
Fascia of the Neck
The Posterior Cervical Triangle

To define neck fascia
To demonstrate the borders, roof & floor of the
posterior triangle
To list the main contents of the triangle (vessels,
nerves, nodes,
…)
To relate to some clinical conditions
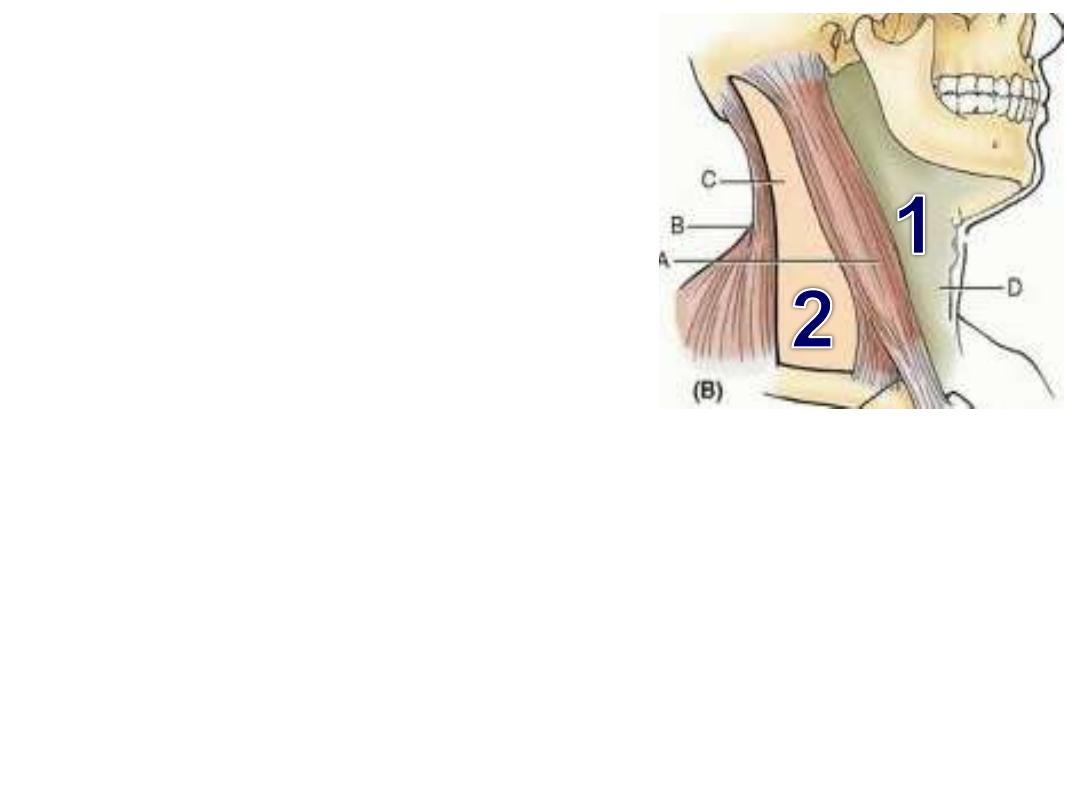
Boundaries of cervical triangles:
1- Anterior:
-
Midline
-
Mandible (lower border)
-
Anterior border of SCM
2- Posterior:
-
Clavicle (middle third)
-
Anterior border of trapezius
-
Posterior border of SCM
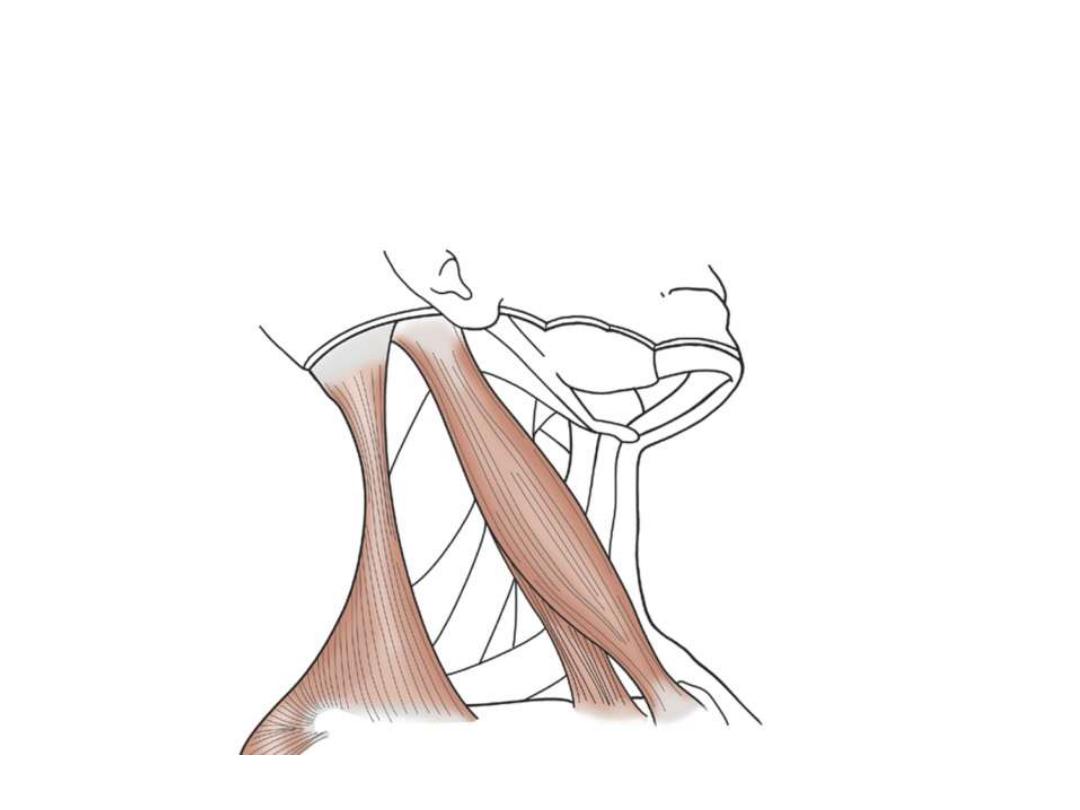
Sternocliedomastoid:
Arises from the manubrium sterni & medial third of clavicle
Inserted in the mastoid process & lateral third of superior nuchal line
Supplied by the spinal accessory nerve

Action:
Unilateral:
-Approaching the mastoid process to the shoulder (ipsilateral lateral flexor)
-Turns the face to the opposite side (contralateral rotator)
Bilateral:
-Extends the skull
-Flexes the neck
-Accessory muscle of respiration
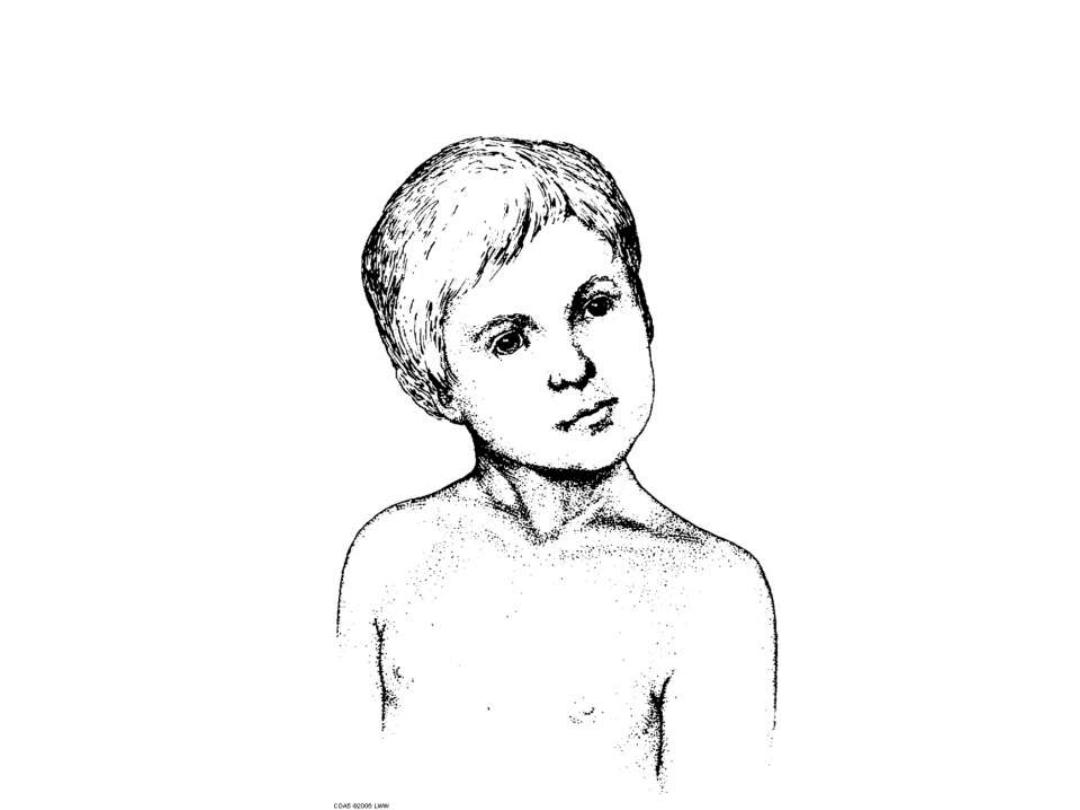
TORTICOLLIS
SCM contracture
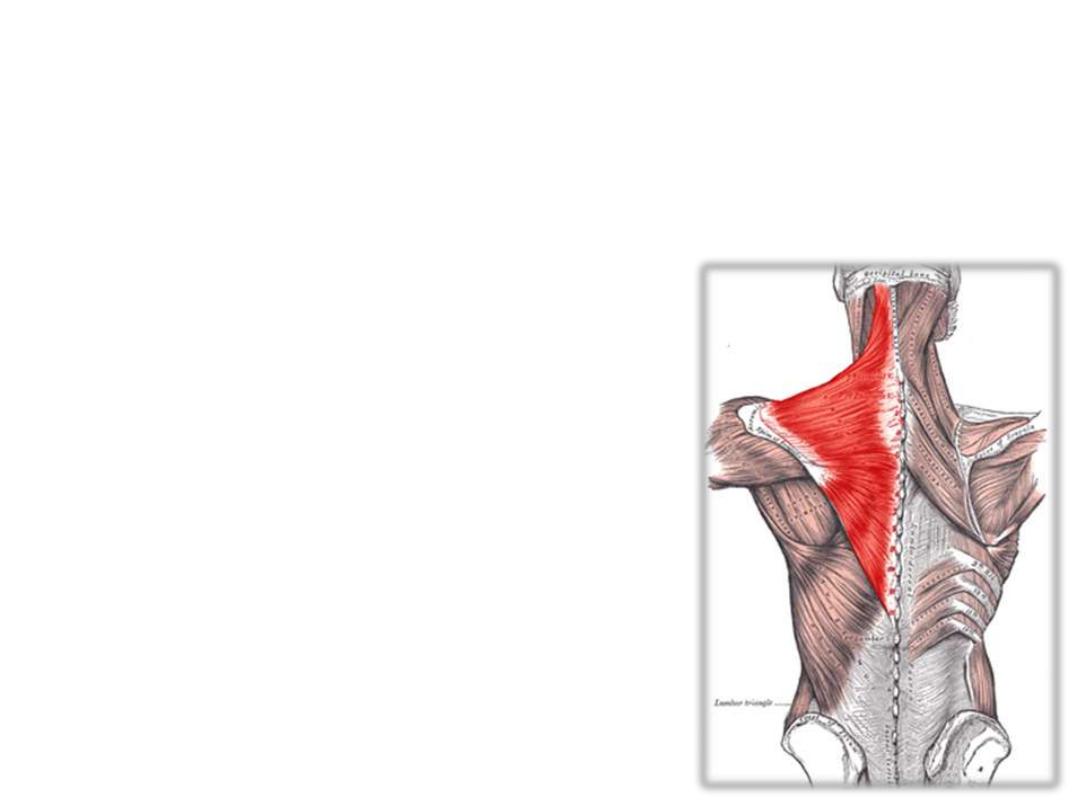

Trapezius:
Arises from the skull, ligamentum nuchae & thoracic spines
Descending fibers are inserted into the lateral 1/3 of clavicle (bound
the triangle)
Supplied by the spinal accessory nerve
Trapezius shrugs the shoulder

Whenever you decide to do an operation, you have to know the
followings
before you start
:
1- How not to leave a scar
…
Langer lines
2- How to give local ansthesia
…
Cutaneous nerves
3- Expected structures in each layer
…
Successive layers of the neck
4- What the mass could be
…
Contents of the area
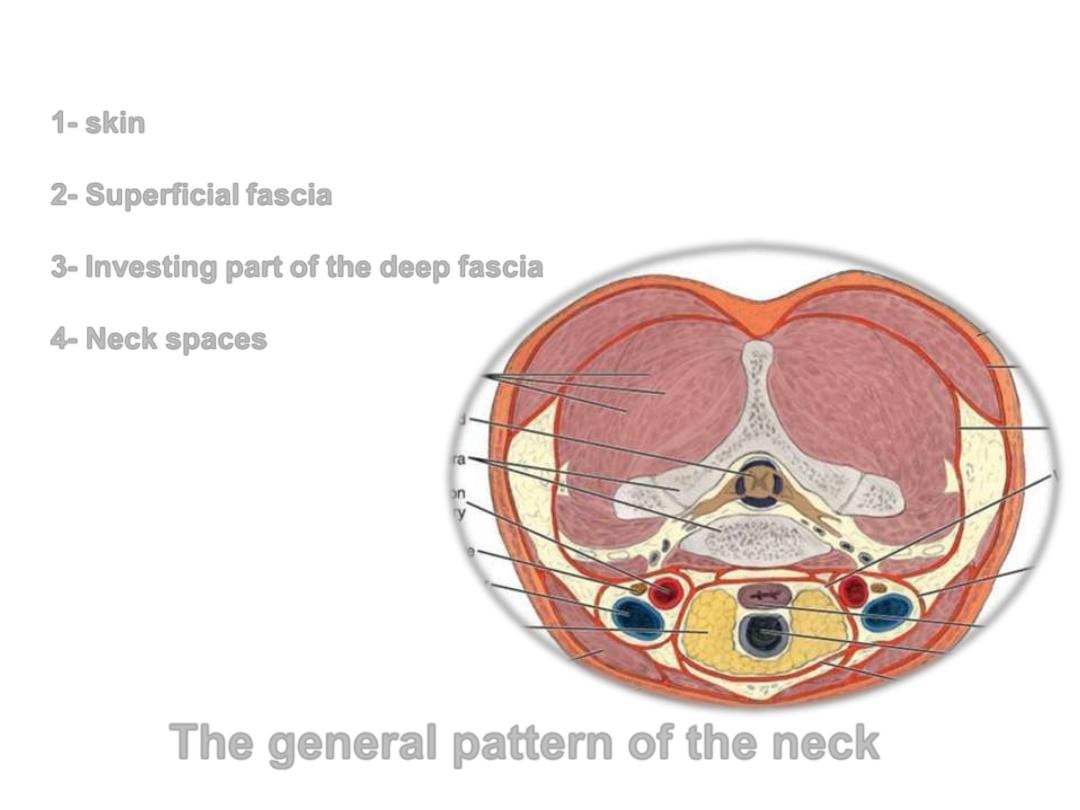
Layers of the neck:
1- skin
2- Superficial fascia
3- Investing part of the deep fascia
4- Neck spaces
The general pattern of the neck
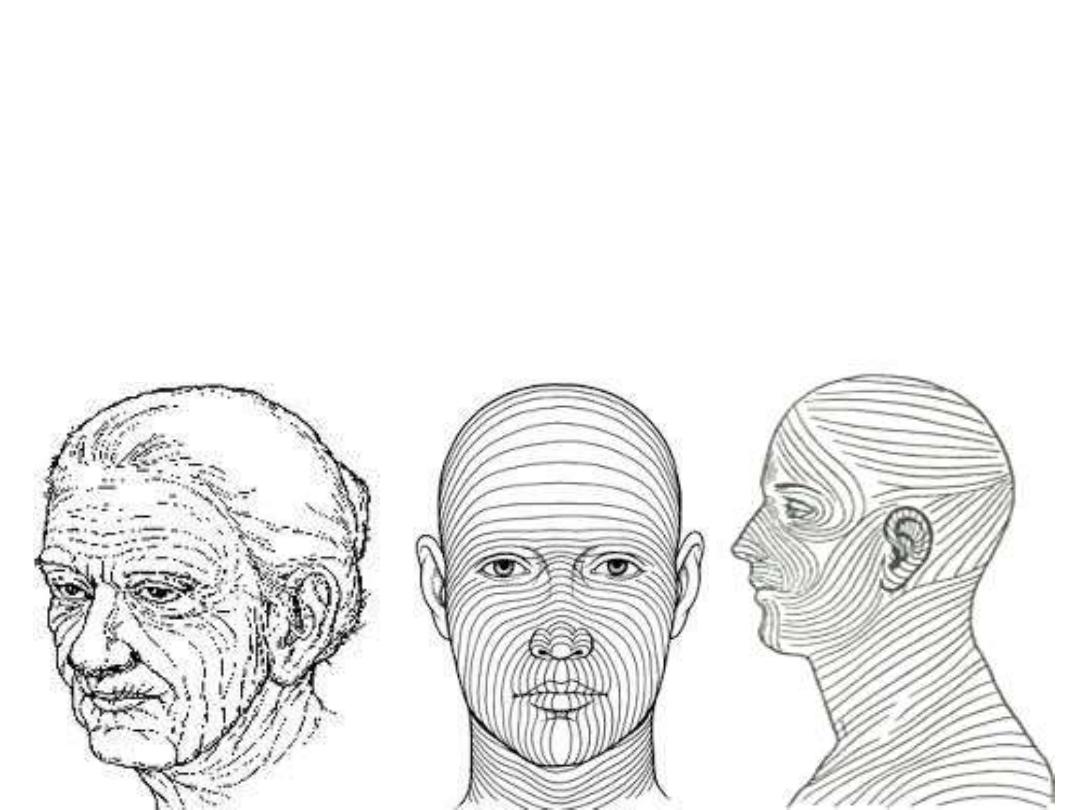
Skin incisions in the Head & Neck
…
Surgical incisions should follow a map of skin lines called tension lines
Tension lines of the skin (Langer or cleavage lines):
-Follow collagen arrangement
-Incisions along them end with minimum scars
-In the neck, they are transverse
-Senile wrinkles follow these lines
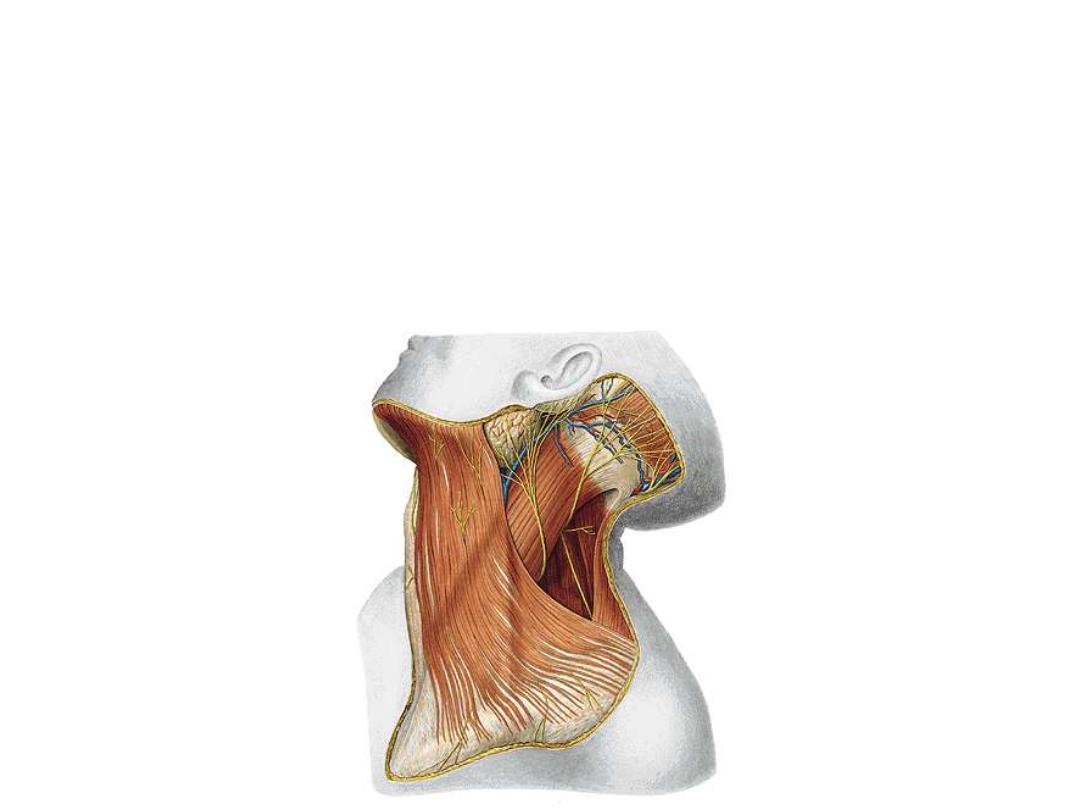
Structures within the superficial fascia:
1- Platysma (modified part of the panniculus adiposus):
Origin;
Upper part of pectoral fascia
Insertion;
Lower border of the mandible & skin of the corners of the mouth
Nerve supply;
Cervical branch of VII
Action;
Depresses the corner of the mouth & lower border of the mandible
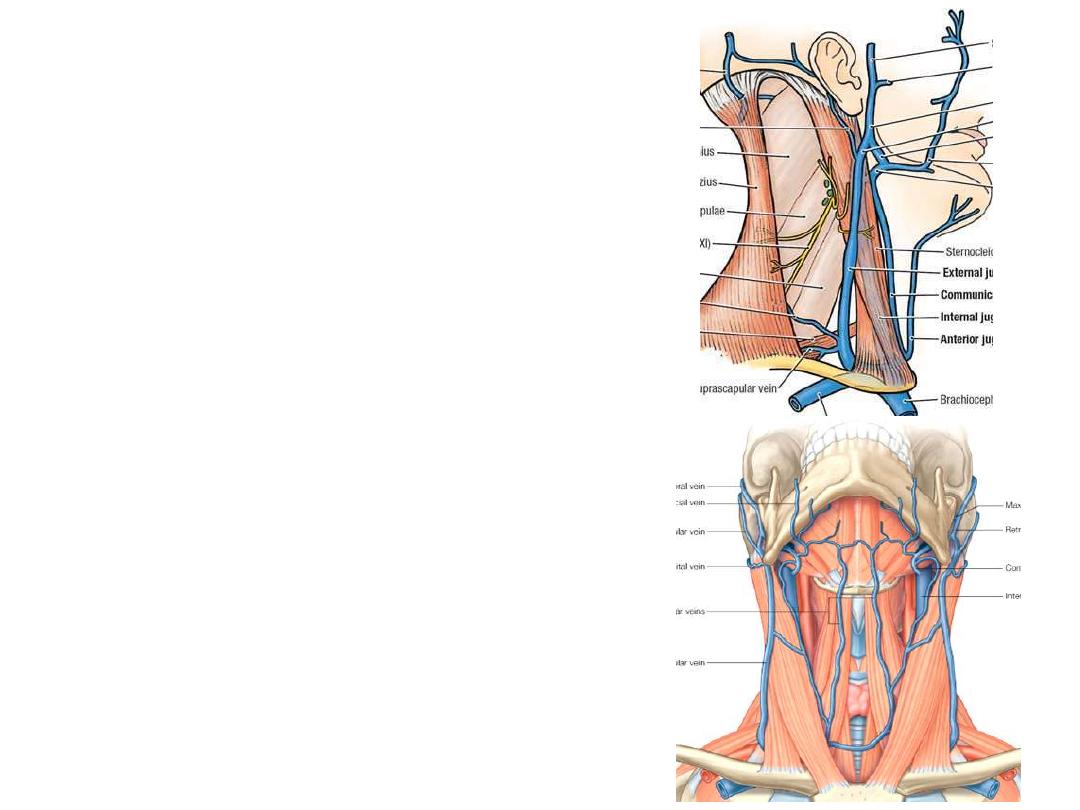
2- Veins:
External jugular vein:
•Formed just below the auricle
•Extends between the angle of mandible
& the middle of the clavicle
•Drains into the subclavian vein
•Contains 2 weak valves
•Distended in heart failure & increased
intrathoracic pressure
Anterior jugular vein:
•Formed below the chin
•Run each side of the midline
•Connected to each other by the jugular
venous arch in the suprasternal space
•Empty in the EJV
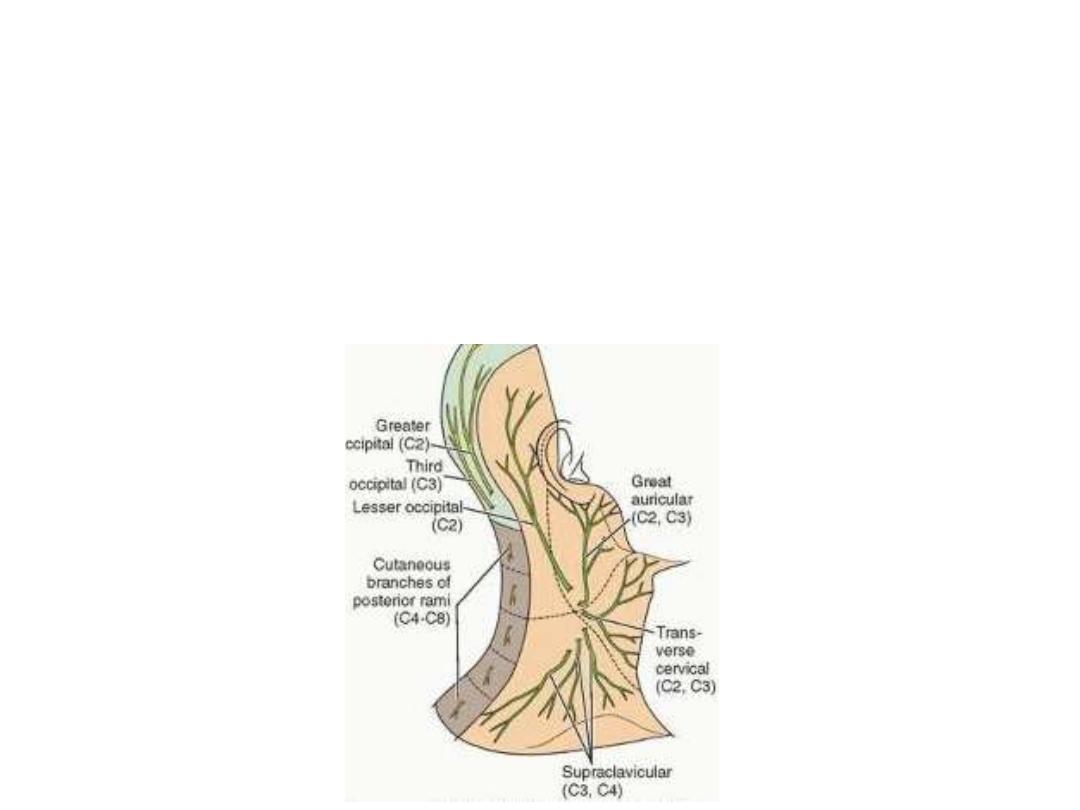
3- Nerves (cutaneous branches of cervical plexus):
Lesser occipital (C2):
-Along the posterior border of SCM
-Supplies skin & subcutaneous tissue at the insertion of the muscle
Great auricular (C2,3):
-Ascends in the direction of the auricle
-Supplies the auricle (except the upper
½ of lateral surface) & skin over the
angle of mandible
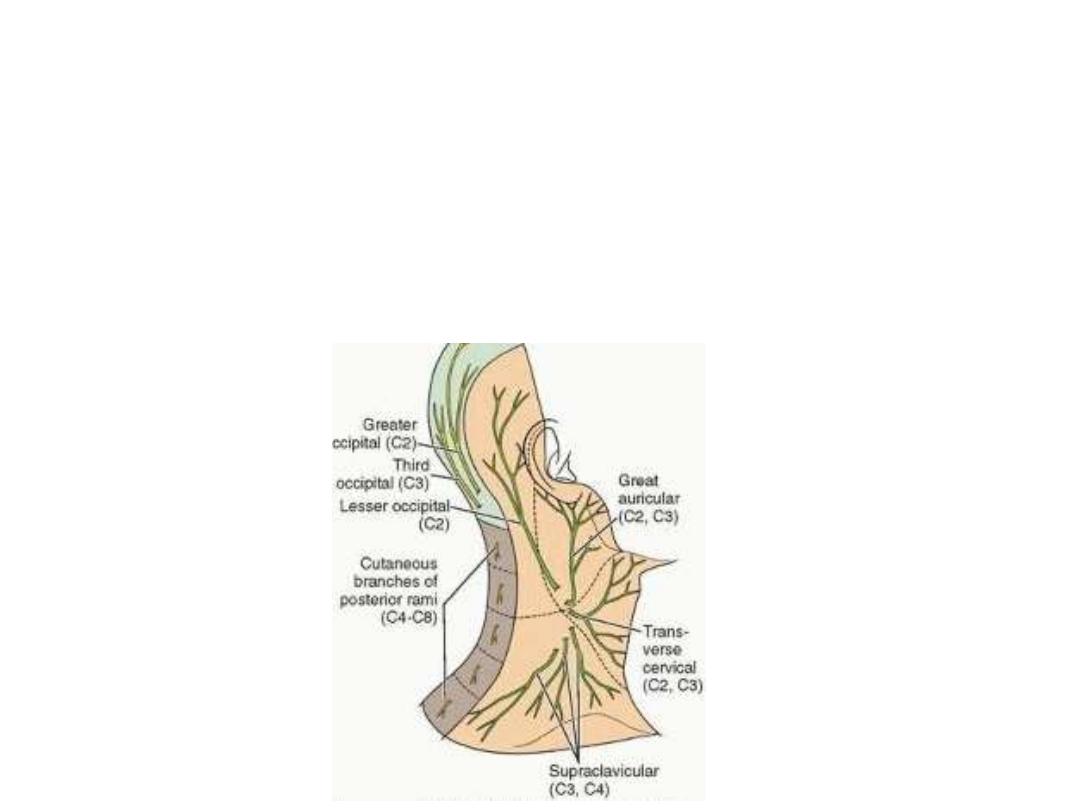
Anterior cervical cutaneous (C2,3):
-Crosses SCM horizontally forward
-Supplies skin & subcutaneous tissues of the cylinder of the neck
Supraclavicular (C4):
- Medial; skin over manubrium sterni
- Intermediate; skin over the pectoral region down to the sternal angle
- Lateral; skin over deltoid as far as the distal 1/2 of muscle
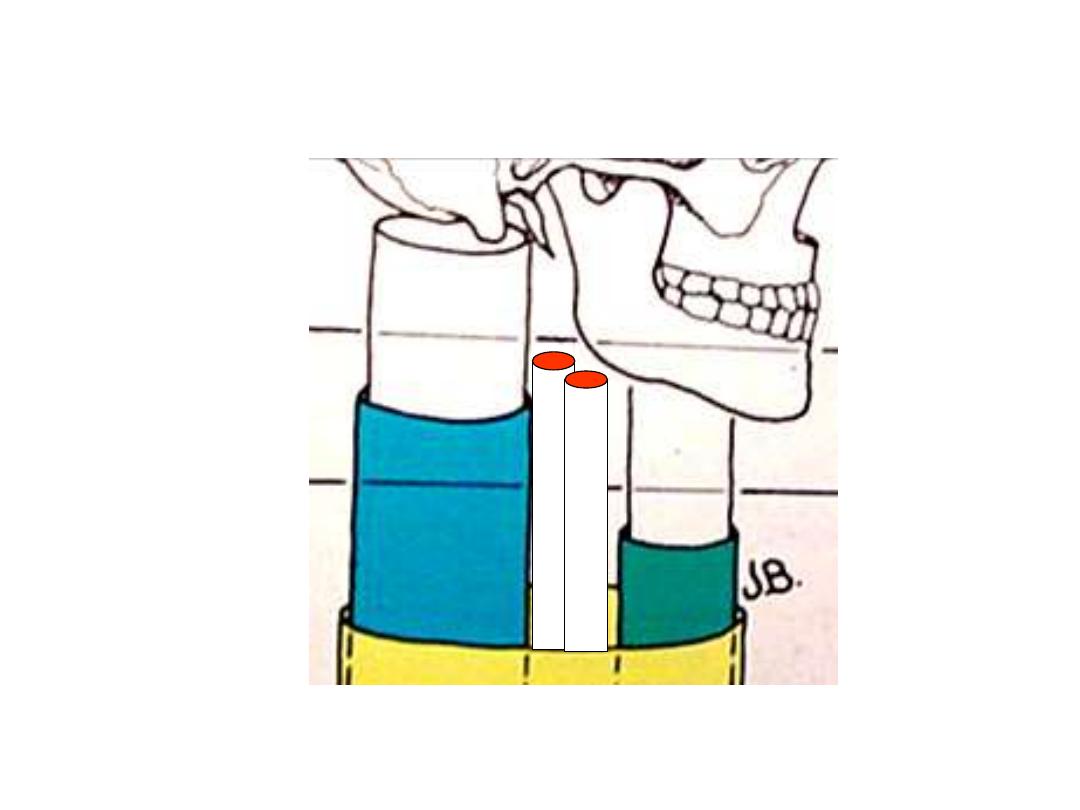
Deep fascia of the neck:
1- Investing
2- Prevertebral
3- Pretracheal
4- Carotid sheath

The investing fascia:
Double layered fascial cylinder
surrounding the neck
Attached
superiorly
to
the
superior nuchal line
– zygomatic
arch
– mandible
Attached inferiorly to the clavicle
& spine of scapula
Has hyoid bone attachment
Encloses two muscles on each
side (sternomastoid & trapezius)
Encloses 2 glands on each side
(parotid & submandibular)
It roofs all neck triangles
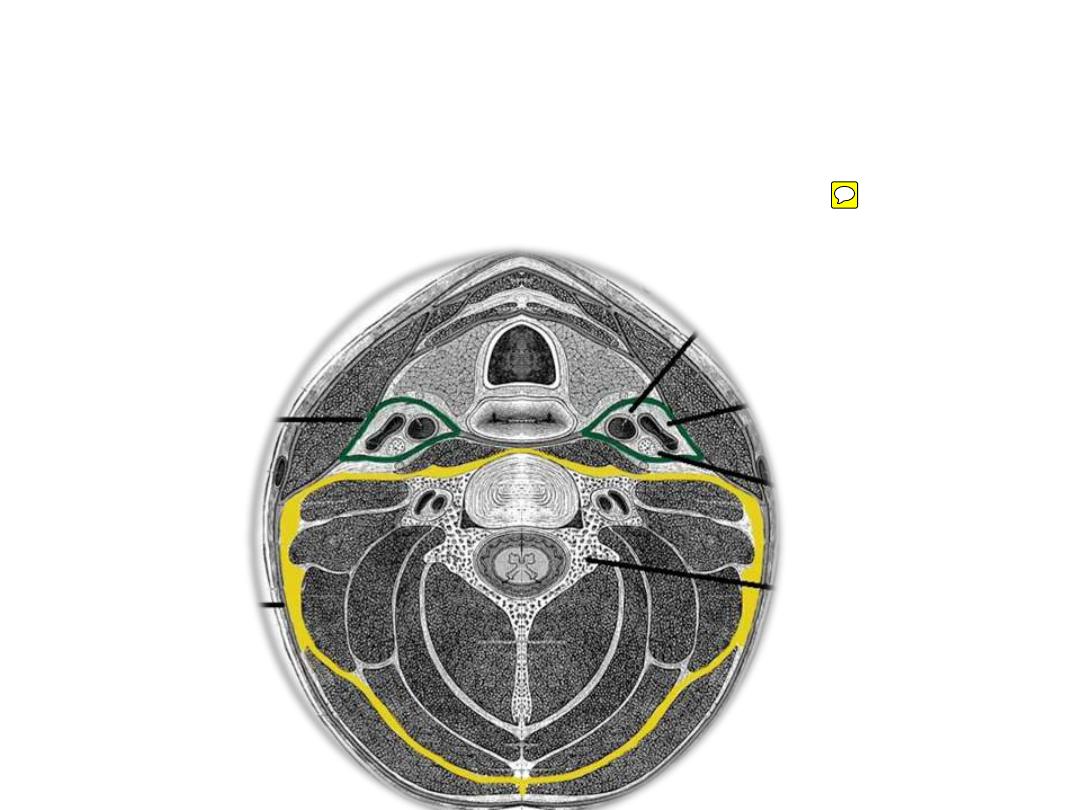
The prevertebral fascia:
Surrounds the vertebral column & surrounding muscles
Extends from skull base down to T4
Forms the floor of posterior cervical triangle
Forms the axillary sheath
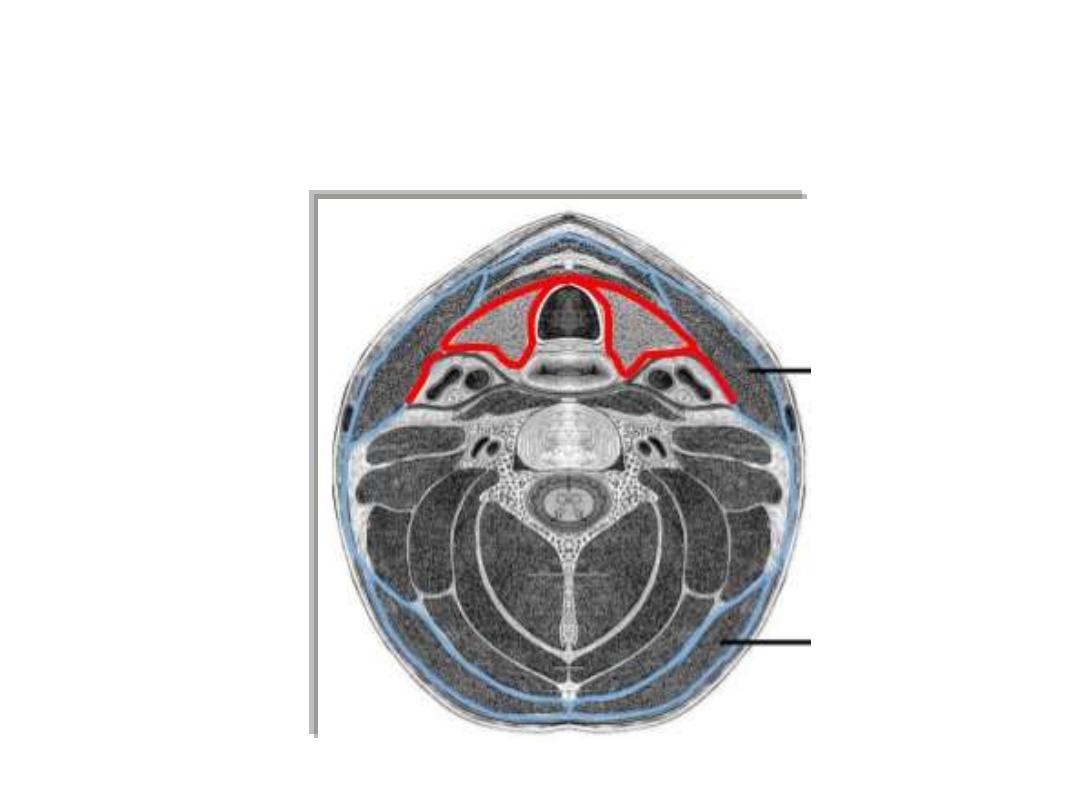
The pretracheal fascia:
Surrounds the thyroid gland
Attached to thyroid cartilage of larynx
Makes the thyroid moves up with swallowing
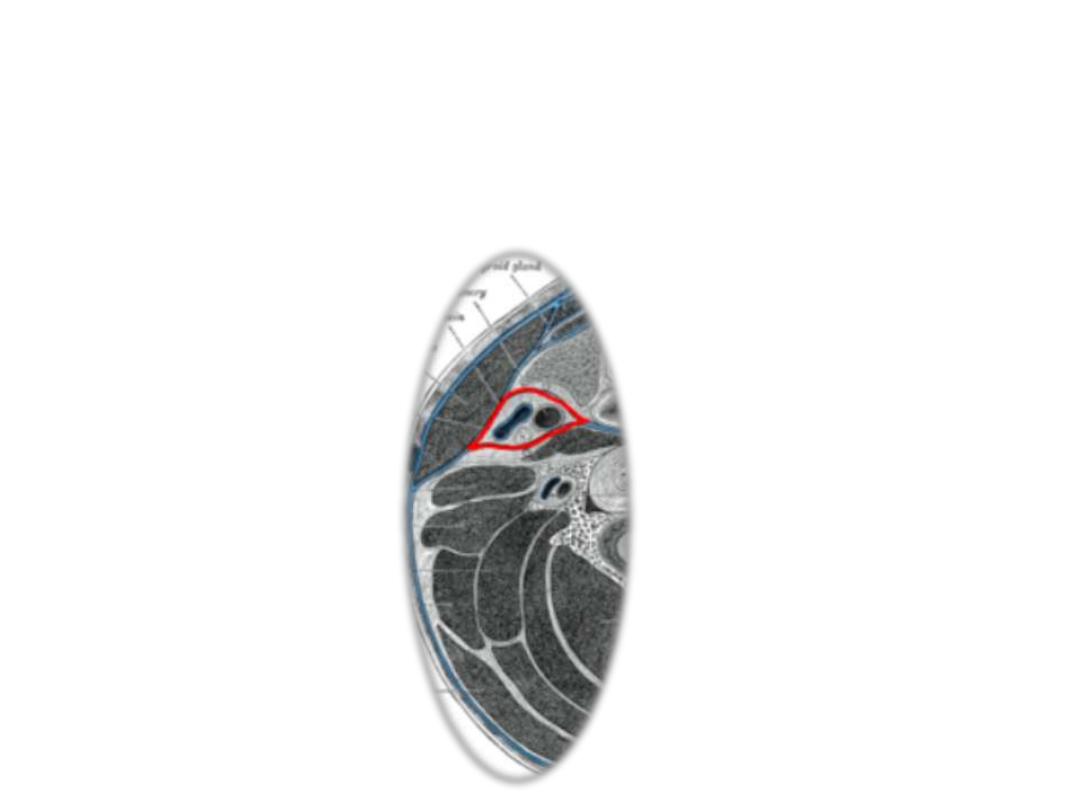

The carotid sheath:
Surrounds the carotid arteries, IJV & vagus nerve
Extends from skull base (margins of carotid canal) down to aortic arch
Fuses laterally with investing fascia
Fuses medially with pretracheal fascia

Tissue spaces of the neck:
Behind the prevertebral fascia (
perivertebral space
):
Reaches the lowest attachment of the fascia at T4
In front of the prevertebral fascia:
-
From the base of the skull down to the posterior mediastinum
-
Divided into
retropharyngeal & posterior cervical spaces
Anterior to the pretracheal fascia (
visceral space
):
Reaches down through the superior to the anterior mediastinum
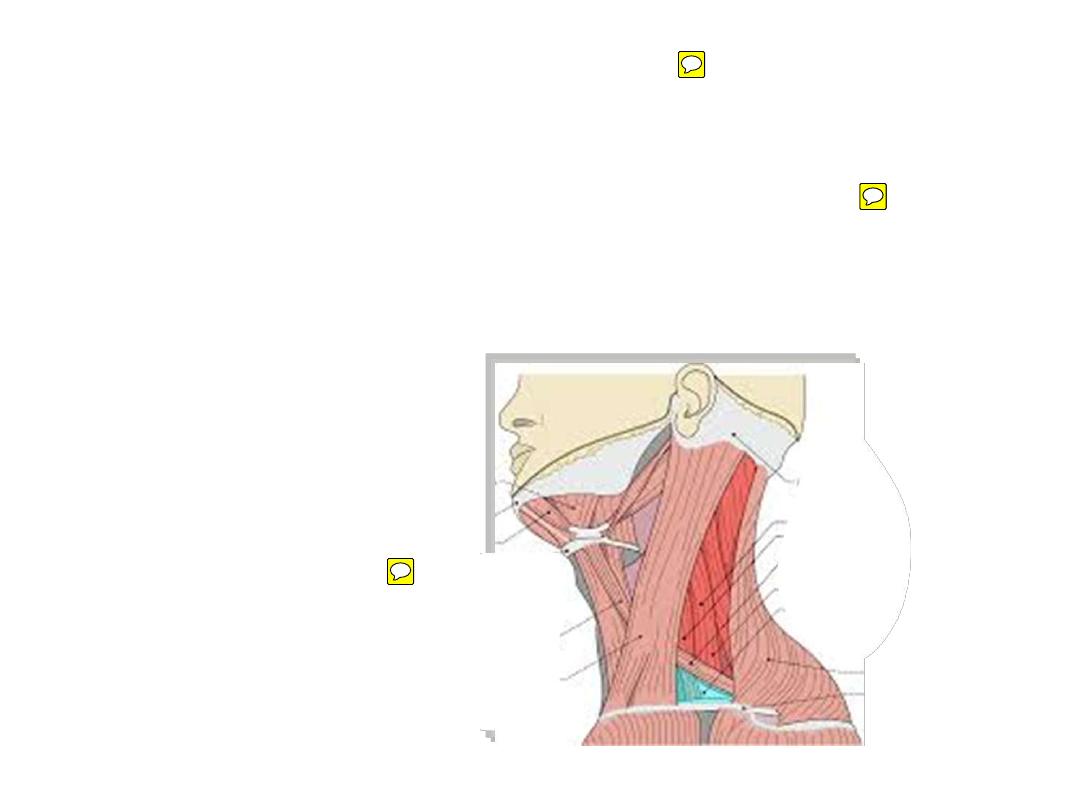
The posterior cervical triangle:
-
Apex lies in the back of the head just below the superior nuchal line
-
Base lies anteriorly (middle 1/3 of the clavicle)
-
Anterior border (posterior border of SCM)
-
Posterior border (anterior border of trapezius)
-
Roof (investing fascia)
-
Floor (prevertebral fascia)
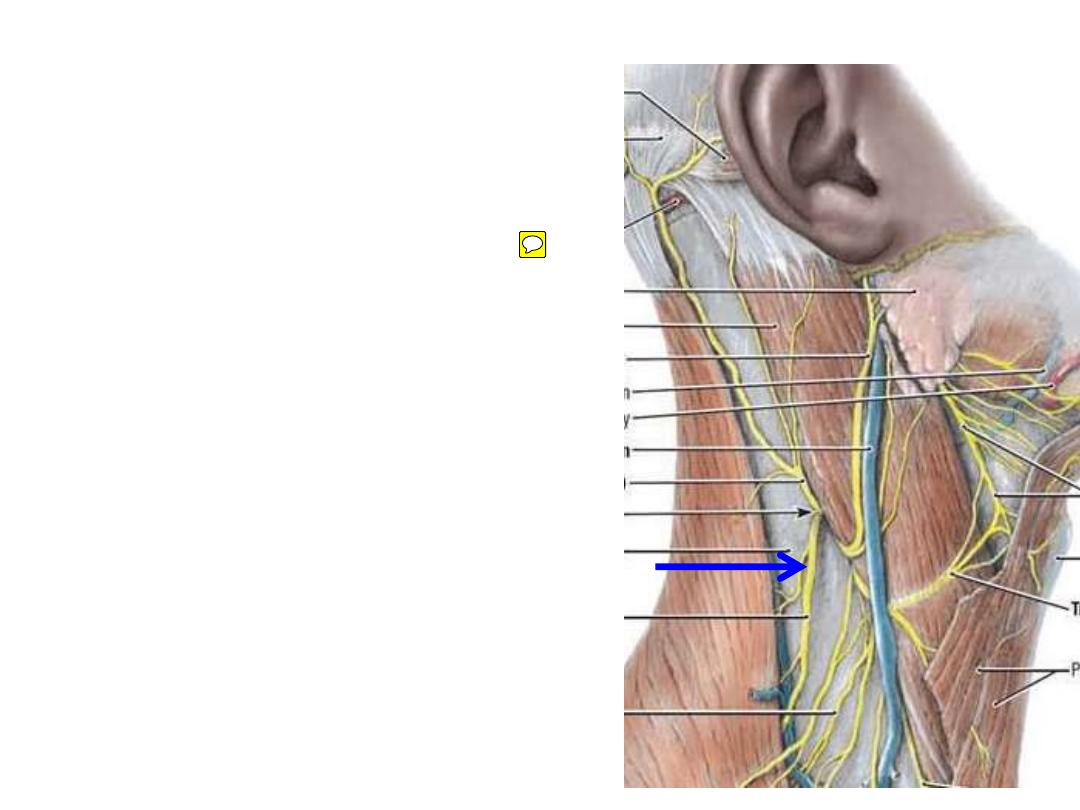
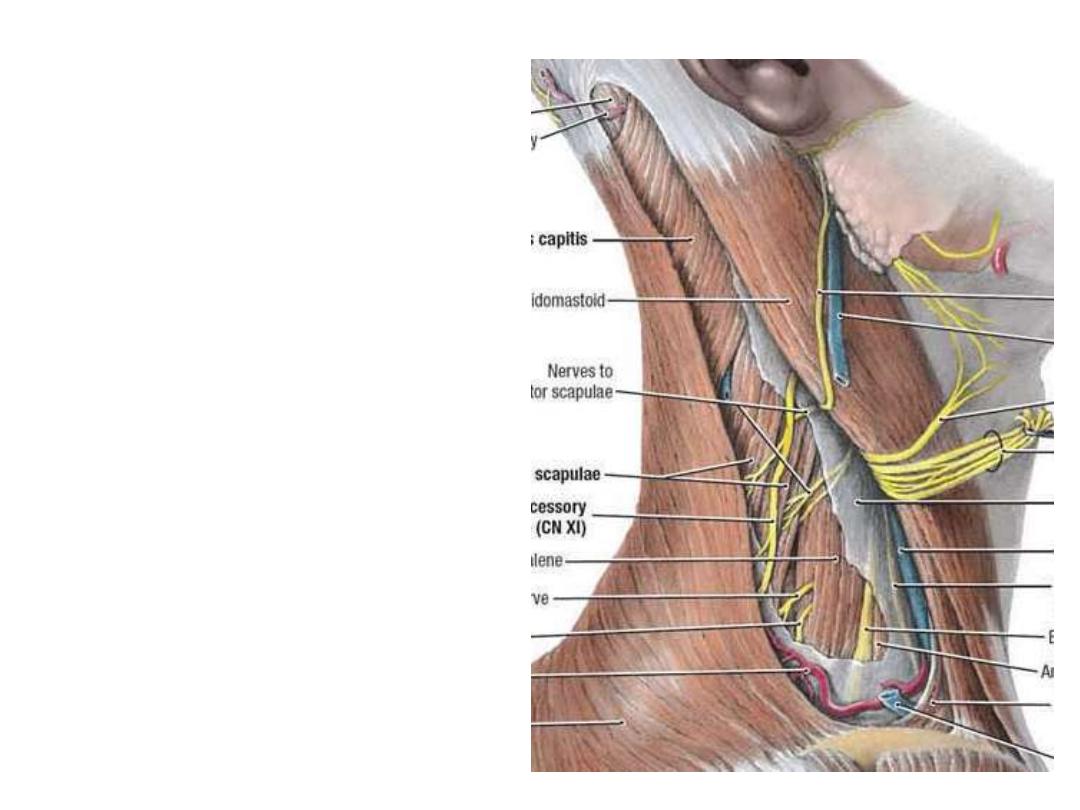
Spinal accessory nerve (CN XI):
-
Extends between SCM & trapezius
supplying them
-
Nearer to the roof (easily injured)
-
Its injury due to penetrating
trauma
or
surgery
results in
torticollis (wry neck)
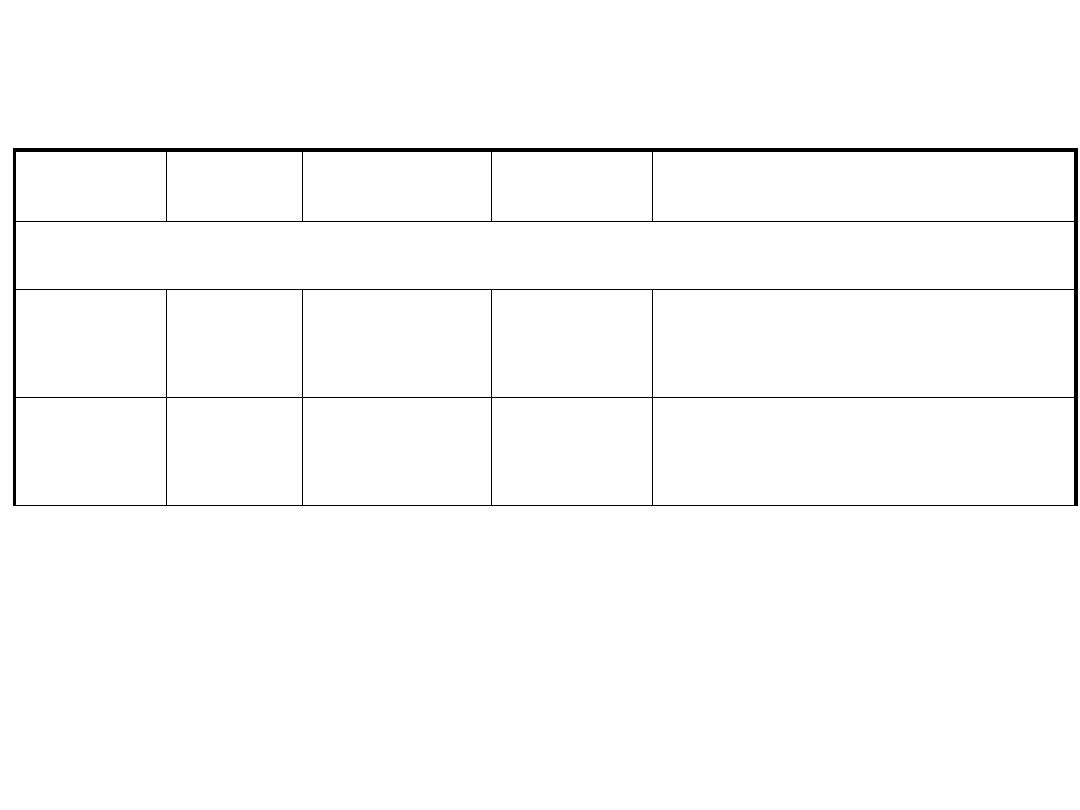
Distribution
Position
Nucleus
Modality
Nerve
Accessory (XI)
Join X nerve & distributed to
pharyngeal & laryngeal
muscles
Medulla
N ambiguus
SVE
Cranial
Motor to trapezius & SCM
Spinal
cord
Anterior
horn cells
C1-4
GSE
Spinal
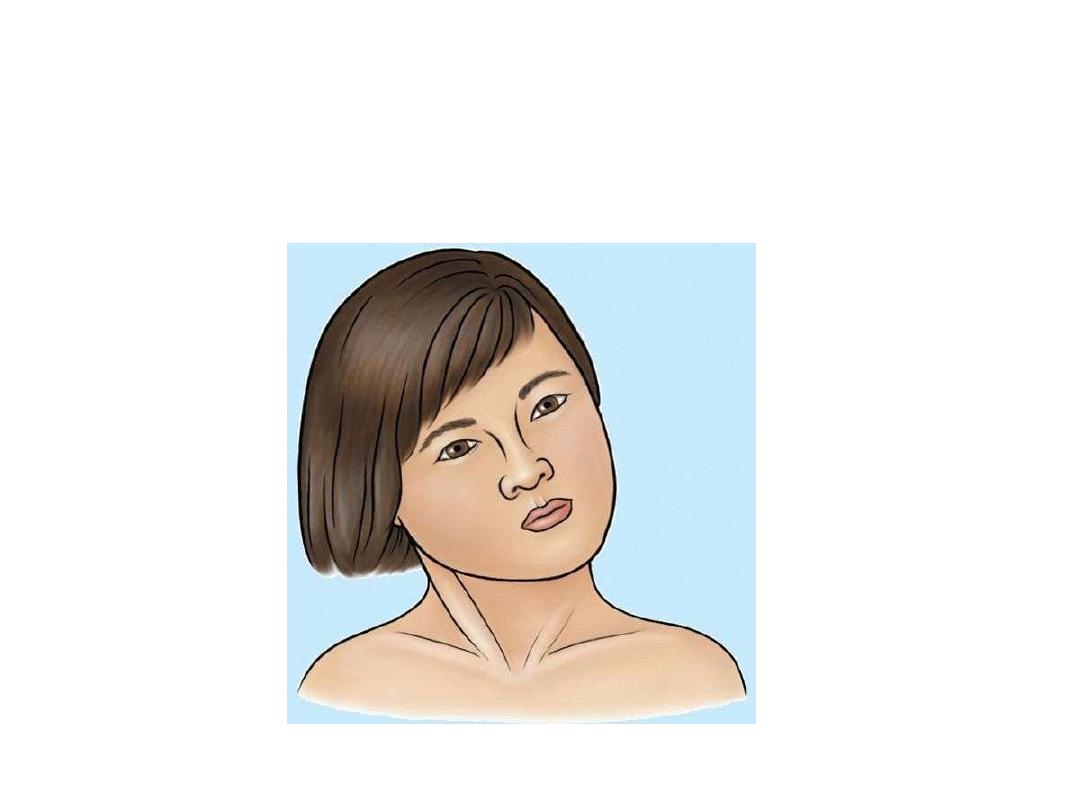
Wry neck (torticollis)
Un-apposed unilateral spasm of trapezius & sternomastoid
resulting in turning of the face to the .?. side
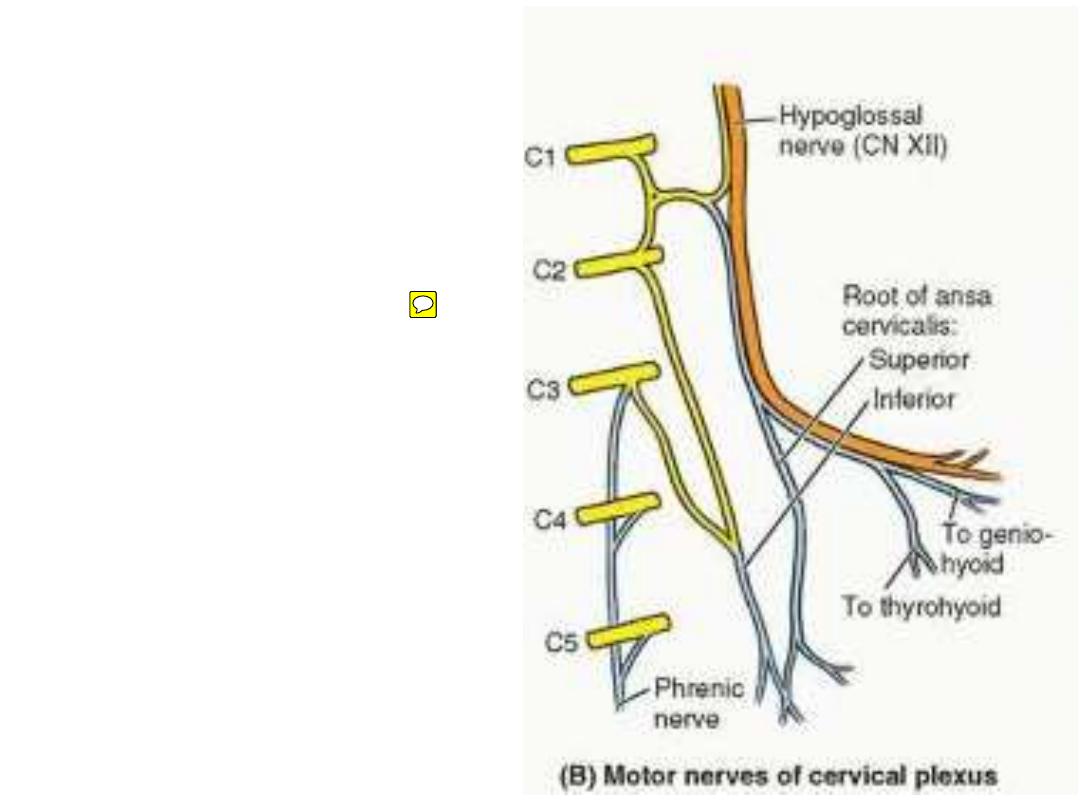
Motor branches of cervical plexus:
1-
C1
fibers
distributed
by
hypoglossal nerve as:
1- Meningeal branch
2- Superior ramus of ansa C.
3- Nerve to thyrohyoid
4- Nerve to geniohyoid
2- Inferior root of ansa cervicalis
(C2,3).
3- Phrenic nerve C4).
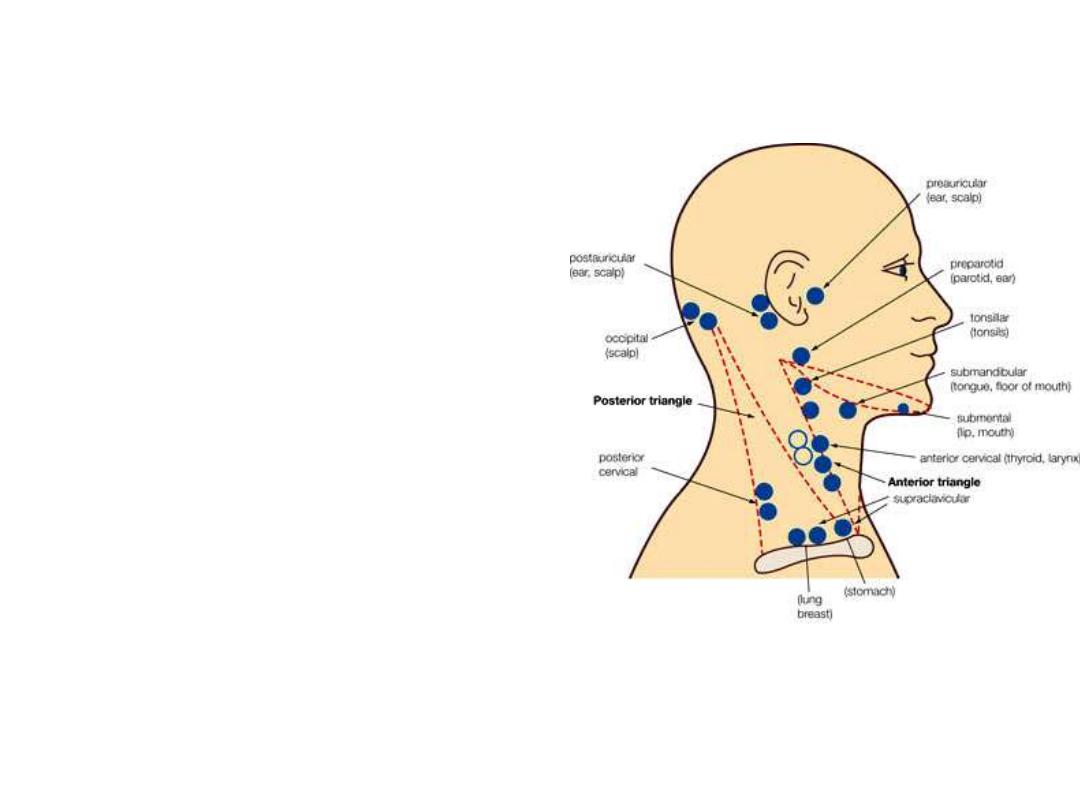
Lymph nodes:
1- Occipital:
-Along the occipital artery
-In the apex of triangle
2- Supraclavicular:
-Along
transverse
cervical
&
suprascapular arteries
-In the base of the triangle
-They represent a group of deep
cervical nodes
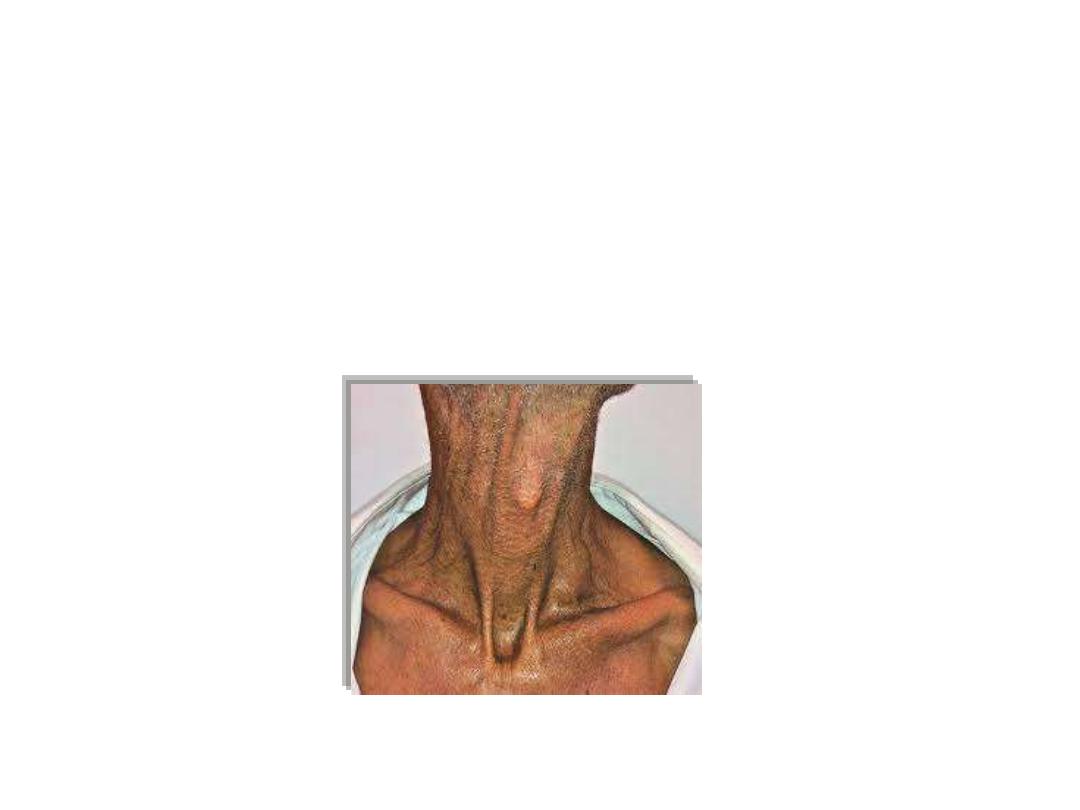
Supraclavicular lymphadenopathy
Right
Mainly thoracic disease
Left
Mainly abdominal disease
(Virchow’s node)
Troisier sign
Enlargement of Virchow’s node secondary to abdominal malignancy
LS
Sp
SP
SM
Muscles in the floor:
Removing the fascial carpet of
the floor of the triangle will
expose the following muscles:
Splenius
Levator scapulae
Scalenus posterior
Scalenus medius
Scalenus anterior
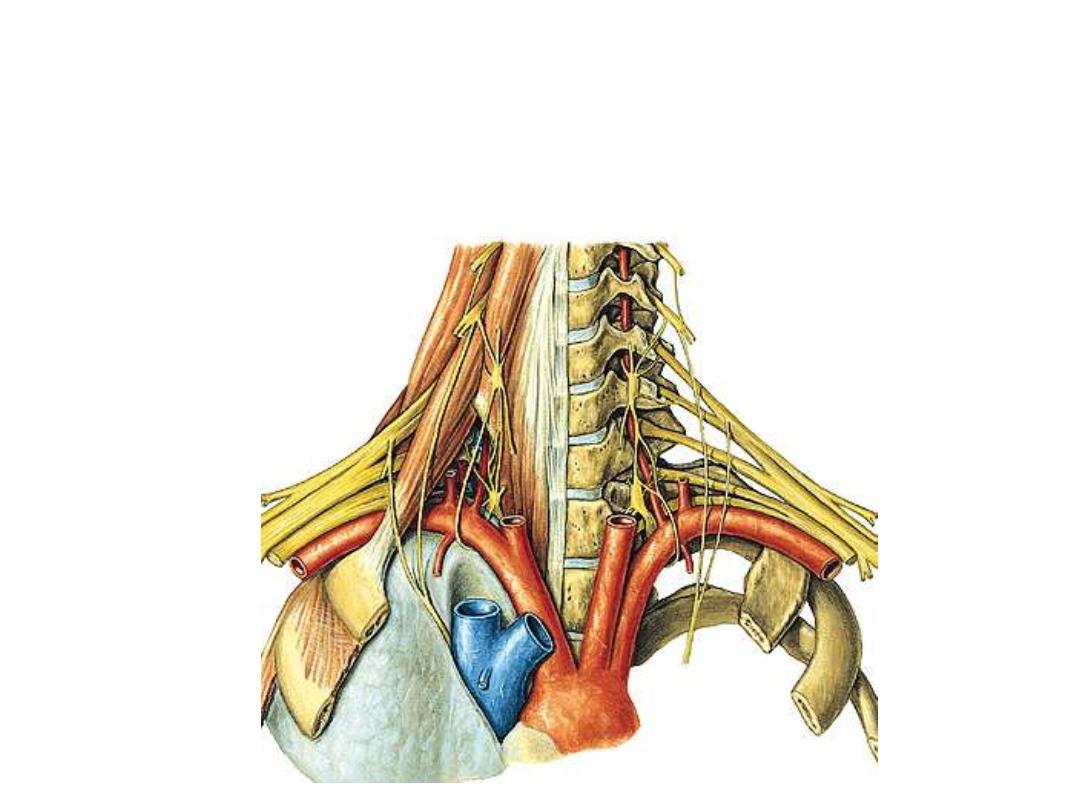
Vital structures are emraced between scalenus anterior & medius:
1- The roots of brachial plexus
2- The subclavian artery
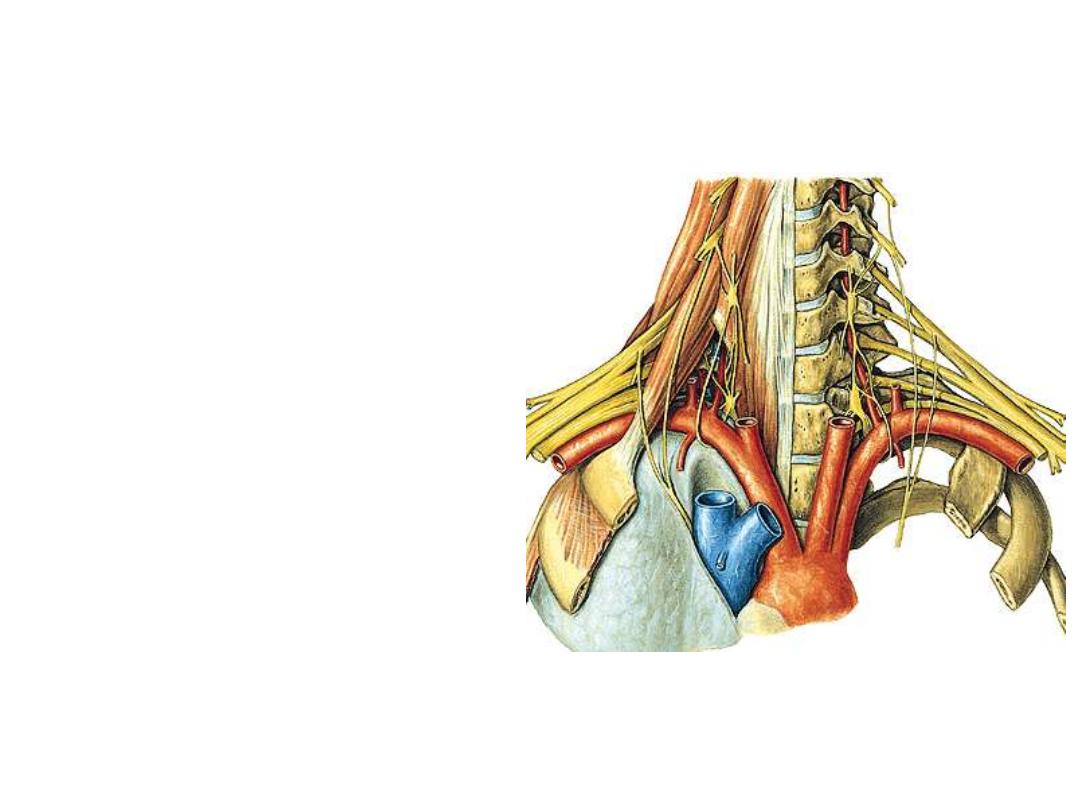
Subclavian artery:
Arises from the brachiocephalic
trunk on the right & from aortic arch
on the left side
Passes behind scalenus anterior
which divides it into three parts
Continues beyond the outer border
of the first rib as the axillary artery
surrounded by fascial sheath
Branches:
First part:
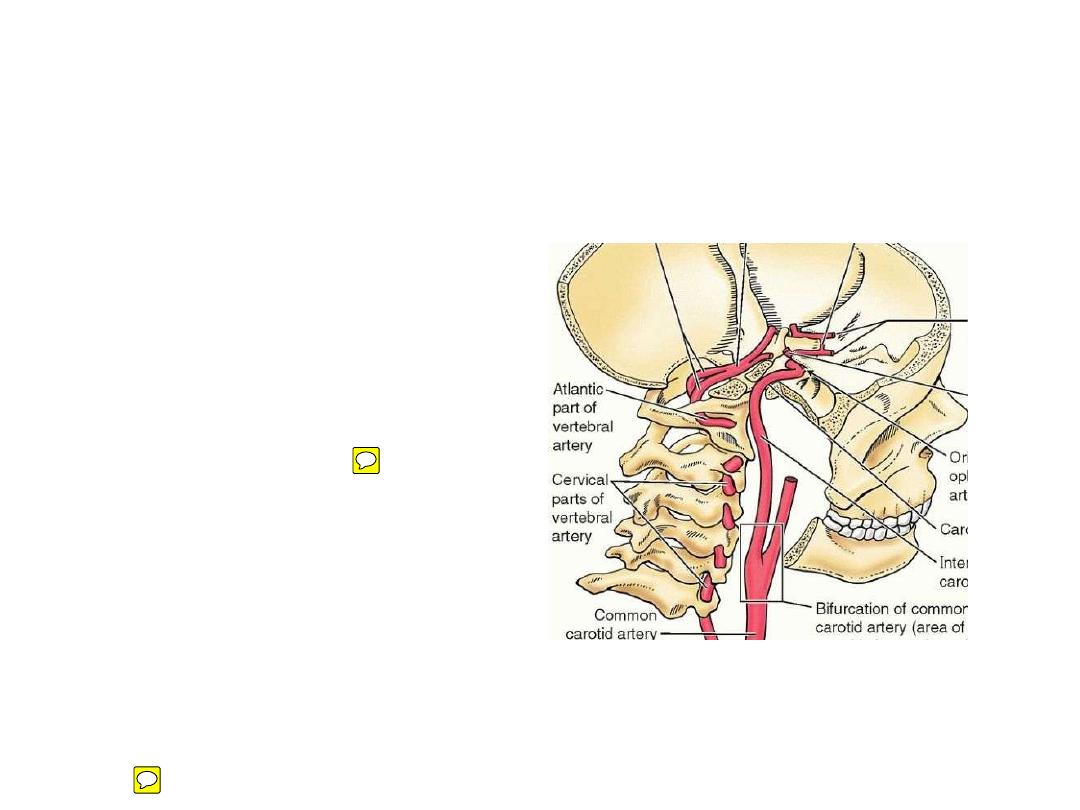
1- Vertebral artery:
- Ascends in F transversaria of C6-C1
Supplies the neck muscles, spinal
cord & hinbrain
2- Internal thoracic artery:
-Descends to the chest wall
-Supplies the anterior chest wall,
pericardium & breast
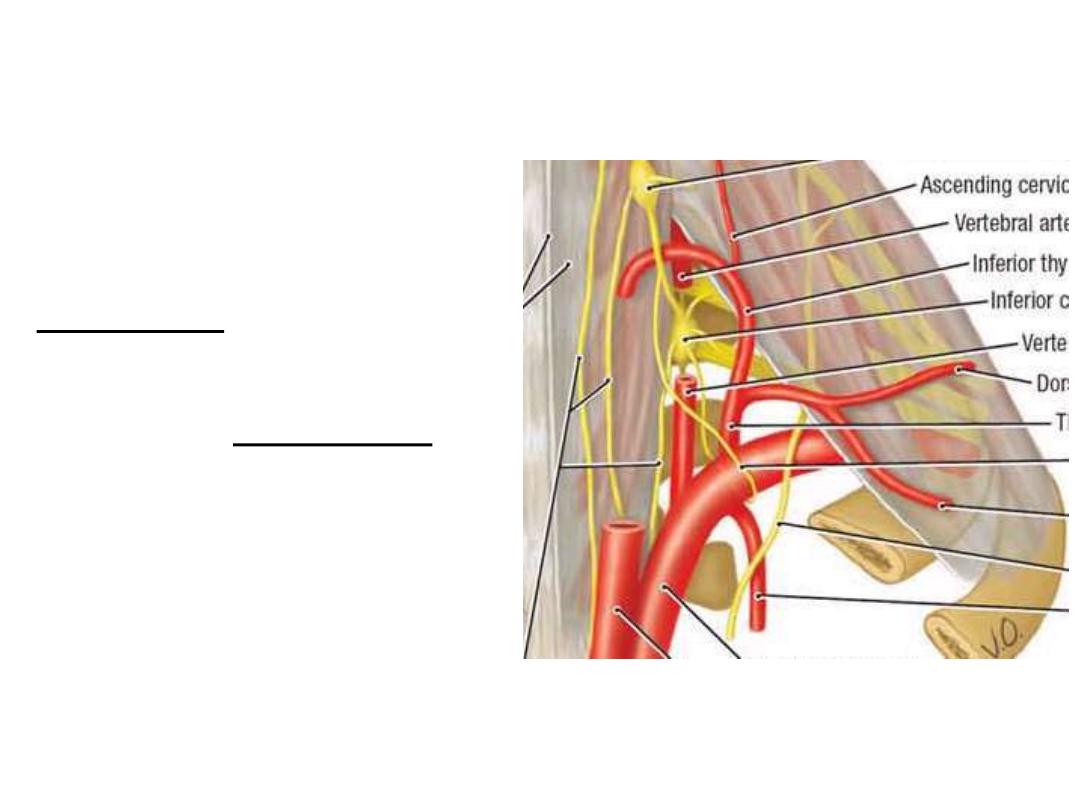
3- Thyrocervical artery:
Form arched trunk which gives:
-Ascending cervical; ascends on
scalenus anterior
-Suprascapular; to scapular region
-Transverse cervical; divides into
deep cervical & dorsal scapular
-Inferior thyroid; enters the gland
Second part:
Costocervical trunk:
-Gives the deep cervical & superior
intercostal branches
