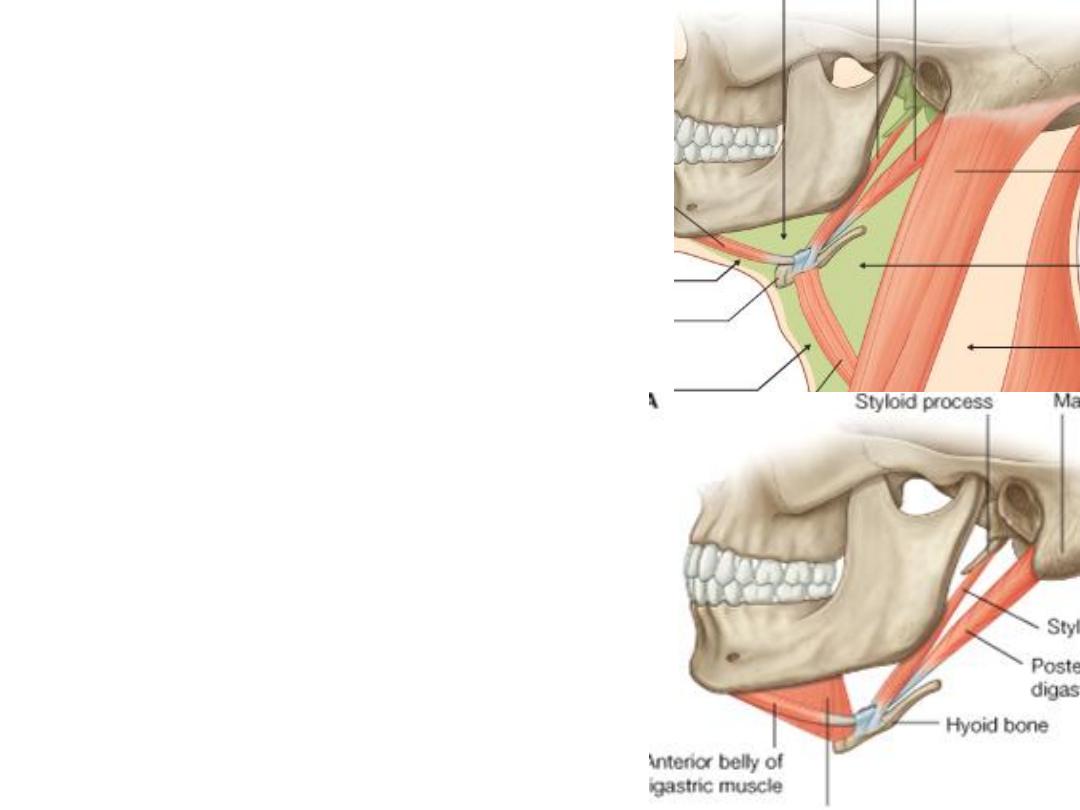
Digastric:
Origin:
-Anterior belly: digastric fossa
-Posterior belly: digastric notch
Insertion:
Intermediate tendon, hyoid bone
Nerve supply:
-Anterior belly: myelohyoid n. (Vc)
-Posterior belly: facial nerve (VII)
Action:
-Elevate the hyoid bone
-Opens the mouth widely
Stylohyoid:
-From the styloid process to the hyoid bone
-Overlies the posterior belly of digastric with
the same innervation & action
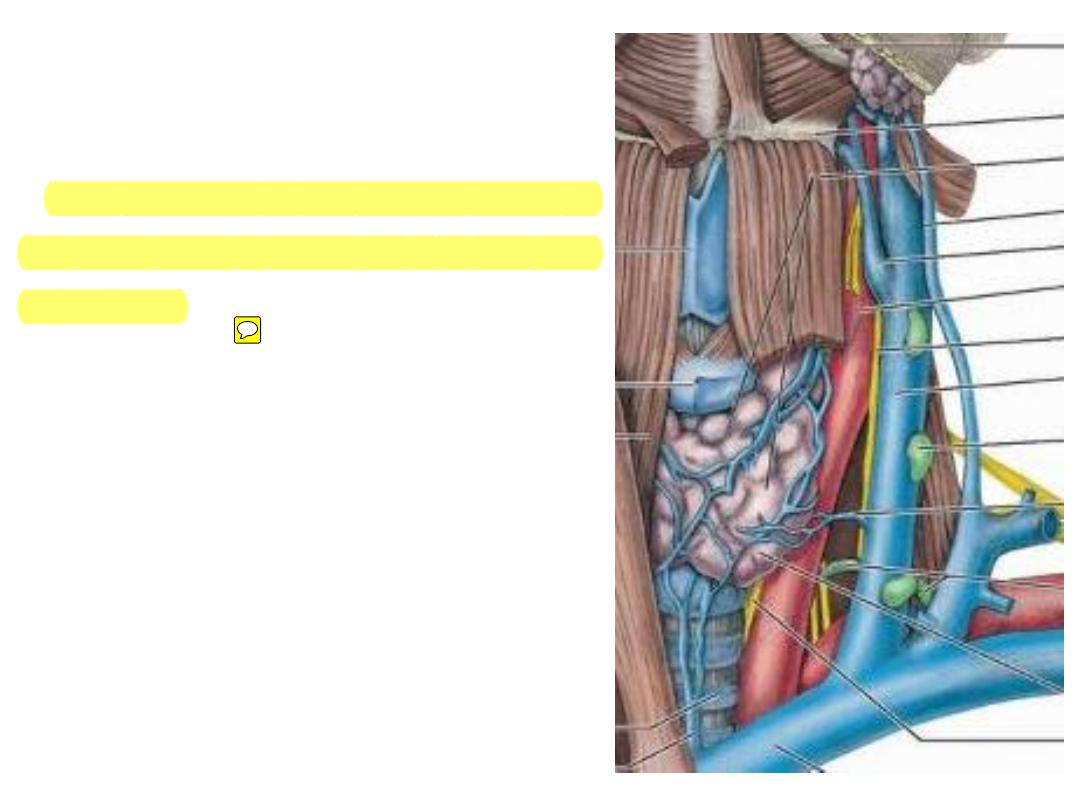
Submandibular triangle:
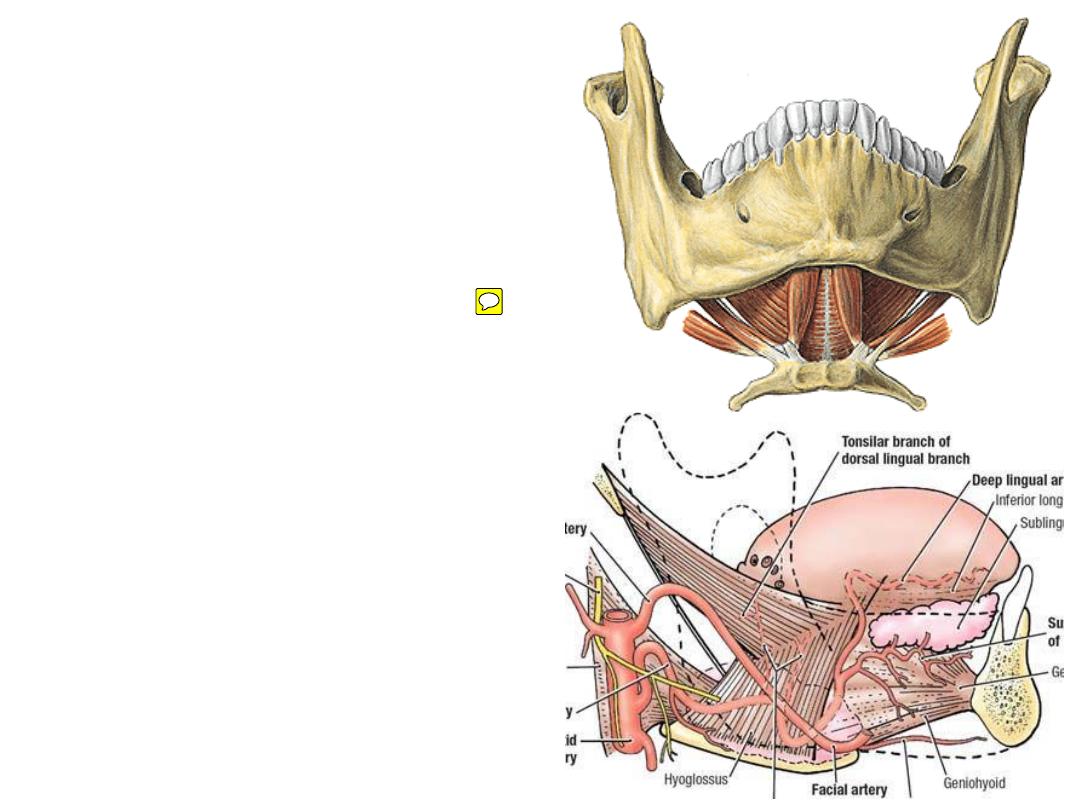
Mylohyoid:
Origin:
mylohyoid line
Insertion:
mylohyoid raphe & hyoid bone
Nerve supply:
nerve to mylohyoid
Action:
-Forms the floor of the mouth
-Plays a major role in swallowing
Hyoglossus:
Origin:
greater cornu of the hyoid
Insertion:
side of the tongue
Nerve supply:
XII nerve.
Action:
-Elevates the hyoid
-Depresses the tongue
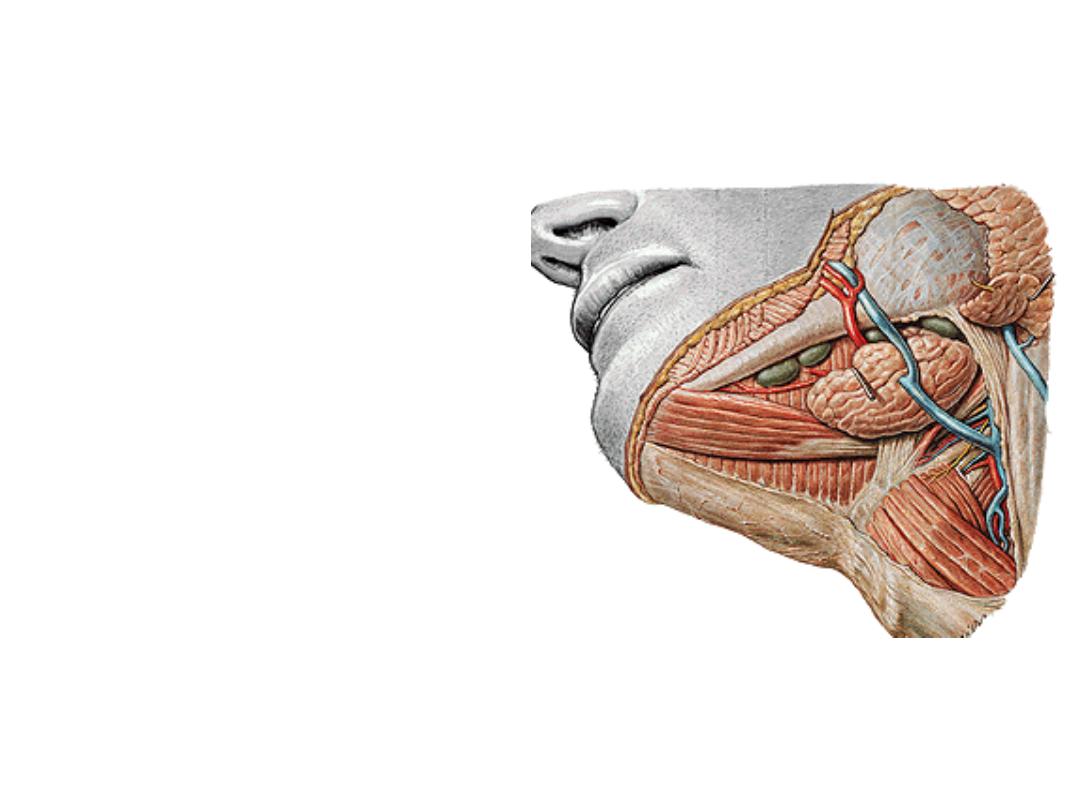
Contents of the triangle:
1- Submandibular gland
2- Facial artery:
-Crosses the triangle in S shape
course
-Before reaching the face it supplies
the gland, tonsils & palate
3- Common facial vein:
-Anterior facial + anterior division of
retromandibular veins
-Passes superficial to the gland
-Drains to the IJV
4- Submandibular lymph nodes
5- Cervical branch of VII
1
2
3
4
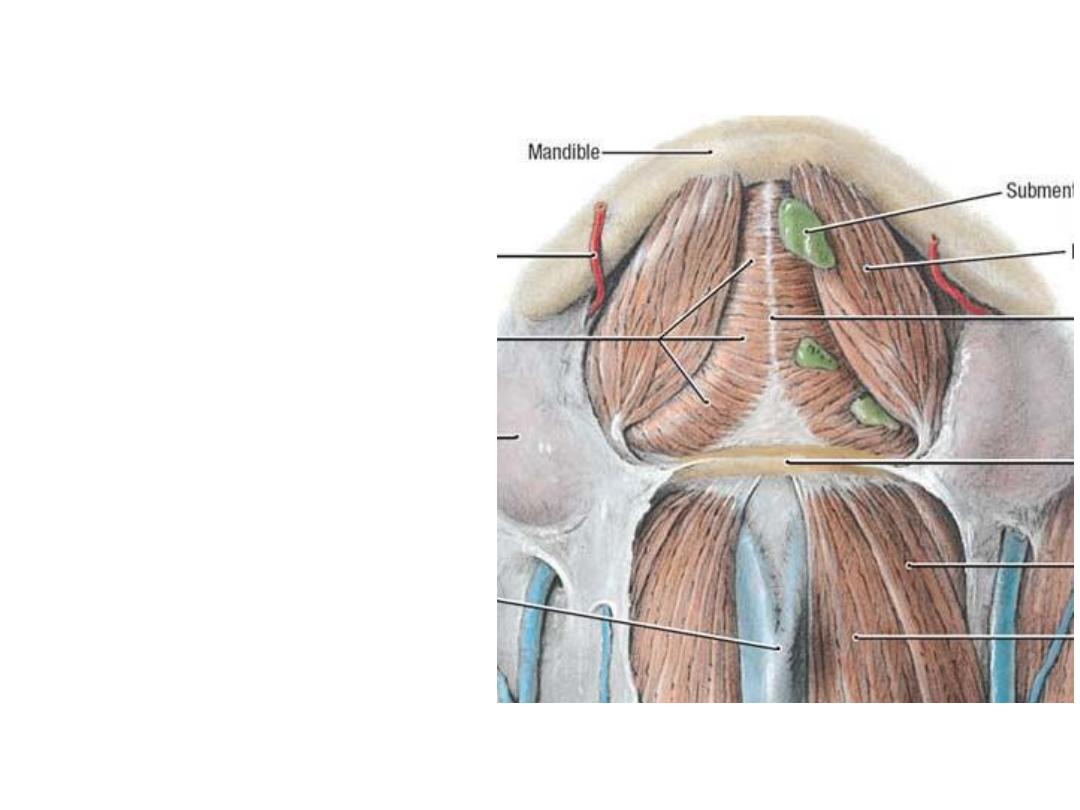
Boundaries:
-Digastric anterior bellies
-Hyoid
Contents:
1- Submental branch of facial artery.
2- beginning of AJV.
3- Submental lymph nodes.
4- Nerve to myelohyoid:
Submental triangle:
