
Dr. Esraa AL
– Qassab
FICOG\CABOG
Fertilization
The union of egg and sperm.
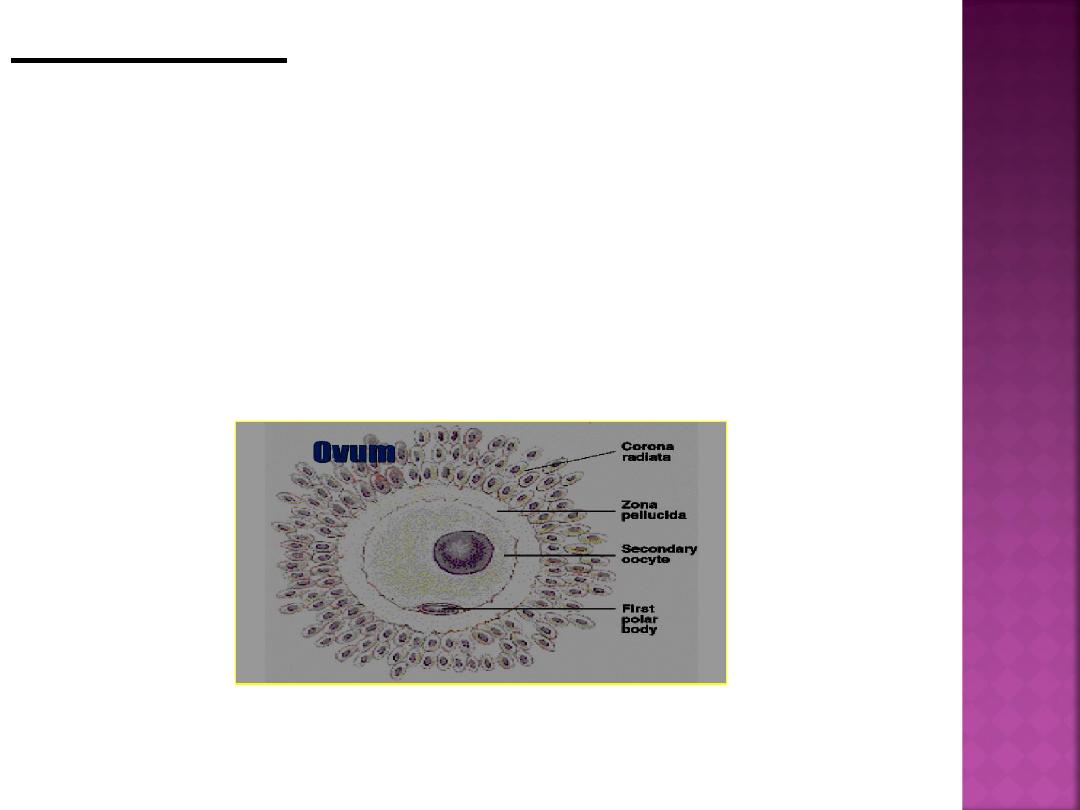
Ovulation frees the secondary oocyte and
adherent cells of the cumulus-oocyte
complex from the ovary.

Although technically this mass of cells is
released into the peritoneal cavity, the
oocyte is quickly engulfed by the
infundibulum of the fallopian tube.
Further transport through the oviduct is
accomplished by directional movement
of cilia and tubal peristalsis.

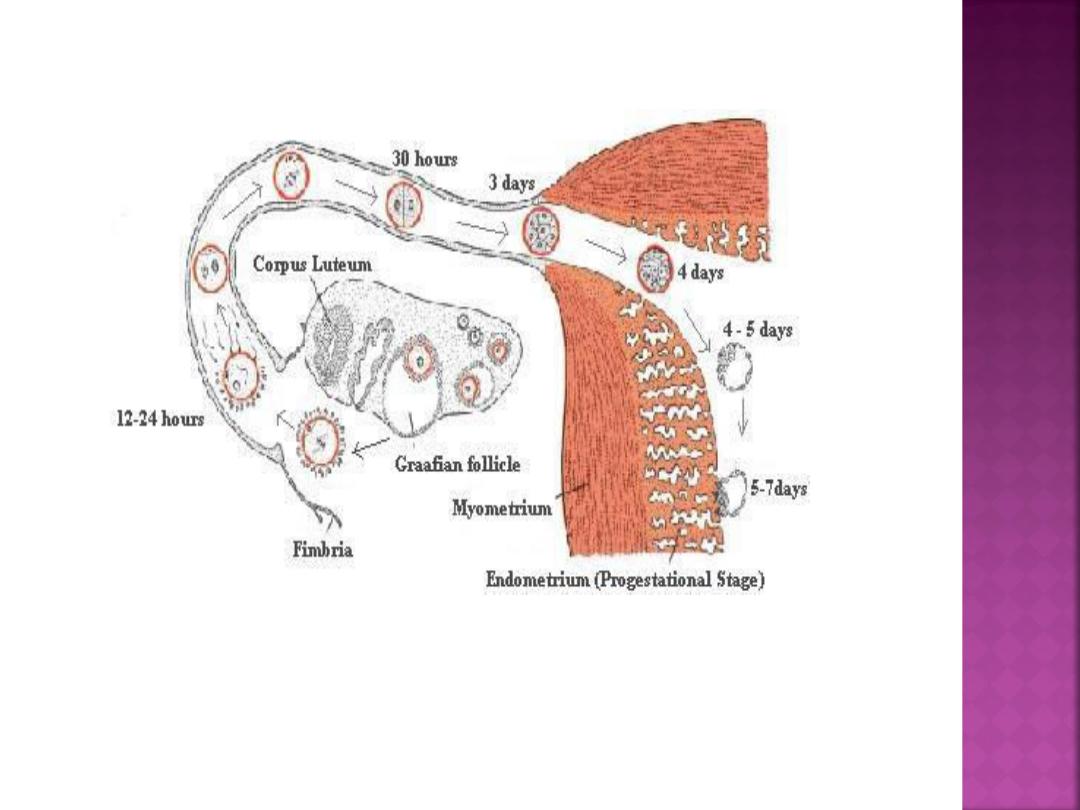
So Fertilization is fusion of male and
female gamates, normally occurs in the
oviduct, and it is generally agreed that it
must take place within a few hours, and
no more than a day after ovulation.
Because of this narrow window of
opportunity, spermatozoa must be
present in the tube at the time of oocyte
arrival.
Almost all pregnancies result when
intercourse occurs during the 2 days
preceding or on the day of ovulation.

Spermatozoa are not able to fertilize the oocyte
immediately upon arrival in the female genital
tract but must undergo (a) Capacitation and (b)
acrosomal reaction.
1-Capacitation, during which time a glycoprotein coat
and seminal plasma proteins are removed from the
spermatozoon head
2.Acrosomal reaction , during which acrosin
– and
trypsin-like substances are released to penetrate
the zona pellucida .
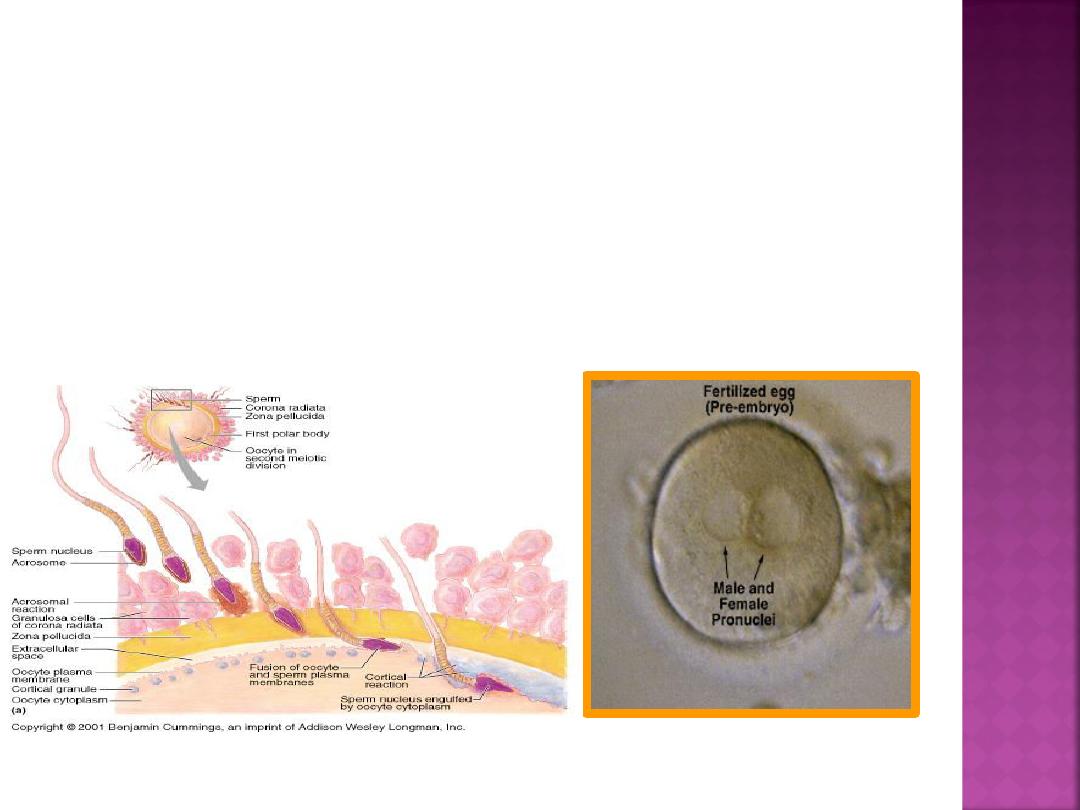
This will allow passage of spermatozoa
between follicular cells, through the
zona pellucida, and into the oocyte
cytoplasm leading to the formation of
the zygote.
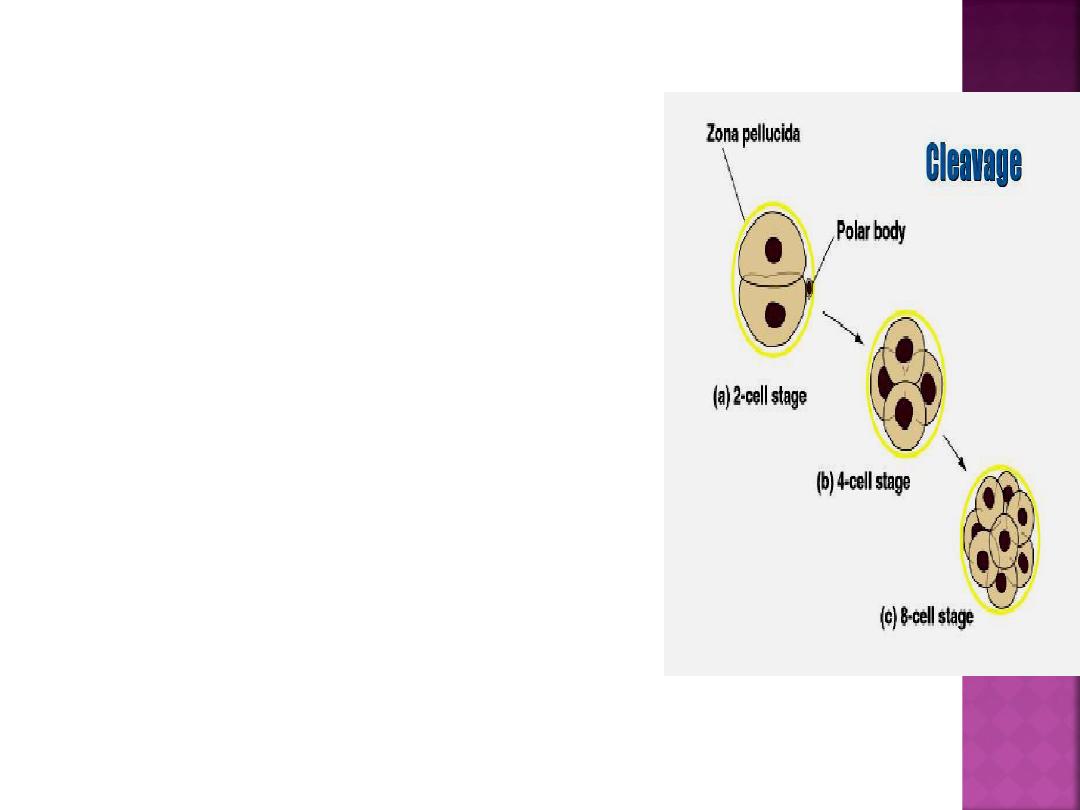
zygote
—a diploid cell with
46 chromosomes
—that then
undergoes cleavage into
blastomeres.
The blastomeres
surrounded by a thick zona
pellucida. The zygote
undergoes slow cleavage for
3 days while still within the
fallopian tube.
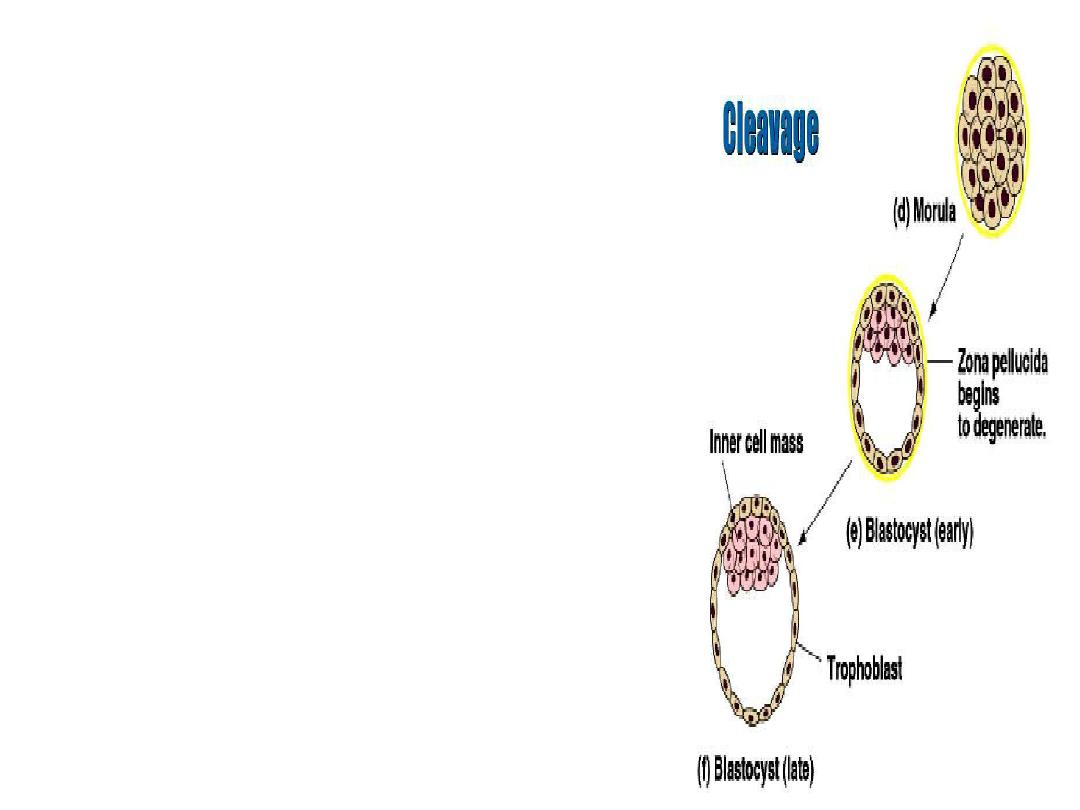
As the blastomeres
continue to divide, a
solid mulberry-like ball
of cells
—the morula—is
produced. The morula
enters the uterine cavity
about 3 days after
fertilization.
Gradual accumulation of
fluid between the cells
of the morula results in
the formation of the
early blastocyst.
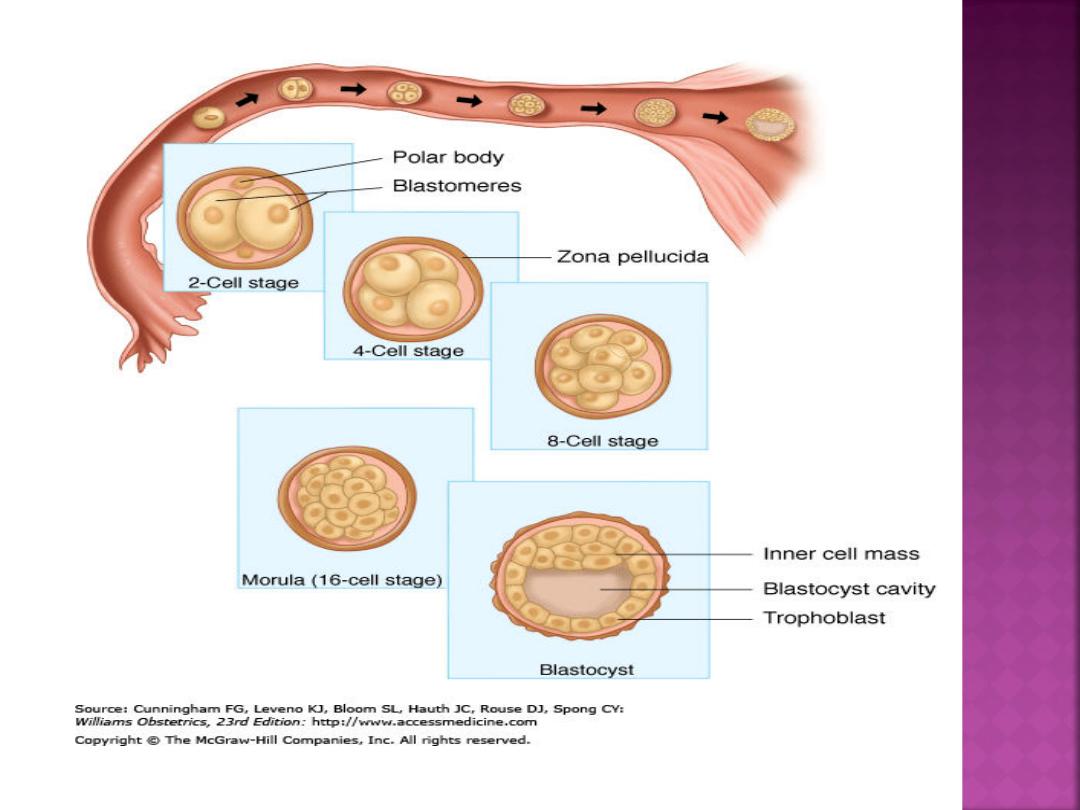

As early as 4 to 5 days after
fertilization, the blastocyst
differentiates the inner cell mass,
and outer cells, called the
trophoblast, can be distinguished
from the inner cell mass that forms
the embryo.
blastocyst is released from the zona
pellucida as a result of secretion of
specific proteases from the secretory-
phase endometrial glands

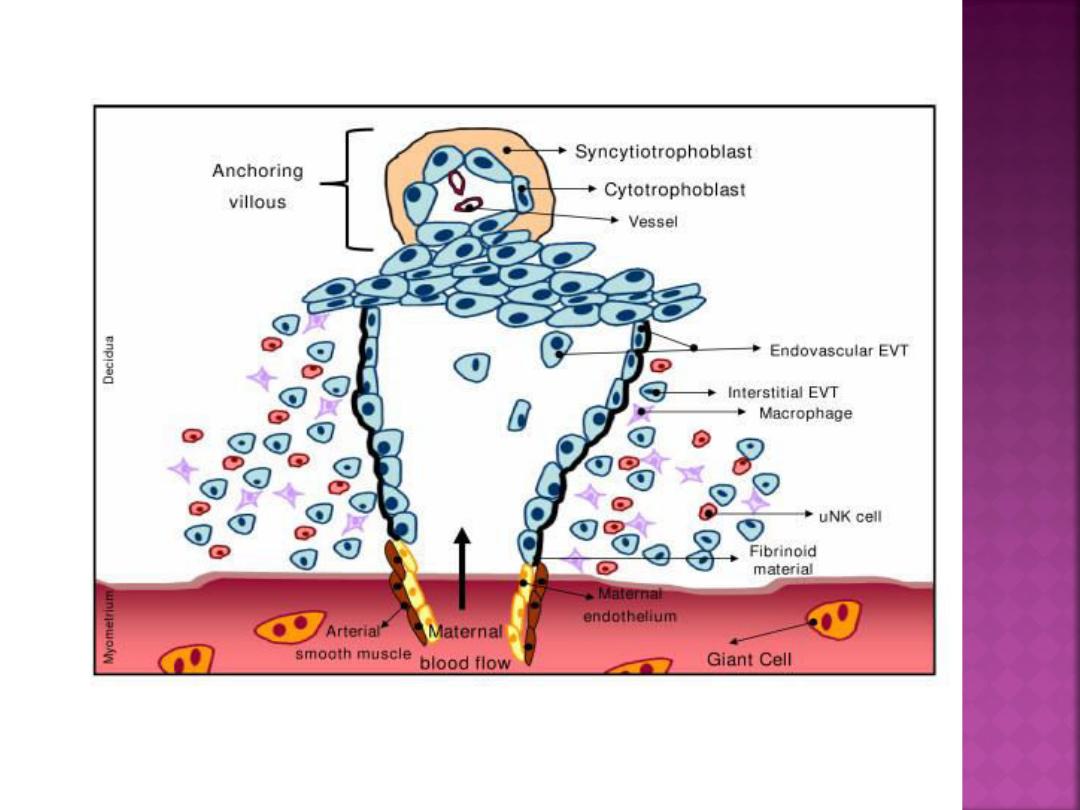
Implantation:-
Implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall
takes place 6 or 7 days after fertilization. This
process can be divided into three phases:
(1) apposition
—initial adhesion of the blastocyst to
the uterine wall.
(2) adhesion
—increased physical contact between the
blastocyst and uterine epithelium.
(3) invasion
—penetration and invasion of
syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast into the
endometrium, inner third of the myometrium, and
uterine vasculature.
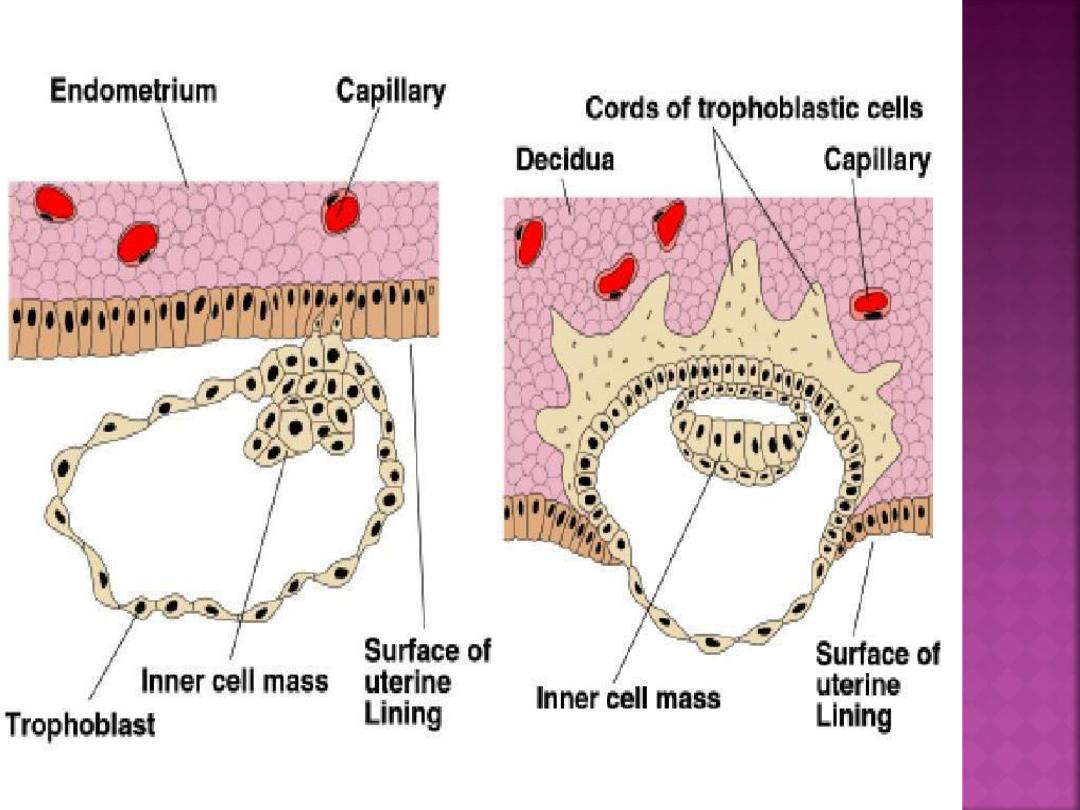

Successful implantation requires
receptive endometrium appropriately
primed with estrogen and
progesterone. uterine receptivity is
limited to days 20 to 24 of the cycle .
Development of a receptive
epithelium results from the
postovulatory production of estrogen
and progesterone by the corpus
luteum.

If the blastocyst approaches the
endometrium after cycle day 24, the
potential for adhesion is diminished
because synthesis of anti adhesive
glycoproteins prevents receptor
interactions .
The blastocyst loosely adheres to the
endometrial epithelium by
apposition. This most commonly
occurs on the upper posterior uterine
wall.
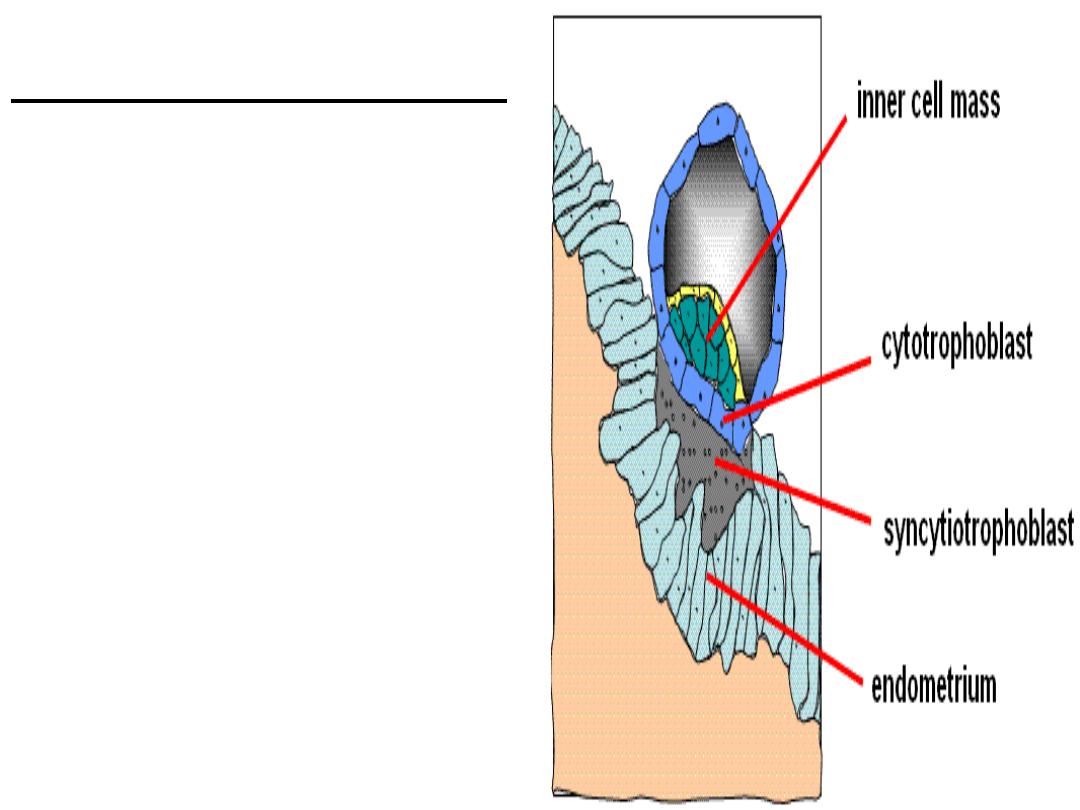
Trophoblast Differentiation
By the 8th day post-
fertilization, after initial
implantation, the
trophoblast has
differentiated into an outer
multinucleated
syncytiotrophoblast, and an
inner layer of mononuclear
cells
—cytotrophoblast
.

The
decidua
is a specialized, highly
modified endometrium of pregnancy.
Decidualization
—transformation of
secretory endometrium to decidua
—
is dependent on estrogen and
progesterone and factors secreted
by the implanting blastocyst.

The decidua is classified into three parts.
1.Decidua basalis:
Decidua directly beneath
blastocyst implantation is modified by
trophoblast invasion.
2. Decidua capsularis
overlies the enlarging
blastocyst, and initially separates it from the
rest of the uterine cavity. This portion is most
prominent during the second month of
pregnancy, consisting of decidual cells covered
by a single layer of flattened epithelial cells.
Internally, it contacts the avascular,
extraembryonic fetal membrane
—the chorion
laeve.
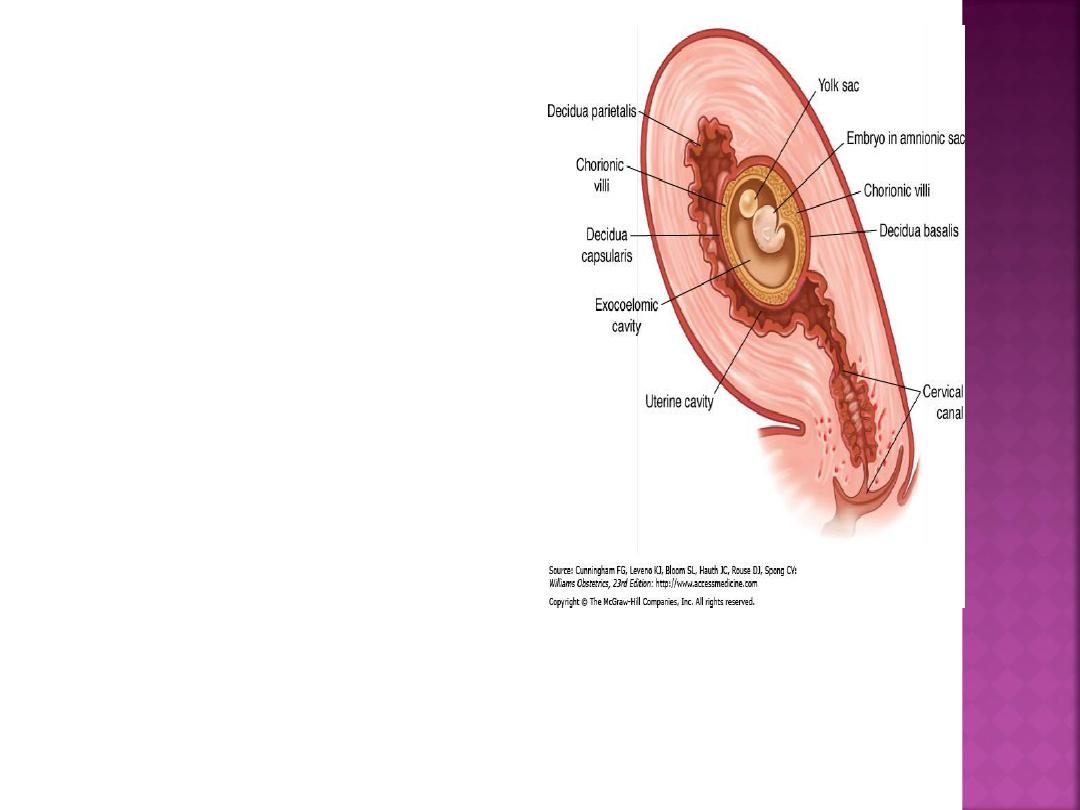
3.
The remainder of
the uterus is lined by
decidua parietalis
—
sometimes called
decidua vera when
decidua capsularis
and parietalis are
joined.

During early pregnancy, there is a
space between the decidua
capsularis and parietalis because the
gestational sac does not fill the
entire uterine cavity.
By 14 to 16 weeks, the expanding
sac has enlarged to completely fill
the uterine cavity. With fusion of the
decidua capsularis and parietalis, the
uterine cavity is functionally
obliterated.

Embryonic period: starts with generation
of embryonic disk during 2
nd
week post
fertilization(4wk after LMP), ends on last
day of 8
th
week post fertilization(10
th
week after LMP). At this time all organ
systems are formed, but are not
necessarily mature.
GPA
G: gravida is a total number of
pregnancies regardless of outcome.
P: parity is the number of deliveries
after 24
th
week of gestation whether
stillbirth or live birth.
A : abortion or miscarriage is the
expulsion of the conceptus before 24
th
week of gestation

Women at 12 week gestation and never
had a pregnancy before is G1 P0---
primigravida
Twin counts as 2 : pregnant at 12wk with
previous delivery of twin ---- G2 P2.
Women in her eighth pregnancy , she has
had 6 miscarriage and 1 delivery at 32
wk of alive baby--------G8 P1 A6

LMP: 1
st
day of last menstrual
period.
The median duration of pregnancy is
280 days (40wk) and this give
expected date of delivery EDD. EDD
is calculated by counting forward 9
months & adding 7 days.
Calculate the gestational age
37-40 wk ----- term
<37 wk --------preterm
40-42 wk ------postdate
>42 wk---------postterm
Every 2 months = 9wk
Every 3 months = 13wk

But the cycle should be reliable , this
assumes that:
The cycle length is 28 days
The cycle was not straight after stopping
COCP or after previous pregnancy.
At least 3 regular cycles before conception.
------------------------------------------------------
1
st
TMS
–up to 13 wk
2
nd
TMS
–14- 27completed wk
3
rd
TMS
– 28wk - delivery

E,g
4 / 2 / 2012
1 / 7 /2011
31 / 1 /2011
25 / 7 /2011
If the cycle is unreliable ,depend on
late 1
st
trimester or early 2
nd
trimester US
