
Overview of H&N Anatomy
The Skull 1

To describe the H&N in terms of
regions, structures & relations to each
other & other regions
To define the structure of the skull
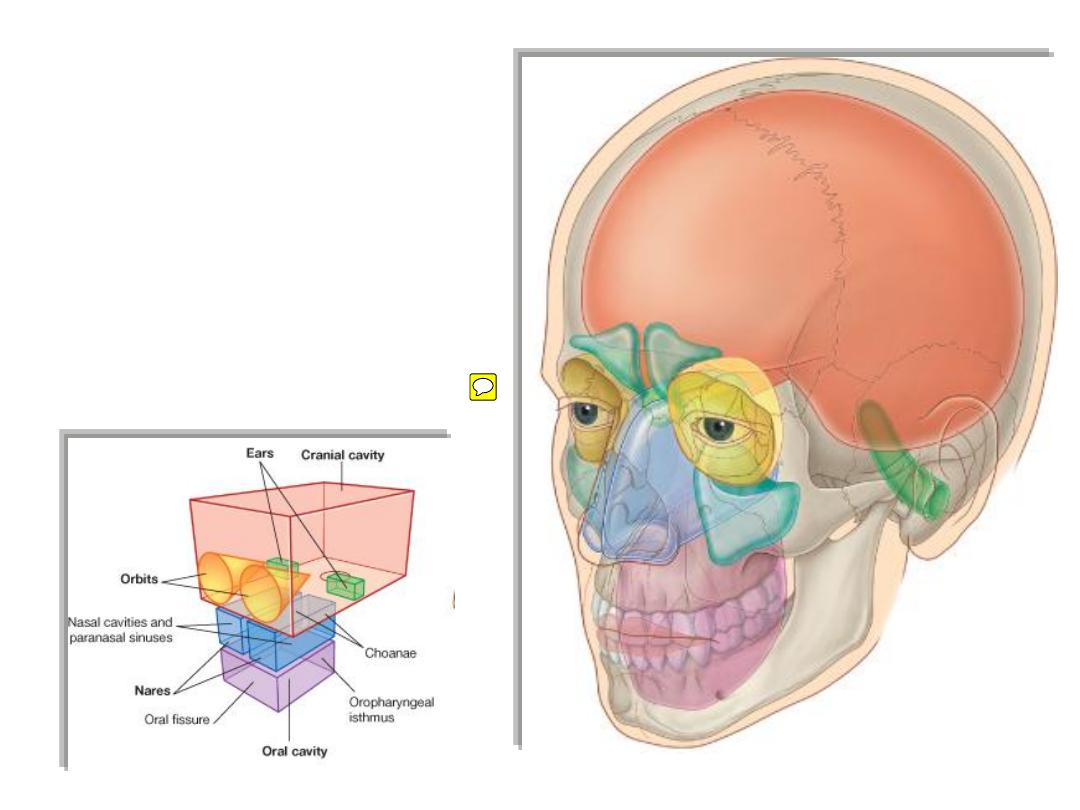
The head
is composed of a series of
compartments, which are formed by
bone and soft tissues, they are:
Cranial cavity
• Ears
• Orbits
• Nasal cavities
• Oral cavity
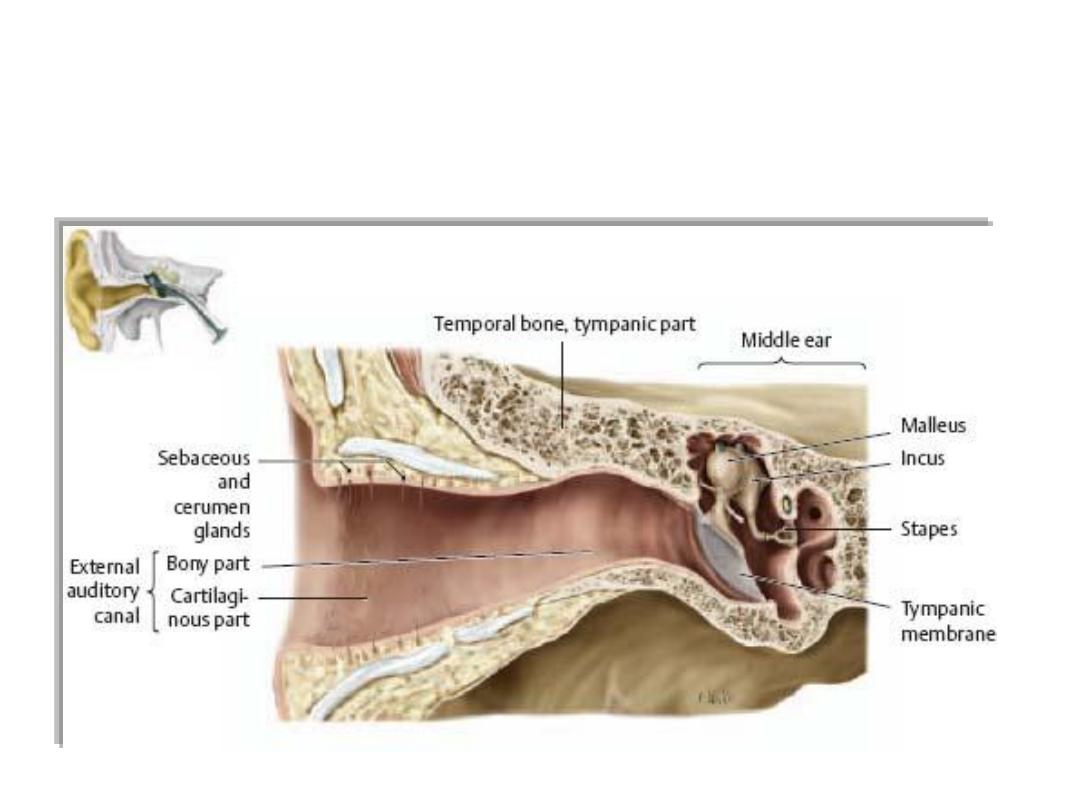
• Most of the ear apparatus on each side is contained within one of the
bones forming the floor of the cranial cavity.
• The external parts of the ears extend laterally from these regions.
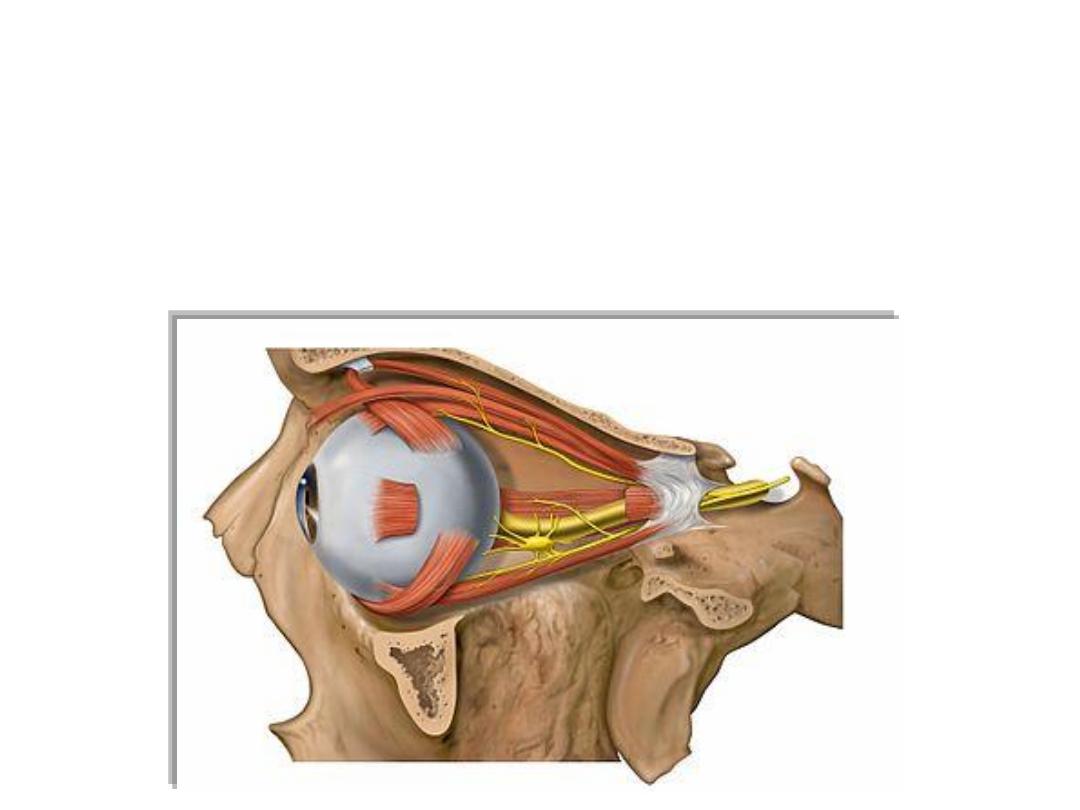
• The two orbits contain the eyes. They are cone-shaped chambers
immediately inferior to the anterior aspect of the cranial cavity, and the
apex of each cone is directed posteromedially.
• The walls of the orbits are bone whereas the base of each conical
chamber can be opened and closed by the eyelids.
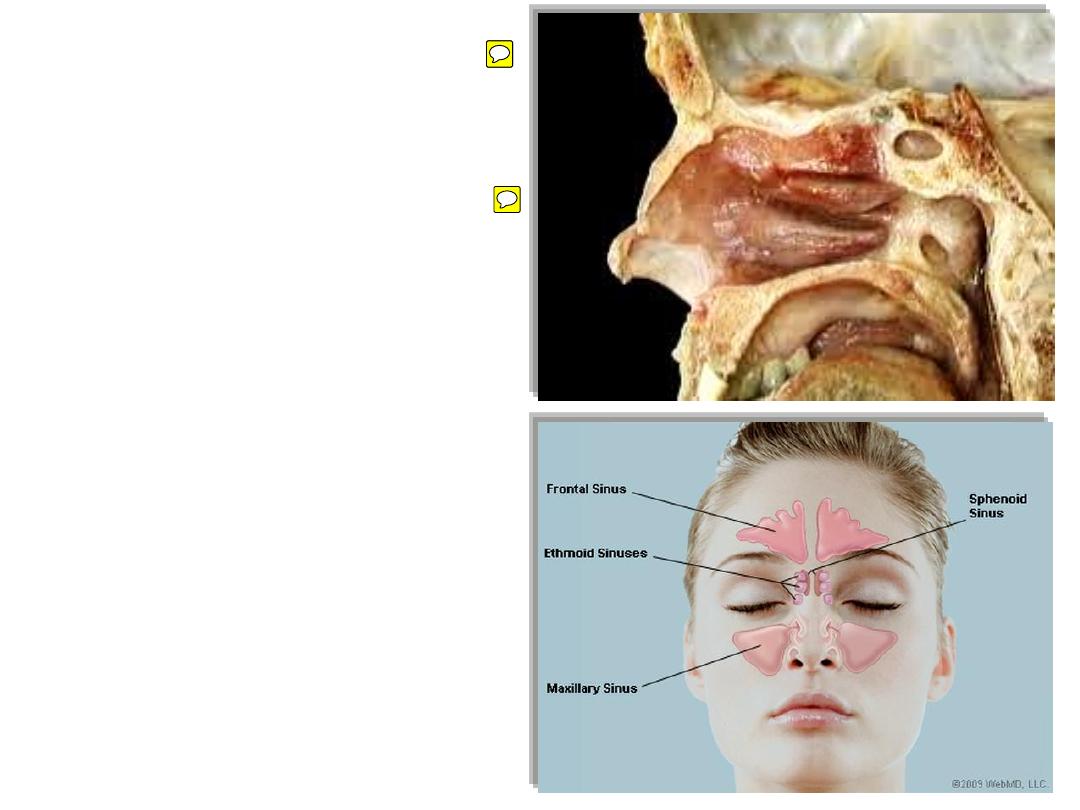
• The nasal cavities are the upper
parts of the respiratory tract and
are between the orbits.
• They have walls, floors, and
ceilings, which are predominantly
composed of bone and cartilage.
• The anterior openings to the nasal
cavities are nares (nostrils), and the
posterior openings are choanae
(posterior nasal apertures).
• Continuous with the nasal cavities
are air-filled extensions (paranasal
sinuses), which project laterally,
superiorly, and posteriorly into
surrounding bones.
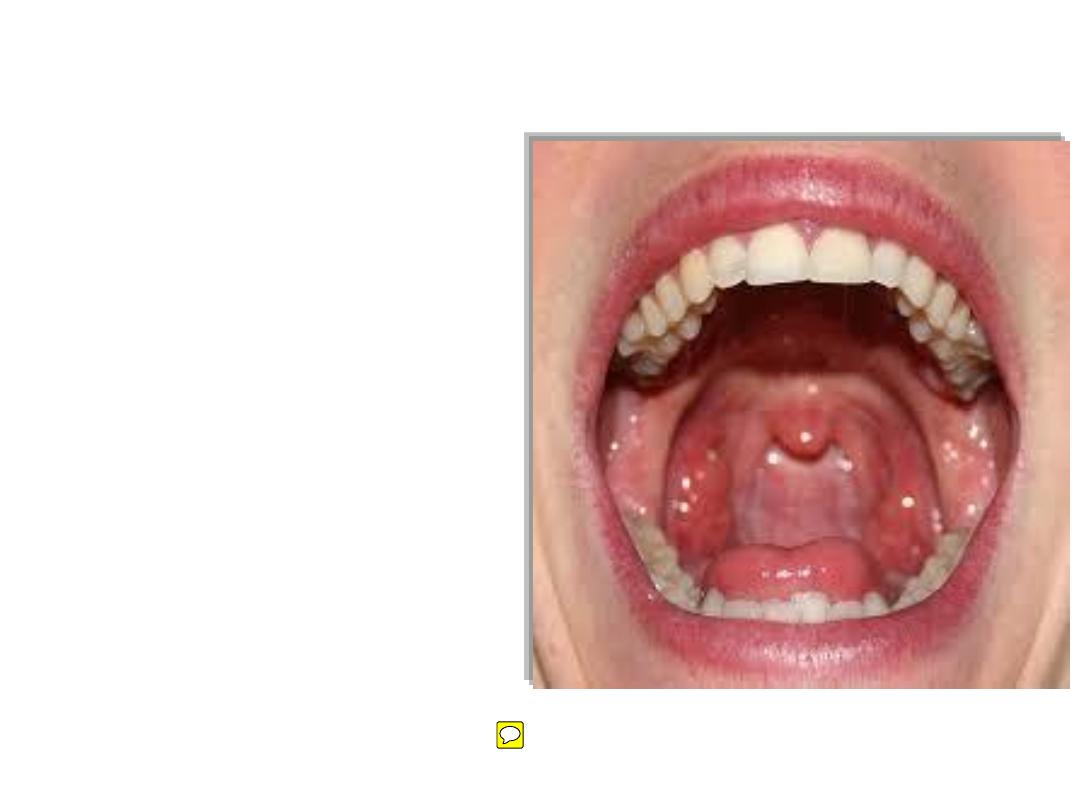
• The oral cavity is inferior to the
nasal cavities, and separated from
them by the palate.
• The floor of the oral cavity is
formed entirely of soft tissues.
• The anterior opening to the oral
cavity is the oral fissure (mouth),
and the posterior opening is the
oropharyngeal isthmus.
• Unlike the nares and choanae,
which are continuously open, both
the oral fissure and oropharyngeal
isthmus can be opened and closed
by surrounding soft tissues.
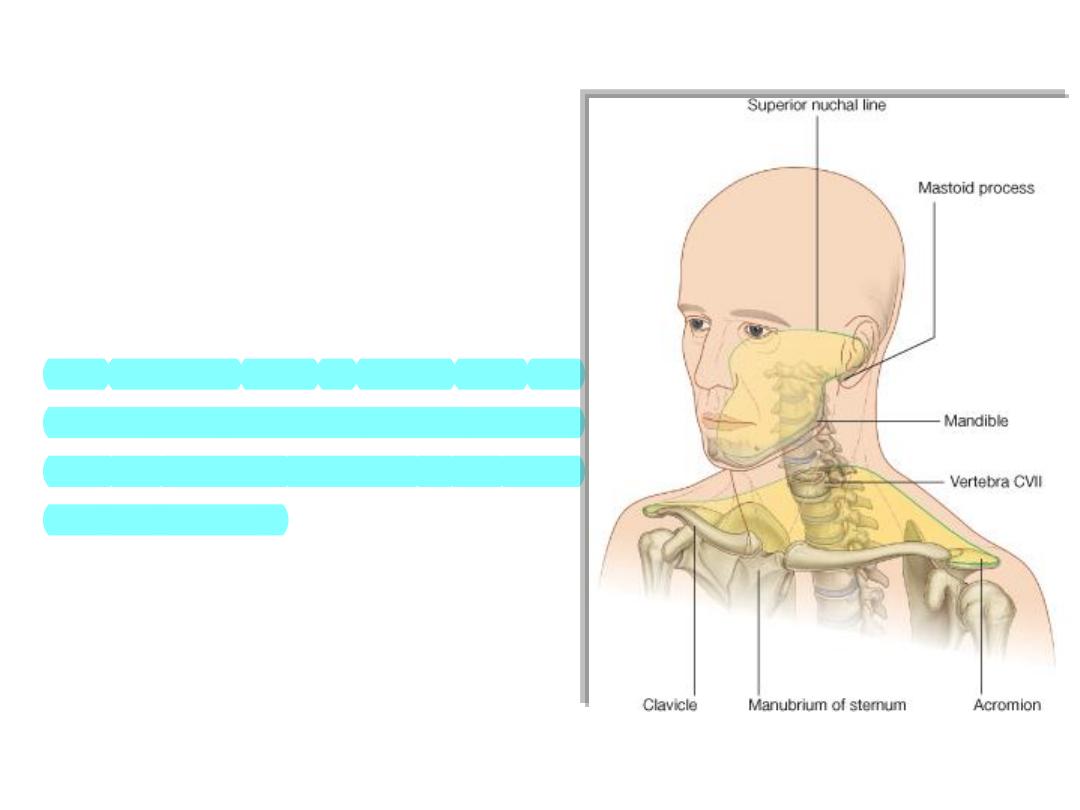
• The neck
extends from the head above
to the shoulders and thorax below Its
superior boundary is along the inferior
margins of the mandible and bone
features on the posterior aspect of the
skull.
• The posterior neck is higher than the
anterior neck to connect cervical viscera
with the posterior openings of the nasal
and oral cavities.
• The inferior boundary of the neck
extends from the top of the sternum,
along the clavicle, and onto the adjacent
acromion, a bony projection of the
scapula..
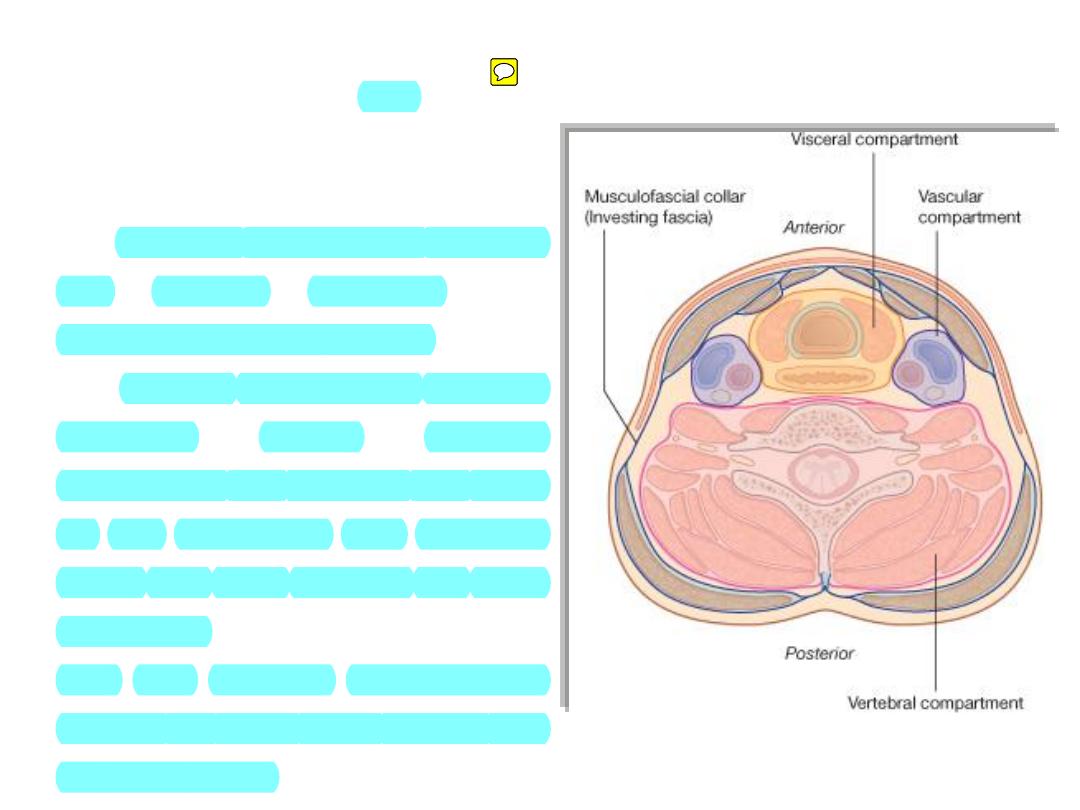
Compartments:
• The
neck
has
four
major
compartments which are enclosed
by an outer musculofascial collar
• The vertebral compartment contains
the
cervical
vertebrae
and
associated postural muscles
• The visceral compartment contains
important
glands
(thyroid,
parathyroid, and thymus), and parts
of the respiratory and digestive
tracts that pass between the head
and thorax
• The two vascular compartments
contain the major blood vessels and
the vagus nerve.
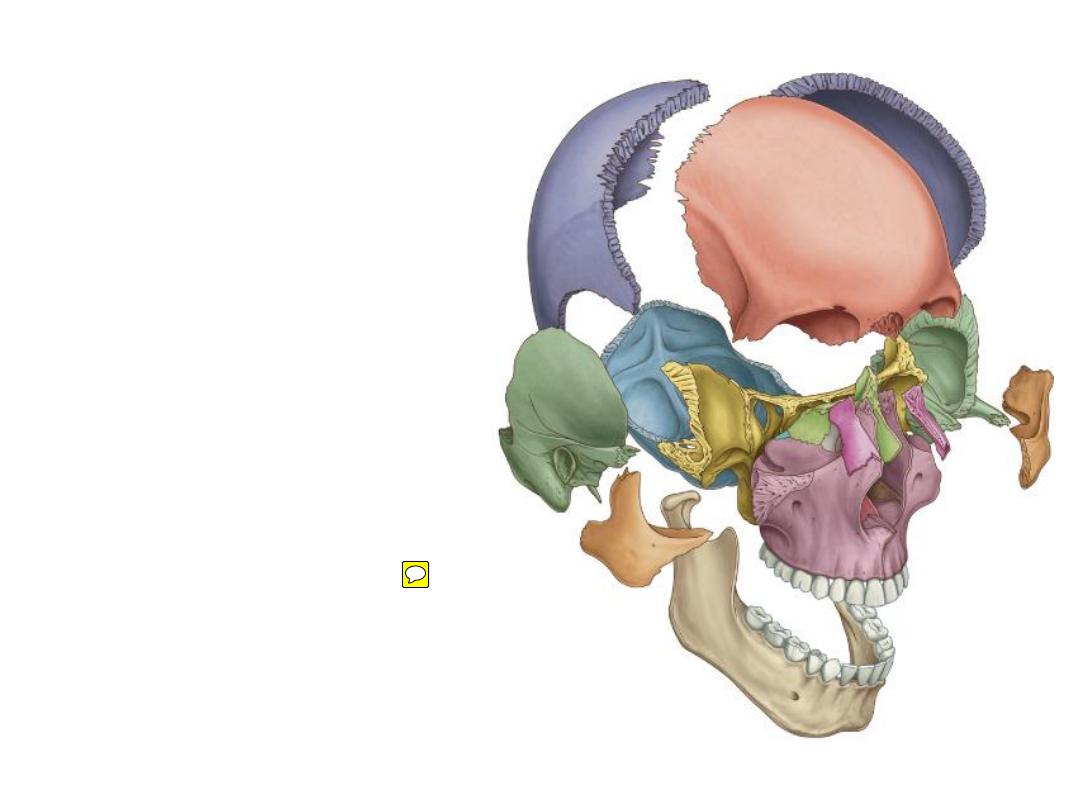
Skull = 22 bones
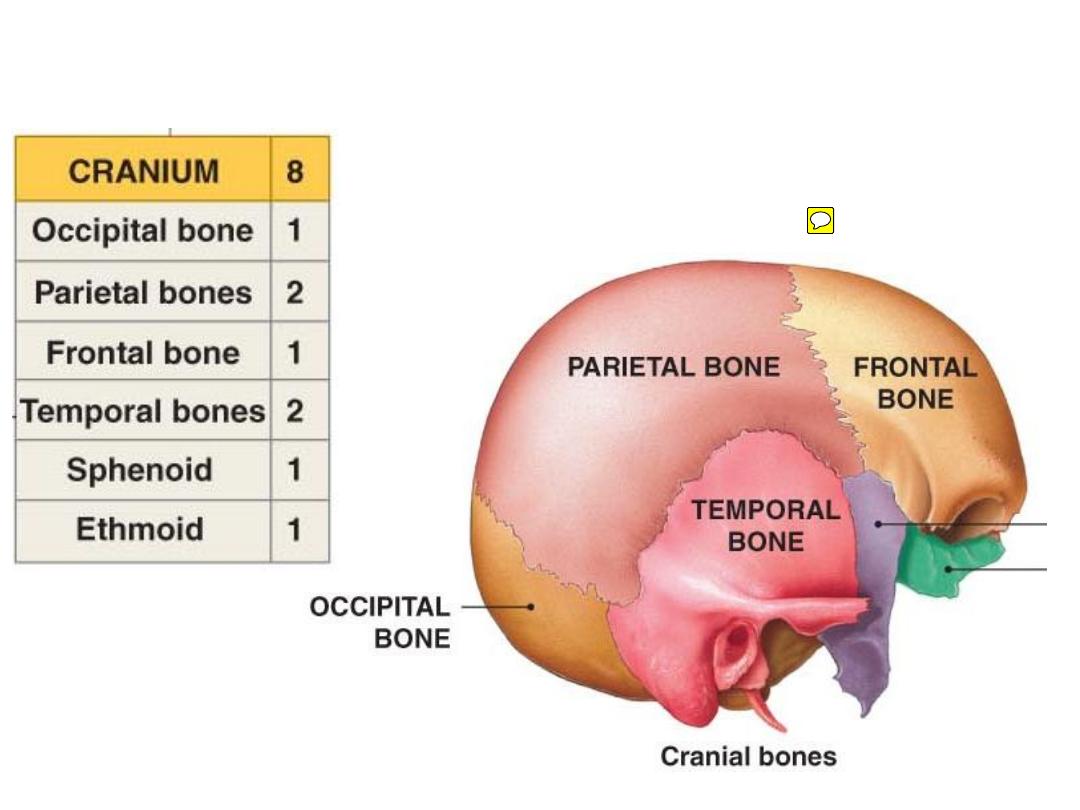
The
neurocranium
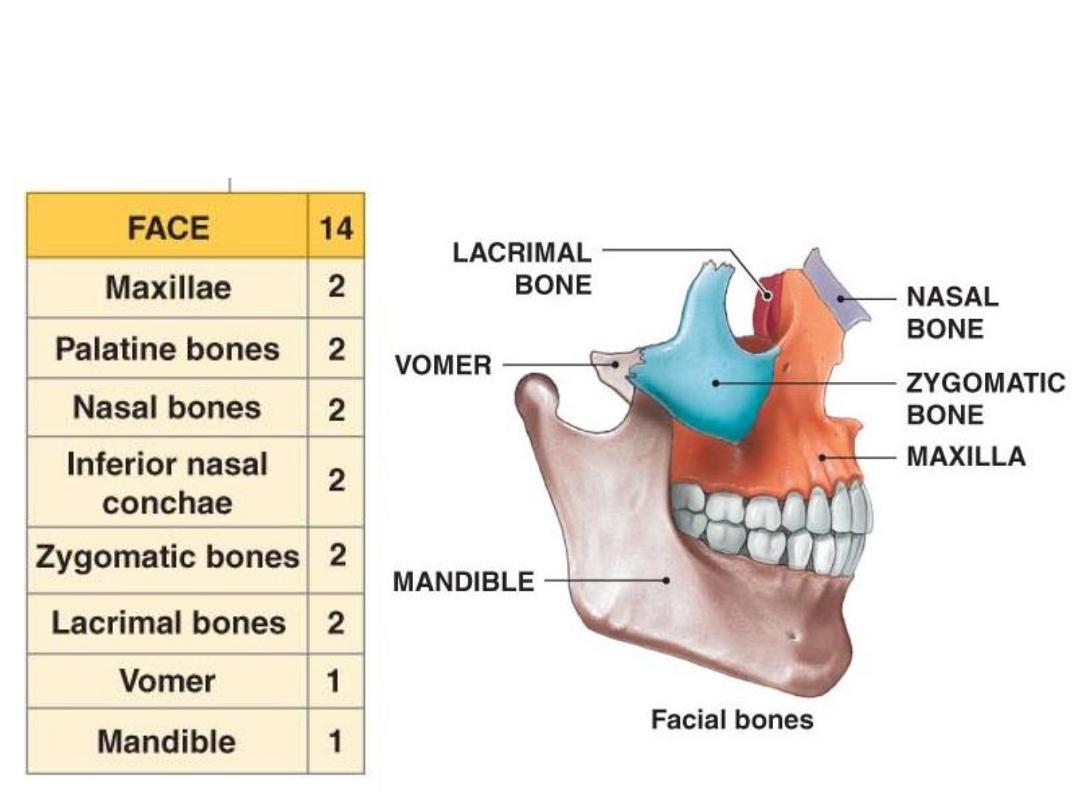
The
viscerocranium
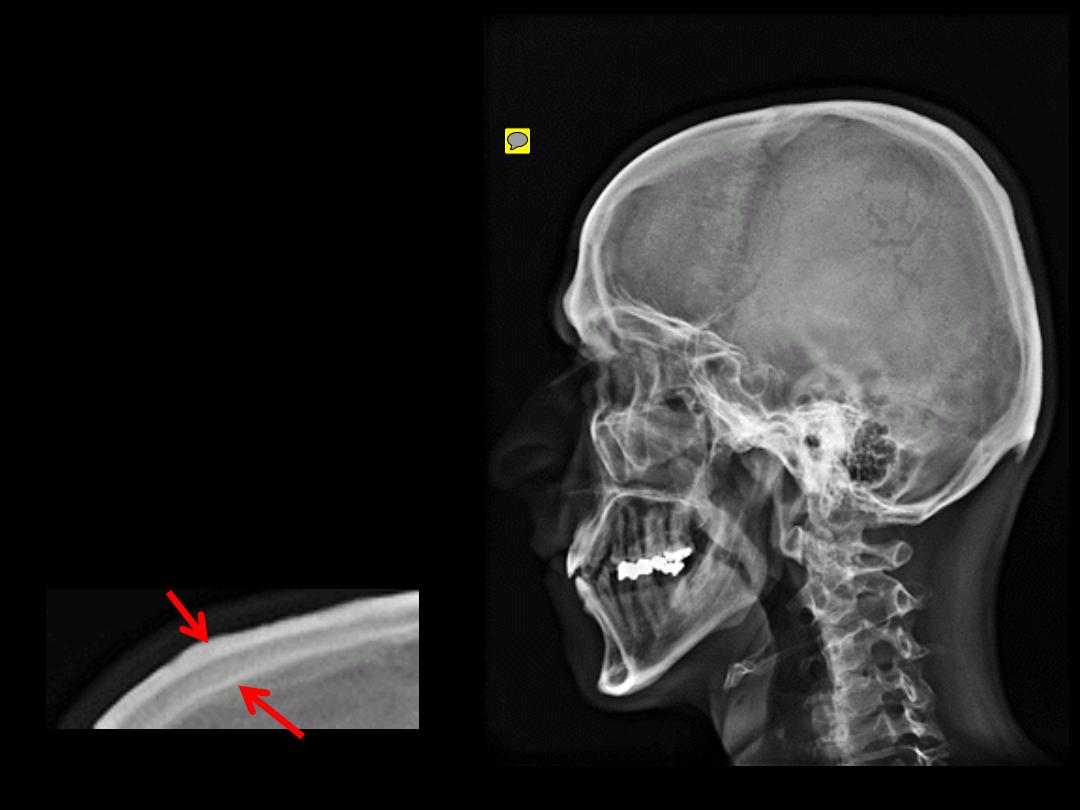
Most cranial bones are
diploic
Most facial bones are
spongy
Diploic
= 2 compact bone
with a spongy one in
between
Lamina externa
Lamina interna
The skull contains multiple
cavities to accommodate
certain vital structures
Relations between these
areas are of extreme
importance
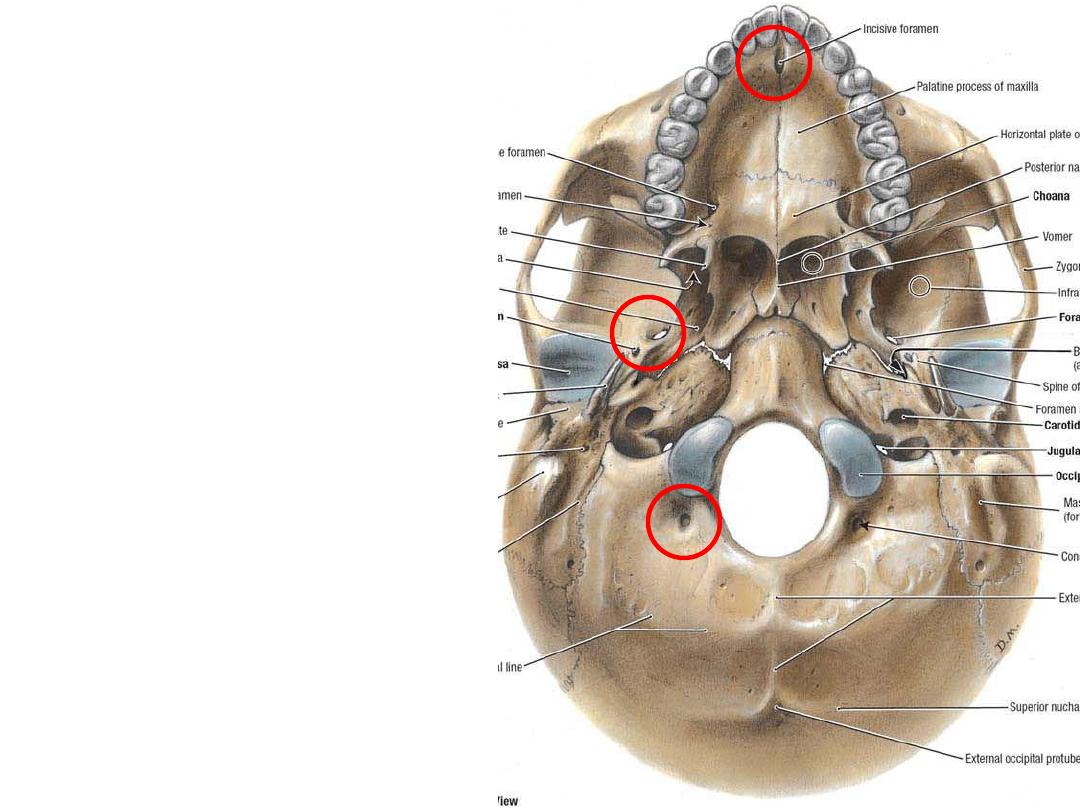
Many foramina are
present in the skull to
provide passage for
vessels & nerves
Processes,
prominences, lines …
are mainly for soft
tissue attachments
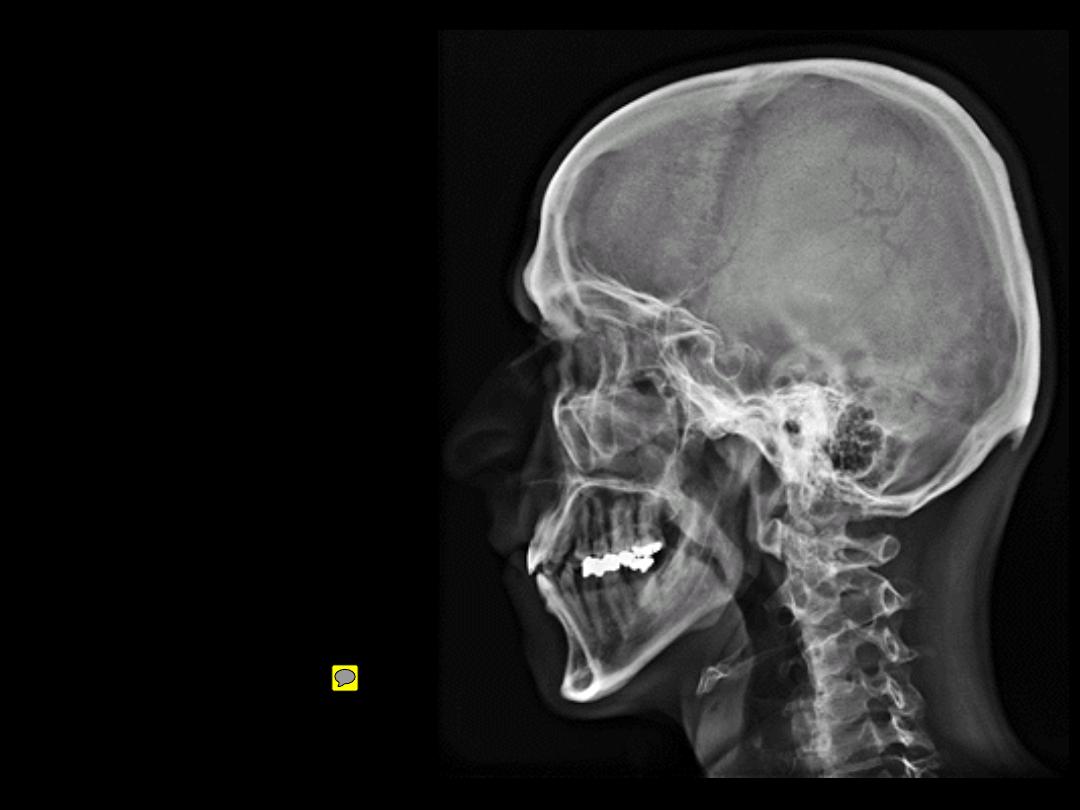
There are 2 mobile joints
for the skull:
1- The atlanto-occipital
joint; with C1 vertebra.
2- The TM joint; with the
mandible.
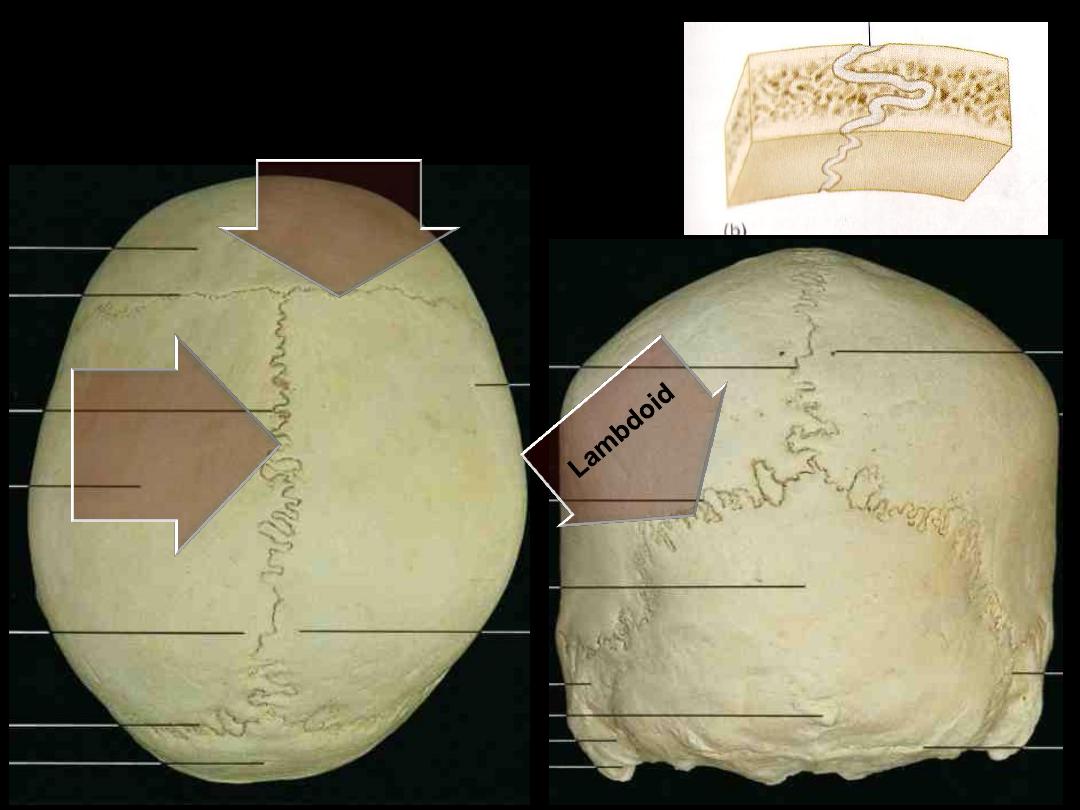
Coronal
Sagittal
Sutures are fibrous
joints
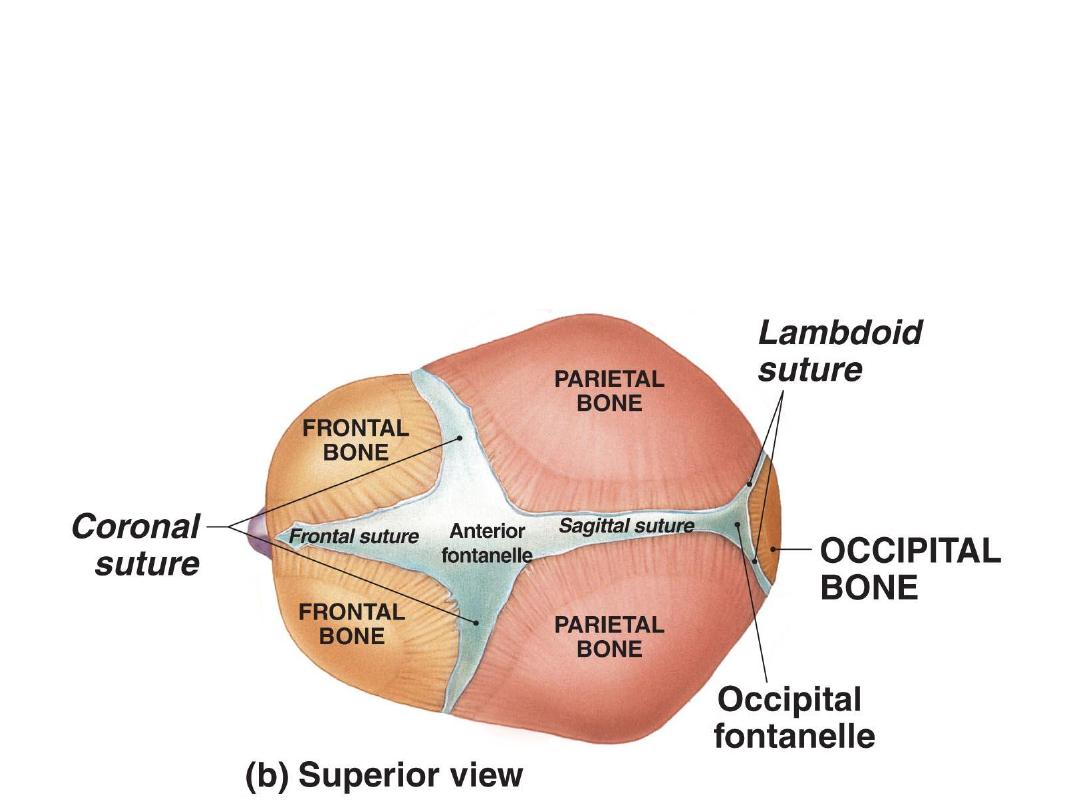
Are spaces between some neurocraneal bones
Lie at the ends of main sutures
Allow the skull to shrink in size during birth
Are six in number (2 unpaired & 2 paired)
Fontanelles
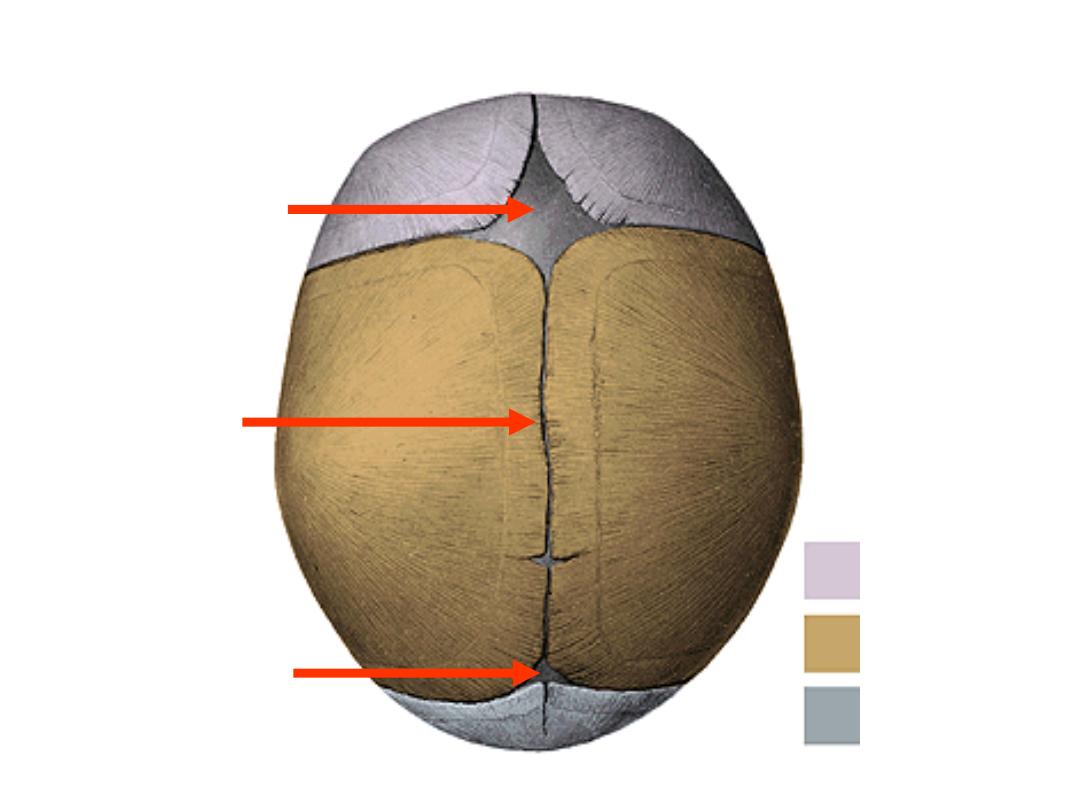
Bregma
18 months
Lambda
3 months
Vertex
Anterior & posterior fontanelles:
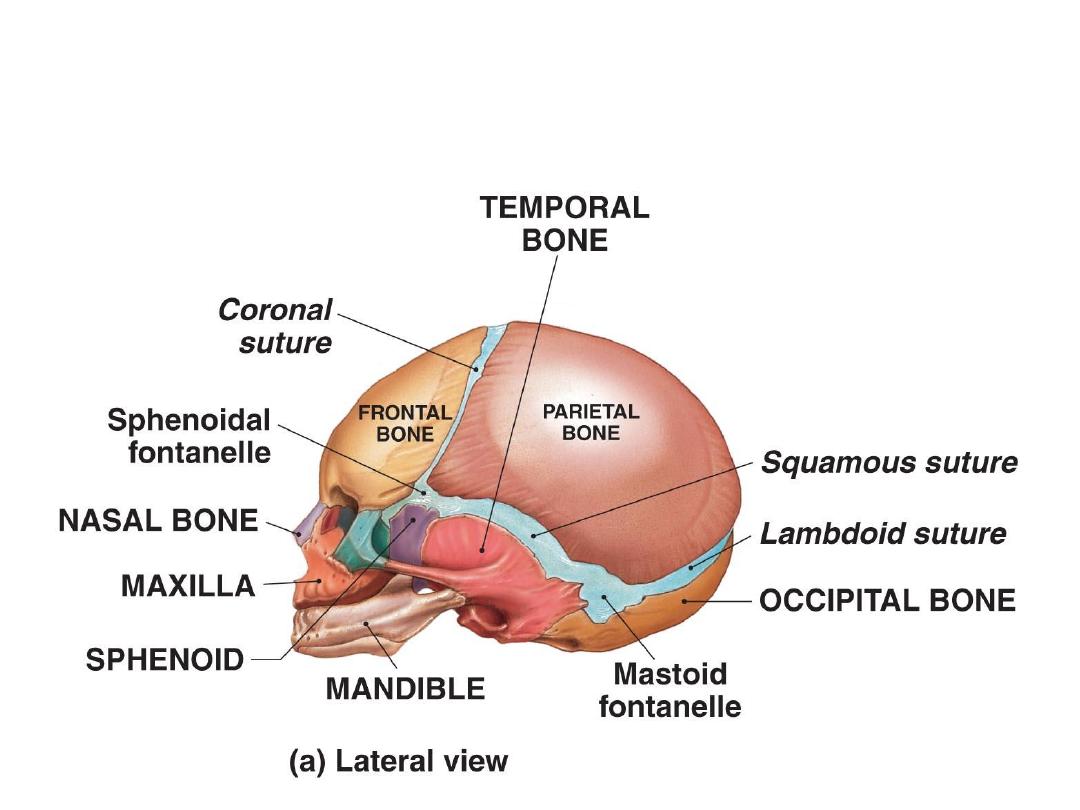
Lateral fontanelles (paired fontanelles):
-Sphenoidal; pterion
-Mastoid; asteriorn
anteriolateral
posteriolateral
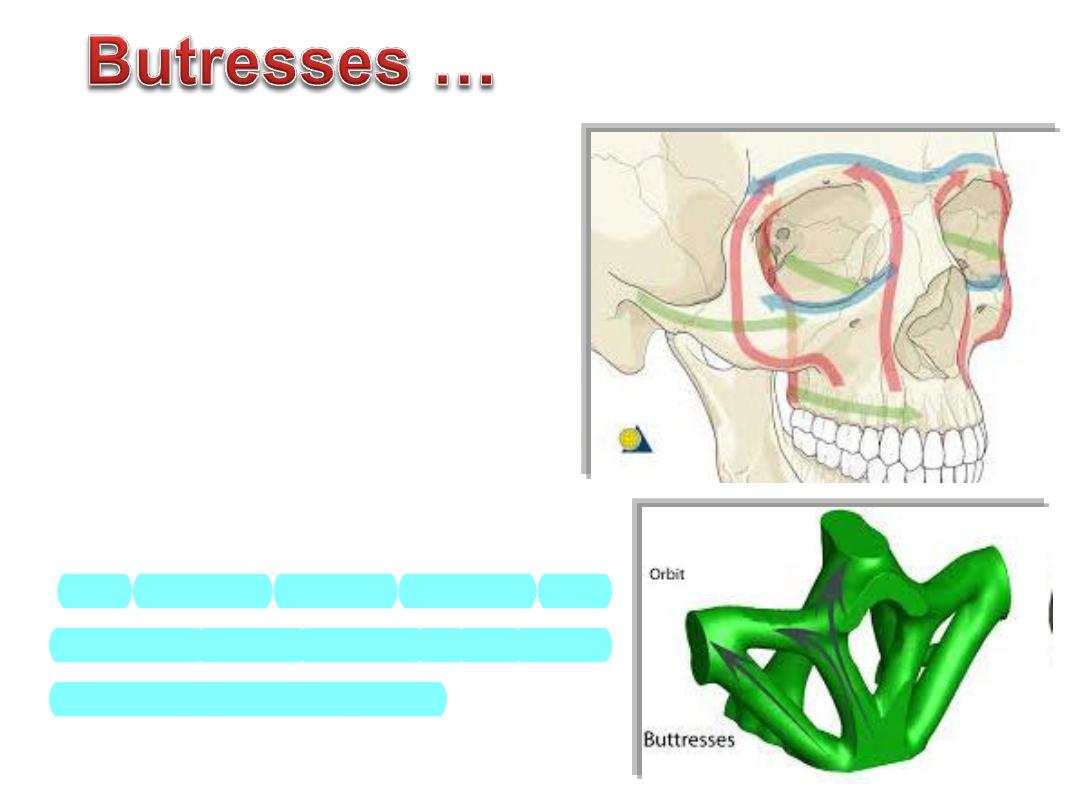
Thin segments of bones are encased
&
supported
by
a
more
rigid
framework of "buttresses"
The midface is anchored to the
cranium through this framework
The buttress system
absorbs and
transmits forces applied to the
facial
skeleton to stronger bones
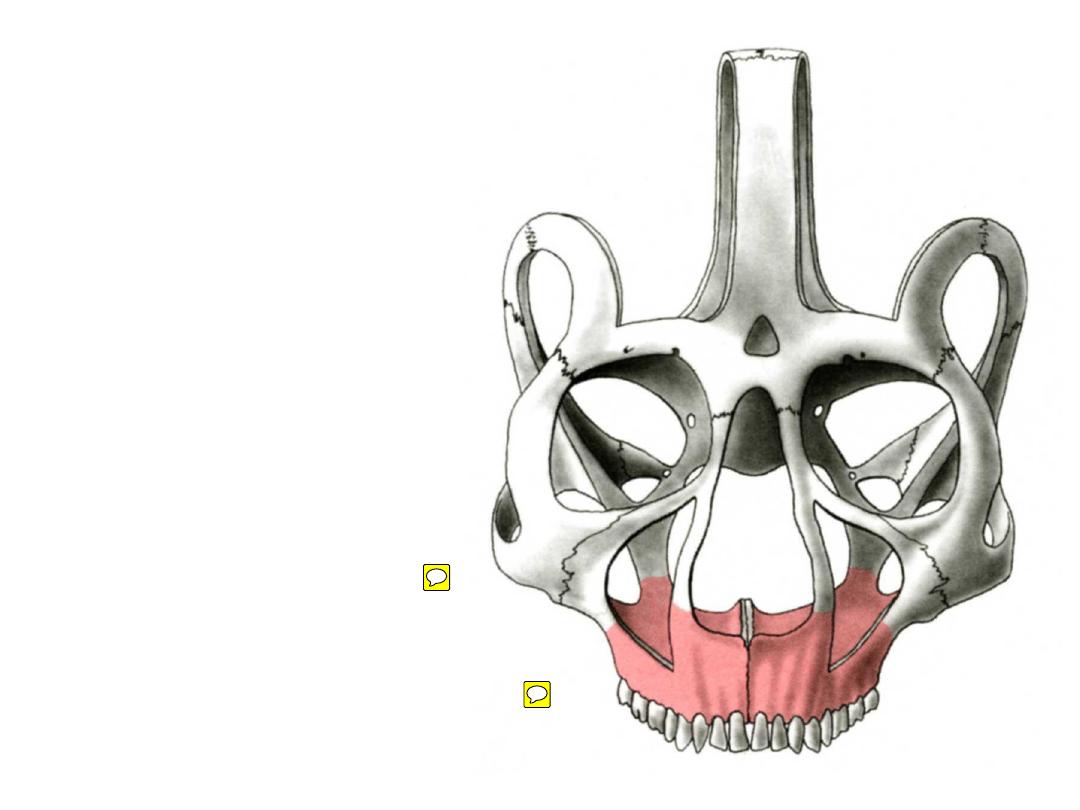
Vertical buttress
nasomaxillary
zygomaticomaxillary
pterygomaxillary
Horizontal buttress
glabella
orbital rims
zygomatic processes
maxillary palate
